Monday, October 28, 2019
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is one of the painless ways to examine internal organs. Due to timely detection of the disease, progressive treatment is prescribed, including surgery.
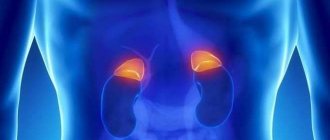
Ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space allows you to accurately determine the functional state of each organ without harming the patient’s health.
What is ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands?
Ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure for examining the human body, which is based on the use of ultrasonic waves. Using ultrasound, you can examine in detail the shape of the organ, structural features, size, location, as well as motor activity. Also, an ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands shows the presence or absence of pathology and disease in these organs.
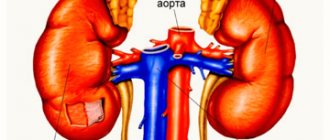
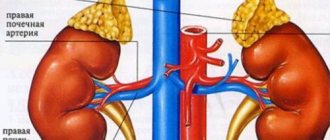
The kidneys and adrenal glands are located in the retroperitoneal space and are easily accessible for ultrasound examination
How to decipher the result
The diagnostician issues a sheet with the examination results. The first paragraph provides general information about the size, shape and structural characteristics of organs. The normal kidney is:
| Magnitude | Parameters, mm |
| thickness | 40-50 |
| width | 50-60 |
| length | 100-120 |
| parenchyma | 11-23 |
For children, the data is different and depends on the child’s growth. The norm for school age is:
| Magnitude | Parameters, mm |
| thickness | 40 |
| width | 22-25 |
| length | 42-62 |
| parenchyma | 9-18 |
In the second paragraph, deviation indicators indicating diseases are printed. At the end - one of the conclusions:
- corresponds to the norm;
- echo positive formations were detected.
In addition to the examination sheet, an image and a sonogram are issued, which indicates the location of pathological changes. In any case, the doctor who issued the referral will tell you more detailed information and prescriptions.
Diseases that diagnostics of the retroperitoneal space helps to identify:
- inflammation of the bladder mucosa;
- nephritis and pyelonephritis;
- cysts and tumors on organs;
- stones (size) and sand;
- disruptions in the functioning of blood vessels.
To eat or not before an ultrasound?
When it comes to nutrition, preparation is very important. Whether a specialist can correctly perform and evaluate an ultrasound depends on its correctness. Before the procedure, you need to avoid foods that cause gas. The main ones will be baked goods, sweets, alcohol, cabbage, carbonated drinks, bread, fruits, milk, legumes. The method of preparation is of great importance. It is better to avoid frying. It is preferable to eat boiled or steamed food. You can eat porridge, lean meat and fish, cheese products, and eggs. Meals are fractional, 5-6 times a day, in compliance with the water regime. The last meal is 8 hours before the intended test.
How to prepare for a kidney ultrasound?
This procedure, depending on the reason for the study (disease or preventive examination), may require additional preparation. Following a certain diet or taking certain medications - you can find out about this here - Preparing for an ultrasound.
If you have identified symptoms of a particular kidney disease or pathology of the adrenal glands, or you want to undergo a preventive ultrasound to exclude or early diagnose diseases of these organs, contact the Stolitsa network of clinics. Our functional diagnostic doctors will conduct research using the most modern equipment and help you correctly interpret the results. If necessary, you will be able to undergo additional consultation with a medical specialist (generalist, nephrologist, urologist, endocrinologist), who will clarify the diagnosis and give recommendations for the treatment and prevention of kidney and adrenal diseases.
Ultrasound of the kidneys - price, Ultrasound of the adrenal glands - price (see price list)
Make a choice in favor of professional medicine!
Drinking regime
The main feature of ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands, as well as other organs of the retroperitoneal space, is compliance with the correct fluid intake regimen.
In this case, preparation for the study requires drinking 1.5 liters of liquid before the ultrasound. This is also true for ultrasound of the bladder. This is done to better contrast these organs.
To increase the information content of a kidney ultrasound, you need to adhere to the drinking regimen recommended by your doctor.
Can I eat and drink before the procedure?
If you are following a diet, you should stop eating eight hours before the ultrasound examination. During this period, previously consumed food will be completely digested in the body.
Doctors recommend including low-fat varieties of fish baked in the oven and porridge cooked in water with a minimum amount of salt in your diet on the eve of the examination. Children need to eat five hours before the examination. Infants must be fed according to a set schedule; the clinic’s doctors will try to adapt to the baby’s diet.
It is also not recommended to overeat heavily after following a diet. In this case, the stomach is not ready for a large consumption of various dishes, so sharp and prolonged pain in the pancreas may occur, which will lead to an inflammatory process that must be treated.
During ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space, preparation includes regular, plentiful consumption of clean, plain water. The procedure is performed when the bladder is full.
When is an ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands prescribed?
The main indications for this study are:
- Painful sensations in the lower back.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Pastosity of unknown origin.
- Headache.
- Problems with urination.
- Suspicion of the presence of tumors.
- Infertility on the part of the woman.
- Pigmentation of the skin.
- Inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, inflammation in the adrenal glands).
- Hormonal disorders.
- Cystic formations and trauma to the abdominal cavity.
Using ultrasound, you can diagnose a large number of diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Direction and indications of diagnostics
The pictures taken during the examination using special equipment show the condition of the kidneys (left, right), paired endocrine and pancreas glands, and ureters. The lymph nodes from the diaphragm to the pelvis are also clearly visible.
Ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space in Moscow is performed in specialized clinics. The main thing for the patient is a full examination by a professional doctor. Therefore, you need to choose clinics that specialize in the treatment of diseases of the retroperitoneal organs, for example, “Clinic for Men’s and Women’s Health”, where the price of an ultrasound is 1150 rubles. Indications for prescribing diagnostics are many factors. Basic:
- high blood pressure (more than 140 over 90), which is observed for a long time;
- sharp and aching pain in the lumbar area;
- dizziness;
- rashes and pigmentation on the skin;
- problems with the genitourinary system, inflammatory processes;
- hormonal problems, infertility;
- formations (tumor, cyst, etc.).
It is also recommended to do an ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space during a comprehensive examination of the organs and if there is a body temperature of 37.2℃ or higher for more than 15 days.
How does the examination take place?
The procedure is absolutely painless. A gel mass is applied to the skin in the area of study, which improves ultrasound performance. The sensor is used to make circular movements over the skin. To locate the adrenal glands, the patient is usually instructed to inhale. The study begins with the right kidney, the right adrenal gland is also looked at first, because it's much easier to find. If it is difficult to find structures, the patient is asked to change position. An ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands can be done on average in half an hour. The patient is given documents on the basis of which his attending physician issues a conclusion on the presence or absence of the disease.
Diagnostics - technical issues
The diagnostic technique is simple. The client lies down on a special couch, which is covered with a disposable sheet, having previously freed the lower back and stomach from clothing. The doctor applies a gel mass to the skin. Using a sensitive sensor, the liquid is distributed in the area of examination of the organ and the specialist carefully conducts the examination using circular movements.
A thorough analysis of each kidney and adrenal gland requires attention. Therefore, the client needs to cooperate with the doctor, performing the necessary turns, bends and breaths.
Results are issued on the day of the examination process. The cost of an ultrasound is on average 1000-1300 rubles.
Ultrasound picture of the adrenal glands
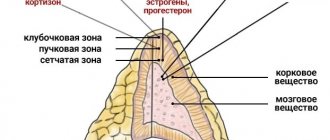
The adrenal glands are normally visualized as hypoechoic linear formations up to 45 mm * 28 mm * 6 mm in size. The right one has a triangular shape, and the left one has a crescent shape. In adults, the adrenal glands are poorly visualized by ultrasound, so this method is a screening method for identifying pathology.
Most often, the adrenal glands are susceptible to metastatic damage from tumors of the mammary glands, lungs, ovaries, and urinary tract. Ultrasound signs are nonspecific; a feature is predominantly bilateral involvement of the adrenal glands. Adenomas and adenocarcinomas are also detected in the form of isoechoic round formations with clear contours of various sizes.
Adrenal calcifications are often detected, which have the appearance of hyperechoic structures with an acoustic shadow. If an enlarged adrenal gland or a space-occupying lesion of any size is detected, CT and MRI are necessary.
What does an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands show?
What parameters and what pathology can be detected on an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands, what does it show? Normally, in an “average” person with moderate and increased fatness, these glands are not visualized; they are visible only if their size increases and their structure changes.
Normal organ parameters
Visualization determines the shape, location and size of the glands. On the right the shape resembles a triangle, on the left it resembles a crescent, both are located on the upper poles of the kidneys.
The normal sizes of both adrenal glands according to ultrasound results are: the right one is 1.5-2.0 cm long, 0.5-1.6 cm wide, the left one is 1.5-2.5 cm and 0.8-1 cm, respectively. 5 cm. The structure is normally homogeneous, that is, homogeneous.
Signs of pathological changes
The main diagnostic criteria for pathology are:
- an increase in the size of the glands, which indicates tissue hypertrophy, the presence of a cyst or tumor;
- changes in echogenicity, with adenomas and cysts the tissue becomes less dense, becomes hypoechogenic, that is, it reflects less ultrasonic waves, such an image on the screen will be darker;
- heterogeneity of the structure; a malignant tumor process is characterized by alternation of hypoechoic (dark) areas with hyperechoic areas - of greater density, which look lighter on the screen.
During a duplex study, the configuration of blood vessels is obtained on the scanner screen based on the nature and volume of blood inflow and outflow. Their abundance and tortuosity in a certain limited area indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
Additional diagnostic measures
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is an important, but not the only diagnostic stage. When identifying dysfunctions of these glands, it is necessary to obtain detailed information about the state of health in general. In particular, whether the pathology of the adrenal glands affected the functioning of other organs and systems. Along with ultrasound, the following examination methods may be prescribed:
- laboratory tests of blood and urine (general, biochemical, clinical, hormone levels, etc.);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- consultations with specialized specialists (gynecologist, urologist-andrologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, etc.) and undergoing diagnostic procedures prescribed by them.
results
Based on the scanning results, an ultrasound diagnostic specialist deciphers and establishes a presumptive diagnosis of the following pathology:
- hyperplasia of glandular tissue - an increase in its volume with a homogeneous structure;
- cysts are hollow echo-negative formations with reduced echogenicity and a lighter echo-positive capsule;
- benign tumors - adenoma, aldosteroma, with a decrease in the density of the structure, smooth contours;
- malignant tumors - pheochromocytoma (cancer), heterogeneity of the structure and uneven contours of the formation are noted.
All these are just preliminary diagnoses, identifying the fact of the presence of pathology. To clarify, a set of data is required, including complaints, clinical manifestations, results of laboratory tests and accurate diagnostic methods - CT, MRI, angiography, scintigraphy (radioisotope scanning).
Congenital malformations
Congenital defects and developmental anomalies of the genitourinary system are often detected in patients who do not complain of complaints from the urinary system. Kidney duplication is the most commonly diagnosed pathology:
- Incomplete duplication is characterized by the presence of two collecting systems, but there is one pelvis and one ureter.
- With partial duplication, there are two pelvises and two ureters that merge into one.
- Complete duplication is characterized by a separate course of the ureter along its entire length, but this diagnosis requires confirmation by excretory urography.
Dystopia is characterized by an atypical position of the organ. Can be lumbar, iliac and pelvic. Most often, dystopia is one-sided, but bilateral displacement of the organ is also possible.
Anomalies of relationship (fusion) include:
- horseshoe-shaped - the kidneys are connected to each other by one of the poles;
- biscuit-shaped - characterized by fusion along the entire length of the medial surfaces;
- L-shaped - fusion occurs at right angles to a normally located organ;
- S-shaped - fusion of the lower pole of one and the upper pole of the other.
These anomalies do not affect function, but pathological processes in these organs are more common, so an annual examination is necessary.
In what cases is diagnostics necessary?
A study of the adrenal glands is carried out in all cases when symptoms of dysfunction of their function appear - insufficient or excessive production of certain hormones. This happens most often with tumors, congenital pathologies, consequences of injuries and operations.
Indications and contraindications for ultrasound
Indications for ultrasound examination are:
- Persistent increase in blood pressure.
- Rapid weight gain in the absence of excess nutrition.
- Unmotivated general weakness, physical inactivity.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- The appearance of pigmented areas on the skin.
- Increased volume and decreased specific gravity of urine.
- Increased blood sugar.
There are certain symptom complexes for which a study is prescribed:
Addisson-Biermer syndrome, manifested by irregular periods, infertility and increased growth of body hair in women, decreased sexual function in men.
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, in which body weight increases, multiple “stretch marks” appear on the body, acne, blood pressure rises, muscles atrophy, and myopia develops. In women, hirsutism and atrophy of the uterus and vagina appear, and menstruation disappears. In men, erection decreases to the point of impotence, and baldness quickly develops.
Contraindications to the procedure are the presence of inflammation, rashes, wounds on the skin, which can complicate and distort the results. A relative contraindication is pregnancy; the study is carried out if necessary. Also, the study is not useful in highly obese patients because the abundance of retroperitoneal fat will interfere with imaging.
How is ultrasound diagnostics of retroperitoneal organs performed?
The answer to the question: “Ultrasound of the adrenal glands, what is it and how is it carried out” must be answered by saying that this is the most acceptable and widespread method of primary diagnosis of dangerous conditions associated with this anatomical area, which makes it possible to prevent its further spread or completely exclude the presence of the disease. This diagnostic method itself consists in the fact that with the help of ultrasonic waves passing through the tissues of the body, the organs located there, their structure and possible formations or pathological changes are determined.
It is also necessary to understand how ultrasound of the adrenal glands is done and what is needed to perform it. To do this, the patient is asked to bare to the waist and lie on the couch, first on his stomach, back, and then on his right and left sides, and, if necessary, in a sitting position. It should be noted that it is possible to identify such an appendage of the kidney on the right in 90% of cases, and on the left in a maximum of 50%, since the structure of this formation allows an echo signal to pass through and it is no different from the fiber located there. Therefore, it is possible to explore its location, despite careful preparation. All of the above is indexed as a variant of the norm, since when an organ degenerates or thickens, it begins to become noticeable to an ultrasound sensor.
After a standard examination, an examination begins on the right side to visualize the left renal appendage, and subsequently an examination on the left side, respectively, to diagnose a formation that is the same, but located on the right. All this can be done only after special training, which will be described below. If such an examination does not give any clinical results, then the study begins to be carried out in a sitting position, but only in thin people. In all positions, it is necessary to ask the patient to take as deep a breath as possible and hold it a little, since this will allow the diaphragm to move down and change the position of the kidneys in the retroperitoneal space, after which they will become more accessible for visualization. It should be added that ultrasound of the adrenal glands in women is carried out with a mandatory examination of all pelvic organs.