Kidneys
Poisoning is the penetration of dangerous substances and microorganisms into the body: drugs, salts of heavy metals, poisons, plant and animal toxins, bacteria. The kidneys remove harmful substances from the body, so in case of poisoning they are damaged. The extent of damage depends on the severity, amount and duration of action of the toxin.
Kidney intoxication
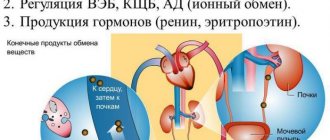
Harmful substances are excreted from the body in the urine. If the outflow of urine and the ability to produce urine are impaired, kidney failure develops. Most often, it develops gradually in chronic diseases - glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus. Kidney intoxication develops quickly when poisoned by alcohol substitutes, mushrooms, or after snake bites.
A decrease in the excretory function of the kidneys leads to self-poisoning of the body with nitrogenous wastes - uric acid, creatinine, urea, indican. The listed poisons, which were supposed to be eliminated, are absorbed from the urine into the blood. As a result, the electrolyte balance is disrupted and changes in protein metabolism occur.
Acute renal failure occurs when there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure due to frequent diarrhea and vomiting. The complication is caused by the loss of water and electrolytes.
Your actions
In case of poisoning that affects the functioning of the kidneys, you must first of all call an ambulance.
In case of kidney intoxication, it is important to start taking any action even before the ambulance arrives, since every minute is important. Carrying out pre-medical measures, as well as qualified medical care, guarantees a quick recovery without serious complications.
Causes of prolapsed kidney: symptoms and treatment
In case of poisoning that affects the functioning of the kidneys, you need to do the following:
- First of all, call an ambulance.
- While waiting for the ambulance, the patient needs to have his stomach pumped if there is a suspicion that toxins have entered the body through the digestive system. If poisons enter the body through the skin, the patient must be wiped first with a damp and then with a dry cloth.
- In case of poisoning with ethyl alcohol, it is necessary to take an antidote, which is ethyl alcohol.
Attention: upon the arrival of the ambulance, doctors must announce the suspected cause of poisoning. If there is a possibility of food poisoning, it is advisable to save leftover food or drinks to facilitate identification of toxins.
Causes of pain in the kidneys during poisoning
All toxic substances and their decomposition products damage certain organs. The kidneys suffer to a greater extent when consuming nephrotoxic foods, drinks, and drugs. After vomiting, the lower back hurts when agents of various origins enter the body:
- phosphorus-containing substances used in agriculture to control weeds, rodents, insects - thiophos, octamethyl;
- alcohol surrogates - methyl alcohol, denatured alcohol, ethylene glycol, BF glue, cosmetic lotions, cologne;
- oxalic or acetic acid often causes lower back pain when poisoned;
- toxins of nephrotoxic fungi - fly agaric, cobweb, toadstool;
- the poison of the plant kirkazon, contained in Chinese weight loss and herbal remedies, causes kidney failure and kidney cancer;
- solvents, salts of heavy metals;
- poisons of animal origin (insects, snakes, amphibians);
- drugs with nephrotoxic side effects - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (with long-term use), antibiotics - Amphotericin B, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides;
- immunosuppressants – Methotrexate, Cyclosporine;
- kidney function is impaired with an overdose of Revita;
- Kidneys may hurt due to poisoning with radiocontrast agents used in coronary angiography.
ethnoscience
Toxic nephropathy is a disease that requires immediate outpatient treatment. Thus, it is advisable to use any traditional medicine only in the recovery period after drug therapy.
Medicinal decoctions and infusions can be used provided the patient is in good health and has positive dynamics. Their independent use is strongly not recommended. Traditional herbs and recipes can only be prescribed by the attending physician. They have a general strengthening effect on the body, improve immunity and prevent the development of complications.
Lingonberries are often used to normalize urinary function. The berries are mixed with sugar in a 1:1 ratio, the mixture is placed in jars, diluted with water and drunk as a compote. Watermelon peel can be used to prevent edema for patients in remission. It is brewed and drunk as a decoction.
Symptoms of kidney poisoning
2–3 hours after the harmful substance enters the stomach, symptoms of poisoning appear:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- inhibited or excited state;
- after absorption of the product, vomiting occurs and the kidneys hurt;
- increased blood pressure;
- muscles hurt, body aches;
- limb spasms.
Disturbances in electrolyte metabolism cause cardiac arrhythmias. Urine with a strong odor becomes cloudy and contains flakes.
One of the technical liquids used for intoxication is ethylene glycol. Dihydric alcohol is a component of antifreeze and brake fluid. After ingestion of an alcohol surrogate, a state of euphoria initially occurs. Then signs of intoxication appear:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- stomach ache;
- when poisoned, pulls the lower back.
Preventive measures and prognosis
Toxic nephropathy most often affects people whose work is directly related to hazardous production. At a special risk group are those who already have any kidney diseases, as well as a predisposition to the formation of tumor processes.
A solution may be to switch the enterprise to mechanized labor, where the possibility of contact with harmful substances for the employee is minimized. In addition, it is necessary to use all possible means of protection (wear special clothing, observe occupational hygiene) and undergo an annual medical examination as a preventive measure.
If incipient or progressive nephropathy is detected, it is strongly recommended to choose another area of work activity that is not related to toxic production.
In general, the prognosis for recovery and complete cure is very favorable if therapy was started on time and carried out in full. An exception may be nephropathies that arise under the influence of the toxic effects of cadmium, silicon or hydrogen arsenate.
Kidney disease is a very common and serious pathology that can lead to disability and death. Often, the patient does not understand the full danger of kidney inflammation and consults a doctor when changes in the urinary organs become irreversible.
Depending on the location of inflammation, two forms of pathology are distinguished:
- glomerulonephritis (predominantly the glomeruli are affected);
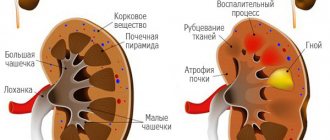
- pyelonephritis (develops in the tubules and pelvis of the kidney).
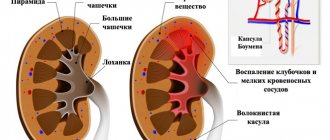
Glomerulonephritis is a consequence of the action of toxins and inflammatory products on the kidney tissue. The disease often appears several weeks after acute infection. Pyelonephritis occurs when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the kidneys during inflammation of other organs.
Kidney diseases
Discomfort in the lumbar region often occurs in patients with diabetes, gout, and amyloidosis. When kidneys hurt and feel sick, the most common causes are acute and chronic pathologies of the urinary organs:
- pyelonephritis;
- polycystic kidney disease;
- hydronephrosis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- kidney stone disease.
- congenital anomaly.
Signs of pyelonephritis are dull pain in the lower back and fever. Libido decreases in both men and women. Urine analysis determines an increased number of leukocytes. A characteristic pain symptom in urolithiasis is renal colic.
Glomerulonephritis affects the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. The onset of the disease is preceded by a streptococcal infection. The clinical picture is manifested by increased blood pressure and edema.
Over a long period of time, chronic diseases lead to kidney intoxication.
Nature of pain
General intoxication of the body during poisoning is often indicated by pain in the lumbar region.
General intoxication of the body during poisoning is often indicated by pain in the lumbar region. This indicates that pathological processes began in those parts of the urinary system that are responsible for the accumulation and removal of urine from the body. The kidneys can also hurt due to disturbances in the water and salt balance of the body, changes in the chemical composition of the blood, and metabolic disorders.
The pain syndrome in kidney poisoning is of a cramping, bursting nature. In addition, this condition is characterized by dull pain that is localized in the lower back or throughout the lower back. The pain may continue for a long time. If pain in the kidneys is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, impaired diuresis, and general weakness, then this indicates toxic damage to the kidneys, and not problems with the muscular system.
Treatment of kidneys in case of poisoning
When the kidneys hurt after vomiting, medical tactics depend on the reasons that provoked the serious condition. After the diagnosis has been established, the toxicology department provides comprehensive treatment:
- to restore functions, first of all, detoxification of the body is necessary;
- elimination of acidosis;
- correction of electrolyte balance;
- prescription of antibiotics;
- use of corticosteroid hormones;
- forced diuresis using diuretics, saline and glucose;
- If the kidneys hurt after poisoning, blood replacement therapy is performed.
- For glomerulonephritis, glucocorticoids are prescribed. Blood pressure and blood protein levels are normalized. Antibiotics are used to treat kidney inflammation.
Treatment for poisoning with ethylene glycol and methyl alcohol includes gastric lavage with activated charcoal and taking a laxative. A specific antidote - ethyl alcohol - is prescribed orally for 5 days at the rate of 1 gram per kilogram of a person’s weight.
In an unconscious state or when vomiting, liquid is administered intravenously by drip. Cardiac activity is corrected. To eliminate metabolic acidosis, alkalizing solutions are used - sodium bicarbonate, Trisamin, Lactosol.
note
Kidney diseases are treated by an experienced specialist
If the kidneys hurt after poisoning, the urine becomes cloudy, the temperature rises, nausea and headache appear - treatment at home is impossible. The skin becomes pale and dry, the person feels tired all the time. Such a patient may develop pyelonephritis, and it can only be dealt with in a hospital setting.
You should not rely on folk remedies and herbal decoctions. They may temporarily relieve symptoms, but will not eliminate the cause of the disease. A sluggish process can become chronic. Without targeted treatment, the kidneys can completely stop functioning.
Nutrition after kidney poisoning
The basis for successful treatment of poisoning is proper nutrition. If your back hurts after poisoning, diet is just as important as taking medication. Patients must adhere to the following principles:
- restriction in the diet of protein foods - meat, fish;
- salt-free diet with fractional intake of easily digestible dishes;
- Drinking plenty of water will speed up the removal of toxins;
- exclusion from the menu of smoked meats, marinades, chocolate, mushrooms, and spicy dishes;
- Drinking alcohol, coffee and even strong tea is prohibited.
A protein-free diet and salt restriction reduce the load on the kidneys. Vegetable and cereal soups and pumpkin porridge are recommended. Products with a diuretic effect are useful - cucumbers, zucchini, watermelons, melon. To add flavor to your food, you can sprinkle lemon juice on it.
Possible complications
If the patient is not provided with timely assistance after poisoning, uremia develops - end-stage renal failure syndrome. The most severe consequence of poisoning can be recognized by special signs:
- breathing becomes uneven and intermittent;
- strong smell of ammonia from the mouth;
- gray-yellow dry skin;
- oliguria – reduced urination, or anuria – complete absence of urine;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- decrease in body temperature;
- stuporous state - the patient is not oriented in space and time;
- inappropriate behavior;
- characteristic puffiness of the face.
In case of poisoning, lower back pain may be accompanied by the development of heart failure with a risk of death. In severe cases, the toxins poison the brain, symptoms of which include convulsions, loss of consciousness, involuntary bowel movements and urination. Patients fall into a comatose state. In the terminal stage, the chances of survival are minimal.
Diagnostics
In the case of poisoning, the diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis, since it is not permissible to waste precious time on lengthy diagnostic procedures.
In the case of poisoning, the diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis, since it is not permissible to waste precious time on lengthy diagnostic procedures. However, in the future, to assess the extent of organ damage, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Clinical tests of urine and blood (they are done immediately upon admission of the patient to the hospital).
- Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky. To do this, all the daily urine is collected, after which a medium portion is poured into a container for analysis.
- An ultrasound of the kidneys will allow you to evaluate the structure of the organ, its size and location.
- In some cases, CT and MRI may be performed to assess the condition of the kidneys and the extent of their damage.
Prevention
Poisoning with chemicals, mushrooms, and alcohol substitutes leads to dire consequences. The kidneys will work properly if you lead a correct lifestyle, follow the rules of working with toxic substances, and get rid of bad habits:
- avoid frequent feasts with alcoholic beverages;
- drink only certified alcoholic beverages in moderation;
- limit marinades and pickles in your diet, which overload the kidneys;
- when using insecticides at home, wear a mask, wash your hands thoroughly, and ventilate the room after the procedure;
- When cleaning a room from insects and rodents with chemicals, put food in the refrigerator;
- Use caution when using organophosphates in the garden.
Do not pick unknown mushrooms in the forest. A piece of toadstool can poison the entire basket, and then the kidneys. Take care of prevention - prevent the problem.
If you experience vomiting and lower back pain after poisoning with any substance, rush to the doctor. A timely diagnosis and qualified treatment will prevent dangerous complications and restore kidney function.