Distinctive features of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis
Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are the most common kidney diseases. Although they are similar in many ways, they must be differentiated, since correct and effective treatment requires an accurate diagnosis.
Any kidney disease can be quite dangerous due to its consequences and complications.
They can lead to the development of kidney failure, so at the first signs of illness you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms and manifestations of diseases
These diseases are similar in nature, namely, the development of inflammation when pathogenic microorganisms enter the kidneys. A decrease in immunity caused by hypothermia, stress, or previous infection creates favorable conditions for the active proliferation of microbes and the development of the disease.
Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis have some common symptoms, which is explained by the developing inflammation, as well as the fact that in both cases the kidneys are affected:
Differences in symptoms
All the differences that exist between these two diseases are explained by the fact that different kidney structures are affected.
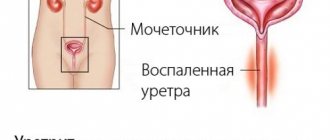
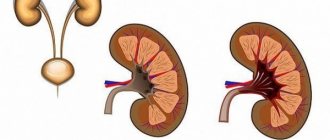
With pyelonephritis, the tubules and vessels of the organ are affected, then the inflammation spreads to the renal calyx and pelvis, and the process of urine excretion is disrupted. Most often, one of the kidneys is affected. The inflammatory process in glomerulonephritis extends to the glomeruli and, as a rule, is bilateral. Glomerulonephritis most often occurs in children after respiratory tract infections.
Due to the characteristics of each disease, such common symptoms as hematuria and pain have some differences. With pyelonephritis, the pain is usually more severe.
The appearance of blood in the urine is not always observed; it occurs due to damage to the mucous membranes by stones passing through the urinary tract. Glomerulonephritis gives a symptom such as hematuria due to vascular permeability.
It can be very pronounced, and the urine can have a noticeable red-brown color.
Comparative characteristics
| Pyelonephritis | Glomerulonephritis |
| Symptoms appear suddenly, they are pronounced, the disease develops quickly | The disease manifests itself gradually, symptoms increase slowly and are mild |
| More often it first appears in an acute form, which under unfavorable conditions becomes chronic | More often chronic |
| The pelvis and calyces are affected | The renal glomeruli are affected |
| Uneven distribution of the pathological process: either one kidney, or both, but partially | Inflammation spreads evenly to both kidneys |
| Frequent excessive urination | Rare urination, decreased amount of urine produced |
| Gastrointestinal disturbances: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation | The gastrointestinal tract is working normally |
| Swelling is often absent | Swelling is characteristic |
| Changes in blood composition characteristic of inflammatory processes | Pronounced changes in the composition of the blood, leading to a deterioration in the general condition |
The course of pyelonephritis is aggravated by the presence of kidney stones. They injure the mucous membranes, their passage through the urinary tract causes spasms and significantly increases pain. With glomerulonephritis, pain is caused only by inflammatory tissue damage, so it is not so intense.
What are the dangers of diseases?
Both diseases can lead to negative consequences due to damage to kidney tissue and the spread of infection. With glomerulonephritis, hypertension quickly develops, metabolic processes are disrupted, which can affect the functioning of the heart, large vessels, and brain.
Possible complications of pyelonephritis
- Kidney abscess due to a purulent process.
- Kidney failure.
- General blood poisoning (sepsis).
Possible complications of glomerulonephritis
- Acute heart failure.
- Acute or chronic renal failure.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage.
- Visual impairment.
- Preeclampsia, eclampsia.
Diagnostics
If you have kidney complaints, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Standard diagnostic tests are usually prescribed:
- urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- urography.
Differential diagnosis comes to the fore, especially with mild symptoms. To make a diagnosis, all the patient’s symptoms and complaints, as well as the results of the examination, are taken into account.
The diagnosis of pyelonephritis is made based on the results of a blood test and ultrasound. An increase in leukocytes is detected in the blood and urine, and the pathogen is determined by urine analysis. When performing an ultrasound, changes are noticeable in the pyelocaliceal system of the affected organ.
With glomerulonephritis, ultrasound diagnostics does not reveal any changes; a urine test reveals a high content of protein and blood. A blood test shows the presence of an inflammatory process and anemia.
Similarities and differences in treatment
Since both diseases are infectious and inflammatory in nature, in both cases antibacterial therapy is prescribed. In acute conditions, treatment is carried out in a hospital with strict adherence to bed rest.
In both cases, symptomatic treatment is prescribed to reduce pain and eliminate inflammation. A mandatory part of the treatment of all renal pathologies is diet.
Table No. 7 is shown, in which all foods that irritate the kidneys are excluded: smoked foods, spices, spicy foods, alcohol.
The significant difference lies in the drinking regime. For pyelonephritis, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended, which helps cope with inflammation and intoxication.
With glomerulonephritis, the amount of fluid consumed is limited, as the filtering function of the kidneys suffers and congestion occurs. Restricting fluids helps reduce swelling and reduce stress on the affected organ.
A special feature in the treatment of glomerulonephritis is the need to normalize blood pressure, as well as correct immunity.
At the end of treatment, complete recovery and rapid restoration of kidney function are more likely with pyelonephritis. The features of the pathological process with glomerulonephritis are such that after a course of treatment the patient needs to be monitored by a nephrologist.
It is registered and preventive diagnostics are carried out at least once a year. If this is an adult, then observation lasts for at least two years; children are registered for five years.
If during this period at least one case of exacerbation occurs, then a diagnosis of chronic glomerulonephritis is made, and the patient remains under observation for life.
Source: https://beregipochki.ru/bolezni-pochek/glomerulonefrit/otlichitelnye-osobennosti-ot-pielonefrita.html
Forecast
Acute pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, with early diagnosis and promptly started rational treatment, end with complete recovery. The fight against their chronic form requires persistence and perseverance from the patient and the doctor.
If a patient comes to a medical institution with an already advanced disease, there will be little hope for a positive outcome. The end result of both chronic inflammatory processes with frequent exacerbations, left to fate, will be the steady replacement of the kidney parenchyma with connective tissue and its atrophy. Progressive bilateral renal failure with a disturbance in the body's acid-base and water-electrolyte balance and the accumulation of toxic metabolic products forces a person to resort to cleansing his own blood almost every day using a hemodialysis machine. And if he does not undergo an operation to transplant a donor kidney in time, then a very sad outcome of the disease awaits him.
Untreated kidney inflammation will inevitably end in chronic renal failure, in which the patient’s life can only be saved by regular hemodialysis
A patient with chronic glomerulonephritis must follow a gentle regimen for life. Types of professions associated with the following activities are contraindicated for him:
- business trips;
- contacts with pesticides;
- prolonged exposure to the cold;
- irregular working hours;
- lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- night shifts.
At the first signs of renal failure, a person should be provided with an appropriate disability group.
Both pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are serious kidney diseases that lead to irreversible damage to the systems and organs of the human body. At first glance, they are very similar in symptoms, but upon detailed study it turns out that these ailments differ quite significantly from each other. Their main similarity is that without treatment they equally inevitably lead to renal failure and death of the patient. To avoid this sad consequence, every person who has a predisposition to pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis should be extremely attentive to themselves. At the first alarming symptoms, you need to contact a medical institution for diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis are kidney diseases.
If untimely and incorrectly selected treatment can lead to functional failure of the organ.
What is the difference in the clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment of diseases?
Differences between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. How is pyelonephritis different from glomerulonephritis?
With pyelonephritis, inflammation develops in the intermediate tissue of the kidneys, glomeruli and blood vessels. Gradually, inflammation spreads to the renal parenchyma, calyx, and pelvis. The pathology affects one kidney or both at once and progresses rapidly.
The cause of the disease is considered to be an infection that enters the kidneys through the genitourinary system or from the blood. The development of the disease is facilitated by spasms, disruption of the process of urine outflow from the kidneys, and stones.
The main difference from glomerulonephritis is the spread of inflammation to the renal pelvis.
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys. The disease is mainly diagnosed in people who often suffer from sore throats and colds. Hypothermia, weak immunity, and allergies contribute to vascular damage. Often the renal glomeruli become inflamed due to their damage by streptococcus or staphylococcus. The disease can occur as a complication of pyelonephritis.
Symptoms
Kidney disease is dangerous because it can cause kidney failure, which leads to death. Urological diseases occur in people of all ages.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately, but first it is important to make a correct diagnosis. Nephritis (inflammatory processes in the kidneys) have a number of similarities, which makes them difficult to distinguish.
You need to know the characteristics of a particular disease for effective treatment.
General symptoms
The following symptoms are common to pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis:
- Loss of strength, loss of appetite.
- Increased body temperature. With pyelonephritis, the temperature is especially high - 38 ° C and above.
- Laboratory tests determine the presence of blood in the urine. In pyelonephritis, this is explained by damage to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract by stones; in glomerulonephritis, this is due to increased permeability of blood vessels.
- Pain in the lumbar region. With pyelonephritis, the pain is severe, and renal colic develops. With glomerulonephritis, the pain is less intense.
Distinctive symptoms of pyelonephritis
To determine the presence of pyelonephritis, you need to know its main differences:
- Inflammation affects the renal parenchyma, pelvis, and calyx.
- Asymmetry of the disease. Mostly one kidney is affected. If both, then the pyelonephritis is uneven.
- Frequent, copious urination, absence of edema.
- Pyelonephritis disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and causes constipation.
Distinctive signs of chronic glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by changes in the blood, which negatively affects the general well-being of the patient. Besides:
- The pathology affects both kidneys at once, the inflammation is uniform.
- Due to impaired filtration, the blood picture changes, urine goes into the blood. A number of metabolic processes are disrupted and blood pressure increases. Possible wheezing in the lungs and shortness of breath.
- Blood circulation in the brain is impaired. Swelling is possible.
- Intoxication provokes mental disorders.
- The electrolyte balance is disrupted and intracranial pressure increases.
- Little urine is produced and urination is rare.
- Swelling appears. With pyelonephritis there is no swelling.
Pyelonephritis - what is the pathology characterized by?
This disease is also characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys
This disease is also characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys. However, the source of inflammation does not affect the functional tissue of the organ, being localized in the renal cavities, where secondary (ready for excretion) urine flows through the distal (external) tubules. Mostly the mucous membrane of the pelvis is inflamed, partially the calyces and proximal segments of the ureters.
The nature of inflammation in pyelonephritis is often of bacterial origin, less often the pathology is provoked by pathogenic species of protozoa or viruses. Microorganisms cause acute inflammation with pronounced symptoms and rapid progression. But there are pyelonephritis with an aseptic type of inflammatory process.
This happens when there is mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the pelvis, for example, with urolithiasis. In this situation, a chronic process develops, which can worsen at any time due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the renal cavities.
Often chronic inflammation of the pelvis is a consequence of insufficient treatment of acute pyelonephritis.
With the development of an acute inflammatory process, there are pronounced symptoms that cause discomfort to the patient literally from the first hours of the onset of the disease. Signs of acute pyelonephritis are the following symptoms:
Causes of prolapsed kidney: symptoms and treatment
- severe or moderate pain in the area of the affected organ (lower back, less commonly, lower abdomen), possible renal colic;
- moderate fever (up to 38 degrees);
- pain of varying intensity when urinating;
- frequent (imperative) urge to urinate (the symptom is especially pronounced if the ureters and bladder are involved in the inflammatory process);
- the urine may become cloudy with possible bloody inclusions.
Urine tests performed in the laboratory reveal white blood cells. Red blood cells occur if pyelonephritis is aggravated by urolithiasis. The reaction of the medium shifts towards alkali.
Instrumental studies (ultrasound, urography) show thickening and loosening of the mucous membrane of the pelvis, sometimes adjacent anatomical formations (calyces, ureters).
Concretions (stones) are often found in the renal cavities, which are often the cause of the resulting inflammation.
Although it happens the other way around - the inflamed mucous membrane of the pelvis becomes (under conditions favorable for stone formation) the cause of the formation of large stones.
Impaired urination (renal dysfunction) is not typical for pyelonephritis, so a biochemical blood test will be normal. A general analysis of physiological fluid will show signs of acute inflammation (leukocytosis, increased ESR).
Acute pyelonephritis is treated with antibacterial drugs (antibiotics, uroseptics, sulfonamides), symptoms are relieved with non-narcotic analgesics in combination with antispasmodics.
Inflammations of the pelvis not burdened by urolithiasis and general immune deficiency can be successfully cured with timely seeking medical help.
The treatment prognosis is favorable, in most cases leading to complete recovery.
Source: https://stopzaraza.com/pochki/otlichiya-xronicheskogo-glomerulonefrita-i-pielonefrita.html
Prevention
Glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis are kidney diseases of various etiologies. In order to prevent these diseases from developing again, it is necessary to eliminate all unfavorable factors. Prevention of glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis consists of following the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to adhere to a dietary diet, exclude spicy foods, salty, fatty foods, carbonated drinks and water, chips and crackers from the diet.
- All urological diseases should be treated promptly.
- Avoid hypothermia of the lumbar spine.
- Add a variety of greens to your food.
- Take vitamin and mineral supplements to strengthen your immune system.
- Personal hygiene rules must be observed daily.
- A routine examination should be performed annually to monitor the disease.
- It is worth drinking enough fluid to improve urine flow.
- Systematization of physical activity.
- Provide a comfortable emotional and psychological climate.
- You should not drink alcoholic or low-alcohol drinks.
If you follow all the recommendations listed, you can prevent the development of relapses of the disease.
How is pyelonephritis different from glomerulonephritis?
Common urological diseases are pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. Both diseases are similar to each other, are inflammatory in nature and affect the same organ - the kidneys. Due to the similarity of symptoms, it is quite difficult to correctly diagnose and, as a result, apply the correct treatment. Therefore, it is especially important to study the characteristics and differences of each disease.
Glomerulonephritis
This is an inflammatory disease of the internal vessels and capillaries of the kidneys. Inflammation occurs in the filtration glomeruli of the kidneys - glomeruli. That is why glomerulonephritis has such a name.
More often it occurs in young people aged 20 to 40 years, and is often found in children. Glomerulonephritis can be either chronic or acute and usually affects both kidneys.
The disease has severe complications that can cause kidney failure in the future.
Causes
The disease is often caused by influenza.
The cause of inflammation in the glomeruli is considered to be autoimmune formations that enter the organ with the blood, and instead of removing foreign bacteria and infections, they damage their own tissues.
Glomerulonephritis is often found in people who suffer from colds, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis or scarlet fever. Quite often, the disease is caused by bacteria such as staphylococcus and streptococcus.
The disease can also occur after hypothermia or due to often reduced immunity.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed at the initial stages of the disease.
Acute glomerulonephritis is treated conservatively, without surgical interventions. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory and antitumor agents, and complex vitamins. If the body is severely intoxicated, blood cleansing may be necessary.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is treated with the same medications. In addition, it is important for patients to follow a strict diet, reduce protein intake, and eliminate salt, spices, and smoked products from the diet. Patients should beware of hypothermia. In complex advanced situations, when the kidney cannot be saved, organ transplantation or removal is possible.
It is not recommended to make a diagnosis or self-medicate on your own, since improper treatment of glomerulonephritis can cause kidney failure and other complications.
Pyelonephritis
This is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the pelvis and calyx of the kidneys. Often, pyelonephritis affects one kidney, but sometimes there are cases of bilateral organ disease.
After infection of the kidneys, pyelonephritis spreads to the genitourinary system. It is the location of kidney damage that distinguishes pyelonephritis from glomerulonephritis.
Pyelonephritis can be primary and secondary, acute and chronic, develops quickly and has obvious symptoms, so it can be easily diagnosed.
Etiology
Pyelonephritis develops when E. coli enters the body.
The causes of pyelonephritis are often infectious and bacterial in nature.
Infections enter the kidneys through the blood or urethra. The disease is often caused by Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other fungal viruses.
Often, pyelonephritis is formed as a result of nephrolithiasis and other kidney diseases.
Treatment options
Urine analysis will help make a diagnosis.
It is extremely important to begin treatment of the disease on time to prevent complications and the transition of the disease from acute to purulent or chronic. The fastest way to diagnose the disease is a laboratory urine test. If the urine has an increased number of red blood cells and white blood cells, this is a clear sign of the disease.
In the initial stages, pyelonephritis is treated conservatively with medications. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, uroseptics and other antibacterial agents to remove infections. Antispasmodics and analgesics are prescribed to reduce pain.
Advanced chronic pyelonephritis is eliminated by surgical drainage of the pelvis, catheterization, decapsulation of the kidneys and other methods.
Table of the main differences between glomeronephritis and pyelonephritis
In addition to their similarities, these diseases have a number of differences in symptoms and treatment methods. The table describes the distinctive features in more detail:
DifferencesGlomerusnephritisPyelonephritis
| First stage of the disease | Gradual, no symptoms | Sudden, obvious symptoms |
| Nature of inflammation | Aseptic or autoimmune | Septic or alternative |
| Swelling | Present | Absent |
| Urination | No violations observed | Acute pain |
| Protein in urine | Present | Absent |
| Body temperature | Increased | High, about 38-49 °C |
| Symmetry of the disease | Both kidneys are affected | Most often one kidney is affected |
| Constipation | None | Present |
| Shortness of breath, wheezing in the lungs | ||
| Urine test results | Increased red blood cells and protein, low hemoglobin | Leukocyturia and bacteriuria are observed |
Source: https://ProUrinu.ru/nedugi/nefrity/pielonefrit-i-glomerulonefrit.html
Differential diagnosis
To carry out a differential diagnosis of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, the patient’s complaints are clarified, an anamnesis is collected, an examination, laboratory, instrumental and morphological research methods are performed.
Glomerulonephritis studies
Glomerulonephritis is supported by recent tonsillitis, vaccination, allergic diseases, and the presence of the disease in close relatives.
With glomerulonephritis, both kidneys are affected, so the pain syndrome is evenly expressed on both sides. Since the vascular glomeruli are damaged, the patient notes a change in urine color from pink to rusty.
In a general urine test, the following changes are observed:
- hematuria (red blood cells in the urine, normally absent);
- proteinuria (protein in urine);
- decreased urine density (concentrating ability of the kidneys decreases).
Ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging reveal changes in the renal parenchyma.
A reliable diagnosis can only be made after a morphological study. In this case, a kidney biopsy (a fragment of organ tissue) is taken and its cortex and medulla are studied. Based on this study, a prognosis of the disease can be made.
Study of pyelonephritis
Since pyelonephritis often affects one kidney, the pain syndrome is clearly localized to the right or left. The disease is accompanied by massive intoxication of the body (fever).
The urine becomes cloudy and has a foul odor due to the presence of bacteria in it.
A general urine test contains leukocytes and bacteriuria (a large number of microorganisms).
Ultrasound of the kidneys shows dilation of the collecting system.
In chronic pyelonephritis with frequent exacerbations, renal failure gradually develops.
Differences between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis
| Sign | Pyelonephritis | Glomerulonephritis |
| Kidney damage | Most often unilateral | Always two-sided |
| Symptoms | Fever, cloudy urine with a strong foul odor, lower back pain | Swelling on the face mainly in the morning, change in urine color from pinkish to red |
| General urine analysis | Cloudy urine with a large number of white blood cells and bacteria | Red blood cells and protein in urine |
Differences between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis in the table. What is the difference between glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis?
With glomerulonephritis, inflammation occurs in the medulla (medullary) layer of the kidneys, where the main functional renal formations - glomeruli - are located.
With glomerulonephritis, inflammation occurs in the medullary layer of the kidneys, where the main functional renal formations are located - glomeruli, also known as glomeruli, in which the main processes of filtering blood serum with the formation of urine occur. Involvement of functional renal tissue (parenchyma) in the inflammatory process leads to the main danger that glomerulonephritis poses - the development of failure of the excretory organs.
In addition to the characteristic localization of the pathological process, this disease has a specific nature of inflammation, which is not a consequence of the activity of microorganisms, injuries or other damage.
In glomerulonephritis, the cause of inflammation is autoimmune factors - in other words, the kidney tissue is affected by atypical immune complexes that enter the medulla of the kidneys from the blood.
Normally, immune formations are designed to fight foreign substances and microorganisms (viruses, bacteria), but under some circumstances, antibodies (immunoglobulins) begin to damage the tissues of their own body.
The autoimmune mechanism of tissue damage with the subsequent development of aseptic inflammation is inherent not only in glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of most systemic connective tissue diseases (SLE, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, etc.) is similar. Inflammatory processes caused by an autoimmune attack have many common features, such as:
- sluggish, prolonged course;
- does not spread to neighboring organs and tissues;
- predominance of proliferation (growth) of inflamed tissues;
- as a result of inflammation, loss of tissue functionality.
All these signs are inherent in inflammation of the renal parenchyma in glomerulonephritis. The disease extremely rarely begins acutely and does not have severe symptoms. In most cases, noticeable symptoms appear much later than the onset of the disease and may not cause the patient much discomfort for a long time, which is the danger of the pathology.
Seeing a doctor, diagnosing the disease and starting its treatment often occurs when inflammation has already caused irreversible organic damage that reduces the functionality of the organ.
With glomerolonephritis there is no severe pain or problems with urination. Typically, symptoms are detected only through laboratory tests of urine, during which such signs of the disease are detected in urine;
Symptoms of drug-induced kidney damage and treatment
- red blood cells (hematuria);
- protein (proteinuria);
- leukocytes (leukocyturia).
The presence of erythrocytes and leukocytes in the urine can also occur in other renal pathologies, including pyelonephritis
The presence of red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine can also occur in other renal pathologies, including pyelonephritis. But the presence of protein in the urine, especially in large quantities, indicates disturbances in filtration processes, which only happens with serious disorders of renal function that accompany inflammation of the kidney parenchyma.
The diagnosis of glomerulonerite is confirmed by instrumental studies. Characteristic signs of the disease, which are detected during ultrasound or tomographic studies, are reduction and compaction of organs, the formation of cysts and focal atypical inclusions in their bodies.
The clear line between the cortex and medulla that characterizes a normal kidney is blurred. It is characteristic that the lesions are symmetrical and affect both kidneys equally. The pelvis and calyces look absolutely normal, that is, the renal cavities are not involved in the process.
Glomerulonephritis is treated with powerful anti-inflammatory (corticosteroid hormones) and cytostatic (antitumor) drugs. Both have an immunosuppressive effect (suppress immune reactions), the cytostatic effect inhibits the proliferation of renal cells involved in inflammation.
Important! Glomerulonephritis is considered a serious disease; the prognosis for some of its forms is very unfavorable - the outcome of the disease is total bilateral renal failure with the need for a donor kidney transplant.
Glomerulonephritis: symptoms and diagnosis
This disease affects young people aged 25 to 35 years. It often affects children, especially boys aged 5 to 10 years. Glomerulonephritis or glacial nephritis is accompanied by damage to the renal blood vessels.
People who are prone to frequent colds, chronic tonsillitis, sore throat and scarlet fever suffer from this disease much more often than others. Medical experts often call streptococcus and staphylococcus the main causative agents of glomerulonephritis.
This inflammation of the renal glomeruli may result from an infectious infection.
Changes in blood vessels can also occur with sudden hypothermia. The development of glomerulonephritis can be affected by persistent allergic reactions and reduced immunity. The disease can be diagnosed by the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and headache;
- painful sensations in the kidney area (possibly slight tingling);
- decreased frequency of urination;
- the appearance of severe swelling on the face.
If treatment is not started promptly, serious complications may occur. At a later stage, acute pain syndrome appears in the indicated area. A sharp decrease in urine output is one of the main symptoms by which glomerulonephritis can be distinguished from pyelonephritis.
In 20% of cases, damage to the circulatory system of the kidneys becomes chronic. This development of the disease is characterized by sluggish symptoms. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the consequences can be disastrous.
The kidney shrinks, the destruction of the glomeruli progresses, which leads to its failure. Ultimately, a kidney transplant may be required. The danger of glomerulonephritis is that the diagnosis can be erroneous.
Its symptoms at an early stage are too mild.
When conducting diagnostics, doctors pay special attention to urine tests. Already at an early stage of the development of the disease, a large number of red blood cells and proteins are found in the urine.
Changes in peripheral blood also occur, which are detected by medical specialists. We are talking about severe anemia and a decrease in red blood cells in the patient’s blood.
Prognosis for recovery
Acute glomerulo- and pyelonephritis, with timely diagnosis and correct treatment, result in complete recovery of the patient.
The subacute form of glomerulonephritis is malignant, requires the use of cytostatics, is difficult to treat and leads to renal failure.
In chronic pyelo- and glomerulonephritis, prevention of exacerbations of the disease is important. The more often exacerbations occur, the more the kidneys suffer.
Kidney failure progresses steadily, and then treatment is hemodialysis and kidney transplantation.
Photo from thegolfclub.info