What is nephrectomy and what are its consequences?
The procedure that involves removing a kidney as a result of medical intervention is called “nephrectomy.” It is carried out in serious cases, for example, with:
— organ oncology;
- renal dysfunction due to illness;
— life-threatening anomalies of kidney development;
- polycystic disease - a congenital problem when there is a cyst in the kidney;
- complex organ damage due to a fall, accident, accident.
In addition, the operation in question helps save the life of someone in need of an organ. The donor and the patient must give their consent to the nephrectomy.
Whatever the problem, rehabilitation after surgery can last 12-18 months. During this period, a person operated on with one kidney must:
- stick to a diet;
- do light physical exercise;
- do not lift heavy objects (more than 3 kg);
— carry out sanitary and hygienic procedures;
- do not overheat or overcool;
- do not smoke, do not drink alcohol.
It is very important during recovery to periodically undergo tests and be observed by a specialist. Moreover, after the operation there is a risk of deterioration of the general condition, complications and problems with other organs.
As soon as the rehabilitation period is completed, the attending physician will assess the condition of the person with one kidney and, if necessary, refer him to MSE (for example, if health is not normal, etc.).
Classification of the disease
Symptoms of chronic renal failure largely depend on the type of disease.
The disease requires immediate medical intervention. Self-therapy will only hasten death.
Chronic renal failure is treated by a nephrologist. Treatment tactics depend on the severity of the disease.
Medicines for chronic renal failure are used at any stage of development of the pathology in order to treat the disease that led to the problem, relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life.
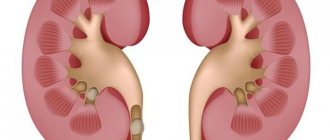
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney or right kidney is observed in equal frequency, and bilateral development is much less common, in only 10% of cases.
Even unilateral hydronephrosis is fraught with many dangers for the patient. Stagnation of urine in the kidneys can cause a bacterial infection, which develops as acute pyelonephritis. and then it can develop into a purulent abscess. The second danger of hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys is atrophic changes in the parenchyma and subsequent death of the organ. The entire load falls on the healthy kidney, which has a bad effect on the general condition of a person and his performance.
Is disability given after kidney removal?
After nephrectomy, the current condition of the person undergoing the operation plays a key role. If you are feeling well and your indicators are not critical, you should not count on the group. Special status is given only if appropriate grounds for this are identified.
What are the grounds for establishing disability?
A patient without one kidney may be given a disability group if:
— postoperative prognosis is unfavorable;
— there is no improvement and the overall condition after the manipulation is severe;
- problems in the urinary system due to disease of the second kidney - for example, they found a cyst, cancer, abscess, kidney failure;
- a person’s sudden need for help due to a decrease in his self-care skills.
If the attending physician identifies any of the listed reasons, he will send the patient for testing. For example, you will need to donate urine, blood, and also obtain data from the Rehberg test, ultrasound, urography, etc.
Which group can be assigned
The specific group is determined based on the results of the examination. The decision is made by members of the ITU commission based on the provisions of Government Resolution No. 95. Taking into account the observed criteria, the subject can be assigned one of three groups, each of which has its own nuances and privileges. In particular:
— 3 group
is prescribed for a year or two if a person with one kidney has moderate health limitations. Or, if the patient requires a period of wound healing after surgery, he has hard work.
— 2nd group
They are also given for a period of one to two years against the backdrop of unoptimistic forecasts and low chances of recovery, when there are persistent restrictions. Often this category is assigned if kidney failure, pyelonephritis, oncology, etc. are diagnosed.
— 1 group
rarely and for a couple of years (most often) they are left with severe health limitations, obvious problems with self-care and the inability to cope without outside help.
What documents are needed?
The applicant for the group must prepare:
— referral to ITU;
— application for examination form 088/у-06;
— passport and copy (or other ID);
— SNILS;
— a copy of the work book certified by a personnel employee;
— a document from the place of work about the nature of work and working conditions;
— characteristics from the place of education (for students);
— copies with originals of examination data, medical reports, etc., as confirmation of the progress of health problems;
— IPRA and the previous conclusion of the ITU (if the medical commission is not the first).
Passing the ITU
The collected documents are submitted to the ITU regional office. About a month later, on the appointed day, the patient comes for examination.
The commission consists of three specialists. Also, each of the parties has the opportunity to invite an independent doctor, who is vested with the same powers within the process as ITU members (asks questions, takes part in meetings, etc.).
Since 2020, according to the law, it is possible to be examined in absentia on the basis of documents. This preference applies to persons who find it difficult to get to the office (the locality is not suitable) or are diagnosed with a disease from the established list. In these cases, the decision is made without examining or interviewing the patient.
Attention
! During an in-person medical examination, a protocol is kept so that then, taking into account the observations and records entered into it, the commission can make a decision on refusal or assignment of a disability group.
Can they refuse?
It should be understood that simply not having a kidney is not enough to obtain special status. That is, the chances of getting a disability if the second kidney is functioning normally and you are feeling well are zero.
It is relevant to undergo MSE only against the background of restrictions that have developed after surgery, difficulties with self-care, work, functions of the second kidney, etc. In other words, the condition of the applicant for disability should not be the most favorable.
If, based on the results of the medical examination, a potential beneficiary is refused and does not agree with the decision, he can file a complaint with the same ITU bureau. At the appointed time, a new examination will take place, which, if necessary, can also be appealed by appealing to a higher ITU body. The final stage is the trial in court.
Let us note an important point: with each review of the case, the applicant must attach new evidence of work and health restrictions.
Signs that indicate kidney disease
The kidneys in the human body perform the most important function - removing metabolic products and toxins. In addition, the kidneys are involved in the regulation of the acid-base balance of the blood plasma. Dysfunction of these paired organs negatively affects the functioning of the urinary system and the functioning of the entire organism.
General signs of diseases
Kidney diseases are among the fairly common human pathologies. There are quite a few kidney diseases, and every person needs to know what signs indicate them. This is necessary not in order to diagnose yourself and prescribe therapy, but in order to know when and under what signs you need to go to the clinic. As a rule, the first signs of kidney disease appear in the first stage of the disease.
Kidney diseases can be congenital or acquired. Pathologies inherited from parents are usually detected immediately after birth - during examinations using ultrasound or after urine and blood tests. Typically, the signs of kidney disease in adults are more pronounced than the symptoms of kidney disease in a child. Acquired diseases can strike a person at any age. Doctors consider the following signs of kidney disease in humans to be a cause for concern:
- Pain of various types, localized in the lower back (sharp, cutting pain may indicate the presence of stones);
- Bedwetting, frequent urination (or vice versa, long-term absence);
- Increased temperature or blood pressure;
- General weakness;
- Swelling and red-brown circles under the eyes;
- Yellowish or pale skin tone;
- Bloating, flatulence, nausea, vomiting.
These signs do not directly indicate kidney disease, but are certainly a reason to consult a doctor.
A cause for health concern may be the appearance of blood (hematuria), sand or stones in the urine.
What kidney diseases occur in humans?
The presence of such signs may indicate the most common kidney diseases:
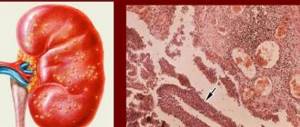
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the small vessels (glomeruli) of the kidneys, usually bilateral, disrupting the outflow of urine and causing fever, swelling and other symptoms of general malaise;
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease caused by infectious microorganisms that affect kidney tissue: the pathology can be acute or chronic;
- Nephroptosis or wandering kidney is a rotation of the kidney around its axis with kinks and pinching of blood vessels, causing disruption of the blood supply to this organ;
- Renal failure (dysfunction) is a condition in which the kidneys partially cease to perform their functions, which causes an imbalance in water and electrolyte balance, accumulation of excess amounts of urea and other harmful substances;
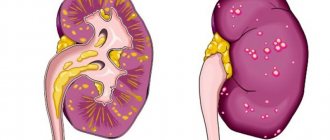
- Hydronephrosis is a violation of the outflow of urine, characterized by an enlargement of the renal pelvis.
Symptoms of diseases
Let us consider the symptoms of each of the renal pathologies in more detail.
Pyelonephritis
This disease may begin with acute and sudden symptoms. The disease can be primary (independent) or secondary, caused by other infectious diseases - from caries to pulmonary pathologies. Signs of acute pyelonephritis are:
- High temperature and fever;
- Frequent urination;
- Pain syndrome in the lumbar region;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Intense sweating;
- Weakness, headache and joint pain;
- Dryness and paleness of the skin.
- The patient's urine may contain pus (this phenomenon is called pyuria by doctors), red blood cells, protein and bacteria.
Glomerulonephritis
Bilateral damage to the renal glomeruli, causing disruption of blood filtration processes, manifests itself as follows:
- Blood pressure increases;
- The daily volume of urine decreases (oliguria);
- Swelling appears on the face.
Laboratory tests reveal protein, red blood cells, and cylindrical bodies in the urine. The appearance of glomerulonephritis can be affected by diseases such as tonsillitis and impetigo (pustular skin disease).
Nephroptosis (prolapse of the kidney)
The development of the syndrome, which is also called “wandering kidney,” can be affected by sudden weight loss, traumatic injuries, childbirth and pregnancy. There are no obvious signs of this disease, since a violation of the blood supply can cause various symptoms. Indirectly, the presence of nephroptosis may be indicated by lower back pain, which appears in a standing position and disappears in a horizontal position. Later, the pain may shift to the abdomen or pelvis.
Kidney failure
With kidney dysfunction, the first sign is a decrease in the amount of urine, as well as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and swelling. A deterioration in the functional state of the liver may also develop. Chronic renal failure manifests itself in the gradual replacement of healthy renal tissue with connective tissue.
Hydronephrosis
For a long time, this disease can occur without visible manifestations. Sometimes there is constant lumbar pain in the right or left side of the body. There may be an increase in temperature and the presence of blood in the urine if the cause of hydronephrosis is kidney stones.
General dietary recommendations
The diet should consist mainly of foods that have a diuretic effect (zucchini, beets, pumpkin, cucumbers, watermelons, melons, vegetable salads). You should strictly limit the salt content in dishes (you can season them with lemon juice or wine vinegar). It is also recommended to exclude from the diet: sausages, smoked meats, hot sauces, meat- and fish-based broths, greens, legumes, chocolate, canned food and marinades, coffee and strong tea.
You can consume milk, cereals, baked goods, and dietary meat.
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Video: Symptoms of chronic kidney disease and diagnostic methods
Features of disability assignment
To kid
For minors, disability is assigned in the same way as for adults - if it is proven that the remaining kidney cannot cope with the load and the body is significantly damaged. This fact is the reason for introducing a diet without spicy and salty foods.
In addition, sports where kidney injury is possible may be contraindicated for the child. He constantly needs to donate blood and urine for analysis, have an ultrasound of his organs, and visit a doctor.
The question of establishing a special status comes when renal failure has developed. The second is the presence of a disease that provoked the removal of the kidney and partially affected the surviving organ. Then the load on the kidney is minimized, so you inevitably have to face restrictions in your life.
For oncology
If an organ was simply removed due to cancer without consequences, this is not a basis for assigning a group. For example, relapses and the presence of metastases after treatment are taken into account. If there are none, and if contraindications for work and its conditions are not specified, status is unlikely to be given.
But in case of obvious impairments in the functioning of the body, the need to receive help, with restrictions on work and in general, disability is prescribed.
Features of chronic pyelonephritis
Chronic pyelonephritis is a problem that often affects both children and adults. The disease is an infectious type of inflammation. Typically, pathology occurs due to a localization process in interstitial tissue. It is worth noting that the cup-scapular system is also affected.
Attention! Most often, this disease is observed in men over 50 years of age. Women predominate in statistics under 40 years of age.
The main reason for the appearance of this disease is gram-negative flora, which, with prolonged development, forms an association of microbes. Among the factors contributing to the development of the disease are the following:
- General characteristics and health status of the child and adult;
- In case of local causes of urodynamic disorders;
- Various infectious diseases that destabilize the functioning of the genitourinary system.
If the passage of urinary secretions is disrupted, the infectious component can move further throughout the body, for example, into the lower genitourinary tract, and even into the interstitial renal tissue.
Who is given the second group
The second group is characterized by deviations from the norm ranging from 70 to 80%. A person with moderate illness is forced from time to time to resort to the help of other people. It can serve itself using special equipment. A citizen’s life activity is severely limited, but he is able to take care of himself without resorting to the help of others.
Disabled people in this group include the hearing impaired, the visually impaired, patients with epilepsy, and oncologist patients who have undergone chemotherapy or radiotherapy. List of diseases for obtaining disability of the second group:
- severe circulatory disorders;
- chronic tuberculosis (fibrous-cavernous form);
- severe atherosclerosis with a pronounced decrease in intelligence;
- liver cirrhosis with ineffective rehabilitation;
- absence of one lung due to pulmonary insufficiency;
- irreversible vision loss;
- paralysis;
- condition after organ transplantation;
- mental illness lasting more than 10 years;
- condition after surgery to remove cancerous tumors of the lungs, stomach and other organs;
- severe form of stomach ulcer;
- infectious diseases affecting the central nervous system;
- epilepsy with frequent seizures;
- limb stumps, etc.
People with the second group are not always deprived of the ability to work. True, to carry out their labor functions they often require specially equipped workplaces.
What diseases give disability?
Art. 1 Federal Law No. 181 of November 24, 1995 gives the following definition: a disabled person is a person with impaired health with a persistent disorder of the functioning of the body, caused by a disease resulting from injuries or defects, manifested in the inability to carry out activities and making his social protection necessary.
Limitation of activity is understood as a person’s loss of the ability to provide care for himself, the ability to move and navigate in space, the ability to communicate with other members of society, control his behavior without outside help, the ability to acquire new knowledge and conduct work.
The list of diseases for disability and the types of main pathologies in the body leading to disability are grouped as follows:
- disorders of mental functions (consciousness, intellect, cognition, etc.);
- disorders of language and speech functions;
- sensory dysfunctions;
- problems with movement-related functions;
- inhibition of the functions of the cardiovascular, endocrine, digestive, respiratory and other systems;
- problems mediated by external physical deformity.
The disability group is fixed according to the order of the Ministry of Labor dated September 29, 2014 No. 664n based on the results of assessing a number of criteria. In this case, the degree of deviation from the norm (in %) is taken into account. For such a type as a disabled child, division into groups is not made.
The legislation specifies the conditions for assigning a group to a citizen:
- Changes in health with a persistent disruption of the body's vital processes, which arose under the influence of diseases, injuries or defects.
- Deterioration in life activity, manifested in a person’s loss of self-care, movement, spatial orientation, communication, behavioral self-control, learning or work.
- The need for social protection measures.
The fulfillment of only one of the conditions is not sufficient to establish the status of a disabled person.
Terms for determining disability
The period for determining disability of group 1 is two years, groups 2 and 3 – one year. For a “disabled child” – 1 year, 2 years, 5 years, and in some cases – up to 18 years.
At the end of the specified period, disabled people are required to undergo re-examination to confirm or refute their disability. If confirmed, the disabled person remains in the previous disability group or is assigned a new group.
Certain categories of disabled people have the right to receive permanent disability - here are some of them:
- disabled men over 60 years of age and women over 55 years of age (for all disability groups);
- disabled men who must undergo regular re-examination after turning 60 (for all disability groups);
- disabled women who must undergo regular re-examination after turning 55 (for all disability groups);
- disabled military personnel who have been diagnosed as disabled as a result of injuries and diseases received during military service (for all disability groups).
Permanent disability can also be established in the presence of certain diseases, which include:
- malignant tumors;
- benign brain tumors;
- incurable mental illness;
- severe nervous diseases;
- irreversible changes in the brain;
- systemic diseases of internal organs with a constant tendency to worsen a person’s condition;
- severe limb defects, including amputations;
- complete blindness and deafness.
A detailed list of diseases and conditions under which permanent disability is established is presented in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled.”
Limitations and benefits for people with mental illness
After being assigned a disability group, the citizen is subject to dispensary observation. After this, the person will no longer be able to perform a certain range of work, and he will also be denied further adoption or guardianship.
Disabled people of the first and second groups have privileges to improve their living conditions. In the case when a citizen cannot do without the help of a guardian, he performs a number of certain actions on his behalf. To receive the services of a social worker or nurse, a citizen must write a written application for the provision of such a service.
Every disabled person can receive free medicines, provided that they are directed by the attending physician. Many disabled people have the right to undergo annual treatment in sanatoriums and health centers.
In addition, taking entrance and final exams for students is carried out with privileges. Group 1 disabled people are the first to receive a place in a boarding school.
First disability group: list of diseases, criteria
A person who claims to be in the first group, due to persistent disturbances in the functional systems of the body, cannot care for himself; he constantly needs outside help. The cause itself - disease, injury, defect - does not matter to the ITU.
List of diseases that give the right to receive disability of the first group:
- progressive tuberculosis in the stage of decompensation;
- inoperable cancer;
- severe variant of schizophrenia;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- paralysis of limbs or body;
- complete blindness;
- epilepsy with frequent, treatment-resistant seizures;
- moderate or severe dementia;
- limb stumps, etc.
A person with the first disability group should undergo re-examination after a two-year period.
The procedure for obtaining disability
Referral for medical and social examination
The following institutions can issue a referral:
- medical and preventive institution - health care facility (hospital, clinic, clinic);
- social security institution;
- body performing the functions of pension provision.
A healthcare facility can refer a person for examination only after diagnosing persistent disorders of body functions and carrying out appropriate treatment and rehabilitation.
Bodies performing the functions of pension provision and social protection have the right to issue a citizen a referral for examination under a combination of the following conditions:
- The presence of violations of the basic functions of the body. These violations must be confirmed by medical documents issued by the health care facility, in addition, the necessary measures for the treatment and rehabilitation of the person have been taken.
- Limitation of human life activity.
- The need for human social protection.
If these institutions refuse to issue a referral to a person, they are obliged to issue him an appropriate certificate. Based on this certificate, the citizen or his representative can contact the bureau themselves.
Documents for conducting a medical and social examination
- Passport of the person who submitted the application for disability (birth certificate - for children under 14 years of age).
- For the legal representative of the applicant - a document that confirms his authority.
- An application for an examination, which must indicate the purpose of the examination.
- Referral for examination from health care facilities, form f088/u-06.
- Medical documents (cards, extracts, certificates, examination results) that confirm health problems.
- Other documents that are provided upon request by the bureau.
Carrying out an examination
The bureau's specialists conduct a comprehensive study of the state of the human body (based on the submitted documents and examination of the applicant), while analyzing the clinical, psychological, social, professional and other data of the person.
During the examination, there may be a need for special additional examinations of the applicant. In this case, the bureau specialists draw up a detailed program of these examinations, which the applicant is informed about. A person undergoing an examination may refuse additional examinations - then the bureau makes a decision based on the available data.
If a disability is established, the person is issued a corresponding certificate, which indicates the disability group and a personal rehabilitation program.
Place of examination
If a citizen is unable to appear at the bureau due to health reasons, the examination is carried out at home or in a hospital, or in absentia (in the absence of the citizen) based on the submitted documents.
The local bureau may refer the citizen to the main bureau if additional special examinations are needed.
To appeal the results of the examination (including those based on the assigned disability group) conducted at the local bureau, the applicant may contact the main bureau with a request to conduct an additional examination.
The Main Bureau may refer a citizen to undergo an examination at the Federal Bureau if it is necessary to conduct additional particularly complex special examinations.
To appeal the results of the examination (including those based on the assigned disability group) conducted at the main bureau, the applicant may apply to the Federal Bureau with a request to conduct an additional examination.
New conditions for registering disability
The new rules for 2020 are designed to make life easier for citizens who intend to get diagnosed at the ITU. Starting this year, it will be easier for people to apply for permanent disability and not have to undergo re-examination from time to time.
- Firstly, documents are now sent directly to the ITU without the intervention of the patient and his family.
- Secondly, in some regions electronic document management for ITU and healthcare is already in place. Disabled people will not have to stand in long lines and wait for an invitation to the office. This innovation will subsequently spread to other cities of the Russian Federation.
- Thirdly, due to complete automation, the issue of assigning a group will be resolved in a matter of days, not months.
Attention! Assignment of disability occurs solely on the basis of the stipulated conditions of each disabled group.
First group
The ITU Commission can assign this disability group only to a citizen who has:
- confirmed malignant neoplasms (tumors);
- complete blindness in both eyes;
- constant manifestation of mental disorders;
- complete or partial absence of upper or lower limbs;
- joint contracture;
- impaired renal function;
- incurable disease of the cardiovascular system;
- chronic respiratory disease;
- violations of the central nervous system.
Second group
This group is designed for sick citizens who have body disorders in the form of:
- fecal fistula;
- absence of a second lung;
- impaired vision that cannot be restored;
- mental illness;
- liver cirrhosis;
- paraplegia;
- severe damage to the skull;
- ankylosis or contracture of the hip joints.
Third group
This group of disabled people may include citizens who have the following health impairments:
- functioning of only one eye or blindness of both;
- development of deafness;
- jaw and throat disorders;
- pituitary dwarfism;
- chest changes;
- disorders during organ transplantation;
- there are foreign substances in the brain;
- moderate sensory aphasia;
- osteochondropathy;
- osteochondrodystophy.