What is salt in the kidneys?
Anyone can have salts in their urine or kidneys. They play an important role in the functioning of internal organs and systems. Only in some their quantity is in an acceptable concentration, which cannot be called a pathology, while in others it is not. Moreover, both the absence of salts and their excess are considered pathology. As the disease develops, deposits of mineral components become large, and salt diathesis .
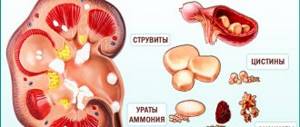
Salt crystals in paired excretory organs depend on the acidity of the blood, urine and other components of the internal environment of the body. For example, increased acidity of urine leads to the formation of elements such as uric acid, urates and oxalates. And an increase in alkalinity leads to the development of elements of the phosphorus group, as well as ammonium salts.
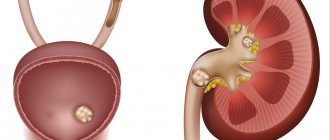
If the content of mineral substances deviates from the norm, salts are retained in the renal pelvis and are not excreted with urine. Next, the formation of kidney stones occurs.
Pathology can affect not only the elderly, but also children.
Symptomatic manifestations
In 2/3 of patients, the clinical symptoms of salt diathesis are mild or absent. The first signs arise due to irritation of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract with salts that are excreted from the kidneys in the urine.
Symptoms of salts in the kidneys:
- burning in the urethra when urinating;
- feeling of partial emptying of the bladder;
- blood or cloudy urine;
- mild pain in the lower back.
If the urinary ducts are severely damaged, the pain spreads to the lower abdomen and genitals. Women and men complain of increased sweating, chills, fever, and lack of appetite. In rare cases, pale skin and blueness of the oral mucosa are noted.
Causes
The main function of the paired excretory organs is to protect the blood from waste and toxins . The formation of salt deposits in the kidneys occurs when the acid-base balance is disturbed.
In women, these deviations are more common, which is due to the characteristics of metabolism and hormonal levels.
The cause of excess mineral deposits in paired organs is not always kidney pathology. Often, excess salts appear due to nutritional disorders, for example, when consuming large amounts of mineral water and table salt.
Factors that have a negative impact on the mineral content of the kidneys:
- Lack of fluid in the body.
- Heredity.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract.
- Tumor formations of the excretory organs, leading to compression of the kidneys.
- Enlarged uterus.
- Hormonal imbalances due to taking hormonal drugs.
In women, excess mineral compounds are associated with the endocrine system, in men - with prostate adenoma, physical inactivity, excessive consumption of alcohol and spicy foods. In children, the reason for the high content of minerals may be dietary patterns and an incompletely formed excretory system.
Etiological factors contributing to salt deposition
- The main reason that causes the deposition of salts in the kidneys is a hereditary tendency, which is detected very often in a child.
- Excess calcium concentration in the body and uric acid in the bloodstream due to improper metabolism contribute to the deposition of salts.
- The volume of fluid that enters the human body also affects the function of the kidneys: a lack of fluid or its excessive loss due to the use of diuretics provokes the formation of highly concentrated urine, which causes the deposition of salts and, later, the formation of stones.
- Infectious lesions of the organ are also often the causes of salt deposition.
The presence of salt in a child’s kidneys is not necessarily an indicator of the disease and indicates the onset of the inflammatory process. This condition sometimes develops due to the fact that the child’s nutrition is characterized by certain peculiarities, since the urinary system has not yet fully formed.
Symptoms
In the early stages, the disease usually does not manifest itself in any way and the person does not experience any unpleasant symptoms. But the constant presence of salts in urine subsequently becomes the cause of urethritis and chronic cystitis. As a result of inflammation of the renal pelvis and excess minerals, first small and then larger stones occur.
These pathological processes are manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain when urinating.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Reddish or brown urine color.
- Frequent urination.
- Heaviness in the lower abdomen.
When stones occur and move towards the ureter, renal colic occurs, which requires immediate medical intervention.
In newborns, symptoms of mineral deposits in the kidneys include sleep disturbances and frequent urination. Older children have allergies, gastrointestinal diseases, and excess weight.
Symptoms of salt deposits
Signs of salt deposition are sometimes completely absent, but if salt is constantly present in the urine of a healthy person, this can cause the development of chronic cystitis and urethritis. Then, provided there is inflammation in the pelvis and a high concentration of mineral components, initially small stones can form, and then large stones.
It is important! As a result of the described pathological process, a person complains of frequent and painful urination, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. When stones form and move along the ureter from the kidneys, an attack of acute renal colic may occur, when the patient needs urgent medical attention.
Inflammation can cause the appearance of salts in the urine, and can also be a consequence of a high concentration of these salts in the urine. With constant non-compliance with proper nutrition, it becomes simply impossible to cure or slow down the activity of the pathological process.
Diagnostics
It is difficult to independently identify the presence of pathology, and you should not self-medicate; it is best to consult a specialist. It is not difficult to diagnose phosphate or urate compounds; most often they are discovered accidentally during a general urine test.
In addition to these minerals, urine may contain an increased concentration of blood elements : red blood cells and white blood cells. This indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. Usually in this case, the urine is turbid and contains sediment.
In addition to a general urine test, the doctor takes a blood test. With the development of the pathological process, an increased concentration of urea and creatinine is detected.
Such a modern method as ultrasound is not able to recognize sand in the kidneys. But it plays an important role in complications arising from the disease. Using an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, stones are searched for and their size is determined.
Diagnosis of salt type
To find out the type of salts in the body and begin proper treatment of diathesis, it is necessary to submit your urine for a general analysis. The laboratory technician will determine the predominant type of minerals in the body. At home, you can also identify the type of salts by the appearance of your urine. It must be collected exclusively in the morning after sleep in a clean, transparent container.
To find out the type of salts in the body and begin proper treatment of diathesis, you need to submit your urine for a general analysis
The biomaterial is left to settle for 24 hours and then subjected to visual examination:
- If the urine appears whitish after collection, and after settling it has a white, chalky-type sediment, it means that carbonates predominate in the body.
- If reddish or yellowish crystals are detected in the urine and they settle on the walls of the container, then these are urates.
- If urine, when collected, has mucus and visible turbidity on the surface, and after the required period of settling, crystals are visible at the bottom, then these are phosphates.
- If almost black crystals are visible at the bottom of the container, then these are oxalates.
Important: a simple magnifying glass will help improve the visibility of the crystals at the bottom of the container.
Treatment, methods, what and how
Only a doctor who can prescribe effective treatment can help get rid of salt deposits in the kidneys
The treatment process depends on the stage of the disease and begins with the prescription of a diet, as well as the normalization of work and rest. It is recommended to significantly reduce the consumption of animal protein and increase the amount of plant protein. In addition, the diet involves reducing table salt in the diet, as well as completely eliminating flour and sweets.
To treat mineral compounds in the kidneys, you need to drink up to two liters of fluid per day, which stimulates the removal of salt from the body. Proper alternation of work and rest is also recommended.
Drug treatment of salts involves taking the following drugs:
Any medications must be prescribed by your doctor. Therapy is recommended to be carried out under strict medical supervision as treatment may be painful.
If stones are present, surgical intervention is permitted. The following methods are distinguished:
Lithotripsy is also used to remove small stones . This is a way to get rid of stones using electromagnetic waves, as a result of which they come out of the body with urine. The same method is used to remove sand from the kidneys. But in order to prevent the disease from making itself felt again after some time, it is necessary to take a number of preventive measures.
Treatment
Based on the results of the diagnostic study, treatment is prescribed by a urologist or nephrologist. It is often possible to normalize the concentration of salts in urine with minor deviations from the norm using a specially selected diet.
Diet features
Correction of salts in the kidneys with the help of diet consists of a salt-free diet or a significant reduction in the consumption of table salt. The diet should reduce the amount of foods rich in potassium, calcium, and phosphorus.
Fried, smoked foods, strong tea, coffee, and alcohol are excluded. The volume of fluid entering the body should not be less than 2 liters, and to ensure urine excretion at night, you need to drink a glass of water at night.
When urates appear in a child’s urine, the diet is enriched with magnesium, calcium, zinc, vitamins A and group B. The consumption of chocolate, legumes, and meat is limited.
The content of oxalates in urine decreases when tomatoes, sorrel, figs, rhubarb, and spinach are excluded from food. Lemon juice, oatmeal, and buckwheat help get rid of phosphates in the urine.
A diet for salts in the kidneys should be accompanied by the introduction of carrots, pumpkin, and broccoli into the diet, which improve the condition of the urinary tract and have a mild diuretic effect.
Prescriptions for children
At a young age, some excess of salts in the kidneys in children is normal. This is due to imperfect kidney function, slower elimination of salts and breakdown of substances compared to adults.
If excess salt content is observed repeatedly, the child should definitely be consulted by a pediatric nephrologist. The child’s appointment is made by a pediatric nephrologist based on the results of ultrasound and urine analysis. In the video, features of the treatment of salts in the kidneys in children:
Drug therapy for adults
Elimination of pain during urination and nagging pain in the lower abdomen is achieved by prescribing antispasmodics and painkillers. At the next stage, the task of treatment is to eliminate the cause that caused the appearance of salts in the kidneys. This could be recent cystitis, urethritis, a gynecological disease, a metabolic disorder, or changes in hormonal levels.
If salt diathesis is caused by a previous urogenital infectious disease, the following is prescribed:
- Canephron;
- Cyston;
- Cystenal;
- Phytolysin;
- antibacterial drugs that are sensitive to the causative agent of an infectious disease.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies, namely drugs that are included in the state pharmacopoeia, is widely used to cleanse the kidneys. In official medicine, folk remedies such as bearberry, birch buds, and corn silk have been used.
You need to purchase these drugs at a pharmacy. This guarantees the absence of foreign impurities and makes it possible to accurately brew an infusion or decoction, following the instructions.
Prescribing medication on your own is dangerous, since there may be a stone in the urinary tract, which, under the influence of self-medication, will move out of place, causing an attack of painful renal colic.
The danger with salts in the kidneys is the use of diuretic herbs containing anthraglycosides.
St. John's wort, madder, senna, rhubarb rhizomes, sorrel, and buckthorn bark have an irritating effect on nephrons, and increased urination is achieved at the cost of decreased viability and even death of nephrons.
Herbal preparations containing anthraglycosides, although they increase urination and the removal of salts from the body, at the same time irritate the bladder, causing cystitis, and in men also prostatitis.
Herbs with anthraglycosides should not be used during pregnancy, hemorrhoids, or gynecological diseases. In the video about folk remedies for treating salts in the kidneys:
Traditional methods
Often, in the absence of complications, the doctor prescribes conservative treatment. In this case, herbal decoctions are used to help remove salts.
The following methods are often used:
- Lemon juice dissolved in 100 ml of boiled water.
- A mix of cucumber, carrot and beet juices. Take three times a day for two weeks.
- A decoction of herbs (St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile, horsetail) is prepared in a water bath. The liquid should be strained before use.
- Strawberry syrup, which is an excellent remedy even for children. A kilogram of strawberries is filled with a glass of sugar. After some time, the berries will give juice, which should be drunk half a glass before eating.
Treatment and diet
In the initial stages, medication and diet are prescribed. If the salts have already formed stones, surgical intervention is indicated. Medicines are selected as a complex, which includes diuretics, antibiotics, antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory (nonsteroidal) and uroseptic drugs. It is important that when stones appear, you should not drink diuretics, as the stones can move, which will cause blockage of the urinary tract.
Fortunately, now a small patient does not have to undergo surgery using a conservative method to rid him of small stones. They can be completely removed by remote lithotripsy (electromagnetic waves).
What kind of diet is needed:
- the child needs to consume less sweets (especially chocolate), meat, legumes, rhubarb, spinach, sorrel, figs, tomatoes, salt, smoked meats, cottage cheese, nuts, dried fruits;
- It is undesirable to eat too salty foods containing oxalic acid, potassium, calcium, phosphorus (in any case, you need to reduce its amount);
- in accordance with the recommendations of herbalists, the diet should include juice of carrots, cucumbers, beets, lemon (the latter - no more than 100 ml per day and only in diluted form);
- make decoctions of herbs that are useful for salts in the kidneys - milk thistle, coltsfoot, horsetail, thyme, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort (remember that the dosage for children is different from that for adults).
Prevention
As preventive measures, it is recommended to periodically diagnose the organs of the urinary system, monitor your diet and drink, work and rest schedule, and also treat infections of the excretory system organs in a timely manner.
Salt diathesis is a person’s predisposition to diseases of the urinary system. Complications lead to the development of urolithiasis, and then to surgical intervention. But by following preventive methods, the development of these diseases can be avoided.
Symptoms and signs
For some time, the pathology may be asymptomatic or be a transient phenomenon against the background of some infectious-inflammatory process (acute intestinal infection, acute tonsillitis, etc.). In most cases, excess salt excretion is detected during a routine urinalysis.
If the release of oxalates, urates or phosphates is a complication of the underlying kidney disease, then the following symptoms may appear:
- Increased blood pressure. The kidneys have a renin-angiotensin system, which also regulates the level of systemic pressure.
- The appearance of edema. Against the background of chronic pathology of the urinary system, in addition to crystals, blood cells and proteins penetrate through the glomeruli. Increased loss of protein fractions contributes to a decrease in oncotic pressure and the appearance of external edema.
- Weakness, increased fatigue, loss of appetite. Violation of the detoxification function of the kidneys leads to the development of intoxication.
If a child has excessive deposition of salt crystals in the kidneys, the urine collected for analysis will have a whitish sediment visible to the eye. Also characterized by a lack of transparency and a standard straw-yellow color.
How to treat
The key goal of therapy is to remove mineral-crystalline suspension from the kidneys and prevent repeated salt formation. With salt diathesis, special attention is paid to non-drug methods. If necessary, treatment is supplemented with medications.
Medications
When treating salt diathesis and microlithiasis in adults, medications are used that:
- normalize urine pH;
- eliminate inflammation in the urinary tract;
- stimulate kidney function;
- restore mineral metabolism;
- relieve painful sensations.
Features of therapy depend on the severity of symptoms. Typically the treatment regimen includes:
- antispasmodics (Papaverine, Drotaverine) - relax smooth muscles, thereby facilitating the removal of urine from the ureters and urethra;
- NSAIDs (Brustan, Ketorolac) – relieve inflammation, swelling of the urinary ducts and fever;
- herbal uroseptics (Canephron, Urolesan) – disinfect the mucous membrane of the urinary system, prevent bacterial complications;
- litholytics (Blemaren, Fitoren, Cyston, Fitoliton) – normalize the acid-base balance and prevent salt formation;
- diuretics (Britomar, Uriflorin) - stimulate urination and leaching of salts from the renal pelvis.
Stone-dissolving preparations are selected taking into account the composition of the mineral-crystalline suspension in the CLS.
How to remove salt from the kidneys using folk remedies
Treatment of salts in the kidneys with folk remedies allows you to achieve complete cleansing of the urinary system from microconcretions. To normalize the pH of urine and mineral metabolism, eliminate inflammation in the kidneys, the following are used:
- Sunflower. The roots of the plant are ground in a blender. 3 tbsp. l. raw materials are boiled in 1 liter of water for 4-6 minutes. Cooled and filtered broth is consumed 1 glass up to 5 times a day.
- Strawberries. 1 kg of berries are mixed with 250 g of granulated sugar. After 6-8 hours, the resulting juice is poured into a glass jar. Take 2 tbsp. l. up to 3 times a day.
- Garlic with lemon. Grind 3 large lemons in a blender. Add 150 g of chopped garlic. Pour the mixture into 1 liter of hot water and leave it in a thermos for 10-12 hours. The strained infusion is drunk 50 ml 30 minutes before meals up to 4 times a day.
No less effective are anti-inflammatory and diuretic decoctions prepared from medicinal herbs - bearberry, St. John's wort, thyme, chamomile, peppermint.
Therapeutic diet
To speed up the removal of salts from the kidneys, you need to follow a diet. Avoid foods that negatively affect metabolism and disrupt the acid-base balance of urine:
- caffeine;
- fat meat;
- figs;
- sorrel;
- alcohol;
- legumes;
- spices;
- marinades;
- canned vegetables.
With uric acid salts, limit meat products, with phosphates - dairy products, and with oxalates - leafy vegetables.
Microconcrements leave the kidneys faster if you follow the drinking regime. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2.5 liters of water per day.
In what cases is surgery necessary?
If salt crystals in the kidneys transform into stones, the effectiveness of conservative therapy is greatly reduced. It is almost impossible to dissolve mineral stones with litholytic agents. If salt diathesis develops into kidney stones, surgical treatment is resorted to.
Indications for surgery:
- urinary tract obstruction;
- hydronephrosis;
- coral stones;
- kidney block;
- secondary pyelonephritis;
- purulent inflammation.
In the absence of complications, minimally invasive techniques are prescribed - percutaneous nephrolithotripsy. In all other cases, open operations are performed:
- pyelolithotomy - dissection of the renal pelvis followed by removal of stones;
- nephrolithotomy - removal of stones by dissecting the functional tissue of the kidney.
In case of necrotization (death) of the parenchyma at the site of stone formation, a partial nephrectomy is performed - an operation to remove the damaged area of the kidney.
Diagnosis of pathology
When a patient comes with complaints to a specialist, the first thing he does is collect an anamnesis of the disease. It is important to identify existing symptoms, hereditary predisposition, and dietary habits.
The patient also receives a referral for a diagnostic examination.
Table 1 Tests and studies to detect kidney salts
| Name of examination or analysis | What is revealed in the presence of salt formations? |
| Analysis of urine | Microhematuria (red blood cells in urine); Leukocyturia (white blood cells - leukocytes); Mucus and epithelial particles; Changes in the acid-base balance of urine - with the accumulation of uric acids, it becomes more acidic, with infectious formations - alkaline. |
| General blood analysis | Not a particularly informative analysis, but in case of complications (kidney inflammation, renal colic) it shows an increased level of leukocytes. |
| Blood chemistry | Determines the level of individual components - creatinine, uric acid, urea, etc. If their quantity does not correspond to the norm, then we are most likely talking about serious disturbances in the functioning of the affected organ. |
| Ultrasonography | The method allows you to identify the accumulation of salt fractions in the calyces and renal pelvis. The advantage of the method is that it is easy to carry out, painless, and there is no radiation exposure. Minus - small, isolated formations may not be detected. |
When the doctor finds out that indeed salt deposits in the kidneys cause unpleasant symptoms and determines their nature, he prescribes mandatory treatment.