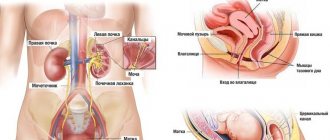
Causes of nausea and kidney pain
When complaining of pain in the kidney area, doctors usually give a preliminary diagnosis - a disorder of the genitourinary system. Which specific organ is damaged becomes clear upon detailed examination and diagnosis. But if the symptoms include nausea and vomiting, it becomes clear that it is the kidneys that are affected by the disease. Renal colic is observed in people who have suffered severe hypothermia and cystitis.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney, provoked by the presence of pathogenic microflora, causing a reaction in the form of nausea and severe pain. It is carried into this organ through the urethra or blood vessels. Pathogenic bacteria are transported through the lymph and affect the pelvis and parenchyma. The list of pathogenic microorganisms includes:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- enterococci.
Return to contents
Urolithiasis disease
In medicine, this disease is called urolithiasis. It appears when the body ceases to properly break down and remove processed substances in a timely manner, which provokes poisoning, nausea and vomiting. At the same time, salt and calcium accumulate in the kidneys and bladder. After interacting with urea, they begin to form stones and calculi. The process of stone formation is accelerated by lack of activity, vitamin deficiency, and lack of fluid in the body. The chances of stone formation increase in those people who are sick or have already suffered from:
The formation of stones in the urinary system can begin in people with joint inflammation.
- stomach ulcer;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum;
- gastritis;
- chronic diseases of the urinary system;
- joint inflammation.
Return to contents
Nephroptosis
When the kidney is displaced or prolapsed, it is referred to as nephroptosis. Such excessive mobility of this usually static organ leads to renal colic and severe nausea. In the usual situation, these paired organs are located at the same height from the bladder. If the disease was not identified at the beginning, complications develop. Representatives of the fair sex are at risk if they have:
- weakening of the peritoneum after resolution of pregnancy;
- complications of the musculoskeletal system due to rickets;
- rapid weight loss due to illness and diets;
- ligament injuries;
- lower back injuries;
- excessive stress due to walking;
- strong straining during bowel movements.
Return to contents
Chronic deficiency
It passes without any special external changes or manifestations. The essence of this kidney disease is that they do not stop working immediately, but gradually. The disease progresses unnoticed by the patient until irreversible changes occur in this organ. This entails a change in water, electrolyte and nitrogen balance, which causes delayed external manifestations in the form of pain and dizziness with nausea.
Different types of tumors
Benign
When immune function is impaired and does not work properly, it manifests itself in inappropriate cellular behavior. They begin to divide and form growths and additional layers of tissue where they should not be, which is why benign tumors form. When exposed to chemicals, radiation and toxins, the likelihood of the formation of tumor-like seals on the kidneys increases. A genetic predisposition to excessive cell division is inherited. Severe inflammation that occurs in a chronic form increases the risk of tumors. The disease is characterized by a sluggish course and mild symptoms in the form of nausea and pain in the kidney area.
Malignant or cancerous
Among kidney diseases, cancer causes the most vivid and unbearable sensations, manifested as pain in the kidneys and vomiting. People who smoke too much or are overweight are at risk of getting cancer of this organ. Malignant kidney tumors are more often diagnosed in the male half of the population, especially if they had to undergo hemodialysis for a long time.
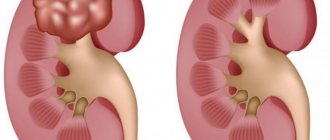
Hydronephrosis
With prolonged disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidneys, the functioning of a specific tissue called parenchyma is disrupted. It is responsible for the balance of fluids and when its atrophy occurs, the kidney cannot work productively and perform its functions. The occurrence of the disease is provoked by diseases with impaired urine excretion and stagnation, illnesses in which there is no irritation of the receptors responsible for the excretion of urine. Accompanied by sudden urges of nausea and sometimes vomiting.
Common diseases
Most often, patients suffer from urolithiasis, nephroptosis, hydronephrosis, and renal failure.
Signs of kidney mobility (nephroptosis):
- aching pain in the kidneys, which periodically intensifies and then subsides;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- the patient loses appetite;
- the temperature rises and cold sweat appears;
- dizziness;
- insomnia and apathy;
- heart rate increases;
- neurotic disorders;
- the skin takes on a pale pink tint.
The right kidney is most often affected. In this case, at the initial stage there will be no disturbing pain.
To make a diagnosis, an examination will be prescribed - a general analysis of urine, blood, ultrasound of the kidneys, biochemical blood test, x-ray. In some cases, you will need to do an MRI and CT scan.
There are 2 methods of treatment. If there are no pronounced symptoms, a conservative method is used. It consists in the fact that the patient wears a special bandage throughout the day, removing it before going to bed. The bandage should be put on while exhaling. Gymnastics and massage will be useful.
If a complication develops in the form of pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, arterial hypertension, spontaneous miscarriage, surgical intervention may be required.
When the outflow of urine is disrupted, the pyelocaliceal system expands, and hydronephrosis of the kidney develops, which most often affects young women.
Signs:
- localization of pain on the side of the diseased kidney;
- nausea, vomiting;
- high blood pressure;
- temperature increase;
- bloody discharge in the urine.
Conservative treatment involves taking anti-inflammatory, painkillers, and, if necessary, blood pressure-lowering medications.
The causes of pyelonephritis are hypothermia of the body, inflammatory processes in the tissues of the genitourinary system. Infectious agents can affect both kidneys.
If a person has a cold in the kidney, a serous form of pyelonephritis may develop: the organ increases in size. If treatment is not started, this form becomes purulent.
Cold symptoms:
- urine color changes;
- headache;
- the temperature rises to 39°C;
- the skin turns pale and becomes dry;
- lower back hurts.
Prevention: limit protein foods, drink more, take vitamins, try not to experience hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather, take hardening procedures, eat well. You should not get carried away with black tea and coffee, which contribute to fluid retention in the body; you should give preference to mineral water and herbal teas.
What accompanying symptoms should you pay attention to?
In addition to nausea and pain, each disease is accompanied by a list of additional symptoms, knowing which the doctor recognizes a particular disease.
Based on the accompanying sensations, it is possible to determine the severity of the lesion and the danger to life. If pain and nausea are unbearable, you need to call an ambulance. All kidney diseases for the most part occur with similar symptoms, but there are also certain symptoms unique to them that help distinguish one disease from another. They are shown in the table:
Disease
| Symptoms | |
| Pyelonephritis | Temperature 40 °C |
| Fever | |
| Chills | |
| Lack of appetite | |
| Urolithiasis | Changing position does not relieve pain |
| Nephroptosis | Hypertension |
| Increased heart rate | |
| Feeling of the kidney “wandering” | |
| Lack of normal sleep | |
| Kidney failure | Presence of skin rash |
| Taste and smell of ammonia in the mouth | |
| Absent-mindedness | |
| Benign and malignant tumors | Anemia |
| Weight loss | |
| Severe weakness | |
| Hydronephrosis | Abdominal enlargement |
| Indigestion | |
| Glomerulonephritis | Increased blood pressure |
| Edema |
Return to contents
Prevention
There are a number of factors that cause the kidney to pull on the right or left. They need to be excluded to prevent kidney disease, especially if there is a predisposition. First of all, it is advisable to lead a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Proper nutrition.
- Optimal drinking regime.
- Control of bowel function.
- Timely treatment of other diseases.
- Movement and sports: yoga, dancing, swimming.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Weight control.
If you notice symptoms of stones, change in urine color, or your lower back hurts, you need to be examined by a therapist, urologist or nephrologist. Correct diagnosis and effective treatment are needed on time, otherwise a chronic disease or surgery cannot be avoided. Lost time can result in loss of health.
Especially if your kidneys are straining
, is a signal of kidney dysfunction or disease. Several different diseases can be hidden behind nagging or acute pain, and before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the causes of the pain.
However, renal pathologies have one property - the disease is asymptomatic in the initial stages.
Therefore, when you notice pain or any other symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor and get tested.
What to do with kidney pain and nausea?
The importance of timely diagnosis
When visiting a doctor, the patient is prescribed a blood and urine test and an ultrasound examination of the internal organs or specifically the urinary system. If it is impossible to identify the disease, they undergo a comprehensive examination, which includes a biochemical blood test, MRI and CT.
Treatment options
Treatment is selected individually, it depends on the identified pathology, the stage of development of the disease and the general health of the patient. For pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. With nephroptosis, the patient is offered a series of physical exercises to strengthen the muscles that hold the affected organ, and is recommended to wear a medical bandage. Urolithiasis involves taking a course of medications to dissolve stones or undergoing surgery to remove them. The presence of any tumors and hydronephrosis requires immediate surgery and reconstructive procedures. Any methods of traditional medicine are considered auxiliary, including herbal infusions of motherwort, bearberry, cornflower petals and licorice root. When used, pain is relieved and metabolic processes in the urinary system are improved.
What to do for prevention?
Regular examination by a doctor helps to recognize the disease in the early stages of its formation and prevent pathogenic changes from becoming irreversible and leading to complications. Following a healthy diet and moderate physical activity will allow the body to stay in shape and resist disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking vitamin complexes will prevent your immune system from weakening. It is worth paying attention to working conditions and environmental pollution, and if possible avoid being in hazardous areas with increased background radiation and other pollution.
Every person who has ever experienced acute or chronic kidney disease knows firsthand about a condition in which one feels sick and the kidneys hurt. There is a whole list of various diseases of the paired organ, in which so-called renal intoxication of varying degrees of intensity is observed.
The main cause of this symptom is the accumulation of metabolic products and toxic substances in the body, which is caused by a violation of the detoxification function of the kidneys. Symptoms such as nausea, pale skin, urinary disorders and nagging pain in the lumbar region are an absolute indication for immediate consultation with a medical specialist.
The kidneys are an indispensable life-support organ, since their main function is not only to remove excess fluid from the body, but also to cleanse it of accumulated metabolic products, as well as toxic substances.
When a paired organ is affected by acute or chronic diseases, the detoxification function is impaired or absent altogether. When nausea occurs in kidney disease in combination with other signs of intoxication, we can confidently talk about structural and functional changes in the paired organ.
Below are the main diseases in which this symptom complex comes to the fore.
Need to be examined
Unfortunately, just listing the symptoms is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. If nagging pain in the lower back occurs, it is important to consult a doctor - a therapist, nephrologist or urologist - as soon as possible. The standard examination plan for patients with suspected renal pathology includes:
Laboratory tests
- blood tests (general clinical, biochemical);
- urine tests (general, according to Nechiporenko, according to Zimnitsky).
Instrumental tests
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- excretory urography;
- MRI, CT – according to indications.
Using modern diagnostic methods, a specialist can assess the position, size, internal structure and functional activity of the organs of the excretory system.
Urolithiasis disease
In urological practice, this condition is called urolithiasis. The formation of kidney stones occurs when calcium salts, uric acid crystals and other mineral salts accumulate in the renal pelvis.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that full-fledged stones, when spontaneously moving, cause blockage of the ureter, which leads to the development of acute urinary retention. The advanced form of urolithiasis is characterized by renal intoxication, accompanied by acute pain, decreased daily diuresis or anuria, the appearance of a sallow skin color, nausea and vomiting.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammatory damage to the renal pyelocaliceal apparatus occurs, as a rule, under the influence of an infectious factor. Other potential causes of this disease include traumatic kidney injuries, previous surgical interventions, as well as congenital or acquired abnormalities of the ureter structure.
Symptoms of renal intoxication with pyelonephritis do not have characteristic differences. Patients complain of severe nausea, vomiting, nagging pain in the lumbar region, discomfort and pain when urinating, general weakness and increased body temperature. Infectious pyelonephritis can be provoked by pathogens such as enterococci, staphylococci and E. coli.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
If the kidneys are strained, this is not necessarily a sign of a serious illness. In some cases, the symptom disappears after the body’s functioning stabilizes.
- If you have chronic pulling sensations that begin to impede movement and are felt when breathing, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause of the discomfort.
- The presence of acute pain is another reason to urgently call a doctor, since this symptom may indicate the presence of a disease that requires surgical intervention, for example, appendicitis or.
- Consultation with a doctor is necessary if, simultaneously with painful sensations, discharge in the urine (flakes, blood, etc.) is observed.
- Serious problems with the kidneys may be accompanied by increased blood pressure and fainting.
Nephroptosis
This condition is characterized by a change in the anatomical position of the kidney due to its descent downwards. As a rule, the paired organ extends beyond its bed with a sudden significant loss of body weight, with regular weight lifting, as well as under the influence of other internal factors.
Most often, nephroptosis is diagnosed in young and middle-aged women who tend to indulge in various diets and therapeutic fasting. Very often, nephroptosis is formed under the influence of such factors:
- Long-term chronic constipation;
- Traumatic damage to the ligamentous apparatus fixing the kidney in the anatomical bed;
- Previously suffered rickets;
- Complications caused by pregnancy;
- Injuries of the lumbar spinal column.
Glomerulonephritis
This pathological condition is of an autoimmune nature and is characterized by severe damage to the renal glomeruli. In addition to the autoimmune factor, the development of glomerulonephritis can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the kidney through the ascending, hematogenous or lymphogenous route.
This severe pathological condition is accompanied by symptoms of renal intoxication, headache and dizziness, a decrease in the volume of daily diuresis or a complete absence of urine.
Along with the listed conditions, the causes of nausea and pain in the kidneys can be benign or malignant neoplasms in the area of the paired organ, as well as hydronephrosis, which is characterized by the accumulation of fluid inside the kidney, with its subsequent increase and the development of structural and functional failure.
Kidney intoxication
The causes of nausea and pain in the kidneys are not only the above conditions, but also the entry of toxic substances and poisons into the human systemic bloodstream. Often this condition occurs when using certain groups of drugs, which with their metabolites damage the parenchyma of the paired organ.
If we say literally that this is kidney intoxication, then this is a pathological condition, as a result of which structural changes occur in the tissues of the organ, with the subsequent development of its failure. The so-called toxic nephropathy is characterized by rapid development and increased danger to human life and health.
In the initial period of structural and functional changes, intoxication is not accompanied by clinical symptoms or has a mild clinical picture. As structural and functional changes progress, the symptoms of renal intoxication take on the following form:
- Dyspeptic disorders, manifested by nausea and vomiting.
- Swelling in the face, neck, upper and lower extremities. This symptom complex indicates the development of functional renal failure.
- Pain syndrome localized in the lumbar spine. In some cases, patients complain of nagging pain in the lower back, which radiates to the perineum, left, and lower abdomen.
- Urinary disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of changes in the color of urine, the appearance of a characteristic sediment, a decrease in the volume of daily urine output or a complete absence of urine.
- Asthenovegetative syndrome. With the development of renal intoxication of various origins, a person experiences psychomotor retardation, general weakness, suppressed appetite, and decreased performance.
- Signs of hyperkalemia. When the filtration function of the kidneys is impaired, there is an increase in the concentration of potassium in the systemic circulation, resulting in changes affecting the functioning of the cardiovascular system and skeletal muscles.
This condition manifests itself in the form of depressed heartbeat, muscle weakness and a decrease in cardiac output.
Why does the kidney on the left side hurt?
There are many causes of kidney disease. These include inflammatory and tumor diseases, injuries to this area, and developmental anomalies of the urinary system, which “raise their heads” under the influence of provoking factors. Let's look at everything in order.
Glomerulonephritis
This is a disease when the kidney tissue suffers from an attack by its own immune cells, which, starting to fight the infection, mistake the kidney cells for microbes. The pathology most often develops after a streptococcal disease (for example, tonsillitis).
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis:
- lower back pain;
- blood visible to the eye in the urine;
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling on the eyelids, legs.
Kidney stone disease
Treatment
Therapy of renal intoxication of various origins requires an integrated approach, therefore such patients are usually treated in a specialized hospital. A comprehensive plan of therapeutic measures for this condition includes the following points:
- Detoxification measures. This set of measures is aimed at accelerating the elimination of toxic and metabolic substances, the accumulation of which served as a factor in the occurrence of intoxication. The components of infusion therapy are Ringer's solution, 5% glucose solution, and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- The technique of forced diuresis, which consists of performing infusion therapy with one of the above solutions, followed by taking diuretics.
- Exchange transfusion of whole blood or plasma.
- In severe cases, patients are prescribed hemodialysis.
- Symptomatic therapy, including taking antiemetic, antiarrhythmic, analgesic and antihistamine (antiallergic) drugs.
If, against the background of severe renal intoxication, a person has developed exotoxic shock, glucocorticosteroids such as Prednisolone or Hydrocortisone are used to eliminate its manifestations. If a serious condition was provoked by the influence of poisonous and toxic components on the human body, then specific antidotes are administered to him.
Complications
Kidney intoxication of various origins is dangerous due to the complications it can cause. If a patient with a similar diagnosis is not provided with timely medical care, he may encounter the following complications:
- Development of DIC syndrome;
- Chronic renal failure;
- Exotoxic or septic shock;
- Renal failure;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia;
- Hypochloremic or uremic coma;
- Violation of cardiac conduction, which manifests itself in the form of arrhythmia and extrasystole.
Differences between the main symptoms and pain in the kidneys
If you feel pain in the kidneys, you should also pay attention to the following manifestations:
- A sharp decrease in the volume of urine excreted throughout the day.
- Cloudiness of urine, darkening of it, admixture of blood and small stones or sand.
- Pain during urination.
- Frequent urge to pass urine.
- Edema.
- Skin rash.
- Fever.
- Nausea.
At the same time, nausea and pain in the kidneys, and other manifestations indicate a disease of the kidneys, and not other organs. It is important to differentiate the disease from renal colic, attacks of appendicitis, intestinal dysfunction and other pathologies with similar symptoms.
Diagnostics
At the first appointment, the doctor examines the patient and palpates the kidneys.
If you feel pain in the kidney area on the right, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist who will prescribe the necessary tests. Diagnostics is carried out in 4 stages:
- A survey of the patient, during which the doctor asks the patient about the symptoms of pain in the right kidney and how long ago they began. This is followed by inspection and palpation. This is done to confirm or refute symptoms that do not relate to the reasons why problems in the functioning of the organ appeared.
- General blood and urine analysis. It is used to study the presence of inflammation in the organ and the condition of urine.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidney, which shows the appearance of the organ, the condition of its tissues and possible problems in its functioning.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is used in situations where there are doubts about the diagnosis. MRI makes it possible to obtain more accurate readings of kidney function.
Causes and possible diagnoses for kidney pain
There are types of pathologies that are always accompanied by pain in the kidneys - this is an inflammatory process that develops after hypothermia or after cystitis.
It is important! The pain is usually dull or sharp, pressing in nature, covering the entire lumbar region, upper abdomen, causing discomfort to the patient.
At the same time, the temperature rises and the urge to urinate becomes frequent.
- Glomerulonephritis is an infectious-allergic pathology that progresses in the body after an infection. At the same time, headaches, weakness, swelling are observed, body temperature rises, and the volume of excreted urine mixed with blood sharply decreases. The disease usually begins with severe headaches.
- Chronic kidney failure is irreversible kidney damage that progresses over three or more months.
- Nephroptosis or kidney prolapse is a displacement of the organ due to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus. Pain in the kidneys is aching, stabbing, and does not appear immediately, but only after physical exertion. The disease is characterized by lack of appetite, stool disturbances, and nausea. At times, throbbing pain develops.
- Due to improper discharge of urine, pathological changes in the organ may occur - hydronephrotic transformation. Often the disease passes without symptoms and manifests itself as a result of infection or injury. Often the pain affects the lumbar region and provokes an increase in pressure.
- A symptom of urolithiasis is urolithiasis when the stones are in the kidneys and urinary canals. The disease occurs frequently and is correlated with human living conditions, hard water, abuse of soybean, spicy and salty foods. Associated symptoms include blood in the urine, fever and pain during urination.
- A tumor in the kidneys is benign - it may not appear at all and is not dangerous. Most often it involves surgery.
- Renal oncology is the most terrible diagnosis, which is accompanied by constant weakness, fever and the presence of blood in the urine. A lump is felt in the lumbar area and the lower back hurts.
Causes
Nagging pain in the kidney area appears mainly in the morning, intensifies with palpation and, in addition, has a change in the color of the urine appeared?
Most likely, we are talking about a developing kidney disease. The main kidney diseases that most often cause nagging pain in the kidney are:
- Chronic inflammatory (including viral) kidney diseases. They are always accompanied by feelings of discomfort and aching (pulling) pain, in contrast to acute inflammation, characterized by sharp pain and fever. In addition, if nagging pain appears some time after an upper respiratory tract infection, this may indicate developing pyelonephritis.
- Prolapse of the kidney (nephroptosis) causes painful and pulling sensations in the lumbar region. This occurs due to a violation of the natural position of the kidney, kinks of the ureters and, as a result, obstructed outflow of urine. Nephroptosis can be provoked by physical stress, childbirth, sudden weight loss, trauma and congenital pathologies.
- Hydronephrosis of the kidney most often results from the prolapse of the organ described above. With hydronephrosis, nagging pain appears on one side, since it develops unevenly in both kidneys. The cause of pain in this condition is the process when, due to incomplete outflow of urine, it accumulates in the cavity of the kidney, thereby stretching and thinning it. This pathology can lead to inflammation, so the pulling sensation in the kidney area cannot be ignored.
- Nagging pain may be the first sign of urolithiasis. Gradually accumulating sand and growing stones prevent proper urination. And if at the initial stage of the disease this is manifested simply by aching, pulling sensations, then in the future renal colic is possible, which is fraught with a critical condition of the patient.
Traditional recipes for pain
If pain develops in the kidneys and it is impossible to visit a doctor, you can try using folk remedies for pain.
These are herbal teas that are consumed instead of regular ones. Herbs such as motherwort, bearberry, cornflower petals, and licorice root have a good effect on the functioning of the organ.
The listed herbs are mixed in three tablespoons each and 300 ml of boiling water is poured. This tasty and healthy drink will significantly improve the patient’s health and well-being.
>
Diagnostics
If a distinct feeling of tightness in the kidneys becomes permanent, urgent diagnosis and proper treatment are required.
To confirm or exclude the diagnosis, the examination begins with a urine test and blood tests: general and biochemical.
If suspicions are justified, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed. The most common method is ultrasound examination of the kidneys. An X-ray examination is also used - excretory urography, which allows assessing the functionality of the kidneys and urinary tract.