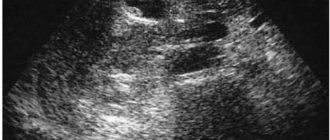
When performing an ultrasound of the kidneys, neoplasms may sometimes be detected in them, which do not contain fluid.
A stably functioning organ has a normal structure, and ultrasound does not show reflection of ultrasonic waves from the kidneys.
When the organ reflects sound waves during an ultrasound, we can talk about the presence of hyperechoic inclusions in the kidneys.
What is hyperechogenicity?
Echogenicity is the property of various objects to reflect sound waves from themselves. An ultrasound machine operates on the principle of echogenicity. All human organs have this property. When sound waves are passed through them, they reflect them away from themselves with varying degrees of intensity.
Echogenicity is a normal natural phenomenon. But if the degree of reflection of ultrasonic waves by an organ is exceeded, we can talk about problems in its operation.
An ultrasound examination of the kidney gives a signal in the form of a white spot on the organ that there is some foreign body or neoplasm inside it.
Small hyperechoic inclusions
An ultrasonic wave hitting such a body is reflected from it in the form of a clot. This cluster is called an acoustic shadow. Based on the acoustic shadow, the specialist determines the type of tumor inside the kidney. It can be:
- volumetric;
- point;
- hyperechoic linear inclusions in the kidneys.
Since an ultrasound wave is denser than air, only an object with a very dense structure cannot transmit it. Such inclusions should not be classified as a separate type of disease. They only clearly indicate the presence of any pathology.
A number of experts believe that such formations in the overwhelming majority of cases appear against the background of the development of a renal neoplasm.
Prevention of discharge pyramidal syndrome in the kidneys
Few people know about the echogenicity of their organs, and even fewer think about it. Meanwhile, the hyperechogenicity of the kidneys indicates the presence of dangerous inclusions, which indicate the syndrome of isolated pyramids developing in the body.
Sharp outlines or white spots in an ultrasound image of the kidneys are signals of ongoing pathologies and even insufficient body weight. In any case, everyone needs to know about the condition of their kidneys.
Briefly about the syndrome
Echogenicity is characterized by the degree of reflection of sound from the tissues and fluid of internal organs, and the appearance of strong reflections on ultrasound signals the presence of various foreign inclusions.
Hyperechoic kidneys on ultrasonogram
Most often, hyperechoic formations form in the renal pyramids and parenchyma.
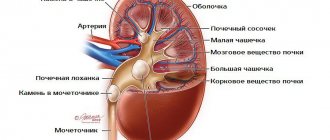
Pyramids are the triangle-shaped areas of the kidneys through which, after filtration, urine exits into the pyelocaliceal system, and parenchyma refers to the tissue that fills the organ from bone and cortex.
Any extra element of the structure, being a consequence of the pathology occurring in the organ, introduces dissonance into its functioning, and often developing on one, soon affects the second kidney.
The degree of negative impact of hyperechoic inclusions directly depends on their size, composition and the possible development of malignant cancer processes in them.
All excess elements are divided into calcium stones, stones, sand and neoplasms. The last group includes formations of various types:
- Small formations appear as white dots during ultrasound. The absence of an acoustic shadow indicates their safety;
- The following type of inclusions is characterized by a large size, which can be either benign or malignant, cancerous tumors. They are extremely rare and require constant monitoring by doctors;
- Large light spots on ultrasound indicate cancerous inclusions, which, unlike other formations, necessarily have an acoustic shadow, areas of sclerosis, and also contain calcifications and psammoma bodies.
8 main causes of hyperechogenicity
Hyperechoic renal pyramid syndrome is not an independent disease, but an accompanying ailment, as it is a consequence of a pathology developing in the body. The cause of their appearance may be the following pathological renal processes:
- Polycystic disease;
- Sclerosis of blood vessels;
- Injuries;
- Bleeding;
- Purulent inflammation of tissues;
- Accumulation of several abscesses and boils in one place;
- Oncological processes;
- Fatty formations in the pyramids of the kidney.
Hyperechoic inclusions on ultrasound
Symptoms and diagnosis
Hyperechoic pyramid syndrome can be suspected by the following characteristic clinical manifestations that occur against a general background of weakness and fatigue: high temperature (up to 39°C), dark brown or red urine, stabbing pain in the kidney area; spasms in the abdomen and groin, vomiting, nausea, nagging pain in the groin.
The symptoms of the syndrome are characteristic of many renal diseases, however, with the help of ultrasound, a specialist will immediately diagnose the presence of hyperechoic inclusions, and will also assess the condition of the kidney parenchyma against the background of prominent pyramids.
When a diagnosis of “hyperechoic pyramid syndrome” is made during diagnosis, additional procedures are prescribed to identify the root causes of the process and prescribe appropriate therapy. Thus, general blood, urine, and stool tests are required.
Diagnosis of hyperechogenicity
Therapy and prescriptions
Treatment of hyperechoic pyramid syndrome is complex and is aimed at relieving pain syndromes and eliminating pathological preconditions.
Timely detection of illness involves drug therapy, during which a urologist or nephrologist prescribes antibiotics, analgesics, antispasmodics, as well as drugs that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects to the patient. A change in routine and diet is required, including proper rest, drinking plenty of fluids, eating low-fat foods, fresh vegetables and fruits.
When the disease passes into the chronic stage, physiotherapeutic procedures and homeopathic medicines are recommended.
A fruit and vegetable diet is required
Advanced cases require a more individual approach and surgical intervention.
Types of hyperechoic inclusions and associated diseases
Hyperechoic inclusions come in three main types:
Small, not casting an acoustic shadow. In this case, a person undergoing an ultrasound is dealing with calcifications and psammous bodies.
Calcifications are calcium-based salts. They enter the soft tissue of the kidneys, resulting in inflammation. The process becomes chronic over time.
Psammous bodies have a round shape and consist of proteins, fats and calcium salts. In half of all diagnostic cases, such small hyperechoic inclusions in the kidneys indicate the development of a malignant tumor.
In 70% of cases in the presence of a cancerous tumor in the kidney, sclerotic tissue is observed. 30% of the total size of the tumor is occupied by calcifications. With ultrasound, the presence of a cancerous tumor can be highly likely if sclerotic tissue is present in the inclusions. Corpuscles are also observed in the membranes of the brain and in the vessels.
Large without acoustic shadow . May indicate the following possible phenomena:
- urolithiasis disease;
- benign or non-benign tumor;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- inflammatory diseases;
- cyst;
- sand in the kidneys;
- hematoma;
- scar.
Large formations casting an acoustic shadow . They are a clear sign of the presence of kidney stones or some inflammatory disease.
Several types of hyperechoic formations can be diagnosed at once. They often indicate the development of inflammation against the background of glomerulonephritis and paranephritis.
Echogenicity
The darker areas of the ultrasound image are called areas of low acoustic density or hypoechoic. These are the areas through which ultrasound passes practically without reflection - cysts, blood vessels, adipose tissue. Lighter areas reflect sound much more strongly and are called areas of high acoustic density or hyperechoic areas. Most often these are stones, calcifications or bone formations and structures.
Types of echogenicity of objects during ultrasound
In most cases, the ultrasound picture of individual organs and structures is an image that is more or less homogeneous in echogenicity, therefore the identification of hypo- or hyperechoic inclusions unusual for the organ very often indicates pathology and requires particularly careful analysis.
Symptoms in the presence of inclusions
Neoplasms cannot be detected without ultrasound. But a number of symptoms indicate the presence of a foreign body or neoplasm inside the kidney. The most pronounced signs include:
- the appearance of colic in the kidney area of a paroxysmal or sporadic nature;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- aching pain in the lower back, accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of constipation, which over time turns into severe diarrhea;
- when urinating, there is a change in the color of urine, which takes on shades from bright red to brown;
- groin pain of varying intensity, but constant.
If such symptoms appear, immediate referral for diagnosis is required.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
Most often, the formation of areas of increased density is accompanied by negative signs:
- painful renal colic;
- change in the appearance of urine;
- temperature increase;
- vomiting, nausea;
- pronounced pain in the abdomen;
- chills, feverish syndrome;
- constant pain in the groin area.
Warning! The malignant process in the early stages often occurs without characteristic signs. Reluctance to be examined provokes the development of advanced stages of oncological pathologies, the treatment of which is very difficult and ineffective. An annual ultrasound of the kidneys is an accessible, simple and painless method that allows you to identify even the smallest tumors in the form of pinpoint hyperechoic inclusions.
Diagnosis of hyperechoic formations
The general diagnostic method for suspected hyperechoic formation in the kidney is ultrasound. The study gives results about the presence or absence of foreign bodies and formations inside the organ. After this, additional examinations and tests are required.
A urine test is required. Its implementation plays an important role if the presence of kidney stones is suspected. The analysis clearly shows what salts the urine consists of.
Kidney MRI
A blood test is necessary in all cases, since it provides complete information about possible metabolic disorders.
If ultrasound reveals a kidney injury or detects hemorrhage into it, then magnetic resonance imaging becomes an additional examination method. It indicates the specific location of the inclusion within the organ. Tomography is carried out and is indispensable if there is a suspicion of hyperechoic formations resulting from the growth of a cancerous tumor.
Sonoelastography of the kidney
Additionally, the presence of cancer is detected:
- blood test for the presence of tumor markers;
- kidney biopsy;
- sonoelastography.
The last type of examination is a type of ultrasound, with the help of which a specialist can detect a tumor at an early stage of its development. Sonoelastography accurately determines the size of the tumor and the location of the kidney where it is located.
The specialist conducting the kidney ultrasound draws up a conclusion after the examination, but does not make a specific diagnosis. Additional examinations are required to make a diagnosis.
Reasons for appearance
Areas of increased density are not a disease, but a sign of the development of negative processes in the kidneys. The structures reflect ultrasound waves well and create hyperechogenicity.
The main reasons for changes in parenchyma:
- development of kidney stones or urolithiasis, deposition of mineral salts due to problems with metabolism;
- tumor process of a benign or malignant nature;
- the appearance of a kidney cyst against the background of congenital anomalies. A growth is a cavity containing liquid inside. As the cystic formation grows, the pressure on surrounding tissues and vessels increases, the outflow of fluid is disrupted, and pathological processes develop in the parenchyma;
- sclerotic changes in renal tissues;
- the course of acute pyelonephritis, increased infiltration of leukocytes, development of hyperechogenicity of the renal pyramids merging with the parenchyma;
- inflammatory process with pronounced tissue damage: kidney abscess, carbuncle in the tissue of the bean-shaped organ;
- formation of a hematoma with active blood clotting. The cavity with blood clots is clearly visualized during an ultrasound of the kidneys;
- development of glomerulonephritis (acute form) with a high density of individual areas in the parenchyma tissues.
Treatment Options
Treatment of diseases that arise against the background of hyperechoic inclusions in the kidneys depends on the diagnostic results and the type of disease diagnosed.
In cases associated with the presence of kidney stones, diuretics and herbal decoctions are prescribed.
With their help, small stones are removed from the body.
If the size of the formation exceeds 5 mm, then endoscopic surgery using a laser or ultrasonic device that crushes the stone is required. For large formations in the kidneys, the only treatment method is abdominal surgery followed by suturing of the kidney.
Inclusions that represent tumors are treated only by surgery:
- benign - resection (partial removal) of the affected area of the kidney;
- malignant - complete removal of both the tumor and the entire kidney along with it.
After surgery to remove a kidney, chemotherapy is additionally prescribed to prevent the spread of metastases to other organs.
Small kidney stones can be removed using external beam lithotripsy. The method is non-invasive and effective.
Read about the nuances of performing a computed tomography scan of the kidneys here.
How to perform a kidney removal operation and what surgical methods are used, read in this publication.
Treatment of cancer with a Mishin coil:
The device, developed by a Russian scientist, allows you to effectively fight cancer using an electrostatic field. A huge number of tests and studies by doctors have confirmed the positive effect of the device on...
Treatment of tumors with a Mishin coil (video):
ORDER MISHIN REELS
Do not delay diagnosis and treatment of the disease!
Sign up for an examination with an oncologist online!
source: OnkoExpert.ru
Ultrasound examination is one of the most progressive, reliable and fastest methods of visualizing the organs of the human body, which is also completely harmless and financially accessible to almost every person. The very principle of ultrasound - varying degrees of reflection of sound waves from objects with different densities - has been used for more than a hundred years in the navy, industry, and military affairs, and only recently has it been used in medicine.
Over the past fifty years, the possibilities of ultrasound diagnostics have become so wide that modern obstetrics, cardiology, gynecology, urology, surgery and many other branches of medicine cannot be imagined without the use of this indispensable method for studying the human body.
During an examination of a patient, an ultrasound diagnostic doctor uses a sensor to direct high-frequency sound waves, inaudible to the ear, through the thickness of the human body to the organ of interest and with the same sensor receives the reflected signal, which is subsequently amplified, deciphered by a powerful computer and displayed on the screen in the form of black and white - or three-dimensional image.
Preventive actions
All preventive measures come down to the fulfillment of certain conditions:
- compliance with the diet and fluid intake according to the established norm;
- constant physical activity, avoiding a sedentary lifestyle;
- rapid detection and prompt treatment of kidney diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature;
- inclusion in the diet of vitamins A, C, E, which increase immunity;
- carrying out preventive examinations by a urologist and nephrologist.
Examinations for the presence of hyperechoic inclusions in the kidneys are recommended every 6 months. A preventive measure will make it possible to timely identify serious pathologies in the functioning of the organ and carry out surgical treatment with minimal consequences for the entire body.
An increased level of calcium in the body, as well as a metabolic failure, can provoke the formation of calcifications in the kidneys. The disease is diagnosed in both children and adults.
Salts of oxalic acid in urine indicate the process of oxalaturia - the formation of oxalate stones. Read about the reasons for the formation of such stones and treatment methods in this topic.