In the group of urological diseases, the proportion of urolithiasis (UCD) reaches 38-40%, and recently there has been a tendency to increase the number of female patients aged 20-50 years.
Factors such as unhealthy and monotonous food, physical inactivity, hormonal changes (for example, with frequent pregnancies) and genetic predisposition can provoke the formation of stones in the urinary system. Complex therapy of KSD, aimed at preventing renal colic and removing stones, is impossible without a high-quality nursing process.
The main tasks of the nursing process in ICD
There are two groups of patient problems:
- Clinical are characteristic symptoms of ICD that cause discomfort: painful urination, lumbar pain, malaise, nausea and weakness.
- Psychological is a lack of knowledge about the peculiarities of the course of the disease, possible complications and methods of self-help in acute conditions; Against this background, fear of surgical treatment often develops.
The priority task of nursing care is to eliminate both the clinical and psychological problems of the patient. Therefore, the general responsibilities of a nurse in the urology department include:
| 1 | Survey | · identification of previous nephrological and urological pathologies in the patient’s medical history. · Establishing information about the daily diet, quality of nutrition and amount of fluid consumed. · establishing the characteristics and frequency of the patient’s stay in the nephrology department earlier. |
| 2 | Inspection | · measurement of pulse and pressure. · "test" of tapping on the lower back. · assessment of the patient's condition as a whole. |
| 3 | Conversation | · familiarizing the patient with the clinical picture of urolithiasis, possible complications, methods of diagnosis and treatment, in particular, regimens for taking prescribed medications. · explaining to the patient and his relatives the importance of following all medical recommendations, including diet, exercise, drinking plenty of fluids and urinating in a timely manner. · convincing the patient of the effectiveness of therapy and combating fear of new methods of treating urolithiasis, such as “crushing” stones with ultrasound. · teaching the patient self-help skills in acute conditions. |
| 4 | Control | · checking food “transfers” from relatives to ensure that the provisions comply with the diet rules. · patient compliance with all medical recommendations: diet, drinking regimen, taking prescribed medications. · regular checks of general condition and biological indicators. · daily weighing to monitor the patient's fluid balance and timely detection of developing dehydration or swelling. |
| 5 | Therapy | · relief of pain attacks. · maintaining the prescribed therapeutic regimen. · notifying the attending physician about the patient’s dynamics and sudden exacerbation of urolithiasis. · performing catheterization. |
| 6 | Preparing the patient for diagnostic procedures | |
| 7 | Providing emergency assistance | |
| 8 | Filling out documentation |
Most of the time of the nursing process in ICD is spent on diagnostic and therapeutic tasks. With timely assistance, complications and further relapses can be avoided.
The concept of the nursing process (theoretical part)
The nursing process is one of the basic concepts of modern nursing models. In accordance with the requirements of the State Educational Standard for Nursing, the nursing process is a method of organizing and performing nursing care for a patient, aimed at meeting the physical, psychological, social needs of an individual, family, and society.
The goal of the nursing process is to maintain and restore the patient's independence and meet the basic needs of the body.
The nursing process requires from the nurse not only good technical training, but also a creative attitude towards patient care, the ability to work with the patient as an individual, and not as an object of manipulation. The constant presence of the nurse and her contact with the patient make the nurse the main link between the patient and the outside world.
The nursing process consists of five main stages.
1. Nursing examination
.
Collection of information about the patient’s health status, which can be subjective and objective.
The subjective method is physiological, psychological, social data about the patient; relevant environmental data. The source of information is a survey of the patient, study of medical documentation data, conversation with the doctor, and the patient’s relatives.
The objective method is a physical examination of the patient, including assessment and description of various parameters (appearance, state of consciousness, position in bed, degree of dependence on external factors, color and moisture of the skin and mucous membranes, presence of edema). The examination also includes measuring the patient's height, determining his body weight, measuring temperature, counting and assessing the number of respiratory movements, pulse, measuring and assessing blood pressure.
History taking Physical Laboratory
examination examination
The end result of this stage of the nursing process is the documentation of the information received and the creation of a nursing medical history, which is a legal protocol - a document of the independent professional activity of the nurse.
2. Identifying the patient's problems and formulating a nursing diagnosis.
The patient's problems are divided into existing and potential. Existing problems are those problems that are currently bothering the patient. Potential - those that do not yet exist, but may arise over time. Having established both types of problems, the nurse determines the factors that contribute to or cause the development of these problems, and also identifies the patient’s strengths that he can counteract the problems.
Since a patient always has several problems, the nurse must establish a system of priorities. Priorities are classified as primary and secondary. Primary priority is given to problems that are likely to have a detrimental effect on the patient in the first place.
The second stage ends with the establishment of a nursing diagnosis. A nursing diagnosis is a patient's condition established as a result of a nursing examination and requiring intervention by a nurse. The American Nurses Association, for example, identifies the following as the main health problems: limited self-care, disruption of normal functioning of the body, psychological and communication disorders, problems associated with life cycles. As nursing diagnoses, they use, for example, phrases such as “deficiency of hygiene skills and sanitary conditions”, “decreased individual ability to overcome stressful situations”, “anxiety”, etc.
Existing Potential
problems problems
Primary secondary intermediate primary secondary
3. Determining the goals of nursing care and planning nursing activities
.
The nursing care plan must include operational and tactical goals aimed at achieving specific long-term or short-term results.
When forming goals, it is necessary to take into account the action (execution), criterion (date, time, distance, expected result) and conditions (with the help of what and by whom). For example, “the goal is for the patient to get out of bed by January 5th with the help of a nurse.” Action - get out of bed, criterion January 5, condition - help from a nurse.
After determining nursing goals and objectives, the nurse develops a written nursing care manual that details the nurse's specific nursing actions to be recorded in the nursing record.
Goal Setting Patient Participation Nursing Standards
and his family practices
Written Guide
care
4. Implementation of planned actions.
This stage includes measures that the nurse takes to prevent diseases, examine, treat, and rehabilitate patients.
There are three categories of nursing interventions. The choice of category is determined by the needs of the patient.
Independent nursing intervention involves actions carried out by the nurse on her own initiative, without direct demand from the doctor. For example: teaching the patient self-care skills.
Dependent nursing interventions are performed based on physician orders and supervision. For example: preparing a patient for a diagnostic examination.
Interdependent nursing intervention involves the joint activities of the nurse with the doctor, as well as with other specialists.
In all types of interactions, the sister's responsibility is exceptionally great.
categories patient needs care methods
in helping
independent temporary
dependent constant
interdependent rehabilitative
5. Assessing the effectiveness of nursing care
.
Its purpose is to assess the patient's response to nursing care, analyze the quality of care provided, evaluate the results obtained and summarize. Evaluation of the effectiveness and quality of care should be carried out by the senior and chief nurses. The patient’s opinion about the nursing activities carried out is important at this stage. When the intended goals are not achieved, the assessment makes it possible to see the factors that hinder their achievement. Thus, evaluating the results of nursing interventions enables the nurse to identify strengths and weaknesses in his professional practice.
assessment of the nurse's actions patient's opinion or assessment of the nurse's actions
(himself) his family leader
Brief anatomical and physiological data on the structure of the kidneys
Kidneys
- a paired organ, they are located symmetrically on both sides of the spinal column and are covered with several membranes and adipose tissue. In a cross section, the kidney consists of a cortex and medulla. The medulla forms renal pyramids, which at their base are adjacent to the cortex, and the apices are facing the renal calyx.
Nephron –
The structural and functional unit of the kidney, it consists of a glomerulus and an associated tubule. In the cortical layer there are glomeruli of the renal corpuscle formed from the branched renal artery, each glomerulus is surrounded by a special capsule, between the walls of the capsule there is a cavity into which primary urine is filtered. Primary urine passes into the convoluted tubule of the first order, then into the loop of Henle, then into the convoluted tubule of the second order and ends with the collecting duct. The collecting duct carries secondary urine into the renal pelvis
The kidneys are excretory organs. They have the main function of releasing decay products and maintaining the water-salt balance of the body. Excess water and mineral salts, ammonia, urea, uric acid and some other substances formed in the body or taken with food are excreted through the kidneys. The kidneys maintain a constant blood pH, regulate the hemoglobin content in the blood, as well as blood pressure.
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are diverse, but are mainly divided into local (tuberculosis, cancer, kidney stones and pyelonephritis) and general (nephritis, nephrosis) diseases.
Kidney and urinary tract diseases
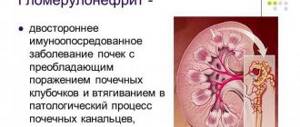
Glomerulonephritis
is an inflammatory disease of both kidneys of an infectious-allergic nature with initial and predominant damage to the glomerular apparatus of the nephron.
The most common causes of acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) are sore throat, tonsillitis, and upper respiratory tract diseases. Chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) in most cases is the result of untreated AGN. In this case, a significant role belongs to the reactivity of the microorganism, which is manifested by a hyperergic reaction and autoimmune disorders.
The clinical picture of AGN is determined by three syndromes : edematous, renal hypertension, urinary
Edema
are one of the most common signs. The localization and degree of swelling vary. The most typical appearance of swelling on the face, and especially the eyelids, is in the morning. Swelling of the lower extremities and in the sacral area is common. With severe fluid retention, swelling spreads to the external genitalia and cavitary edema appears (ascites, hydrothorax, hydropericardium), sometimes fluid retention reaches 15-20 kg.
Renal hypertension
. Typically, the rise in blood pressure corresponds to the severity of the disease; the degree of increase may vary. Typically, the systolic pressure level rises to 180 mm. rt. Art. diastolic up to 120 mm. rt. Art. A persistent and prolonged (more than 3 weeks) increase in blood pressure is prognostically unfavorable and indicates the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Hemodynamic disturbances are common
. which are based on sodium and water retention, which leads to an increase in circulating blood volume. The occurrence of hypertension in this case can lead to overload of the heart, causing expansion of its cavities and severe circulatory failure. Venous pressure can also increase with hypervolemia by 100-200 mm. RT., Art. water column and manifest itself as a sharp swelling of the veins and enlargement of the liver.
renal dysfunction is added to the above syndromes
.
Currently, the following clinical forms of CGN are distinguished: nephrotic (edematous-albuminuric), hypertensive, mixed (edematous-hypertensive), latent form.
Some researchers identify
the terminal form
of CGN (stage of chronic renal failure)
Nephrotic
the form is characterized by the presence of a large amount of protein in the urine (hyperproteinuria), a decrease in plasma protein (hypoproteinemia), hypercholesterolemia and massive edema. There is no increase in blood pressure
Hypertensive
form: arterial hypertension has been the leading syndrome for a long time, and urinary and edematous syndromes are less pronounced
Mixed form
. in this form, signs of both nephrotic and hypertensive forms are observed. It is the most severe form and quickly leads to the development of chronic renal failure.
Latent form
- the most common one. It usually manifests itself only as mild urinary syndrome. This form can have a rather long course (10-20 years) and later leads to the development of chronic renal failure.
Pyelonephritis
- inflammatory kidney disease caused by direct infection of the collecting system and renal tissue.
The immediate cause of pyelonephritis is infection of the urinary tract, pelvis, and renal parenchyma. Penetration of infection into the pelvis and kidney can occur by lymphogenous, hematogenous and ascending routes. Urinary stasis is one of the main factors contributing to infection and the development of the disease. Pyelonephritis most often occurs in waves, in the form of alternating exacerbations. Untreated or poorly treated acute pyelonephritis becomes chronic. Unlike OP, chronic often begins and goes on latently for a long time. During this period, the only manifestations of the disease may be signs of intoxication (weakness, sweating, headaches, lack of appetite and low-grade fever. The protracted course of CP can be replaced by sudden exacerbations, similar to the clinical picture of AP: the temperature suddenly rises, at the same time chills, weakness, weakness, muscle soreness appear. pain.In addition to general symptoms, local symptoms of acute inflammation also appear: lower back pain, painful and frequent urination
Chronic renal failure (CRF)
is a symptom complex caused by the irreversible gradual death of nephrons
due to primary or secondary progressive kidney disease. The first place among the causes of chronic renal failure is occupied by chronic glomerulonephritis, the second – chronic pyelonephritis.
In Russia, there are four stages of chronic renal failure: latent, compensated, intermittent and terminal stages.
In the latent stage
the patient may not complain. A biochemical blood test reveals a slight disturbance in the electrolyte composition, sometimes protein in the urine
In the compensated stage
fatigue occurs during physical activity, dry mouth, this is accompanied by an increase in the amount of urine up to 2.5 liters per day, changes are detected in biochemical blood tests and urine tests
Intermittent stage
characterized by a persistent increase in the blood products of nitrogen metabolism. The patient experiences weakness, fatigue, thirst, dry mouth, and appetite decreases sharply. The skin acquires a yellowish tint and becomes dry.
In the terminal stage
the filtration function of the kidneys drops to a minimum. The amount of urea, creatinine, and uric acid in the blood is constantly increased, and the electrolyte composition of the blood is disturbed. All this causes uremic intoxication or uremia (uremia-urine in the blood). The amount of urine excreted per day decreases until it is completely absent. Other organs are affected: cardiac muscle dystrophy, pericarditis, circulatory failure, pulmonary edema, encephalopathy, hormone production and immunity are disrupted, and changes occur in the blood coagulation system. All changes are irreversible.
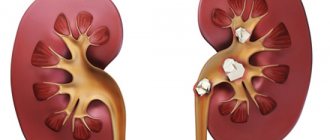
Urolithiasis disease
is a disease in which stones form in the organs of the urinary system, in most cases in the kidneys and bladder.
The main cause of the occurrence and development of urolithiasis is considered to be a metabolic disorder, which leads to the formation of insoluble salts that form stones. The number of stones and their location can be very different. Young people most often have stones in the ureters and kidneys; bladder stones are more often diagnosed in older people and children.
The main predisposing factors for the development of the disease include: anatomical malformations of the urinary tract, hereditary nephritis-like or nephrosis-like syndromes, chronic diseases of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, etc.), chronic diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, colitis, etc. .), a certain composition of food and water, etc.
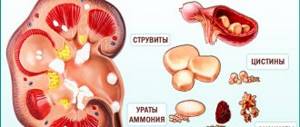
Depending on the reasons for their formation and composition, stones are divided into several types of stone formation: Uric acid (urate)
consist of uric acid salts, have a yellow-brown color, dense, with a smooth surface
Oxalate
– these stones consist of salts of oxalic acid, they are black-brown in color, dense with a rough surface on which there may be thorns
Phosphate stones
soft, gray-white, they crumble easily
Mixed stones
– the inner part of such stones is called the “core” and is formed from one type of salt, and the shell from another.
Cystine
stones are the hardest, have a smooth surface
Determining the mineral composition of stones is necessary to prevent recurrent stone formation. For patients with recurrent stone formation, after determining the causes of stone formation, a set of measures (metaphylaxis) is prescribed to prevent recurrent stone formation.
Depending on the location of the stone, the patient may complain of different symptoms, but the main ones for this disease are considered to be: paroxysmal pain (renal colic), blood in the urine, deterioration in general health
With a kidney stone, pain often occurs during physical activity, and other diseases of the genitourinary tract may worsen in patients. If the stone is in the bladder, then the patient is bothered by frequent painful urination, as well as pain that appears when moving. When a stone is located in the ureters, the patient experiences a frequent urge to urinate, pain moving from the lower back to the inner thigh, groin and lower abdomen. If a stone blocks the lumen of the ureter and urine accumulates in the kidney, renal colic begins. The patient experiences acute pain in the lower back, spreading to the abdomen. The colic continues until the stone changes its position or leaves the ureter.
Treatment of urolithiasis is carried out under the constant supervision of a doctor. Depending on the size of the stone, a medical or surgical treatment method is selected. Currently, there are many non-surgical methods that can achieve good results without surgery.
Nursing process in the nephrology department
To accurately diagnose kidney diseases, the following laboratory tests and instrumental studies
.
general blood test (detects possible inflammatory processes in the body, a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, which can happen with renal pathology)
biochemical blood test (uric acid, creatinine, cholesterol, triglycerides, chlorides, acid-base status of the blood)
general urine analysis
cellular and humoral immunity
study according to Nechiporenko or Kakovsky-Addis, Amburge (analysis according to Nechiporenko is used to determine the number of formed elements in 1 ml of urine using a counting chamber.)
blood pressure over time
urine culture for flora
ECG
according to indications: blood test for VK, atypical cells, plain radiography of the kidneys, intravenous urography, retrograde pyelography, chromocystoscopy, radioisotope radiography, scanning and biopsy of the kidneys
Based on the results of collecting anamnesis, physical examination and laboratory tests, a database about the patient is formed (nursing medical history). Since in most cases there are several health problems, the nurse cannot begin to solve them all at the same time. Therefore, to successfully resolve the patient’s problems, the nurse must consider them taking into account priorities
Once the nurse has begun to analyze the data obtained during the examination, the second stage of the nursing process begins - identifying the patient's problems and formulating a nursing diagnosis.
It should be noted that, unlike a medical diagnosis, a nursing diagnosis is aimed at identifying the body’s responses to the disease. A medical diagnosis does not change unless a medical error has been made, but a nursing diagnosis can change every day and even throughout the day as the body’s response to the disease changes; in addition, a nursing diagnosis can be the same for different medical diagnoses. For patients with kidney disease, the nurse may make the following nursing diagnosis:
swelling of varying severity
headache, dizziness, general weakness
Source: https://koledj.ru/docs/index-11833.html
Related posts:
- Situational task chronic renal failure Chronic renal failure situational tasks clinical task No. 1 CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE SITUATIONAL TASKS Clinical task No. 1 Patient M., 50 years old, was admitted with complaints of severe weakness, headaches, nausea, itching. Ill for more than 20 years, when I was diagnosed with chronic […]
- X-ray classification of nephroptosis Nephroptosis Normally, the kidneys have a certain physiological mobility: thus, with physical effort or the act of breathing, the kidneys are displaced within the permissible limit, not exceeding the height of the body of one lumbar vertebra. In the event that the downward displacement of the kidney in a vertical position of the body exceeds 2 […]
- Pelvic dystopia of the kidney in the fetus How to treat dystopia of the right and left kidney Dystopia of the kidney is a congenital developmental disorder in which a displacement of the normal location of the organ occurs. In this disease, the kidney can be located in the sternum, lower in the pelvic cavity, or in other locations. Dystopia can provoke the development of kidney diseases, as well as [...]
- Tablets for kidneys Furadonin Furadonin - instructions for use, analogues, reviews, price The drug Furadonin Furadonin is an antimicrobial synthetic medicinal agent with a wide spectrum of action. Furadonin is not an antibiotic. it belongs to the group of drugs of the nitrofuran series. For many bacteria - Klebsiella, Staphylococcus. […]
- Tactics for treating kidney stones How to get rid of kidney stones Contents Contrary to popular belief, urolithiasis is not a direct consequence of poor diet or drinking hard water. Although both factors play an important role in the occurrence of the disease. In fact, the formation of kidney stones occurs due to [...]
- Treatment regimens for pyelonephritis in children Treatment regimens for pyelonephritis download. In primary acute pyelonephritis, in most cases treatment is conservative. The patient's mode is bed. They recommend drinking plenty of fluids (juices, fruit drinks) 2 - 2.5 liters per day, foods rich in carbohydrates (puddings, light flour dishes, raw and boiled fruits, etc.), and fermented milk […]
- Scheme for the treatment of pyelonephritis in the hospital Scheme for the treatment of pyelonephritis download. In primary acute pyelonephritis, in most cases treatment is conservative. The patient's mode is bed. They recommend drinking plenty of fluids (juices, fruit drinks) 2 - 2.5 liters per day, foods rich in carbohydrates (puddings, light flour dishes, raw and boiled fruits, etc.), and fermented milk […]
- Stenting of renal vessels Causes and treatment of renal artery stenosis Atherosclerotic - makes up 70% of all renal stenoses, more often damaging the kidneys of elderly men. This type of stenosis is localized at the mouth of the renal arteries. Fibromuscular dysplasia is a less common type of stenosis that is more common in girls and women of any […]
Therapeutic nursing care
ICD has a nonspecific clinical picture, however, individual characteristics of its course are possible in the presence of concomitant pathologies and a complicated medical history. A high-quality nursing process requires the ability of staff to promptly recognize a dangerous condition of a patient and prevent it. To combat worsening symptoms, the following nursing interventions are performed:
| Blood in urine | administration of hemostatic agents recommended by the doctor: dicinone, vikasol or calcium chloride |
| Lumbar pain | · providing the patient with a warm bath or using a heating pad in the lumbar region. · intramuscular administration of an analgesic. · if the pain does not decrease within half an hour, then the nurse calls the doctor and injects the patient with an intravenous solution of promedol and sodium chloride |
| Swelling | · monitoring the patient's diet: limiting salt and liquid. · increasing the room temperature to increase the patient's sweating. · performing catheterization for poor urination. |
| Chills | · wrapping the patient and using heating pads. · control over the normal value of room temperature. |
| Heat | · use of ice. · drink plenty of fluids. · Limiting spicy and salty foods. |
| Renal colic | · administration of NSAIDs (Baralgin, Ketorolac) and antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Drotaverine). · thermal procedures: bath or heating pad. |
The patient needs to describe in detail the methods for eliminating the above symptoms, so that during further outpatient rehabilitation he can independently help himself.
Problems of patients with pathology of the urinary system
Nursing care for urolithiasis and chronic renal failure includes 5 standard stages:
- Formulating patient problems.
- Nursing diagnosis.
- Drawing up an action plan for care and treatment.
- Patient care.
- Assessment of achievement of set goals.
Patients' problems can be divided into several large groups. At the same time, the decision of each is implemented during different nursing procedures.
Pain in the lumbar region associated with the disease
Relieve the patient of pain at the time of discharge or reduce it
1. Strict implementation of doctor’s orders.
2. Provide the patient with a warm and comfortable bed and adherence to bed rest.
3. Nursing care for urolithiasis includes placing a heating pad as prescribed by a doctor and using painkillers if necessary.
4. Ensure the patient adheres to diet No. 7.
5. Tell the patient about compliance with the drinking regime and diet. If the patient does not have edema, then he can drink up to 2 liters of liquid daily.
6. The nurse should teach the patient to assume a comfortable position in bed.
7. Teach the patient to monitor the nature of the pain.
8. Teaching the patient how to relieve psycho-emotional stress and reduce pain through auto-training and relaxation.
Painful and frequent urination
Reduce pain and frequency of urination
1. Follow your doctor's recommendations.
2. Help the patient adhere to the drinking regime.
3. If there are no contraindications, increase the volume of fluid taken.
4. If necessary, warm the lower limbs and lower back with a heating pad.
5. Prepare the patient for urine testing.
6. Monitor the patient’s vital signs (respiratory rate, pulse, pressure).
7. Teaching the patient hygiene of the external genitalia and perineum.
8. Change of bed and underwear of the patient.
Risk of kidney stones
Prevent stone formation
1. Follow the doctor's instructions.
2. In the absence of contraindications, increase the amount of fluid consumed to 3 liters.
3. Following a special diet to increase the acidity of urine, this will prevent the formation of calcium stones.
If in doubt, consult a nutritionist.
4. Explain to the patient that he needs to turn over more often, at least once every 2 hours, and if necessary, he needs help.
5. Explain to the patient and his family what the chemical composition of kidney stones is and that calcium stones can form due to poor diet.
6. If the nurse detects a disturbance in the flow of urine, a doctor should be consulted.
7. Talk with the patient about a healthy lifestyle.
8. Monitor pulse, pressure, temperature and physical properties of urine.
Reduce outflows, improve water-salt metabolism
1. Give the patient diuretics prescribed by the doctor.
2. Maintain bed rest.
3. Review the patient’s diet - exclude large amounts of liquid, limit animal protein and adhere to the general rules of diets No. 7, No. 7a, No. 7b
4. Teach the patient to count the volume of fluid drunk and excreted daily and record this on a diuresis sheet.
5. If necessary, use a heating pad to warm the lower extremities and lower back.
6. Determine the presence or absence of edema daily.
7. Change the patient’s bed and underwear in a timely manner.
8. Ventilate the patient’s room daily.
Presence of fever, chills and chills
Eliminate the risks of complications and prevent overheating. For severe chills, use heating pads.
Preparing the patient for diagnostic procedures
The participation of medical staff in diagnosis is extremely important. It is necessary to have an understanding of all the features of laboratory and instrumental examinations. The responsibilities of nurses include preparing the patient for procedures and directly collecting tests. The reliability of the results and diagnosis depends on the quality of the nursing process. Most often, with ICD, the patient is prepared for the following procedures:
- Urine collection - the patient needs to stop using diuretics and foods that can change the pigmentation of urine (carrots, beets). It is necessary to perform a morning toilet of the genitals. After passing a small amount of urine for a couple of seconds, you need to collect 50 ml of urine in a sterile container.
- Ultrasound – 3 days before the procedure, foods that cause flatulence should be excluded from the diet and enterosorbents should be taken. The day before, a light dinner and colon cleansing with an enema are recommended.
- Urography – a biochemical blood test is first performed to narrow the range of possible diagnoses. 2 days before the examination, the same diet is indicated as during the ultrasound, and 3 hours before the examination you need to refuse food. The patient should remove metal objects and inform the doctor about the medications he has recently taken, allergies to iodine, and the presence of metal crowns or dentures.
Survey
Nursing care for urolithiasis includes a general nursing examination, which is based on clinical examination methods.
The survey consists of several parts:
1. Questioning and medical history:
- entering basic patient data into the documentation;
- studying patient complaints;
- interviewing the patient about the symptoms of the disease and his life history.
2. Objective examination:
- examination of the patient;
- percussion;
- palpation;
- auscultation;
- definition of Pasternatsky's symptom;
- measurement of pulse, pressure, temperature, respiratory rate.
Standard Operating Procedures in the Chief Nurse's folder. In the Library of SOPs in the magazine “Chief Nurse” you will find ready-made and practice-tested samples.
When diagnosing urolithiasis, attention should be paid to some features of the course of this disease:
- patients often complain of fever, headache, swelling, pain, and urinary problems;
- attention should be focused on previous infections - scarlet fever, gonorrhea, syphilis, influenza, tuberculosis, etc.;
- non-infectious causes of the disease include diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, rheumatic diseases, etc.;
- the onset of the disease may be due to reasons such as poisoning with drugs or certain substances, pregnancy, hypothermia;
- instrumental studies of the urinary tract, chronic nasopharyngeal infection.
The nursing process for urolithiasis begins with a detailed examination. During this test, the nurse can identify external signs of damage to the kidneys or bladder.
What to pay attention to:
- position of the patient in bed. During an attack of renal colic, the patient is forced to constantly change his position;
- with renal eclampsia and nephropathy, convulsions may occur in pregnant women;
- palpation can only detect a significant enlargement of the kidney, and the kidneys are also accessible to palpation when they are shifted or enlarged;
- palpation of the ureteral points gives the nurse information about the presence of an inflammatory process;
- for paranephritis and other kidney diseases, the method of tapping the lower back shows a positive result;
- Using percussion, the size of the bladder is determined - when it enlarges, a dull sound appears in the suprapubic region.
You will have time to download everything you need using demo access in 3 days
?
Nursing care for urolithiasis or urolithiasis.
Urolithiasis is detected at any age, more often at 30-35 years old, men are more often affected, stones are localized in the right kidney, less often in the left, bilateral stones in 15-30% of cases.
According to the chemical composition of the stones: oxalates, phosphates, urates.
Stones can be single or multiple, from 0.1 to 15 ml or more, weighing from fractions of a gram to 2.5 kg or more, sometimes stones are performed as a cast by the CLS - these are coral stones, ureteral stones are displaced kidney stones.
1. Changes in the urinary tract (congenital anomalies, dyskinesia and inflammatory processes, trauma, foreign bodies, obstruction, etc.).
2. Functional disorders of the liver and gastrointestinal tract (hepatitis, gastritis, colitis #8230; etc.).
3. Disease of the endocrine gland (hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, pituitary gland disease).
4. Infection of the urinary and genital organs.
5. Metabolic disorders (idiopathic, hypercalcemia, impaired vascular permeability).
6. Diseases that require long-term care and rest (bone fractures, chronic diseases of internal organs, diseases of the nervous system).
Caring for a patient with urolithiasis
For this disease, according to the attending physician, radiography is required. You can order an x-ray at home by calling +7-495-22-555-6-8. The total cost (price) of x-ray services at home in Moscow for May of the year is 5,000 rubles
Urolithiasis is a disease in which urinary stones form in the kidneys and urinary tract from urinary salts, which cause pain, bleeding, impaired urine outflow and an infectious and inflammatory process.
According to the chemical composition of stones, they are classified as oxalates, phosphates, urates, etc.
Most often, stones consist of calcium salts
Promote stone formation:
- heredity;
- features of metabolic processes in the body;
- geographical and climatic conditions;
- stagnation of urine;
- urinary tract infection.
The course of the disease consists of an attack and the interictal period. An attack of urolithiasis - renal colic - develops when there is a sudden occurrence of an obstacle to the outflow of urine from the kidneys.
An attack of ICD can be triggered by:
- exercise stress;
- bumpy ride;
- drinking plenty of fluids.
The main symptom of an attack of renal colic is severe pain, which is localized in the lumbar region and can spread along the ureter towards the bladder, as well as to the groin, thigh, and hypochondrium. The pain can be so intense that loss of consciousness is possible. The patient rushes about in search of a relief position. The skin becomes pale and covered with cold, sticky sweat. There is a frequent urge to urinate, and blood may appear in the urine. Sometimes reflex nausea, vomiting, and increased body temperature occur.
Help during an attack
- put the patient to bed, apply hot heating pads to the lower back;
- if possible, place the patient in a hot bath;
- do not leave the patient unattended, because may faint;
- give cystenal (drops containing tincture of madder root, magnesium salicylate and essential oils), which has anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects - 20 drops per piece of sugar;
- call a doctor.
After the stone passes, renal colic may stop on its own.
Principles of treatment for urolithiasis
- drinking regime;
- restrictive diet;
- herbal medicine (herbal treatment);
- fight against urinary tract infection;
- lithotripsy (crushing stones using ultrasonic waves);
- surgical removal of stones.
Advice for patients with urolithiasis
- it is necessary to find out the basic chemical composition of the stones (determined by the appearance of the stones or by an increased amount of certain salts in a biochemical urine test) and the acidity of the urine (determined in a general urine test), because the choice of mineral water and diet depend on this;
- follow the correct drinking regime - you need to take 2-3 liters of liquid per day (mineral water, compote, fruit juice, juices, decoctions of medicinal herbs, watermelons);
- follow a diet limiting foods containing those salts from which stones form in you;
- do not delay visiting the toilet when you have the urge to urinate - do not allow urine to stagnate;
- avoid hypothermia;
- Get prompt treatment if signs of a urinary tract infection appear.
We treat the liver
Warehouse relocation to Europe. We sell hepatitis C drugs in Russia at the purchase price - warehouse liquidation Go to website
Nursing process for urolithiasis. Urolithiasis (nephrolithiasis) is a metabolic disease characterized by the formation of stones in the urinary system. Stone formation is a complex physicochemical process, which is based on colloidal imbalance, oversaturation of urine with salts, and changes in the reaction of urine, which prevents the dissolution of salts. A monotonous diet can contribute to a change in the reaction: plant and dairy foods contribute to the alkalization of urine, and meat oxidation. Risk factors: Low fluid intake. Urinary tract infection. Urodynamic disturbances: - rare emptying of the bladder; nephroptosis; - prostate diseases; - developmental anomalies of the urinary system: - pregnancy. Geographical factors: — air temperature and humidity; — the nature of the soil; — composition of drinking water and its saturation with mineral salts. Hypovitaminosis A and D. Urinary stones can be of very different composition: oxalates, phosphates, urates, calcium stones, etc. They can be single or multiple, ranging in size from 0.1 to 10-15 cm. Stones that fill the entire collecting system, like a cast, are called coral-shaped. Clinical manifestations of urolithiasis depend on the size of the stone, its shape, location, and the degree of disturbance in the passage of urine. Large, coral-shaped stones are characterized by dull pain in the lumbar region. The most mobile stones of the pelvis, as well as stones of the ureter, cause attacks of acute pain of renal colic. The causes of renal colic can be: - physical overexertion: - fast walking, bumpy driving; - plenty of fluid intake. An attack of renal colic due to urolithiasis begins suddenly. The main symptom is intense cutting pain in the lumbar region, spreading to the entire corresponding half of the abdomen, radiating to the groin, thigh, external genitalia, sacrum, and anus. The pain can last for several hours or even days, periodically subsiding. Renal colic is accompanied by frequent and painful urination, oliguria, and sometimes reflex nausea and vomiting are observed. After an attack of colic, hematuria (often gross hematuria) is almost always observed. Patients constantly change position in bed, rush around, trying to find a position that would ease the pain, and moan. The skin is pale and covered with sweat. On palpation, sharp pain and tension in the abdominal muscles in the area of the projection of the kidneys, tension in the muscles of the lumbar region. The symptom of tapping on the lower back is sharply positive. The pain can be of such intensity that fainting or collapse may develop.
Nursing process for urolithiasis: Patient problems : A. Existing (present): Pain in the lumbar region. Frequent and painful urination. Nausea, vomiting, weakness. Sweating. Lack of knowledge about self-help for renal colic. Lack of information about the essence of the disease, the causes of urolithiasis and the causes of renal colic. The need to constantly diet. Fear of possible surgical treatment. B. Potential: Risk of developing fainting, collapse. Acute and chronic pyelonephritis. Hydronephrosis. Symptomatic hypertension. Chronic renal failure. Collection of information during the initial examination : A. Questioning the patient about: - place of birth and residence; — past diseases (pyelonephritis, prostate diseases, nephroptosis, abnormalities of the urinary system); — features of nutrition and fluid intake; — composition of drinking water; - frequency of bladder emptying; presence of the disease in close relatives; - the frequency of attacks of renal colic and the reasons that cause it; — observation by a urologist and previous treatment; - patient complaints at the time of examination. B. Examination of the patient: - position in bed; - skin color; — measurement of pulse and blood pressure; - definition of the symptom of tapping on the lower back. Nursing interventions, including work with the patient's family : 1. Conduct a conversation with the patient and his relatives about the need to strictly follow the diet prescribed by the doctor, explaining its content. about diet and drinking regimen (drink up to 2-3 liters of liquid per day), about physical activity, and the regularity of emptying the bladder. 2. Ensure that patient deliveries are checked. 3. Provide first aid during an attack of renal colic. 4. Monitor: — the patient’s compliance with the regimen prescribed by the doctor; - diet; - pulse and blood pressure; - the amount of liquid drunk per day; - daily diuresis; urine color; - taking medications. 5. Teach the patient self-help during an attack of renal colic. 6. Inform the patient about medications prescribed by the doctor (dose, rules of administration, side effects, tolerability). 7. Prepare the patient for urine tests, kidney ultrasound, urography, cystoscopy. 8. Train the patient in preparation for additional examination methods. First aid for an attack of renal colic : Call a doctor. Apply a heating pad to the lumbar region or place the patient in a hot bath if there are no contraindications. Due to the possibility of fainting, the patient should not be left alone in the bath. Give the patient 20-25 drops of cystenal or 1 tablet of no-shpa. Prepare medications: No-shpa, papaverine, platifillin, baralgin, analgin, promedol, novocaine, all drugs in ampoules. Preparing the patient for additional research methods Intravenous urography. 1. Inform the patient about the upcoming procedure and the progress of its implementation. 2. Obtain patient consent. 3. 3 days before the test, exclude gas-forming products. 4. For flatulence, as prescribed by a doctor, take activated charcoal or chamomile infusion 2 times a day. 5. Ensure that you take a laxative as prescribed by your doctor the day before lunch. 6. The night before, have a light dinner no later than 7 p.m. 7. Limit fluid intake from the second half of the day before the test. 8. The day before, at about 10 p.m., give cleansing enemas to “conditionally clean” water and in the morning 1.5-2 hours before the test. 9. Do not take food, take medications, do not smoke, do not give injections in the morning before the study. 10. Empty the bladder immediately before the examination. Cystoscopy. 1. Inform the patient about the upcoming procedure and the progress of its implementation. 2. Obtain patient consent. 3. Empty the bladder and wash thoroughly before the examination.
You might be interested in:
We recommend reading:
Source: sestrinskoe-delo.ru