How to treat
How to get rid of frequent urination? Treatment of frequent urination should be carried out only in case of pathological causes of its occurrence, therefore any therapy should be preceded by a thorough diagnosis. If the disease is identified, therapy will be selected by the doctor in accordance with the diagnosis.
For example, if urine output has become more frequent, if the phenomenon is infectious in origin, the following are carried out:
- antibacterial measures;
- therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking nisulin, antihyperglycemic medications, as well as synthetic vasopressin in case of diabetes insipidus;
- measures aimed at removing stones, if any;
- symptomatic treatment, which involves taking painkillers, antispasmodics, antipyretics and others.
Physiotherapeutic procedures and special medical gymnastics have a good effect for the treatment of pollakiuria in women and men; They perform especially well when the symptom is caused by natural changes in the body. If conservative and non-invasive methods do not have the desired effect, the doctor may recommend surgery. For example, this is indicated for patients with prostate adenoma if the size of the tumor is too large and the disease is at an advanced stage.
If you urinate frequently, you can try to correct the body’s behavior on your own.
To do this you should:
- If you drink a lot, reconsider the daily volume of fluid consumed (both with water and with other drinks, and with food) so that it does not exceed the average recommended norm of one and a half to two liters. But you shouldn’t cut down on drinking too much either, since dehydration can lead to serious pathological conditions.
- During urination, you need to try to better empty the bladder, for which you can lean forward a little.
- Avoid hypothermia of the body; hypothermia promotes increased fluid secretion by the kidneys with an increased frequency of elimination.
- Consult a doctor if pollakiuria is accompanied by taking diuretics.
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed. Traditional recipes may include herbs, decoctions and infusions, as agreed and at the discretion of the attending physician, since traditional medicine preparations may contain potentially dangerous components.
Prevention
Treatment of the disease should not be delayed due to the manifestation of characteristic complications that can lead to severe diseases of the bladder and other internal organs, but prevention helps reduce the risk of pathologies and eliminate the causes.
To prevent pollakiuria, the following recommendations must be followed:
- constantly maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid hypothermia, take care of the bladder;
- the fight against colds should not be delayed until severe consequences appear;
- when the urge to urinate appears, try to find an opportunity to immediately empty the bladder;
- Patients with a predisposition to the formation of cancerous tumors of internal organs should be regularly monitored by an oncologist.
Pathology in women and men
If a woman has an increased need to perform minor necessities, this may indicate a variety of pathologies. Frequent urination is accompanied by various kidney diseases; it develops against the background of a cold or with such a dangerous disease as cystitis. The latter in an adult woman is also accompanied by a burning sensation and severe pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of incomplete emptying when urinating, and a slight increase in temperature.
Sexually transmitted diseases that accompany adults who have an unguarded sexual life, as mentioned above, can also provoke this phenomenon; urination with them is very frequent, with a small volume of urine released at a time.
It is important to know that frequent urination during pregnancy, especially in the later stages, is normal: the growing fetus puts pressure on the internal organs, including the bladder, provoking a constant urge to relieve itself. A similar effect is often observed in women after intimate intercourse, and in older women, since their body undergoes some specific changes: muscle tone decreases, which also affects the ability of the bladder to retain fluid
Increased acidity of urine and hormonal problems can also affect the frequency of urination. For example, this phenomenon is typical for the initial stages of diabetes. And, of course, various infectious diseases can manifest themselves with this symptom.
In men, a very common cause of increased urine output is prostatitis; this is one of the most common pathologies among the male population under 50 years of age, accompanied by the symptom of painful frequent urination. When the gland becomes inflamed, it also irritates the surrounding tissues. When irritated, their receptors create false urges, leading to an increase in the frequency of the latter, even with a small volume of urine in the bladder.
Another typically male pathology is prostate adenoma, or prostate hyperplasia. It becomes a common cause of the problem in representatives of the older age group (over 60 years old), when the gland tissues, growing, impede the normal outflow of urine, emptying does not occur completely. In addition, in this condition, the desire to urinate appears when the bladder is less full than with a healthy prostate.
The causes of the symptom may be caused by a variety of sexually transmitted infections, accompanied by increased urine output:
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis, and others.
They also manifest themselves as itching in the urethra, burning, and discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Men may develop cystitis, but this is relatively rare and is associated with infection of the bladder by pathogens.
Another common cause of frequent urination among the stronger sex is urethritis and pyelonephritis, a symptom that occurs in diabetes insipidus (no pain is felt) and in patients with bladder hyperactivity.
Pollakiuria in prostate diseases
Frequent urination, which occurs in men over 50 years of age, usually indicates one of the diseases of the prostate gland: inflammation (prostatitis), benign hypertrophy or cancer.
Prostate pathologies
Also, prostate diseases are often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- fever and chills;
- lower back pain;
- muscle and joint pain;
- feeling of fullness around the genitals;
- tenderness of the prostate gland on palpation.
The most characteristic symptom of prostatitis is nocturia, which is accompanied by sudden urgency and painful urination.
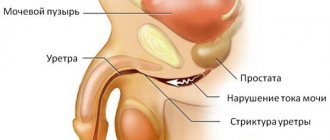
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer are problems with urination - weak urine flow and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, which are the result of compression of the enlarged prostate on the bladder neck.
If the pathology is not treated, it can lead to complete urinary retention. Surgery is necessary to reduce the volume of the prostate.
Frequent urination in a child treatment
The doctor selects the correct treatment regimen in each specific case individually, depending on the reasons and based on the examination. The child’s age and concomitant pathology are taken into account.
For inflammatory processes not associated with abnormalities in the development of the urinary tract, antibacterial drugs are prescribed taking into account sensitivity to the pathogen.
Cephalosporin antibiotics and protected penicillins are most often used. Among uroseptics, pipemidic acid and nitroxoline (Palin, Pimidel, 5 - NOK) are prescribed in pediatric practice.
According to indications, surgical intervention is performed: open or endoscopic.
Indications for surgical treatment: all diseases of the urogenital tract that lead to impaired urine outflow:
- PUJ strictures;
- developmental anomalies;
- strictures;
- blocking stones of the ureter, etc.
Important
Children with a tendency to salt formation must be given clean water to drink, in addition to milk, soup and compotes. It is also necessary to examine the salt composition of urine, this is necessary for the correct preparation of the diet.
Herbal medicine is used as an adjuvant - treatment with decoctions of plants with anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties. It is better to buy herbal infusions at a pharmacy. The following plants (not bitter) that are useful for a urological or nephrological patient are suitable:
- Dill seeds;
- kidney tea.
For a child older than one year, you can buy a ready-made form, for example, Canephron, Fitolysin.
Cranberry juice will be useful as an antimicrobial and diuretic, provided that the child does not have a tendency to diathesis.
In addition, with frequent urination against the background of an inflammatory process in the urinary tract, it is necessary to exclude dishes that increase the irritating properties of urine: spicy, sour, salty, smoked foods, rich broths.
If the cause of frequent urination in children is vulvovaginitis or balanoposthitis, start with local treatment. Use baths with a decoction of calendula, sage, chamomile or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Irrigation can be performed with liquid chlorhexidine or dioxidine.
For thrush in children (fungal infection), soda lotions provide good relief. If the measure is not successful, the pediatrician will select a suitable antifungal agent.
Diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus require treatment by an endocrinologist.
If the cause of frequent urination is due to neurological problems, a neurologist will work with the child. Additionally, drugs that improve blood supply to the brain, sedatives, and multivitamins are used.
Acute glomerulonephritis is treated in a hospital; the regimen is selected taking into account the form of the disease.
Victoria Mishina, urologist, medical columnist
9, total, today
Why you need to see a doctor and how he can help
Treatment is prescribed depending on the etiology of the disease in the following areas:
- destruction of infectious agents;
- cleansing and eliminating foci of inflammation;
- regeneration of damaged body tissues;
- stimulation of neural connections of the brain and genitourinary system;
- strengthening the muscle tissue of the bladder;
- normalization of hormonal levels;
- increasing immunity;
- regulation of the nervous system;
- surgical restoration of patency of the urinary canal;
- excision of tumors.
Each type of disease requires specialized treatment according to a doctor's protocol. Independent uncontrolled use of any drug will lead to irreversible complications, so we will not list the drugs.
Causes
It cannot be said that the reasons for the development of such a pathological condition are always pathological in nature, because urination is influenced by multiple factors. In particular, physiological pollakiuria is caused by excessive fluid intake during the day. This is typical for pregnant women, and sometimes is the first symptom of pregnancy.
In addition, the causes of this disorder may lie in hypothermia of the body, since exposure to cold adversely affects the condition of the bladder. In addition, the disorder sometimes occurs against a background of stress.
Thus, pollakiuria can be of two types: physiological and pathological. And if there is no physiological basis for frequent urination, then a complete examination of the patient is necessary to establish the pathology that caused the disorder.
Pathological reasons due to which such a urinary disorder may develop may be the following:
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- bladder tuberculosis;
- urolithiasis disease.
In men, this disorder occurs with prostate adenoma. In this case, the nocturnal form of pollakiuria predominates, that is, when the main volume of urine is excreted at night, while during the day a man goes to the toilet infrequently. Symptoms of urinary disorder can also be observed in some pathologies of the genital organs. For example, with endometriosis of the uterus and bladder, adnexitis, endometritis.
The reasons for the development of pollakiuria in children are as follows:
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system;
- endocrine causes, namely diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- colds;
- helminthic infestations;
- kidney diseases of an acute and chronic nature;
- poor living conditions;
- treatment with diuretics.
In children, the disorder can also develop due to a passion for carbonated drinks, as well as foods containing large amounts of water, for example, watermelons. It is clear that such pollakiuria in children is physiological and goes away after limiting or stopping the consumption of such foods and drinks.
Pollakiuria also develops in children susceptible to various neuroses, fears and phobias. In particular, if a child is forced to adapt to a new team, he may develop a disorder in which an increase in the number of trips to the restroom is observed during the daytime, while at night the baby does not go to the toilet.
Sometimes the disorder occurs due to damage to the central nervous system. In addition, tumors in the bladder can lead to a decrease in its volume, which reduces the amount of urine produced and increases the frequency of trips to the toilet. Even sexually transmitted diseases in both men and women can provoke the appearance of this disorder, therefore, before prescribing treatment, the doctor must comprehensively examine the person who has turned to him for help.
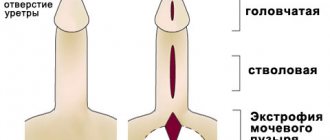
Pollakiuria: what is it, causes, symptoms and treatment
Pollakiuria is a term that refers to increased frequency of urination. Normally, a person goes to the toilet 5 to 8 times a day, but with various diseases, for example, the urinary system, this number can increase up to 20 times. In this case, the patient does not feel that the bladder has completely emptied.
Why is this condition dangerous?
Pollakiuria is only a symptom and does not pose a particular danger to the patient, however, it significantly reduces a person’s quality of life, because frequent urination is in itself an inconvenient phenomenon.
Also, in some cases, this symptom may be accompanied by an imperative urge, in which the patient is unable to restrain the act of urination; pain when passing urine; sometimes there are traces of blood in the liquid, which can frighten a person.
However, if the source of pollakiuria is not determined or the doctor’s prescription is not followed for a certain diagnosis, the patient may face serious consequences, for example, renal failure, which is characterized by the inability of the kidneys to adequately perform their functions.
Diseases that are accompanied by pollakiuria
First of all, it should be remembered that pollakiuria can be a physiological condition when a person drinks copious amounts of liquid. This category includes alcohol intoxication, as well as pregnancy. Frequent urination can often be caused by hypothermia or emotional excitement.
Also, frequent urination occurs while taking diuretics.
Pathological pollakiuria is a symptom of diseases of various organs:
Genitourinary system:
- Urolithiasis, namely a complication in the form of obstruction of the ureter.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases (cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis) and tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the genitourinary organs (hyperplasia or prostate cancer)
- Stress, which provokes frequent urination due to the absence of an infectious agent in the organs of the genitourinary system.
- Radiation (direct effect on the genitourinary system);
- Damage to the organs of the genitourinary system by the body’s own antibodies (observed in autoimmune diseases, when the immune system does not recognize and destroys its tissues)
Endocrine system:
- Diabetes mellitus of the first and second types (observed with absolute or relative insulin deficiency, resulting from the inability of the pancreas to produce the required amount of the hormone insulin, or the inability of receptors to respond to this hormone);
- Diabetes insipidus (observed in pathologies of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, in which the production of vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone, which reduces the amount of urine produced, decreases).
Psychogenic disorders:
- Problems in the sexual sphere of life.
- Fears.
- Neuroses and neurosis-like conditions.
This condition can be observed in old age against the background of many chronic diseases, as well as as a result of the aging process.
Symptoms
A characteristic symptom of this condition is an increase in urination with an unchanged amount of daily urine excreted. After going to the toilet, the patient still feels a full bladder, which indicates incomplete excretion of urine.
Since pollakiuria is only a symptom of a disease, the patient will experience the characteristic symptoms of the pathological process that provoked frequent urination.
With an infectious-inflammatory etiology, an increase in urination is accompanied by fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, weakness and increased fatigue.
The patient may experience pain in the lumbar region of the back or side.
In some cases, urine may contain pathological impurities: blood, secretions.
Treatment of frequent urination in a child
The reasons for going to the toilet can be different and require a qualified approach. You cannot make a diagnosis yourself if we are not talking about simple physiological factors. Self-medication threatens to worsen the patient's condition. It should be remembered that if the patient experiences pain, this may be a sign of stone passage and the child cannot be transported in this condition! You should call an ambulance and prepare to be admitted to a hospital.
Medicines
If frequent urination is observed in boys, treatment begins only after diagnosis - it is impossible to stop pathological pollakiuria without eliminating the underlying disease! The choice of drugs, dosage and treatment regimen depends on the disease; the range of therapeutic measures is quite wide:
- inflammatory processes - uroseptics and a course of antibiotics are prescribed;
- diabetes mellitus - constant use of insulin;
- glomerulonephritis – hormonal therapy, cytostatics;
- neurogenic hyperreflex disease of the bladder - physiotherapy, neotropic drugs, Atropine, etc.;
- neuroses - sedatives;
- tumors, pathologies of the central nervous system - observation, surgery.
Folk remedies
If the baby suffers from excessive trips to the toilet, and the causes of the disease have not been identified, a folk recipe will help. The product is usually prepared on the basis of medicinal herbs and has a mild effect. Here are some recipes:
- kidney collection/tea is a pharmaceutical preparation that is brewed according to instructions and drunk in 0.5 tbsp. twice a day. The course of treatment is no more than 15 days.
- Infusion of birch leaves. Take 2 tbsp. dry leaf, brew in 2 tbsp. boiling water for 2 hours and drink 0.5 tbsp before meals. The course of treatment is 25-30 days.
- Cornflower tea is prepared from 1 tsp. herbs and 1 tbsp. boiling water Leave for half an hour, strain and drink half a glass before meals. The course is no more than 10 days.
- Bearberry, bear's ears - herbal hay helps with kidney inflammation. Brew in a thermos at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. collection or herbs separately per 1 liter. boiling water Leave for 2-3 hours, drink as tea, 0.3-0.5 tbsp.
Rosehip decoction, jelly or compote with honey relieves inflammation of the urinary tract well and helps eliminate pollakiuria, but caution is in order - rosehip can become an allergen
Treatment
If frequent urination occurs while taking diuretic medications, you should stop using them (with mandatory consultation with your doctor!).
If a patient is dealing with pathological pollakiuria, then, first of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease . For diabetes mellitus, diet therapy, insulin therapy (for type 1 diabetes mellitus), as well as various medications that affect glucose metabolism and insulin production (for type 2 diabetes mellitus) are used.
If the cause of this condition is urolithiasis, complicated by obstruction of the ureters, then the only treatment method is removal of the stones.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases involve the use of antibiotics to eliminate the pathological process in the organs of the genitourinary system.
In cases of detection of oncological problems, it is necessary to immediately contact an oncologist to determine further treatment tactics.
Diagnostic methods
If frequent urination was not preceded by taking diuretics or drinking large amounts of liquid, you should visit a doctor to identify the causes of this symptom. Diagnosis for pollakiuria may include:
An oral interview to collect anamnesis (information about previous diseases, the patient’s living conditions). Examination by a urologist. It includes palpation of the kidneys and abdomen. In men, the external genitalia are also examined. Examination by a gynecologist (for women). It includes a visual examination of the cervix and palpation of the appendages. Study of the characteristics of the act of urination during the day
It is important for the doctor to obtain information about the frequency of urination and the volume of urine released during each urination. It is also necessary to report whether urine leaks on its own, whether urgent urges are disturbing
In this case, you need to keep track of the amount of liquid you drink. Urinalysis (general and Nechiporenko). They can be used to judge the presence of elements in the urine that should normally be absent from it. These include leukocytes, erythrocytes and proteins. Complete blood count to determine the level of white blood cells, hemoglobin and blood sugar. Blood test for glucose tolerance test (necessary to rule out diabetes mellitus). Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder). Ultrasound of the scrotum and prostate gland (for men). Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries (for women). Uroflowmetry (test to determine the rate of urine excretion).
Kidney ultrasound is a common method for diagnosing kidney diseases.
The patient may also need to consult the following specialists:
- neurologist;
- psychologist;
- psychotherapist;
- nephrologist (a doctor who diagnoses and treats kidney disease);
- urologist-andrologist (a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the male genitourinary system).
If the diagnostic methods described above do not help establish the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed additional tests. These include:
- Urography is an X-ray examination of the organs of the urinary and urinary system. Urography can be survey or excretory. The survey method consists of obtaining an x-ray taken at the lumbar level. Excretory urography is performed in a similar way, but this procedure is preceded by the injection of a contrast agent into a vein to obtain a better image of the organs.
- Cystography is an x-ray examination of the bladder. This procedure is carried out after filling the organ cavity with a solution of a contrast agent.
- Urethrography. This is the name for an X-ray examination of the urethra, which is carried out after filling the canal cavity with a contrast solution.
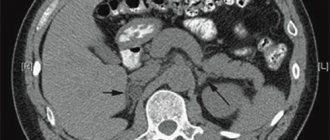
- CT (computed tomography) of the kidneys and organs of the urinary system is an X-ray examination, as a result of which the doctor receives high-quality images of tissues that can be examined layer by layer. CT can be performed either with contrast (injection of a contrast agent into a vein) or without it.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the urinary system. The results of the procedure are similar to those that can be obtained with a CT scan. However, MRI machines do not contain x-rays. The procedure can be performed with or without contrast.
MRI is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, allowing to detect malignant neoplasms at the initial stage of disease development
When should you see a doctor?
Most women are embarrassed by their problem and rarely go to the doctor. In the early stages, solving the problem is much easier than curing an advanced form of the disease.
An increase in the urge to urinate from 10 per day or more for three days is already a cause for concern.
If there is a sharp increase in temperature or pressure, burning and pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, consult a doctor immediately. Chronic cystitis contributes to the penetration of infection into the kidneys and progresses to pyelonephritis.
Severe cystitis - vesicoureteral reflux - leads to loss of kidney function. Cystitis therapy is carried out by a gynecologist and a therapist. Advanced STIs - chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis - can lead to disruption of the reproductive system, resulting in infertility. Gonococci cause disruption of all human organs
Anamnesis collection consists of an examination, analysis of drinking and eating habits, and questions about taking medications.
Then a general urine test and culture for the presence of bacteria are performed.
Hardware examination includes ultrasound of the genitourinary system, x-ray methods, urodynamic tests.
When changing the frequency of migration, record the content of pus or blood in it, and the change in color.
Causes and symptoms of frequent urination
If the first urge begins more than 10 times in 24 hours, you should carefully listen to your body when urinating. There are a large number of reasons that cause frequent urination. There is a list of factors and certain symptoms that affect the frequency of urination.
Pathological
A painful process with frequent urination - sometimes this manifestation is caused by the presence of a large tumor in the lower abdomen. An increased urge may appear only when the tumor has grown so large that it puts pressure on the bladder and there is not enough fluid to fill it. In this case, pollakiuria is accompanied by other pathological signs:
- severe weight loss;
- bloody urine;
- weak urination;
- body temperature is constantly elevated;
- chronic fatigue;
- sharp pain in the abdominal area;
- lymph nodes are enlarged.
Hyperaldosteronism is the excessive production of the hormone aldosterone by the adrenal glands.
A disease such as hyperaldosteronism inevitably leads to frequent urine output. The disease provokes increased production of hormones that affect the functioning of the kidneys. Heart and kidney failure affect the frequency of urges in the evening. Hyperparathyroidism is another pathology that causes frequent urge to urinate. With hyperparathyroidism, excessive amounts of parathyroid hormone are produced, which regulates the process of urine production. Morning urination is especially painful. Associated symptoms:
- urolithiasis disease;
- frequent bowel movements and constipation;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- abdominal pain;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- poor appetite.
Endocrine
Diabetes insipidus increases the frequency of bowel movements. Its symptoms are similar to diabetes mellitus, but the amount of glucose in the blood remains within normal limits. The process of regulating fluid excretion through the kidneys is disrupted. But frequent and strong urges are a sign of the development of diabetes. With this disease, glucose levels begin to rise, and its excess is excreted through the urine. This frequent, excessive urination is called hyperglycemia. In addition to urination, a pathological condition occurs, which is characterized by:
- thirst and dry mouth;
- weakness;
- chronic fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- skin itching.
Problems with the urinary system
Contacting a urologist will prevent complications with the urinary system.
Kidney infections and bladder diseases are sufficient reasons for increased urine output. If frequent urination becomes painful, then this problem requires contacting a doctor and conducting the necessary research. Self-treatment can relieve or partially reduce painful urination, but does not always cure poplakiuria completely. This leads to a chronic course and serious consequences. If you suspect infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs, you should consult a urologist. The following diseases can cause frequent painful urination:
- urethritis - infection in the urethra;
- cystitis is an infection in the bladder;
- pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidneys.
Gynecological diseases
A frequent and strong urge to urinate, which is not accompanied by pain symptoms, is observed in pathologies of the reproductive organs. This condition is caused by the formation of fibroids and other tumors in the uterus. As the tumors grow, they put pressure on the bladder and cause increased urine output. The main sign of such pathologies is frequent urination with blood, pain in the bladder, pain symptoms due to thrush. In such cases, the diagnosis is made by a gynecologist. Complications after an abortion can also cause frequent urges.
Non-pathological
Frequent non-pathological urination is provoked by drinks that have a diuretic effect.
Increased fluid intake provokes frequent urination without pain. Drinks that have a diuretic effect - for example, green tea or milk tea, cranberry juice - can cause frequent urges. Some berries also help the body remove more fluid than usual. These berries include:
- cowberry;
- cranberry;
- viburnum.
Doctors note that during stress, physical exertion and hypothermia, frequent urination is normal. Psychosomatics also affects morning and afternoon urges. In women, after menstrual bleeding, the frequency of urges increases as the accumulated fluid is eliminated. Taking diuretics (diuretic medications) also increases the frequency of urination.