When Escherichia coli is detected in a urine test, you should consider consulting a doctor. Therapy should be started immediately. After all, this microorganism can cause inflammatory diseases of the vagina, urinary system, and kidneys. Where does the bacterium come from in the body, what symptoms can it cause, and how to deal with its presence?
E. coli belongs to the normal microflora of the body. The bacterium is present in the stomach and intestines and should not leave them. When escherichia coli may appear in urine culture:
- The analysis was carried out incorrectly (hygienic washing was not performed).
- The test container was dirty.
- When alternating anal and vaginal sex, without observing the rules of personal hygiene.
Sometimes E. coli gets into the urine during trauma to the urinary system. This is noted in cases of weakened immunity. The bacteria rarely spreads through sex. escherichia coli in the urine of women can be caused by cystitis. It develops due to damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder. Other diseases are also associated with Escherichia, for example:
- pyeloephritis;
- inflammatory processes of the vulva;
- inflammation of the vaginal glands;
- endometritis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
Men are less susceptible to E. coli infection. But sometimes, Escherichia appears in their urine. This is observed during inflammatory processes in the genital urinary organs (prostatitis, orchitis, urethritis, vesiculitis). Hemolytic streptococcus also provokes diseases.
Video : E. coli
Escherichia coli
Symptoms of E. coli in urine
Among the main symptoms of damage to the genitourinary tract by E. coli are the following :
- manifestation of inflammatory processes, cystitis and pyelonephritis most often appear;
- additionally, intestinal upset occurs;
- from time to time there are aching or nagging pains in the abdomen;
- problems with urination;
- itching inside the vagina, urethra, or urethra.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
In most cases, bacteriuria is asymptomatic . That is why, if you suspect the pathogenic spread of E. coli, you should take a urine test through catheterization .
Additional symptoms of Escherichia coli infection
In a number of cases, the insidious rod, quickly multiplying, behaves peacefully: it does not bother a person in any way. However, indirect signs of its presence in urine are:
- unpleasant odor of urine, detection of white flakes, pus or blood in it;
- pain when urinating, accompanied by burning, itching;
- chills, fever, weakness;
- painful menstruation;
- nausea - with kidney inflammation;
- lumbar pain or disturbing sensations in the side;
- incontinence, frequent urination;
- diarrhea, constipation.
An advanced infection is indicated by purulent discharge from the urethra and a red rash near the genitals.
Urine test standards for Escherichia coli
To determine the amount and danger of E. coli in urine, the following scale :
- if the indicator is less than 10 to the 3rd power - normal ;
- if the indicator is 10 to the 3rd degree - the presence of infections and the possible subsequent development of cystitis or urethritis;
- with an indicator of 10 to 4 degrees, infections and pyelonephritis are possible;
- in a latent asymptomatic form can be diagnosed .
The analysis for E. coli must be correlated with the general one; only after this can its meaning be interpreted and treatment prescribed.
What kind of microbe is E. coli?
The E. coli bacterium found in urine is a wake-up call. The microorganism is classified as opportunistic. In the intestinal microflora of a healthy person, many bacteria peacefully coexist, performing useful work. This rod - its harmless strains - is involved in the synthesis of vitamins B and K, actively helps maintain metabolism, and blocks the reproduction of unfriendly “brothers”.
Under unfavorable conditions for the body (for example, decreased immunity), this opportunistic bacterium turns into an enemy. Some of its strains become the culprits of urethritis, others - meningitis or coli-sepsis.
Dangerous varieties of this intestinal bacterium penetrate from the outside and cause escherichiosis - infections that provoke diarrhea. The presence of a rod in the urine is an anomaly, a symptom that needs to be eliminated as quickly as possible.
Escherichia coli in the urine of an adult
E. coli in the urine of an adult can cause a number of serious diseases. According to studies, 80% of patients with prostatitis received it as a result of the pathogenic growth of gram-negative bacteria. In women, the spread of E. coli can cause not only cystitis and urethritis, but also cause inflammation of the vaginal mucosa and dysbiosis.
Sometimes the spread of bacteria becomes so severe that it causes endometriosis . This process is accompanied by severe pain and problems with conceiving a baby. Gradually rising, the bacteria provoke inflammation of the ovaries and testicles, which sometimes even requires surgical intervention .
Reasons for the indicator in the analysis
There are often cases when E. coli is detected in urine culture due to a banal reason, an incorrect sample collection. To do this, it is recommended to follow a number of rules:
- Before taking an analysis for the presence of E. coli, it is necessary to wash the external organs of the urinary system.
- Use sterile collection containers. They are sold in pharmacies for both adults and children.
- For analysis, the middle portion is taken, the initial and final portions are excluded, they will not give a reliable result.
- The container is closed and delivered to the laboratory. In extreme cases, it is allowed to store the container with the analysis for the presence of E. coli in the refrigerator for no more than four hours.
For E. coli to enter the urine, the cause may be a serious disease of the urinary system in both men and women or poor personal hygiene. Strains from the intestine penetrate in several ways:
- if genital hygiene is neglected, E. coli from the anal passage enters the genitals;
- various types of infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra or vagina;
- penetration of E. coli through blood channels or lymphatic vessels is possible.
Often the stick enters the urine through the ascending route. It is an indicator of the presence of kidney disease, urethritis or infection in the pelvic organs. In people with the same diagnosis, the indicator of the microorganism in the urine may differ. This depends on the patient’s age, gender, state of the immune system, and hormonal levels.
Presence of infection during pregnancy
During pregnancy, coli bacteria are dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the baby, as they can be transmitted to him during childbirth . As at any other time, during pregnancy, E. coli can provoke vaginal dysbiosis , inflammation of the mucous membrane, cystitis, inflammation of the kidneys and ureters.
The danger of such processes lies not only in their effect on the fetus, but also in those medications required to eliminate diseases . To protect yourself from infection, be sure to change your underwear every day, wash yourself with clean water at the end of the day, and wash fruits and vegetables. When coming from outside, be sure to use antibacterial gel or simply wash your hands with soap.
Pathologies
Depending on age, as well as general health, the presence of E. coli in the body can affect a person in different ways. But, even without taking this into account, we can safely say that this gram-positive bacterium is quite dangerous and insidious. Let's take a closer look at what it threatens for adults, children and pregnant women.
In adults
There are a lot of diseases that can develop due to the penetration of E. coli. For example, if you look at medical research data, you can find out that about 80% got prostatitis due to the active proliferation of E. coli. As for the female sex, these patients develop cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, dysbacteriosis, and inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
The bacterium can trigger the development of urethritis. Source: neboleem.net
If the bacterium is not identified in a timely manner, then in the future it will definitely cause the development of more serious diseases, including endometriosis. As a result, women will suffer from menstrual irregularities, they will experience bleeding that is difficult to stop, and they will also develop infertility. Inflammation of the ovaries, testicles and appendages is possible, and surgical treatment may be required.
In pregnant women
E. coli for women who are in the process of bearing a child is very dangerous, both for the mother herself and for the developing fetus. This is due to the fact that during labor an infection can affect the baby’s body. Also, a girl may suffer from vaginal dysbiosis, cystitis, inflammation of the kidneys and ureters.
In such conditions, drug treatment is required. As you know, all medications, one way or another, affect the process of intrauterine development of the fetus. To protect yourself and your unborn child, you need to regularly change bed and underwear, wash your hands after walking and traveling in public transport, and do not eat dirty fruits and vegetables.
The child has
In most cases, the penetration of E. coli into a child’s body occurs in situations where he rarely washes his hands, fruits and vegetables before consumption. As for the presence of bacteria in urine, it gets here along with feces if traces of them remain on the external genitalia.
Young children often develop cystitis due to the active proliferation of E. coli. Source: oprostatit.ru
Often, the penetration of the microorganism is not accompanied by any symptoms, and its number does not increase. But it is possible that the child may develop cystitis or urethritis, which is accompanied by problems with urination and cutting pain in the urinary canal area.
As for infants, E. coli enters their urine along with feces, but infection could also occur during labor. If bacteria actively multiply, the child will develop inflammation in the urinary system or kidneys, which will cause the development of pyelonephritis.
Bacteria in a child's urine
A child becomes infected with E. coli due to poor hygiene or eating unwashed fruits and vegetables . Most often, bacteria enter the urine from feces, traces of which could remain on the genitals.
In most cases, the infection is asymptomatic and does not cause problems. But sometimes children begin to develop cystitis and urethritis , which are additionally manifested by pain in the abdomen and when urinating.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
If left untreated, the infection rises and affects the kidneys, which can cause pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis .
Types of E. coli: pathogenic and non-pathogenic
As we mentioned earlier, E. coli has a large number of strains, many of which are not only harmless, but also beneficial - non-pathogenic species.
What is their use?
It's simple - they ensure good intestinal function, prevent the increase in the number of harmful microorganisms and help synthesize (reproduce) vitamins in the body when digesting food in the intestines.
However, some strains of E. coli have a negative effect on the host. They are called pathogenic (harmful) species. They can cause problems with stool (diarrhea or constipation), bloating, poisoning, digestive problems, and even be fatal, in other words, death.
Moreover, they not only cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also, when they reach the genitourinary organs, they can cause cystitis, colpitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases.
Let's look at these two large groups in detail. And we will start with useful strains.
Non-pathogenic (beneficial) types of E. coli
Thanks to research, it is known that such strains perform certain functions in the digestive system, namely:
- prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms;
- help synthesize vitamins B and K;
- participate in the digestion process.
Also of great importance is not only the presence of non-pathogenic (beneficial) strains of E. coli inside the human digestive canal, but also its quantity. When the quantitative level decreases below the permissible level, all the processes described above deteriorate. And this can cause an imbalance in the microbial balance in the digestive canal, which leads to dysbiosis.
It is known that for normal functioning of the intestine, the number of E. coli bacteria should not exceed 0.1% of the total intestinal microflora.
As you can see, we should not underestimate the role and positive impact of these bacteria on our body, which once again proves that not all bacteria are “bad”.
Now let's move on to dangerous varieties of E. coli and figure out where we can encounter them and what effect they have on our body.
Pathogenic (harmful) types of Escherichia coli
Among pathogenic (harmful) strains of E. coli, scientists distinguish four groups, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
Let's look at each of them:
- Enteropathogenic types of Escherichia coli affect the small and large intestines of young children under 1 year of age, mainly those who are bottle-fed. The source of infection becomes medical personnel or relatives. The infection is transmitted through contact and household contact (through household items and medical instruments).
- Enteroinvasive species can cause acute intestinal disorders in older children and adults. The source of infection is also humans, but the bacteria are transmitted through food.
- Enterotoxigenic species cause intestinal disorders in children under 7 years of age. Often found in countries with tropical and subtropical climates. It is transmitted by water, but a large dose of pathogenic Escherichia coli is required to develop clinical symptoms.
- Enterohemolytic species of Escherichia coli have been studied relatively recently and affect the digestive system of an adult. The presumed source of infection is cattle, and the route of transmission is the consumption of animal products that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment. Or eating stale meat, where E. coli begins to grow at the moment of rotting.
Thus, it can be noted that for each species there is not only its own symptoms, but also a group of lesions and transmission routes.
Next, we will look at what symptoms appear when you “catch” cystitis.
In the urine of a baby
As in children, in infants E. coli appears from the anus or during passage through the mother's birth canal . To avoid complications after childbirth, you should definitely use uroseptics before labor begins . It is also worth washing your baby properly.
With excessive spread of Escherichia in infants, an inflammatory process may occur in the genitourinary system and kidneys. This can lead to the development of chronic pyelonephritis and inflammation of the genital mucosa .
General rules for preparing for urine analysis
There are frequent cases of false positive bacterial culture results. The cause of the error is incorrect collection of biomaterial. To avoid unnecessary worries, you need to follow the recommendations of doctors.
- Be sure to collect morning urine immediately after waking up, skip the first and last portions. The required volume is at least 70 ml.
- It is better to collect urine in a sterile pharmaceutical container.
- The day before, you should not eat foods that stain urine or take diuretics.
- Before collecting material, you need to wash your genitals using neutral products.
- For women, inserting a tampon into the vagina is mandatory.
- 2 hours is the maximum shelf life of biomaterial. Urine can be kept in the refrigerator for 4 hours.
To avoid an incorrect result, doctors recommend a different procedure - collecting urine with a catheter. It is not very pleasant, but does not cause painful sensations.
Treatment of Escherichia coli
In cases where the appearance of Escherichia coli in urine does not provoke the development of infections and inflammatory processes, no special treatment is carried out. Doctors simply recommend sticking to proper nutrition and drinking plenty of water and fruit drinks, and eating fermented milk products .
Personal hygiene must be improved and anal intercourse is excluded. fluoroquinols, bacteriophages and the amoxicillin group of drugs are chosen to eliminate Escherichia
Pregnant women and patients awaiting surgery and having inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system undergo a short course of therapy, including antibiotics, uroseptics and diuretics. All this can be combined with traditional medicine.
Treatment methods for infection
If E. coli is detected, but there are no acute symptoms, no therapeutic measures need to be taken.
They are trying to combat the problem with diet. You need to increase your water intake in your diet and consume fermented milk products. If inflammatory changes in other organs appear, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Among them, preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics - Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin. These drugs quickly reduce the acute symptoms of the disease.
Monural is considered a popular drug for the fight against Escherichia coli. A single dose is enough to keep him in orgasm for 4 days. It is important to conduct an antibiotic sensitivity test before prescribing the drug. For additional therapy, uroseptics (Canephron) and folk remedies are prescribed. It must be remembered that treatment must be comprehensive. First, lifestyle modification is carried out (sleep is normalized, stress factors are eliminated, bad habits are abandoned, and moderate physical activity must also be undertaken).
Next, diet number four is prescribed, which can then be replaced by the second. If one antibacterial drug is not suitable, you need to change it to another. Aminoglycosides have been found to be effective. There are cases where several drugs are prescribed at the same time, but these are rare. Therapy is often symptomatic.
For persistent pain, analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed; for obvious kidney problems and the appearance of edema, diuretics are used.
Treatment with folk remedies
Shilajit powder
The substance should be taken for 30 days before main meals. All you need to do is take 1.5 g of mumiyo , divided into three doses. Take the substance with a glass of clean water. If the powder is difficult to swallow, it can be diluted in liquid or purchased in tablet form. After a month of use, a pause must be taken .
Sweet clover infusion
in equal quantities with flowers of coltsfoot and centaury. Divide the herbal mixture into several servings, one tablespoon at a time, and prepare each serving separately as needed. To do this, pour 250 ml of boiling water over it and cook for another 10-15 minutes. Immediately from the heat, strain the broth and drink it 5-6 times during the day, a few sips. One tablespoon of herbal mixture is the daily dose. The course of treatment is 15-30 days.
Prevention
If E. coli was found and eliminated in time, the person needs to adhere to preventive measures that will help prevent re-infection. First of all, this means observing the rules of personal hygiene, regularly changing underwear, and using protection during sexual intercourse. Along the way, it’s worth tempering yourself, increasing your immunity, and doing physical therapy. If you drink 1.5-2 liters of water a day, the organs of the genitourinary system will function better and the infection will not linger in the body, since water removes all pathogenic microflora naturally. By following these simple rules, you can protect yourself from dangerous diseases and complications.
Escherichia coli, or Escherichia coli, is an enterobacterium that is part of the normal microflora of the human stomach and intestines. This microorganism lives only in the digestive system and normally should not penetrate other organs.
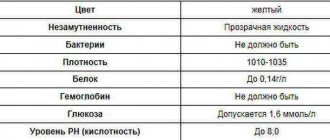
Human urine is normally sterile (there are no pathogenic microorganisms in it), but the presence of isolated bacteria is allowed. If the content of bacteria in the urine exceeds the permissible norm, this condition is called bacteriuria and is a pathology.
Escherichia coli appears in the urine of a healthy person in a number of cases:
- If the rules for collecting urine are not followed, E. coli from the rectum gets into the urine (if washing was not carried out before collecting urine);
- The container for collecting urine was not sterile;
- After anal sex, which was performed while ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
Also, Escherichia coli can get into the urine due to injuries to the genitourinary organs. However, in this case, if a person's immune system is weakened, they can lead to diseases.
Infection with E. coli cannot be achieved through sexual contact. The only possible way to become infected with this microorganism is autoinfection (infection from one organ to another).
Symptoms
You should begin to suspect the presence of Escherichia coli in urine if there is severe pain during urination. Moreover, the urge becomes an order of magnitude more frequent than usual, and the amount of urine coming out is minimal. Painful sensations can be localized in different places. Thus, symptoms common in women are associated with pain in the lower abdomen, and in men - near the rectum. Such gender characteristics are associated with differences in the structure of the genitourinary system. Can the intestines bother and put pressure on the bladder if there is E. coli in the urine? The answer is yes. Such sensations are possible when there is a feeling of heaviness and constriction in the bladder due to ongoing inflammatory processes in it.
How does E. coli spread and enter the bladder? If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner and there is no treatment, the number of bacteria rapidly increases and, after a short period of time, the kidneys become infected with E. coli; the infection can be found in the bladder, as well as in other organs associated with the human genitourinary system. Complications caused by the spread of E. coli are characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness and aches;
- intoxication signs;
- possible fever.
If the kidneys are damaged, in addition to the presence of E. coli in the urine, the analysis shows the presence of purulent and blood clots, mucus, nagging or sharp pain in the lumbar region. It should be noted that the presence of blood clots indicates certain disorders in the blood circulation.
Properties of the pathogen
Based on their ability to cause diseases, this type of bacteria is divided into pathogenic and opportunistic forms.
The former enter the body from outside and are the causative agents of escherichiosis, an infectious disease whose leading symptom is diarrhea. One of the common pathogenic bacteria of this form is hemolytic Escherichia coli. The hemolyzing bacillus is considered the most dangerous, capable of causing death in pediatric patients. Opportunistic pathogens are part of the normal microflora of the body and are mostly localized in the large intestine. Under favorable factors (for example, a decrease in immunological reactivity), they lead to the development of endogenous infection:
- certain strains of E. coli initiate the development of meningitis;
- others - sepsis;
- third (uropathogenic) – are the cause of urethritis.
Causes
Escherichia coli may appear in the urine due to the following conditions:
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra);
- in the presence of chronically ongoing processes in pregnant women;
- lack of proper hygienic care of the external genitalia;
- a risk factor is also an overly active sexual life with non-compliance with safety precautions;
- non-sterile container for collecting samples.
Not all patients develop an inflammatory process in the presence of E.coli. This is due to the work of powerful protective mechanisms in the form of a constant change of epithelium, chemicals produced by cells, as well as the physiologically determined process of urination, in which bacteria are naturally removed from the urinary tract. If the protective functions fail, E. coli is capable of rapid colonization and reproduction, which causes the development of a pathological process.
Predisposing factors include:
- decrease in urine pH values;
- reduction in the process of urination and the presence of residual urine;
- the presence of other foci of infection;
- non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, for girls - improper washing (the direction of water and washing movements should always be towards the anus, and not vice versa);
- decreased immune properties and hormonal levels in various conditions (pregnancy, diabetes).
Escherichia coli, or Escherichia coli (abbreviated E. coli) is a bacterium that is part of the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. If a person is healthy, has a strong immune system, it does no harm. However, there are factors that contribute to its provocation of urinary tract infections:
- Immunodeficiency.
- Failure to comply with hygiene requirements (for example, fragments of feces getting into the urethral area due to improper use of cleansing wipes, infrequent washing, wearing underwear contaminated with feces).
- The presence of urinary tract diseases in acute or chronic form.
- Infection through contact with a carrier of a pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli (household, sexual).
- Trauma to the urethra (during sexual relations, medical procedures).
In addition, so-called pathogenic strains are isolated - these are Escherichia coli species that can cause diseases. They can be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person, including a child from the mother during pregnancy and during childbirth, and subsequent contacts.
E. coli is the leading bacteria that causes urinary tract infections in children and adults. According to statistics, more than 80% of cases are associated with this microbe, which can provoke conditions such as:
- asymptomatic bacteriuria (excretion of Escherichia coli in the urine in the absence of complaints and signs of damage to the kidneys, urethra and other parts of the excretory system);
- acute infection (with vivid manifestations characteristic of a specific disease - cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- chronic inflammatory process (periodically activated or sluggish, sometimes latent (hidden)).
Women experience infections caused by Escherichia coli more often than men. The reason is the proximity of the urethra to the anus, which is a potential source of pathogens.
Therapeutic measures
It is necessary to get rid of E. coli in the urine and eliminate the undesirable consequences of its uncontrolled growth in the early stages. The identified causes and treatment will be interconnected. After the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed for the area of the pelvic organs affected by the inflammatory process.
Therapeutic measures in the presence of the opportunistic microorganism Escherichia coli are aimed at:
- to eliminate the source of the inflammatory process;
- to restore the mucous membrane of the urinary system;
- to eliminate discomfort, pain and signs of intoxication;
- to strengthen the immune system.
To solve this problem, drugs are used medicinally:
- uroseptic;
- antibacterial;
- immunomodulators;
- painkillers;
- antipyretic.
All of them are used in a complex that eliminates E. coli in the urine and is treated with antibiotics:
- Ampicillin, Amoxiclav - drugs are penicillin derivatives and have a wide range of actions;
- Furagin or Furadonin are agents from the nitrofuran group;
- Fosfomycin, Monural are urological antibiotics, widely used because of their effectiveness in cleaning canals from E. coli and other types of pathogens.
Therapeutic therapy is prescribed by a doctor in compliance with individual dosage. Detection of E. coli in the urine indicates the presence of an infection in the genitourinary system, which must be treated at an early stage.
Treatment of pregnant women and children
When treating women carrying a child, treatment for inflammatory processes of the bladder is prescribed:
- In the period from 13 weeks to 26 - Ceftriaxone or Cefepime.
- Starting from 27 weeks and up to 37 weeks - Cefotaxime.
- From 38 weeks until the birth of the baby - Furagin.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Ceftriaxone | from 22 rub. | |
| Cefepime | from 67 rub. | |
| Cefotaxime | from 24 rub. | |
| Furagin | specify |
If the rod does not manifest itself in any way, then the doctor decides to treat with cephalosporins, second-generation quinolones or Nitrofurantoin. Of the medications based on plant substances, it is recommended to use Canephron N, Urolesan, Phytolysin, Cyston. It is imperative to drink a lot of liquid, including cranberry fruit drinks or dried fruit compotes.
For the treatment of young children aged 0 to 15 years, the following drugs are administered:
- Augmentin or Amoxiclav (clavulanic acid) in addition to Amoxicillin.
- Co-trimaxazole (children under three years of age).
- Cefuroxime is the second generation of cephalosporins (for children over three years old).
- Nitrofurantoin, Furadonin or Furamag - for children under three years of age.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Augmentin | from 253 rub. | |
| Amoxiclav | from 125 rub. | |
| Co-trimaxazole | from 25 rub. | |
| Cefuroxime | from 594 rub. | |
| Furadonin | from 75 rub. |
For adolescents over 15 years of age, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed that eliminate a large number of pathogenic bacteria in the urine, including E. coli. Most often prescribed are Monural or Norfloxacin.
Treatment of bladder problems with medications reveals a positive effect in eliminating E. coli in the urine within three days (72 hours). If the result does not appear, it is recommended to change the antibiotic.
Treatment
Getting rid of unpleasant symptoms, pressure on the walls of neighboring organs, the presence of E. coli in urine, and also improving the general condition of the patient becomes possible with the correct diagnosis. Having reliably determined the localization of the areas affected by the disease, as well as the form and complexity of the inflammatory processes, the specialist selects the appropriate medication therapy.
Traditional treatment
Treatment with medications means an integrated approach to eliminating the disease, including relieving inflammation, accelerating the recovery process of the mucous membrane, increasing the patient’s immunity, eliminating pain and signs of intoxication. In view of all this, the specialist prescribes a number of drugs:
- antibacterial agents;
- uroseptics;
- anesthetic and painkillers;
- drugs whose action is aimed at normalizing body temperature;
- medications that increase and strengthen the human immune system.
Antibiotics are the leading agents that can kill the infection and are prescribed in the treatment of E. coli in urine. Their action is aimed not only at combating the pathogen, but also at eliminating other symptoms, including restoring the walls of the intestinal blood vessels. The remaining funds on the list are intended to assist in the fight, as well as to strengthen the achieved result. Therefore, the key to a speedy recovery is the correct selection of an antibacterial agent.
To combat Escherichia coli, broad-spectrum antibiotics are most often used, in particular, the class of penicillin, fluoroquinolone, and nitrofuran agents. However, the leader among them is Monural, which can get rid of E. coli after a single use.
In addition to antibiotics, uroseptic medications are an important drug in the treatment of urinary organs affected by E. coli. Their action is aimed at maintaining the normal functioning of the kidneys, removing excess fluid, and relieving swelling.
If E. coli is detected in the urine, but in the absence of characteristic symptoms, the specialist will recommend delaying the use of antibiotics. Instead, he will prescribe medications that boost and strengthen the human immune system. You should also pay more attention to personal hygiene, normalization of proper nutrition and drinking regime. With strong immunity, the presence of E. coli is reduced and, ultimately, they die.
E. coli in urine
For the treatment of newborns, the same scheme is used as for adults: a course of antibiotics, diuretics that can remove pathogenic organisms along with urine, and a course of immunotherapy drugs. The same therapy is prescribed when an infection is detected in a child.
The treatment of pregnant women is approached more thoughtfully, and the course of antibiotics is selected in such a way that they have maximum effect and minimal negative impact on the body of the mother and child. In addition, gentle dosages of drugs are prescribed that minimize possible side effects. In addition to antibiotics, the specialist selects diuretics and a complex of vitamins. It is strictly not recommended to self-medicate and self-prescribe a course of antibiotics or urinary medications, especially for pregnant women. Such rash actions are fraught not only with the fact that they will not cure the illness, but there is also a possibility that the disease will become chronic. The same reasons are used when doctors recommend not interrupting the course of antibiotics. If you wish to use traditional medicine, consultation with your doctor is strongly recommended.
Recommended topic:
Urine salt test
Traditional treatment
How to get rid of E. coli using folk remedies? First you need to consult your doctor. Folk remedies are effective in the fight against E. coli. It is best to use them after a positive response from the attending physician. So, an effective remedy is to wash it with a decoction of the herbs Chamomile, Cherry and Calendula . These herbs have proven themselves to be excellent disinfectants and antimicrobial drugs.
Jerusalem artichoke
A widely known recipe using Jerusalem artichoke. To prepare a medicine from Jerusalem artichoke, you need to take 0.25 kg of the plant, peel it and cut it into small slices. Then take 200 g of milk and 200 g of water, mix, put on fire and bring to a boil. Sliced fruits are dipped into boiling liquid and cooked until soft. Then the resulting broth is drained, 1 tbsp is added. l. flour, a little butter, put back on the fire and cook, stirring, until thick. Boiled Jerusalem artichoke is smeared with the resulting mass and eaten as breakfast or dinner.
The recipe from Plantain is no less popular for E. coli . You need to take 1 tbsp. l. leaves of grass, pour 200 g of boiling water. The resulting decoction is taken 3 tbsp. l. morning, afternoon and evening.
of goose Cinquefoil will also help get rid of E. coli . To prepare it you need to take 1 tbsp. l. plants, pour 300 g of boiling water and cook for 15 minutes over low heat. The resulting infusion is left for 12 hours in a dark place. It must be taken, divided into three equal parts, 3 times a day.
And here is an effective recipe from Celandine : 1 tsp. pour 300 g of boiling water over the plants, let stand for a while and take 1 tbsp half an hour before meals. l.
You can get rid of E. coli in urine using a decoction made from 2 tbsp. l. mixed in equal parts Sweet clover, Centaury and Coltsfoot , and then poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let the infusion brew for a quarter of an hour and the resulting liquid should be drunk over the course of one day.
Characteristic symptoms
Infection with E. coli causes pain, purulent-bloody discharge, weakness, and fever.
If the cause of E. coli is infection of the genitourinary tract, the symptoms will be as follows:
- pain when emptying the bladder;
- chills;
- changes in the smell of urine;
- purulent impurities released along with urine;
- blood spots;
- general weakness;
- pain in the area where the kidneys are located;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, partial incontinence.
Decoding
E. coli found in urine can mean several pathological conditions at once. This may include:
- Development of active infection.
- The emergence of a chronic lesion.
- Presence of asymptomatic bacteriuria.
| Clinical situation | Result of culture culture | Presence of health complaints and signs of urinary tract damage | |
| Free bladder emptying | Constant use of a catheter | ||
| Norm | No growth of Escherichia coli or up to 102 CFU/ml | Up to 100 colonies in 1 ml | – |
| Active infection | ↑ 104 CFU/ml | Eat | |
| Asymptomatic bacteriuria | ↑ 105 CFU/ml | – | |
Samples taken by puncture (suprapubic puncture) of the bladder are normally sterile.