Registration of disability after pyelonephritis
Kidney stones are a very common and widespread problem in society, since, unfortunately, in the modern world the water supply, ecology and quality of food are spoiled. Very often there is a complication leading to a serious illness, such as chronic pyelonephritis. The formation of stones and all serious consequences are usually cured surgically, which in some cases can turn a person into a disabled person. In this article, we will look at when disability appears after removal of stones and pyelonephritis.
Basic conditions for recognition of disability
To assign disability, there are a number of norms and conditions, under which a person is assigned to the group with limited abilities. Its assignment is made in the following situations:
- If, after an illness or surgical intervention, disturbances in the functional characteristics of the body important for life are noticed;
- In the case where there are some impairments in the ability to care for oneself, move in space, learn, work, and so on;
- When a person needs social protection and rehabilitation;
Attention! If all of the above conditions are present, the commission must assign a disabled degree.
There are situations when the kidney cannot be saved, so it is removed. Most often, after this, the status of a disabled person is assigned for 1 calendar year. This degree belongs to the 2nd and 3rd groups. If a person has very severe complications, then group 1 is diagnosed. As soon as the period for which the assigned category expires, you must undergo the diagnosis again.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis in children
Acute glomerulonephritis in children usually develops 2-3 weeks after an infection, most often of streptococcal origin. In the typical version, glomerulonephritis in children is cyclical in nature, characterized by a rapid onset and severe manifestations: fever, chills, poor health, headache, nausea, vomiting, and lower back pain.
In the first days, the volume of urine excreted noticeably decreases, significant proteinuria, micro- and macrohematuria develop. Urine takes on a rusty color (the color of “meat slop”). Swelling is characteristic, especially noticeable on the face and eyelids. Due to edema, the child’s weight may be several kilograms higher than normal. There is an increase in blood pressure to 140-160 mm Hg. st, in severe cases becoming long-lasting. With adequate treatment of acute glomerulonephritis in children, kidney function is quickly restored; full recovery occurs after 4-6 weeks (on average after 2-3 months). Rarely (in 1-2% of cases) glomerulonephritis in children becomes chronic, which has a very diverse clinical picture.
Hematuric chronic glomerulonephritis is the most common in childhood. Has a recurrent or persistent course with slow progression; characterized by moderate hematuria, with exacerbations - gross hematuria. Hypertension is not observed, edema is absent or mild.
Children often show a tendency to a latent course of glomerulonephritis with scanty urinary symptoms, without arterial hypertension and edema; in this case, the disease can only be detected through a thorough examination of the child.
Nephrotic glomerulonephritis in children typically has an undulating, constantly relapsing course. Urinary symptoms predominate: oliguria, significant edema, ascites. hydrothorax. Blood pressure is normal or slightly elevated. Massive proteinuria and slight erythrocyturia are observed. Hyperazotemia and decreased glomerular filtration appear with the development of chronic renal failure or exacerbation of the disease.
Hypertensive chronic glomerulonephritis is rare in children. The child is worried about weakness, headache, dizziness. Characterized by persistent, progressive hypertension; urinary syndrome is mild, swelling is insignificant or absent.
List of basic documents for disability
The process of registering a group for a disabled person is quite lengthy, so you should know in advance what official documents will be useful for this:
- Application to the ITU commission requesting the assignment of disability;
- Passport and its copies;
- Medical referral for commission;
- An extract from the hospital about the person’s condition and health;
- Other medical certificates;
- Results of diagnostic examinations;
- A copy of the work record;
- Certificate from place of employment: study, work;
- Pensioner's certificate.
After the certificate of disability is issued, you need to go to the social security authorities and apply for a pension. Its size will be based on the group and additional benefits. If you are denied disability, you have the right to challenge the decision.
Rheumatoid arthritis
The frequency of observation depends on the DN group. But, in the absence of systemic manifestations, at least twice a year; in the presence of systemic manifestations at least four times a year. When treated with gold preparations, cytostatics, glucocorticoids - 3 - 4 times a year.
Examination plan:
1. Clinical blood test.
2. General urine test 4 times a year.
3. When treating with basic medications, a blood test is performed 2 times a month.
4. Blood for platelets - once a month.
5. Urinalysis weekly.
6. Blood test for rheumatoid factor - 2 times a year.
7. X-ray of joints - 1-2 times a year. ECG-1 time per year.
8. Blood test for “C” - reactive protein, sialic acids - once a year. Dispensary observation is carried out by a rheumatologist, or in his absence - by a local therapist.
During clinical observation, the following tactics are determined:
- drug treatment,
- physiotherapeutic treatment,
- need for employment,
- spa treatment,
- indications, timing of referral to MSEC.
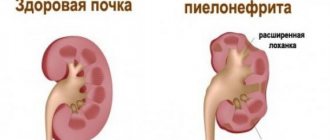
Features of chronic pyelonephritis
Chronic pyelonephritis is a problem that often affects both children and adults. The disease is an infectious type of inflammation. Typically, pathology occurs due to a localization process in interstitial tissue. It is worth noting that the cup-scapular system is also affected.
Attention! Most often, this disease is observed in men over 50 years of age. Women predominate in statistics under 40 years of age.
The main reason for the appearance of this disease is gram-negative flora, which, with prolonged development, forms an association of microbes. Among the factors contributing to the development of the disease are the following:
- General characteristics and health status of the child and adult;
- In case of local causes of urodynamic disorders;
- Various infectious diseases that destabilize the functioning of the genitourinary system.
If the passage of urinary secretions is disrupted, the infectious component can move further throughout the body, for example, into the lower genitourinary tract, and even into the interstitial renal tissue.
Causes of glomerulonephritis in children
It is possible to identify the etiological factor in 80-90% of acute glomerulonephritis in children and in 5-10% of chronic cases. The main causes of glomerulonephritis in children are infectious agents - bacteria (primarily nephritogenic strains of group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, as well as staphylococci, pneumococci, enterococci), viruses (hepatitis B, measles, rubella, chickenpox), parasites (the causative agent of malaria Toxoplasma), fungi (candida) and non-infectious factors (allergens - foreign proteins, vaccines, serums, pollen, toxins, drugs). Most often, the development of acute glomerulonephritis in children is preceded by a recent (2-3 weeks before) streptococcal infection in the form of a sore throat. pharyngitis. scarlet fever. pneumonia. streptoderma. impetigo.
Chronic glomerulonephritis in children usually has a primarily chronic course; less often, it can be a consequence of untreated acute glomerulonephritis. The main role in its development is played by the genetically determined immune response to the influence of the antigen inherent in a given individual. The specific immune complexes formed in this case damage the capillaries of the renal glomeruli, which leads to disruption of microcirculation and the development of inflammatory and dystrophic changes in the kidneys.
Glomerulonephritis can occur in various connective tissue diseases in children (systemic lupus erythematosus, hemorrhagic vasculitis, rheumatism, endocarditis). The development of glomerulonephritis in children is possible with some hereditary anomalies: T-cell dysfunction, hereditary deficiency of C6 and C7 fractions of complement and antithrombin.
Predisposing factors for the development of glomerulonephritis in children may include: family history, increased sensitivity to streptococcal infection, carriage of nephritic strains of group A streptococcus, or the presence of foci of chronic infection in the nasopharynx and on the skin. Hypothermia (especially in a humid environment), excessive insolation, and ARVI can contribute to the activation of latent streptococcal infection and the development of glomerulonephritis in children.
The course of glomerulonephritis in young children is influenced by features of age-related physiology (functional immaturity of the kidneys), the unique reactivity of the child’s body (sensitization with the development of immunopathological reactions).
Existing disability criteria
Today, three groups of disabilities are known. In this section, we will get to know them in more detail. The third category is assigned to such people:
- If a person is diagnosed with chronic pyelonephritis and works in industries with moderate to high levels of physical activity. In such situations, people need easier work, so when assigned to a group, they must be transferred to other work conditions.
- If a person works in the field of mental or physical activity, but suffers from chronic pyelonephritis or has stable arterial hypertension, then he needs another job, or a reduction in workload.
- If there are complications of pyelonephritis, for example, stage PA stage chronic renal failure, and employment in a position with high mental or physical stress, disability group 3 is assigned.
As for the second group, this is a more severe stage, for example, it is assigned in the following circumstances:
- At the stage of chronic renal failure, chronic pyelonephritis;
- If, in the presence of a disease, complications of blood circulation in the brain are observed, for example, due to secondary blood pressure with a complicated course;
- If a child or adult experiences extrarenal complications.
The first group is considered the most difficult, and it is assigned in the following situations:
- Stage CRF ShB refers to the 1st stage of disability;
- If there is stage 3 HF, stroke, anemia and other problems that arise in severe extra-real complications of the disease.
- If a person cannot exist without additional help.
So we looked at all the conditions when disability is assigned to people after removing kidney stones or suffering from chronic pyelonephritis.
Causes of the disease
Unfavorable factors and triggering points are:
The causes of glomerulonephritis can be diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, childhood rheumatism. hemorrhagic vasculitis. Agents for the occurrence of glomerulonephritis are also:
Source: https://doktordetok.ru/urolog/glomerulonefrit-u-detey.html
Symptoms and diagnosis of chronic renal failure
Signs of chronic renal failure include changes in a person’s appearance that occur at the 2nd and 3rd stages of the disease. At the level of well-being, a person may notice dryness and the appearance of yellowness on the skin, causeless hematomas, red spots that are very itchy, swelling of the limbs and face, sagging muscles and decreased performance. Most often, the disease causes a malfunction of the nervous system. There is apathy, insomnia, fatigue, absent-mindedness and inattention, difficulties arise with the perception of new information, and memory noticeably deteriorates.
Laboratory tests reveal increased levels of uric acid and creatine in the blood. As a result, a person notices bad breath. Degenerative processes in the joints begin. Against the background of the disease, swelling is observed, and water-salt balance is disrupted. All this provokes disruptions in the functioning of the midvascular system. Almost always, chronic renal failure causes dizziness, thirst and difficulty breathing.
Chronic renal failure, if we are talking about its last stage, can cause many complications. First of all, the heart suffers, hypertension can develop, and as a result, a heart attack.
Chronic renal failure inevitably disrupts the functioning of the nervous system, which is manifested by convulsions. There are situations when patients are diagnosed with dementia. But the most serious complication in this situation is kidney necrosis. Without timely treatment, it is deadly to humans.
What is the glomerulus and how do the kidneys work?
The blood entering the kidneys through the renal artery is distributed inside the kidney into the smallest vessels, which flow into the so-called renal glomerulus.
What is a renal glomerulus?
In the renal glomerulus, the blood flow slows down, as through a semi-permeable membrane, the liquid part of the blood with electrolytes and organic substances dissolved in the blood seeps into Bowman’s capsule (which, like a wrapper, envelops the renal glomerulus on all sides). From the glomerulus, the cellular elements of the blood with the remaining amount of blood plasma are removed through the renal vein. In the lumen of Bowman's capsule, the filtered part of the blood (without cellular elements) is called primary urine.
What is Bowman's capsule and renal tubules (loop of Henle)?
But in addition to toxic substances, many useful and vital substances are dissolved in this urine - electrolytes, vitamins, proteins, etc. In order for everything useful for the body to return to the blood, and everything harmful to be excreted in the final urine, primary urine passes through a system of tubes (loop of Henle, renal tubule). It undergoes constant processes of transition of substances dissolved in primary urine through the wall of the renal tubule. Having passed through the renal tubule, primary urine retains toxic substances in its composition (which need to be eliminated from the body) and loses those substances that cannot be eliminated.
What happens to urine after it is filtered?
After filtration, the final urine is excreted through the renal tubule into the renal pelvis. Accumulating in it, urine gradually flows into the bladder in the lumen of the ureters.
It is accessible and understandable about how the kidneys develop and work.
Source: https://www.polismed.com/articles-khronicheskijj-glomerulonefrit-01.html
Diagnosis of chronic renal failure
Any disease must first be diagnosed, because without this treatment is not possible. Chronic renal failure is determined by laboratory tests, which are prescribed by the attending physician. To ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, the following activities can be carried out:
• biochemical blood and urine tests; • Zimnitsky test; • ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
This way it will be possible to accurately establish a decrease in the main indicators of the kidneys, such as the level of glomerular filtration, urea and creatine. These results are the main criteria for chronic renal failure. A special period in the life of every woman is pregnancy. The load on the organs increases, and if there is chronic renal failure, then pregnancy may be accompanied by complications. It is important that even during pregnancy planning, a woman undergoes appropriate examinations by specialized specialists. If it turns out that the disease is progressing, then dreams of motherhood will have to be postponed for a while. Otherwise, complications - from anemia in the mother to pathologies of fetal development - cannot be avoided.
Hypertonic disease.
The frequency of observation depends on the DN group. Patients are observed by a therapist at least once a year, a cardiologist, a psychotherapist - as indicated.
Examination plan:
1. Clinical blood test.
2. Blood test for cholesterol, prothrombin, beta-linoproteins.
3. General urine analysis.
4. ECG
11 pages, 5182 words
Features of examination of a surgical patient
... the epicrisis should include studies (blood tests, urine tests, stool tests for ... years 3. General plan for examining the patient Features of examining a surgical patient Clinical examination of the patient is ... or contact your local physician yourself, who will refer him to ... Character of the “chair” Genitourinary system. Urination: frequency, pain. Diuresis. Kidneys: palpable, not...
3. Examination by an ophthalmologist (fundus).
Main directions of prevention:
— Promoting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Combating physical inactivity.
— Maintaining normal body weight.
— Creation of an optimal psycho-emotional environment.
— Creation of optimal working conditions (work associated with significant physical and emotional stress, exposure to unfavorable production conditions: hot, humid, cold and damp rooms, production noise, vibrations, night shifts, duty) are contraindicated.
— Creation of optimal living conditions
- Quit smoking, alcohol and salt abuse.
Nutrition for chronic renal failure
Once the diagnosis of chronic renal failure has been established, recommendations for food restrictions will immediately follow. You will have to exclude foods from your diet that can worsen your kidney condition. You need to eat less protein products, while giving preference to dairy. Doctors advise consuming fish and meat boiled, stewed or baked. The following should be reduced to a minimum: eggs, cereals, legumes, cocoa, cottage cheese and nuts. Bananas, potatoes and animal protein can have a negative effect on the kidneys. Accordingly, you can eat them only in small portions.
A patient with chronic renal failure should forget about garlic and onions, as well as foods high in potassium. Diet selection is carried out individually for each patient by his attending physician, taking into account concomitant diseases. It is important to know that special nutrition can have a positive effect on the patient’s well-being and slow down the development of chronic renal failure.
Treatment methods for chronic renal failure
The doctor will be able to prescribe adequate treatment after the diagnosis is confirmed and the stage of the disease is established. Rarely can the disease be diagnosed at an early stage. If the disease has already reached the second stage, then sometimes surgical intervention is required. All measures are aimed at not only returning chronic renal failure to the initial stage, but, if possible, curing the patient. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of success.
When the disease is in late stages, the doctor must choose treatment methods wisely and with caution. Human life is at stake, and only the joint efforts of doctors and the patient will be the key to success in the fight against chronic renal failure. Physiotherapy is often used to combat the disease, which can speed up the process of removing toxins from the body.
Patients benefit from infrared baths and a trip to a sanatorium. If there is excess calcium, then specialists may prescribe cleansing enemas. Some doctors are inclined to another option - taking laxatives. But the result will be the same - the level of this microelement will return to normal.
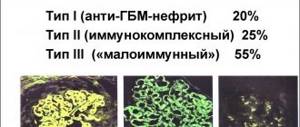
Types of glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis occurs when the glomeruli are damaged, in which the blood is filtered and released from metabolic products. When glomerular function is impaired, blood elements and proteins are filtered.
When an infection or virus enters the body, the body normally produces antibodies - protective proteins that bind to damaging factors.
This complex should normally be eliminated from the body, but it remains and affects the glomeruli. And the antibodies perceive the kidney tissue as an infectious agent and settle on it, disrupting the function.
There is a classification of the types of this pathology, which reflects the course of the disease, kidney damage, the agent of inflammation, and the predominant symptom.
There is a primary one, which occurs as an independent disease, and a secondary one, which occurs as a complication of a chronic lesion in the body.
By damage: diffuse, when almost the entire kidney is affected, and focal - in one place.
According to the damaging agent: bacterial, viral, parasitic.
According to the flow there are:
There are forms of glomerulonephritis according to the leading manifestation of symptoms:
How to get a disability group for chronic renal failure
Only after the medical commission gives an official conclusion about the presence of chronic renal failure in the patient does he have the right to count on receiving a disability group. It’s worth knowing these nuances first. When the diagnosis indicates that one of the three initial stages of the disease is occurring, doctors will simply advise switching to light work, but will confirm the fact of ability to work. In this case, they may assign a 3rd disability group.
When we are talking about disruption of the functioning of other organs and chronic renal failure is noticeably progressing, then most likely the medical commission will assign a 2nd disability group. Those who have undergone a kidney transplant or who cannot cope without the help of other people have the right to apply for the 1st group. But the main task of doctors is to make every effort to cure the patient. A person must find time for himself and undergo a comprehensive medical examination every six months, which will give a chance for an early diagnosis and timely treatment. Then the likelihood of a full recovery will be extremely high.
Classification of glomerulonephritis in children
Glomerulonephritis in children can be primary (an independent nosological form) and secondary (occurring against the background of another pathology), with an established (bacterial, viral, parasitic) and unknown etiology, immunologically caused (immune complex and antibody) and immunologically unconditioned. The clinical course of glomerulonephritis in children is divided into acute, subacute and chronic.
According to the prevalence of the lesion, diffuse and focal glomerulonephritis in children is distinguished; according to the localization of the pathological process - intracapillary (in the vascular glomerulus) and extracapillary (in the cavity of the glomerular capsule); according to the nature of inflammation - exudative, proliferative and mixed.
Chronic glomerulonephritis in children includes several morphological forms: minor glomerular disorders; focal segmental, membranous, mesangioproliferative and mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis; IgA nephritis (Berge's disease). According to the leading manifestations, latent, hematuric, nephrotic, hypertensive and mixed clinical forms of glomerulonephritis in children are distinguished.
Nephrectomy and its consequences
Patients with kidney failure, cysts or malformations of the organ are often prescribed its removal. Many of those who are about to undergo a complex surgical operation think about the possible serious consequences for their health. It is difficult to predict what the state of the body will be, since everything depends on the outcome of the intervention itself and the complications that inevitably arise after it.
Most often, patients in the late period develop the following conditions:
- pneumonia;
- stroke;
- thrombophlebitis;
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction.
Some people experience disturbances in the functioning of the spleen and adrenal glands. In addition, during the first time of the adaptation period, a healthy kidney begins to increase in size, since it performs the functions of both organs. Therefore, in order to reduce the load, the patient is forced to adhere to a special lifestyle and restore his own health. In this regard, it is considered reasonable to ask: does removal of a kidney provide disability, and what documents must be provided for this.
Forecast and prevention of glomerulonephritis in children
With adequate treatment, acute glomerulonephritis in children in most cases ends in recovery. In 1-2% of cases, glomerulonephritis in children becomes chronic, and in rare cases, death is possible.
With acute glomerulonephritis in children, serious complications may develop: acute renal failure. hemorrhages in the brain. nephrotic encephalopathy, uremia and heart failure. posing a threat to life. Chronic glomerulonephritis in children is accompanied by shrinkage of the kidneys and a decrease in renal function with the development of chronic renal failure.
Prevention of glomerulonephritis in children consists of timely diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal infections, allergic diseases, sanitation of chronic lesions in the nasopharynx and oral cavity.
Source: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/children/glomerulonephritis
Obtaining disability after kidney removal
According to the laws of the Russian Federation, the absence of one kidney is not a compelling argument for disability. However, there are a number of amendments that allow you to make an exception and resolve the issue positively for the patient, adult or child.
Grounds for assignment of disability
Many people believe that a complex operation and a diagnosis gives the patient some advantages, because he can no longer perform his functions, engage in work, and lead his previous lifestyle as before.
But you should know that a disability group is assigned in the presence of three circumstances:
- impairment of the patient’s health due to complex disorders in the functioning of the body;
- inability to self-care, need for help and services of another person;
- the need for rehabilitation measures and social protection.
If a person has one or more of these conditions, he is sent to the ITU commission, providing a complete package of documents. She, in turn, is obliged to consider the situation - whether to grant disability or not and make an appropriate decision.
Required list of documents
In order for the expert commission to consider an application for assignment of disability, regardless of degree, for the first time, it is necessary to provide a complete package of documents, the list of which is established at the legislative level.
- application according to the established form;
- identification documents - birth certificate, passport, TIN;
- a referral issued by the attending physician for examination;
- a complete extract from the patient’s medical record;
- documents that can complement the picture of health status;
- results of completed studies (ultrasound, MRI, ECG, laboratory tests);
- a copy of the work book certified by a notary office and the original for comparison;
- a certificate characterizing the availability of work activity and its conditions;
- characteristics provided by the educational institution (for students);
- pension certificate, insurance policy.
Guidelines for living with a disability
To maintain a long and comfortable life after nephrectomy, a person must change his habits, eliminating harmful ones, adhere to certain dietary rules, and not feel disabled, that is, maintain a positive attitude and presence of mind under any circumstances.
Diet
Nutritional therapy plays an important role in the lives of people with one kidney. It allows you to minimize the load on the urinary system and its main organ. Excluded from the diet: fatty, fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, preserved foods. Limit consumption of foods high in protein and salt. Dishes should be light and quickly digestible. Cooking should be done by boiling, stewing or steaming. At the same time, you need to control the amount of liquid consumed. Coffee, strong tea, alcohol, and carbonated drinks are prohibited.
Sports activities
Physical activity is a great way to maintain normal well-being and physical activity. They are suitable not only for healthy people, but are also necessary for people with any pathology, or those who have undergone surgery. The main condition is the correct choice of type of activity and amount of physical activity.
Today, doctors are increasingly less likely to place restrictions on sports activities for patients who have undergone kidney removal surgery. They advise only to closely monitor your well-being during training, and stop exercising if the slightest discomfort appears.
It is definitely necessary to exclude from the list such traumatic sports as bodybuilding, football, basketball or boxing. Even mild mechanical stress increases the risk of damage to the only kidney. Swimming is considered beneficial because it helps strengthen all muscle groups and improve immunity.
In addition to playing sports and following a balanced diet, a person must radically change his lifestyle and set his priorities correctly. This will only improve his condition and allow him to fully exist and work.