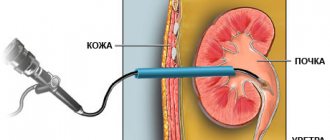
Indications for this operation are the presence of a stone in the renal pelvis, which causes a disturbance in the outflow of urine with severe pain and impaired function of the entire kidney. Laparoscopy for urolithiasis is the method of choice and is used when it is impossible to use the endoscopic method. The reason may be the large size of the stone, its long-term presence in the kidney, or the lack of appropriate endoscopic equipment and instruments. The operation is performed under general anesthesia through 3-4 miniature incisions on the anterior surface of the abdomen. Using an ultrasonic scalpel and laparoscopic instruments, the kidney and pelvis are isolated from the surrounding tissues. Using a miniature scalpel, the pelvis is opened and the stone is removed. A stent is placed in the kidney. The pelvis defect is sutured with special sutures. Rehabilitation of the patient after surgery in the hospital occurs within 3-4 days. After discharge from the hospital, return to normal activities occurs within 1 to 2 weeks.
Typically, kidney stones require surgery. Previously, they were removed during a major abdominal operation, which required a long recovery and left a large scar on the patient's body. Modern technologies make it possible to eliminate kidney stones without incisions or even punctures.
Unique surgical equipment allows surgeons to reach the kidney stone through the natural urinary tract. Everything that happens in the patient’s body during surgery is seen by the surgeon using an endoscopic camera on a monitor.
Gentle access
Urologist Oleg Teodorovich, professor, doctor of medical sciences comments: “Through the external opening in the genital organs, we first enter the bladder, then the ureter, then we can reach the kidney with a flexible or rigid instrument, see the stone through the chamber, which is located in end of the endoscope, insert a laser light guide and destroy the stone.”
The crushed stone is removed from the patient’s body in the form of small fragments. This operation is effectively used in the treatment of urolithiasis when the stone is less than two centimeters. If it is very large - its size exceeds two or three centimeters, it has to be removed in other ways.
Laparoscopy
“We provide puncture access to the kidney. We puncture the kidney, expand the passage to seven or eight millimeters, insert an endoscope there and, using various methods of destruction, we fragment the stone and remove these parts. We put a thin tube into the kidney for about three to four to five days for better healing, which is then removed,” says Oleg Teodorovich.
After such gentle methods of treating urolithiasis, patients are usually discharged on the fourth to sixth day. When stones are removed the old fashioned way, the hospital stay can last up to two to three weeks. And recovery after surgery can last for months.
Big operation
“An incision is made in the skin tissue in the projection of the kidneys, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, the kidney is exposed, or, say, the ureter, the abdominal system is opened, and the stone is removed. Then all this is sutured in layers. This method is historical; the treatment of urolithiasis began with it. It is quite traumatic and requires intubation anesthesia (through the respiratory tract). After this method, postoperative hernias quite often occur. And of course, today it is not the method of choice, that is, the best method in the treatment of urolithiasis,” says Oleg Teodorovich
Remote methods
When using the method of removing stones using ultrasound or laser, the patient is sent home after twenty minutes. Immediately after finishing the stone crushing procedure.
“For example, a device for remote wave crushing of stones. This is a non-invasive method that allows, as the name suggests, to destroy stones at a distance,” says Stanislav Naryshkin, urologist, candidate of medical sciences
“The essence of this method is that with the help of special equipment, X-ray or ultrasound guidance, a shock wave is created, which enters the patient’s body with a wide front and then accumulates with a narrow focus, i.e. gathers on a stone. And in the stone area, a high shock pressure is thus formed, which allows the stone to be destroyed,” adds Professor Teodorovic.
This procedure cannot be prescribed to all patients. The effectiveness of the method depends on the density of the stone and its location. If there is any infection in the kidneys, crushing the stone using this method is contraindicated. Another inconvenience: the crushed stone must leave the body naturally. This process drags on for months and can be accompanied by severe pain.
Indications for surgery
Surgery may be performed in the following cases:
Ureteral obstruction. This problem requires an immediate solution, so the use of conservative therapy, which gives a slow effect, is not acceptable. Increasing renal failure, acute renal failure. If these symptoms are ignored, serious consequences, including death, are possible. Pain that cannot be controlled with medication. Purulent inflammation. Kidney carbuncle. This is the name given to the site of purulent necrosis caused by stones. The patient's desire to undergo surgery.
Depending on the degree of damage, the methods of surgical intervention may vary:
Unilateral urolithiasis. Localization of stones in one kidney makes it possible to preserve the functions of the genitourinary system in case of unsuccessful surgery. Bilateral urolithiasis. If the location of the stones is established, the operation can be performed on two kidneys simultaneously. Otherwise, it is carried out in two stages, with a break between them of 1-3 months.
Types of surgery
The following methods for removing stones are distinguished:
Lithotripsy. The stone is crushed by exposure to ultrasound through the skin, after which it is removed through the ureter or catheter to the outside. Endoscopic operations. A special instrument, an endoscope, is inserted through the ureter or urethra and approaches the location of the stone. Removal is carried out through it. Open surgery. Involves direct incision of the kidney and surgical removal of salt deposits. Resection. The operation is a type of open, but involves partial removal of the kidney.
Symptoms
The pain from kidney stones does not appear immediately, that is, at first the disease does not manifest itself. The appearance of pain begins only when the stone begins to move in the urinary tract.
Here are the symptoms of kidney stones:
- Colic or dull pain in the lumbar region, which can intensify due to various physical activities, including such mild ones as long walking. (But there is also the opposite opinion that physical activity makes it easier for the stone to pass)
- Unbearable or simply extremely severe pain, which can also radiate to the thighs, lower abdomen, and genitals
- Unpleasant sensations or difficulty urinating, as well as frequent urge to urinate
- In rare cases, nausea and even vomiting are possible
- Bloating
- The appearance of yellow or red sediment in the urine, blood in the urine
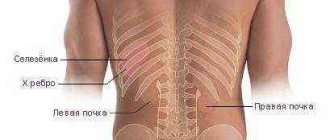
It is also possible to approximately determine the location of the stone or stones: if the pain radiates to the genitals, then the stones are located at the bottom of the ureter, and if in the groin area, then in the ureter itself or the so-called renal pelvis.
Lithotripsy
The essence of the procedure
Since its discovery and introduction into practice (in Russia - in the late 90s of the last century), lithotripsy has earned recognition and taken a leading place in urolithiasis surgery. It eliminates the trauma of surgical intervention and the risk of infection, since the effect is performed percutaneously without any incision.
The essence of the method is based on the effect of ultrasound on various environments of the body. It spreads freely in the soft tissues of the body without causing any harm. When ultrasound encounters a dense salt deposit, it creates cavities and microcracks in it, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the stone.
Modern lithotriptors are generators of ultrasonic shock waves; depending on the country of origin, they can be driven by an electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric element, or even a laser. However, there are no significant differences between them. Visual control of the location and condition of the stone can be carried out using x-rays or ultrasound.
Indications and contraindications
Lithotripsy is performed to remove small stones (up to 2 cm), the localization of which can be unambiguously determined by one of the indicated methods, from living kidneys. In the fifth and final stage of urolithiasis, using this removal method can be dangerous. Note. Some authors (O.L. Tiktinsky) believe that even with large coral deposits it is possible to use ultrasound. But in this case, constant monitoring of the location of all their fragments and readiness for additional endoscopic surgery is necessary.
Surgery is not performed in the following patient conditions:
Pregnancy. Injuries to the musculoskeletal system that do not allow you to take the correct position on the couch. The patient's body weight is above 130 kg, height is more than 2 m or less than 1 m. Blood clotting disorder.
Progress of the operation
At the very beginning of the use of the technique, general anesthesia was widely used, but today it is obvious that in most cases it is not necessary and doctors limit themselves to epidural anesthesia. Analgesics are injected into the lumbar spine. They begin to act within 10 minutes, and the duration does not exceed 1 hour. In emergency cases and when epidural anesthesia is contraindicated, they are administered through a vein.
Removing kidney stones
If the stone is small, up to 1 cm, and smooth, it can come out on its own. Stones that cause long-term symptoms can be removed by various non-surgical methods, including:
- Herbal medicine - herbal treatment (nettle, corn tassels, horsetail, motherwort, rosehip)
- Treatment with alternative methods (diluted apple cider vinegar, lemon juice and olive oil, pomegranate juice, watermelon juice)
- Physiotherapy (general thermal baths, diathermy, inductothermy)
- Dietary food (unlimited consumption of fruits)
- Exercises (bicycle, raising legs at different angles, squeezing a ball in the knees, alternately pulling legs to the stomach)
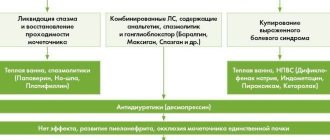
- Drug treatment: an attack of renal colic is relieved by painkillers (Baralgin, Maksigan, Analgin, Spazmalgin), for acute pain they take antispasmodics and diuretics (Madder, Avisan), drive urine, relax muscles, improve blood flow in the kidneys (Enatin, Cyston , Urolesan), to facilitate the passage of small stones, antispastic agents are used (Atropine, Platyfillin, No-shpa, Papaverine).
If acute pain is not relieved, a catheter is inserted into the patient's ureter.
Endoscopic operations
Depending on the location of the stone, the endoscope can be inserted into the urethra (urethra) or higher into the bladder, ureter, or directly into the kidney. The lower the deposits are located, the easier the operation is. It is performed under general anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia to remove stones up to 2 cm. Indications are:
Ineffectiveness of lithotripsy; Long-term presence of a stone in the path of the ureter; “Stone paths” (residual formations) after exposure to ultrasound.
The operation, despite its apparent simplicity, requires a highly qualified surgeon and high-quality modern equipment. A urethroscope is inserted into the patient's urinary canal. This device consists of a tube with a mirror that allows the surgeon to directly detect stones. Once the tube reaches them, they will be removed. The most modern technique is laser removal of kidney stones. The action of the beam is transmitted through a special fiber, which is inserted into the urethroscope.
In some cases, the installation of a stent is required - this is a catheter that prevents compression of the ureter (obstruction). It is placed for up to several weeks. Removal also occurs without incisions using an endoscope.
Laser crushing of kidney stones
At the moment, the laser method is considered more reliable and effective than the previous one. The impact on stones is carried out not with the help of ultrasound, but with a special apparatus; most often, a holmium laser is used to crush kidney stones.
Along the urethra, the endoscope moves directly to the stone, is brought close and acts directly on it, instantly melting the stone into particles no larger than 0.2 mm in diameter. The laser only affects the stone, so it does not damage surrounding tissue.
This method is the only alternative to surgery in cases where the use of ultrasound is ineffective. Such indications include: large size of stones, their high density or unusual shape.
When choosing a method, proceed from the opinion of the doctor
Laser crushing is always preferable to surgery; it is a minimally invasive method, since laser exposure is carried out very precisely, and the overall effect on the body and the risk of complications are largely related to the correct insertion of the endoscope and postoperative rehabilitation.
Another advantage of using a laser is its high efficiency already in the first procedure; you most likely will not need a repeat procedure, and this reduces the risk of complications. In addition, the stones are completely removed, so the likelihood of recurrence due to remaining stone pieces is minimal.
And it is much easier to remove molten stones than fragments crushed by ultrasound, so postoperative recovery is faster. In most cases, the patient returns home from the hospital within an hour after the procedure.
On the other hand, this is a more expensive method, and not all clinics are equipped with appropriate laser systems. Although it should be noted that crushing kidney stones with a laser is much cheaper than surgery. And in most cases, this method is preferable to other non-invasive ones; it gives much fewer complications with higher efficiency.
Knowing how to treat your illness is very helpful. But when choosing, listen first of all to what your attending physician says, he will weigh the pros and cons and choose the safest and most effective procedure in your case. If the diagnosis is made early, crushing by any remote method will solve your problem once and for all.
Open surgery
In recent years, this type of intervention has been performed extremely rarely. Indications for it are:
Constant relapses; Large stones that cannot be removed in any other way; Purulent inflammation.
Open surgery is performed under general anesthesia and is abdominal . This means that it affects the body cavity. Excision occurs through all layers of tissue. The presence of a stone in the renal pelvis is considered favorable. This reduces the invasiveness of the operation. It is also possible to open the ureter and remove the stone from there.
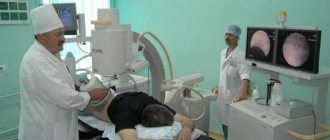
The modern option for performing the operation is laparoscopy. Removing the stone through a small incision. A camera is inserted into it to transmit images to a large screen. Laparoscopic stone removal is carried out only for special indications and is often replaced by endoscopic operations.
Removal of part of the kidney
Indications and contraindications
This operation allows you to save the organ, which is especially important if you have only one working kidney. Resection is performed in the following cases:
Multiple (multi-locular) stones located at one pole of the organ. Constant relapses of the disease. Necrotic lesions. The last stages of urolithiasis.
Important! A contraindication is the patient's serious condition, if doctors assume that the operation may aggravate it.
Progress of the operation
Resection is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is placed on his healthy side, under which a cushion is placed. The surgeon makes an incision. After this, he pushes the underlying layers of tissue apart. A clamp is applied to the part of the kidney with the ureter to prevent bleeding, since this is where the maximum concentration of blood vessels is located.
Kidney functions
The kidneys are designed to filter liquid waste products and subsequently remove them from the body as urine, i.e. urine. During these processes, individual chemical elements and their compounds contained in the urine settle on the inner surface of the kidneys, which causes the formation of so-called kidney sand, i.e. small crystals. Gradually, small particles form stones, i.e. kidney stones. They are larger in size.
The diameter of the ureter in adult men does not exceed 0.8 cm, its length is no more than 40 cm. In women, these dimensions are slightly smaller. The passage of large stones is made difficult not only by their size, but also by their irregular shape. Such neoplasms may have sharp protrusions, edges, etc. If they go along the ureter, they cause damage to its internal walls.
Complications
Each of the described types of operations may have a different probability of undesirable consequences, but in general they can be presented in the form of the following list:
Relapses. Recurrent stone formation is not uncommon with urothiasis. The operation only combats the consequences, but does not eliminate the cause. That is why it is important in each specific case to find out why urolithiasis developed, to give the patient recommendations for lifestyle changes, diet and, possibly, taking medications. False relapses. This is the name given to the remaining unremoved stone fragments. This outcome of the operation is becoming less and less common due to the improvement of methods of its implementation and constant monitoring of its progress. Infection. Even with minimally invasive operations such as endoscopic ones, there is a risk of pathogens entering internal organs. To prevent infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed even if the patient is in good condition. Acute pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal pelvis. It occurs due to the displacement of stones, prolonged residence of their fragments in the kidney and the accumulation of infiltrate (fluid) around them. Bleeding. Most often occur during open operations. To prevent them, irrigation of the kidney with a solution containing antibiotics is used. Progression, exacerbation of renal failure. For prevention, hemodialysis (connection to an artificial kidney machine) is used before and after surgery. Heart rhythm disturbances, hypertension (high blood pressure). The complication occurs more often after ultrasonic destruction of stones due to an incorrect assessment of the patient’s condition.
Cost of surgery for urolithiasis, carried out under compulsory medical insurance
The most common type of intervention is lithotripsy. It is carried out in most clinics and medical centers dealing with urological diseases. The average price is 20,000 rubles. The operation is free of charge only for persons under 18 years of age in public medical institutions.
According to the compulsory health insurance policy, endoscopic, open surgeries and kidney resections are usually performed in hospitals. The first type of procedure in private clinics costs from 30,000 rubles. The price does not include medications necessary for rehabilitation and a place in a hospital. Open abdominal surgeries are rarely performed in private clinics; the price must be determined privately. The cost of partial kidney removal starts from 17,000 – 18,000 rubles and can reach 100,000 rubles. The price is shown only for the procedure.
Patient reviews about the operation
The largest number of reviews on the Internet are devoted to lithotripsy. Many patients were satisfied with the result. As a rule, the following negative aspects are noted:
High price. Often the decision to undergo surgery must be made suddenly and as soon as possible. Not every patient has a reserve of several tens of thousands of rubles. Painful sensations during surgery. This happens quite rarely, and patients note that the discomfort cannot be compared with the agony of renal colic. Risk of relapse and lack of guarantees.
With other operations to remove kidney stones, especially those performed free of charge, patients are concerned about the tactics of the chosen treatment. Not every doctor explains to the patient the essence of his actions and prescriptions, especially when it comes to elderly patients or their relatives. The wrong choice of the type of surgical intervention and the lack of improvement are usually difficult for people entering a medical facility.
Urolithiasis is a common disease that develops as a result of the combined action of many factors. And although modern methods of surgical treatment can successfully solve this problem, the latest developments in the field of ultrasonic crushing are not available to everyone. The outcome of treatment cannot always be predicted, and with any type of therapy the risk of relapse remains. Therefore, if there is a predisposition to the disease or its presence in relatives, all measures must be taken to prevent urolithiasis.
Causes of stone formation
To prevent the formation of kidney stones, it is recommended to install filters for water purification
Stones in the genitourinary system are formed due to metabolic disorders, which provoke the formation of insoluble salts. Contribute to the development of pathology: systematic consumption of hard water with a high content of calcium salts, lack of vitamins, injuries and diseases of the bone and genitourinary system. The formations cause pain in the lower back, colic, slight fever, and vomiting.
Urolithiasis of the kidneys is diagnosed using ultrasound, non-contrast computed tomography, excretory urography (x-ray method for examining the urinary tract). The patient is also recommended to undergo a urine test for the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, a test for bacteriuria - the number and type of bacteria, and urine culture.
A stone of a non-standard shape may form in the kidney (coral-shaped, has at least one branch). It is dangerous because it can completely fill the renal cups and pelvis. Such patients are prescribed the same therapy as for large stones. Most often this is remote shock wave therapy, percutaneous lithotripsy (laparoscopic surgery).
Often in such situations, it is necessary to expand the lumen of the urinary tract for normal outflow of urine using a special flexible tube - a stent. But kidney stenting is done if the functionality of its vessels is impaired (the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in them, high blood pressure).
Advice: if you ignore kidney stones and do not carry out the necessary treatment, this will lead not only to the development of acute, chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis, but also cause purulent melting of the kidney. Then the only way to save the patient’s life will be surgery to remove the organ.