Author of the article
Anatoly Shishigin
Reading time: 3 minutes
AA
The structure of the bladder is an unpaired organ, hollow inside. Its main purpose is to accumulate, excrete and expel urine from the body. In order to understand how an organ works, it is necessary to compare its structure in males and females. If necessary, you can always look at the bladder, a photo of which is in any medical reference book.
Anatomy of the bladder
The bladder in men and women has the same anatomical and histological structure and does not differ in its blood supply and innervation.
Structure
The anatomy of the bladder is quite simple, and you can quickly understand the structure of the organ. It has a variable shape, which can be pear-shaped or oval, depending on how much urine is in the organ in a certain period of time. According to its anatomical structure, this organ consists of a number of sections:
- Apex , a part that has a pointed shape directed towards the abdominal wall;
- The body , the largest part of the organ, is located respectively in the middle of the bladder;
- Bottom , part facing downward and posteriorly;
- The bladder neck , the narrowest part, located at the bottom of the organ.
The bladder has a special anatomical structure called the vesical triangle. The orifices of the ureters are located at two corners of this structure , and the internal sphincter of the urethra . , urine enters the organ in about .
The walls of the bladder, in turn, are divided into anterior, posterior and lateral. And the front edge of the organ almost touches the pubic symphysis; between them there is a thin layer of loose fiber, forming the prevesical space .
From below, the organ is fixed by ligaments, and its apex is freer. In the male body, this organ also has a connection with the prostate .
The bladder (photo below) is quite clear in its anatomy from the illustration.
Functions
The functions of the human bladder are quite simple and there are only two of them:
- Urine collection , that is, reservoir function;
- Evacuation of urine , its removal from the body.
The first function is carried out as urine enters the cavity of the organ through the ureters. And the second is performed by contracting the walls of the organ.
Volume
The normal volume of the bladder in women is from 250 ml to half a liter, and in men 350-700 ml , the numbers vary depending on the age of the person. However, depending on how individually the body has developed and how extensible the walls of the bladder are, about a liter of urine can accumulate .
Location Features
Quite an interesting question is where the bladder is located .
In general, the location of the bladder in men and women is quite similar. Normally, it is localized in the pelvis and is separated from the symphysis pubis with the help of loose fiber located in a thin layer behind the pubis. Regarding which side the bladder is located, we can say that it is located approximately along the midline of the human body, and deviates to the sides only with pathology of neighboring organs.
In men, this organ is located next to the prostate gland , and the seminal ducts run on either side of it. And among representatives of the fairer sex, this structure is located closer to the uterus and the entrance to the vagina. But the greatest difference for different sexes is not so much in localization, but in one part of this hollow organ. This is the bladder canal or the urethra, also known as the urethral canal. In men it reaches about 15 cm , and in women approximately 3 cm .
Blood supply
The bladder is well supplied with blood. To its upper part and to the body itself there are branches from the right and left umbilical arteries, which are called the superior vesical arteries. In turn, the inferior vesical arteries, originating from the internal iliac arteries, approach the side walls and the bottom.
As for the venous outflow, the blood is directed from this organ to the venous plexus of the bladder. In addition, through the vesical veins it flows into the internal iliac veins.
When to see a doctor
A few isolated cases of urinary incontinence do not require medical attention. But if the problem worsens the quality of life or affects the state of health, you should seek help from a medical institution.
Symptoms that should alert you:
- Constant leakage of urine.
- The sudden emptying of the bladder precedes the trip to the toilet.
- Constant urge to urinate without emptying.
- Frequent urination in small quantities.
- Appearance of blood in the urine.
- The urine became cloudy, opaque, the color and smell changed.
- Pain in the back or bladder area appears.
Many problems arise during menopause and the aging of the body. But if urination is accompanied by pain, a feeling of incomplete emptying and frequent urges, you should check with a doctor.
The bladder, which holds urine for a long time, is more likely than the kidneys or ureter to become the site where tumors develop.
Innervation
In the walls of this hollow organ there are a large number of receptors through which impulses through a reflex arc to the spinal cord . Autonomic parasympathetic innervation, in turn, is carried out through the pelvic nerves, and sympathetic innervation through the inferior hypogastric plexus.
With the help of the sympathetic nervous system the process of filling the organ is controlled ; the nerve cells of this system are localized to a greater extent in the ganglia at the level of the first and second lumbar vertebrae.
The parasympathetic system regulates the release of the bladder from its contents and is located at the level of the second to fourth sacral vertebrae in the spinal cord. There is also a conscious regulation of urination, when the cerebral cortex exhibits functional activity.
Urine excretion
As soon as the baby is born, his bladder begins to descend. Already 4 months after birth, the organ is located above the pubic symphysis, at a distance of 1 cm from its edge. About once every three minutes, the ureters open and release small streams of urine.
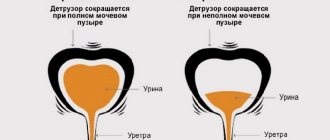
The urinary system is characterized by two phases:
- transport phase, when urine moves through the urinary tract with the help of expulsion muscles;
- retention phase - retention, when the sphincters block the exit, the urinary tract stretches and accumulates urine.
More on the topic: How to rinse the bladder with Furacilin solution?
The entire urinary system, including the renal cups and urethra, is a hollow organ, muscular in structure. All its organs are inseparable from each other, ensuring the alternation of excretory and secretory phases.
Histology
The structure of the bladder from a histological point of view is represented by four main membranes. This:
- Mucous;
- Submucosal layer;
- Muscular;
- External adventitia.
The first membrane is a transitional epithelium, somewhat similar to that which lines the inner lining of the ureters.
The submucosal layer is folded. These folds are necessary to enlarge the organ as it fills ; due to their smoothing, the volume of the organ changes in accordance with the incoming urine.
This layer is also rich in blood vessels, nerve endings and lymphatic vessels. However, in the area of the bladder triangle there is no this layer.
The muscles of the bladder located in its wall are of particular importance They consist of three layers:
- Longitudinal fibers;
- Circular fibers;
- Longitudinal and transverse muscles.
Together they form the detrusor, which is necessary for the functions of the bladder to proceed normally.
The outer adventitia, in turn, is rich in glands that secrete mucous secretions and lymphatic follicles.
Blood supply and lymphatic system
Enrichment of organ cells with oxygen occurs through the branches of the paired vesical arteries. Through the upper ones, blood enters the lateral sections and the upper sector of the bladder, and the lower ones provide supply to the bottom and neck. The organ is also connected to the circulatory system by the uterine, inferior gluteal, rectal, and obturator arteries. The outflow of waste blood flows through the veins of the same name into others - the internal iliac veins.
A large number of lymphatic vessels are located between the submucosa and the inner membrane; there are also plenty of them in the muscle layer. First, the outflow of lymph goes to the iliac nodes, then to the lumbar nodes. The lymphatic system of the bladder is interconnected with the lymphatic capillaries of nearby organs.
Diseases
Bladder diseases are considered the most common group of reasons why a man seeks medical help. These include congenital anomalies of structure or location, inflammatory processes, infections, innervation disorders and injury to this organ.
Symptoms of bladder diseases
There is a group of main symptoms that are characteristic in certain combinations for bladder pathologies.
Among these signs are:
- Increased frequency, reduction of urination, retention, incontinence or the need for effort for the process, increased frequency of urination at night;
- Feeling of pain in the lower abdomen;
- Pain during urination;
- Changes in the color of urine, the appearance of an unpleasant odor, its cloudiness, the appearance of blood or other impurities.
Methods for diagnosing diseases
Diagnosis of any bladder disease begins with collecting an anamnesis from a specialist. Then standard laboratory tests , including a general blood and urine test. Diagnosis also includes methods of visualizing a hollow organ, often ultrasound, less often X-ray examination with contrast. A medical professional may also prescribe a cystoscopy.
Major diseases
Bladder diseases are diverse, but we can highlight the most common ones and some of their features.
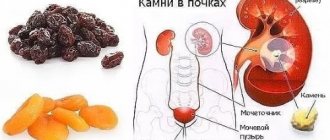
Urolithiasis or urolithiasis
It is characterized by the fact that metabolic processes in the body are disrupted , and stones begin to form in any structure of the urinary system, including in the bladder.
Symptoms include the presence of dull pain in the lower back, which is constant, a persistent feeling of the urge to urinate, intensifying with movements, the appearance of blood in the urine , its cloudiness and the acquisition of an unpleasant odor, general intoxication in the form of fever and chills.
Cystitis
It is an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the bladder, which causes disruption of its functions. It can occur in acute and chronic form.
In acute cases, there is an increase in urination, including at night, the appearance of a false urge to urinate, the appearance of pain during urine excretion, the appearance of blood impurities and cloudy urine.
There may also be signs of intoxication in the form of fever, general weakness and chills. In the chronic form, the course is most often wavy, blood or mucus periodically appears in the urine in small quantities, pain is mild, and signs of intoxication may be absent.
Leukoplakia
In the case of the bladder, it is a chronic process when the cells lining the walls of the organ are normally replaced by cells of squamous keratinizing epithelium.
The main sign of pathology is chronic dull pain in the pelvic area, pain or burning during urination, and disturbances in this process.
Tumor
A bladder tumor that affects the bladder causes such clinical signs as the appearance of blood in the urine, urinary disturbances in the form of difficulty and the process accompanied by itching or cutting pain, pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, perineum and sacrum.
SRMP
Irritable bladder syndrome is essentially a psychosomatic pathology of the process of urine excretion. The clinical picture will be represented by urination disorders in combination with pain and itching , increased nighttime urge to visit the restroom, a constant feeling of an organ full of urine, and a small amount of evacuated urine.
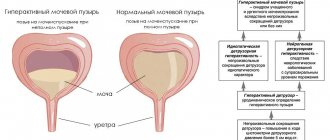
Hyperactivity
The disease manifests itself in the form of a sudden and irresistible desire to visit the toilet for minor needs, there may be incontinence, increased urination, especially at night.
Neurogenic
A variant of a complex urination disorder associated with disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. The clinical manifestations and course of the disease are very diverse .
Cold
In the case of this anatomical structure, it begins with general weakness and cutting pain in the area where it is located. Then the process of urine excretion becomes more frequent, but the amount released at a time decreases, down to a few drops. There is also sharp and severe pain in the lumbar and lower abdomen, fever, and a change in urine to a darker shade with a pungent odor.
Endometriosis
quite specific to men , which develops due to the fact that they sometimes retain the rudiments of embryonic tissue that gives rise to the entire genitourinary system, and is also characteristic of the female body.
These cells become the basis for the development of endometriosis, especially often when a man receives estrogen therapy.
Atony
It manifests itself in the form of uncontrolled urination , its spontaneity, but with a purposeful visit to the restroom there may be urine retention or incomplete excretion . Patients note that the stream becomes weak.
exstrophy
It is a malformation of the genitourinary system , when the bladder is not localized intraperitoneally, as it opens from the outside. In this case, there will be no anterior wall of this organ, and the ureters will open to the outside world.
Polyps
They represent an abnormal process of tissue proliferation on the mucous membrane of the bladder . The disease can be completely asymptomatic. But when straining, the polyps can become injured or even tear off, since they are located on a thin stalk, and then an admixture of blood appears in the urine.
Cyst
It manifests itself primarily as dysuria, fever, abdominal pain, general malaise, the appearance of swelling or hyperemia on the abdominal wall below the navel.
Diverticulum
This sac-shaped depression is a developmental anomaly that is formed in utero or acquired with a prolonged increase in intravesical pressure, combined with overstretching of the weakened walls of the organ.
It manifests itself in the form of dysuric disorders, urinary retention, the process of urination becomes two-stage (the first part is normal urine output, the second is from the diverticulum and during straining). Blood or pus may appear in the urine.
Weak bladder
It can be in this state due to infections or pathologies of the prostate in men. The main symptoms will be an increased urge to urinate , especially at night, and urinary incontinence.
Prolapse or cystocele
It manifests itself as a constant feeling of needing to go to the restroom, but when you try to urinate, nothing happens. In turn, urinary incontinence may also occur, especially with abdominal strain and lifting heavy objects. Pain in the lower abdomen also appears, radiating to the lower back.
Cancer
Bladder cancer is a terrible diagnosis for any person ; it proceeds for a long time without any symptoms, and then general weakness and hematuria appear.
Urinary incontinence
This disease in men is often associated with diseases of the bladder sphincter or with increased activity of the muscle layer in the walls of the organ.
The pathological processes of the bladder are quite similar in their symptoms and the result of a number of tests is necessary for a conclusion, so you cannot try to make a diagnosis yourself .
Folk recipes
Alternative medicine has gained extensive experience in the treatment of urological infections. The recipes have many positive reviews, which confirms the effectiveness of the methods. But they can only be used in combination with drug treatment.
Good results are obtained by ingesting decoctions of parsley root, chamomile, and tincture of lingonberry leaves. Drinking lingonberry juice has an excellent sanitizing effect. The healing qualities of “bear ears” and cranberries have long been known. You can prepare the following composition and take it three times a day after meals:
- take dry herbs of rosemary, lovage, centaury, and rose hips in equal proportions;
- pour boiling water for 30 minutes;
- boil in a water bath for 20 minutes;
- leave for 30 minutes;
- strain and drink as above.
It is contraindicated to drink alcohol, strong drinks, or smoke during treatment.
Basic treatment methods
Treatment of the bladder in men can be carried out in several ways:
- Medication;
- Surgical;
- Complex.
Drug therapy consists of prescribing certain drugs.
Antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, drugs to eliminate dysuria, immunotherapy and herbal medicine are mainly used.
The use of any drug should be discussed with a medical professional to ensure the appropriateness of its use.
Sometimes a bladder lavage is prescribed, which is most often necessary for patients with an inflammatory process in this organ.
Bladder surgery in men can be represented by one of four options:
- Cystolithotripsy/cystolitholapaxy;
- Resection;
- Transurethral resection;
- Cystectomy.
Cystolitholapaxy and cystolithotripsy are the removal of stones from the bladder cavity. Resection is the removal of part of an organ, and transurethral resection is similar to the removal of part of an organ, but without an incision in the abdominal wall. Cystectomy or removal of the bladder in men is a radical operation, the choice of which occurs only in the case of organ pathology that threatens the patient’s life.
Functions
The main role is to control the periodic act of releasing urine into the external environment. Storage and emptying of urine occurs about 8 times in 24 hours, with a yield of 1500 ml. During the storage phase, the muscles relax to facilitate expansion of the bladder during filling, while at the same time the internal sphincter contracts to prevent leakage.
Together with urine, waste products leave the body, and by diagnosing them, existing or developing diseases can be identified.
Bladder rupture
There is such a thing as bladder rupture . Since the walls of this organ are very elastic, they stretch when urine accumulates. If the urge to urinate is ignored for a long time, the walls of the organ gradually become overstretched , and if there is any injury or even a slight blow, they may rupture.
A rupture can also occur due to injury, such as in a traffic accident or a fall from a great height . Organ rupture is also possible gunshot or knife wounds
This type of damage can be extraperitoneal or intraperitoneal. The first case is typical for an incompletely filled state of the organ, when the contents will leak into the soft tissues surrounding the bladder. The second case is more complex and occurs exclusively when the organ is overcrowded, then there is a rupture of the apex of the bladder and the release of urine into the peritoneum.
In the event that a rupture of this organ occurs, restoration surgery is prescribed .
Understanding where the bladder is located in men , its structure, functions, as well as possible diseases and their treatment, makes it possible to understand the need to take seriously the maintenance of the health and integrity of this organ. It also helps to understand or suggest certain reasons that could cause discomfort associated with disturbances in the functioning of this structure.
Features of postpartum cystitis
The postpartum period requires close attention and monitoring of the postpartum woman, especially at home. Compliance with the rules of careful hygienic care and a regime of frequent urination will help to avoid possible complications of the period after childbirth and the addition of urinary tract infections.
Postpartum cystitis occurs in the same way as any other, but its treatment is difficult because not all medications can be taken by a nursing woman. In addition, this period is characterized by the presence of damage to the external genitalia, which makes it difficult to urinate and use the usual toilet.
Severe forms of the disease rarely develop, since treatment of cystitis does not cause significant difficulties. But most often we have to deal with a chronic form that is difficult to correct with drugs if the causative agent is a multidrug-resistant microorganism.