Protein in the urine during pregnancy should definitely alert a woman, because in a normal state of the body, a urine test should correspond to the norm. After the patient finds out that she is expecting a child, she needs to register with a gynecologist, and at each visit to the doctor she needs to take a series of tests, namely blood and urine. Any, even minor, deviations indicate that pathology has developed in the expectant mother’s body. Even a routine analysis can notice deviations from the norm, which are so unnecessary for a woman expecting a child. What is the normal level of protein in urine during pregnancy, and what does proteinuria mean during pregnancy?
Taking a urine protein test correctly during pregnancy
The amount of protein contained in the urine is determined using a general analysis. Here is an algorithm that will allow you to pass urine correctly:
prepare a sterile container (it is better to use a plastic container sold in a pharmacy); In the morning after waking up, wash your genitals thoroughly; if you have any vaginal discharge, be sure to cover it with a cotton pad while collecting urine; collect an average portion of urine in a container (50-70 ml is enough); Deliver the container to the laboratory within a couple of hours.
If a general analysis shows the presence of protein, the doctor may prescribe a daily test for protein in the urine during pregnancy . To do this, during the day, urine is collected in a large, clean jar (it is convenient to use a container with a volume of 2.7-3 liters), and the first morning portion should be poured out.
Before submitting to the laboratory, the contents of the jar are mixed and about 120 ml of urine is poured into another sterile container, but sometimes it is necessary to submit the entire volume of daily urine (before taking the test, check with your doctor which method is needed).
Proper preparation for analysis
Quite often, unreliable results are associated with improper urine collection. In order to exclude extraneous influences on the result, it is necessary:
- a week before the examination, discuss with your doctor the need to discontinue medications, if prescribed;
- a day before, give up any coloring foods (all food should be white or green). This is extremely important, since laboratories use a colorimetric method based on color changes;
- a thorough toilet of the perineum and then drying is necessary;
- For a single portion you need the middle part of morning urine, which is placed in a sterile container.
To analyze daily urine, you do not need to collect the first portion, but starting from the second urination, the entire portion is poured into a sterile three-liter jar, which is kept in the refrigerator throughout the day. Thorough washing is required before each collection. The last portion is the morning urine of the next day. Then you need to accurately measure the volume per day and take 100 ml from it for research.
The norm of protein in urine during pregnancy: table
A small amount of protein in urine can be detected in any person. During pregnancy, the kidneys are under a lot of stress, so protein levels often increase.
Normally, this figure does not exceed 0.033 grams per liter , but in some cases this figure increases to 0.14 g/l, and this is not considered a serious deviation.
The norm of protein in daily urine during pregnancy is 50-100 mg/day.
Prevention of proteinuria during pregnancy
The statistics of proteinuria during pregnancy indicate a frequent manifestation of the pathology. To monitor the progress of pregnancy, women undergo blood and urine tests every month. After 30 weeks and if there is a risk of preeclampsia, the tests will have to be repeated once a week. The monitoring is carried out by a doctor, but it is possible to detect changes in the composition of urine on your own. To prevent gestosis in the early stages, it is necessary to monitor the quality of urine excreted. The detection of a large amount of foam on the surface of the urine indicates that the protein level is exceeded. In this case, the gynecologist is notified.
To prevent the dangerous condition of eclampsia, pregnant women undergo repeated laboratory tests every trimester. The presence of chronic kidney disease indicates the risk of developing preeclampsia. In such cases, women are prescribed the correct diet with limited salt and sufficient fluids. At each scheduled visit to the doctor, you will have to measure your blood pressure and monitor your weight gain.
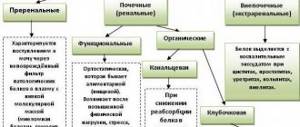
Increased protein in urine during pregnancy: dangers and causes
What does increased protein in urine mean during pregnancy? There are many reasons for the appearance of an increased amount of protein in the urine of a woman who is carrying a child:
improper collection of urine (contaminated container, poorly washed genitals); physical exertion and nervous shock before collecting urine for analysis; eating large amounts of food that contains protein (dairy products, eggs); pyelonephritis (in addition to protein, the urine contains leukocytes, and a woman may experience fever and pain in the lumbar region); gestosis, preeclampsia, dropsy, eclampsia and nephropathy (these diseases appear at the end of the second trimester, they are very dangerous for the baby); glomerulonephritis, or acute inflammation of the kidneys (accompanying symptoms: pink or red coloration of urine, presence of leukocytes and red blood cells in urine).
Urine protein in pregnant women
23.08.2018
The kidneys are organs that filter substances from the blood plasma and are part of the urinary system. This is the initial level of urine formation. Pregnant women develop an increased load on this organ due to increased metabolic processes.
As the fetus grows, compression of the urinary structures increases, and the penetration of proteins into the urine increases. The reason is the emerging or worsening of the disease. To find out what protein in urine means during pregnancy, come for a consultation with a therapist.
What does protein in urine mean during pregnancy?
Proteinuria is the excretion of proteins in the urine; normally this indicator is not detected.
Normally, there should be no protein in the urine of a pregnant woman.
The state of pregnancy is characterized by fluctuations in the amount of protein in the urine of a pregnant woman. The kidneys filter all the proteins from the blood and return them back. If there is proteinuria during pregnancy, the doctor will prescribe additional tests that will help make a diagnosis.
The reasons lie in physiological processes (compression of surrounding organs by the uterus) and pathologies (diseases of various origins).
If an increase in the indicator is detected after the first test, a repeat study is carried out, which will reveal the true data.
Traces of protein during pregnancy - what does it mean?
Traces of protein in urine during pregnancy, detected during testing of biological fluid, may appear if the rules for collecting urine for analysis are violated. If a woman does not wash her genitals well or uses an unsterile container, traces of protein and bacteria are always found.
A small amount of protein in the urine of a pregnant woman indicates the initial degree of glomerular filtration impairment. Because the more proteins found, the more damaged or inflamed the organ is.
Important! If traces of protein are detected after 2-3 tests, the doctor will suspect the onset of gestosis (a disturbance in the course of pregnancy, accompanied by increased blood pressure, proteinuria, and the development of edema).
How to properly collect urine for protein during pregnancy
There are rules for collecting urine for testing that people follow when taking the test so that they can collect their 24-hour urine during pregnancy and the test result is accurate. This will help the doctor monitor the condition of the pregnant woman’s body and avoid complications that will affect both the woman and the fetus.
- In 4-5 days, the woman cancels the medications. Exceptions are drugs that cannot be excluded as prescribed by the gynecologist together with the therapist.
- The pregnant woman's diet begins 2 days before testing. Fatty, fried, overly salty foods are excluded. The amount of meat and dairy products is decreasing.
- The patient must maintain a drinking regime (1.5-2 liters of fluid per day), provided there is no swelling.
- First buy a sterile container from the pharmacy. The use of other containers is unacceptable; inside them there are microbes and foreign substances that will distort the result.
- Before urinating, a pregnant woman washes her genitals and closes the vaginal opening. This prevents the entry of foreign microorganisms into the biomaterial. The urine of a healthy woman does not contain bacteria and is initially sterile.
- Protein is determined using a general clinical urine test (UCA), so the entire portion of biological fluid is collected.
- The sample will be delivered as soon as possible. If there is a reason why this cannot be done, the container is placed in the refrigerator. Freezing is prohibited. The storage time of refrigerated material is no more than 2 hours.
- A piece of paper is attached to the container on which the patient’s name is written.
Table of the norm of protein in urine in pregnant women by trimester
As the fetus grows, the vital processes of the body and the space of the abdominal cavity change. Blood flow can be slowed down after the vessels are compressed by the uterus. Therefore, there are norms for protein in urine during pregnancy, depending on the trimester.
Duration, trimestersDaily protein intake, g/l
| 1 | Up to 0.002 |
| 2 | Increase to 0.1 |
| 3 | Maximum limit up to 0.33 |
If protein is detected in the urine during late pregnancy, the doctor will suspect the development of preeclampsia.
Causes of increased protein in urine
Physiological causes of increased protein levels in the urine include:
- shift in the level of curvature of the spine, which changes the position of the kidney;
- change in the position of the kidney due to pressure on it from the fetus;
- release of traces of protein after changing the patient’s body position;
- intense sports activities;
- release of albumin into the urine due to loss of body fluids (dehydration, insufficient water intake, increased sweating);
- stressful situations;
- a diet containing large amounts of meat and dairy products;
- disruption of blood outflow due to compression of blood vessels by the fetus, causing a change in glomerular filtration;
- compression of the glomeruli, causing leakage of blood elements.
There are pathological reasons for increased protein in the urine during pregnancy, which cause diseases:
- gestational pyelonephritis - renal inflammation of bacterial origin, which occurs in pregnant women due to impaired movement of urine through the urinary tract (urine does not move, microbes accumulate and multiply);
- glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the glomeruli that causes impaired filtration of elements;
- nephritis - inflammation of any area of the kidneys that occurs for various reasons;
- the formation of renal cysts (the formation of a cavity in an organ containing fluid);
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- stone formation is a disease caused by the accumulation of salt crystals;
- gestosis.
Signs of protein in urine during pregnancy
The symptoms of increased protein in the urine depend on the patient’s condition, the functioning of his internal organs, and the presence of the disease. If the condition causes compression of the kidneys, pain in the lumbar region and fever appear. Pain sensations spread to the entire back area.
After the development of gestosis, the main signs are lower back pain, severe swelling, high blood pressure and proteinuria.
The passage of stones through the genitourinary tract causes unbearable pain in the abdomen and bleeding into the urinary tract.
Urine becomes cloudy after proteinuria. If inflammation develops, mucus appears. The stones form sediment when the sample stands.
Why is protein in urine dangerous in pregnant women?
The appearance of proteinuria is dangerous for the body; it leads to disorders that are dangerous for the mother and fetus. Urgent medical consultation is required. There are the following consequences of increased urine protein during pregnancy:
- insufficiency of functioning of internal organs (heart, lungs, kidneys);
- the appearance of edema of the lungs, extremities (arms, legs);
- increased intravascular pressure;
- danger to pregnancy;
- the appearance of a child with mental retardation;
- the development of an infection of the genitourinary system, which can cause sepsis (infection of a woman’s blood) or the entry of bacteria into the intrauterine fluid, which causes infection of the baby even before birth (protein and bacteria appear in the urine during pregnancy).
Diet for high urine protein
It is allowed to eat dietary meat, honey, and berries.
If proteins penetrate into the patient’s excretory fluid, the doctor will tell you which foods should be excluded, which ones should be consumed to remove the indicator, and how to reduce protein in the urine during pregnancy.
Legumes, cereals, mushrooms, onions, garlic, and rich broths are excluded from the patient’s diet. The consumption of vegetables and fruits is reduced. Meat is consumed only of dietary grades (turkey). The amount of dairy products and bread is decreasing.
If protein appears in a urine test, it is allowed to consume dietary meat, honey, berries, and a small amount of dairy products that do not contain phosphorus before lunch (sour cream, cream). Fish is allowed in small portions. Salt is removed completely (pickles and table salt are excluded). You cannot eat smoked or pickled foods. Pumpkin, raisins, beets, dried apricots, melon, and watermelon are allowed.
Meals are divided into 6 times per day, this promotes better absorption and eliminates an excess of elements and minerals.
Drinking water and other liquids during the day should be moderate; this will eliminate swelling and help the excretory system filter out protein.
Conclusion
There is no protein in the urine during pregnancy in healthy women. It appears only after a violation of the internal state of the body. If proteinuria is detected after several laboratory tests, consult a doctor immediately.
This is especially true for pregnant women, since the condition is dangerous not only for the woman herself, but also for the fetus. Self-medication is not acceptable; it will lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and the death of the pregnant woman during childbirth. The doctor will tell you more accurately and effectively how to get rid of edema and proteinuria.
If a patient experiences painful symptoms for which he does not see a doctor, this is fraught with the development of kidney failure.
Urine protein in pregnant women Link to main publication
Source: https://ruanaliz.ru/mocha/belok-mochi-u-beremennyh/
Repeated urine test for protein: what is it for?
To confirm the increased amount of protein, the doctor will definitely prescribe a donation
reanalysis
, since a one-time deviation from the norm does not always indicate the presence of pathologies.
False proteinuria (high protein content) in a woman during pregnancy can be a consequence of nervous shock, excessive physical activity, or consumption of certain foods. In this case, the results of the re-analysis will be within normal limits.
Symptoms and signs
With proteinuria, the main symptoms are identified that will direct the attending physician to more closely monitor the patient:
- weakness;
- reduced ability to work;
- vomit;
- pain in the kidney area;
- blood pressure instability;
- signs of deterioration in the condition of the fetus - increased or slowed heartbeat, the woman feels a decrease in its activity.
If the main symptoms of the pathology persist throughout pregnancy and protein is excreted in the urine in the later stages, damage to the nervous system, rejection of the fetus by the mother's body, hormonal disorders in pregnant women, edema, and convulsions are observed.
During inflammatory processes, in addition to a significant increase in protein, bacteria can be detected in the urine. Urine is submitted for analysis according to Nechiporenko, in which leukocytes can be significantly increased. The number of white blood cells in the blood increases, and biochemical parameters may change. When examining the expectant mother, signs of intoxication are detected.
With the development of late toxicosis in pregnant women, a triad of symptoms appears: increased blood pressure, edema, proteinuria. Severe forms of gestosis include preeclampsia and eclampsia. With preeclampsia, the triad of gestosis is accompanied by symptoms of worsening blood circulation in the brain (headaches, visual disturbances). Eclampsia is characterized by the occurrence of seizures at high blood pressure in a pregnant woman. Severe signs of gestosis require treatment in a hospital or intensive care unit.
Treatment for increased protein in urine during pregnancy
How to reduce protein in urine during pregnancy? First of all, the doctor must determine the exact cause of the increase in protein in the urine . If there is a strong deviation from the norm, the doctor will recommend fighting the disease in a hospital setting.
Each disease has its own treatment regimen:
Pyelonephritis and other inflammatory processes . For treatment, antibiotics are used (for chronic and acute disease), herbal anti-inflammatory drugs (Canephron or Phytolysin) and diuretics. It is not recommended for a pregnant woman to sleep on her back a lot. With such diseases, it is useful to stand on all fours more often and walk a lot. Preeclampsia. This condition is very dangerous for both the mother and the unborn baby. With gestosis there is a high risk of premature birth. With this disease, a woman must follow a diet that will reduce the amount of protein (chocolate, coffee, citrus fruits, junk food, spices, and carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet). If edema is present, the amount of fluid consumed should be reduced.
What should you be wary of?
The classic “trio” of symptoms of gestosis looks like this: protein in the urine, persistent increase in blood pressure, edema. The latter arise due to increased vascular permeability, as a result of which plasma (the liquid part of the blood) enters the tissues. As a rule, swelling is especially noticeable in the morning and evening. First of all, a pregnant woman's legs swell, then her face and hands (they become numb, it becomes difficult to bend her fingers). Many women try to get rid of edema using diuretics. But in the case of gestosis, this can only worsen the situation. Therefore, it is better not to abuse diuretics and certainly should not use them without consulting a doctor.
Also, the presence of gestosis may be indicated by constant nausea and pathological weight gain. It is very important to keep track of this moment. After all, many people believe that during pregnancy you need to eat whatever you want (which, in general, is true, but within reasonable limits), and it is quite normal that weight increases. However, you should be wary if your weight continues to increase with your usual diet.
Another sign of gestosis is severe thirst. Therefore, it is very important to control the amount of fluid consumed during the day. And correlate it with how much urine is released. If the difference is significant, this may be a sign of pathology. By the way, now there are many special programs for both iPhone and Android that allow you to track water consumption throughout the day, which is very convenient.
In especially severe cases, the condition can worsen suddenly - blood pressure rises sharply, spots appear before the eyes, headaches, congestion in the ears, nausea and abdominal pain. If all this happens, you must immediately call an ambulance, otherwise the consequences could be disastrous.
Video about protein levels in urine during pregnancy
We invite you to watch a video that talks about the protein content in urine during pregnancy.
If kidney disease is suspected, the patient is given a referral for diagnostic testing in the laboratory of a medical institution. As a result of screening, protein in the urine is determined. To do this, you need to collect the discharge per day. If the protein concentration in the material exceeds the norm, this may indicate the presence of a deviation in the body. However, other factors that do not indicate disease can also affect an increase in the amount of protein in the urine. This could be hypothermia, prolonged physical activity, or nervous tension. Therefore, in order to clarify the diagnosis, control tests are carried out after 2 weeks.
Types of proteinuria
During pregnancy, depending on the factors influencing the formation of protein in the urine, the following types of proteinuria are classified:
- Physiological in nature - the protein level is slightly elevated compared to the norm (no more than 0.033 g/l). The woman does not feel any significant discomfort. The protein periodically appears, then disappears. The influencing factors are compression of the lumbar spine, lowering of the kidneys, constant tension, and increased load on the kidneys. This condition is not dangerous. It is enough to adjust the mother’s lifestyle and nutrition.
- Pathological in nature. The higher level is 0.25-0.33 g/l. Such indicators are observed in acute kidney diseases, inflammation and problems with the urinary and reproductive systems, and with the appearance of malignant tumors. With increased compression of the internal organs and kidneys by the uterus, stagnant proteinuria may develop. There are also disruptions in the blood supply to the kidneys, resulting in the penetration of large amounts of protein into the urine.
When identifying traces of protein, it is first important to exclude the possibility of distorted proteinuria (incorrect analysis), the main reason for which is improper hygienic measures taken before taking the analysis or refusal to take them, the presence of chronic problems of the urinary system and their untimely treatment during exacerbation.
It is necessary to re-analyze to eliminate the possibility of incorrect sampling. In this case, it is necessary to comply with hygienic requirements: thoroughly wash the genitals, isolate the vagina with a tampon (cotton), collect urine in a sterilized container. Only by observing these requirements can you get the correct picture.
Analysis of urine
In order to determine the level of protein concentration in the urine, it is necessary to correctly collect the discharge for analysis. To do this, collect the daily portion of urine in a clean, sealed container, while skipping the morning emptying of the bladder. All portions are collected in one container. It is necessary to collect all bladder secretions for the day. If, as a result of the examination, a protein whose norm is exceeded is detected through a urine test, based on the data obtained, the doctor diagnoses kidney disease.
Signs of diseases with high protein levels
Often, large amounts of protein indicate diseases of the genitourinary system. Women who had problems with the kidneys or urinary tract before conception should inform their doctor about this, which will greatly facilitate diagnosis. Pregnancy quite often is a kind of catalyst for such ailments, and after its onset they can return and progress. If such diseases are detected, the expectant mother needs to be under close supervision of a urologist and nephrologist throughout the entire period of bearing the baby. Kidney disease in expectant mothers is detected not only by elevated levels of protein found in urine test results. They are often accompanied by high levels of white blood cells and red blood cells in the urine. A woman may also experience pain in the lower back and bladder area. Cloudy urine during pregnancy may be an additional sign of such diseases. Very often, increased protein during pregnancy is a sign of gestosis. This disease poses a serious danger to both the woman’s health and the life of the child she is carrying. With this disease, the functioning of the placenta decreases, in which blood flow is disrupted and the fetus does not receive vital oxygen and other useful substances. Signs of gestosis, along with elevated protein levels, are the following symptoms:
- severe swelling;
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- high blood pressure;
- dizziness.
Causes of protein in urine
The most common kidney disease during pregnancy is gestosis, which is an extremely dangerous pathology. The disease is characterized by severe swelling of the tissues, accompanied by hypertension, dizziness and severe weakness. Most often, women in the second trimester of pregnancy are susceptible to gestosis. Other infectious kidney diseases that develop during pregnancy include pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. The disease progresses when protein is observed in the urine, the norm of which should not be exceeded. At the initial appointment with a doctor for suspected pyelonephritis, a pregnant woman complains of characteristic pain in the lumbar region and bladder. With glomerulonephritis, a specific red color of urine is observed. Laboratory tests reveal the presence of increased levels of leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine.
Lifestyle correction
During pregnancy, women can partially or completely stabilize the concentration of proteins in urine on their own. To do this you need:
- Visit your doctor regularly to monitor proteinuria;
- eliminate excessive physical activity;
- minimize stress;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- use loose clothing;
- follow all doctor's orders.
Additionally, we must not forget about proper sleep and rest. Very often, the appearance of protein in the urine is not a serious problem. To stabilize kidney function, it is enough to exclude the influence of negative external and internal factors.
Treatment of a pregnant woman
After making a diagnosis, the doctor tries to provide treatment to eliminate the root cause of the disease. In order to stabilize the condition of a pregnant woman, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs based on medicinal herbs. When the disease becomes chronic, antibiotics may be prescribed. If a pregnant woman follows the recommendations of her doctor, a decrease in protein concentration is observed during a repeated laboratory test of urine analysis.
Achieving stabilization of indicators, one of which is protein in the urine, the norm of which is off scale, can be extremely difficult in the complicated form of gestosis. In this case, doctors try to prevent a further increase in the protein content in the urine until delivery. In some cases, it is possible to bring a woman’s pregnancy to a full nine months. Most often in such cases, pregnancy ends in premature birth.
Treatment methods
Proteinuria is a symptom indicating a dysfunction of a particular organ or entire system. Adequate therapy is based on identifying the root cause of the clinical symptom with further impact on it.
Medication
Treatment with tablets and injections is justified for moderate and severe proteinuria. Depending on the root cause of the symptom, doctors use the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics. Antimicrobial agents are effective only if the presence of a pathogen in the patient’s body that causes the disease is confirmed. During pregnancy, penicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin), macrolides (Erythromycin) and cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefepime) are allowed;
- insulin. Pancreatic hormone, which is used in patients with diabetes;
- diuretics. Drugs (“Furosemide”, “Hydrochlorothiazide”) are used for severe edema syndrome;
- antihypertensive drugs. Proteinuria is often accompanied by increased blood pressure. To reduce it in pregnant women, Labetalol, Amlodipine, and Methyldopa can be used.
The selection of medications is carried out on an individual basis depending on the severity of the patient’s condition.
Diet
Reducing the concentration of protein in the urine can also be achieved through dietary restrictions. Fried and smoked dishes are excluded from the menu. Salt consumption is reduced to a minimum. The drinking regime is selected by the doctor individually, depending on kidney function. In most cases, it is recommended to limit the amount of fluid consumed to 1.5-2 liters per day.
The therapeutic diet involves increasing the amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals, and dairy products. At the same time, the volume of protein foods decreases.
Reasons for the appearance of protein in the urine of an adult
It is necessary first of all to determine why the protein in the urine has increased and the reasons. The norm of daily urine allows for a small amount of protein. If the indicator does not correspond to the established value, then this signals a possible pathology. A high concentration of protein in the urine is a consequence of the following diseases:
kidney tuberculosis; pyelonephritis; nephropathy; metabolic disorders; hypertension; urinary tract infections.
Typically, kidney diseases are characterized by the appearance of other specific symptoms. In some cases, there is an increase in temperature, chills, and pain in the lumbar region. If no action is taken at this stage, the disease begins to progress, dizziness and nausea appear, which can result in vomiting. In the future, in the absence of proper treatment, the structural elements of the body begin to collapse.
Pathological proteinuria
Warning symptoms to look out for:
- the appearance of protein in the urine in early pregnancy;
- repeated detection of protein in the urine;
- protein level is above 0.3 g per day.
Laboratory signs are combined with a deterioration in the woman’s general condition. The development of pathology is indicated by:
- severe weakness;
- headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- visual impairment (blurred vision, flickering spots before the eyes);
- swelling of the face in the first half of the day;
- swelling of the hands, feet, and legs;
- involuntary muscle twitching;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- dysuric phenomena: pain, itching, burning during urination, increased frequency of urination, urinary incontinence or retention.
The combination of these symptoms with proteinuria is an unfavorable sign and requires mandatory medical supervision.
Among the causes of pathological proteinuria in late pregnancy, special attention deserves:
Preeclampsia
The appearance of protein in the urine after 20 weeks most likely indicates the development of gestosis. This specific condition occurs only during pregnancy, childbirth, or the early postpartum period. The development of gestosis is accompanied by a triad of symptoms:
- arterial hypertension (increase in systolic blood pressure above 15 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure above 10 mm Hg from baseline);
- swelling;
- proteinuria.
The appearance of protein in the urine is a late symptom of gestosis and indicates a violation of the kidneys. In this situation, the expectant mother is monitored with constant monitoring of blood pressure and the condition of the fetus. If indicators worsen, hospitalization in a hospital is necessary. The shorter the pregnancy due to gestosis, the worse the prognosis and the higher the likelihood of complications.
In the absence of adequate therapy, severe gestosis develops into preeclampsia. In this state, diuresis decreases, blood pressure increases significantly, and protein in the urine increases. Without treatment, preeclampsia progresses to eclampsia - the most dangerous complication of pregnancy. Convulsions develop, and there is a real threat to the life of the woman and the fetus. The expectant mother and her baby can only be saved by providing emergency medical care. In this situation, a caesarean section is performed regardless of the stage of pregnancy, infusion therapy and other measures to save the woman’s life are prescribed. Neonatologists provide care to the newborn.
Prevention of eclampsia includes:
- Regular monitoring by a gynecologist throughout pregnancy.
- Timely delivery of OAM and other tests.
- Control of blood pressure, weight and diuresis.
- Timely treatment of gestosis.
Women who are overweight and have pre-existing arterial hypertension are at risk for developing gestosis. This category of expectant mothers should especially carefully monitor their health and, if they have the slightest doubt, consult a doctor.
Kidney problems in children
The kidneys perform the function of filtering blood in the body; with kidney pathology, proteins cannot penetrate the kidney filters and end up in the urine. The level of protein in a child’s urine should be no more than 60 mg/day. If protein excretion exceeds the established values, this most likely indicates an infectious inflammation of the kidneys. Moreover, the earlier treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis of the disease will be. This is why it is important to have your child's urine tested regularly.
In order to establish a final diagnosis, a laboratory test reveals daily protein in the urine, the norm of which does not yet indicate that the preliminary diagnosis was erroneous. Its concentration changes several times during the day. Protein in the urine can be released in large quantities during high physical activity, also as a result of prolonged stay in an upright position.
Daily loss of protein in urine during pregnancy is normal
articles
Pregnant women have to constantly visit the doctor and undergo various tests.
On the one hand, this is very tiring, but on the other hand, the woman has the opportunity to control the course of pregnancy and the chance to identify any violations before they cause harm to her and the baby.
Urinalysis is a very convenient and fairly simple way to diagnose abnormalities in the health of mother and child.
An alarming signal may be, for example, the appearance of protein in the urine during pregnancy.
Normal level of protein in urine during pregnancy
In the human body, blood is constantly filtered in the main organs of the urinary system - the kidneys.
This is necessary to remove excess water, salts, products of protein, carbohydrate, lipid metabolism and some harmful substances.
At the first stage of urine formation in a person, tens of liters of liquid are extracted from the blood per day, most of which returns to the bloodstream during reabsorption in the renal tubules.
At the second stage, only about two liters of urine are produced per day, which is excreted from the kidneys through the ureters, bladder and urethra.
Normally, only substances consisting of small molecules are filtered into primary urine. Large molecular compounds, such as proteins, are not excreted from the blood during urine formation.
Although there are conditions in which a healthy person experiences proteinuria, that is, the release of protein in the urine:
1 Working proteinuria manifests itself after prolonged physical activity; it is also called proteinuria of athletes, since it occurs most often in this category of people.
2 Limentary proteinuria can occur with an unbalanced diet, when a person often consumes foods high in protein.
3 Orthostatic proteinuria develops due to prolonged stay in an upright position, during which venous congestion forms in the kidneys for some time.
4 Emotional proteinuria occurs during nervous overexcitation and stress, for example, during conflicts, during serious events in a person’s life.
5 Protein may appear in the urine even after a medical bimanual examination by palpation of the kidneys. This condition is called palpable proteinuria.
It also happens that protein is detected during analysis not due to impaired filtration during urine formation, but due to improper collection of biomaterial.
That is, protein substances enter the jar from the genital organs, which secrete mucus. This is called false proteinuria, which does not recur with repeated analysis if the patient collects the biomaterial correctly.
All the described cases refer to the so-called physiological albuminuria; they arise due to changes in the physiological state of the body in the absence of pathologies.
The daily norm of protein in urine during pregnancy is 0.75 g, and in the morning analysis its concentration should not exceed 0.002 g/l.
When the fetus reaches a large size, the load on the expectant mother's kidneys increases significantly. Therefore, the protein content in urine in late pregnancy is considered normal even at 0.033 g/l.
Causes of protein in urine during pregnancy
The following factors can increase protein in urine during pregnancy:
1 Inflammatory processes of the urinary system: kidneys (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), bladder - cystitis.
They provoke the appearance of protein and leukocytes in the urine during pregnancy.
2 Preeclampsia is a dangerous condition that can only develop in pregnant women and is manifested by an increase in the permeability of blood vessels throughout the body.
3 Other pathological conditions of the body: oncological tumors in the kidneys, epileptic seizure, heart failure in a pregnant woman, diabetes mellitus, hypertension.
Any of these reasons can negatively affect the condition of the pregnant woman and her child.
Inflammatory lesions in the urinary system (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis) usually develop due to the penetration of an infectious agent into these organs, for example, E. coli.
Infection occurs in two ways: through the urethra (ascending infection) or through the blood (descending infection).
Symptoms of cystitis include pain and discomfort when urinating, blood in the urine, frequent urge to urinate with a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after visiting the toilet.
Kidney disease may be indicated by symptoms such as lower back pain, fever up to 38-39 degrees, swelling of the body, increased blood pressure and changes in urine volume.
Only a doctor can diagnose this or that disease of these organs, and this will require additional examinations.
Protein may appear in the urine due to gestosis, the manifestations of which can be confused with kidney disease.
This condition also causes swelling and increased blood pressure, disruption of the kidneys, liver, nervous system and placenta.
This makes it extremely difficult to bear a child.
Preeclampsia is accompanied by damage to the blood vessels, which entails their spasm and a shift in the hormonal background of the pregnant woman.
Sometimes the excretion of protein in the urine can be caused by poisoning of a pregnant woman with various toxins, heavy metals, vitamin D hypervitaminosis, or radiation.
Why is protein in urine dangerous during pregnancy?
The danger of protein appearing in the urine is that the metabolic processes in the mother’s body are disrupted.
Unfavorable factors for the baby are the spread of infection in the body due to diseases of the urinary organs, increased temperature, and changes in the water-salt balance.
The condition of the pregnant woman, which is observed with these diseases, complicates the process of bearing the fetus.
The loss of protein in the urine changes the composition of the blood; its coagulation processes and immune reactions in the body may be disrupted.
The degree of danger of proteinuria depends on what type of protein is excreted from the pregnant woman’s body in elevated concentrations.
Preeclampsia can cause retardation of growth and development in the baby, because its nutrition through the placenta is disrupted, and proteins necessary for development are removed from the mother’s body.
The symptoms that develop with this disorder pose a danger to the health and life of the pregnant woman herself.
How to test urine for protein during pregnancy
Traces of protein in the urine during pregnancy may appear due to vaginal mucous secretions getting into the biomaterial; in expectant mothers, this is a fairly common reason for a false positive result in such a study.
When prescribing an analysis, a gynecologist usually reminds the pregnant woman of the rules for collecting biomaterial.
The container must be clean and sterile.
Recently, pharmacies have been selling special jars for such purposes, which, for convenience, are equipped with a sticker where you can indicate the patient’s data (last name, address, age) and the name of the attending physician.
For the analysis, an average portion of urine is required, that is, for the first few seconds you need to urinate in the toilet, and not in a container for biomaterial.
After collection, the jar is tightly closed, ideally it should be delivered to the laboratory within two hours. Any deviation from these rules may lead to an error in the analysis with the detection of protein in a pregnant woman.
Protein in urine during pregnancy: treatment
Increased protein in the urine during pregnancy is a signal to immediately determine the causes of the disorder.
When the diagnosis is made, you need to move on to treating the identified disease. Ignoring the appearance of protein in the urine is very dangerous for a pregnant woman and her baby.
If kidney disease is diagnosed, antibiotic therapy is necessary to clear the infection.
At the same time, they fight individual symptoms of the disease: when the temperature rises, antipyretics approved for pregnant women are prescribed, and diuretics are used for swelling and urinary retention.
Sometimes a doctor can recommend treatment with medicinal herbs, but you cannot choose your own means of treatment. Repeated tests will be required to monitor the condition of the kidneys and the healing process.
Preeclampsia, unfortunately, cannot be treated. But the doctor prescribes maintenance therapy for the pregnant woman.
High blood pressure, swelling and malnutrition of the fetus may be indications for termination of pregnancy. If a complication occurs in the later stages, a caesarean section can be performed to save the life of the mother and baby.
If the condition of the pregnant woman is satisfactory, the attending physician strives to maintain the pregnancy for as long as possible so that the fetus develops sufficiently and is more viable.
If protein is lost for other reasons (disorders of the cardiovascular system, epilepsy), treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causes of such a disorder.
If the disease is not treated, the pregnant woman’s condition must be maintained so that she can carry and give birth to the baby safely.
If a woman has protein in her urine during pregnancy, she should be very careful about this disorder. Under no circumstances should you delay repeated testing and visiting a doctor to establish a diagnosis.
On the other hand, this symptom often occurs when there are errors in the research, so when you hear this result for the first time, you should not be scared.
High protein in the urine during pregnancy in repeated tests should also not cause panic, because a pregnant woman in any case has a chance of safely carrying a baby, but only with timely and thorough treatment of the disease.
Preeclampsia is also not a death sentence; modern medicine makes it possible to save the life of a child.
And in a pregnant woman, with proper supportive therapy, all the symptoms of this disorder go away on their own after the baby is born.
12172 times
Source: moe1.ru
Source: https://presidentofrussia.ru/sutochnaja-poterja-belka-s-mochoj-pri-beremennosti-norma/
Consequences
First of all, you should pay close attention to your own health and follow the recommendations of your doctor. The main parameters that the diagnostician focuses on during the examination are protein in the urine, the causes, the norm of protein concentration in a healthy person and any deviation from it. Usually, the doctor prescribes a laboratory test during the treatment process in order to determine how effective the prescribed drugs turned out to be. This also helps to establish the reasons that influenced the development of the disease, and to correct treatment if no visible results are observed.
Source: medic-sovet.ru
Consequences for the expectant mother
Proteinuria, with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, can usually be treated, and pregnancy can be maintained. A woman should be under medical supervision throughout the entire period of bearing a child.
Newborns are examined by a neonatologist to exclude signs of intrauterine hypoxia and its consequences. With a successful outcome after childbirth, kidney function improves, proteinuria and edema disappear, and blood pressure normalizes.
If protein in the urine is detected in the early stages, its daily loss is more than 1 g, the pressure exceeds 175/115 mm Hg. Art., there are signs of visual impairment, liver enlargement or myocardial damage, the risk of complications increases:
- eclampsia;
- abortion;
- fetal development disorder;
- insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrition to the fetus;
- premature birth;
- placental abruption;
- pathology of the birth period, bleeding;
- fetal death;
- death of a pregnant woman.