Blood urea level
In adults, the amount of the substance is determined during a biochemical blood test. To make the results more accurate, it is advisable to take it in the morning and on an empty stomach. Indicators that are considered normal differ for all people - it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body:
Urea is a blood component that should not be underestimated. It can tell you a lot about the condition:
- The excretory function of the kidneys is how successfully they cope with the removal of all excess substances accumulated in the body.
- Muscle tissue - it mainly contains protein, the breakdown of which forms urea.
- The liver is the one that produces this substance from ammonia.
Urea in the blood signals the functioning of various organs and systems, and its increase indicates severe disorders that require mandatory treatment.
Ammonia transportation
Blood transports ammonia in a bound form, which is much safer. Since self-poisoning of the body does not occur. In a free state, the blood cannot deliver this substance to the liver, where it is completely neutralized thanks to urea formation enzymes, which are found only in the liver.
The liver is the only organ capable of converting ammonia into urea. Then the less toxic urea enters the kidneys through the bloodstream. Only 90% of this substance is excreted here, the rest is removed through the pores of the skin. This mechanism works equally in both women and men.
The body must maintain urea levels in the blood at a certain level.
When is the test ordered?
Donating blood for urea is indicated in the presence of symptoms characteristic of renal pathologies. Among them are:
Blood biochemistry is often carried out during a hospital stay, after treatment for various pathologies. The analysis shows an increase or decrease in indicators, but does not determine the cause of the violations. If measures are taken immediately and treatment is not delayed, the pathology is reversible. To ensure accurate results, you need to follow simple rules before taking blood:
- Eight hours before your visit to the hospital, do not eat anything.
- Two days before the analysis, it is advisable to give up unhealthy foods and alcoholic beverages.
- During the previous 24 hours, it is advisable to avoid physical and emotional stress.
Briefly about the main thing
A high concentration of urea, produced by the liver and excreted from the body by the kidneys along with nitrogenous compounds, is only a symptom, but not an independent disease. Since a similar condition can be observed with many ailments, attending physicians do not make a diagnosis, relying only on the results of a blood test; if an abnormality is detected, they prescribe other clarifying studies to patients.
Excess urea is a common medical phenomenon that does not always manifest itself externally. If we talk about symptoms, it is worth noting that uremia mainly causes swelling, hypertension (high blood pressure), psychological disorders, shortness of breath, chronic fatigue and headaches. The person also suffers from sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, poor concentration and tachycardia.
The following parameters indicate an increased urea content:
- {amp}gt;6 mmol/l – newborn babies;
- {amp}gt;7 mmol/l – children from one month to 14 years;
- {amp}gt;7.2 mmol/l – adults under 60 years of age (in men, the uremia rate is slightly different - more than 7.7-7.8 mmol/l);
- {amp}gt;8.6 – elderly people (sometimes the urea value exceeds this parameter, which is not considered dangerous).
The number of urea molecules increases significantly against the background of gastric ulcers, polycystic kidney disease, thrombosis, dysentery, urolithiasis, cholera, hepatitis, measles and rubella. However, pathology is especially often observed in renal failure, rubella and sore throat. The breakdown of protein structures, which increases the concentration of urea in the blood, occurs in those who prefer to engage in dancing and sports (especially when it comes to strength training).
People who eat too much protein and are chronically apathetic and depressed may also have test results indicating uremia. By the way, even the use of a number of pharmaceutical drugs leads to a harmless increase in urea levels. If you use any medications on an ongoing basis, it is advisable to discuss this nuance with a specialist - this will help to avoid false results.
Reasons for deviations
If an adult has high urea in the blood, what does this mean? The factors that provoke an upward change in this indicator are quite varied and not in all cases they are caused by serious illnesses. Physiological ones include:
- taking certain medications,
- frequent consumption of protein foods or, conversely, fasting,
- physical exercise,
- emotional turmoil
- chemical poisoning.
In all of these situations, the indicator normalizes without any therapy. Other reasons for increased urea levels in the blood include:
- Various kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, glomeluronephritis, failure, tuberculosis.
- Poor circulation or bleeding.
- Obstruction of the ureters or mechanical obstructions that interfere with the process of urine excretion.
- Vascular pathologies.
- State of shock.
- Long-term dehydration.
To establish the exact reason why there is an increased level of urea in the blood, experts evaluate it over time. In this case, the patient is asked to take a urine test to determine the amount of the substance in this biological material. When making a diagnosis, other blood parameters and clinical signs must be taken into account, which can be used to adequately assess a person’s well-being.
Causes of the disease
If there are pathologies or disturbances in the functioning of the organs involved in the production of this component, changes in indicators and deviations from the norm appear. In most cases, there is an increase in the concentration of the substance, called uremia or hyperazotemia. In particular, the destruction of muscles in the body leads to a sharp increase in the indicator, since the main part of the protein is located in muscle tissue.
Let's look at the reasons why urea in the blood is elevated, and a little later you will know how it can be treated.
If any inflammatory processes occur in the body over a long period, and there are also malignant tumors or various diseases, including those of the endocrine system, a strong increase in urea occurs against the background of depletion of the body, since many of these disorders lead to increased processes of protein breakdown . For this reason, the concentration of urea in the body, not only in the blood, but also in the urine, increases sharply.
The level of the substance may also increase in the presence of kidney diseases, for example, pyelonephritis, renal amyloidosis, glomirulonephritis and other ailments. The same situation arises if there are problems in the functioning of the excretory system as a whole, in particular with prostatitis in men, with stones in the kidneys or inside the bladder, with inflammation, or with the formation of tumors in the bladder.
High levels of urea in the blood are often observed in people with severe heart and kidney failure, and problems with the circulatory system.
The level also increases when receiving extensive burns, with intense bleeding, as well as in conditions that cause dehydration of the body.
But an increase in this value does not always indicate the presence of a disease; in some cases, such research results may be erroneous or falsely elevated. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to follow the general rules for preparing for submitting material for research. And you should come to the blood sampling procedure on an empty stomach and early in the morning, since blood counts change throughout the day.
A false increase in element level can be observed due to:
- Serious physical activity before the procedure or during the day before it.
- Taking medications of certain categories.
- Fasting or, conversely, eating too much food containing large amounts of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Eating smoked, sweet, fried, salty, pickled foods the day before.
Elevated urea in the blood is detected in a wide range of different abnormalities. Their number is so large that sometimes even specialists are not able to determine at first what causes the increase in carbonic acid diamide. Uremia is a consequence of both pathologies that require immediate treatment, and multiple biochemical processes that do not pose any danger to human health.
Diseases
What is uric acid responsible for in the blood?
- renal failure (chronic and acute);
- thyrotoxicosis (excess of hormone synthesized by the thyroid gland);
- stomach ulcer;
- nephritis (kidney inflammation);
- diabetes;
- thrombosis;
- pneumonia of viral origin;
- BPH;
- intestinal obstruction;
- myocardial infarction;
- typhoid fever;
- rubella;
- nephroblastoma (malignant tumor of the renal parenchyma);
- heart failure;
- peritonitis;
- measles;
- dysentery;
- severe dehydration;
- calculi (stones) in the bladder and kidneys;
- abscess;
- thrush;
- cardiac ischemia;
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney glomeruli - glomeruli);
- myositis (damage to muscle fibers);
- polycystic kidney disease;
- meningitis;
- cholera;
- sepsis;
- angina.
Receiving 3-4 degree burns forces the body to intensify the process of protein breakdown, as a result of which the urea indicator increases significantly.
Diseases associated with the hematopoietic and circulatory systems can increase urea levels: pernicious anemia, leukemia, leukemia, etc. In people suffering from cirrhosis, hepatosis (fatty liver), hepatitis or hepatic tuberculosis, it will most likely also appear in the biochemical analysis. high urea content.
Another cause of uremia in some cases is hemorrhagic fever. We are talking about an extremely dangerous anomaly, which is expressed by the manifestation of severe symptoms: chills, increased body temperature, convulsions, heavy bleeding, swelling, paralysis, hardening of muscles.
Patients experience paresthesia (impaired sensitivity of the mucous membrane and skin), dyspepsia (stomach dysfunction), the formation of extensive hematomas and destruction of vascular walls. If this disease is not treated, then all internal organs will soon begin to fail, which will lead to death. If you identify the above symptoms, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Poisoning with toxic substances can provoke an increase in urea: phenol, trichloromethane, arsenic, ethylene glycol, lead and sublimate (mercuric chloride)
And it also increases the level of urea in the blood. Leptospirosis is an infectious disease characterized by the negative impact of pathogenic worm-like bacteria on the cells of the kidneys, liver, skin, blood vessels, stomach, heart, muscles, brain and spinal cord. This disease is accompanied by muscle pain, hyperpigmentation, skin rash, red eyes, sleep disturbance and difficulty breathing. Bleeding occurs (uterine, intestinal, nasal).
Such a deviation must be treated immediately to avoid severe complications or even death (for example, from pulmonary edema). Not so often, high levels of urea are observed in young children due to impaired synthesis of enzymes that are responsible for protein metabolism.
As a rule, such diseases develop as a result of a malfunction in the genetic program of babies at the stage of their formation in the womb. Information on various methods for reducing urea is contained in this article.
Excess urea indicated in the results of biochemical analysis is in many cases explained by dietary habits. The indicator increases with a significant predominance of protein foods in the diet: seafood, fish, fermented milk and dairy products, meat. If the patient ate a large portion of protein-rich food the day before donating blood, the carbamide content will be high, but completely harmless.
To obtain more objective information about the state of your health, it is better to limit the consumption of such products at least a day before diagnosis. Any diet that excludes sodium chloride (table salt) also causes uremia. Regular sports or dancing, as well as prolonged stress, lead to accelerated breakdown of proteins in the body.
Excess urea is observed during the use of such drugs:
- androgens (male sex hormones of steroid origin);
- thyroxine (the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland);
- sulfonamides;
- some aminoglycoside antibiotics;
- aristolochic acid in dietary supplements;
- diuretics (diuretics);
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect).
If you are using medications that belong to the previously designated groups, you should inform your doctor.
The reasons for increased urea in the blood can be physiological and pathological. Physiological factors include:
- physical and emotional stress (a high concentration may mean that the person underwent physical activity or was exposed to stress shortly before donating blood);
- a high-protein diet with the consumption of animal proteins - meat and eggs, and fasting for a long time (the so-called protein diets combine both prerequisites for increasing urea).
Fluctuations in this indicator are observed after drug therapy using tetracyclines, corticosteroids, and cephalosporins. And medications such as Streptomycin, Levomycetin and Somatotropin can reduce the concentration of urea. The level of this substance also decreases in pregnant women.
An increase in urea in the blood may indicate pathological processes. This change is observed when:
- acute and chronic renal failure;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- obstruction of the urinary tract with a hard stone or tumor;
- diseases of the endocrine glands;
- intestinal obstruction and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- dehydration;
- leukemia, lymphoma and plasmacytoma;
- oncological diseases with extensive metastases;
- burn injuries;
- septic processes;
- heart diseases.
An increase in urea in the blood is observed during infectious diseases and chemical poisoning, after blood transfusion and in the postoperative period, as well as with significant tissue damage.
Symptoms
If urea is significantly increased in a biochemical blood test, it is important to understand the cause of the disturbances. To do this, you should evaluate the accompanying symptoms, which usually appear after some time. Among the main ones are:
- frequent urination,
- brittle nails and hair,
- chronic diarrhea,
- general malaise,
- joint pain,
- decreased performance,
- dry skin,
- high pressure,
- iron deficiency in the blood.
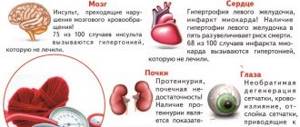
If a kidney disease develops in the body, it will certainly manifest itself with quite serious symptoms:
- problems with emptying the bladder,
- blood impurities in the urine,
- pain in the lower back,
- pale skin,
- swelling,
- anemia,
- blurred vision.
An upward change in urea levels can cause poor circulation and other serious consequences. If a person is not aware of the problem, the body becomes infected with ammonia, which is very toxic. As a result, even the skin begins to smell of urine. In the absence of proper therapy, brain cells die over time, which can cause serious problems. That is, high urea in the blood is an alarming sign, quite dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the patient.
Decrease in urea
A decrease in UREA is associated with physiological or pathological reasons. So, temporary reasons include: 1. Infancy. 2. Bearing the fetus. 3. Retirement age. 4. Vegetarianism, diet. 5. Excess fluid in the body - overhydration. 6. Hemodialysis – blood purification. With a significant decrease in indicators, a number of signs appear, namely: decreased appetite; weakness; swelling; bloating; sudden weight loss; belching with a bitter taste; pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
If there are 60% matches, the doctor prescribes an additional examination to identify one of the following pathologies: • Kidney failure. • Cirrhosis of the liver. • Poisoning. • Hepatitis. • Decreased efficiency of the thyroid gland – hypothyroidism. • Acromegaly – enlargement of body parts due to increased production of growth hormones. • Pancreatitis. • Helminthic infestation. • Oncology. The treatment method is determined depending on the type and severity of the disease. So, in case of physiological abnormalities, it is enough to normalize the diet and maintain a healthy lifestyle. But if serious pathologies are detected, the doctor prescribes medications, IV drips or chemotherapy.
Treatment
If elevated urea is detected in the blood of men and women, the doctor must determine the cause of this condition and only then select the optimal treatment option. Its main task is to eliminate the disease and normalize test results. Therapy includes several important activities:
- Correction of nutrition and drawing up the correct menu with a reduction in protein foods and an increase in the amount of plant foods.
- Reducing physical activity to avoid overwork.
- Complete absence of worries and stress.
- Control of the balance of water and salts in the body.
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases.
Diet
When a blood test reveals a urea level of 7-7 mmol or higher, the patient is advised to reconsider his usual diet. Nutrition should be healthy and proper. The main goal is to normalize the indicators and prevent them from changing again. Among the products that are allowed for patients:
- fruits and vegetables in unlimited quantities,
- dairy dishes, eggs,
- cereals and pasta - no more than twice a week,
- lean meats,
- Fish and seafood,
- freshly squeezed juices, weak tea or coffee, herbal infusions,
- Homemade preserves and jams.
If the level of urea changes, you should avoid all fatty foods, smoked meats and pickles, canned food, store-bought sausages, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, mayonnaise, spices, and mushrooms. Compliance with the diet should be supported by an optimal drinking regime - up to two liters of water per day. You should not starve or reduce the number of calories - this can worsen the condition. Food should be taken up to six times a day, in small portions.
Drug therapy
One of the effective options for lowering blood urea is taking medications. The specific drug and dosage are determined by the doctor. Most often, patients are prescribed Probenecid - it effectively removes acid, but in combination with other medications it can be dangerous. An alternative option is Allopurinol. The drug promotes the excretion of urea and dissolves urates. You need to take the medicine until your blood counts normalize.
In case of chronic kidney diseases, it is very difficult to restore the optimal level of urea. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- Intravenous infusion therapy, in which it is necessary to monitor the volume of urine output.
- Diuretics.
- Means for detoxification of the body. The patient is shown sorbents to remove decay products and lower urea levels.
One of the methods of treating kidney pathologies is dialysis. This medical procedure is performed when the kidneys are unable to remove excess substances from the body on their own. Additionally, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can take medications to normalize blood counts.
Folk remedies
You can normalize urea levels using various folk remedies. The most commonly used are teas and infusions made from medicinal herbs. It can be:
- juniper,
- St. John's wort,
- elder,
- rosehip leaves,
- black currant fruits.
Before using any product, be sure to talk to your doctor and get his approval. He will help you choose herbs that do not cause allergies and prescribe the optimal dosage.
One of the most popular treatments for high urea is bearberry leaves. They need to be crushed, poured with hot water, sent to a water bath and cooked for a quarter of an hour. Strain the finished product and consume thirty minutes before meals. Licorice root has a good effect. It is poured with boiling water and kept on low heat for about ten minutes, after which it is infused for eight hours. Strain the medicine and use up to three times a day.
If the urea level has changed due to stress or physical strain, there is no reason to worry. Healthy kidneys will quickly restore the natural balance of substances. A persistent change in normal values indicates severe pathologies in which alternative medicine recipes will not give a positive result.
What does increased urea mean?
A slight increase in UREA is often associated with the following reasons: • Intense training. • Taking medications. • Diets or excess protein in the body. • Frequent stress. • Dehydration of the body. If all of the above points are excluded, then you need to look for the cause among various diseases: 1. Kidney, heart failure. 2. Oncology. 3. Poisoning. 4. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). 5. Myocardial infarction. 6. Diabetes mellitus. 7. Anemia. 8. Tuberculosis. 9. Sepsis. 10. Typhoid fever. 11. Urolithiasis – problems with the outflow of urine due to the presence of stones in the ureter and kidneys.
The main symptoms of increased urea include: fatigue; frequent urination; high blood pressure; dry skin; headache; nausea; back pain; sudden deterioration of vision. If urea increases, the patient must repeat the test after 3-5 days. If there are repeated elevated results, the doctor prescribes an additional examination and subsequently treatment and preventive measures, for example: • Normalization of nutrition - consume more vegetables, fruits, natural juices, but reduce the consumption of meat products. • Reduced physical activity, especially for professional athletes. • Reducing stressful situations. • Taking medications. • Elimination of bad habits. • Sleep – at least 8 hours. • Consumption of regular still water – from 1.5 liters per day. • Surgical intervention.
In conclusion, we note that urea is a waste product of the breakdown of amino acids, which is excreted in the urine. Moreover, deviation of UREA from the norm is often associated with physiological or pathological reasons, about which you can read more in our material.
Reasons for the downgrade
A low level of urea may be a consequence of fasting, a strict diet, or indicate unfavorable processes occurring within the body. Very low levels of urea are especially dangerous. Most likely, the patient has serious liver problems. Low urea accompanies viral or alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and various cancers. Indicators below normal may occur due to dysbacteriosis or severe poisoning. Reduced urea in vegetarians, pregnant women and after hemodialysis.
Diet for high urea
To reduce the urea content, doctors must prescribe a diet with
When treating pathology, a special diet is recommended
protein restriction. The amount of salt consumed in the diet is also reduced to avoid fluid retention in the body. Although it is not recommended to completely give up salt.
To reduce urea, it is recommended to limit or eliminate the use of:
- meat, fish, poultry
- cottage cheese, milk, eggs, cheese
- spices, sausages
- marinades and smoked meats
- White bread.
It is undesirable to overuse pasta, peas and beans. The main menu for a patient with high urea should include:
- baked, boiled potatoes
- carrots, cabbage, cucumbers, beets
- buckwheat, oatmeal, millet, barley porridge
- vegetable salads with vegetable oil
- nuts, fruits, berries
- dairy products.
Among sweets, honey, jam, and candies (with the exception of chocolate) are allowed. The natural diuretic watermelon promotes urine excretion, so it is recommended to eat as much of it as possible during the season.
To quickly reduce urea levels, nutritionists advise drinking alkaline water:
- Borjomi
- Essentuki
- Polyana Kvasova
- Luzhanskaya
- Svalyava
In addition to mineral water, the diet includes tea with lemon, tomato juice, and rosehip decoction. But it is better to exclude cocoa from the usual menu for a while.
You can reduce the concentration of urea by regularly consuming a decoction of lingonberry or birch leaves.
It is advisable to draw up a detailed diet together with your doctor, based on the urea levels of a particular patient.
If urea levels have increased as a result of severe stress or physical strain, there is no need to worry: healthy kidneys will restore the balance of substances. But persistent excess of the norm indicates serious pathologies in which traditional methods will be powerless.
Experts will tell you about the normal level of urea in the blood in the video:
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Liked? Like and save on your page!
Urea is a protein recycling product that does not cause harm to the body, but also does not perform any useful functions. This substance is secreted by the liver from ammonia, which is characterized by its toxicity. After this, it enters the bloodstream, is transported to the kidneys, filtered and ultimately excreted in the urine. If tests show that urea in the blood is elevated, then the doctor will decide the causes and how to treat the disease after conducting a comprehensive examination.
Urea in the blood
Increased concentration: causes and symptoms
A persistent increase in the level of urea in the blood indicates the presence of kidney problems
In addition to physiological aspects, urea content is also affected by diseases of internal organs, namely:
- Kidney diseases (urolithiasis, polycystic disease, nephrosis, renal failure, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis)
- Intestinal infections (cholera, salmonellosis, dysentery)
- Blood diseases (leukemia, leukemia, hepatitis)
- Diseases of the muscular system (progressive dystrophy, myositis, gangrene)
- Burn disease, traumatic or septic shock
As a result of a violation of the filtration function of the kidneys, urea returns to the body and begins to accumulate in the blood. In addition to urea, the content of ammonia, creatinine, acetone and other substances toxic to the body increases in the blood.
It is impossible to determine elevated urea levels without a blood test.
Symptoms of accumulation of nitrogenous waste are accompanied by symptoms of fatigue: headaches, weakness, increased fatigue. If you don’t consult a specialist at this stage, attributing the symptoms to fatigue, other signs will soon appear:
- swelling
- muscle pain
- decrease or increase in urine
- increased sweating
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, vomiting, nausea)
- decreased visual acuity.
Unable to find a way out in the urine, urea and nitrogenous compounds seep through the skin: a phenomenon called “uremic frost.” It is possible to save the life of a person in this condition only with the help of hemodialysis.
In chronic kidney disorders, it is very difficult to reduce urea concentrations. Conservative methods of reducing urea levels are advisable only in the absence of a serious disease.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on identifying the cause of the increase in urea.
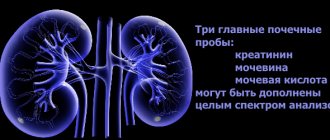
How to reduce creatinine in the blood with kidney failure - treatment and diet
Creatinine is the end product of protein metabolism involved in energy metabolism in muscle cells. The formation of creatinine occurs in the liver tissue, then this substance enters the blood.
Disposal of this substance from the body is carried out by the kidneys. When the kidneys are fully functioning, creatinine is completely filtered without subsequent reabsorption of this substance. In this regard, creatinine level is a highly accurate marker reflecting kidney function.
The levels of this substance in the blood are relatively stable and are determined primarily by muscle volume.
An analysis of creatinine levels is carried out when:
- study of kidney function;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy for acute renal failure and chronic renal failure (acute and chronic forms of renal failure);
- taking medications that may have a negative effect on kidney function (nephrotoxic drugs);
- bleeding;
- dehydration (due to vomiting, intestinal infection, etc.);
- damage to muscle structures;
- hyperthyroidism;
- acromegaly, gigantism, etc.
Read further: Table with creatinine levels in the blood of women and men
What can elevated creatinine levels indicate?
Increased creatinine levels may occur in individuals with:
- acute renal failure and chronic renal failure;
- unbalanced diet and consumption of a significant amount of foods that increase creatinine;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- severe internal bleeding;
- large volume of muscle tissue;
- radiation sickness;
- diseases of endocrine origin (gigantism, acromegaly, hyperthyroidism);
- severe injuries or inflammatory damage to muscle tissue.
Also, treatment with nephrotoxic drugs (sulfonamides, thiazide diuretics, aminoglycosides, tetracycline agents, barbiturates, salicylates, androgenic hormones, etc.) can lead to an increase in the level of creatinine in the blood.
A false-positive increase in cratinin levels in the blood can be observed in individuals with high levels of glucose, fructose, ketone bodies, urea, as well as during treatment with ascorbic acid, levodopa, cefazolin, cefaclor, reserpine, nitrofurazone, ibuprofen, etc.
What do the reduced values indicate?
A natural decrease in creatinine levels occurs in older people, pregnant women and vegetarians.
Also, a decrease in creatinine levels can be observed against the background of muscular dystrophies, long-term treatment with corticosteroids, during fasting or following a low-protein diet, as well as during overhydration.
What does it mean if both creatinine and urea in the blood are elevated?
Urea is a name given to nitrogen-containing products formed as a result of protein breakdown. The production of urea is carried out by the liver tissues due to the processing of ammonia, and the utilization of urea is carried out by the kidneys. In this regard, urea levels can be used to determine the rate of protein catabolism and kidney function.
Elevated readings may indicate:
- development of azotemia against the background of glomerulonephritis, acute renal failure and chronic renal failure, renal amyloidosis, pyelonephritis, use of nephrotoxic drugs, etc.;
- the patient has heart failure;
- severe burn damage to the skin;
- bladder tumors;
- severe blood loss;
- intestinal obstruction;
- the patient has a prostate tumor;
- leukemia;
- excessive consumption of protein foods;
- treatment with androgen drugs, etc.
Low values may be detected in patients with:
- liver diseases accompanied by a violation of its protein synthetic function;
- hepatic coma;
- acromegaly;
- malabsorption, etc.
Also, a decrease in urea levels can be diagnosed in pregnant women, vegans and people on a low-protein diet.
The most common cause of a significant increase in creatinine and urea in the blood is acute renal failure or chronic renal failure. In this regard, a blood test for creatinine and urea is used both to diagnose this disease and to monitor the quality of treatment.
Treatment for high creatinine and urea in the blood should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable and can cause irreparable harm to the patient’s health.
Read further: Norms of creatinine in urine and causes of deviations
How to reduce creatinine and urea in the blood using folk remedies
Reducing creatinine in the blood using folk remedies can only be carried out if the patient does not have impaired renal function, and the increase in creatinine levels was caused by poor diet.
In this case, the patient is recommended to drink plenty of fluids and normalize their diet.
How to lower creatinine in the blood at home
A diet with elevated creatinine should be low in protein. This is explained by the fact that these substances appear as a result of protein metabolism.
A diet to reduce creatinine in the blood involves:
- limiting the consumption of meat products;
- refusal to eat sausages, sausages, smoked meats, canned food, red and black caviar, mushroom dishes;
- limiting the consumption of chocolate;
- limiting the consumption of spices, garlic, onions, coffee, strong tea and cocoa.
It is recommended to eat fruit and vegetable dishes, lean meats and fish, and cereals.
The specified diet for elevated creatinine in the blood in women and men can be used provided that the patient does not have pathologies of the kidneys, liver, endocrine glands, etc., and the increase in urea and creatinine levels is caused only by poor nutrition.
The diet for kidney failure and elevated creatinine includes strict restrictions on the amount of fluid, salt and protein consumed. The menu for this disease is compiled strictly individually and depends on the form of the pathology and its stage. The amount of fluid and protein consumed is calculated based on the stage of the disease and the patient’s body weight.
How to reduce creatinine in the blood with kidney failure
Many patients are interested in what drugs are used to reduce creatinine in the blood. It should be understood that with chronic renal failure or acute renal failure, high creatinine in the blood is a reflection of impaired renal function. In this regard, treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of acute renal failure or chronic renal failure and correcting impaired renal function.
How are patients with acute renal failure treated?
In the acute course of the disease, the most important role in treatment is played by the elimination of the pathological condition that caused renal failure (sepsis, infectious-toxic shock, CRASH syndrome, peritonitis, acute blood loss, etc.)
Plasmapheresis is also performed. The volume of plasmapheresis performed depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the severity of intoxication symptoms.
Plasma removed during plasmapheresis is replaced with fresh frozen solutions of plasma, albumin, etc.
According to indications, blood transfusions or blood substitute solutions may be performed. Intravenous drips of prednisolone are also used. Exchange transfusions are performed in patients with severe intravascular hemolysis and a hematocrit below twenty.
Additionally, anti-shock therapy and detoxification are carried out. For bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Antibiotic dosages are reduced according to the severity of renal failure.
According to indications, in the early stages of development of acute renal failure, it is advisable to use mannitol® or furosemide® to eliminate anuria.
Under the control of creatinine levels, Adsorbix® is prescribed.
In addition to drug therapy, a low-protein diet is prescribed (the caloric content of the diet is provided by fats and carbohydrates), and the intake of salt and liquid is limited. The volume of orally consumed fluid depends on the patient's urine output and the volume of intravenous infusions.
Salt intake should be limited to 0.2-0.3 grams per day, and protein to 0.5-0.6 grams per kilogram of body weight. The volume of fluid consumed = the volume of the patient’s urine output over the past day + three hundred milliliters.
Additionally, homeostasis disturbances are corrected.
Patients with urea levels above two grams per liter, as well as decompensated forms of metabolic acidosis or acute uremia, are prescribed hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Dialysis is contraindicated in patients with hemorrhages in brain tissue, gastric and intestinal bleeding, or arterial collapse.
Peritoneal dialysis is contraindicated in patients with adhesions in the abdominal cavity, as well as in cases where the patient has recently undergone abdominal surgery.
Why do you need an analysis for the presence of urea in urine?
When the level of urea in the blood is high enough, the doctor may need to find out its content in the urine. If the urine test shows a low content, and the urea in the blood test is increased, this indicates that the kidneys are not coping well with the nitrogen excretion function. Renal failure or hypovolemia (formed due to weakened blood flow or insufficient volume of circulating blood in the kidneys), heart failure and much more. This analysis is performed much less frequently, but its significance gives a clearer picture of kidney performance.
The level of urea in urine is influenced by concomitant ailments, food preferences, physical overload, use of medications, etc. In adults, the level of urea in urine is from 333.1 to 587.7 mmol/day. In children it is much lower, and increases as they grow older. For example, a one-month-old baby has a urine level of 10 mmol/day. up to 17.0 mmol/day, and by the age of 8 it reaches about 200. Before the analysis, do not consume vegetables or fruits that change the color of urine.