When it comes to suspecting an inflammatory process localized in the urinary system, the patient is asked to undergo an analysis called a urine culture tank. Such a study is needed to find out the specific cause of inflammation. Using this type of diagnosis, doctors identify the presence or absence of specific pathogenic microorganisms.
Determining the type of pathogen is an important step in the diagnosis of diseases of the urinary system. Through urine testing, laboratory technicians also identify the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibiotics and prescribe appropriate medications for effective treatment. In order for the analysis to be as informative as possible, you need to comply with some requirements and collect urine correctly.
Why do you donate a urine culture tank during pregnancy?
During the period of bearing a child, a woman's immunity is weakened, and she becomes susceptible to many infections. The most common are diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.). For timely detection of infection, bacteriological culture of urine is performed. Based on the results of the study, the patient is selected an effective treatment regimen and antibacterial drugs that kill pathogenic microorganisms.
May additional research be needed?
The choice of treatment tactics cannot be based only on the results of one analysis. So, to clarify the diagnosis, the specialist must prescribe additional studies, among which are:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- smear from the genital tract or urethra (assessment of microflora and cells);
- ultrasound and x-ray examination of the kidneys;
- MRI and CT of the genitourinary system.
You may also need to consult a specialist doctor - nephrologist, gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, surgeon.
Urine culture for microflora is one of the most informative methods by which you can find out the cause of the development of an infectious disease in a patient. The study also helps determine the sensitivity of detected pathogenic microorganisms to antibacterial drugs. That is why diagnostics greatly facilitates the selection of medications necessary to treat a patient.
What is a urine culture tank?
Bacteriological culture allows you to detect the presence of viruses, bacteria or fungi in the urine, which are the causative agents of a particular disease. To do this, the resulting biomaterial is cultivated in appropriate nutrient media at a certain temperature.
In addition, tank culture can determine the resistance of identified pathogens to a specific antibiotic. Thus, the doctor selects the most effective drug, which allows for quick treatment and prevents the development of complications (very important during pregnancy).
To monitor the effectiveness of the selected treatment regimen for urological pathologies, the woman undergoes a repeat urine culture after completing the course of antibiotic therapy.
Indications for bacterial culture
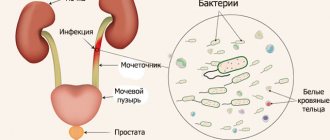
A person in good health has sterile urine. Pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms enter it from urine excretion tracts or from the outside, especially if hygiene rules are not followed. To identify existing microorganisms, the patient must submit urine for bacterial culture in the following cases:
- a large number of leukocytes and bacteria on a general urine analysis;
- suspected infection of the bladder, urinary tract and kidneys, accompanied by frequent urination, abdominal or lower back pain, pyelonephritis or cystitis, vomiting, chills and cloudy urine;
- detection of relapse after pyelonephritis in the acute stage;
- when determining chronic pyelonephritis;
- as a control over the therapy used against urinary tract infections;
- preventive examination of pregnant women during the first trimester and at 36 weeks;
- preventive examinations of newborns up to 3 months.
More on the topic: How is an ultrasound of the bladder performed?
A referral for bacterial culture is issued by a pediatrician, nephrologist, obstetrician-gynecologist, internist and family physician.
Why is it prescribed during pregnancy?
This analysis is very important and mandatory for a pregnant woman. It helps to promptly identify pathologies of the urinary system that occur in acute or chronic form. Very often, in a woman’s body, some diseases are asymptomatic and appear after pregnancy. This is a very dangerous condition, it threatens the development of serious complications. For example, untimely treated bacteriuria causes severe forms of pyelonephritis and poses a threat to the normal course of pregnancy.
Signs of asymptomatic bacteriuria can be identified by the results of a general urine test. To diagnose a specific pathogen and select an effective drug, bacteriological culture is performed.
How often do you test for pregnancy?
Normally, urine culture is required at the very beginning of the 1st trimester and at the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy. The analysis is prescribed at each scheduled visit to the gynecologist. However, the doctor may prescribe an extraordinary study if deviations were detected in the results of the general analysis (excess of coccal forms, rods, total protein, etc.). If a woman has previously been diagnosed with urological diseases, then the culture tank will need to be taken more often during pregnancy. Such measures are taken to timely detect a possible relapse of a chronic infectious process.
What are they watching?
During the research, the resulting biomaterial is sown on a special nutrient medium and placed in a thermostat (certain temperature conditions are maintained in it). After a certain time (at least 5 days), sprouted colonies of fungi, bacteria and other microorganisms are counted. If the norm is exceeded, additional research is carried out to determine the resistance of the identified pathogen to a specific antibiotic, thereby selecting an effective drug.
Localization of infection
Medicine is moving forward every day. The laboratory identifies not only the type of pathogen, but also the location of the infection. This is done using a special test with the addition of the antibiotic Neomycin. After the patient collects urine, a liquid with the addition of Neomycin is injected into his bladder using a catheter. It is worth noting that the sensations when using such a tool are extremely unpleasant. The results are assessed as follows:
- After some time, the patient empties the bladder again. This urine is sent for testing. If there are no bacteria or infection in the liquid, we can conclude that the antibacterial solution coped with the task, and accordingly, the infection is localized specifically in the bladder.
- If the test shows that the urine still contains bacteria or infection, this may indicate that the pathogen is located in the kidneys.
If the culture reveals a serious pathology, you need to retake the urine at least 3 times, preferably in different laboratories.
Rules for taking the analysis
To obtain the most reliable figures, it is very important to follow the rules for collecting biomaterial.
Failure to comply with them leads to false numbers and, as a result, a delay in the treatment process, which is very undesirable and dangerous during pregnancy.
Collection time
The optimal time for urine collection is considered to be early in the morning, after a woman wakes up. Before collecting biomaterial, it is necessary to carry out hygiene of the external genitalia to prevent the entry of unwanted contaminants. Experts recommend using cosmetics with a neutral pH.
Amount of urine
The optimal amount for bacteriological culture is considered to be 50-70 ml of morning urine. At the same time, you need to remember that only the “average” dose of urine should fall into the collection container. During urination, it is recommended to cover the vaginal opening with cotton wool or a cotton pad to prevent sexually transmitted infections. During collection of biomaterial, it is prohibited to place the container against the labia.
Tara
For bacteriological inoculation, it is necessary to use clean, sterile containers. It can be purchased at a pharmacy. Before collecting biomaterial, you need to thoroughly wash your hands, only then remove the lid from the cup.
If you don’t have any pharmaceutical containers at hand, and you need to get tested quickly, you can use the means at hand:
- the selected container is thoroughly washed with baby soap, wiped dry and well sterilized (treated with boiling water or kept in steam);
- After this, it is not recommended to wipe the walls of the container with a napkin, as small fluff may remain on them, which will affect the reliability of the results obtained.
Due time
The collected biomaterial must be delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours. It is strictly forbidden to store urine in the refrigerator or collect it the night before.
What not to eat and drink
A prerequisite before taking the tank culture test is to follow some dietary rules:
- Eliminate fried, fatty and smoked foods from your diet within a few days;
- do not abuse foods that affect the color of urine (beets, etc.);
- exclude the use of diuretics and other drugs that can affect the reliability of the results.
It is also not recommended to perform increased physical activity before collecting urine, as it increases the protein content in urine.
Preparation for microbiological examination
Since the essence of the analysis is to determine the degree of infection of the urinary system, special attention must be paid to hygiene, otherwise third-party microorganisms that get into the urine sample will distort the results. At best, you will have to take the test again, and at worst, incorrect diagnosis and therapy that is not related to the true state of your body. The latter is quite likely, especially if the attending physician is young and inexperienced.
Collecting a sample for analysis:
- First of all, prepare the container. It would be correct to use a special plastic container from a pharmacy,
- Before collecting urine, you need to thoroughly wash and disinfect the outer area of the urethra by wiping it with a cotton swab or napkin soaked in an antiseptic,
- For analysis, take an average portion of urine excreted in the morning after sleep. The first part is flushed down the toilet, then about 10 ml of urine is collected into the container without touching its neck and inside. It is better to do this with sterile gloves,
- The container is tightly closed and sent to the laboratory as quickly as possible - no later than 2 hours after collecting the sample.
It is also possible to collect cultures throughout the day, provided that at least 2 hours have passed since morning urination. For patients suspected of having tuberculosis, urine collection is carried out according to the same principles, but for three days in a row. If the patient has a stationary catheter installed, before collecting urine, it is clamped, disinfected with ethyl alcohol and a sterile needle, the catheter is pierced and 5 ml of urine is collected, after which it is poured into a prepared container.
There are no contraindications in the diet before sowing. You can eat any food, but as for medications, antibiotics, antimicrobial agents and diuretics distort the results. Therefore, it is recommended to test urine for flora no earlier than 5–7 days after taking these medications.
How to properly collect average urine
For donation, only average urine is used, which is collected in the following way: the first portion is poured to the side (it may contain foreign contaminants), and the same is done with the last portion of urine.
That is, the woman needs to begin the act of urination. After a small volume of urine comes out, stop the process and substitute a sterile container. Then continue urinating again, at the end pause the act again, pick up the container and finish the process.
How to collect?
To obtain reliable diagnostic results, it is important to correctly collect urine for culture. Preparation does not require following any diet or giving up your usual diet. What you eat or drink will not affect the composition of bacteria in the body. The collection rules are simple, but the accuracy and reliability of the result will depend on them.
Basic Rules
- When collecting samples, it is better to abandon home containers, because it is not always possible to achieve its absolute sterility. The pharmacy sells a special container, which is important to open during the urine collection procedure.
- Before collecting biological fluid, it is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures. Wash the external genitalia well with clean, warm water and soapy water, then wipe dry with a towel.
- Urine collection is carried out in the morning. For research, you will need the middle portion, and the first and last are flushed into the toilet. The resulting sample is tightly covered with a lid and placed in a cool, dark place or refrigerator.
Interpretation of urine results for Bakposev: norms according to the table
Results can be obtained in the laboratory 5 days after the test. The decoding is carried out by the attending physician. The resulting form will indicate the type of pathogen and its content in 1 ml of urine. Normal values are given in the table.
| Result | Norm, CFU/ml |
| norm | ≤1000 |
| doubtful | 100-100000 |
| infection | ≥100000 |
Any deviation from the norm poses a danger to the health of the pregnant woman and requires mandatory treatment. Delaying the situation leads to the development of serious complications.
2. Rules for collecting material
We will discuss below how to properly take a urine culture test during pregnancy, in adults and children. To ensure the accuracy of laboratory diagnosis of urological infection, it is important to comply with all stages of diagnosis, including its preanalytical part - the collection of urine samples and their delivery.
It is the need to determine the exact amount of bacterial agents in the test sample that places special demands on sample collection.
When conducting research in a hospital setting, the nursing staff of the hospital is responsible for preparing the patient, collecting material and transporting it to the laboratory. For such cases, laboratories have written instructions regulating all diagnostic steps.
- What does a urine culture test show during pregnancy?
When examined on an outpatient basis, the patient collects urine independently, without the supervision of a medical professional. In connection with the above, it is necessary to carefully instruct the patient on the technique of independently collecting the test material in order to avoid false analysis results.
- 1 Urine collection must be done in a sterile disposable container specially designed for this purpose, which can be purchased at the pharmacy chain. It is not allowed to collect urine in non-sterile, previously used containers, jars or bottles;
- 2 If possible, urine collection should be carried out before starting antibacterial drugs or in the intervals between drug courses, to avoid distortion of the information received;
- 3 The most reliable study is the average morning urine sample - after a night's sleep and before breakfast;
- 4 In the evening, on the eve of urine collection, it is recommended, if possible, to refrain from taking diuretics, since when they are taken, the urine is diluted and the total number of bacteria in one milliliter is reduced;
- 5 To collect urine from infants, you should use special children's urinals with a hypoallergenic adhesive; the collected sample is subsequently poured into a urine collection container, labeled and transported to the laboratory.
Figure 1 - Sterile containers for collecting urine for analysis (without a spatula)
If there are deviations from the norm
Normally, the test results should not contain fungi, yeast or bacteria. Deviations are considered:
- If a woman has no more than 10 colonies on a nutrient medium, then doctors talk about the presence of opportunistic microflora, which does not confirm the presence of the disease. The reason for such an increase in results may be a banal failure to comply with the rules for collecting urine (use of non-sterile containers, failure to comply with hygiene procedures, etc.). In this case, the woman is prescribed a repeat tank culture.
- If the number of colonies exceeds 100, then we can confidently say that there is an infectious process in the body. To determine the exact pathogen, a smear is taken from the woman’s cervical canal, with further study for antibiotic resistance. Based on the results obtained, an effective treatment regimen is selected.
- A slight excess of staphylococcus and streptococcus in the urine during pregnancy (no more than 105 CFU/ml) does not cause concern and is considered normal. To track the process over time, the pregnant woman is prescribed a repeat test over time.
Reference indicators
The degree of infection by microorganisms - the level of bacteriuria, is expressed by the number of identified pathogenic bacteria per 1 ml of urine fluid, abbreviated as CFU. Most experts interpret CFU as follows:
- The etiological significance of the identified organism is accepted when its isolation is >.10 5 CFU/ml in monoculture and titer. This significance remains even if obvious symptoms of infection of the ureteral system are not observed,
- In subjects with diseases - urethritis, acute cystitis, the etiological significance of the culture is accepted if its quantity in monoculture and low titer is 10 2 CFU/ml or more. The same applies to situations of infectious lesions of the ureteric tract, their upper sections, and in the case of sowing against the background of the use of drugs that inhibit bacteria,
- In titers of 10 5 CFU/ml or more have etiological significance in cases of infectious lesions of a recurrent nature or occurring chronically, but only on the condition that the identified microorganisms are not classified as contaminants.
- If the study shows more than 10 4 CFU/ml of more than 2 species of organisms, the analysis is considered unreliable and requires repeating.
Some experts adhere to several other interpretations. For example, 10 3 -10 5 CFU/ml of one type of bacterium is considered as likely to have a high degree of bacteriuria, and a CFU value of less than 10 3 of the identified culture in a mid-morning urine sample is accepted as a false positive result and is considered third-party contamination of the sample. Dyzurric syndrome in women with its acute form makes it possible to diagnose bacteriuria even at levels of 10 2 CFU/ml.
The reliability of tank culture is far from clear and depends not only on the state of infection, but also on gender. A single urine test for microflora is almost 100% reliable in men, but in women, due to the difference in their physiology, it is no more than 80%.
If there are no clear clinical symptoms of the disease, a repeat analysis in women increases the reliability of its results to 90%, and the third one gives an almost 100% reliable result. However, this is only true in the case of isolating the same cultures of microorganisms.
Further actions of the doctor
If a woman is found to have abnormalities in the results of bacteriological urine culture, she is promptly prescribed therapeutic therapy. It includes taking antibiotics or uroseptic drugs. Antibacterial agents are selected based on the nature of the specific pathogen. Delaying treatment leads to the development of complications and progression of the disease to the chronic stage.
This poses a huge threat to the full course of pregnancy. To ensure an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will definitely prescribe the woman an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder, as well as taking a smear from the urethra to determine the nature of the pathogen.
Bacteriological urine culture plays a very important role in diagnosing diseases of the urinary system in a woman during pregnancy. Thanks to this research, doctors identify pathologies and prescribe effective treatment.
When collecting biomaterial, it is necessary to take into account all the requirements; failure to comply increases the risk of obtaining unreliable results. The period for performing bacteriological urine culture takes 5 days. If deviations from the norm are detected, doctors prescribe the pregnant woman to take antibiotics or uroseptics with a repeat culture test at the end of the course of treatment.
Antibacterial sensitivity test
Determining the resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to certain antibacterial drugs is necessary in order to prescribe effective therapy. Let's consider how such a study is carried out:
- A special bowl, divided into equal sections, is filled with a nutrient medium (in our case, natural liquid). Pieces of paper soaked in a solution containing various types of antibiotics are placed in the sections.
- Next, it is observed in which of the compartments the bacteria are actively multiplying and in which the growth has stopped. In this case, it is concluded that the microorganisms are not resistant to the bacteriophage.
- Usually the answer takes about a week to prepare. If the research is carried out in a paid laboratory, the period can be reduced to 2-3 days.
During acute treatment of urinary canal diseases, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are prescribed. Treatment begins immediately upon diagnosis of the disease, without waiting for an antibiogram. As soon as the results become known, the treatment is adjusted by the attending physician.
Data decryption
The interpretation of the results directly depends on a competent analysis and the qualifications of the laboratory assistant. Preparation for delivery of material and compliance with transportation rules are also important. The concentration of bacteria is measured in special units - CFU, which means the number of colonies.
Primary and secondary pathogens can be found in urine. In the latter case, they become the cause of the development of bacterial infections as a result of a decrease in human immunity. If more than two pathogens are detected in the material, the doctor prescribes a repeat urine test, suspecting contamination of the urine under the influence of external factors.
The disadvantage of a urine culture tank is the duration of the study. As a rule, doctors prescribe treatment to a patient on the first day of hospitalization, based on the clinical picture and complaints. The detection of opportunistic microflora in urine in small quantities is not a deviation from the norm. Pathology is indicated when the indicators are exceeded. The values of the isolated microorganisms in relation to certain pathological conditions:
- Klebsiella - an indicator of pneumonia, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; urinary system;
- saprophytic staphylococcus – kidney infections;
- Escherichia coli, Proteus – diseases of the intestinal tract.
Bacteriuria is a sign of infection of the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. It can be accompanied by symptoms such as pain when urinating, the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the urine and a change in its transparency. Any of the infections may be accompanied by general malaise and fever. In such cases, bacteriological analysis facilitates diagnosis and selection of the optimal treatment regimen. You can donate urine in a public medical institution or a private laboratory.
This diagnostic method is more informative than PCR or ELISA examination. In this case, an important factor is its lower cost in comparison with them.
Before taking a urine culture, in order to eliminate errors in interpreting the results, you need to take the preparatory stage and the actual delivery of the material seriously. Violations of any of them will make it difficult to determine the titer of microorganisms in the sample.
A procedure in which a urine culture is taken is prescribed if an infection of the urinary system is suspected. A general urine test will not reveal bacteriuria; this is why fluid is taken for bacteriological examination. It is important to collect samples correctly, otherwise the results will be unreliable. The result takes about a week to prepare.
Urine culture is a type of diagnosis that may be required if certain types of diseases are suspected.