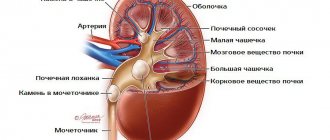
The article talks about a disease accompanied by the formation of salt deposits in the kidneys - microlithiasis. The causes of the pathology, manifestations and treatment methods are described.
Kidney microlithiasis - what is it? This is one of the common urological diseases, characterized by the deposition of salts (stones) in the kidney tissue. Microliths are salt deposits not exceeding 3 mm in diameter. In most people, the pathology is asymptomatic, but can increase the risk of developing other kidney diseases. Conservative methods are used for treatment.
The essence of pathology
What is renal microlithiasis? This diagnosis is made when small stones not exceeding 3 mm in size are detected in the conduction system of the kidney.
Concretions are dense deposits of mineral salts of various shapes and sizes. Microlithiasis occurs in every third person. Usually stones form in one kidney, most often the right one. Microlithiasis of both kidneys is diagnosed quite rarely.
Stones have different chemical compositions - urate, phosphate, protein, oxalate. Sometimes stones consist of different salts - then they are called mixed.
Salts begin to accumulate in the kidney tissue and form stones as a result of two main mechanisms:
- excessive formation of salts in the body;
- their slow excretion by the kidneys.
Either one mechanism or both at once can be implemented.
The causes of these two processes are the following conditions:
- metabolic disease;
- poor nutrition;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- kidney development abnormalities;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition.
Kidney stones form as a result of a combination of different causes. According to ICD 10, the disease is coded N20.
Clinical manifestations
Since salt deposits are small in size, nephromicrolithiasis of the kidney may not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms appear when there are a lot of stones, they obstruct the flow of urine or begin to move, damaging tissue.
Obvious signs of renal microlithiasis are as follows:
- discomfort or pain in the lumbar region, often on the right, as microlithiasis of the right kidney usually develops;
- nagging pain during urination;
- change in the color of urine - it may become cloudy, pinkish, and foam may appear on its surface;
- increased or decreased episodes of urination;
- the appearance of night urination.
An absolute sign of microlithiasis is the passage of sand or small stones at the end of urination.
In addition to the immediate symptoms, microlithiasis of the left or right kidney is accompanied by symptoms of other kidney diseases, the appearance of which was provoked by stones. Most often these are cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Methods for treating microliths in the kidneys
Microlith of the left or right kidney is treated conservatively; surgical intervention is necessary in extreme cases. Treatment of microlithiasis consists of taking a number of medications and following a special diet.
Therapy can only be prescribed by the attending physician. Treating microlithiasis at home is strictly prohibited, otherwise attempts to remove kidney stones on your own will only lead to aggravation of the situation.
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor
The main goal of microlithiasis therapy is to dissolve and remove microliths and salt deposits along with sand, with the flow of urine. It is necessary to take diuretics. And to eliminate pain, antispasmodics are prescribed.
If microlithiasis occurs from an infectious lesion of the urinary system, then antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken. To treat microlithiasis in children, vitamin-mineral complexes and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Diagnostics
The presence of stones in the kidney tissue can only be determined using imaging methods. These include:
- X-ray examination - reveals darkening in the kidney area;
- Ultrasound examination - allows you to assess the density of the stone;
- computed tomography - identifies even the smallest formations, and also allows you to assess the condition of soft tissues.
The most accurate diagnostic method, of course, is tomography. But the price of the procedure is quite high, so the most common diagnostic method is ultrasound. Blood and urine testing is an indirect method of confirming the diagnosis.
The treatment tactics for microlithiasis are determined depending on the size and number of stones. At the initial stage, when there are no obvious symptoms, special treatment for renal microlithiasis is not carried out.
In this case, non-drug methods are sufficient:
- normalization of nutrition;
- drinking enough liquid;
- taking herbal remedies with a diuretic effect;
- rejection of bad habits.
If these rules are followed, isolated small stones are passed out in the urine on their own. If the disease progresses, the number and size of stones increase, more serious treatment is required, aimed at dissolving and removing salt deposits and preventing the development of complications.
Medication
Drugs that promote the dissolution of renal salts are called urolitics. They are prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the chemical composition of the stones.
Table. Medicines against urolithiasis.
Drug treatment continues for at least 21 days. During this period, the kidneys are usually cleansed of sand. If necessary, the course of treatment can be extended.
Folk remedies
In addition to taking medications, treatment with folk remedies is carried out. Plants with diuretic, anti-inflammatory and urolitic properties are used.
- Lingonberry leaf decoction. Wash a handful of leaves and add 500 ml of water. Bring to a boil, simmer for 5-7 minutes. Cool and drink the entire amount throughout the day.
- Infusion of birch buds. Pour 100 grams of kidneys into 1000 ml of boiling water. Cool and strain the liquid. Drink 50 ml in the morning.
- Juniper syrup. Place 100 grams of berries in a saucepan and add 100 grams of sugar. Add 200 ml of water, cook until thick. Take a teaspoon of syrup in the morning.
Other folk methods of getting rid of urolithiasis can be found in the video in this article.
Knowing about a disease such as renal microlithiasis and what it is, everyone can take measures to prevent its development. If the disease does begin, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Microliths in the kidneys are often confused with other pathologies. Therefore, before making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis. The first step if you suspect microlithiasis is to take blood and urine tests.
A urine test can determine the presence of bacteria, infections, and salt crystals. And based on the results of blood tests, the likelihood of inflammation and metabolic changes in the body is determined.
Ultrasound is one of the diagnostic methods
In addition to donating blood and urine for tests, the patient must undergo a number of diagnostic examinations:
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and organs of the urinary system;
- urography;
- excretory urography;
- radioisotope scintigraphy.
After the diagnosis, an accurate diagnosis is made, after which the doctor selects complex therapy, taking into account the research results and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Questions for the doctor
Good afternoon. My grandmother had nephromicrolithiasis of the kidney - what is this disease, and can it be inherited? I recently began to notice difficulties with urination and nagging pain in my back.
Irina, 35 years old, Volgograd.
Good afternoon, Irina. This disease has many names, but its essence is the deposition of salts in the kidney tissue. These salts subsequently form stones, which impair the function of the organ.
The disease itself is not directly inherited. But the hereditary factor plays a role in the development of metabolic disorders, which are one of the causes of microlithiasis. You need an ultrasound examination and consultation with a doctor.
Kidney microlithiasis is the initial stage of urolithiasis, in which small stones form. This pathology is characterized by the appearance of pain in the lumbar region, frequent urge to urinate and other symptoms.
Symptoms
Very often, this pathology is discovered by chance on an ultrasound, since, although it does not occur in an acute form, it does not cause much discomfort. But it also happens that a person experiences certain symptoms that are very similar to full-fledged kidney stones and sand.
You need to pay attention to the color of the urine: in a healthy person it is transparent, in a patient it is cloudy and perhaps has a slightly pinkish tint. Small pebbles that move freely along the ureter are not always equally smooth and of the same shape, which means that when moving they can cause microtrauma and irritate the mucous membrane. Typically, this causes characteristic pain and blood in the urine. If pain is felt in the lower abdomen, this means that the microlith passes into the ureter and you can feel a strong burning and itching, frequent urge to go to the toilet, and the process itself causes great difficulty and pain. But the pain is not permanent and that is why a person cannot fully understand what it is.
Microliths can be right-sided or left-sided . In the right-sided version, the symptoms are very much reminiscent of acute appendicitis and the pain itself is activated in the lower abdomen. If the disease is left-sided in nature, then the symptoms resemble pain in the lumbar region and intensification occurs at the time of changing posture or during strong physical exertion. Therefore, it is very important to conduct an examination and find out the localization of microliths in the body. If you highlight the general symptoms, it will look like this:
- Aching pain in the groin or lower abdomen.
- General body malaise and weakness.
- Increased body temperature.
- High blood pressure.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Blood in the urine.
- Increased swelling.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
Causes
Kidney microlithiasis occurs for a number of reasons, including:
- Heredity. Genetically determined metabolic disorders provoke active salt deposition.
- Chronic pathologies affecting the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. Such diseases disrupt the functioning of the kidneys and bladder, so they are not able to remove deposits from the body normally and in a timely manner.
- Congenital anomalies in the structure of the pelvic organs, which causes frequent stagnation of urine.
- Bone pathologies. Disturbance of the bone structure leads to an increase in calcium levels in the body.
- Regular fluid intake in small volumes. This results in less urine being produced.
- Regular consumption of foods that increase the acidity of urine, which provokes the active growth of some types of kidney stones.
- Living in a hot and dry climate. Such conditions provoke active sweating, due to which the urine becomes more concentrated, and microliths begin to precipitate.
- Excessive consumption of foods high in salt.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of microlithiasis in the initial stages practically do not manifest themselves. Because of this, most patients seek help from a doctor when the disease has become advanced. Microlithiasis of both kidneys often provokes the development of salt diathesis. And the treatment of the latter disease is a rather complex process.
Symptoms of microlithiasis manifest themselves as:
- Pain syndrome. It is usually localized in the lumbar region, but can radiate to the perineum and lower abdomen. Pain often occurs when walking. In this case, it is noted in the sacral and lumbar regions.
- High pressure.
- Frequent urination. With renal microlithiasis, urine becomes dark in color. There may be small blood clots in it.
- Edema affecting various parts of the body.
- Deterioration in health, weakness during physical activity.
Treatment options depend on the chemical composition of the salt deposits:
- Urats. They are crystals obtained from uric acid salts.
- Oxalates. Appears when there is an excess content of oxalic acid.
- Phosphates. They are formed when the permissible norm of phosphate acid is exceeded.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of microlithiasis involves the following measures:
- Urinalysis, which determines the level of salts, the presence/absence of pathogenic microflora and other parameters.
- Blood analysis. It allows you to find out whether inflammatory processes are occurring in the body caused by repeated infection.
- Blood chemistry. It is carried out to identify the nature of metabolic disorders.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound is the main tool in the study of kidney lesions.
- X-ray exposure. A contrast agent is injected into the body, with the help of which the stones appear on the machine. The disadvantage of this method is that some microlites remain hidden from this type of radiation.
Treatment Options
To avoid serious complications, when the first symptoms of renal microlithiasis appear, you should seek help from a doctor.
Treatment of microlithiasis involves following a special diet and taking medications. Medicines are selected depending on the type of salt deposits. In addition, drug therapy involves taking drugs that have antispasmodic and diuretic properties. They are prescribed to facilitate the process of removing microliths naturally.
If the disease is complicated by infection, treatment is supplemented with drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing foci of inflammation and pathogenic microflora.
Good results in treatment can be achieved using traditional medicine methods. They include regular intake of decoctions and infusions that have diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Therapy
Single microliths in the kidneys are treated in three ways:
- diet;
- taking medications;
- use of traditional medicine.
Drug therapy
Microliths in the kidneys respond well to treatment using medications that are aimed at dissolving and removing stones and reducing pain. Canephron and Urolesan will help dissolve small stones in the kidney. To eliminate pain, No-shpa, Ketorolac or Ibuklin are prescribed, which are taken orally or administered intravenously. In case of infectious origin, therapy is carried out using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies for microlithiasis involves regular intake of herbal infusions and decoctions, which have an antispasmodic, diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect. Herbal products dissolve stones and promote their natural removal. Regular use of herbal medicines helps restore the normal functioning of the urinary system.
Regardless of the nature of the microliths, it is recommended to drink decoctions of rosehip fruits and flowers, lingonberry leaves and St. John's wort herb. A decoction can be prepared from each herb separately or brewed together. For 1 liter of boiling water you need to take 30 grams of each component. Brew for 40 minutes. Drink 3-4 times a day, 200-250 ml.
Effective diuretics are melon and watermelon, which help cleanse the urinary tract of stones.
With urate, corn silk will help cure stones, 10 grams of which are brewed in 200 ml of boiling water. This decoction should be drunk before every meal.
If stones are of phosphate origin, infusion of corn silk and birch leaves helps well. To do this, you will need 20 g of each component, which are infused in 250 ml of boiling water. Drink 200 ml before meals.
A decoction of millet has also proven itself to be effective: for 1 kg of millet, about 2 liters of boiling water is required. Infuse the broth and strain. The daily dose of decoction is 7 glasses. Parsley decoction has a general strengthening effect, removes microliths and normalizes the functioning of the genitourinary system. 40 g of parsley pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave overnight. Drink in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed.
Diet therapy
A prerequisite for effective treatment of microlithiasis is adherence to a special diet. Like drug therapy, diet selection depends on the type of salt deposits:
- Phosphates. It is necessary to exclude or limit the consumption of fruits, vegetables and dairy products. They can be replaced with meat, fish, and flour products.
- Urats. Avoid consuming foods rich in calcium. Recommended: boiled meat, fish, eggs, butter and a variety of cereals.
- Oxalates. You should exclude foods containing oxalic acid: sorrel, strong coffee, potatoes, green salad, and so on. Recommended foods: bread, milk, berries, fruits, pasta, eggs and cereals.
Kidney microlithiasis is a disease that rarely causes discomfort to a person. This is primarily due to the fact that the initial stage of the pathology does not have characteristic symptoms. For more effective treatment, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations, follow a diet, and give up bad habits.
The deposition of organic salts in the tissues of the human body often causes pathological changes. For example, alveolar microlithiasis of the lungs causes signs of respiratory failure; deposition of calcium salts on the inner surface of the arteries (atherocalcinosis) leads to progressive disturbances in the blood supply to internal organs. One of the stages of development of urolithiasis is renal microlithiasis: we will talk about what it is, causes, symptoms and effective methods of therapy below.
Nutrition specifics
Microliths in the kidneys require a special diet, so patients are advised to avoid consuming broths based on meat, mushrooms or fish; they are prohibited from eating canned food, smoked and sausage products, pickles and sorrel, beans and spinach, offal, cheeses, etc. It is necessary to limit consumption honey, salt and herbs like cilantro and dill, basil and parsley. A more detailed diet is compiled in accordance with the main composition of the stones.
If the basis of microlites is predominantly carbonates, then it is advisable to minimize the content of foods high in calcium in the diet - cheeses, cottage cheese or milk, yogurt. But boiled meat or stewed fish, eggs and cereal porridge with such stones form the basis of the diet. In the case of a phosphate base of microlites, it is recommended to limit the consumption of fruits, dairy products, vegetables, giving preference to vegetable oil and flour products, lean fish and meat dishes.
With strict adherence to dietary medical prescriptions, it is quite possible to completely dissolve and remove microlites from the body. In addition, a special diet will help avoid urolithiasis.
With the urate nature of microlites, strict limitation of fish and meat products, liver and kidneys, and vegetable fats is indicated.
Stones with an oxalate base require the exclusion of foods rich in oxalic acid from the diet: milk and potatoes, oranges and sorrel, coffee or chocolate. Patients with microliths are recommended to drink more fluids, preferably drinking herbal teas, compotes from dried fruits or berries. Rosehip compote and watermelon effectively remove salts from the kidneys. The main preventive principle is sufficient drinking regime. In summer, heavy sweating causes dehydration of the body, which weakens the leaching of salts from the body. As a result, the stone-forming process is noticeably accelerated. Therefore, it is important to drink more herbal tea, mineral water, and freshly squeezed juices.
The essence of the problem
Microlithiasis is the name given to the initial changes in the body during urolithiasis (UCD). According to the International Classification of Diseases, pathology has code N20. It is characterized by the formation of stones in the lumen of the collecting apparatus, the size of which does not exceed 3-5 mm. According to their chemical structure, small stones are of organic-mineral origin and are divided into:
- urates - formations consisting mainly of uric acid salts;
- oxalates, represented by oxalic acid derivatives;
- phosphates are stones formed from salts of phosphoric acid.
Without timely treatment, microliths increase in size and turn into large kidney stones, which significantly disrupt the functioning of the urinary organs and cause a number of pathological symptoms.
What are kidney microlites?
This is the formation of poorly soluble accumulations of sand and cameos in the genitourinary system. The formation of such substances involves the interaction of uric acid and certain organic and mineral substances. During the reaction, the products are released as sediment, gradually increasing in quantity and forming large accumulations (stones).
The stones themselves are different, it all depends on the substance that interacts with uric acid. Types of stones:
- cystine stones,
- oxalates,
- struvite,
- xanthates,
- urates,
- phosphates.
Causes and mechanism of development
KSD is a complex multifactorial disease. A major role in its development is played by changes in metabolism in the body and various disorders of the physiological outflow of urine. Among the main causes of microlithiasis are:
- heredity – genetically determined metabolic disorders;
- congenital anomalies that provoke stagnation of urine in the kidneys (pyelectasia, hydronephrosis);
- chronic diseases of the urinary organs, renal failure;
- diseases of bone tissue leading to disturbances in phosphorus-calcium metabolism;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- Regular consumption of foods high in salt.
With an excess of salts in the blood and, consequently, urine, they begin to be deposited in the renal pelvis. In this case, they first settle in the form of sand, and then compact and form a dense stone. Clinical symptoms of urolithiasis largely depend on the number, location, structure, size and shape of stones, as well as damage to one or both kidneys.
Clinical manifestations of pathology
At the early stages, ICD almost does not manifest itself at all, so often the development of microlithiasis can only be guessed from the results of laboratory and instrumental data. A little later, patients who are attentive to their health may notice the following symptoms appear:
- malaise, general weakness;
- fatigue even with previously habitual loads;
- swelling of the face and upper body, especially pronounced after a night's sleep;
- nagging, aching pain, discomfort in the lower back;
- pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin;
- increased frequency of urination, urge;
- increased blood pressure;
- low-grade body temperature;
- less often - the appearance of blood in the urine.
Often the first sign of ICD is a change in the nature of urine. Even small kidney stones cause darkening of the urine and the appearance of sediment in it. The consistency of biological fluid becomes thicker and more viscous due to the content of sand - salt crystals.
Clinical picture of microlithiasis
Microlithiasis at the initial stage is asymptomatic, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult. Small microliths, as well as single stones less than 3 mm in size, are discovered by chance during an ultrasound scan of the kidneys or organs located next to them.
Sometimes, at the beginning of the development of microlithiasis, the following symptoms may occur:
- high blood pressure;
- swelling throughout the body;
- flatulence;
- nagging pain in the kidneys and lower back;
- fever.
Nagging pain in the lower back indicates problems in the kidneys
The presence of microliths may be indicated by increased density and viscousness of urine. Due to the presence of sand, urine becomes cloudy and has a pink tint due to injury to the mucous membrane by solid compounds. As the disease develops and microliths grow, symptoms increase:
- Frequent urination.
- Burning and cutting in the urethra during urination.
- Painful sensations in the groin and genitals.
- Presence of blood impurities in urine.
- Discomfort during active body movements.
- General malaise.
When kidney microliths, which are at least 3 mm in size, begin to leave the organ and move through the urinary system, scratching the mucous membrane of the organs, renal colic occurs.
It manifests itself in a clinical picture:
- unbearable pain in the kidneys;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bowel dysfunction;
- false urge to empty the bladder;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
Unbearable pain in the kidneys occurs when stones begin to leave the organ
There is a difference in the symptoms of microlithiasis depending on the location of the microliths. If there is a microlith of the right kidney, then this phenomenon is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, similar to the pain of appendicitis.
The presence of microliths in the left kidney is accompanied by painful sensations only when the stones reach large sizes. A person feels such pain, similar in nature to pain due to diseases of the intestines or muscles.
How to diagnose microlithiasis
A patient with symptoms of microlithiasis is examined according to the standard ICD diagnostic plan. The patient’s initial appointment is carried out by a general practitioner who:
- analyzes complaints and anamnesis (when the symptoms of the disease first appeared, whether any treatment was carried out);
- conducts a general inspection;
- palpates the lumbar region;
- determines Pasternatsky's symptom (effleurage);
- measures blood pressure;
- prescribes the necessary instrumental and diagnostic tests;
- recommends consultation with a urologist.
Principles of treatment: from diet to taking pills
The treatment plan is drawn up individually for each patient. To quickly get rid of renal microlithiasis, treating the disease requires an integrated approach and compliance with all specialist recommendations.
Non-drug methods
Compliance with non-drug methods of treating urolithiasis helps normalize metabolism, dissolve already formed stones and prevent the formation of new stones.
It is important for patients with microlithiasis to follow these rules:
- Quitting smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Regular physical activity (hiking, swimming, exercise therapy and yoga).
- High-liquid drinking regime - drinking up to 1.7-3.0 liters of clean still water daily.
- Regular emptying of the bladder, giving up the habit of holding out for a long time, despite the desire to urinate.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of infections of the urinary system.
Principles of therapeutic nutrition
The diet for patients with urolithiasis is selected individually depending on the chemical composition of the stones. General recommendations include:
- exclusion of coffee, strong tea, and energy drinks from the diet;
- sharp limitation of seasonings and spices, rich broths, pickles, marinades and smoked meats;
- reduction in the intake of table salt into the body - up to 2-3 g/day;
- reducing the amount of fatty fried foods in the usual menu.
If the stones are oxalate in nature, sorrel, rhubarb and other leafy vegetables are excluded from the diet. Read more about the diet for oxalate kidney stones here: https://pochkizdrav.ru/mochekamennaya-bolezn/dieta-pri-okslatnih-kamnyah-v-pochkah.html. Urate stones are treated by reducing the amount of meat, offal, canned meat and fish consumed.
Effective drugs for the treatment of microlithiasis
Drug treatment for small stones is highly effective. Its main goals are:
- facilitating the removal of microliths;
- “dissolution” of stones, reducing their diameter;
- prevention of infectious and inflammatory processes in the kidneys and other complications;
- elimination of symptoms of the disease.
Among the most commonly used groups of drugs are:
- means for litholysis (dissolution) of urinary stones and normalization of pH - citrate mixtures (Uralit U, Blemaren), herbal preparations (Ginjaleling, Canephron N, Cyston, Urolesan);
- antispasmodics – No-shpa, Papaverine;
- NSAIDs – Ketorolac, Diclofenac;
- thiazide diuretics (strictly according to indications).
Surgical treatment for microlithiasis is not indicated, since small stones can pass out on their own.
Traditional medicine recipes for removing sand from the kidneys at home.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis at the stage of microlithiasis is a great success. Treatment of pathology at an early stage is not difficult, and if you follow your doctor’s recommendations, you can clear your kidneys of small stones without waiting for the progression of urolithiasis and the development of dangerous complications such as renal colic or chronic renal failure.
Kidney microlithiasis is the initial stage of urolithiasis, accompanied by the formation of small stones (microliths) with a diameter of up to several millimeters. This disease occurs quite often and regardless of age; according to statistics, 8-10% of people with microlithiasis develop urolithiasis without appropriate treatment.
Treatment methods
The treatment process usually begins with thorough diagnostic studies. Based on the diagnostic results, the necessary treatment plan is selected. In general, therapy can be medicinal or dietary oriented.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to independently prescribe products intended for dissolving microliths, since they are capable of crushing only a certain type of stone, which can only be determined by a qualified specialist.
Conservative treatment
The main direction of conservative treatment is to dissolve and remove salt crystals and microlites along with urine. For this purpose, means are prescribed for crushing stones and drugs with diuretic and antispasmodic effects that help in their removal. If the process of formation of microliths is accompanied by an infection of the urinary system, then the main treatment is supplemented with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents.
Important! The therapeutic measures of microliths should not be neglected, since in the future the stones will become larger and cause many complications such as pathological expansion of the renal cavities, colic or failure. Moreover, large stones can only be removed through surgery.
Since a frequent cause of the formation of stones is a violation of material metabolism, an abundant drinking regime is simply necessary for good flushing of the kidneys. The doctor, taking into account the type of stones, prescribes a preferred diet. Treatment for microliths usually does not involve surgery because the salt particles are too small. The need for surgical help arises if microliths block the urinary tract.
Kidney microlithiasis: causes and symptoms
The reason for the appearance of microliths in the kidneys is an excess of certain substances in the body.
Among microliths there are:
- Urate stones appear as a result of excess uric acid
- Phosphate stones (phosphates in the urine) appear due to a large amount of phosphate acid in the body
- oxalate stones arise from a large amount of oxalic acid salt.
The level of microlites in the kidneys is affected by poor nutrition, genetic predisposition to the accumulation of salt in the body, and bad habits. In addition, consuming large amounts of vitamin C, calcium, certain medications, frequent use of hard water for drinking and cooking, prolonged dehydration and other conditions can also cause the development of the disease.
Symptoms of kidney disease do not appear immediately, so people often consult a urologist with an advanced form of the disease. Thus, advanced renal microlithiasis can cause salt diathesis of the kidneys, the treatment of which is more difficult and longer than the treatment of microlithiasis.
Treatment of microlithiasis with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment are not basic and should be used only in addition to the main treatment and only after consultation with your doctor. It is worth paying attention to methods that have a good diuretic anti-inflammatory effect.
It is recommended to use a decoction of rose hips and St. John's wort . To prepare a decoction, you should take a teaspoon of each ingredient, add boiling water and let it brew. Take 100 ml orally an hour before meals. Also, consuming watermelon, which is an excellent diuretic, has a beneficial effect.
A very quick and effective method is parsley decoction: pour 40 grams of finely chopped parsley with a glass of boiling water and let stand for about 12-15 hours. Drink half a glass in the morning, the other half in the evening. It is mandatory to take it before meals.