What causes the disease?
The urinary system evacuates many salts, wastes and toxins along with urine. Salt diathesis manifests itself with serious dysfunction of the urinary and urinary systems.
Crystalluria does not occur without reason and is not considered an independent disease. It is diagnosed as a complication of an acute or chronic pathological process. By seeking medical help in a timely manner, patients with crystalluria can count on a very favorable prognosis. Even during a period of complete remission, monitoring of urine analysis and regular consultative examinations with a nephrologist or urologist are required. The causes of salt diathesis are usually classified into external and internal.
Return to contents
External reasons
Factors that provoke crystalluria that are not related to the health of the body:
In hot climates, such a pathology can develop.
- negative living conditions (hot climate);
- drinking low-quality hard water;
- non-compliance with drinking regime;
- the diet contains foods containing large amounts of protein,
- alcohol abuse;
- hypovitaminosis;
- excessive use of the sauna;
- use of medications - diuretics, sulfonamides, cytostatics.
Return to contents
Internal factors
The main reason for the appearance of crystalluria is a disruption of metabolic processes at the cellular level. Pathology is provoked by:
- infectious diseases of the urinary system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- developmental abnormalities of the genitourinary system;
- genetic metabolic disorders;
- oncological processes.
Return to contents
Main symptoms and types of crystalluria
Salt diathesis is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
Salt diathesis is characterized by dark urine.
- microhematuria;
- dark shade of urine;
- characteristic pungent odor;
- pain when urinating;
- frequent urge to deurinate;
- aching, pulling pain in the lumbar region, groin, navel;
- swelling of the limbs.
Crystalluria is classified according to the chemical compounds that form the salts. Main types:
- phosphaturia;
- calcium oxalate type;
- cystinuria;
- uricorosis.
Return to contents
Phosphaturia
This type of crystalluria is diagnosed based on the body's high levels of calcium and magnesium phosphates. Poor nutrition and a large number of foods that alkalize the body are the main causes of phosphaturia. Infections of the genitourinary tract of the body can lead to a pathological condition. Pathogenic microorganisms attack uric acid, breaking it down. Because of this, the amount of alkaline salts in urine increases, forming crystals from calcium phosphates.
Return to contents
Calcium oxalate form
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease contribute to the release of calcium into the blood.
According to statistics, this type of salt diathesis is more often diagnosed in childhood. Calcium oxalate crystalluria in children manifests itself even with a slight increase in the level of salts in the urine. The increase in oxalate content in children's urine is caused by an increased intake of calcium from food. If a child is diagnosed with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, these substances quickly enter the bloodstream from the intestines. As a result, a large amount of salts are deposited in the urine.
Return to contents
Cystinuria
An increase in the concentration of cystine salts in the body causes a similar condition. Cystine is an aliphatic acid containing sulfur. This amino acid supports the structure of peptides and proteins in the body. It refers to compounds that are slightly soluble in water. Cystine is not excreted from the kidneys, which provokes its gradual accumulation. The cause of cystinuria is genetically determined pathologies of the kidney structure.
Return to contents
Uricorosia
This type of crystalluria is asymptomatic for a long time. The reason is the precipitation of salts that make up uric acid, the increase in concentration of which is facilitated by the breakdown of purines that appear in the body in the following cases:
The formation of such salts is facilitated by frequent consumption of cauliflower.
- systematic consumption of foods with a high content of purines - cauliflower, broccoli and others;
- increased secretion of uric acid, observed in connection with a genetic predisposition;
- long-term use of medications;
- chronic infections.
Return to contents
Diagnostics and necessary tests
Salt crystals form sediment in the urine, which can be seen with the naked eye. It also contains other substances (protein, epithelium, uric acid, bilirubin, etc.). In the laboratory, the sediment is stained and examined under a microscope. Crystals of oxalates, urates and phosphates have different shapes and react differently with dyes. This allows salts to be accurately classified and their concentration determined.
If salt formations are detected in the urine, additional tests are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. Allows you to identify the presence of sand or stones, disturbances in the structure and location of the urinary organs.
- Magnetic resonance urography is performed for renal colic.
- Analysis of daily urine according to Zimnitsky. Interpretation of the results will help assess the excretory capacity of the kidneys.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. The test allows you to find out about the presence of an inflammatory process in the organs of the urinary system.
- A general and biochemical blood test determines the concentration of phosphorus, calcium, uric acid, and the presence of an inflammatory process.
Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to determine the exact causes of the formation of salts in the urine and prescribe adequate treatment. If the patient has signs of an inflammatory process, a sample of the biomaterial will need to be submitted for bacteriological culture. The analysis will determine the type of microorganisms that caused inflammation and their resistance to antibiotics.
What is used to diagnose the disease?
After a thorough history collection and assessment of the patient’s general condition, the doctor will issue a referral for laboratory tests and instrumental studies. The main types of studies are shown in the table:
| Type of study | Methods |
| Laboratory | General urine analysis |
| Biochemical study of urine | |
| Instrumental | Ultrasound diagnostics |
| Cystoscopy | |
| Radiography |
Return to contents
prourinu.ru
Reasons for the development of pathology
Crystalluria in children (as well as in adults) can occur due to various factors, including taking medications that contain sulfonamides. The causes of the disease are divided into two groups.
Internal factors
They appear against the background of processes that are difficult to change:
- Urinary tract infections.
- Congenital pathologies of the genitourinary system.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Genetic abnormalities leading to metabolic disorders.
External factors
This category contains something that a person can change on his own, sometimes even without the help of specialists.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Drinking hard water regularly.
- The climate is too hot and dry.
- Frequent visits to saunas, baths and other rooms with high temperatures.
- Taking medications with sulfonamides, diuretics and cytostatics.
The development of crystalluria is promoted by both a combination of the above reasons and the influence of individual factors.
Signs of illness
All types of crystalluria have similar symptoms, although the anomaly is very rarely diagnosed at the initial stage. Here are a few symptoms indicating its occurrence:
- causeless headache;
- frequent or false urge to urinate;
- development of nephropathy and other kidney diseases;
- a person consumes less fluid;
- pain in the abdomen or lower back;
- discomfort when urinating.
Signs such as the appearance of blood clots in the urine indicate the presence of the disease. It has an unpleasant odor and becomes cloudy.
When to take a urine test
A urine test to detect sediment is prescribed:
- with severe pain in the lumbar region;
- with kidney pathology;
- during complete preventive examinations of the body;
- if you suspect gout;
- after infectious diseases (meningitis, scarlet fever);
- with difficulty urinating;
- with diabetes mellitus.
Analysis of urine for salt is a way to assess the progression of pathology or the effectiveness of its treatment.
Collection rules
Ideally, the first urine sample in the morning should be collected. Before taking the test, you need to wash your genitals and prepare a clean, dry, preferably plastic, jar. Pharmacies have special containers for tests. After the preparatory procedures, it is enough to empty yourself into a container and close it tightly. The collected material must be delivered to the laboratory no later than 2 hours later. After this period, natural processes of decay and modification will begin to occur in urine, and the analysis will no longer be reliable.
Classification
In the human body, salts are divided into three types: phosphates, urates and oxalates. If the level of one of them prevails over the others, then crystalluria develops.
Oxolate-calcium form
The disease almost always affects the kidneys and is detected in children with impaired oxalic acid metabolism. Calcium oxalate crystalluria leads to the deposition of calcium oxalate on the renal tubules and tissues. With a more severe course of the disease, sediment is observed on the capillaries and organs.
The primary type is caused by genetic predisposition, while the secondary type is caused by excessive consumption of foods rich in oxalic acid. A lack of B vitamins negatively affects the absorption of the substance, and as a result, the functioning of internal organs is disrupted and kidney failure occurs.
Urate form
The disease develops due to an excess of urate in the body, when uric acid is formed by the kidneys in significant quantities. The primary type is caused by increased or decreased enzymatic activity during the metabolism of uric acid. Secondary forms due to long-term use of cytostatics or thiazide diuretics. Frequent causes of the disease are chronic hemolytic anemia or myeloma.
Cystinuria
This form of the disease is provoked by a high concentration of cystine salts. Cystine is a microparticle amino acid that does not mix well with liquid. The substance is not absorbed in the kidneys, so it is deposited in their tubules. Most often, cystinuria develops due to a congenital disorder of the renal structure.
Phosphate form
Diagnosed when calcium and magnesium levels increase, it is a secondary type of cause of the disease. Excessive consumption of foods with these microelements causes pathology. The fight against the disease includes adherence to dietary nutrition and normalization of salts in the human body. In rare cases, the phosphate form is a consequence of a lack of enzymes, which leads to the formation of kidney stones.
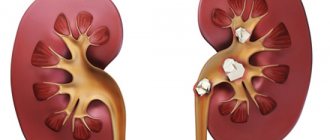
What is crystalluria
Crystalluria is the root cause of the formation of kidney stones. The essence of the phenomenon is easier to explain based on another name for the disorder - “exchange nephropathy.” We are talking about damage to the glomerular system and functional kidney tissue against the background of inadequate metabolism. In this case, salts settle in the renal pelvis, interfering with the normal functioning of the organ.
A tendency to disrupt salt metabolism may be:
- Primary (congenital) - due to genetic predisposition. It is characterized by the early onset of symptoms (in childhood), the increasing severity of the course and the development of complications in the form of renal failure.
- Secondary – resulting from hereditary tissue defects, changes in hormonal balance, inflammatory diseases and intoxications.
Salt diathesis may not manifest itself in any way in the absence of provoking factors. In conditions “favorable” for the disease, symptoms make themselves felt very quickly.
Treatment
Complex therapy of the disease includes normalization of nutrition and drinking regimen, and taking medications. The consumption of chicken, chocolate products, cheese, legumes, liver, and caviar is not recommended. If you have oxalaturia, you should avoid sorrel, beets, chocolate, meat, cocoa, cranberries, carrots, and spinach. With cystinuria, eggs, curd mass, meat and fish are excluded from the diet. Among the medications, the doctor prescribes vitamin B6, Aevit, Canephron.
Attention! Treatment of crystalluria is carried out in conjunction with therapy aimed at combating dysbiosis with the help of Linex, Bifidobacterin and other means. If infection is present, uroseptics are prescribed.
According to statistics, crystalluria is common in childhood; the disease is diagnosed in every third child. If any symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult your doctor. Tests and examination will show the concentration of phosphates, alkaline and potassium salts in a person’s urine.
tvoyapochka.ru
General information
Excess sand or various salts in the human body is called “crystalluria” and is a fairly common disease. There are many different types of salts in human urine. A healthy urinary system prevents sediment from turning into crystals.
Uncontrolled development of pathology in the absence of treatment leads to the development of renal stone pathology.
An unhealthy condition with increased salt concentrations becomes more severe over time. The salts contained in the urine crystallize and precipitate. They settle on the walls of the organs of the urinary system. If there is too much excess salt, it can settle on other organs, for example, the spleen. As a result, this leads to kidney stones.
Causes of the disease
All factors that cause disruption of salt metabolism in the body can be divided into two categories: external and internal:
- External conditions include those reasons that we can influence and change. This means living in an unfavorable climate for the body - arid, systematic intake of hard water and foods high in protein, hypovitaminosis, alcohol abuse, certain medications (diuretics, sulfonamides, cytostatics).
- Internal factors include metabolic disorders in the body associated with genetic predisposition; congenital abnormalities in the development of the genitourinary system and infectious diseases; hormonal disbalance; immobility of the body for a long time.
Types of kidney sediment
Depending on what type of salt settles on the walls of blood vessels and forms crystals, crystalluria is divided into types.
Calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate crystalluria is most common in children. It usually first appears during school or adolescence, when a general urine test is taken.
There is an increased concentration of calcium oxalate. This depends on the substance itself, which is susceptible to enhanced and rapid crystal formation.
An increase in the concentration of oxolate salts in a child is associated with the intake of identical substances into the body with food.
During inflammatory processes of the intestinal mucosa, these salts are actively absorbed. This occurs in diseases such as ulcerative colitis of the intestine and Crohn's disease.
The disease does not affect deviations in the growth and development of the child’s body as a whole.
Phosphaturia
This variety is formed as a result of infections in the genitourinary system of the body.
Harmful microorganisms break down uric acid, so urine becomes predominantly alkaline. In this regard, the formation of crystals of calcium phosphate salts occurs.
Uricorosia
When uric acid precipitates at unacceptable levels, crystalluria is formed. Since uric acid is formed through the breakdown of purines.
This type of disease occurs with excessive consumption of foods containing large amounts of purine. These include foods containing proteins, alcohol, cauliflower and broccoli, asparagus, nuts and beans.
Also, uricorosis can occur due to increased synthesis of this acid in the human body. This often occurs due to a genetic predisposition.
Taking certain medications for a sufficiently long period of time can also provoke this type of disease.
And finally, such an indicator as a chronic infectious disease is a direct consequence of the disorder.
Cystinuria
A very rare type of crystalluria. It is transmitted at the genetic level and is associated with abnormal kidney structure.
Cystine is an amino acid that is already subject to poor dissolution and is also subject to poor absorption in the renal tubules.
As a result, a disease such as cystinuria occurs.
Diet for oxalates in urine
The reasons for the appearance of oxalates in the urine and the basis of the concept of “diet for oxaluria”
Oxalates found in urine are salts of oxalic acid, which are brown crements with sharp edges. A disease accompanied by increased secretion of oxalates in the body is called oxaluria. This disease can develop for several reasons, which can be either hereditary or acquired due to the following factors:
- Intake of vitamin C in large quantities from food and foods enriched with oxalic acid;
- The presence of chronic diseases that increase the content of oxalates in the urine, for example, pyelonephritis or diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and other inflammatory bowel processes;
- Insufficient intake of vitamin B6;
- Consequences of surgical interventions performed on the intestines, which can also increase oxalates in the urine.
Treatment of symptoms that provoke the appearance of oxalates in the urine above normal values is based on a diet that excludes or reduces to a minimum all foods high in oxalic acid, as well as its salts.
Foods prohibited for consumption if there are oxalates in the urine
A diet for oxalates in the urine excludes from the diet such foods as:
- Potatoes, eggplants and tomatoes.
- Soy and beans.
- Celery, chard and beets.
- Chili pepper and green pepper.
- Parsley and leeks.
- Spinach and sorrel;
- Rhubarb.
- Asparagus.
- Parsnip.
In the category of foods that should be limited in intake, many nutritionists include coffee and tea, chocolate and cocoa, pine nuts and walnuts, almonds, peanuts, sesame seeds and sunflower seeds.
A diet with oxalates in the urine gives patients the opportunity to consume the required amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats in the diet and ensures a sufficient supply of calories to the body. Excluding the products listed above from the menu will help avoid the development of calcium oxalate crystalluria, and as a result, the appearance of stones in the bladder and kidneys.
Foods allowed in small quantities for oxalates
Fruits and berries enriched with oxalic acid salts, which should be consumed with caution and in minimal quantities, include:
- apples and grapes;
- plums and oranges;
- gooseberries and cranberries;
- blackberries and raspberries;
- Red Ribes;
- kiwi;
- figs and dates.
Please note that eating fruits that are not fully ripe may increase the excretion of oxalates in the urine, as they contain glyoxylic acid
Recommended list of foods for oxalates
If oxalates are detected in the urine, you must adhere to a certain diet, which includes the following foods:
- cauliflower and white cabbage;
- from vegetables: carrots, eggplant in small quantities, pumpkin, cucumber, cilantro, boiled potatoes;
- berries and fruits: apricot, pear, banana, lingonberry, prune, dried apricot, cherry, watermelon, melon, peach, quince, dogwood, rowan, black currant, sea buckthorn;
- wheat bread made from second-grade flour, gray and yesterday's rye bread;
- dairy products: sour milk, kefir, a little sour cream and cottage cheese;
- chicken egg no more than 1 piece per day;
- soup: vegetable or with the addition of cereals, lean meat and fish;
- from drinks: weak tea and coffee with milk, jelly and compote;
- pasta and cereals.
The clinical picture is blurred
It is almost impossible to recognize the disease in the first stages, since there are no obvious signs.
If symptoms exist, they can be confused with other health problems. However, the importance of detecting the disease is great.
Indeed, in the early stages, treatment occurs much faster and will prevent serious consequences.
The most distinctive symptoms of crystalluria include cloudy urine with bloody discharge and a strong, unpleasant odor.
You can test your urine for crystals at home. Place morning urine in a place protected from light for a day. And watch.
If a white coating remains on the walls of the glass jar, this indicates an increased concentration of phosphates, alkaline and potassium salts.
Red crystals indicate excess uric acid. A black or reddish sediment indicates that oxalates have accumulated in the body.
The most pronounced symptoms include acute pain in the groin and under the navel, as well as in the lumbar region. High temperature. Swelling of the limbs.
Algorithm of the doctor's actions
The disease is characterized by the severity of pain and its localization. First of all, during diagnosis, a general urine test is taken; it is by its results that deviations can be judged.
If the urine is acidic, then most likely it contains an increased amount of oxalates and urates. With a saturated alkaline composition, phosphates are usually found, the presence of which leads to urolithiasis.
High oxalate levels are caused by excessive consumption of acidic foods. It could be sorrel, apples, oranges. Therefore, the doctor must find out what food the patient consumed before taking the test over the past 4-5 days.
After a general urine test has shown that deviations from the norm exist, an x-ray of the urinary tract, cystoscopy, and an ultrasound of the bladder are done.
With a comprehensive combination of all test results, a course of treatment is prescribed.
Why does crystalluria occur in children?
Several groups of its causes can be distinguished. One of them is increased precipitation of calcium oxalate in the urine. Urine is always a saturated solution of calcium oxalate, since at normal urine pH values close to 7 (5.5-7.2), the solubility of calcium oxalate is negligible - 0.56 mg per 100 ml of water. Calcium oxalate reaches its maximum solubility at a pH below 3.0.
The degree of precipitation depends on:
- on the calcium to oxalate ratio (individuals with hypercalciuria excrete more calcium oxalate),
- from the presence of magnesium salts (with magnesium deficiency, precipitation increases),
- from excess or deficiency of substances that support the colloidal properties of urine (citrates, celiac, pyrophosphates),
- from excessive excretion of oxalates.
How to cure a patient?
Treatment of crystalluria is selected separately in each individual case.
Complex therapy includes a number of measures:
- regulation of water metabolism in the body;
- following a diet in accordance with the type of disease;
- taking vitamins and medications.
A potato-cabbage diet is prescribed, following which potassium will enter the body in sufficient quantities, and unwanted oxalic acid salts will be reduced to a minimum.
Products containing large amounts of oxalates are limited. Such as leafy vegetables, beets, tomato and orange juices.
Dried fruits, bran bread, pumpkin, zucchini, in general, everything that contains large amounts of potassium and magnesium are useful.
Drug therapy consists of prescribing vitamins A, B and E. Also small doses of magnesium, which are contained in panangin or aspracam preparations. Canephron, Cyston, Fitolysin are usually prescribed.
They are suitable for all diseases of the genitourinary system; your doctor will advise which medicine to choose, taking into account your body and the degree of the disease.
Thus, the treatment of one or another type of crystalluria comes down to minimizing the formation of certain crystals in the urine.
After carefully studying all the analyzes and identifying the nature of the deviation, a number of measures are prescribed to eliminate this type of violation.
The disease is relatively easily cured with the help of special diets, seasonal intake of a complex of vitamins, and prescribed medications.
By following all the instructions of your doctor, you will get rid of crystalluria and forever forget what it is.
semya-moya.ru
Diet therapy for oxaluria
Vitamin A is found in large quantities in cod liver, pork and beef liver, egg yolks, butter, cream and whole milk, carrots, pumpkin, and sea buckthorn. Vitamin E is found in the largest quantities in vegetable oils: corn, sunflower, soybean, wheat germ, walnuts and almonds. Products containing the largest amount of vitamin B6 pyridoxine include: sea buckthorn, walnuts, tuna, mackerel, beef liver, hazelnuts, sardines, horseradish, garlic, pine nuts, millet, sprouted wheat grain, egg yolk.
Pyridoxine has a diuretic property, regulates metabolism, and takes part in the metabolism of magnesium in the body. It is also necessary to observe the “water regime”. If you drink little water, then the urine becomes concentrated and salts can form oxalate stones in the kidneys, and the more water we absorb, the more urine will be excreted and more salts will be excreted with it.