What does it mean
Ketone (acetone) is a product of metabolic processes occurring in the liver. Normally, carbohydrates are broken down into simpler substances and utilized without residue. Ketone appears in urine if the body does not have enough glucose in food. Liver cells (hepatocytes) begin to break down lipids and proteins, and acetone-like compounds are formed. If there are too many ketones, they do not have time to be utilized and are excreted in the urine. This phenomenon is called ketonuria.
Traces of ketones in urine (up to 20 mg per daily portion) may also be present in a healthy person due to dietary habits. For pregnant women, the norm of ketone bodies is higher (up to 50 mg), since at this time the excretory organs experience increased stress.
Higher than average levels of urinary ketones during pregnancy can have life-threatening consequences. Decay products, if not completely processed, poison the body of the mother and child.
The most common method for determining and monitoring this indicator is urine analysis. Body secretions are often the first to report malfunctions in the body by changes in color and composition. Therefore, a pregnant woman’s urine test is checked at every visit to the antenatal clinic.
Reasons for appearance
If ketones in urine during pregnancy do not exceed the average or appear sporadically, there is no need to worry. This may occur due to an unbalanced diet, too rapidly changing metabolic processes between mother and fetus, and digestive disorders due to toxicosis in the 1st trimester.
Causes of pathological increase in the level of ketone bodies in urine during pregnancy:
- alcohol abuse during planning, conception, pregnancy;
- diet poor in complex carbohydrates, fasting, unbalanced water and nutritional regime;
- sudden change in weight;
- failure of metabolic processes, diseases of hormone-producing organs (adrenal glands, ovaries, thyroid gland);
- diseases and acute disorders of the digestive organs, liver;
- weakened immunity, susceptibility to frequent colds;
- current or past severe infectious disease with general intoxication of the body;
- lack of physical activity;
- stressful situations, chronic lack of sleep;
- severe forms of gestosis (late-term toxicosis) due to Rh conflict, genetic abnormalities.
Important! The use of certain medications may increase the amount of ketone bodies in the urine in pregnant women. Therefore, if a symptom appears for the first time against the background of relatively good health with an uncomplicated medical history, the tests are repeated, stopping the medications for a while and adjusting the diet.
Why does ketonuria occur in the third trimester?
The third trimester causes increased stress on the body due to the active growth of the fetus. If a urine test shows the presence of acetone, obstetricians-gynecologists recommend hospitalization. Ignoring ailments and unwillingness to receive hospital treatment leads to an increase in the concentration of ketones with the appearance of complications, such as dehydration and intoxication of both mother and child. This threatens miscarriage and premature birth. In some cases, severe complications such as coma and death can occur. With timely treatment, complications can be avoided.
Why does an increase in ketone bodies occur in later stages?
Why does an increase in ketones occur at 36 weeks?
The condition occurs due to poor nutrition in the last trimester. The reason for the increase is the abuse of fatty, salty, smoked foods, drinking coffee and tea in large quantities. The increase in ketone levels lasts up to 4 days, then the concentration stabilizes and normalizes. Diet will help you avoid a repeat increase. If the level does not decrease after adjusting your diet, you should seek medical help.
Consequences
Without accurate diagnosis, treatment with diet and medications, ketonuria during pregnancy can have dire consequences. The breakdown products of acetone and acids poison the body of the mother and fetus, complicating the process of pregnancy. Even if the pregnancy goes through and is resolved successfully, toxic substances can provoke long-term complications in the development of the child.
High levels of ketones in urine that persist for a long time and are not corrected can cause:
- dehydration and poisoning of the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus;
- kidney diseases associated with impaired urine excretion;
- osteoporosis and associated symptoms (joint pain, limited movement, muscle cramps, frequent fractures);
- the development of diabetes in pregnant women in the 3rd trimester (gestational), which is dangerous because it can subsequently turn into the classic insulin-dependent diabetic form;
- complications of pregnancy and delivery (frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, premature birth);
- delayed physical and intellectual development of the child due to constant intrauterine poisoning with toxic substances;
- ketoacidotic coma is an extreme degree of intoxication with acetone.
Ketoacidotic coma is a dangerous condition that can lead to death. It develops with a sharp increase in protein breakdown products and inadequate utilization of sugars by the liver. It is especially common in diabetic patients who neglect insulin therapy. Acetone coma leads to serious disruptions in the functioning of vital organs - the heart, lungs, even stopping. Without treatment, this condition causes swelling of the brain and death.
However, coma does not develop immediately, but over several days; signs of poisoning (nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, smell of acetone from the mouth) and dehydration (dry skin, lethargy, low blood pressure and body temperature) increase. If signs of diabetic coma develop, you should immediately call an ambulance and take the patient to the hospital for treatment and observation.
Symptoms
It is almost impossible to suspect a mild degree of ketonuria on your own.
The expectant mother may have nonspecific symptoms - mild headache, dizziness, nausea. However, these symptoms do not occur in all pregnant women. Sometimes this clinical picture is accompanied by increased urination and a feeling of thirst. With moderate ketonuria, the urine smells like acetone. A woman may notice a characteristic odor when going to the toilet. There may be a deterioration in the general condition, the appearance of vomiting, severe headache.
Severe ketonuria is accompanied by ketoacidosis. This syndrome is a strong stress for the body of the expectant mother. A pregnant woman experiences uncontrollable vomiting with the smell of acetone; she complains of severe pain in the head, general weakness, and dry skin. There may be discomfort and a feeling of fullness in the right side due to an increase in the size of the liver.
Diagnostics
For timely successful recognition of signs of ketonuria, it is necessary to collect a detailed medical history of the pregnant woman. Many diseases that disrupt adequate metabolism are genetic and are inherited. It is also necessary to find out the features of the diet. Mono-diets and a small amount of fresh fruits and vegetables in food often lead to the accumulation of ketones. It is necessary to find out whether the woman is drinking enough fluid, since dehydration impairs the excretory ability of the kidneys.
Elevated ketones in the urine are manifested by symptoms of poisoning (weakness, headaches, nausea, lack of appetite, acetone breath) and dehydration (thirst, dry skin, interruptions in heart function). Urine becomes dark in color and has a strong, unpleasant odor.
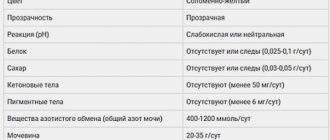
Blood and urine tests for the content of ketone bodies are the most reliable way to diagnose metabolic disorders. Blood is examined using a biochemical analysis, which is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach without any other special preparation. The state of urine most fully reflects the capabilities of the excretory system. Urine for analysis is collected in the same way as for a regular clinical study - a medium portion is taken from morning urine into a sterile container, which must be delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours. Experts evaluate the color, smell, density of the liquid and determine the concentration of ketones. A reading above 80 mg indicates a risk of developing gestational diabetes and requires close attention from doctors.
If there is a hereditary or nutritional (diet-related) risk of developing ketonuria, there is a need to constantly monitor the level of acetone in the urine. This can be done at home using test strips, similar in principle to a rapid pregnancy test. The strip is immersed in a container with urine for a few seconds to the indicated level, then the result is assessed. It appears as plus signs or color changes.
Treatment
If tests show that ketones are slightly elevated, it may be enough to change your diet. A balanced diet, rich in vitamins and varied in composition, can significantly improve the condition and test results of a pregnant woman. To remove toxic products, drink plenty of fluids (pure and mineral water, herbal decoctions, diluted juices). The patient is advised to reduce the number of stress factors and emotional stress, ensure sufficient night rest (8 hours) and light physical activity in the fresh air during the day.
If diabetic disorders are present or suspected, regular monitoring of glucose concentrations in urine and blood will be prescribed. A woman can do this herself at home using a portable glucose meter and test strips. According to indications, insulin therapy may be prescribed. It is important to ensure that glucose levels are uniform throughout pregnancy, without a strong decrease (≤4 mmol) or increase (≥6 mmol).
Important! Blood sugar limits for pregnant women are higher than usual. This is due to the peculiarities of nutrient exchange between the mother and the developing fetus.
If a severe form of poisoning by acetone breakdown products develops, detoxification in a hospital is necessary. The patient undergoes extensive blood and urine tests. Based on their results, droppers may be prescribed to cleanse the body and restore water-salt balance. Tablet or liquid forms of enterosorbents are also used - substances that capture harmful metabolic products and accelerate their evacuation from the body. The process of removing toxins may take several days, which will have to be spent in the hospital under the supervision of specialists.
Severe forms of ketoacidosis and coma require immediate intensive care in the intensive care unit. To quickly reduce the critical concentration of ketones in the body, hemodiafiltration (blood purification using an “artificial kidney”) is possible.
Whatever the reasons for the appearance of ketone bodies in the urine, you should not self-medicate. It must be remembered that during pregnancy a woman has double responsibility. If there is the slightest change or deterioration in health, it is necessary to bring this to the attention of the antenatal clinic doctor.
Prevention
To prevent the accumulation or reduce the amount of ketone breakdown products present in the body, a pregnant woman is recommended to:
- A diet balanced in lipids, proteins and carbohydrates with the addition of fresh vegetables and fruits. Low-fat soups, dietary meat (turkey, rabbit, veal) and fish, cereals are allowed. It is recommended to stew, steam, and bake dishes in foil without oil. You need to eat little and often, maintaining an equal level of nutrients in the body throughout the day.
- Remove canned foods, fast food, smoked meats, and sweets from the menu. Do not use spices, salt, or large amounts of oil for cooking.
- Drink enough fluids. It helps the kidneys remove toxic metabolic products from the body and acts as a natural cleanser. If there is no swelling or contraindications, up to 2.5 liters per day is allowed. Clean drinking water is recommended. Strong tea, coffee, sweet carbonated, fatty and salty milk drinks are undesirable.
- Additional fortification with the help of pharmaceutical preparations. The specific type of medication and duration of treatment should be determined by your doctor.
- Make sure that bowel movements and urination are regular. Pay attention to the nature of the discharge; its change may be the first to indicate an impending problem.
- Regular observation of specialists - obstetrician-gynecologist, nephrologist, endocrinologist. Often pregnant women are dissatisfied with the large number of tests prescribed to them. You need to understand that laboratory diagnostics in the early stages can protect a woman and her unborn child from many problems.
- Maintain adequate rest and wakefulness. A pregnant woman needs 7 – 8 hours of sleep at night. During the day, walks and moderate physical activity in the fresh air are advisable. This is especially important in the third trimester, when many pregnant women sharply limit their activity. In the absence of movement, swelling of the legs may develop and metabolism may slow down. This leads to the accumulation of toxins and poisoning of the body.
During pregnancy, a large number of changes occur in the female body. Attention to well-being and regular visits to the observing gynecologist will help identify the first signs of accumulation of ketone bodies in the urine. If treatment is not delayed, this symptom can be easily corrected with nutrition and medication.
Diet for pregnant women with an increase in acetone bodies in the urine
Nutrition needs correction if a pregnant woman eats a lot of high-calorie foods rich in proteins and fats. To balance the diet, you need to add more proper carbohydrates: introduce whole grain cereals, fruits (with the exception of bananas and grapes).
A diet for pregnant women requires the presence of the following products:
- vegetables;
- cereals;
- boiled, stewed or baked meat of turkey, chicken, rabbit;
- fish (cod, flounder, trout);
- low-fat dairy products (milk, yogurt, cottage cheese).
There should be small snacks between main meals so that the woman does not suffer from hunger.
It is better to eat small portions 4-5 times a day. It is also important to maintain water balance by drinking at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day.