This study is often the only opportunity to identify a digestive infection in a pregnant woman’s body. The consequences of this disease can be dangerous for both the mother and the unborn baby. Therefore, E. coli detected in a smear during pregnancy is the first signal to think about your health and the future development of the child.
- malaise, general weakness;
- frequent loose stools;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting. The vomit may contain a greenish tint;
- decreased appetite.
These are the first symptoms that E. coli is present in the body. As a rule, they appear after one day or even a week. If treatment was started quickly, without naive assumptions that it will go away on its own, the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days. Otherwise, the situation may worsen.
It is important to know that if symptoms do not go away for more than two days, be sure to seek qualified help from doctors. And do not self-medicate, taking information from the public domain as a basis. In the case of pregnancy, such actions can lead to disappointing consequences. Therefore, for treatment, contact your obstetrician-gynecologist strictly!
How does intestinal infection affect pregnancy?
Because when carrying a child, the mother’s immune defenses are weakened, this leads to the appearance of various types of infections. The worst thing that can happen is the breaking of water or premature birth. This, in turn, will lead to infection of the fetus, and there is also a risk of developing pathologies. They can affect not only his health or appearance, but also lead to death.
There is a certain percentage of probability that E. coli during pregnancy in a smear can penetrate through the vagina into the placenta, and from there into the blood of the fetus. This can lead to the development of a disease such as meningitis. When this infection enters the urinary tract, it is not eliminated from the body, but, on the contrary, contributes to the development of the pathogenic process. As a result, the immune defense of a pregnant woman’s body decreases, which makes her most vulnerable to other diseases.
Danger level during pregnancy
The issue of detecting a microorganism in a smear in pregnant women should be considered separately. At this time, the expectant mother’s body and her immunity are weakened, so the likelihood of various infections occurring is very high.
The rod can penetrate the placenta and infect the baby, which can cause meningitis..
The baby can become infected while passing through the birth canal.
E. coli can cause vaginosis, which can cause premature birth. Pregnant women also need to be careful with antibiotics. Under no circumstances take any medications without the permission of a specialist.
You need to go to the doctor as soon as possible - he will help you choose medications that will be safe for the development of the fetus, but will be able to normalize the microflora.
E. coli was found in the urine: what to do?
It may be that the infection entered the body before the woman became pregnant and did not manifest itself until certain moments. Therefore, when taking a urine test for flora and undergoing a medical examination, it is successfully detected. Then the doctor begins to think about what medications can be used to cure it. As a rule, antibiotics are prescribed.
Rules for donating urine:
If these three points are observed, you can be completely confident in the reliability of the results.
In what cases is it not recommended to use
Medicinal suppositories have a number of contraindications for use:
- Genferon is not used if the active ingredients are particularly intolerable or if there are autoimmune disorders.
- Viferon, Hexicon are prohibited for use in case of allergies.
- Kipferon should not be used during the first trimester of pregnancy, if breastfeeding, or if you are allergic to the components.
- Acylact is prohibited in case of intolerance to the active substances or thrush.
- Bifidumbacterin should not be taken if you are sensitive, under the age of three, or while pregnant.
- Sea buckthorn is not used if you are prone to allergic reactions.
To avoid side effects, it is necessary to carefully study the instructions for the drugs. The main key to successfully getting rid of dysbiosis is eliminating the cause of this phenomenon.
How can an infection enter the body?
There are several main reasons for this:
- Wearing a thong. Such panties create a rubbing effect, which provokes the penetration of this infection into the urinary system.
- Washing from anus to vagina.
- A sexual act in which a mixture of the flora of the genitourinary and intestinal systems occurs.
In a pregnant woman, an infection of this kind can occur due to intense enlargement of the uterus. But since there are not very many reasons listed, if you take them seriously, this will help protect yourself from infection.
Why candles?
Dysbacteriosis is treated in stages, following a certain scheme. If you mix up the steps, or start trying to increase immunity instead of eliminating pathogenic flora, then there will be no benefit from such treatment:
- First, it is necessary to eliminate all pathogenic flora from the body, which interferes with the normal functioning of healthy human microflora. For this purpose, special medications and folk recipes are used.
- Then the number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines is increased using other drugs.
- At the final stage, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system so that dysbiosis no longer appears.
You must first remove the cause of dysbiosis - the disease that led to it. In the case of chronic inflammatory and infectious processes, their exacerbation, they try to carry out symptomatic treatment, after which the dysbacteriosis is removed.
Rectal suppositories for dysbiosis can be used for both the first and second stages. There are also immunomodulatory drugs in the form of suppositories.
What to do if intestinal bacteria are found in the vagina?
- improper genital hygiene. First you need to wash the front part, then the anus, and not the other way around;
- constantly wearing thongs. Doctors recommend wearing cotton underwear;
- an intrauterine device is installed;
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners, combined intercourse;
- heatwave;
- diabetes;
- weakened immune defense of the body;
- Frequent douching helps wash out beneficial microorganisms.
Not everyone can guess that E. coli is present in the body. To do this, you need to undergo a medical examination and tests. But, however, there are several signs that suggest the occurrence of such a problem. For example, there may be copious discharge with an unpleasant odor and pain during sexual intercourse. This also includes itching and burning in the genitals. These symptoms are very similar to thrush; if you don’t neglect your health, you will be able to avoid its appearance too.
- Wash your genitals after urination, bowel movements and sexual intercourse. The main thing in this hygiene is its correct implementation (this was already mentioned a minute earlier).
- If possible, do not use deodorized toilet paper and sanitary pads; they provoke irritation of the mucous membranes.
- If you frequently change sexual partners, it is recommended to use contraceptives (condoms).
- Do not douche frequently. This negatively affects the condition of the vagina. Gynecologists recommend doing this only when seriously necessary. In general, it would be very useful for teenage girls to listen to such lectures from their parents or from the specialists themselves. Unfortunately, most girls do not know how to wash themselves properly, use sanitary pads, and so on. Not to mention the age when they become mothers. Therefore, it is possible that such infections arise against the background of illiteracy.
- After using the drug with the applicator, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect it.
In order to protect yourself from the occurrence of this disease, it is important to follow these recommendations. Moreover, there are not so many of them that you can’t remember them, and besides, they are quite basic.
Rules for the use of rectal suppositories
There are certain recommendations on how to properly use suppositories for intestinal dysbiosis:
- Before inserting the candle, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry thoroughly;
- put soft suppositories in the refrigerator for a while;
- then moisten it with water or lubricant to make it slide better;
- the patient is placed on his left side, the right limb is pressed to the stomach;
- With light movements, move the buttock and slowly inject the thin side of the product into the rectum or vagina to a level of 2.5 cm, for children - to 1.5 cm;
- After this, squeeze your buttocks and lie quietly for 15 minutes so that the product has time to penetrate deeply and be absorbed.
It is recommended to use suppositories after emptying the large intestine. This will help you get maximum results. To avoid staining your underwear, you need to put a diaper or sanitary pad.
For each drug, a specific dosage is indicated in the instructions.
| Medicine | Recommended intake |
| Genferon | 1 piece each 2 times a day for 10 days. |
| Viferon | For premature babies, 1 pc. 3 times a day. for 5 days. During pregnancy in the second trimester - 2 times a day, 1 pc. for 5-10 days. |
| Hexicon | The course of treatment is from 7 to 10 days in a dosage of 1 pc. twice a day. |
| Kipferon | Children: 0-1 years – 1 pc. once a day. Children over 12 years old and adults – 1 pc. three times a day. For vaginal dysbiosis – 10 days, 2 pcs. 2 times a day. |
| Acylact | 2 times 1 pc. for 5-10 days. |
| Bifidumbacterin | For acute intestinal disorders and gastrointestinal diseases, 2 pcs. three times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. |
| Sea buckthorn | 1 piece each before going to bed for 10 days. |
E. coli: how to get rid of it?
Most pregnant women do not want to start treatment so as not to harm the baby. But you shouldn’t react so categorically to therapy; now there are a lot of antibiotics that do not have a negative effect on either the mother or the baby. Therefore, you should not worry too much about this and cause the disease. The main thing is to know what medications to treat. And this is part of the work of an obstetrician-gynecologist; he will tell you everything in detail and describe it during a personal consultation.
During pregnancy, E. coli can be treated with the following drugs:
- Amoxicillin, cefatoxime, penicillins. This remedy does not in any way affect the intrauterine development of the fetus, and even more so, does not cause the development of defects in the baby;
- Furagin. It is allowed to be taken during any period of pregnancy, with the exception of 38-42 weeks.
It is very important to know that after completing a course of treatment with antibiotics, the body begins to weaken. To keep it in good shape, it is necessary to follow a diet and use supportive therapy. The doctor himself will tell you more about this when he conducts an examination, based on the results of which he will prescribe appropriate treatment.
If you identify at least one symptomatic phenomenon characteristic of an intestinal infection during pregnancy, you should seek qualified help from a local clinical institution. If tests confirm the presence of this infection, the specialist may prescribe:
If you are unable to get rid of this infection the first time, you will most likely have to go through the entire examination again. But the treatment will be carried out not according to the previously described scenario, but according to a new technique. It is possible that all therapy will take place under the supervision of specialists. You should not fall into hysterics and depress yourself that this will harm the baby; nothing like this will happen if you start treatment in a timely manner.
IMPORTANT! Some strains of bacterial microorganisms are resistant to certain drugs. This is very important information, especially if, before contacting the clinic, steps have already been taken to restore the body. It is also prohibited to engage in uncontrolled and self-administration of antibiotics during pregnancy.
The human body contains a lot of positive and opportunistic microorganisms that are necessary for its normal functioning, proper functioning of the immune system, synthesis of vitamins and a number of other necessary substances.
But sometimes these bacteria can be dangerous, especially if they get into areas of the body where they shouldn't be. Often this situation concerns a microorganism such as E. coli.
E. coli was found in a woman's smear: what are the causes and treatment of this condition, what to do if an infection is found in a pregnant woman and how to cure it without harming the fetus? Everything is detailed and available further in the article.
Escherichia coli in a smear
Hello, I went to the gynecologist with discomfort in the vaginal area, but at the moment I have almost no pain, however, when I took a smear for a culture tank, I was found to have the bacterium Escherichia coli in the smear. Please tell me what symptoms it usually manifests itself, how it is treated (especially if no suppositories are suitable for me), the reasons for its appearance and how terrible a diagnosis it is?
Related and recommended questions
43 replies
You know, unfortunately, I can’t answer this question yet because I don’t have the opportunity to pick up the test result right now (they didn’t tell me over the phone), but they said that I need to be treated. Please tell me how much it should be in order for it to need to be treated?
Up to 10 to 3-4 degrees, you can not treat if there are a lot of lactobacilli. If it’s more, yes, it needs to be treated. Here it is well written what it is - https://www.medicalj.ru/diseases/infectious/1041-kishechnaya- palochka
Please tell me, if Escherichia coli is detected in a gynecological smear, what symptoms does this bacterium manifest? Can it cause periodic pain in the lower abdomen?
And if they say that there is colpitis, but there is no inflammation of the ovaries and there is no odor in the mucous discharge, and there is also no diarrhea, then can one doubt the presence of this bacterium in the body?
Hello, please tell me on which day of your period is it better to do a gynecological ultrasound so that it is the most informative?
HELLO! I went to the gynecologist with discomfort in the vaginal area, when I took a smear for a culture tank, I was diagnosed with Klebsiella pneumoniae 10^7 KOE/tamp, as well as Enterococcus sp.10^5 KOE/tamp, please tell me what symptoms they manifest and whether they are necessary treat?
Hello. This is my first pregnancy, the smear test shows Esherichia coli 10*4, Lactobacillus spp 10*3 and
A woman, having learned about her “interesting situation,” must immediately register and undergo a full medical examination in order to know that her child is not in danger. Significant indicators of the health of the expectant mother are smear and urine analysis. Based on these results, existing pathologies can be identified and immediate measures can be taken to eliminate them.
This study is often the only opportunity to identify a digestive infection in a pregnant woman’s body. The consequences of this disease can be dangerous for both the mother and the unborn baby. Therefore, E. coli detected in a smear during pregnancy is the first signal to think about your health and the future development of the child.
- malaise, general weakness;
- frequent loose stools;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting. The vomit may contain a greenish tint;
- decreased appetite.
What it is
The microorganism was isolated back in 1885. Today many of its varieties are known. Their mass is harmless and necessary for the intestinal microflora. Escherichia coli is involved in the synthesis of a number of vitamins: K, group B.
But there are more than a hundred types of pathogenic microorganisms that can cause serious illness or poisoning.
Even opportunistic bacteria, getting from the intestines to other organs, can pose a danger.
The normal habitat of the stick is the area of the large intestine located closer to the anus.
In small quantities, this bacterium is present in the vagina, but when it multiplies, it leads to problems - bacterial vaginosis and others.
Escherichia coli in a smear is a cause of infection in women
Escherichia coli bacteria are native to the colon, where they help break down food and produce B vitamins and vitamin K. Although they are beneficial in the colon, they are harmful in other parts of the body. Their presence in the vagina is likely due to transmission of microorganisms from the lower gastrointestinal tract. The source of genital tract infection may be the passage of pathogens from the urinary tract . This is especially true for women who have a shorter urethra and its exit close to the vagina and anus, increasing the likelihood of transmitting bacteria between these structures.
Escherichia coli is one of the aerobic bacteria that causes inflammation in the vagina. E. coli in the vagina multiplies uncontrollably, especially as a result of quantitative and qualitative disruption of the natural vaginal microflora. Physiological microflora provides resistance to bacterial colonization and is an important factor that naturally protects mucous membranes from the formation of potentially pathogenic bacteria and fungi. A decrease in the number of lactic acid bacteria from the genus Lactobacillus occurs mainly during a decrease in general immunity. Thus, Escherichia coli in the vagina is often a problem for pregnant women. Hormonal changes that occur in expectant mothers change the vaginal pH to alkaline, which promotes the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the vagina, such as E. coli. Scientists also report that their presence may be due to hormonal changes after menopause and estrogen deficiency, which ensure normal vaginal microflora.
Reasons for appearance
Reasons why a microorganism can enter the vagina:
- Poor hygiene, improper washing. The vagina and anus are located nearby, so you need to wash yourself not from bottom to top, but from top to bottom to prevent the introduction of pathogenic microbes.
Wrong underwear. Microorganisms can enter the vagina due to wearing tight underwear and thongs.
Many people like the latter - it’s beautiful, sexy, but it’s still better not to abuse them, choosing health over beauty. It is worth choosing underwear made from natural materials.
Unprotected sex. You can get E. coli through combined anal-vaginal contact. Therefore, lovers of variety in bed need to be careful about protective equipment.
Constant change of sexual partners, weakened immunity and frequent douching increases the risk of getting the bacillus into the smear.
Don’t know what colpitis is in women, what are the features of its treatment? We have an interesting article that is worth reading.
Rules for the use of rectal suppositories
There are certain recommendations on how to properly use suppositories for intestinal dysbiosis:
- Before inserting the candle, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry thoroughly,
- put soft suppositories in the refrigerator for a while,
- then moisten it with water or lubricant to make it slide better,
- the patient is placed on his left side, the right limb is pressed to the stomach,
- move the buttock aside with light movements and slowly inject the thin side of the product into the rectum or vagina to a level of 2.5 cm, for children - to 1.5 cm,
- After this, squeeze your buttocks and lie quietly for 15 minutes so that the product has time to penetrate deeply and be absorbed.
It is recommended to use suppositories after emptying the large intestine. This will help you get maximum results. To avoid staining your underwear, you need to put a diaper or sanitary pad.
The suppository should be inserted into the anal canal using sterile medical gloves to avoid mechanical damage to the mucous membranes.
For each drug, a specific dosage is indicated in the instructions.
| Medicine | Recommended intake |
| Genferon | 1 piece each 2 times a day for 10 days. |
| Viferon | For premature babies, 1 pc. 3 times a day. for 5 days. During pregnancy in the second trimester - 2 times a day, 1 pc. for 5-10 days. |
| Hexicon | The course of treatment is from 7 to 10 days in a dosage of 1 pc. twice a day. |
| Kipferon | Children: 0-1 years – 1 pc. once a day. Children over 12 years old and adults – 1 pc. three times a day. For vaginal dysbiosis – 10 days, 2 pcs. 2 times a day. |
| Acylact | 2 times 1 pc. for 5-10 days. |
| Bifidumbacterin | For acute intestinal disorders and gastrointestinal diseases, 2 pcs. three times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. |
| Sea buckthorn | 1 piece each before going to bed for 10 days. |
Before using any medicine, you should consult your doctor.
Associated symptoms and signs
The first signs of the presence of E. coli in a smear may appear a day or even a week after it enters. Characteristic symptoms:
- severe diarrhea;
- heat;
- vomiting with greenish impurities;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the stomach;
- constant nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- general malaise.
Symptoms usually disappear on their own within a couple of days. The reason for this is the spontaneous sanitation of the intestines. But if this condition does not go away for more than two days, consult a doctor.
Treatment of E.coli in men
Treatment of E.coli infection (drugs, regimen, duration of administration and dosage) is prescribed by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s condition and manifestations of the disease. It is important that the specialist is confident, thanks to diagnostic data, that the problem is caused by E. coli, since the latter is a conditional pathogen and can be present normally (the presence of signs of the disease and the detection of this pathogen in tests does not always indicate that the first is a consequence of the action of the second).
If E.coli is accidentally detected, treatment is indicated only if there are corresponding complaints, planning surgical manipulations on the organs of the urogenital tract, etc.
Treatment of E.coli in men is carried out with the help of antibacterial drugs, ideally after establishing the sensitivity of the causative agent to the latter (antibiotic resistance is determined by cultural testing).
In general, for the treatment of acute prostatitis, the drugs of choice are oral forms of fluoroquinolones, such as ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, etc., cephalosporins (II, III generations) - cefixime, cefuroxime, etc. Co-trimoxazole and doxycycline may be prescribed. The usual course of treatment should not be shorter than 4 weeks. Chronic prostatitis is treated longer (up to 12 weeks), mainly with fluoroquinolones.
Treatment of orchitis/epididymitis/orchiepididymitis is also carried out with fluoroquinolones, new generation cephalosporins, less often with co-trimoxazole, and ampicillin-based drugs. Duration - at least 4 weeks, the form of administration is determined by the severity of the disease.
As a rule, one drug is sufficient to treat E.coli infection. Treatment of a sexual partner is carried out only with the appropriate recommendation of a doctor. During therapy, you should abstain from sexual intercourse (especially anal-genital) or use barrier contraceptives. Sometimes a specialist may additionally prescribe enzyme and vitamin preparations, courses of massage and physiotherapy, etc.
In men, genitourinary tract infections often occur with complications (some experts consider the episode of UTI in men to be a complicated infection). Complicated infections are most often caused by antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli or an association of several groups of bacteria. The development of complications is facilitated by: • congenital or acquired structural abnormalities (kidney stones, foreign bodies, duplication of ureters, etc.); • metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, etc.); • decrease in the protective functions of the body (age-related, after transplantation, immunodeficiency states, etc.) and other factors.
How to get rid of an infection
If E. coli was detected in a vaginal smear, this is a serious reason to start treatment as early as possible. Of course, only a doctor can describe his tactics correctly. Antibacterial drugs are mainly used.
Sometimes local therapy is sufficient, but if the lesion is quite serious, more thorough treatment is required.
Antibacterial correction is carried out on the basis of an antibiogram of the identified pathogen.
Often drugs from the fluoroquinolone group are used - Levofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin. The required dosage and duration of treatment is determined only by the doctor.
Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, as this may cause the microorganism to become resistant to antibiotics.
Consider popular antibacterial drugs:
Monural. Available in the form of a colorless granular powder, which must be taken after dissolving with water.
The effect is caused by the presence of phosphonic acid derivatives. This remedy is a broad-spectrum antibiotic and can be prescribed to pregnant women.
It is usually recommended to consume 3 grams once a day. If the infection is severe, the drug may be combined with other antibiotics.
Suprax. Available in capsule form. The main active substance is cefixime. Used for a number of infections, in particular E. coli.
It is often prescribed together with Canephron, which simultaneously protects the urinary tract from infections entering it. This is a strong antibiotic.
Fosmicin. Also applies to broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, an absolute analogue of Monural. Contraindications include pregnancy and age under 12 years.
If the damage is serious, symptoms of inflammation appear, and there is a risk of intrauterine damage, this remedy is also prescribed to pregnant women with careful supervision of a specialist.
Preferred formulations also contain an epithelial repair component. The use of Gynoflor vaginal tablets gives good results.
To restore the microflora, the drugs Ecofemin and Vagilak can be used. Normoflorin is indicated for oral use.
If E. coli is present in the smear, local treatment is sometimes sufficient. It involves regular hygiene of the external genitalia.
Sometimes doctors advise using various herbal infusions instead of pharmaceuticals, for example, chamomile infusion.
Therapy may involve therapeutic douching.
It is often recommended to administer vaginal suppositories that have antiseptic properties. Suppositories with nystatin are used. You may receive a recommendation to inject a 20% borax solution into the vagina.
Vaginal suppositories can be prescribed Lactobacterin or Bifidumbacterin. Sometimes sessions of ultraviolet irradiation of the genital area are required.
What level of hemoglobin in women should be normal, what are the reasons for its fluctuations, is described in detail here on the portal.
Why can hemoglobin levels drop, what are the causes of low hemoglobin in women and how to prevent it? Read about it on our project.
Sometimes folk remedies really help. However, before using them, you need to consult a gynecologist so as not to harm yourself.
The following methods are popular among people:
Jerusalem artichoke. Several Jerusalem artichoke fruits need to be thoroughly washed and peeled. Cook until tender, then drain the resulting broth.
Cut the fruits into pieces and pour kefir or sour cream (any fermented milk product will do).
The resulting broth can also be drunk by adding a small amount of sour cream and salt. You need to eat the prepared dish once a day until the symptoms of the problem disappear.
Please note that this measure can be used in complex therapy, but it alone will not cope with the infection.
Kefir lotions. The beneficial fermented milk environment has a detrimental effect on E. coli, so it is often recommended to use kefir, natural yogurt, and sour cream.
You can make lotions with kefir. Take a sterile bandage or cotton wool and soak it well in the fermented milk product.
Place the compress in your underwear and put it on. Lie like this for 10 minutes, then rinse your genitals well with clean water. Repeat for a week.
Chamomile or calendula for washing. This measure will not help eliminate the microorganism itself, but will eliminate the symptoms of the lesion and wash away dead organisms from the mucous membranes and genitals.
Take 20 g of herbs, pour boiling water over them. Cover the container well with a lid and let it cool. Then strain the grounds well and use the broth for washing. 7-10 procedures will be enough.
Does a partner need treatment if a woman's smear shows E. coli?
A smear of the contents of the cervical canal is an important marker for determining the state of women's health. If the obtained data deviate from generally accepted norms, a pathological process is diagnosed. In particular, during the study of a smear, Escherichia coli - Escherichia coli - can be detected. Normally, they multiply and grow in the colon and are absent from the cervical canal. Why is Escherichia coli dangerous in the cervical canal, what symptoms may bother a woman, and how to act if pathology is detected during pregnancy? Answers to all of the above questions are presented below.
Discharge during therapy with antibiotic suppositories
Women often note that during treatment with vaginal suppositories, the amount of vaginal discharge increases. This may be due to the fact that the drug dissolves, fights microbes, and its remains are excreted with vaginal secretions, increasing the volume of discharge. But sometimes discharge after using a suppository with an antibiotic can signal problems in the female reproductive and excretory system.
Let's consider the main characteristics of the discharge and the possible causes of its occurrence during treatment with vaginal suppositories, depending on the color of the discharge:
- Red. Discharge of this color can signal the presence of inflammation in the cervical canal, a tumor in the ovaries, or genitals. If you have reddish discharge, it is better to consult a gynecologist to find out whether it is a symptom of serious health problems.
- Pink. Pale pink discharge often appears as a result of improper administration of the suppository. If you administer the drug carelessly, you can damage the delicate mucous membrane of the vagina, which will cause pinkish spots to appear on your underwear. This is not a reason to panic, you just need to use suppositories more carefully.
- White. White thick discharge. Abundant, transparent, odorless discharge containing lumps similar in appearance and grayish-white color to a champignon mushroom, not accompanied by discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen, only indicates the removal of excess medicine. If the discharge acquires an unpleasant sour odor and does not disappear after a week, you should consult a doctor.
- Green. Green secretion indicates the correct use of antibiotic suppositories for infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. This is how pathogenic bacteria are eliminated. In a week everything should be back to normal. If this does not happen, you should consult a doctor to select a more suitable medication.
IMPORTANT! The discharge can be abundant and have different colors and characteristics. Some of them are considered normal, others require immediate consultation with a doctor. It is necessary to observe the discharge for a week, and then decide to consult a doctor.
Escherichia - Escherichia coli - in the cervical canal
E. coli can normally be detected in stool cultures. We can talk about the development of pathology when it is detected in a smear of the vagina, cervical canal or urine culture. Most often, such a deviation from the norm indicates the development of a serious malfunction in the genitourinary and digestive systems. After determining the diagnosis, treatment must be started as soon as possible, otherwise the process may become chronic.
The danger lies in the resistance of Escherichia coli to various drugs, in particular to many antibiotics and compounds intended for the sanitation of the genital organs. Treatment of a lesion takes a long time, and achieving reliable results is not always possible.
Bacteria do not always pose a threat to the human body. Escherichia is directly involved in the formation of local immunity, therefore the disease is diagnosed when enterococci are detected in an atypical place in sufficient quantities. In such cases, pathological resistance of microorganisms to the immune response and a decrease in its activity are diagnosed.
Tablets for dysbacteriosis
Tablet preparations for the treatment of dysbiosis can be divided into two main groups - antibacterial (eliminate the main cause of the disease - pathogenic microorganisms) and probiotic (promote the proliferation of normal intestinal flora and increase immunity).
The cause of dysbacteriosis can be E. coli, entorococcal, staphylococcal, candidomycosis and other infections. Common drugs for drug treatment are Levomycetin, Streptomycin, Nystatin, Intetrix, Pifamucin, Furazolin, Enteroseptol.
A doctor can prescribe drugs for the treatment of dysbiosis only after bacterial culture and determination of the sensitivity of the causative agent to the chosen drug.
Drugs that enhance immunity, normalize microflora and eliminate the negative symptoms of dysbacteriosis:
Sorbents. Polypefan, activated carbon, Pepidol are sorbent preparations that bind toxic substances and prevent the spread of putrefactive processes in the intestines. Used at the first stage of treatment of dysbiosis.
BS from live strains. Bifikol, Baktisubtil, Enterol, Colibacterin – are used in the first and second stages of dysbacteriosis, are made on the basis of microorganisms that form the normal intestinal flora.
Prebiotics. Duphalac, Normaza, Hilak-Forte belong to the group of prebiotics that do not contain strains of microorganisms, but create favorable conditions for the development of beneficial microorganisms, and can be used at any stage of the treatment of dysbiosis.
Probiotics. Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Narine, Lactobacterin, Bifiform are probiotics that represent a wide group of drugs used to treat dysbiosis of any stage. They contain live strains of beneficial bacteria that normalize the intestinal microflora and inhibit pathological microorganisms.
Enzymes. Mezim-Forte, Polyzyme, Digestal, Panzinorm-Forte belong to the group of enzymes that help normalize digestive processes, digest food and absorb beneficial components in the stomach and intestines.
Immune modulators. Levomizole, Dekaris are immunomodulators, they contribute to the normalization of local immunity of the gastrointestinal tract, and are used in the final stages of treatment to consolidate positive results.
Restorers of motor functions. Duspatalin, Trimedat, Meteospasmil, Immudon - these drugs restore normal intestinal motility, which helps eliminate symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, and flatulence.
Stimulators of intestinal epithelium. Essentiale and other drugs that stimulate the work of intestinal epithelial cells help get rid of intestinal colic.
Reasons for the appearance of Escherichia in the vagina
The bacterium belongs to the group of opportunistic pathogens and is characteristic of the colon. It is directly involved in the processes of food decomposition and produces vitamin B and K. Like other pathogens, Escherichia is useful only in the large intestine; their detection in atypical places is dangerous.
The main reason for their presence in the vagina is the transfer of microorganisms from the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract. Detection of a pathogen in a smear of the cervical canal is not excluded. The risk of infection of a woman’s genital organs remains high due to the anatomical structure. Girls have a short urethra, it is located close to the vagina and anus, so the transfer of bacteria occurs frequently.
Escherichia is an aerobic bacterium that causes the development of an inflammatory process in the vagina. The microorganism actively reproduces in an atypical environment and leads to qualitative and quantitative distortion of the natural microflora. The main problem that appears against the background of such progress is the rapid decrease in the number of beneficial lactobacilli. Since they provide protection to the mucous membranes from pathogens, when creating a favorable basis, immunity decreases and the body’s resistance to various pathologies decreases.
Escherichia coli is often found in cervical smears in women during pregnancy. The basis for the pathological process is created against the background of hormonal changes characteristic of pregnant women. Against this background, the vaginal environment changes to alkaline.
The list of the main reasons that provoke the movement of E. coli into the vagina includes:
- anal sex;
- irregular change of linen;
- wearing underwear made of synthetic materials;
- insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia.
Anal sex is an indirect cause that can provoke infection. Much more often the reason is insufficient hygiene and wearing low-quality underwear. Infection in domestic conditions (through personal hygiene items) occurs quite rarely.
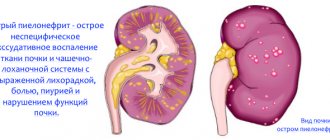
The most dangerous detection of Escherichia coli is in urine culture. This disorder indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the ureters, kidneys and bladder. The danger of the process lies in the rapid progress, against which destructive changes occur in the structure of the kidneys, leading to the development of renal failure.
Opportunistic bacteria - Escherichia coli in a smear
If such a symptom appears, antibiotic treatment should be started immediately. Medicines will help prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
Causes of Escherichia coli
For various reasons, they are able to increase the territory of their habitat, populating, in addition to the intestines, the vagina and urinary tract.
E. coli can multiply in almost any human organ, since they only need a moist environment and a stable temperature to live.
If lactobacilli disappear for some reason (for example, after treatment with antibiotics), then rapid proliferation of Escherichia coli begins, as well as other opportunistic microorganisms: candida, staphylococci, enterobacteria.
It is difficult to find Escherichia coli in a smear from the vagina and cervical canal, since the microbe forms colonies in the form of chains, which are mistakenly diagnosed as staphylococcal. It is easier to detect Escherichia coli in a smear culture.
Before taking a smear for culture, you need to prepare - wash your intimate organs with warm, clean water without soap or gel, and a few days before the test, give up alcohol.
Escherichia coli is resistant to the main types of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs. Treatment of E. coli in a smear is long and complex, and results are not always achieved.
One of the common reasons for the colonization of the vagina with E-coli is insufficient personal hygiene of the genitourinary organs.
You can become infected through sexual contact and through shared bath towels, washcloths, and underwear, but for this you need to have a weakened immune system: people with strong immune defenses cannot become infected with E. coli through household means.
Escherichia coli, having multiplied in the genitourinary tract, leads to the development of inflammation. In addition to smear culture, Escherichia coli can be detected in urine culture.
Source
Symptoms
The activity of a microorganism can be suspected by the following signs:
- constant itching and burning in the vagina;
- painful intercourse;
- difficulty urinating;
- slight discomfort (pain) in the pubic area;
- thick white or gray discharge that smells fishy.
With concomitant damage to the urinary system, other symptoms may occur: nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. Such signs can also be traced due to the rapid increase in the number of bacteria and indicate intoxication of the body.
Why is self-medication dangerous?
E. coli is an opportunistic pathogen; it can be present in smears without causing any harm. There is no need to treat such carriage.
Taking antibiotics without a doctor's prescription will lead to dysbiosis, as well as an increase in bacterial resistance. It turns out that the antibiotic will kill the harmless bacillus, but other strains that are insensitive to this drug will become active. Then treatment, if it is really needed, will be much more difficult.
In addition, under the cover of E. coli, other infections may be hiding that are not detected by microscopy. If they are not detected in time, you may waste time with treatment that is ineffective for such infections.
Only a specialist can prescribe the correct examination and treatment plan.
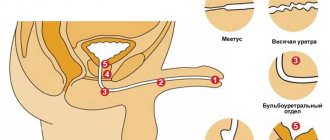
The E.coli bacterium can be present in a man's urethra normally, but can also be transmitted: • through sexual contact (especially anal-genital); • transfer from the intestines as a result of poor hygiene, with blood and lymph flow; • as a result of transplantation.
Factors that prevent the proliferation of a microorganism and the development of an infectious disease in a man’s body include: • mechanical protection – at the entrance to the urethra there is a special element, otherwise Guerin’s valve, which prevents the penetration of bacteria; in addition, there are glands, some of which secrete urethral mucus, and others have a special secretion during ejaculation (such secretions help remove bacteria from the urethra); • slightly alkaline/neutral urethral environment; • immunological local protection; • prostate secretion
Prostate secretion - zinc-peptide complex, otherwise called prostate antimicrobial factor, has an antimicrobial effect and maintains an alkaline-neutral environment.
In boys (in children, the vast majority of cases of UTI (urinary tract infections) are caused by E. coli), the following risk factors are noted: • the first year of life; • an uncircumcised child (circumcised children get sick about 4 to 10 times less often, according to various sources); • long-term catheterization of the urinary tract; • congenital structural abnormalities of the urinary tract; • presence of an episode of similar infection in the past; • stagnation of urine due to phimosis, kidney stones, etc.; • family predisposition.
Symptoms of infection caused by Escherichia coli are not specific to this microorganism and are determined by the location of the inflammation.
Urethritis is characterized by: • increased frequency and pain of urination; • pain during erection/ejaculation; • sometimes – constant urethral pain; • urethral itching; • discharge from the urethra; • in the urethral area – discomfort, irritation, redness, changes in the shape/color of the external opening, etc.
With prostatitis, patients may complain of: • pain and discomfort in the perineal area; • pain in the testicles; • feeling of cutting/pain in the urethra; • burning sensation after urination, ejaculation; • various dysuric disorders – a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after urination, increased frequency of urination, weakness, intermittency of the stream; • prematureness (or, on the contrary, prolongation of sexual intercourse), pain during ejaculation; • erasure of orgasm; • purulent mucous discharge (in case of urethroprostatitis).
The main signs of the acute form of orchiepididymitis are: • dull, severe pain in the scrotum; • visual enlargement of one (or both) testicles; • sometimes – redness of the skin of the scrotum; • sharp pain, hardened, enlarged testicle and/or epididymis revealed by palpation; • Prehn's sign (pain decreases when the scrotum is raised).
With a chronic disease, pain is moderate (or absent at all), and blood may be found in the semen.
Diagnostics
The therapeutic intervention regimen is determined after receiving the results of a smear taken from the cervix. In order for the examination result to be accurate, it is important to comply with the following conditions:
- one day before the examination, exclude sexual intercourse;
- stop using vaginal tablets and suppositories for 2-3 days;
- On the day of the smear test, carry out the hygienic procedure without using soap or any cosmetic chemicals.
A smear for Escherichia is considered positive when E. coli is detected in the cervical canal, provided that a trend towards a decrease in the number of lactobacilli is detected.
When is the use of candles relevant?
Suppositories are used either because it is impossible to use tablets, or if you want to obtain a quick and reliable result. Drugs in this group do not pass through the kidneys and stomach, and therefore have virtually no side effects or contraindications.
On average, treatment with suppositories requires therapy for 10 days, during which time the drug is taken every day. After one course, be sure to visit a doctor for a re-examination and tests. If the achieved result does not satisfy the specialist, then it is possible to change the suppositories or repeat the course.
Suppositories can be used at all stages of the treatment of dysbiosis, so in 1 course you can change 2-3 drugs with short breaks between them. Some will kill infections, others will restore flora.
Treatment
Treatment should be comprehensive:
- the patient should remain in bed and get more rest;
- it is important to normalize nutrition; your daily diet must include fermented milk products;
- use of vaginal and oral medications as prescribed by a gynecologist.
Most often, doctors prescribe Metronidazole and Clindamycin to women. After completion of therapy, a control smear of the vaginal contents is taken. This is necessary to assess the effectiveness of therapy. The exposure scheme is always determined on an individual basis, based on data obtained during testing. Self-treatment often causes the process to become chronic, the pathogen to enter the uterine cavity and the disease to become chronic.
Therapy
An E. coli infection should be treated by a specialist. Self-medication and traditional methods are completely excluded in the acute stage.
Before undergoing the necessary therapeutic course, the patient undergoes a bacterial culture. The study will accurately determine the strain of the pathogen, and this will determine the intensity and duration of drug therapy.
Comprehensive treatment of E. coli includes antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, probiotics, and local procedures.
In gynecology, vaginosis caused by E. coli is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a doctor. Local procedures include washing with chamomile infusion, medicinal douching, and administering vaginal suppositories with nystatin. The doctor prescribes a course of physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation on the genitals.
Antibacterial therapy
To suppress pathogenic microflora, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for 7 days. For vaginosis caused by E. coli, the following are indicated:
- Oral preparations based on clindamycin phosphate, metronidazole and tinidazole: Cleocin, Flagyl, Tindamax. Pros of taking: allowed for treatment during pregnancy. Disadvantage: drugs can cause side effects such as a metallic taste in the mouth and dyspepsia.
- Vaginal antibiotics (suppositories, creams, gels): Metro-gel, Kleotsin, Clindess. Advantages of local treatment: symptomatic side effects are excluded, the drug acts directly on pathogenic microflora. Disadvantage: vaginal route of administration is contraindicated during pregnancy.
To suppress pathogenic E. coli, the antiseptic Miramistin is additionally prescribed. The product reduces the resistance of flora, enhances the effect of antibiotics, and stimulates the body's immune response.
Maintenance therapy
In order to restore the vaginal microflora, probiotic and antifungal agents and immunomodulators are prescribed after antibacterial treatment. Medicines for maintenance therapy:
- Probiotics with lactobacilli: Laktogin, Vagilak, Gynoflor. The drugs restore normal pH levels and stimulate the development of healthy microflora.
- Immunomodulators Likopid, Kagocel, Viferon. The tablets prevent and stop purulent-septic processes and strengthen the immune system.
Complex treatment necessarily includes a diet with a sufficient amount of fermented milk products.
Danger to pregnant women and fetuses
During pregnancy, the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and foreign bacteria in the vagina, cervical canal and other organs of the reproductive system is extremely dangerous. Treatment should be carried out in a gentle manner so as not to harm the fetus.
First of all, the sensitivity of E. coli to antibacterial drugs is determined. There is no need to stop using them. New products are absolutely safe for women and children, and E. coli can cause significant harm and disrupt the process of normal development of the fetus in the womb.
Detection methods
Most women are examined once a year at the antenatal clinic.
While examining the genitals, the gynecologist takes material - a smear on a piece of glass. This material is then sent to a laboratory where it is examined in detail. The vagina is home to a mass of particles that make up the microflora. They protect the woman from pathogens entering this area.
A smear test allows you to determine how healthy the local microflora is. Analysis under a microscope and with chemical reactions makes it possible to identify E. coli in the taken material.
Prevention
The main role in the prevention of the initial and reappearance of the problem is played by intimate hygiene and compliance with the rules for ensuring it by the patient. For toileting the genitals, it is better to use special hygiene products or regular glycerin soap (without fragrances). Such compositions ensure the prevention of irritation and do not change the natural acid balance.
A fertile environment for the proliferation of pathogens are washcloths and sanitary sponges left by a woman after procedures in the bathroom. Moisture and heat are a positive environment for the growth of bacteria, so you should avoid using these accessories. When ensuring hygiene, you need to follow the basic rule - you need to wash your genitals from front to back. To remove moisture, use a special towel.
To reduce the risk of infection, it is necessary to wear underwear made of breathable fabrics and change it regularly. Avoid wearing tight clothing that interferes with natural air circulation. During the course of treatment, you must follow a drinking regime, drinking up to 2 liters of clean water per day. Sexual rest is necessary until complete recovery.
Escherichia enters the cervical canal from the rectum. The main cause of infection is insufficient hygiene and wearing underwear made of synthetic materials. A woman may not notice the problem for a long time and attribute it to recurrent candidiasis (thrush). The symptoms of such lesions are really similar. E. coli causes itching, irritation and redness around and inside the vagina.
All kinds of folk remedies in the fight against Escherichia are ineffective, because E. coli penetrates the epithelium quite deeply. Douching will not help restore the microflora; it can cause a woman’s well-being to deteriorate. The required course of therapy should be selected by the doctor based on the results of the examination.
In some women and men, E. coli is detected in a smear.
Let's talk about how dangerous this microorganism is and what to do if it is detected.
What is Escherichia coli?
Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) is a bacterium from the Enterobacteriaceae family.
It normally lives in the human body, mainly in the intestines.
Since the exit from it (the anus) is very close to the genitourinary organs, bacteria can colonize them.
There are usually no symptoms.
But sometimes Escherichia coli can cause inflammatory processes:
- urethra;
- vagina;
- internal genital organs;
- Bladder;
- kidney
If Escherichia is present in the vagina or urethra, they can be detected in a smear.
Benefits of suppositories
In gynecological practice, vaginal suppositories inserted into the vagina are often used. The use of suppositories is sometimes compared to injections, since the active substance of the drug exerts its effect quite quickly, being absorbed through the walls of the vagina into the bloodstream.
The vaginal mucosa has a large number of blood vessels, which facilitates the rapid entry of the medicinal substance from the suppository into the bloodstream. This will take no more than 20 minutes. The active substance moves through the bloodstream and enters the site of inflammation, where it fights pathogenic microflora. Suppositories quickly help eliminate symptoms of gynecological diseases such as itching, swelling, burning, pain, and discomfort.
Their main advantages are:
- low percentage of side effects;
- fast absorption;
- local effect on the site of inflammation;
- quick results;
- the medicine enters directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, there is no need to decide how to restore the intestinal microflora.
A distinctive feature of gynecological antibacterial suppositories is that the effect is only on the pelvic organs, practically does not affect the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract (a small part of the drug gets there). Therefore, after taking antibiotics in this form, you do not need to take drugs with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Therapeutic effect
Treatment of a man for E. coli infection is carried out with several pharmacological agents. The following groups are used for therapy: antibiotic, antimicrobial, bacteriological, adsorbent.
In order to cleanse the urethral mucosa of pathogenic microbes, it is necessary to use antibiotics. For this purpose, many specialists use broad-spectrum drugs. Prescriptions include prescriptions for drugs such as: gentamicin, lincomycin, doxycycline. Doxycycline has the greatest activity on the condition of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system.
Modern doctors often use imported doxycycline - Unidox Solutab. This form is available in the form of dispersible tablets. They completely dissolve in water and are not absorbed in the stomach. This form helps to avoid stomach complications. The absorption of the drug occurs in the intestines. The dosage and frequency of use are selected by the attending physician.
For urethral infection, drugs based on bacteriophages have a good effect. Bacteriophages are enemies of a variety of pathogenic microorganisms. Staphylococcal bacteriophage is used to eliminate E. coli. It is available in the form of a lyophilized powder. Part of the powder is diluted with water for injection. The resulting solution is injected into the bladder using a catheter. When the infection is low, the solution is used in the form of douching. Therapy is carried out with periodic examination of a smear from the urethra. When the smear is cleared of the rod, the bacteriophage is no longer used.
To completely eliminate the spread of the rod, it is necessary to use adsorbent preparations. They help eliminate waste products of pathogenic microbes. If such drugs are not used, severe intoxication may develop. Poisoning can also be avoided with the help of enterobiotics. They are administered as a liquid. These medications should be taken until the smear is completely cleared.
How is the analysis carried out?
The final diagnosis is based on the isolation of the microorganism in a bacteriological laboratory from the patient’s biofluids. The latter may be feces, blood, urine, sputum, or other fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid, bile fluid and peritoneal fluid. Most often, a stool sample is tested.
Gram stain results determine whether the organism is gram-negative, but the bacteria themselves are not distinguished from other aerobic gram-negative bacilli that cause similar infectious diseases. E. coli grows well on commonly used culture media, such as blood agar.
An E. coli test will allow you to accurately establish the diagnosis.
emedicine.medscape.com
Symptoms of pathological infection
E. coli is detected in the body after the incubation period has passed. The duration of its spread is short. The first signs of infection are detected two days after infection. Rarely, this period is longer. This phenomenon is observed in men with good immune protection.
p, blockquote 9,0,1,0,0 —>
After infection, various symptoms similar to acute respiratory illness may occur. A man complains of the following signs of infection:
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
- increase in temperature indicators;
- development of weakness;
- pain in various parts of the abdominal area.
The first sign of damage to the urethral mucosa is a sharp increase in body temperature. The measurement results can reach 39 degrees. These indicators last for several days. Many patients mistake this symptom for a sign of ARVI. This leads to incorrect selection of treatment and the development of severe infection.
p, blockquote 11,0,0,0,0 —>
Gradually, weakness is added to the temperature. The man cannot perform usual actions. Any work leads to fatigue. The body becomes weak.
p, blockquote 12,0,0,0,0 —>
Pain in various parts of the peritoneum is also detected. The localization of the pain syndrome depends on the organ that is infected with E. coli. The proliferation of the microorganism is accompanied by an expansion of the area of pain. Palpation allows you to establish a slight compaction in the affected area.
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
After the general symptoms, specific symptoms develop. Infection with Escherichia coli is characterized by the appearance of dyspepsia. During the day, a man is forced to visit the toilet several times to empty his bowels. Feces become less dense. There is mucus in it. The masses may have a liquid structure. A person complains that the stool looks like water.
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
There is severe vomiting. Vomit has greenish inclusions. The released liquid foams strongly. A putrid taste appears in the mouth. Prolonged vomiting and diarrhea are accompanied by rapid dehydration of the body. When these symptoms appear, a man needs urgent medical attention.
p, blockquote 15,0,0,0,0 —>
Features of the microorganism
Escherichia coli are microorganisms that are most often found in the upper parts of the large intestine, on the skin and mucous membranes. They are found in most warm-blooded animals, can persist for a long time in stagnant bodies of water, and contaminate meat, milk, fruits and vegetables.
Most strains are harmless and coexist peacefully with the macroorganism without causing harm. They appear in the human intestine within 40 hours after birth. Harmless strains are commensals; they live in symbiosis with the human body, use substances entering the intestines for their own purposes and participate in the synthesis of vitamins B, K and some other compounds.
Throughout life, the intestine maintains a constant concentration of E. coli 10 to 6 degrees, sometimes reaching 10 to 8 degrees. But for the vaginal mucosa, such a number of colony-forming units (CFU) is atypical. E. coli is an indirect indicator of fecal contamination.
A high number of CFU for any biological media of the body, except feces, should be alarming. Even facultative microflora under certain conditions can lead to inflammation.
Escherichia coli is a gram-negative microorganism. It is relatively stable in the environment. The optimal environment for the development of microorganisms is pH 7.2-7.4, which corresponds to an alkaline reaction. Normally, the vagina has an acidic environment with a pH of 3.8-4.5; a shift to the alkaline side to a pH of 5-6 is observed in the first days after the end of menstruation. Such conditions are not optimal for the active reproduction of E. coli. Therefore, its quantity is minimal.
Features of E. coli are rapid reproduction, which ensures the variability of the microorganism. Therefore, it easily becomes resistant to antibiotics and treatment becomes ineffective. Women who often take antibacterial drugs create colonies of microorganisms resistant to them in their intestines. Inflammation of the genitourinary organs caused by Escherichia coli will be difficult to treat.
How the virus is transmitted
How is E. coli transmitted? Among the many Escherichia strains, only serotype O157:H7 produces a powerful toxin that damages the intestinal lining, which can cause bloody diarrhea. The infection develops when a bacterium is swallowed, and a small number of microorganisms is sufficient for this.
The most common way to become infected with E. coli is by eating contaminated food:
- Ground beef. When cattle are slaughtered and processed, bacteria from the intestines can transfer to the meat.
- Unpasteurized milk. Microorganisms present on the udder or milking equipment may end up in raw milk.
- Fresh products. Livestock farms can pollute fields where fruits and vegetables are grown. Spinach and lettuce are particularly common means of spread.
Human and animal feces can contaminate ground and surface waters, including streams, rivers, lakes, and water used to irrigate crops. Therefore, the disease is transmitted quite easily.
Some people also become infected after swimming in pools or lakes contaminated with feces. Bacteria can be easily transmitted from person to person, especially if personal hygiene is not maintained. This is extremely important in families with small children.
www.mayoclinic.org
Complications of infection
E. coli should not be taken lightly. It can cause serious illnesses in the human body. In case of enteropathogenic infection, the following complications are diagnosed:
- sepsis;
- stomach ulcer and tissue perforation;
- urolithiasis disease;
- erectile disfunction;
- infertility of various etiologies.
One of the dangerous complications is sepsis. This disease is characterized by the spread of pathogenic microbes through the bloodstream. Severe inflammation of the vascular system appears. In case of sepsis, urgent purification of blood fluid is necessary. A slight delay can be fatal.
E. coli causes changes in tissue properties. The spread of bacteria along the stomach wall leads to the death of beneficial microflora. Pathogenic microbes feed on tissue cells. Prolonged residence of the microbe on the stomach wall leads to peptic ulcer disease. A more serious problem with infection is perforation. This problem is accompanied by the appearance of a hole in the wall of the stomach. Remains of food enter the abdominal cavity. With such a complication, the man needs urgent surgical intervention.
The appearance of a microorganism in the genitourinary system can cause negative processes in the renal pelvis. Bacterial infection causes disruption of this organ. The kidneys perform an absorptive function. Under the influence of a special layer, various beneficial microelements are absorbed into the bloodstream. Harmful substances are excreted in the urine into the bladder. When urinating, some of the harmful substances accumulate in the lower part of the bladder. Flakes are formed. A more dangerous form of complication is urolithiasis.
Danger of pathology
For a man, the pathology is dangerous due to various complications from the reproductive system. The spread of the disease through the genitourinary canal leads to infection of the prostate gland. The prostate is responsible for maintaining testosterone levels and producing the basis of ejaculate. The development of the disease in one of the lobes of the prostate gland causes inflammation of the entire organ. At the same time, there is a decrease in the fulfillment of the main responsibilities of the body. Testosterone helps strengthen the pituitary gland. The production of a substance is accompanied by the appearance of an impulse. Signal transmission affects the nerve endings of the penis. Muscle tissue is irritated. Increased elasticity causes blood flow to the cavernous bodies. The penis fills with blood fluid. An erection occurs. Bacterial disease is accompanied by hormonal imbalance. These impact phenomena lead to changes in erectile function. A man's sexual arousal disappears or becomes unstable.
Inflammation of the prostate can affect the composition of seminal fluid. The sperm becomes thicker. The motor ability of sperm is lost. Such germ cells cannot participate in fertilization. Conception does not occur in such a patient. When examining a bacterial culture, the presence of Escherichia coli is diagnosed. This form of infertility can only be eliminated with long-term drug treatment.
It is for these reasons that infection of the urethral canal must be treated promptly.
Preventive measures
To avoid the appearance of a stick in a smear, certain rules must be followed. The patient must carefully monitor compliance with intimate care. After visiting the toilet, you should rinse your genitals under warm running water.
Visits to open bodies of water should only be done in specially designated areas. It is not recommended to visit wild beaches.
It should also be used during sexual intercourse. It will help prevent intestinal microflora from entering the urethra. After contact, you need to shower with detergent.
It is not recommended to wear tight and tight underwear. Such underwear leads to direct contact of the anus with the fabric. Part of the intestinal microflora easily enters the urethra.
Following all these rules will help you avoid an unpleasant problem. If for any reason an infection with E. coli occurs, you must immediately visit a doctor. Only a specialist can study the composition of the smear and select effective treatment.
General concepts
Escherichia coli has an elongated shape and belongs to the group of anaerobic facultative bacteria. The human body is the natural habitat of E. coli. As long as its strain remains unchanged and it does not leave the intestines, the stick brings benefits to a person:
- responsible for the production of vitamins;
- suppresses the production of pathogenic organisms;
- actively participates in digestion.
If the Escherichia strain changes and enters other organs, pathological conditions occur, including death.