Kidneys are organs responsible for the excretory function of the body. Thanks to the work of these organs, all substances entering the bloodstream are filtered. They are responsible for maintaining water-salt and electrolyte metabolism. In addition, they produce the hormone “erythropoietin”, which is necessary to ensure the function of hematopoiesis. Kidney function can be assessed using a urine test. There are many different laboratory techniques for conducting this study. In addition to the fact that the state of the excreted fluid can indicate the presence of inflammatory processes and impaired filtration capacity of the kidneys, sometimes crystals are found in the urine. Normally they shouldn't be there. Therefore, the appearance of crystals in a urine test indicates functional disorders. In some cases, these changes are observed in the presence of stones. Sometimes this phenomenon indicates a predisposition to certain kidney diseases. At the same time, the pathology itself may not yet develop.
Crystals in urine: the cause of their appearance in healthy people
The crystals are an accumulation of salts that form urinary sediment. Their appearance in small quantities is not always a deviation and sometimes occurs in healthy people. If the crystals in the urine are significantly increased, this indicates a violation of mineral metabolism. The following reasons for the appearance of salts in OAM are identified:
- The predominance of certain foods in the diet. These include meat, tomatoes, asparagus, sorrel, and lingonberries. The fact is that this food contains a large amount of acids, which crystallize and precipitate.
- Increased sweating during physical activity.
- Taking certain antibacterial medications (drugs of the sulfonamide group, ampicillin).
- Drinking unfiltered tap water.
- Alkaline urine reaction. It is observed in the presence of inflammation in the kidneys.
If, due to the above reasons, amorphous crystals appear in the urine, this is not a pathological condition. However, chronically eating large amounts of foods containing acids is considered a predisposing factor for the formation of kidney stones.
Diet for phosphates in urine in children
Serious diseases accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, as well as emerging changes in metabolic processes and problems in the functioning of the parathyroid gland stimulate the development of phosphaturia.
In addition, a number of other reasons are identified that are identified when the problem is fixed. To eliminate the increased level of phosphates in the urine, doctors prescribe specific treatment, such as a diet for phosphaturia and medication. Such therapy will prevent the preconditions for the formation of consequences.
Phosphaturia is a condition in the body in which stones (phosphates) are found in urine. The latter are formed due to improper phosphorus-calcium metabolism. Diagnostics identifies insoluble particles as sediment.
The following situations become factors for the development of phosphaturia:
- Increased calcium level in the liquid submitted for analysis.
- Changes in the acid-base balance, where the pH environment increases above 7.
- Imbalance between calcium and phosphorus levels.
- Consumption of food enriched with phosphorus exceeding the permissible limits.
In some situations, phosphate stones become fixed in the kidneys during pregnancy. Neoplasms develop in the cavity over a long period of time, reach a certain size and then begin to move through the urinary system.
Elevated phosphates in a patient can only be determined by performing a general urine test. Indirect symptoms signaling the development of problems with alkaline balance are:
- Vomiting, severe nausea.
- Feeling of full bladder.
- Painful sensations in the lower back or groin.
- The appearance of precipitation in the form of large flakes when going to the restroom.
- Increased flatulence.
- Frequent urge to go to the bathroom, pain during urination.
But in most cases, the appearance of phosphates in the urine is not accompanied by negative signs. The problem is identified by the appearance of the urine and laboratory tests performed.
The analysis reveals the level of acidity in the urine: phosphates are formed only in an alkaline environment. Salts precipitate, which, when examined under a microscope, look like small grains of a grayish tint, and are also endowed with the shape of butterfly wings or look like snowflakes.
Normally, a healthy person should contain the following amount of phosphates:
- In a healthy person, regardless of gender and age, it is 0.8-1.3 g/kg. With normal levels, an adult should receive 1200 mg of phosphates per day, and at least 800 mg should be excreted.
- In a child under 12 years of age – 2-4 g/kg.
- Urine at normal pH contains phosphates from 5.0 to 7.0 g/kg.
In case of a serious violation of the alkaline balance, when elevated levels of phosphates are detected, it is necessary to adjust the diet and follow a certain diet for phosphaturia in children and adults.
As a result of the diagnostics, phosphates are normally recorded as “+” or “++”. If there are more than 2 “+” signs, then there is the possibility of developing salt metabolism. To accurately identify the diagnosis, you need to specifically prepare and collect daily urine.
To obtain reliable results from the analyzes carried out, it is necessary to prepare specifically:
- 1 week before the upcoming examination, completely exclude from the diet foods that increase the alkali in urine, such as sweets, alcohol or smoked meats.
- Purchase special containers for testing at a hospital pharmacy.
- For a general urine test, morning urine of the middle type is taken, before meals. Within 2 hours, the resulting liquid should be submitted to a laboratory for testing.
- In the case of collecting daily urine: urine is collected at 6 a.m. and then every 3 hours.
- Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform hygiene of the genital tract, but without using any type of soap. This is required so that foreign impurities do not get into the collected liquid.
- Until delivery to the laboratory, the collected urine is stored in a dark place, at a cool temperature, but not in the refrigerator.
When handing over a container with tests, the time and date of the collected liquid and the patient’s name must be indicated on the container.
When urolithiasis is detected, tests are initially performed and the size of the kidney stones is determined using an ultrasound examination. Based on the diameter of the tumor and its nature, specific treatment is prescribed in the form of taking medications and prescribing a gentle diet.
For treatment, a diet is recommended for phosphates detected in the child’s urine, No. 14. In a number of situations, the attending physician, based on the research conducted, prescribes other therapeutic diets or a certain type of metabolic diet.
When fixing phosphaturia, the diet implies nutritional features:
- Consume proteins of various natures (vegetable or animal) - no more than 100 grams, and the ratio of proteins should be 70 to 30.
- Carbohydrates of various natures are consumed in amounts up to 0.5 kg.
- The amount of salt per day is up to 0.07 kg.
- Water – up to 2.5 l. within 24 hours.
- The energy value of products per day is no more than 2500 kcal.
As a result of such a diet, the patient eats throughout the day in fractional approaches, from 4 times a day. At the same time, not all dishes are allowed; a number of foods that a person can consume and those that are strictly prohibited are highlighted.
To completely eliminate the increased phosphorus content in the urine, you should adhere to a healthy diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume the following dishes and products:
- Marinades, smoked, overly salted or canned foods.
- Any alcoholic beverages or other strong drinks.
- Dishes with high fat content.
- Bakery products and confectionery sweets.
To adjust the diet of a patient with a fixed pathology, it is necessary to limit foods that contain a large amount of calcium. The latter helps to increase alkali in the body - milk, pine nuts, and cheeses.
The patient should lean on cereals, eat more lean meat and different types of fish, in other words, increase the acidity in the digestive organs.
They highlight useful products necessary to improve the patient’s general condition and normalize his tests:
- Introduce dietary salads from green vegetables, such as sorrel, various types of cabbage (cauliflower, white cabbage), peas, onions or broccoli.
- Eggs - chicken and quail, but when eating eggs, the yolk should be removed.
- Only natural sweets: honey, beet sugar.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables: pear, pomegranate, apples, lingonberries, goji berries, as well as any sour fruit.
- Vegetable oils.
- Porridge, as well as grains and legumes.
Due to the very limited list of permitted products, therapy should be carried out for a short period of time and under the constant supervision of the attending physician, due to the possibility of excessive weight loss. Additionally, on the recommendation of a doctor, the diet includes fortified complexes.
As recipes for implementing a diet in various age categories or for pregnant women, some options for a therapeutic diet are highlighted.
To normalize metabolism, pregnant women are prescribed foods such as bran bread, birch sap, asparagus, dried fruit drinks, lean meat and fish, berry fruit drinks, sour in their type and various jelly, Brussels sprouts and pumpkin.
When phosphaturia is detected in young patients under 5 years of age, the daily diet is planned in the following order:
- Breakfast - cereal porridge, not strong tea.
- Lunch – some strawberries or a bunch of grapes.
- Lunch – soup with meat and jelly.
- Afternoon snack - bran decoction.
- Dinner: minced fish cutlets and vegetables in small quantities.
For an adult patient, the diet contains an almost identical list of products as for a child, only dinner is replaced with a decoction of rose hips, which must be drunk before going to bed.
When following a diet for phosphaturia, you should not drink carbonated drinks, and season your dishes well with green seasoning or spicy spices. It is forbidden to consume rich meat broth, as well as drink a lot of coffee and tea.
During the diet, you should gradually change the diet; a sudden change in food products can negatively affect both the patient’s stomach and general well-being. It is forbidden to starve and torture your stomach with heavy diets. You need to eat often, but so that the portion fits in the palm of your hand. Overeating should be avoided, as fat deposits will negatively affect the kidneys.
Thus, a diet for phosphaturia implies a balanced diet. If there is no treatment for a long time, amorphous phosphates gradually increase in volume, forming sand in the urinary system, and often stimulate the formation of kidney stones. This pathology can no longer be treated with a certain diet, but undergoes surgical intervention. Therefore, if negative results are detected in the tests, you should carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Based on materials from pro-analiz.ru
With phosphaturia, there is a failure of the material metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. As a result, urine comes out with sediment, which consists of calcium and magnesium phosphates.
After a certain time, insoluble phosphate salts increase in quantitative content, which is why sand then forms, as well as the appearance of large stones in the urinary tract. Therefore, timely detected pathology can be eliminated if the patient follows a phosphate diet. The most common cause of phosphaturia is an increased level of calcium in the urine, which has an alkaline environment that exceeds the norm and is Ph 7. Children may suffer from phosphaturia if the ratio between calcium and phosphorus is disturbed.
A diet for phosphaturia in children is prescribed to limit the consumption of calcium salts. In this case, it is necessary to consume an amount of liquid that exceeds the normal norm for a person. The presence of phosphates in the urine makes it quite cloudy; in its hue it can resemble milk that is diluted with water. Phosphatruria can be real or false. True phosphaturia acts as an independent diagnosis, while false phosphaturia is a consequence of a person having diseases such as diabetes mellitus, gastric ulcer, chronic gastritis with high acidity of gastric juice.
A diet for phosphates in the urine is prescribed only after a thorough examination of the patient, when an accurate diagnosis has been established. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a series of tests, as well as attend an ultrasound examination. Then, after the possible presence of stones has been established, and the amount of phosphates in the urine has been determined, the diet is prescribed individually according to a specific scheme.
A therapeutic menu is drawn up in such a way as to ensure a decrease in the concentration of calcium in the urine. This result is achieved by increasing diuresis, as well as limiting the amount of calcium excreted from the urine. The diet for phosphate in the urine of a child refers to table No. 14. When a patient is treated through a diet, a large number of dairy products, as well as some fruits and berries, are excluded from his diet. On the contrary, it is necessary to increase the frequency of consumption of foods that increase the acid content in the urine, since the acidic environment does not allow phosphate salts to form.
If you have phosphaturia, you are allowed to consume foods that are described in the detailed list:
- the child should eat a variety of cereals;
-all legumes and grains are also allowed without restrictions on their variety;
- It is necessary to eat fish and meat, but it should not be fatty;
- you can eat vegetables only in limited quantities, including green peas, zucchini, pumpkin, cucumber, potatoes;
- the presence in the diet of such sour fruits and berries as grapes, lingonberries, apples, cranberries, currants, plums, strawberries is allowed;
— it is very important that the patient consumes a large amount of liquid during the diet, but unless there are any contraindications to this. The drinks you can drink are: weak coffee, tea, medicinal mineral water, a variety of juices.
Since the therapeutic diet does not include all the variety of foods that are necessary for the full development of a small organism, such a diet should not be too long. Observation by a urologist is required, who will regularly prescribe urine tests to monitor how the recovery process is progressing.
There is also a list of unauthorized products for phosphaturia:
- any alcohol, regardless of its strength;
- the slightest consumption of chocolate, caramel, marmalade, sweets and other sweets is prohibited;
— products from cans, any pickles, spices and smoked meats;
- table salt in minimal quantities;
- whole milk, yoghurt, kefir, cottage cheese are excluded;
- all products that contain a lot of fat (lard, fatty fish and meat);
The diet involves dividing food into small portions and eating them five to six times throughout the day. Nutrition should be fractional in nature, then the diet will make sense and have an effect.
Based on materials from medizone.ru
Phosphaturia is a malfunction of the body during calcium-phosphorus metabolism, leading to the formation of a precipitate in the form of insoluble phosphates (magnesium phosphate and calcium). Over time, amorphous phosphates become larger and form sand in the urinary canal and sometimes stones.
The causes of this disease are considered to be an increased level of calcium in urine, the acidity of which exceeds pH 7 and an imbalance between phosphorus and calcium levels. There are often cases where the root cause of the disease was the consumption of foods rich in phosphorus in unlimited quantities or a failure in metabolic processes. Phosphates in the urine can also be diagnosed during pregnancy.
Phosphate stones can form without clinical manifestations until they reach a certain size and begin to move through the urinary system. Any part of this system can be affected by this kind of deposits. Their localization is diagnosed in the ureter, kidneys and bladder.
Phosphate urolithiasis brings many unpleasant sensations to the patient: obstruction of the upper urinary tract, worsening chronic diseases, unbearable pain during any movement (running, walking), frequent urination.
Stones with sharp edges are the most dangerous because... when moving, they cause injury to all adjacent tissues and contribute to the formation of inflammation processes.
To prescribe treatment for phosphaturia, a full examination of the patient is initially carried out, including ultrasound diagnostics of the urinary system.
The location and size of the stone are decisive factors for prescribing one of the treatment options. Cases without complications usually respond well to the following therapeutic methods:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy (pressotherapy, shock wave therapy, therapeutic massage);
- adherence to a dietary diet;
- additional vitamin complex, multivitamins;
- the use of diuretic herbal preparations;
- exercise and exercise.
A diet with phosphates in the urine provides an opportunity to correct and eliminate the consequences of an imbalance in the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium in the body. Violation of the main acid-base balance in the direction of increased alkali content is eliminated by diet therapy. It helps to compensate for the valency of the acid residue when adjusting the diet.
Dietary table No. 14 corresponds to ensuring the normal functioning of the body in case of disturbances in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, and as a result, the formation of insoluble stones in the urinary canals.
By adhering to the recommendations of diet No. 14, which specifies all the requirements for the list of permitted ingredients, the number of daily meals, portion sizes and food processing methods, you can restore normal urine pH and prevent further formation of amorphous phosphates in the urine.
When following diet No. 14, the consumption of many dairy-containing products is excluded. Products that form an “acidified” environment are recommended. They are easy to identify because... they have a characteristic sour taste.
Meals should be prepared as a fractional ration, the serving size is reduced, the number of meals is increased up to 6 times. The numerical characteristics of the diet of diet No. 14 must be compiled by taking into account 2800 kcal per day, of which:
- proteins 70 g;
- carbohydrates 410 g;
- salt 9 g;
- fats 90 g.
The menu is not mono-diet, so it is possible to eat a balanced diet, which will help improve the patient’s emotional state during the treatment period. All dishes must be fresh, without seasoning and with a minimum amount of salt.
Fluid intake increases to 2-3 liters per day - and this is one of the most important aspects of the diet.
The drinking regime has a strong influence on the regulation of urine pH. Exceeding the norm entails a shift towards the alkaline side, but we need to achieve “oxidation”. You can use a decoction of rose hips and birch sap. Herbal mixtures No. 11 and No. 12 are also recommended.
Mineral water for urinary tract diseases helps increase acidity. It is recommended to drink 1 hour before and after meals: Narzan or Arzni.
- Mix 1 tbsp. fringed grass, lingonberry leaves and heather.
- Add 4 tbsp. crushed madder root.
- Pour 1 tbsp into an enamel bowl. collection and pour 300 ml of boiling water.
- Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Drink 3 tbsp of the finished broth. half an hour before meals, 3 times a day.
- 1 tbsp. crushed madder root.
- Add 2 tbsp. crushed madder root, wheat grass and salvia leaves.
- Mix with 4 tbsp. flax seed.
- 3 tbsp. collection, pour one liter of boiling water.
- Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Take 250 ml warm, an hour before meals, 2 times a day.
Due to the fact that the list of products allowed for consumption is quite limited, it is impossible to adhere to diet therapy for a long time. Equally important is monitoring the patient’s condition by a urologist, with periodic testing.
It is allowed to diversify your diet several times a week with egg whites, vegetables and dairy products indicated in the table.
Based on materials from onamag.ru
Diets are the most effective way to prevent the occurrence of urolithiasis and alleviate the course of an already existing disease. The diet for phosphaturia consists of prohibiting the consumption of fermented milk and dairy products, hot spices, fried foods and large amounts of coffee.
If phosphaturia appears as a concomitant disease, then for a long time it occurs without pronounced symptoms, but the period of remission is usually short. Exacerbation of the disease can lead to significant deviations from the normal state, which ultimately leads to severe pain and long recovery.
Primary phosphaturia can occur for the following reasons:
- metabolic disorder;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- deterioration of the parathyroid glands;
- congenital damage to the kidneys or ureter;
- problems with phosphate absorption;
- viral and bacterial infections.
All diseases result in the deposition of phosphate deposits, which provoke the formation of stones in the kidneys and ureter.
The diet for phosphaturia in adults is based on normalizing the acidity level, as well as preventing the appearance of precipitation of salts and phosphates in the urine. For the best effect, experts advise using diet No. 14, as it helps suppress the manifestation of this disease and alleviate the symptoms. Nutrition for phosphaturia will be based on the following indicators:
- the number of calories consumed per day is no more than 2500 kcal;
- the patient needs to drink no more than 2.5 liters of water per day;
- the salt content in consumed food is no more than 5-7 g;
- daily intake of simple/complex carbohydrates – 300-500 g;
- fats - no more than 100 g.
If the doctor has not identified any special contraindications to the drinking regime, then you are allowed to drink 2.5 liters of liquid: this norm includes juices, teas, and decoctions drunk per day.
It is very important for a patient who suffers from phosphaturia to strictly maintain a balance of vegetable and animal oils: there should be as much of the latter on the menu as possible. It is very important to give up heavy insoluble fats and limit the consumption of foods high in calcium: nuts, milk, sour cream, cheese.
It’s good if your diet includes cereals, boiled fish, and lean meats, which will help increase the acidity in the urine. Drinking a large amount of fluid per day is another important action for recovery. Drinking before and after meals is important, but experts do not recommend drinking water during meals.
Products that will help quickly restore acidity:
- any green vegetables: peas, cabbage, sorrel;
- fresh fruits and berries: pomegranates, raspberries, green apples;
- grains and legumes (you can make porridge from them);
- lean meat and boiled fish;
- eggs (only whites are eaten);
- natural sweet products: beet sugar, honey;
- sweet products with a minimum amount of yolk and milk in the composition;
- vegetable oil;
- compotes with a minimum amount of sugar, herbal tinctures, weak tea and coffee.
Nutritionists also recommend that patients with phosphaturia drink mineral water, which leads to an increase in acidity. Mineral water “Narzan” or “Naftusya” is good - they contain the right amount of minerals that acidify the urine. You need to drink mineral water 30 minutes before meals or 1.5 hours after.
Experts have identified a group of products that are important to completely remove from your diet.
- any alcoholic drinks (non-alcoholic beer, wine and energy drinks);
- cakes, pastries with creams;
- high fat meat, lard;
- all dairy products.
Menu number 14 for phosphaturia for adults consists of a complete refusal of fractional meals; it is important to eat food 4 to 5 times a day. Fasting or fasting days are prohibited.
Nutritionists have compiled a sample menu for patients that will help quickly normalize the acidity level and the general condition of the patient:
- first breakfast: pasta baked with mushrooms and egg whites. Cranberry juice;
- second breakfast: a couple of green apples, toast;
- lunch: cabbage and pea salad, dressed with butter, buckwheat with chicken breast, soup with cereal. Compote or fruit drink - you need to drink about two glasses, not including soup;
- afternoon snack: any pastry product without sweet filling, raspberry juice or rosehip compote;
- dinner: porridge with fish cutlet, toast and compote.
Before going to bed, you can drink a glass of rosehip decoction. If suddenly the patient feels hungry, he can eat toast or a bun without filling - fasting while on a diet is strictly prohibited. You can process food in any way: boil, fry until crusty without animal lard, steam bake. Dairy products are excluded for phosphaturia, but one spoon of low-fat sour cream added to a baked dish will not affect your health in any way. Dairy products in this form are allowed to be consumed until 13:00.
If, after re-diagnosis of urine, the amount of phosphates in it remains the same, then the disease will have to be treated with medications. Diet is a way to avoid the appearance of phosphaturia or reduce the likelihood of relapse.
At the beginning, the child may not feel any changes in the body, but only until the stone reaches a large size. After the stone begins to move through the urinary system, the baby will feel pain and discomfort. If the stone has sharp edges, then during movement it will damage the tissues of the ureter and provoke inflammation.
A diet for phosphaturia in children involves the use of:
- all porridges;
- poultry, meat, fish and other low-fat foods that contain a lot of animal protein;
- pumpkins, zucchini, peas, potatoes, cucumbers;
- any sour fruit.
If there are no contraindications, then drinking plenty of fluids is allowed.
Since the diet is very limited, the diet lasts as little time as possible, and the child must be regularly monitored by a doctor and undergo frequent urine tests.
After determining a large amount of phosphates in the child’s urine, the diet should exclude the following foods from the diet:
- any sweets: sweets, chocolates;
- confectionery products: filled rolls, cakes;
- canned and pickled products, smoked meats;
- reducing the amount of table salt consumed;
- exclusion of fried foods and deep-fried cooking.
If, after following a diet, a repeated urine test reveals a large amount of phosphates, then the doctor determines secondary phosphaturia, which can occur against the background of other diseases. Depending on the specific cause, a specialist will prescribe a comprehensive treatment for the disease for a pregnant woman.
After determining the cause of the disease, the pregnant woman is prescribed a diet that excludes foods that lead to the formation of phosphates in the body and the development of phosphaturia. The diet during pregnancy prohibits the following foods:
- vegetables;
- dairy products;
- strong tea or coffee;
- spicy dishes;
- sweet sodas.
The diet for phosphaturia in pregnant women should include as much protein as possible. Among vegetables, more attention should be paid to asparagus, pumpkin, and Brussels sprouts. You can add berries to the menu - lingonberries and currants. It is forbidden to eat stale products, as many of them are treated with phosphates to extend shelf life.
Experts recommend that a pregnant woman with toxicosis take various vitamin complexes. To increase the acidity level of urine, it is allowed to add vitamins D, B and A, as well as magnesium.
It is important to be especially careful when eating a diet. The consumption of dietary products must remain within medicinal limits, otherwise severe acidification of the urine can occur, which will lead to the formation of oxalates with sharp edges. A week after starting the diet, you need to re-take a urine test to detect phosphate levels.
Based on materials from fb.ru
The appearance of amorphous crystals in pathology
Crystals in urine can vary. It depends on what salts they are formed from. Crystals are divided into phosphates, urates and calcium oxalates. All of these substances can form kidney or bladder stones. In some cases, stones contain several different salts at once. Phosphates often precipitate during bladder infections (cystitis), and they also appear due to increased secretion of parathyroid hormone. Urates are accumulations of uric acid salts. Excessive production of this substance indicates a violation of mineral metabolism in the body (gout). In addition, urates are often present in the urine in chronic diseases of the kidney tissue (nephritis, chronic renal failure). Most often, stones consist of calcium, which is released in large quantities and forms crystals. Oxalates in the urine are observed in diseases such as pyelonephritis and diabetes mellitus.
The presence of certain types of crystals always indicates pathological conditions. These include salts of hypuric acid, accumulation of cholesterol, bilirubin, leucine, tyrosine, hematoidin. Normally, these substances should not be excreted by the kidneys.
Nutrition and lifestyle during illness
The diet for phosphaturia should be tasty and varied. Let's look at the daily menu option.
For breakfast we prepare scrambled eggs or an omelet from one or two eggs. Season with a little milk and add chopped tomatoes. You can drink a glass of cranberry or lingonberry juice.
For second breakfast we drink berry jelly.
For lunch we eat pureed pumpkin soup with durum wheat pasta. As an alternative, you can offer cutlets with a salad of cucumbers and herbs. The drink is herbal tea.
The afternoon snack is limited to sour apples, preferably baked, or with honey and cinnamon.
For dinner we prepare pilaf from polished rice with any lean meat. We complement it with a salad of cucumbers and herbs. The drink is herbal tea. As alternative drinks, you can take birch sap or rosehip decoction. Instead of meat, you can cook any fish - it also belongs to the list of permitted foods.
In addition to the diet for phosphaturia in adults, for speedy healing it is recommended to engage in physical activity, unless, of course, stones interfere with this. The doctor prescribes medications that will help dissolve the stones and also prescribes a diuretic.
Get tested periodically to make sure the phosphate diet is working and the amount of phosphate excreted in your urine is decreasing.
Symptoms of crystals in urine
Most often, the presence of crystals in the urine does not manifest itself in any way. Especially if the accumulation of salts is present in small quantities. Symptoms occur with the formation of stones and the development of urolithiasis. In this case, the functioning of the kidneys is disrupted due to obstruction of the collecting system. Also, stones can accumulate in the bladder and enter the ducts. As a result, a syndrome such as renal colic develops. The patient complains of severe pain in the lower back, radiating down the abdomen and groin area. Due to the fact that there is a stone in the ureter, the release of fluid is difficult. The pain with renal colic is so strong that the patient takes a forced position: on his side with his legs brought to his stomach. Crystals in a child’s urine are most often observed due to inflammatory pathologies (acute and chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis). Such ailments are accompanied by increased body temperature, nausea, pain in the lower back and abdomen (usually on one side).
Where to begin
The attending physician will conduct all the necessary studies to identify the cause of the disease and draw up the correct treatment regimen. A balanced diet will help to calm down the rebellious salts and phosphates in the child’s urine.
Products with oxidizing effects should be included in your daily diet. These include:
- all fruits;
- sour berries;
- among vegetables, preference should be given to white cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkin, potatoes, beets;
- lean varieties of meat and fish.
Butter, vegetable fats and pasta are acceptable in the diet. It is necessary to regulate the baby's drinking regime. He should drink up to 2 liters of ordinary water per day. Alkaline mineral water should be excluded. Salt intake should be minimized or completely eliminated.
The doctor will definitely recommend taking multivitamins and vitamin A in increased dosages. A urine test will have to be taken periodically in order to adjust the treatment and clearly understand the picture of what is happening.
Diagnosis in the presence of crystals in urine: interpretation of tests
Urates, phosphates and calcium crystals in the urine are detected by microscopic examination. In addition to OAM, a biochemical blood test is performed. The presence of crystals in the urine is indicated by a “+” sign. For example, the entry “urate+++” means that these substances are present in large quantities. The pH level is also determined. If this indicator is normal, a more in-depth examination is carried out. Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky, Nechiporenko, kidney ultrasound, excretory urography is performed. In some cases, it is necessary to conduct a study of the parathyroid glands. In addition to laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, you should find out: what foods the person consumed before taking the OAM, and whether he drinks unfiltered water.
Authorized Products
What can you eat if you have phosphate kidney stones? Despite significant restrictions, there are still many available products in the diet that allow you to prepare delicious dishes. Moreover, there are no restrictions on the type of culinary processing.
Allowed and recommended dishes:
- meat broth soups with cereals and pasta;
- any lean meat, poultry, fish;
- bakery products except fresh baked goods and muffins;
- vegetable oils;
- whole grain cereals;
- sugar, honey;
- weak tea or coffee.
The diet for phosphate urinary stones includes a small amount of vegetables and berries: lingonberries, red currants, cherry plums, Brussels sprouts, legumes. Asparagus and green onions are allowed once a week. You can eat mushrooms as a side dish.
Also, if you have phosphate stones, it is recommended to drink mineral waters that alkalize urine. The diet includes “Naftusya” or “Narzan” half an hour before meals or 60 minutes after.
How to prevent crystals from forming in your urine
To prevent the formation of crystals in the urinary sediment, it is necessary to periodically take an OAM. After all, often the accumulation of salts is not accompanied by any symptoms. It should be remembered that crystals rarely form with proper nutrition. Therefore, it is worth consuming foods containing acids in limited quantities. It is not recommended to drink “raw” unfiltered water. In the presence of inflammatory and metabolic diseases, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s prescriptions.
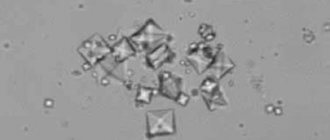
Phosphates are calcium and magnesium phosphate salts. They are formed in an alkaline environment, have a gray-white color and a loose structure. Because of their structure, they are also called amorphous crystals.
Treatment methods
The results of the examination are studied by a pediatrician, who determines the cause of the phosphates and draws up a treatment method. If the provoking factor is the development of the disease, then therapeutic therapy is aimed at eliminating it.
The treatment is complex, that is, in addition to drug therapy, a diet is prescribed
Treatment will be effective if you follow the doctor's recommendations. After a course of therapy, you should undergo an examination and take urine samples. Normalization of phosphate levels is considered a favorable result and indicates the elimination of the cause of the pathological process.
If the increase in indicators is caused by vomiting or diarrhea, the excess salt is eliminated on its own when the child’s body recovers. To speed up this process, the doctor prescribes a complex of vitamins and minerals to strengthen the immune system.
Common causes of phosphaturia are poor diet, consumption of high-calorie foods, and excess of foods containing calcium. The disease is eliminated with the help of a special diet, which is prepared for the child.
Lack of treatment causes complications associated with the functioning of the genitourinary system, the development of an inflammatory process or an infectious disease.
Reasons for the appearance of phosphates in urine
Phosphaturia can have physiological and pathological causes. The first include:
- Vegetarianism.
- The predominance of foods rich in phosphorus in the diet (caviar, fish, dairy products, buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, alkaline mineral waters)
- Changes in metabolism in pregnant women.
- Children's age (up to 5 years).
Pathological conditions leading to the appearance of amorphous crystals in the urine are:
- Slowing down of glomerular filtration.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract (pyonephrosis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.)
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Diabetes.
- Fanconi syndrome (impaired reabsorption of substances in the renal tubules)
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
- Fever.
- Anomalies in the development of the urinary tract.
- Lack of fat-soluble vitamins D, A, and B in food.
- Injuries of tubular bones.
Features of phosphaturia in children
In children under 5 years of age, metabolism is imperfect; the diet contains a lot of dairy products, so their phosphaturia may be physiological. But at an older age, if there are complaints and poor heredity (relatives have urolithiasis), it is worth paying close attention to it. In these cases, amorphous crystals in the urine may indicate the presence of:
- Urolithiasis.
- Rickets (vitamin D deficiency)
- Inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
- Diabetes mellitus or phosphate diabetes (genetically determined disease)
- Fanconi syndrome.
Pathological phosphaturia
If, with a varied, balanced diet for 2 weeks - 1 month, a large amount of phosphates in the urine remains, the doctor will definitely prescribe a kidney ultrasound to the patient. Excess phosphates in an alkaline environment can trigger the formation of kidney stones. If stones are still found, do not panic: phosphate stones are soft and porous and can be easily dissolved. For some time, the patient must take medications that soften the stones; then he undergoes several lithotripsy procedures - crushing stones using waves. It is necessary to follow a special diet.
Under no circumstances should urolithiasis be ignored or neglected, as it can cause life-threatening complications: blockage of the ureter, chronic inflammation, hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney, and oncology.
Consequences
The only consequence of an increased amount of amorphous phosphates in the urine, which is caused by poor nutrition, is urolithiasis. Constantly maintaining high levels of these substances causes their accumulation into one whole. As a result, a stone is formed. It does not pose such a threat as urate or oxalate stones, since it has a smooth surface.
However, urolithiasis must be treatable. Otherwise, the formed stones can provoke renal colic, sepsis, impaired blood supply to the filtering organ, or the growth of malignant tumors. The consequence of these processes will be various deviations in the functioning of organs and systems.
Nutrition
It is necessary to exclude products during the processing of which an alkaline reaction occurs:
- fermented milk products of all types;
- all kinds of sweets, chocolate, cocoa;
- alcohol;
- fatty foods of animal origin;
- fresh baked goods;
- smoked meats, pickles, pickled products, canned food;
- Salt is limited to a minimum.
For excess phosphates, the following products are recommended:
- cereal porridge;
- legumes;
- low-fat meat, fish;
- some vegetables: potatoes, zucchini, cucumbers, peas, pumpkin.
- berries and fruits with sour taste;
- you need to drink more, especially sour juices, fruit drinks, special mineral water.
You should take vitamins, consume milk and eggs little by little (infrequently). You need to eat 6 times a day, drinking regime - at least 2.5 liters of liquid per day.
Diet No. 14 (for phosphaturia)
Prohibited: milk and dairy products with the exception of sour cream, egg yolk, baked goods made with milk, vegetables, fruits, berries with the exception of the above, canned snack foods, smoked meats, mustard, pepper, horseradish. Substances and products that excite the nervous system and have a strong juice effect are excluded - alcoholic beverages, coffee, spices, strong tea, concentrated broths and infusions, pickles and smoked meats.
These substances, irritating the gastrointestinal tract, cause acid-base imbalance and alkalinization of urine. Vitamins are given in the form of rosehip infusion, wheat bran decoction, and lingonberry juice. Table salt is introduced into food in normal quantities. Chemical composition: proteins - g, fats - g, carbohydrates - up to g; calories - Diet - general. Liquid 1. l per day. Oatmeal soup with meat broth with meatballs, fried cutlets, buckwheat porridge, cake, tea.
Tea, bun. In addition to diet, urine acidification should also be achieved by taking acidifying juices: cabbage, apple and grape in the absence of diabetes. Juices are taken once a day a minute before meals in a volume of ml. In the case of existing gastritis with increased stomach acidity, sour juices can be taken during meals, towards the end of the meal, but not after meals.
In the future, the dose of juice you take should be adjusted yourself, based on urine pH measurements and maintaining its acidity at the level of 6.6. Stronger acidification of urine can lead to loss of urate. Increasing the solubility of phosphates - the phosphatolytic effect is achieved by taking a decoction of elecampane roots, knotweed roots, and burdock roots. Decoctions are taken in a volume of ml one minute after meals once a day.
Despite the high beneficial properties, the Anti-Cancer Nutrition System was one of the undeniable advantages of berries
Medicinal plants that promote the removal of phosphates are largely the same as those used for oxalate diathesis. In addition to them, you can assign fees of the following composition. Phosphaturia is a disorder of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the human body. This leads to the presence of sediment in the urine in the form of calcium and magnesium phosphates.
After some time, insoluble phosphate salts increase their quantitative content, resulting in the formation of sand, as well as large stones in the urinary tract. Therefore, a timely detected problem can be eliminated if the patient follows a phosphate diet.
The most common cause that provokes phosphaturia is an increased level of calcium in the urine, which has an alkaline environment exceeding seven. This can also occur in children when there is an imbalance in the ratio between phosphorus and calcium.
A diet for phosphaturia in children should set restrictions on the consumption of calcium salts, increase acid valency, and also increase the amount of fluid consumed. With phosphates in the urine, its color becomes quite cloudy, which resembles the appearance of diluted milk.
Phosphaturia can be the result of the presence of diseases such as gastric ulcer, chronic gastritis with high acidity of gastric juice, diabetes mellitus.
In this case, phosphaturia is defined as secondary. If this disease acts as an independent disease, then it is primary. A diet for phosphates in the urine is prescribed during examination and establishment of an accurate diagnosis of the patient, after tests and ultrasound of the urinary organs.
After it has been determined whether there are stones and the amount of phosphates in the urine, the diet is prescribed according to a certain scheme. The treatment menu is aimed at reducing calcium concentration in the urine.
This is achieved by increasing diuresis and limiting calcium excretion in urine. During the period of therapeutic nutrition, the consumption of almost most dairy products, as well as selectively fruits and vegetables, is limited. The consumption of foods that increase the acidity of urine is encouraged, because phosphate salts are not formed in such an environment. It is strongly recommended to consume increased amounts of fluid if there are no contraindications to this.
Among the drinks that are allowed to drink: coffee or tea not brewed strongly, juices, medicinal table mineral water. Due to the fact that the range of foods consumed is limited and very poor for normal nutrition, such a diet should not be long-term, and should also be strictly under the supervision of a urologist.
Urine tests must be done periodically to monitor the dynamics. As with any diet, you need to eat fractionally, in small portions, but often. The approximate number of calories consumed per day should not exceed kcal.
Compliance with a prescribed diet may also be accompanied by the use of decoctions and infusions prepared from medicinal plants, herbal teas and teas, which are recommended for phosphaturia. Phosphates are commonly called salts of phosphoric acid; they are called amorphous because they do not have a clear shape.
If your baby's urine contains a small amount of them, then everything is fine with your child.
Phosphaturia is a malfunction of the body during calcium-phosphorus metabolism, leading to the formation of a precipitate in the form of insoluble magnesium and calcium phosphates. Over time, amorphous phosphates become larger and form sand in the urinary canal and sometimes stones. The causes of this disease are considered to be an increased level of calcium in urine, the acidity of which exceeds pH 7 and an imbalance between phosphorus and calcium levels. There are often cases where the root cause of the disease was the consumption of foods rich in phosphorus in unlimited quantities or a failure in metabolic processes.
As a rule, deviations occur in children no older than 5 years. An increased content of phosphates in the urine of a baby may be evidence of malnutrition of the baby or mother if the child drinks breast milk. But it can be a harbinger of serious deviations: improper metabolism of phosphorus and calcium, kidney problems. A cold can lead to the appearance of phosphates in the urine in large quantities.
Sample diet menu
If the repeated analysis does not find them, then everything is fine with the child’s health. Before re-testing, keep your baby on a phosphate-free diet for some time. Try to eliminate or minimize the consumption of dairy and fermented milk products from your diet. It is also better to wait with eggs, nuts, carrots, beans, peas, herbs and spices.
All of these products contain quite a lot of phosphorus. Confectionery and baked goods are also prohibited, including products containing cocoa. Carbonated drinks, chips, and frequent inclusion of buckwheat, barley and oatmeal in the diet provoke an increase in phosphates. If phosphates in a child’s urine are detected during repeated examination, we can say that the baby has phosphaturia.
This is a pathology and it is necessary to identify the causes causing disturbances in phosphorus-calcium metabolism. The attending physician will conduct all the necessary studies to identify the cause of the disease and draw up the correct treatment regimen.
Preventive measures
The most important measure to prevent metabolic disorders is adherence to the principles of a healthy, balanced diet. You can’t get carried away with diets, it’s harmful to your health!
Metabolism is normalized with an active lifestyle, regular physical activity, and hardening.
If you have diseases of the urinary system, especially organic pathologies of the kidneys, constant medical supervision is necessary: visit a urologist at least 2 times a year, do an ultrasound of the kidneys, undergo regular tests, take uroseptics, herbal remedies. During exacerbations, hospitalization is necessary, during remission - sanatorium-resort treatment.
Treatment and diet
Stones, reaching significant sizes, begin to interfere with a person’s movement. They show no signs of existence until they reach a critical size. After this, discomfort and even pain begin to appear when walking and running. The quality of life is significantly reduced. Therefore, it is clear that a disease such as phosphaturia must be urgently treated.
But based on some signs, you can suspect something is wrong and correct the problem in time, before you feel the stones. The urine will be cloudy and may even resemble diluted milk in color. This will let you know that there is something wrong with your urinary system. It is necessary to undergo tests, and then the doctor will identify and determine the disease. If it is phosphaturia, the doctor will prescribe a diet.
Conclusion
The presence of phosphoric acid crystals in the urine is not necessarily a sign of kidney or bladder disease. Excess phosphates can be caused by dietary errors. If you eat a varied diet for 1-2 weeks, urine tests in healthy people will normalize.
In pregnant women, phosphaturia can be associated both with an unbalanced diet and with kidney overload in the second half of pregnancy. Strict medical supervision is required.
Phosphaturia occurs in young children due to a tendency to rickets and immaturity of metabolic processes.
If excess phosphates in the urine are associated with urolithiasis, the patient undergoes treatment in 2 stages: first, under the influence of drugs, the stones are softened, then they are crushed, and they are removed from the body naturally. In case of urolithiasis, lifelong adherence to a diet and general improvement of the body through regular physical activity, hardening, and vitamin therapy are necessary.
For screening diagnosis of the condition of the renal filter, a general urine test is used. This study allows you to determine the functional state of the kidneys, as well as the urinary tract.
Several types of tests are used for assessment, which in turn also have their own division:
- organoleptic properties;
- physico-chemical;
- biochemical;
- microscopic;
- microbiological
Already at the first stage of the examination, the presence of pathology can be determined. If there are impurities in the urine, its color and transparency change. Cloudy urine may indicate the presence of a cellular component or salts.
Amorphous crystals in the urine may indicate kidney pathology, but in small quantities they are a reflection of a person’s diet.
Properties of amorphous phosphates
Salts in the urine appear in a person due to poor diet or due to pathological conditions of the body. Amorphous phosphates are small crystals that usually do not group together, but are excreted in their original form. The level of these substances in the patient’s body can only be determined through laboratory testing. It is not possible to independently diagnose amorphous phosphates in urine. When the amount of salts in urine increases, a person does not notice obvious clinical manifestations. This condition is characterized only by cloudy urine, but this is also difficult to notice.
Phosphates do not pose a serious threat to humans. These substances are rarely combined, but the formation of stones cannot be excluded. In order to reliably determine their presence in the body, it is necessary to pass a general urine test. To obtain a reliable analysis result, it is also necessary to examine the daily volume of urine. Normally, the human body receives up to 1200 mg of phosphates every day. About 400 are excreted in feces, and the rest in urine. If the indicators are higher, then this already indicates an excess of salts.
What it is
The word “amorphous” itself means that the crystals formed by salts do not have a clear structure but simply represent a chaotic accumulation of poorly soluble salts. It is customary to distinguish three types of amorphous crystals found in urine: phosphates, urates and oxolates.
Causes of appearance in urine
Depending on which salt forms the crystal, the main etiological factors vary. The most commonly detected phosphates are salts of orthophosphoric acid and can appear in a completely healthy body due to dietary habits, which should always be taken into account.
However, they should not be treated with disdain. For patients, especially those with long-term phosphaturia, the level of phosphates, as well as other salts, should be interpreted in conjunction with the clinical picture, as well as other laboratory and instrumental studies.
Phosphorus is normally used by the body for the synthesis of bone tissue in combination with calcium, brain function, myocardial contraction and the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. At its normal amount (the level in the blood is half the level of calcium), it is almost completely consumed by the body.
Only 12% of what is consumed is excreted by the kidneys. This process is regulated by a system of hormonally active substances: somatostatin, thyroxine and calciferol. Parathyroid hormone, thyrocalcitonin and calcitriol also have an indirect effect on excretion.
However, increased consumption of phosphorus-containing foods leads to its excess excretion through the kidneys.
It is customary to identify the following reasons for the increase in phosphates:
- nutritional errors: vegetarianism or, conversely, excessive consumption of meat, seafood, consumption of tomatoes, asparagus, sorrel in large quantities, deficiency of vitamins A and E. The use and abuse of alkaline water, coffee, tea, cocoa, chocolate also affects phosphorus metabolism;
- heavy physical activity with excessive fluid secretion;
- antibacterial agents related to sulfonamides and penicillins;
- drinking unfiltered tap water.
The appearance of phosphorus in all these cases is not a sign of disease, but can subsequently lead to the formation of stones.
Pathologies
Most often, pathological excretion of phosphorus salts is observed in children and adolescents, as well as in pregnant women and the elderly. This is due to changes in the hormonal background of these categories of people.
It is customary to distinguish the following diseases accompanied by the detection of phosphorus in the urine:
- the main cause is infectious diseases of the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis);
- chronic kidney disease, leading to decreased filtration capacity;
- urolithiasis disease;
- decreased secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, resulting in increased absorption of phosphorus;
- intestinal infections, accompanied by profuse vomiting and diarrhea and leading to dehydration;
- endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, thyrotoxicosis);
- lymphomas and myeloma;
- genetic diseases (hypophosphatemic rickets);
- Fanconi disease;
- poisoning with phosphorus-containing substances.
Urates are salts of uric acid, and, in most cases, their excretion in the urine is associated with disorders of mineral metabolism or gout. Also, these crystals can be found in chronic kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and chronic renal failure. The crystals in this case contain a lot of calcium.
Oxalates are found in pyelonephritis and diabetes mellitus.
Amorphous crystals during pregnancy
Amorphous crystals in pregnant women occur for three main reasons:
- Disturbance of acid-base balance towards bases due to changes in eating behavior: refusal of some foods and predominance of others in the diet.
- Prolonged toxicosis in the first trimester of pregnancy, and sometimes in the second, leads to significant dehydration and a decrease in the rate of urine formation.
- If there is a history of kidney pathology, excretion of a double volume of waste can lead to impaired filtration capacity of the kidneys and excessive excretion of phosphates.
The appearance of phosphates in the urine of pregnant women should not be ignored. Women should also regularly retake urine tests and register with a urologist.
Phosphates in children
In infancy and childhood, the presence of phosphates in the urine is considered a physiological norm. It is necessary to start looking for a problem when the age norm is exceeded.
The detection of excess crystals in the urine of children is most often associated with hormonal changes in the body and active growth. A possible cause may be malnutrition and children's consumption of sweets and dosages.
In early preschool age, it is also possible to have phosphaturia as the only sign of rickets. Urinary tract infections often occur in children, especially girls.
Treatment
If phosphaturia has been detected repeatedly, then a course of therapy is necessary. This will prevent the formation of phosphate stones in the kidneys and the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms.
The situation when the increased content of phosphates in the urine is a symptom of the underlying disease, then it is necessary to cure the primary pathology: eliminate inflammatory, congestive phenomena in the urinary tract.
In case of an infectious process (for example), antibiotics may be prescribed. Herbal preparations are widely used that can reduce inflammation and normalize kidney function. Vitamin A is also prescribed, which restores the epithelium of the urinary organs.
Phosphaturia in children
Main reasons:
Treatment involves the administration of vitamins A (retinol), D, canephron is widely used, which prevents the formation of stones and protects kidney tissue. For genetic diseases, symptomatic therapy is carried out to correct electrolyte disturbances in the blood.
Phosphaturia in pregnant women
Reasons for the appearance of phosphates in the urine during pregnancy:
- Increased serum calcium concentration. As a result, the element is excreted from the body in larger quantities, which disrupts the acid-base balance.
- Urolithiasis disease. This disease is dangerous for the mother and fetus and will require treatment.
- Inflammation in the organs of the urinary system (and others).
- Toxicosis with frequent vomiting or diarrhea.
Therapy for phosphaturia during pregnancy will depend directly on the reasons that caused it. In the absence of diseases of the genitourinary organs, the doctor may advise adjusting the diet.
Diet
If phosphates appear in the urine, you must adhere to table No. 14. The diet should be prepared by a urologist with regular monitoring of laboratory parameters.
Authorized products:
- Various cereals.
- Legumes.
- Lean meat and fish.
- Limited amount of vegetables.
- Sour fruits and berries: cranberries, currants, apples, strawberries, figs.
- Drink plenty of fluids if there are no contraindications.
Prohibited products:
- Alcohol.
- Sweets: chocolate, caramel, marmalade.
- Confectionery and bakery products.
- Salty, fatty and smoked foods.
- Dairy products: milk, cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir.
Sample menu for 1 day
- Breakfast: boiled pasta, baked with sour cream (150 g), cranberry juice (200 ml).
- Second breakfast: 2 medium-sized sour fruits.
- Lunch: borscht with lean beef (300 ml), pea cutlets (150 g), lingonberry jelly (250 ml).
- Afternoon snack: lean bun, rosehip tea (250 ml).
- Dinner: boiled rice (100 g), baked chicken breast (150 g), currant juice (250 ml).
- Second dinner: sour fruit compote (250 ml), grain bread.
The kidneys in general are described in detail in the video:
A diet for phosphaturia prohibits the consumption of dairy and fermented milk products, does not allow improving the taste of food with spices and hot seasonings, and requires giving up coffee.
Urinalysis showed that the test sample contained phosphates in the urine. Should I immediately sound the alarm and start treating kidney disease? There is no need to be scared. The analysis should simply be retaken, preferably after two to three days.
The formation of phosphates may be related to diet. The urine of vegetarians is characterized by the presence of phosphates. A decrease in the intake of animal proteins into the body also causes their formation. Metabolic products of acidic consistency reduce the phosphate content in urine, and they are released by the body only if there is meat and meat products in the diet.
Phosphate sand is represented by gray and white inclusions; it consists of calcium salts and phosphoric acid. When metabolic processes are disrupted, sand is retained in the kidneys, forming stones that grow quite intensively.
At the first stage of their occurrence, they are porous and easily dissolve if a special diet for phosphaturia begins. If the growth of stones has not been prevented, there is a danger that they will turn into coral stones with numerous growths and sharp edges. If such a fossil gets into the ureter, it will be impossible to do without surgical intervention.
The formation of phosphates is explained not only by the fact that the diet with phosphates in the urine was not followed. Stones of this type accumulate in diseases associated with dysfunction of the parathyroid glands, inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, myeloma, endocrine diseases and rickets. Also, the formation of phosphates is affected by a sedentary lifestyle and impaired outflow and formation of urine.
The presence of phosphate stones is indicated by the same symptoms as the presence of stones of any kind. These are pain in the lower back or ureters, urinary retention, renal colic, segments of blood in the urine, cloudy urine and increased body temperature in acute cases.
The presence of phosphate stones can be detected by a general urine test. Their location is determined after examination with an ultrasound machine or after radiography. In the latter case, it is necessary to inject a contrast agent into the kidney. Treatment of urolithiasis can be conservative and surgical.
In the first case, spasm of the urinary tract is relieved, and drugs are prescribed that dissolve phosphate stones. In the second, an operation is prescribed, during which the stones that cause pain are removed. After surgery, recurrence of attacks of urolithiasis may occur.
If it turns out that the formation of sand from phosphoric acid and calcium is not associated with the predominance of dairy and plant products in the diet, then a thorough examination is required. It is impossible to stop the excess formation of phosphates without identifying diseases. In the case when the disease is identified and it becomes clear why phosphates are formed in the urine, a diet will help reduce their content.
Antiphosphate diet is a diet based on the exclusion and limitation of foods of many categories in the diet. Foods with a high calcium content should be excluded from your diet. This includes lactic acid products and whole milk. It is necessary to avoid foods that contribute to the formation of alkaline urine. This group includes mushrooms and poultry eggs.
Like any diet, the phosphate diet prohibits the consumption of smoked foods, sweet carbonated drinks, spicy snacks, and spices, including those of plant origin. Absolutely no to chocolate, coffee and cocoa. It is advisable to give up tea, especially strong tea.
What to eat? Cereals and pasta, fish and meat, sour and sweet and sour fruits and berries in their natural form and in compotes, jelly, in the form of jam or marshmallows.
The consumption of raw vegetables is limited. Since the diet prohibits many foods that contain nutrients necessary for the body to function normally, it is necessary to take a vitamin complex.
It is necessary to drink more liquid, especially medicinal mineral waters: “Naftusya”, “Narzan” and others of similar composition. Mineral water helps reduce the amount of phosphates formed in the urine. There is a special therapy that involves its use. The treatment course is designed for a year. Drink water for two or three weeks, with a break of seven to ten days, half or a third of a glass before meals.
If there is phosphaturia, diet No. 14 for a day will look something like this.
Fractional meals are not encouraged; food should enter the body 4 times a day or 5. Fasting is not encouraged.
You can boil pasta for breakfast. If you bake them with a small amount of sour cream, making a casserole, the processed dairy product will not cause harm. It is advisable to wash down breakfast with cranberry juice or sour apples, and if you are not full, add cookies or dried bread to the liquid.
Snack – sour apples, tangerines or cherries. Depending on the season.
Lunch: meat soup or broth, pea cutlets, bread, jelly - less than one and a half glasses.
Afternoon snack: a bun with rosehip tincture or tea from the same berry.
Dinner: chicken or fish cutlet, rice - preferably brown, fruit drink.
Before going to bed, you can treat yourself to apple compote and grain bread. Food can be boiled, fried, steamed, baked until golden brown. But at the same time, avoid eating cooking oil. Lard is not considered a healthy product.
If phosphates are constantly formed in the urine, diet alone cannot cope with them. It is necessary to find what is causing their formation and treat the systemic or chronic disease with medication.
Good afternoon Please tell me, amorphous phosphates +, SG 1.020 and pH 7.0 were found in the TAM of a boy (one year and four months old). Other indicators are within normal limits. What could this mean? What recommendations can you give?
Found quite often in children. In small quantities they are quite safe and usually do not alarm doctors. The child should be periodically taken for examinations by a specialist and have his urine tested.
Phosphaturia
Pathological phosphaturia is a symptom complex characterized by the long-term existence of phosphates in the urine.
These people require long-term monitoring and nutritional adjustments. If, during diet therapy, there are still a lot of crystals in the OAM, then a planned ultrasound examination is required.
An ultrasound will detect the presence of kidney stones, the likelihood of which is high if phosphaturia persists for several months.
Such patients are diagnosed with urolithiasis and treated according to the following scheme:
- a course of drugs that soften the structure of already porous stones. This is done to reduce the size of the stone and improve the effectiveness of the next stage of treatment;
- lithotripsy - wave action on stones in order to destroy them and remove them from the renal pelvis. Possibly invasive, when the emitter is retrogradely inserted directly into the pelvis through the urinary tract, and non-invasive (percutaneous) crushing of stones.
It is important not to ignore the disease, since without medical control there is a risk of complications: stone passage into the ureter, rupture of the ureter or urethra, infectious and oncological processes, hydronephrosis.
Symptoms of phosphaturia
The initial symptoms of the disease are nonspecific:
- Cloudy urine with white sediment.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Anxiety.
- Decreased appetite.
- Decreased performance.
Patients attribute these symptoms to high stress, lack of sleep and stressful situations. As a result, the disease progresses and forms and develops.
Diagnostics
To determine phosphaturia, it is enough to take a test. This is the most common study due to its simplicity and information content. During diagnosis, a laboratory technician may detect an acidity of less than 7, an atypical precipitate of a large amount of salts, which means the presence of phosphates in the urine. To obtain more detailed results, a daily urine test for salts may be required, which will allow you to assess the condition of the urinary system.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a thorough examination of the patient is necessary.
- An important part of the diagnostic search is the existing clinic. Typical phosphaturia are:
- Frequent urination in small portions and false urges;
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen and back;
- Vomit;
- Bloating.
- General urine analysis over time.
- Urinalysis according to Nichiporenko.
- Urinalysis according to Zemnitsky.
- Quantitative determination of phosphorus release per day.
- Complete blood test to determine the inflammatory component.
- Biochemical blood test: C-reactive protein, creatinine, urea and uric acid, protein.
- Urethral smear for microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Urine culture for microflora and its sensitivity.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, abdominal organs, thyroid and parathyroid glands.
- Excretory urography.
- Computed tomography of the kidney area.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnostic method is urine analysis, which takes place in laboratories. In order for the results to be accurate, you need to approach the analysis responsibly and follow the rules:
- It is prohibited to make adjustments to the baby’s diet a couple of days before taking the test.
- For analysis, you need to submit morning urine - it will show the exact result.
- Before collecting urine, parents should prepare a vessel into which the liquid will be poured, and also wash the baby’s genitals. The use of antibacterial agents is prohibited; they may affect the results.
The resulting urine will be delivered to the laboratory office within two hours.