Primary phosphaturia occurs in many pathological conditions, but most often with metabolic disorders, diseases of the central nervous system and parathyroid glands. The primary appearance occurs with congenital enzymopathy, due to a violation of the reverse absorption of phosphates at the cellular level. In the case of secondary phosphaturia, it always occurs with a bacterial or viral infection and an increase in urine pH. This leads to the precipitation of phosphate compounds with their normal total amount in the urine.
It must be remembered that with an alkaline or slightly acidic reaction of urine, when it is kept warm, fermentation develops very quickly and phosphates, which were previously in a soluble state, precipitate, as a result of which it becomes cloudy.
Nutrition for phosphates in urine
The diet for phosphaturia is aimed at preventing the following pathological processes - restoring normal pH levels and preventing the formation of salt deposits. In this case, the most suitable dietary table is No. 14.
Basic nutritional features for phosphates in the urine:
- daily energy value should not exceed 2500 kcal;
- liquid – no more than 2.5 liters per day;
- daily dose of table salt – no more than 5–7 g;
- content of simple and complex carbohydrates – from 300 to 500 g;
- fat consumption – up to 100 g;
- plant and animal proteins - up to 100 g, and there should be more of the former (approximate ratio 70/30).
Basic rules of table No. 14:
- Limit calcium-containing and alkalizing foods - milk, cheese, walnuts.
- The predominance of cereals, fish, lean meat, that is, increasing acidity.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- green vegetables (cabbage, broccoli, onions, peas, sorrel);
- fruits and berries (apples, pears, lingonberries, raspberries, pomegranate);
- grains, as well as legumes and various cereals;
- lean meat and fish;
- chicken and quail eggs (preferably without yolk);
- natural sweets (honey, beet sugar);
- bakery products, in the preparation of which a small amount of yolk and milk is used;
- vegetable oils;
- drinks (compote, uzvar, tea and coffee);
- mineral water (increasing acidity).
- all alcoholic drinks;
- prepared sweets (chocolate, marmalade, etc.);
- cakes;
- fatty animal meat and fish, lard;
- all dairy products without exception;
Menu for phosphaturia
Meals must be fractional and at least 4 times a day. For breakfast, you can eat several boiled egg whites, as well as buckwheat and oatmeal. It is recommended to drink no more than 150 milliliters of weak tea or instant coffee.
For lunch you need to eat chicken and fish soup, boiled rice and juice (jelly).
For an afternoon snack, a few slices of bread and any berry juice.
For dinner, up to 50 grams of chicken or other lean meat, vegetable salad and tea (coffee) are allowed.
Before going to bed, you can drink a glass of rosehip decoction.
Diet for phosphaturia is the most important measure in the treatment of increased amounts of phosphates and the formation of their sediment in the urine. Strict adherence to dietary table No. 14 is guaranteed to normalize the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the human body.
A diet for phosphaturia prohibits the consumption of dairy and fermented milk products, does not allow improving the taste of food with spices and hot seasonings, and requires giving up coffee.
Urinalysis showed that the test sample contained phosphates in the urine. Should I immediately sound the alarm and start treating kidney disease? There is no need to be scared. The analysis should simply be retaken, preferably after two to three days.
The formation of phosphates may be related to diet. The urine of vegetarians is characterized by the presence of phosphates. A decrease in the intake of animal proteins into the body also causes their formation. Metabolic products of acidic consistency reduce the phosphate content in urine, and they are released by the body only if there is meat and meat products in the diet.
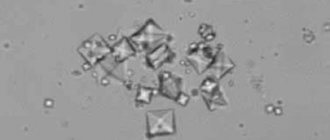
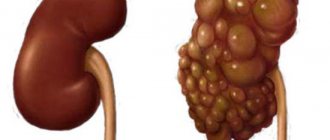
Phosphate sand is represented by gray and white inclusions; it consists of calcium salts and phosphoric acid. When metabolic processes are disrupted, sand is retained in the kidneys, forming stones that grow quite intensively.
At the first stage of their occurrence, they are porous and easily dissolve if a special diet for phosphaturia begins. If the growth of stones has not been prevented, there is a danger that they will turn into coral stones with numerous growths and sharp edges. If such a fossil gets into the ureter, it will be impossible to do without surgical intervention.
The formation of phosphates is explained not only by the fact that the diet with phosphates in the urine was not followed. Stones of this type accumulate in diseases associated with dysfunction of the parathyroid glands, inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, myeloma, endocrine diseases and rickets. Also, the formation of phosphates is affected by a sedentary lifestyle and impaired outflow and formation of urine.
The presence of phosphate stones is indicated by the same symptoms as the presence of stones of any kind. These are pain in the lower back or ureters, urinary retention, renal colic, segments of blood in the urine, cloudy urine and increased body temperature in acute cases.
The presence of phosphate stones can be detected by a general urine test. Their location is determined after examination with an ultrasound machine or after radiography. In the latter case, it is necessary to inject a contrast agent into the kidney. Treatment of urolithiasis can be conservative and surgical.
In the first case, spasm of the urinary tract is relieved, and drugs are prescribed that dissolve phosphate stones. In the second, an operation is prescribed, during which the stones that cause pain are removed. After surgery, recurrence of attacks of urolithiasis may occur.
If it turns out that the formation of sand from phosphoric acid and calcium is not associated with the predominance of dairy and plant products in the diet, then a thorough examination is required. It is impossible to stop the excess formation of phosphates without identifying diseases. In the case when the disease is identified and it becomes clear why phosphates are formed in the urine, a diet will help reduce their content.
Antiphosphate diet is a diet based on the exclusion and limitation of foods of many categories in the diet. Foods with a high calcium content should be excluded from your diet. This includes lactic acid products and whole milk. It is necessary to avoid foods that contribute to the formation of alkaline urine. This group includes mushrooms and poultry eggs.
Like any diet, the phosphate diet prohibits the consumption of smoked foods, sweet carbonated drinks, spicy snacks, and spices, including those of plant origin. Absolutely no to chocolate, coffee and cocoa. It is advisable to give up tea, especially strong tea.
What to eat? Cereals and pasta, fish and meat, sour and sweet and sour fruits and berries in their natural form and in compotes, jelly, in the form of jam or marshmallows.
The consumption of raw vegetables is limited. Since the diet prohibits many foods that contain nutrients necessary for the body to function normally, it is necessary to take a vitamin complex.
It is necessary to drink more liquid, especially medicinal mineral waters: “Naftusya”, “Narzan” and others of similar composition. Mineral water helps reduce the amount of phosphates formed in the urine. There is a special therapy that involves its use. The treatment course is designed for a year. Drink water for two or three weeks, with a break of seven to ten days, half or a third of a glass before meals.
If there is phosphaturia, diet No. 14 for a day will look something like this.
Fractional meals are not encouraged; food should enter the body 4 times a day or 5. Fasting is not encouraged.
You can boil pasta for breakfast. If you bake them with a small amount of sour cream, making a casserole, the processed dairy product will not cause harm. It is advisable to wash down breakfast with cranberry juice or sour apples, and if you are not full, add cookies or dried bread to the liquid.
Snack – sour apples, tangerines or cherries. Depending on the season.
Lunch: meat soup or broth, pea cutlets, bread, jelly - less than one and a half glasses.
Afternoon snack: a bun with rosehip tincture or tea from the same berry.
Dinner: chicken or fish cutlet, rice - preferably brown, fruit drink.
Before going to bed, you can treat yourself to apple compote and grain bread. Food can be boiled, fried, steamed, baked until golden brown. But at the same time, avoid eating cooking oil. Lard is not considered a healthy product.
If phosphates are constantly formed in the urine, diet alone cannot cope with them. It is necessary to find what is causing their formation and treat the systemic or chronic disease with medication.
PressFoto/master1305
Phosphaturia is a malfunction of the body during calcium-phosphorus metabolism, leading to the formation of a precipitate in the form of insoluble phosphates (magnesium phosphate and calcium). Over time, amorphous phosphates become larger and form sand in the urinary canal and sometimes stones.
What is phosphaturia?
Phosphaturia is a condition in the body in which stones (phosphates) are found in urine. The latter are formed due to improper phosphorus-calcium metabolism. Diagnostics identifies insoluble particles as sediment.
The following situations become factors for the development of phosphaturia:
- Increased calcium level in the liquid submitted for analysis.
- Changes in the acid-base balance, where the pH environment increases above 7.
- Imbalance between calcium and phosphorus levels.
- Consumption of food enriched with phosphorus exceeding the permissible limits.
In some situations, phosphate stones become fixed in the kidneys during pregnancy. Neoplasms develop in the cavity over a long period of time, reach a certain size and then begin to move through the urinary system.
Urinalysis and its main parameters
Elevated phosphates in a patient can only be determined by performing a general urine test. Indirect symptoms signaling the development of problems with alkaline balance are:
- Vomiting, severe nausea.
- Feeling of full bladder.
- Painful sensations in the lower back or groin.
- The appearance of precipitation in the form of large flakes when going to the restroom.
- Increased flatulence.
- Frequent urge to go to the bathroom, pain during urination.
But in most cases, the appearance of phosphates in the urine is not accompanied by negative signs. The problem is identified by the appearance of the urine and laboratory tests performed.
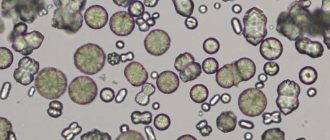
The analysis reveals the level of acidity in the urine: phosphates are formed only in an alkaline environment. Salts precipitate, which, when examined under a microscope, look like small grains of a grayish tint, and are also endowed with the shape of butterfly wings or look like snowflakes.
Normally, a healthy person should contain the following amount of phosphates:
- In a healthy person, regardless of gender and age, it is 0.8-1.3 g/kg. With normal levels, an adult should receive 1200 mg of phosphates per day, and at least 800 mg should be excreted.
- In a child under 12 years of age – 2-4 g/kg.
- Urine at normal pH contains phosphates from 5.0 to 7.0 g/kg.
In case of a serious violation of the alkaline balance, when elevated levels of phosphates are detected, it is necessary to adjust the diet and follow a certain diet for phosphaturia in children and adults.
As a result of the diagnostics, phosphates are normally recorded as “+” or “++”. If there are more than 2 “+” signs, then there is the possibility of developing salt metabolism. To accurately identify the diagnosis, you need to specifically prepare and collect daily urine.
Rules for preparing for urine analysis
To obtain reliable results from the analyzes carried out, it is necessary to prepare specifically:
- 1 week before the upcoming examination, completely exclude from the diet foods that increase the alkali in urine, such as sweets, alcohol or smoked meats.
- Purchase special containers for testing at a hospital pharmacy.
- For a general urine test, morning urine of the middle type is taken, before meals. Within 2 hours, the resulting liquid should be submitted to a laboratory for testing.
- In the case of collecting daily urine: urine is collected at 6 a.m. and then every 3 hours.
- Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform hygiene of the genital tract, but without using any type of soap. This is required so that foreign impurities do not get into the collected liquid.
- Until delivery to the laboratory, the collected urine is stored in a dark place, at a cool temperature, but not in the refrigerator.
When handing over a container with tests, the time and date of the collected liquid and the patient’s name must be indicated on the container.
When urolithiasis is detected, tests are initially performed and the size of the kidney stones is determined using an ultrasound examination. Based on the diameter of the tumor and its nature, specific treatment is prescribed in the form of taking medications and prescribing a gentle diet.
For treatment, a diet is recommended for phosphates detected in the child’s urine, No. 14. In a number of situations, the attending physician, based on the research conducted, prescribes other therapeutic diets or a certain type of metabolic diet.
When fixing phosphaturia, the diet implies nutritional features:
- Consume proteins of various natures (vegetable or animal) - no more than 100 grams, and the ratio of proteins should be 70 to 30.
- Carbohydrates of various natures are consumed in amounts up to 0.5 kg.
- The amount of salt per day is up to 0.07 kg.
- Water – up to 2.5 l. within 24 hours.
- The energy value of products per day is no more than 2500 kcal.
As a result of such a diet, the patient eats throughout the day in fractional approaches, from 4 times a day. At the same time, not all dishes are allowed; a number of foods that a person can consume and those that are strictly prohibited are highlighted.
List of prohibited products
To completely eliminate the increased phosphorus content in the urine, you should adhere to a healthy diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume the following dishes and products:
- Marinades, smoked, overly salted or canned foods.
- Any alcoholic beverages or other strong drinks.
- Dishes with high fat content.
- Bakery products and confectionery sweets.
To adjust the diet of a patient with a fixed pathology, it is necessary to limit foods that contain a large amount of calcium. The latter helps to increase alkali in the body - milk, pine nuts, and cheeses.
List of foods recommended for consumption during phosphaturia
The patient should lean on cereals, eat more lean meat and different types of fish, in other words, increase the acidity in the digestive organs.
They highlight useful products necessary to improve the patient’s general condition and normalize his tests:
- Introduce dietary salads from green vegetables, such as sorrel, various types of cabbage (cauliflower, white cabbage), peas, onions or broccoli.
- Eggs - chicken and quail, but when eating eggs, the yolk should be removed.
- Only natural sweets: honey, beet sugar.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables: pear, pomegranate, apples, lingonberries, goji berries, as well as any sour fruit.
- Vegetable oils.
- Porridge, as well as grains and legumes.
Due to the very limited list of permitted products, therapy should be carried out for a short period of time and under the constant supervision of the attending physician, due to the possibility of excessive weight loss. Additionally, on the recommendation of a doctor, the diet includes fortified complexes.
Recommended diet options for adults (men, women, pregnant women) and children
As recipes for implementing a diet in various age categories or for pregnant women, some options for a therapeutic diet are highlighted.
To normalize metabolism, pregnant women are prescribed foods such as bran bread, birch sap, asparagus, dried fruit drinks, lean meat and fish, berry fruit drinks, sour in their type and various jelly, Brussels sprouts and pumpkin.
When phosphaturia is detected in young patients under 5 years of age, the daily diet is planned in the following order:
- Breakfast - cereal porridge, not strong tea.
- Lunch – some strawberries or a bunch of grapes.
- Lunch – soup with meat and jelly.
- Afternoon snack - bran decoction.
- Dinner: minced fish cutlets and vegetables in small quantities.
For an adult patient, the diet contains an almost identical list of products as for a child, only dinner is replaced with a decoction of rose hips, which must be drunk before going to bed.
Phosphates in urine: reasons for the formation of salt stones
The causes of this disease are considered to be an increased level of calcium in urine, the acidity of which exceeds pH 7 and an imbalance between phosphorus and calcium levels. There are often cases where the root cause of the disease was the consumption of foods rich in phosphorus in unlimited quantities or a failure in metabolic processes. Phosphates in the urine can also be diagnosed during pregnancy.
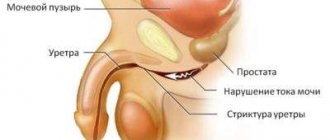
Phosphate stones can form without clinical manifestations until they reach a certain size and begin to move through the urinary system. Any part of this system can be affected by this kind of deposits. Their localization is diagnosed in the ureter, kidneys and bladder.
Phosphate urolithiasis brings many unpleasant sensations to the patient: obstruction of the upper urinary tract, worsening chronic diseases, unbearable pain during any movement (running, walking), frequent urination.
Stones with sharp edges are the most dangerous because... when moving, they cause injury to all adjacent tissues and contribute to the formation of inflammation processes.
What is phosphaturia?
Phosphorus is involved in all metabolic processes, performs a transport function - distributes energy throughout all organs and tissues, stimulates the production of digestive enzymes.
It enters the body with food. A person rarely experiences a deficiency of phosphorus - there are enough products with this substance in the daily menu. High amounts of the nutrient are found in plant foods, alkaline mineral waters, fast food and sausages. The body tries to get rid of excess phosphates and removes them along with urine.
Periodic cloudiness of urine, especially when changing the diet, is not considered a pathology. The disease does not cause deterioration in the initial stage. If stones constantly fall out in the urine, you should consult a doctor.
What do phosphates in urine mean in increased quantities:
- Development of osteoporosis;
- Increased fragility of dentin (tooth tissue);
- Increased skin dryness;
- Separation of nails and hair.
The diagnosis of “phosphaturia” is made when several tests show a consistently elevated level. One-time changes are not considered a disease.
Treatment methods
To prescribe treatment for phosphaturia, a full examination of the patient is initially carried out, including ultrasound diagnostics of the urinary system.
The location and size of the stone are decisive factors for prescribing one of the treatment options. Cases without complications usually respond well to the following therapeutic methods:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy (pressotherapy, shock wave therapy, therapeutic massage);
- adherence to a dietary diet;
- additional vitamin complex, multivitamins;
- the use of diuretic herbal preparations;
- exercise and exercise.
Myths about urolithiasis
Owners often blame themselves for the fact that their pet is sick, and this happens after a friend or veterinarian voices common myths about the disease. The first and most common misconception sounds different, but has the same meaning - a sterilized pet needs to be fed only medicated food, otherwise he/she will develop urolithiasis.
The only factor that can support this statement is the natural decrease in the animal’s mobility. If you devote time to your pet, feed it properly and play with it, castration or sterilization is not a risk factor or cause of the development of urolithiasis.
Fish is a healthy, but not entirely unnatural, food for dogs. Recently, a diet containing fish has been considered the cause of urolithiasis, which is not very correct. The risk increases if you feed the animal only fish, and urolithiasis is not the only consequence. If the pet receives a balanced diet with fish, there is no threat.
Urolithiasis is a treatable disease if it is properly diagnosed and treated. It is worth understanding that if you do not feed your dog properly when it has urolithiasis, no medications will help. A properly selected diet is an integral part of treatment.
Diet for phosphate kidney stones
A diet with phosphates in the urine provides an opportunity to correct and eliminate the consequences of an imbalance in the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium in the body. Violation of the main acid-base balance in the direction of increased alkali content is eliminated by diet therapy. It helps to compensate for the valency of the acid residue when adjusting the diet.
Dietary table No. 14 corresponds to ensuring the normal functioning of the body in case of disturbances in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, and as a result, the formation of insoluble stones in the urinary canals.
By adhering to the recommendations of diet No. 14, which specifies all the requirements for the list of permitted ingredients, the number of daily meals, portion sizes and food processing methods, you can restore normal urine pH and prevent further formation of amorphous phosphates in the urine.
When following diet No. 14, the consumption of many dairy-containing products is excluded. Products that form an “acidified” environment are recommended. They are easy to identify because... they have a characteristic sour taste.
Meals should be prepared as a fractional ration, the serving size is reduced, the number of meals is increased up to 6 times. The numerical characteristics of the diet of diet No. 14 must be compiled by taking into account 2800 kcal per day, of which:
- proteins 70 g;
- carbohydrates 410 g;
- salt 9 g;
- fats 90 g.
The menu is not mono-diet, so it is possible to eat a balanced diet, which will help improve the patient’s emotional state during the treatment period. All dishes must be fresh, without seasoning and with a minimum amount of salt.
Drinking regime
Fluid intake increases to 2-3 liters per day - and this is one of the most important aspects of the diet.
The drinking regime has a strong influence on the regulation of urine pH. Exceeding the norm entails a shift towards the alkaline side, but we need to achieve “oxidation”. You can use a decoction of rose hips and birch sap. Herbal mixtures No. 11 and No. 12 are also recommended.
Mineral water for urinary tract diseases helps increase acidity. It is recommended to drink 1 hour before and after meals: Narzan or Arzni.
Collection No. 11
- Mix 1 tbsp. fringed grass, lingonberry leaves and heather.
- Add 4 tbsp. crushed madder root.
- Pour 1 tbsp into an enamel bowl. collection and pour 300 ml of boiling water.
- Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Drink 3 tbsp of the finished broth. half an hour before meals, 3 times a day.
Collection No. 12
- 1 tbsp. crushed madder root.
- Add 2 tbsp. crushed madder root, wheat grass and salvia leaves.
- Mix with 4 tbsp. flax seed.
- 3 tbsp. collection, pour one liter of boiling water.
- Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Take 250 ml warm, an hour before meals, 2 times a day.
Diet for dogs with kidney and urinary tract disease
Glomerulonephritis is an infectious-allergic disease of dogs that occurs acutely and chronically. The disease is characterized by damage to the glomeruli (glomeruli) of the kidneys and various forms of edema, arterial hypertension and changes in the composition of urine (presence of protein - albuminuria), blood (hematuria).
If the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired and their insufficiency is impaired, the removal of metabolic products from the body worsens. The purpose of dietary feeding and its duration depends on the characteristics of the disease and the severity of renal dysfunction.
For acute nephritis
The basic principles of diet therapy are to sharply limit the amount of protein, extractive substances of meat and fish, essential oils, vegetables and table salt. In severe cases of acute nephritis with urinary retention and edema, a starvation diet is prescribed for 1–2 days (“hunger and thirst” treatment). Then, for 2–3 days, a sugar diet is prescribed (75 g of sugar per 1 glass of weak tea) at 4–5 doses per day. For moderate nephritis, a sugar diet is used from the first days of the disease. You can also use other carbohydrate fasting diets: potato, watermelon, compote, grape. The choice of a fasting diet is determined by the sick dog’s tolerance of individual foods. On fasting days, water is not given to a sick dog. Next, the sick dog is transferred to a diet compiled according to diet No. 7. In case of mild acute nephritis, from the first days of illness, the sick dog can be fed a diet according to diet No. 7. The food of this diet is prepared without salt, the diet is enriched with vitamins.
Since the protein content in the diet is limited by 15–20% compared to the norm, the amount of energy to the normal level is replenished with fats and carbohydrates. To avoid depletion of the dog’s body in sodium and chlorine, which is manifested by loss of appetite and weakness, it is necessary to add salt to the food 2–3 days after the onset of the disease (15–20% below the norm of table salt). When swelling appears or increases, table salt is again limited.
For chronic nephritis
part of the kidney glomeruli ceases to function. Chronic nephritis in dogs can be asymptomatic, with varying degrees of edema, hypertension, albuminuria, as well as without disturbances in nitrogen excretion function or with its disturbance, i.e. with chronic renal failure. In case of chronic nephritis without exacerbation, without impaired renal function, in the absence of edema, hypertension and the presence of only slight changes in the urine, it is recommended to feed the sick dog a diet corresponding to diet No. 7 or even a regular diet, compiled according to the existing norms for the energy and nutrient needs of dogs with a moderate restriction of table salt (25–30% below the norm). In this case, it is recommended to give the dog carbohydrate fasting days once, approximately every 10 days.
In case of kidney failure,
which occurs in dogs with chronic nephritis, bilateral pyelonephritis, renal amyloidosis, renal nephrosclerosis, as a complication of other diseases, metabolic products accumulate in the dog’s body, the content of residual nitrogen in the blood increases (azotemia), water-salt metabolism and acid-base balance are disturbed (metabolic acidosis). In extreme cases of kidney failure, self-poisoning of the body (uremia) occurs.
Basic principles of diet therapy for kidney failure: restriction of protein in the diet by 15–30%, depending on the severity of kidney failure; ensuring normal energy requirements from fats and carbohydrates; regulation of table salt and water in the diet, taking into account the presence of edema, hypertension and impaired renal excretory function in the sick dog.
In the initial stage of kidney failure, it is recommended to feed a sick dog a diet prepared in accordance with diet No. 7, in which the protein content is reduced by 30%, of which 40–50% is animal proteins.
In the advanced stage of kidney failure, taking into account the condition of the sick dog, the amount of protein in the diet is reduced by 50% or more, of which animal proteins should account for up to 70% from meat, fish, dairy products and eggs. The length of time a sick dog stays on a low-protein diet depends on the time the animal’s condition improves. Against the background of a low-protein diet, a small amount of table salt is periodically added to the feed, which reduces azotemia. When edema appears, salt is completely eliminated and carbohydrate fasting days are used, which helps reduce the phenomena of metabolic acidosis and azotemia. On fasting days, the diet includes rice-compote, apple-sugar, and potato diets.
In case of terminal kidney failure with a sharp deterioration in their function, the content of table salt in the diet is slightly increased, but not to the full norm, but 30–40% below it and the sick dog is given more drinking water, the protein content in the diet is also reduced by 30–40% from the norm. In the final stage of kidney failure with uremia (self-poisoning), hemodialysis is performed using an artificial kidney apparatus - purification of the blood from nitrogenous and other metabolic products. With regular hemodialysis, the diet corresponding to diet No. 7 should contain the full amount of energy, fat and carbohydrates, but the protein content should be reduced, in which 65% should be of animal origin. The food is prepared without table salt.
In case of acute renal failure against the background of some acute infections, injuries, extensive burns, acute nephritis, the sick dog is fed according to a diet corresponding to diet No. 7, but with a minimum amount of protein, of which 75% is of animal origin, at the same time the amount of energy should be normal due to fats and carbohydrates.
For urolithiasis
(urolithiasis), which occurs in dogs with various metabolic disorders, the formation of stones is facilitated by a urinary tract infection, and urolithiasis itself can be complicated by a urinary tract infection.
Stones can be formed from salts of uric acid (urate), oxalic acid (oxalates), phosphoric acid (phosphates). In dogs, stones are found from salts of all of the above acids.
The basic principles of diet therapy for urolithiasis: limiting feed substances that form sediment or stones in the urinary tract; changing the urine reaction (pH) due to feeding to prevent excretion and better dissolve the sediment; Regular intake of water to remove sediment from the urinary tract.
Dietary rations are made taking into account the characteristics of metabolism, the chemical composition of stones and the reaction of urine. Excessively long-term feeding of a dietary diet for urolithiasis can have an unfavorable effect, since in diets, mainly for uraturia and phosphaturia, the amount of food products of certain groups is limited or increased. When diet therapy for urolithiasis, concomitant diseases are taken into account. Obesity in a dog is a risk factor for the development of urolithiasis and worsens its course, so combined diet therapy for urolithiasis and obesity is more effective than urolithiasis alone.
If one of the types of protein metabolism - purine metabolism - is disrupted, uric acid accumulates in the dog's body, uraturia occurs, in which the diet must correspond to diet No. 6. In this diet, foods rich in purines are limited or excluded: meat, especially meat by-products, fish. Dairy products, cereals, eggs, and vegetables are low in purines. When cooking meat and fish, up to 50% of purines go into the broth, so boiled meat and fish are used in the diet and broths are excluded.
Since urates are more often formed during an acidic reaction of urine, vegetables and dairy products are widely used in the diet to alkalize urine, and cereals are somewhat limited. Due to the frequent formation of mixed stones from uric and oxalic acids, feed products rich in oxalic acid are excluded from the diet.
If purine metabolism is disrupted, it is advisable to reduce in the diet food products whose fats are rich in saturated fatty acids. When uraturia is combined with obesity in the diet, diet No. 6 reduces the amount of energy from fats and carbohydrates by 20–40%, depending on the degree of obesity.
If there is a violation of the metabolism of oxalic acid and oxaluria, foods rich in oxalic acid are excluded from the diet: sorrel, spinach, rhubarb, etc. Moderate content of oxalic acid is in beets, potatoes, carrots, onions, black currants, blueberries. These products are somewhat limited in the diet in case of severe oxaluria, but are not excluded from the diet. Most other vegetables and fruits are low in oxalic acid. Decoctions from fruit peels help remove oxalates from the body.
The occurrence of urolithiasis with oxaluria in dogs is facilitated by a lack of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and magnesium in the feed rations, so the diet should include foods rich in these substances, in particular wheat bran, as well as preparations of pyridoxine and magnesium salts. In the dietary diet, the content of carbohydrates and gelatins (jelly), which can be a source of formation of oxalic acid, salt, smoked products, extractive substances (broths, meat and fish without boiling) is limited. For oxaluria, it is recommended to feed sick dogs a diet prepared in accordance with diet No. 5 with a limit of 15–20% carbohydrates and the inclusion of fasting days in the feeding regimen.
When the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium is disturbed in dogs, phosphaturia and calciuria occur. Animals with this disease are fed according to a diet corresponding to diet No. 9. The diet should be dominated by foods that increase the acidity of urine (meat, fish, eggs, cereals, bread, biscuits) and a limited amount of vegetables and dairy products. Vegetables and dairy products are periodically included in the diet so as not to cause a sharp depletion of calcium in the body. The diet according to diet No. 9 is poor in vitamins C and P (bioflavoid), which must be replenished by including rose hips and vegetables (pumpkin, green peas, cranberries, lingonberries) in the diet.
For any type of urolithiasis, dogs’ diets should contain 10–20% higher than normal vitamin A, which has a beneficial effect on the mucous membranes of the urinary tract.
In dogs, when infection penetrates into the renal pelvis and bladder, inflammation occurs - pyelocystitis; when infection penetrates deep into the kidney - pyelonephritis. These diseases can be acute or chronic and often complicate other diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, for example, urolithiasis.
In case of pyelocystitis, it is first necessary to examine the urine reaction in order to create unfavorable conditions for the development of microbes by changing it. In the case of an acidic urine reaction, feeding sick dogs is carried out according to a diet compiled in accordance with diet No. 6, and in case of an alkaline reaction - according to diet No. 9. Against the background of these diets, it is recommended to give decoctions of rose hips, vegetables and fruits as a drink. Avoid foods containing essential oils (onions, garlic, radishes, etc.), which irritate the urinary tract, from the diet.
In case of acute or exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis with fever and symptoms of intoxication, vegetable and fruit purees and decoctions are given on the 1st–2nd day of illness. Then they are fed according to the diet corresponding to diet No. 7, with the predominant inclusion of dairy and plant products in the diet. In case of chronic pyelonephritis, the sick dog is fed a complete diet in accordance with the physiological norms of the need for energy, protein, fat, carbohydrates and other nutrients with a moderate limitation of extractives and oxalic acid.
BLOATING IN A DOG: DESCRIPTION, TREATMENT, CAUSES
AUSTRALIAN CAVE DOG OR AUSTRALIAN HEELER KEEPING AT HOME
AUSTRALIAN SHEPHERD OR AUSSIE KEEPING AT HOME
ALASKAN MALAMUTE KEEPING AT HOME
AKITA INU KEEPING AT HOME
Authorized Products
Due to the fact that the list of products allowed for consumption is quite limited, it is impossible to adhere to diet therapy for a long time. Equally important is monitoring the patient’s condition by a urologist, with periodic testing.
It is allowed to diversify your diet several times a week with egg whites, vegetables and dairy products indicated in the table.
| Name | |
| Cereals | Buckwheat, rice, barley porridge, millet, oatmeal, pearl barley |
| Legumes | Beans, peas |
| Protein products | Lean meat, egg (white) 1 pc. in a day |
| Vegetables | Fresh green peas, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, mushrooms |
| Berries and fruits | Apples, sea buckthorn, pomegranates, dogwood, gooseberries, cranberries, wild strawberries, strawberries, black and red currants, lemons, grapes |
| Beverages | Not strong tea and coffee, still mineral water, juice, compotes and fruit drinks from sour fruits and berries, rosehip decoction, birch sap |
| Seafood | Fish, shellfish and caviar (fried) |
| Sweets | Honey, halva |
Allowed food
1. Meat products:
- some by-products (lungs, brain);
- chicken fillet and breast;
- lean beef;
- turkey;
- lean meats.
2. Fish products:
3. Dairy products are allowed to be consumed in limited quantities in their pure form and for preparation as a filling for dishes:
4 eggs.
5. Fruits and berries can be consumed fresh, canned or dried:
6. Drinks:
- mineral water;
- herbal decoctions;
- bran drink;
- fruit drink;
- oat smoothie;
- rosehip drink.
7. Cereals and pasta are allowed to be consumed as they contain little calcium.
8. Legumes.
9. Vegetables:
- mushrooms;
- pumpkin;
- cucumbers;
- onion;
- potato;
- Brussels sprouts, Chinese cabbage, white cabbage.
10. Vegetable and butter.
11. Sugar, honey.
12. Weak tea, hibiscus.
The diet must be supplemented with multivitamin complexes.
Prohibited Products
The consumption of dairy products should be completely eliminated or reduced as much as possible - no more than 150 ml of milk-containing products. In this way, self-regulation of calcium is carried out in the body of a patient with phosphaturia, because it is precisely in the problem that salt stones are formed due to insufficient excretion of calcium and phosphorus from the body.
Extractive foods such as smoked sausages, dishes with spicy seasonings, and pickled vegetables are completely prohibited.
| Name | |
| Protein products | Fatty meat and fish |
| Beverages | any alcohol-containing drinks, cocoa, strong tea and coffee. Alkaline waters |
| Sweets and confectionery | Chocolate, candy, marshmallows, marshmallows, cakes, pastries |
| Bakery | Fresh bread, buns |
| Fats | Cooking fats, lard |
| Long shelf life products | Preservation, canned food, pickled vegetables |
| Dairy | Milk, cheese, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt |
| Vegetables | Potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, onions, carrots, Brussels sprouts, sorrel, spinach, horseradish |
The first courses in the diet are of particular importance. The basis for them should be low-fat meat, fish or mushroom broth. You can diversify your diet by preparing gravy for porridge using the same broths.
A decoction of rose hips is an active assistant in normalizing calcium-phosphorus metabolism. Its “acidifying” effect on the body has invaluable benefits, so the drink can be safely included in your daily drinking diet. Doctors recommend drinking the decoction after meals. In addition, patients with phosphate salts in the urine are prescribed to consume various fruit drinks, compotes and jellies from berries and fruits with high acidity (cranberries, lingonberries, etc.). The morning should begin with a glass of purified water on an empty stomach.
If the patient first encounters the disease phosphaturia, after completion of treatment, twice a year he needs to take preventive measures in the form of a course of mineral waters or herbal remedies.
During the diet, you must avoid sweets containing trans fats, dyes and flavors. An alternative is moderate amounts of sugar, homemade jam and honey.
Features of the diet for phosphaturia in children
Phosphaturia is rarely diagnosed in children. Amorphous crystals in a child’s urine do not subsequently form salt stones. Vegetable and milk soups, sweet berries and fruits, including juices from them, are excluded from the children's diet. Allowed 1 tbsp per day. sour cream.
Due to the fact that during the diet you will have to give up foods with a high calcium content, which can negatively affect the metabolic processes in the child’s body, therefore, the diet must be supplemented with sweet fruits twice a week. Supplementing treatment with decoctions of medicinal herbs will also be useful.
The child’s diet is structured according to the principle of maximum protein content: fish, meat products, cereals and permitted vegetables.
Symptoms of kidney failure
In case of acute renal failure, the symptoms are as follows:
- loss of appetite,
- vomit,
- weakness, the dog sleeps a lot,
- drinking disorders: the dog drinks either too much or too little,
- problems with urination.
In case of chronic renal failure, the following symptoms are observed:
- loss of appetite,
- weight loss,
- strong thirst
- frequent urination,
- weakness,
- poor coat condition,
- diarrhea or constipation,
- blood in urine.
The sooner a veterinarian detects kidney failure, the better the chance of helping your pet. Unfortunately, chronic renal failure often does not manifest itself externally until 70% of the kidneys are destroyed. To determine if your pet has kidney problems, a urine test and blood chemistry test are performed.
Diet menu table No. 14
Menu 1
Calorie content - 2750 kcal
Breakfast:
fish cutlets, buckwheat porridge with butter, fresh grapefruit.
Lunch:
apple, rose hip decoction.
Dinner:
meatball soup, baked cabbage pie, berry jelly.
Afternoon snack:
cranberries with honey, tea.
Dinner:
meat cutlets, rice with butter, cranberry juice.
Second dinner:
apple-carrot fresh juice.
Menu 2
Calorie content - 2610 kcal
Breakfast:
lasagna with fish or meat and sour cream, berry juice.
Lunch:
fruit jelly, biscuits.
Dinner:
borscht with beef, pea zrazy with mushrooms, jelly.
Afternoon snack:
apples, tea with lemon.
Dinner:
baked chicken fillet with rice, rosehip broth.
Second dinner:
compote, rice biscuits.
Menu 3
Calorie content - 2780 kcal.
Breakfast:
sandwich with ham and butter, rosehip infusion.
Lunch:
dry biscuits, tea.
Dinner:
vermicelli soup with chicken fillet, rice casserole, compote.
Afternoon snack:
fresh or frozen berries with sugar, tea with lemon.
Dinner:
chop with buckwheat porridge, squash caviar, berry juice.
Second dinner:
compote, rice biscuits.
Diet therapy is the main condition for successful complex treatment of phosphaturia.
Elevated phosphates and salts in the urine do not always lead to phosphaturia, but they are definitely the first harbingers of a possible disease. To prevent the development of the disease, a diet with salts and phosphates in the urine must be followed. Well, if phosphaturia is nevertheless diagnosed, then nutrition during the disease must be strictly adjusted and must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Features of treatment of phosphaturia
The therapeutic regimen includes drugs to eliminate the underlying disease and primary pathology that cause phosphaturia. Traditional medicine methods accelerate recovery and restore the acid-base balance of urine.
Medicines against phosphate in urine
To restore the functioning of the urinary system, it is necessary to completely eliminate inflammatory processes in the kidneys or bladder.
Antibiotic therapy may be required. Preference is given to complex products: Augmentin and analogues - Ecobol, Amoxil, Bactoclav. Broad-spectrum antibacterial agents can be prescribed - Flemoxin Solutab, Ceftriaxone or Azithromycin, as well as narrow-acting ones - Nolitsin, Palin, Nitroxoline. Children are advised to choose medications in the form of syrups or suspensions.
Antispasmodic drugs are used: No-shpa and Spazmalgon, analogues - Baralgin, Papaverine.
For diseases of the digestive tract and intestines, the following medications may be required:
| Group of drugs | The main thing | Analogs |
| Antacids | Maalox | Gastal or Rennie |
| Proton pump inhibitors | Omez | Rabeprazole, Nolpaza, Pantoprazole |
| Enzymatic agents | Mezim Forte and Festal | Enzistal, Creon, Pancreatin |
Children are prescribed medications to prevent the development of rickets.
An oil solution of vitamin D or its analogue, Aquadetrim, is used. This drug can be given to babies from the first days of life to prevent rickets and increase the absorption of phosphorus and calcium. If the patient has severe excretion (increased excretion of phosphorus in the urine), medications are prescribed that reduce the rate of the process. In this case, it is recommended to use Almagel and analogues - Almagel A with an anesthetic component, Almagel Neo with a composition that eliminates flatulence, Gastracid or Phosphalugel.
The therapeutic regimen may include other pharmaceuticals aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked phosphaturia.
Folk remedies for phosphaturia
Herbal preparations help to quickly remove excess phosphoric acid from the body.
Birch sap and rosehip decoction are effective. Adults can take 2 glasses per day, children - one. Recipes from medicinal plants:
- Collection No. 1
. Mix 1 part of heather and lingonberry leaves, fringed grass and 4 parts of madder root. Brew a tablespoon with a glass of boiling water and leave in a water bath. Drink 3 tablespoons 3 times a day 40 minutes before meals. - Collection No. 2
. Combine 1 part of madder root, 2 parts of anemone and gland leaves, 4 parts of flaxseed. Brew 1.5 tablespoons of 0.5 liters of boiling water. Infuse and strain. Drink 2 glasses a day: one half 1 hour before breakfast, the second before dinner. - Decoctions of rosehip and bearberry
. The proportions of the infusion are 2 tablespoons of bush or bearberry roots per 250 ml of water. Boil for 5 minutes, leave covered, filter. Treatment regimen: an hour after eating, first drink rosehip decoction, and then bearberry. You need to drink a glass of each decoction per day. - Oregano decoctions and knotweed infusion
. Brew oregano in a thermos in the evening, 1 tablespoon per 300 ml. Knotweed, 1 tbsp, pour 1 liter of water and let it brew for 2 hours. Before meals, drink 1/3 cup of oregano, after meals - 3 tablespoons of knotweed.
When treating children, you should limit yourself to juice therapy.
To prevent the accumulation of phosphates, adults are recommended to drink at least 2.5 liters of fluid per day, avoid hypothermia, and exercise regularly. Cardio exercises are preferred. Children's drinking regime is expanded, they are put on a special diet, their urinary organs and all infections are treated in a timely manner, vitamin D is ensured, and they take walks during the daytime.
How to treat phosphaturia - watch the video: At the first signs of worsening of the condition or the appearance of cloudy urine, you should consult a doctor. Phosphaturia has a tendency to recur.
Elevated phosphates and salts in the urine do not always lead to phosphaturia, but they are definitely the first harbingers of a possible disease. To prevent the development of the disease, a diet with salts and phosphates in the urine must be followed. Well, if phosphaturia is nevertheless diagnosed, then nutrition during the disease must be strictly adjusted and must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Therapeutic nutrition for phosphaturia and increased phosphates in the urine
Phosphaturia is characterized by a violation of the acid-base balance towards alkalosis and the precipitation of poorly soluble calcium phosphate in the urinary tract. The development of phosphaturia is associated with a violation of the ratio of calcium and phosphorus in the urine as a result of increased excretion of calcium in the urine and loss of acid valencies by the body. With phosphaturia, there is a complex chain of neurohumoral-renal disorders.
Treatment for phosphaturia is aimed mainly at acidifying the urine and limiting calcium-rich foods in the diet. Spicy snacks, spices, drinks that excite the nervous system, as well as foods and substances that strongly stimulate secretory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, especially with hypersecretion of gastric and pancreatic juice, are excluded from the diet.
Sodium and potassium phosphates are soluble in urine that has both an acidic and alkaline reaction; calcium and magnesium phosphates are insoluble in urine that has an alkaline reaction.
It is recommended (if there are no contraindications) to include a sufficient amount of liquid (up to 2 liters) in the diet for phosphaturia in the form of weak tea, coffee without milk, fruit and berry juices. Bread, eggs and egg dishes are provided in limited quantities. In therapeutic nutrition for phosphaturia, meat, fish soups, meat, fish, dough products are allowed in all forms.
Of the vegetables in the diet with phosphates in the urine, varieties that are poor in calcium and alkaline valencies (peas, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, pumpkin) are used. Berries and fruits are limited; lingonberries, red currants, and sour apples are recommended. During long-term use of a diet with elevated phosphates in the urine, it is necessary to periodically introduce foods containing calcium (milk, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.) into it in a zigzag manner.
Results, reviews and recommendations from doctors ^
If you follow all the recommendations, the results of the diet for phosphaturia will become noticeable within a week: the tests will improve and the disease will completely disappear, because Human health largely depends on nutrition.
Tips on how to avoid phosphaturia
- Do not change your diet suddenly: if you want to become a vegetarian, then meat should be eliminated gradually;
- Do not abuse strict diets;
- Eat right and drink enough plain water;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- See a doctor periodically.
To prevent phosphaturia and avoid relapse, proper nutrition is sufficient: limit the amount of salt in food, eat only healthy foods and maintain a caloric intake of 2000 kcal per day.
Diet menu for phosphaturia in adults
An approximate one-day diet menu for phosphaturia in adults is given in the table:
| Name of products and dishes | Output, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g |
| I breakfast | ||||
| Fish cutlets (cod) | 105/5 | 14,9 | 4,8 | 8,7 |
| Crumbled buckwheat porridge with butter | 145/10 | 8,9 | 9,5 | 34,6 |
| Grapefruit juice | 100 | 0,3 | — | 0,8 |
| II breakfast | ||||
| Sour fresh apples | 100 | 0,3 | 0,3 | 8,6 |
| Rose hip decoction | 200 | 0,6 | — | 15,2 |
| Dinner | ||||
| Meat broth with meatballs | 450/40 | 10,6 | — | |
| Baked meat pies | 130 | 4,4 | 21,7 | 40,2 |
| Redcurrant jelly with sugar | 100 | — | — | 21,6 |
| Afternoon snack | ||||
| Cranberries with sugar | 75/30 | 0,3 | — | 32,7 |
| Tea with lemon | 200 | 0,2 | — | 15,2 |
| Dinner | ||||
| Fish cutlets fried in vegetable oil | 110 | 15,8 | 12,5 | 12,0 |
| Baked belyashi | 210 | 25,8 | 26,0 | 57,3 |
| Tea with lemon | 200/7/15 | 0,2 | — | 15,2 |
| For the night | ||||
| Apple juice | 100/100 | 0,5 | — | 9,1 |
| All day | ||||
| White wheat bread | 300 | 24,6 | 4,2 | 108,3 |
| TOTAL | 120,0 | 89,5 | 368,5 | |
| Calorie content | 2760 kcal | |||
Even more on the topic
Despite its high beneficial properties, Manchurian nuts are rarely used for food purposes immediately after collection: this is associated with great difficulties...
Several diets have been developed for proper nutrition of patients diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease. In the acute stage, it is prescribed...
The diet for phosphaturia is aimed primarily at eliminating the consequences of disturbances in phosphorus and phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the human body. These disorders manifest themselves as a shift in the acid-base balance in the body in favor of an alkaline environment. Therefore, therapeutic diet therapy for phosphaturia must first of all compensate for the lack of an acidic environment (acid valencies) by correcting the diet.
Diet therapy for phosphaturia
It should be noted that to ensure the full functioning of the body in case of disturbances in phosphorus metabolism in the case of phosphaturia, as well as in the formation of stones in the urinary tract, dietary table No. 14 is indicated. This diet is part of a therapy system with specially designed diets and includes requirements for the set of products used, frequency of meals, recommended volume of fluid consumed and methods of heat treatment of dishes.
It must be said that the daily diet of dietary table No. 14 has the following numerical characteristics:
- Energy value - from 2800 to 3000 kcal.
- Nutritional value: carbohydrates - 450 g, fats - 100 g, proteins - 90 g.
- The volume of liquid consumed is 2.5 liters.
- The amount of table salt is 10 g.
In addition, all dishes must be freshly prepared and varied. Since diet No. 14 is not a mono-diet, tasty and balanced food significantly improves the psycho-emotional and physical condition of patients with phosphaturia.
Goals and objectives of diet No. 14
It must be said that since with phosphaturia there is a shift in the urine reaction to the alkaline side, the content of phosphoric acid salts in the urine increases. Phosphorus-calcium stones are formed, and the diet for phosphaturia is aimed at preventing and preventing these pathological processes. Therefore, the main goals of diet therapy for phosphates in the urine are:
- shift in urine reaction to the acidic side;
- increasing the intensity of excretion of phosphorus-calcium salts;
- prevention of the formation of new stones.
This is achieved through the consumption of a certain set of products. Thus, dietary table No. 14 provides for the inclusion in the diet of foods that change the pH of urine in an acidic direction. These products include those that have a sour taste, as well as a number of others. First of all, this is meat of any kind and products made from it, seafood (various shellfish), fish and caviar from it, sour berries, fruits and vegetables. The consumption of cereals prepared in various ways, bakery products, vegetable oils and butter is allowed without restrictions.
As for legumes, Diet No. 14 allows the consumption of green peas; in addition, mushrooms and dishes made from them are allowed.
It is recommended to pay special attention to first courses, which should be prepared using various types of broths - from fish, meat or mushrooms. Broths can also be used to make cooking sauces and dressings.
Of the berries, fruits and vegetables in diet No. 14, neutral or sour to taste are allowed:
- lemons, pomegranates, sour apples, dogwood, sea buckthorn, cherry plum;
- cranberries, gooseberries, lingonberries;
- pumpkin.
For desserts, sugar, jam, honey, halva, Turkish delight, and high-quality baked goods are recommended. Store-bought sweets with trans fats, dyes, flavors and sweeteners should be avoided.
Rosehip decoction has a good acidifying property for the body, so it should be regularly included in the diet of those suffering from phosphorus-calcium metabolism disorders. The best option is to drink brewed rose hips between meals. In addition to rosehip decoction, patients with phosphaturia are advised to drink fruit drinks, jelly and jellies made from sour berries and fruits - blackberries, cranberries, lingonberries, etc.
Particular attention in the menu of dietary table No. 14 is paid to consuming enough liquid, which should be drunk on an empty stomach in the morning and between meals. As for the number of meals, medical science recommends dividing the daily diet into 4 times.
Saint Bernards
Natural food for animals with a tendency to urolithiasis using the example of Dalmatian dogs.
Again, the Dalmatian's diet should prevent the formation of uric acid, but should be rich in foods containing vitamins, minerals and fatty acids. The best foods for such a diet would be the following foods that are moderate in purine content: chicken wings, chicken necks, chicken backs and tails, turkey necks, chopped and stewed vegetables, including large amounts of greens; eggs, cottage cheese, homemade cheese, yogurt, olive oil, flaxseed oil and peanut oil. In addition, the diet should contain vitamin B complex, vitamin E, and fish oil (cod). Consumption of offal should be kept to a minimum and ensure that the dog receives plenty of fluids. And, although natural food contains a sufficient amount of moisture, it is worth giving more liquid so that the urine is as neutral as possible and uric acid is eliminated well. At the same time, do not underestimate the importance of long-lasting and active products that promote good elimination of harmful substances. In addition, you should not force dogs to endure for a long time - this leads to an overflow of the bladder and an increase in the concentration of uric acid. When transferring a Dalmatian to natural feeding, tests should be done - ultrasound, blood biochemistry, urine analysis - to make sure that urolithiasis has not begun and, depending on the results, adapt the diet. In addition, at the initial stage of transferring a dog to BARF, tests should be quite frequent to ensure that the body is functioning normally and adaptation has been successful. In fact, for Dalmatians, as dogs at risk for urolithiasis, tests every six months are a necessity.
Natural food for animals with a tendency to urolithiasis using the example of Dalmatian dogs.
Prohibitions of therapeutic nutrition for phosphaturia
Since the main goal of diet therapy for phosphaturia is to shift the pH of urine to the acidic side and general “acidification” of the body, the following should be excluded from the menu of patients:
- spices, herbs, marinades, pickles, canned food, smoked meats, etc.;
- dairy products and milk;
- fruits, berries and vegetables, except those listed above.
It must be said that milk and dairy products are excluded from the diet of patients in order to regulate the calcium content in the body, since in this disease calcium phosphorus salts are not sufficiently excreted in the urine, which leads to the formation of stones from them.
As noted above, a number of extractive products (smoked meats, pickles, spicy dishes, etc.) are prohibited. The same applies to tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee. Alcohol and nicotine consumption is not recommended.
These restrictions contribute to the “acidification” of the internal environment of the body, which, in turn, leads to an improvement in the patient’s well-being and alleviation of the symptoms of the disease.
General symptoms of phosphaturia
At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself in adults.
In children, parents immediately notice cloudy urine. Nonspecific symptoms are anxiety, insomnia, lack of appetite and constant fatigue. If such conditions cause anxiety in parents of young children, then adults attribute everything to fatigue and frequent stress and turn to the help of official medicine when their general condition worsens, the signs of which are:
- Frequent urination;
- Pain in the lower back, intensifying when emptying the bladder;
- Flatulence, intestinal colic and bloating;
- Unstable stool, constipation followed by diarrhea.
Patients complain of periodic nausea, heartburn, and false urge to defecate. Diseases of the digestive tract are getting worse.
Some aspects of table No. 14
It should be noted that if there is a violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the process of diet therapy, the consumption of dishes from products that are subjected to any known types of culinary processing is indicated.
Thus, for adequate nutrition for those suffering from phosphaturia, you can include in the daily menu foods recommended by dietary table No. 14 that have been fried, stewed, boiled or baked. Vegetables, fruits and berries can be consumed fresh, not thermally processed. In addition, the degree of grinding of food does not play a decisive role in this diet.
Main symptoms
The process of increasing alkaline phosphatase levels does not have specific clinical signs. The dog owner should be alert to the following signs:
- dark color of urine;
- light shade of stool;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- lethargy, low mobility, fatigue of the pet.
Only diagnostic studies can confirm or refute an increase in enzymes.