General information about the disease
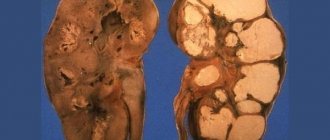
This disease is an inflammatory process in the renal glomeruli. The pathology is provoked by the appearance of an autoimmune reaction in the patient’s body.
That is, the production of inflammatory complexes occurs, the action of which is directed against the kidney tissue, which leads to necrosis of the organ structures and their sclerosis. This process threatens with a serious complication - renal failure.
Glomerulonephritis can occur with increased blood pressure, swelling (up to anasarca), and large loss of protein. Symptoms can be combined with each other, and the pathology sometimes occurs secretly.
The disease can become chronic. This happens when the recommendations of specialists are not followed and the acute form is inadequately treated.
Priority problems of the patient in acute glomerulonephritis
Most often, the patient feels weak and unwell during illness. Over time, performance and appetite decrease. Fatigue increases. Fever may develop, accompanied by hot flashes.
Are they recruited into the army with acute glomerulonephritis?
If you are diagnosed with this disease, you will be able to avoid being drafted into the army. If, after your recovery, tests show that pathological changes persist in your urine, then you will be unfit for military service. A conclusion about your fitness category is made after a re-examination. In the absence of renal dysfunction, it will not be possible to avoid conscription into the army.
Structure of the nursing process and patient care
A nurse, like a doctor, must know the patient’s diagnosis, study his medical history, and have an idea of the person’s complaints and general condition. Mid-level hospital staff are in contact with both the department’s doctors and the patient’s relatives.
Upon admission and stay of the patient, the nurse monitors his condition daily, interviews him in order to identify new symptoms of the disease and assess the dynamics of existing complaints. An employee of the institution can carry out the following procedures:
- assessment of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- measurement of blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature;
- conducting an examination for the presence of edema;
- monitoring the patient’s mental state;
- measurement of height and body weight;
- conducting a survey for the presence of some characteristic symptoms of kidney disease (in addition to edema) - pain in the lumbar spine, the nature of urination, the appearance of dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting), level of weakness.
In addition, nursing staff prepares the patient for the upcoming examination methods, informs the person about the features and progress of the proposed procedure, and provides full information on all questions that arise, including from the patient’s relatives.
The patient must undergo the following examinations upon admission to the hospital for treatment of glomerulonephritis:
- complete blood count and urinalysis;
- biochemical blood test;
- analysis to assess the immunological status of the body;
- determination of daily diuresis;
- testing for the presence of pathogens and their sensitivity to drugs;
- electrocardiography;
- if necessary, radiography of the urinary organs (with contrast) and chest, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
The results obtained are entered into the medical history by the nurse for further analysis by the doctor and determination of patient management tactics and correction of the therapy.
It is important to note that the patient can approach the nursing staff if their health worsens to conduct an examination and call a doctor (if necessary).
At the end of the working day, the nurse reviews the medical history, makes recommendations for treatment and necessary examinations, thereby forming a program of action for each person for the coming day.
Afterwards, during the evening and at night, patients are monitored by nurses on duty, who, first of all, resolve issues related to emergency care.
Nursing process for glomerulonephritis: structure and implementation – About the Kidneys
Diseases of the urinary system often lead to disability. Although the nurse does not prescribe a treatment regimen on her own, her role is very important.
The professionalism of nurses in pediatrics is especially important, because glomerulonephritis also occurs in children of different ages.
Since the nurse is constantly near the patient, she must have the necessary skills to care for patients in the nephrology department.
Assessment of the patient's condition and first aid
Glomerulonephritis is an infectious kidney disease that occurs primarily due to hemolytic staphylococcus A. As a rule, before the development of glomerulonephritis, a person suffers from acute tonsillitis, scarlet fever, or skin diseases of an infectious nature.
The activities of personnel, in particular nursing care for glomerulonephritis, are divided into several stages:
- Examination and collection of general data about the patient and the nuances of the disease, assessment of physical and mental condition.
- Determination of patient problems associated with manifestations of glomerulonephritis.
- Planning a set of procedures necessary for the patient, timing and methods of their implementation.
- Implementation of planned actions (according to the doctor’s prescriptions or together with him).
- Assessing the patient's response to help, analyzing the quality of care provided.
When starting to work with a patient, the nurse questions him about complaints. Manifestations of glomerulonephritis that may bother a person and should be taken into account by the nurse:
- severity of edema syndrome;
- intensity of pain in the lumbar region;
- attacks of arterial hypertension;
- weakness or fatigue;
- nausea, vomiting.
Actions of the nurse to assist the patient:
- For pain in the lumbar region that occurs at rest or during movement, the nurse must first reassure the patient. Then the patient applies a warm heating pad to the source of pain. If the hospital has the opportunity, the patient is offered to take a bath. To relieve severe pain, it is allowed to administer intravenously:
- 2-4 ml of Papaverine in combination with Baralgin;
2-4 ml of No-shpa in combination with Analgin.
If there is no response to the measures taken, the patient must be taken to a surgeon for examination.
- provide dietary table No. 7;
control the transfer of food to the patient from his relatives, who must be informed about the purpose of dietary nutrition and the necessary limitation of salt in prepared foods;
- place a heating pad at the location of the bladder;
offer a warm boat;
Knowledge of nursing helps nurses quickly and effectively alleviate the mental and physiological condition of patients with glomerulonephritis.
Help in properly preparing for tests
A patient with glomerulonephritis spends several weeks in a hospital setting. Every day during the treatment period, patients undergo mandatory examinations and tests.
After studying the medical history, the nursing process for glomerulonephritis is to inform the patient about how to properly prepare for collecting urine, blood, and other procedures.
The list of mandatory tests includes:
- general urine analysis;
- 24-hour urine test for sugar levels;
- control of blood pressure dynamics;
- immunological studies;
- general and biochemical blood test (important for determining the level of leukocytes, hemoglobin, as well as for monitoring creatinine, uric acid, cholesterol, chlorides, triglycerides, acid-base balance);
- ECG;
- bacteriological culture of urine for flora analysis;
- determination of potassium, sodium, calcium indicators;
- coagulogram;
- radiography of the kidneys.
Before ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys, the nurse must tell the patient how to properly prepare for the test:
- Before an ultrasound scan, the patient should eat diet table No. 4 to avoid increased gas formation: the intestinal loops are located in front of the kidneys, and due to bloating, the study will give a false result.
- The last meal should take place 8-12 hours before the examination.
- On the eve of the ultrasound, the nurse is obliged to monitor the decrease in the volume of fluid the patient drinks, and also give the patient a laxative or activated charcoal.
- If there are difficulties with emptying, the nurse can give a cleansing enema.
- The nurse must make sure that the patient understands the information about the rules of preparation before diagnosis and understands the responsibility for violating them.
Another important test for glomerulonephritis is urine collection. The responsibilities of a nurse include:
- Before the analysis, make sure that the patient does not take diuretics (they distort the results of the analysis);
- Explain to the patient how to properly sign and prepare a container for urine collection;
- explain the algorithm of actions if urine collection occurs several times a day;
- check that the procedure is carried out correctly.
The duties of the medical staff also include such diagnostic procedures as daily measurement of blood pressure, determination of the patient’s daily urine output and water balance.
Ensuring comfortable conditions in the hospital
A well-constructed nursing process for acute glomerulonephritis contributes to the patient’s adaptation to hospital conditions. Medical staff provides the most gentle treatment for the body and restoration of kidney function.
Nurses must comply with the following instructions:
- The room must be ventilated twice a day;
- wet cleaning is carried out at least 3 times a day;
- it is necessary to monitor the condition of the vessel into which the patient defecates;
- it is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of bed linen (especially in patients who suffer from urinary incontinence);
- it is important to provide conditions for proper day and night sleep, to maintain silence in the department;
- the patient must be taught to note changes in pulse, swelling, and blood pressure;
- it is necessary to explain to the patient about measures to prevent relapse of glomerulonephritis.
It is important to follow a diet during therapy.
The nurse is obliged to control the food that the catering department prepares.
Features of the diet for patients with acute glomerulonephritis:
- the main rule is fluid restriction;
- salt is completely excluded in the first days of treatment;
- a few days after the start of therapy, the patient is allowed a volume of fluid up to 1.5 per day;
- patients are allowed to eat steamed and boiled dishes;
- consumption of vegetables, fruits, cereals is recommended;
- After a certain time, the patient is given some added salt to ready-made meals (3-5 g per day).
Medical personnel must have the skills to provide emergency care for complications. A patient with glomerulonephritis may sometimes develop acute renal failure. If symptoms occur, the patient is provided with medical care, and the diet is immediately changed: proteins are completely eliminated.
For other complications of glomerulonephritis (acute left ventricular failure, renal encephalopathy), patients are advised to rest completely. The nurse should ensure that the patient is in a semi-sitting position. According to the indications of the attending physician, it is possible to take Nitroglycerin, Promedol, and heart medications.
If the disease develops into chronic renal failure, the patient must be taken to a department equipped with a hemodialysis machine.
Important! At the slightest deterioration in the patient’s condition, the nurse must reassure the patient, call the doctor and alleviate the patient’s condition until the specialist arrives.
Symptoms that determine the characteristics of care
The characteristics of patient care are influenced by a large number of factors: age, gender, personal characteristics and the psychological state of the person. The stage and form of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies also matter.
In the inpatient department, when treating glomerulonephritis, the nurse needs to pay attention to the severity of pain, body temperature, blood pressure, the presence of edema, headaches, and the amount of urine excreted.
An objective assessment of these symptoms helps to create a complete picture of the course of the disease, which is important for the correct management of the patient and his full recovery.
Nursing care for various symptoms
Complications. Care for complications has its own nuances. When acute renal failure is detected, strict control of water balance, protein-free nutrition, alkalization of the body, forced diuresis, hemosorption, and peritoneal dialysis are required. If renal encephalopathy is detected, care includes ensuring complete rest, forced diuresis, monitoring the intake of Eufillin, administration of glucose, for convulsions - Relanium, Seduxen, for hypertension - Pentamin.
Acute left gastric failure requires complete rest in a sitting position; therefore, nitroglycerin, promedol, and cardiac glycosides are prescribed; forced diuresis.
Patients with chronic glomerulonephritis are examined and treated in an inpatient setting. The principles of observation and treatment are the same as for the acute form of the disease. If the disease progresses to the stage of chronic renal failure, patients are sent to a hospital where hemodialysis is possible. There, care is carried out taking into account these features.
Edema. The goal is to gradually reduce swelling and normalize body weight.
Activity:
- the relatives and the patient are explained the need to follow a diet with table No. 7a (with a small amount of salt, proteins, potassium);
- transmission check is ensured;
- skin care, care and disinfection of mucous membranes;
- daily monitoring of water balance;
- control over the regime of physiological functions;
- providing a heating pad to warm the bed;
- daily patient weighing;
- monitoring the intake of medications prescribed by a doctor.
Lumbar pain. Help is provided only after diagnosis by a doctor. Care includes the following activities:
- a heating pad is applied to the lumbar region;
- antispasmodics are administered intravenously, non-narcotic analgesics are administered intramuscularly or intravenously;
- the patient is reassured, after which his blood pressure is measured;
- together with the doctor and according to his prescription, a narcotic analgesic is administered intravenously if the pain does not stop;
- If there is a suspicion of acute pathology, analgesics are not administered, but a surgeon is consulted.
Renal colic. The nurse should be ready to help the patient with intense lower back pain, nausea, vomiting, chills, and dysuric disorders.
Her primary actions are: call a doctor, position the patient comfortably, ensure peace, and warm the lower back. Cardiovascular equipment should be available at the ready, as fainting is possible with colic.
Dysuric disorders. Painful urination and increased frequency are associated with an inflammatory process (cystitis, urethritis). It also appears with prostatitis, the passage of stones through the urinary tract. Acute urinary retention may also occur: the patient is unable to urinate with a full bladder.
The nursing process for glomerulonephritis and care in such cases consists of the following:
- reflex call to urinate - apply a warm bedpan, heating pad to the bladder, etc.;
- calling a doctor;
- preparing containers for collecting urine, a sterile catheter, a warm antiseptic solution for washing;
- washing the patient;
- catheterization with a soft catheter.
Source: aurolog.ru
Taking tests
The nursing staff prepares the patient on the eve of various examinations. The nurse informs the person about the procedure and the recommendations that must be followed. It is important to mention that ignoring the latter will distort the results, which will negatively affect further treatment.
It is necessary to monitor the patient’s diet, monitor the intake of prescribed medications, or, conversely, eliminate medications that may interfere with the study.
If necessary, a cleansing enema is performed and daily urine is collected in special containers. The specifics of preparation depend on the study itself.
Components and planning
The nurse must provide a protective regime for the patient, which is aimed at resting him during the period of illness. It is important to ensure that the patient remains in bed for a certain period, takes medications, and does not consume harmful foods. A patient with glomerulonephritis should have proper rest, especially at night.
The nursing staff monitors the general condition of the person (including hygienic), analyzes his complaints, prevents complications, and carries out all the doctor’s instructions.
Basic principles of dietary nutrition for glomerulonephritis
The most important condition for your rapid recovery is to eliminate alcohol from your diet. Ideally - forever. It is a powerful poison for the kidneys, and it makes no difference whether you drink expensive or cheap alcohol. The following products will have to be avoided or limited during treatment:
The diet for glomerulonephritis involves eating natural foods in fractional portions on an hourly schedule. You can't skip meals. Overeating or fasting is also prohibited. Make sure that the time interval between each meal is equal. Your housing complex should work in a relaxed manner.
As for protein products, it is allowed to consume low-fat meats, fish, and seafood in small quantities. Include fermented milk products and cottage cheese in your diet, even if you don’t like them. They improve intestinal function and have adsorptive and antitoxic properties, which is very helpful for kidney diseases. But regular whole milk should not be consumed. It creates a good environment for the proliferation of microbes in the body.
Of all the variety of cereals, you can only eat rice, but only if the form of the disease allows its consumption. Pasta is allowed in very small quantities. Vegetable, unrefined oils are not prohibited, but their consumption should not be excessive. You can eat fruits and vegetables, but you should avoid those rich in potassium. With glomerulonephritis, there is an excess of this element in the body, so it is better not to force the development of hyperkalemia by taking foods rich in this element. Berries with glomerulonephritis can be eaten unlimitedly.
Implementation of care
Care differs slightly depending on the form of glomerulonephritis. The approach to the patient is always individual, taking into account the clinical picture and course of the pathology.
For acute glomerulonephritis
This form of the disease requires mandatory hospitalization with bed rest.
Mid-level medical personnel need to monitor the level of diuresis, water-alkaline balance of the body, ensure the exclusion of protein-containing foods from the diet, monitor the amount of fluid drunk, and also ensure that the person does not become hypothermic.
As soon as the patient is admitted, the nurse places him in the ward, conducts an examination and carries out the doctor’s orders. In acute glomerulonephritis, there is a risk of serious complications - renal and heart failure, encephalopathy.
When they appear, particularly careful monitoring of the patients’ condition is required with the joint participation of department doctors.
In case of chronic manifestation
Chronic glomerulonephritis is characterized by a course in which exacerbations and remissions of the pathology occur. There are several types: with increased blood pressure, the appearance of swelling and a combination of these symptoms.
In case of exacerbation of chronic glomerulonephritis, hospitalization is carried out in a hospital, during which the process of nursing care is no different from that in the acute form. It is important to note that the exacerbation may not be so severe and it is possible to manage treatment on an outpatient basis.
In chronic glomerulonephritis, the course of the disease depends on the patient. If you follow the recommendations on nutrition, lifestyle and take the necessary medications, the risk of exacerbations is minimal.
In case of illness in children
Nursing care in pediatrics has its own characteristics. The staff has to take into account that the child experiences severe stress while in the hospital without his parents.
The latter also have to be contacted in order to obtain consent to the manipulation behavior and inform adults about the dynamics of their child’s treatment and his general condition.
It is important for the nurse to provide comfortable conditions for children and provide psychological support. These activities are carried out in addition to those listed above.
When treating a child, it is especially important to observe ethics; it is necessary to organize useful pastime (reading, drawing, board games) and school lessons.
Components of nursing care
Patients with an acute form of the disease must be hospitalized. Strict bed rest is prescribed, hypothermia is excluded. Full recovery occurs within a few weeks with proper care and treatment. For chronic glomerulonephritis, patients are treated inpatiently during the period of exacerbation.
Care provided by a nurse includes the following items:
- control of bed rest, semi-bed rest, diet, prescribed treatment;
- ensuring rest, sleep, limiting physical activity;
- monitoring edema, diuresis, blood pressure, pulse;
- teaching the patient to monitor his condition, blood pressure, pulse, diuresis;
- informing about prevention methods to prevent exacerbation of the disease;
- identification of chronic infectious foci, diseases, their sanitation, treatment;
- actions to prevent complications, identifying their first signs.
Diet therapy is determined. In the first days, only a small amount of water with jam, juices, cranberry juice, a small amount of semolina porridge, and milk are allowed. Salt is excluded from the diet. Fluid intake is reduced. Subsequently, a diet with a small amount of salt is prescribed. The patient is prescribed to drink no more fluid than urine output (about 1500 ml per day).
If there are foci of infection, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. In acute nephrotic syndrome, the use of steroid hormones and diuretics is allowed. For hypertensive syndrome, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed, as well as antihistamine therapy and vitamin C in large doses.
If treatment is ineffective, cytostatics and anticoagulants are prescribed; for hematuria, aminocaproic acid is prescribed.
The nurse should listen to the patient, pay attention to pain, discomfort in the lumbar region, changes in the color of urine, and urination problems. The patient is examined, and special attention is paid to color, moisture, skin condition, and swelling. One of the purposes of the examination is also to identify the body's response to the disease.
When providing care, medical staff must monitor the state of the cardiovascular system, diuresis, provide assistance with nausea and vomiting, provide hygienic care, and monitor adherence to the regimen and diet. And also regularly measure blood pressure, daily diuresis, and determine the level of water balance.
Care before examinations and tests
Nursing responsibilities include preparing the patient for various types of tests. The nurse should know about the methods and process of instrumental and laboratory examinations.
One of the examinations is an x-ray examination. Its purpose is to diagnose kidney diseases.
The nurse should:
- Teach the patient how to prepare for the study.
- Make sure that the patient has assimilated and remembered the information, ask to repeat it, and give written instructions.
- Warn about the consequences of violating recommendations.
- Make sure you exclude gas-forming foods from your diet a few days before the test. The kidneys are located retroperitoneally, so failure to properly cleanse the intestines gives distorted results.
- Monitor compliance with dietary table No. 4, slag-free. The diet will ensure the prevention of intestinal bloating: its loops are located in front of the kidneys, and bloating interferes with obtaining reliable research results.
- Ensure that you take activated charcoal and laxatives as prescribed by your doctor; Limit fluid intake on the eve of the procedure.
- Make sure that the patient does not eat 18–20 hours before the test procedure.
- Give cleansing enemas.
- To collect urine while caring for a patient, before submitting it for analysis, the nurse must do the following:
- explain the importance of maintaining the usual water-salt, motor regimen, exclude the use of diuretics, as they distort diuresis;
- teach the patient the rules for preparing and signing containers;
- explain that urine collection will take place throughout the day;
- control the execution of the procedure. Keep records of water balance;
- Provide the patient with written instructions when necessary.