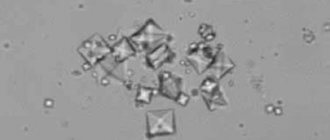
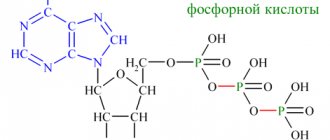
Combinations of coprogram analysis results
Not detected – During normal digestion, connective tissue is not detected in the stool.
Detected - The presence of meat food residues indicates insufficient function of the digestive glands, or an excess of meat in the diet. The connective tissue may visually resemble parts of helminths, thick mucus, or a fungal infection. Microscopy gives an idea of the structure of connective tissue fibers. Children who receive meat feeding before the age of one year have a large amount of undigested muscle fibers in their feces.
Oxalates in feces in a child and calcium crystals in an adult
In order for the baby to grow up healthy, it is important to prevent diseases or recognize them in time. For such purposes, mothers are asked to collect the baby’s stool and submit it for analysis.
It is the feces that provide a more complete picture of the state of the internal organs, metabolic processes, the functioning of the intestines, and stomach, and allow one to observe the entire etiology, as well as prescribe proper treatment.
The coprogram will also show crystals of salts, in particular oxalates. Why, why and how to treat oxalates in feces - this is worth talking about in more detail.
Coprogram - why do it?
The coprogram will also show crystals of salts, in particular oxalates
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases, pathologies of the kidneys and ureter in a small child is a problem.
Determining diseases is often impossible using techniques used for adults, so laboratory diagnostics remains one of the most productive methods. When collecting stool for analysis, mothers themselves do not always expect the results that are revealed.
For example, the presence of oxalate crystals is frightening, alarming and forces you to immediately seek the best treatment.
What does a stool test provide:
- identification of disorders of acid-forming and enzymatic activity of the stomach, intestines, and pancreas;
- liver function failure;
- instability of juice evacuation from the stomach/intestines;
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- disturbances in the state of intestinal and stomach microflora;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in internal organs.
With this analysis, it is easy to identify whether there are crystals, what kind they are, what they are associated with, and choose the desired treatment option. During normal life processes, there should be no oxalate crystals in the feces.
Oxalates in feces: why do they appear?
The cryptogram reveals the presence of several groups of formations, which are “fragments” of cells subjected to destruction during the digestion process
The cryptogram reveals the presence of several groups of formations, which are “fragments” of cells subjected to destruction during the digestion process. Thus, there are crystals:
- Epithelial. These are the remains of epithelial cells that are destroyed under the influence of gastrointestinal enzymes. A small accumulation does not cause concern; an increased level means the presence of an inflammatory process in the colon mucosa.
- Scharko-Leiden. Formed from cells responsible for allergic reactions, they indicate the presence of helminthic infestation.
- Tripelphosphates. They occur during an accelerated reaction of evacuation of intestinal contents and can mean massive bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Oxalates. Crystals have minimal diagnostic value and appear due to low acidity of gastric juice, as well as from eating vegetarian foods.
Important! The absence of free hydrochloric acid converts calcium oxalate to calcium chloride and is detected by the formation of crystalline formations that precipitate in the feces.
Epithelium in feces
Not detected – Normal
Found in small numbers – Normally, a small number of squamous and columnar epithelial cells may be present in the stool. This occurs as a result of the mechanical effect of feces on the walls of the digestive tract.
Found in large quantities, brown feces with red deposits, red blood cells - With an increased number of epithelial cells, one can judge the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. Squamous epithelium enters the stool from the lower rectum. Usually, red blood cells or blood are present along with the epithelium in this case. This can happen with constipation, hemorrhoids, fissures.
Found in large quantities, mucus, digestible fiber, altered fibers, starch, foamy feces, semi-liquid consistency, liquid consistency, mushy - With an increased number of epithelial cells, one can judge the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. The detection of columnar epithelium indicates inflammation in the upper intestines; the level of inflammation helps determine other changes in the coprogram.
When is a study prescribed, and what is its essence?
Stool analysis is considered one of the most important tools for assessing the functionality of the intestines, liver, pancreas and gall bladder, allowing a preliminary diagnosis to be made for the patient. Like a clinical urine test, coproscopy provides a detailed physical characteristic (by appearance), and also allows you to determine the microscopic and chemical composition of the biomaterial under study using special reagents. Scatology is a way to detect bacteria and occult blood that are not visible to the human eye.
A general stool analysis is rarely prescribed to a patient as a separate study and often acts as an additional, but extremely informative diagnostic tool. He is appointed:
- during preventive examinations of children and adults in the clinic (dispensary examination);
- if you suspect dysbiosis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS);
- in case of malabsorption (celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, malabsorption);
- in the complex diagnosis of secretory insufficiency and inflammation of the upper gastrointestinal tract (duodenitis, GERD, gastritis);
- for acute and chronic hemorrhoids, rectal hernia;
- in the diagnosis of genetic pathologies, oncology, HIV infection.
A coprogram is also a way to detect the antigen of rotavirus infection in the event of infection with it. In addition to the above, the study allows you to learn about the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment for gastrointestinal diseases.
Scatological analysis includes macroscopic indicators of the resulting sample: volume, consistency, smell, shade, nature of possible impurities. Biochemical examination reveals pigments, protein structures, fats and hemoglobin. Stool microscopy determines the presence of leukocytes, red blood cells, fibers and crystals.
Soap
Not detected – Normal
Soaps, digestible fiber, unchanged muscle fibers, modified fibers, starch, bilirubin, neutral fat, fatty acids - Soaps in combination with unchanged and modified muscle fibers, fiber and starch are a sign of accelerated passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract, for example, in case of intestinal infection, poisoning , enhanced peristalsis.
Soaps, fatty acids, neutral fat - Lack of normal activity of the pancreas, a decrease or absence of bile secretion leads to the appearance of neutral fat, fatty acids, and soaps in the feces.
Symptoms and diagnosis
You can suspect the presence of calcium oxalates in the urine even without an existing test result. Typically, the symptoms in all patients are quite typical, although they require careful differential diagnosis. Calcium oxalate salts in the urine can manifest themselves as a combination of several symptoms, in particular:
- pain in the kidneys, bladder or ureter;
- colic in the abdomen, appearing unexpectedly, in attacks;
- increased urge to urinate;
- impurities of oxalic acid salts in the urine;
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted by the kidneys per day;
- staining of urine brown when internal organs are damaged by stone fragments;
- patient fatigue and irritability.
Diagnosis of oxalic acid salts in urine is carried out in a laboratory manner. To do this, general and biochemical urine tests are performed, based on the results of which the amount of oxalates can be assessed. Their presence is also indicated by blood impurities. With concomitant inflammation, an excess of protein and leukocytes is found in the urine. As a rule, a single urine test does not diagnose oxaluria, but this gives reason to prescribe repeated and additional research methods. When collecting 24-hour urine, the doctor’s suspicions are mostly confirmed.
In case of possible oxaluria, it is very important to examine the formed calculus at an early stage, evaluate its shape, size, location, and possible causes of the disease. All this will influence the choice of treatment method. To do this, the patient undergoes an ultrasound examination, which can determine all the parameters of interest to the doctor.
Calcium oxalate salts are very visible on ultrasound and are difficult to confuse with other types of stones. With early diagnosis, calcium oxalates can be removed with the least difficulty for the patient and the development of urolithiasis can be prevented.
Oxalates and urates
The transcript of the analysis may indicate an increased amount of urates and oxalates in the urine. What do these results mean? Urates are salts of uric acid. Together with oxalates, these compounds are released in large quantities, most often due to poor nutrition. This occurs if the patient eats too much protein food. Another reason for increased urate and oxalate levels may be foods rich in purines. These are by-products, yeast, fish and seafood, cocoa, chocolate.
In addition, the reason for the increase in the amount of oxalates and urates is dehydration of the body. This is often observed in pathologies accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea. The level of uric and oxalic acid salts increases with kidney disease and gout.
Oxalates and leukocytes
Often, patients have elevated leukocytes and oxalates in the urine. What does it mean? Typically, such indicators indicate inflammatory diseases of the excretory organs. This may be a sign of pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis. Leukocytes and oxalates are also elevated during inflammation of the genital organs. In this case, mucus is found in the urine.
Oxalaturia and protein
Protein and oxalates in the urine may appear after physical overexertion and hypothermia on the eve of a urine test. A similar analysis result is also possible for infectious inflammations: hepatitis, scarlet fever, osteomyelitis. If protein with oxalates are observed in pregnant women, this is most often associated with gestational nephropathy.
Oxalates and phosphaturia
Phosphaturia is the excretion of phosphate compounds of magnesium, calcium or lime with urine. Quite often there is an increased amount of phosphates and oxalates in the urine. What do these analysis results mean? Most often, this indicates abuse of foods such as sea fish, dairy products, buckwheat and oatmeal dishes. These foods are rich in phosphorus.
The presence of increased levels of phosphates and oxalates in the urine can also be a manifestation of diseases of the parathyroid glands, diabetes mellitus, leukemia and some mental pathologies. Oxalaturia in combination with phosphaturia in children under 5–6 years of age is most often associated with a lack of vitamin D (rickets).
Indigestible fiber
Not detected – In the absence of plant foods in the diet, there is no fiber in the feces.
Discovered – Plant fiber can only be partially digested by the human gastrointestinal tract, under the influence of enzymes from intestinal microorganisms. Fiber is mainly excreted unchanged in feces. Indigestible fiber is the coarse fibers of plants and the cell walls of their membranes. This fiber creates volume in feces and is also a sponge that adsorbs toxins and removes them out. Coarse fiber stimulates peristalsis and improves digestion processes
Calcium oxalate crystals in urine: causes, symptoms and treatment
The following types of crystals exist:
- Epithelial crystals. It is found in small quantities in normal feces and represents the remains of epithelial cells destroyed by enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract. An increase in this indicator or their separation in the form of solid layers indicates an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the colon. A disease characterized by a similar symptom is called colitis.
- Charcot-Leyden crystals are fragments of cells responsible for the elimination of allergic reactions and a marker of helminthic invasion, namely eosinophils. The human body perceives intestinal parasites as a foreign object, therefore it activates its forces to eliminate this factor with the help of immune cells, eosinophils.
- Tripelphosphate crystals occur in profuse diarrhea, when bilirubin loses its ability to be converted into stercobilin due to the rapid evacuation of intestinal contents.
- Hematoidin crystals are fragments of red blood cells destroyed by hydrochloric acid in the stomach. These crystals appear when there is massive bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, and are usually associated with tarry, black stools called melena.
- Oxalate crystals do not have any diagnostic value. They usually appear in supporters of vegetarian cuisine or with a general decrease in the acidity of the gastrointestinal tract.
An informative way to study the condition of internal organs is a copogram. With the help of this examination, it is possible to identify disorders of metabolic processes, intestinal and stomach functioning, and then prescribe the necessary treatment. The copogram makes it possible to detect salt crystals, in particular oxalates.
Crystals are fragments of cellular formations that have been destroyed during digestive activity. There is a possibility of fixing special crystals in the stool, which are usually found in sputum in case of bronchial asthma. In medicine they are known as Charcot-Leyden crystals.
Decoding coprogram indicators: norm and pathology
| Type of coprogram study | Basic indicators |
| Macroscopic analysis of stool |
|
| Chemical analysis of stool |
|
| Microscopic analysis of stool |
|
Number of bowel movements per day. Depends on the volume of food eaten and its nature. With proper nutrition, a healthy person excretes 100-200 g of feces per day. When consuming large amounts of plant fiber, the amount of feces increases to 350-500 g. Consistency and shape. Normally, stool is dense. Designed in the shape of a “sausage”.
Color. It largely depends on the nature of the food consumed. With a balanced diet, feces have a brown color with various shades. Consuming large amounts of dairy products reduces the color intensity of stool. The color is approaching yellow. Excess meat in the diet increases the coloration of stool to dark brown.
When beets are consumed, the stool becomes reddish in color. But eating large amounts of greens (lettuce, spinach, dill, parsley) changes the color of stool to swampy. Coffee and cocoa drinkers have stools that take on a charcoal hue. Stool has the same color when there is a large amount of black currant berries in the food.
Some medications can influence this sign of coprogram. Taking iron and bismuth supplements changes the color of stool to greenish-black. Laxatives with senna give stool a yellow-brown color.
Activated carbon changes the color of stool to black. Barium sulfate, used in x-ray practice, colors stool light yellow and white.
This knowledge will help to avoid false diagnosis of diseases of the digestive system when evaluating coprogram studies.
Smell. It is caused by the presence of aromatic breakdown products (indole, skatole) of protein compounds. Normally, stool is soft. With an abundance of meat in the diet, the smell intensifies.
Visible impurities. Normally, feces are a homogeneous mass without foreign objects. If you chew food poorly, large lumps of undigested food debris may appear in your stool. Also in feces there are seeds of berries and fruits (cherries, grapes, watermelon, apricots, etc.), which are accidentally swallowed and transit through the digestive tract.
They are not digested. In young children, foreign bodies (buttons, parts of small construction toys, etc.) may be found in the stool. Other impurities (mucus, pus, blood) are visible only with pathology of the digestive organs. After anthelmintic therapy, bodies and segments of parasitic worms (roundworms, pinworms and others) may be found in the feces.
General fecal reaction (pH). Normally neutral or slightly alkaline (7.0 – 7.5). In infants the reaction is acidic.
Hidden blood. It can be detected by the Gregersen reaction. For the test to be reliable, it is necessary to adhere to a 3-day diet before the study. To do this, exclude foods containing a lot of protein (meat, fish, sausage, eggs), as well as green vegetables. Iron supplements are discontinued. Laboratory technicians perform a benzidine test for occult blood. Normally it is negative.
Stercobilin. In children from 7 months of age and adults, it is always present in the stool. It is an indicator of brown stool coloration.
Bilirubin. Normally absent. In the meconium of newborns and the feces of infants up to 4 months of age, bilirubin is determined.
Soluble protein. The Vishnyakov-Triboulet breakdown is detected. The protein is inflammatory in nature and includes mucus, exudate, and mucin. Normally not found in feces.
Detritus. This is the main background of normal feces. It is a mass of small particles consisting of cell breakdown products, food residues and bacteria.
Muscle fibers. Found in feces in small quantities. With frequent consumption of meat foods, there are a lot of muscle fibers.
Connective tissue. Normally absent. But there are times when remains of undigested connective tissue (bones, cartilage) are found in the stool. This is not a pathology.
Source: https://SilverMed.ru/bolezni/tripelfosfaty-v-kale-u-rebenka.html
Factors
What are the reasons? Salts of fatty acids in feces are a pathological condition. Specific factors are determined by further diagnosis. Among the most common options are the following:
- Disruption of the pancreas. To break down neutral fats in the intestines into fatty acids and glycerol, the pancreas produces a special water-soluble enzyme - pancreatic lipase. If the functioning of this organ is disrupted, there is a corresponding deficiency of lipase in the body. Triglycerides are not completely broken down. Why may neutral fat be present in the patient’s stool?
- Bile acid deficiency. With insufficient flow of bile into the intestinal tract, a violation of the breakdown and absorption of fats is observed. And these elements are subject to the action of digestive enzymes only if they are in a state of thin emulsion. Bile mixes fat masses with water, which is necessary for their further digestion. If there is not enough bile, then the fat droplets remain large, so aqueous solutions of enzymes can no longer mix with them. The consequence of this is the detection of fatty inclusions in the stool.
- Impaired absorption of fat in the intestinal tract and its accelerated elimination from the body. The bolus of food (hummus) moves through the intestinal tract due to contraction of the intestinal walls. If its motor function is impaired, this leads to accelerated movement and removal of food masses from the intestines. Accordingly, in this state of affairs, fats do not have time to be completely absorbed. This changes the appearance of feces - they become light, grayish, acquire an oily sheen, and a foul odor that is not characteristic of feces.
- Excessive fat content in the diet. This can also lead to disruption of the small intestine. Especially when consuming refractory fat - for example, lamb fat.
- A large amount of fatty components in case of obstruction of the lymphatic tract.
- Taking castor oil and other types of rectal suppositories.
Coprogram
The coprogram allows you to assess the functional activity of the stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas, and identify the presence of inflammatory processes and dysbacteriosis.
This analysis makes it possible to study the efficiency of the body’s digestive processes and assess the speed of food passage through the gastrointestinal tract. Chemical analysis of stool
within the framework of the coprogram, it includes determination of blood content, bilirubin, stercobilin, pH reaction.
The fecal pH reaction primarily depends on the activity of the intestinal microflora. With the predominance of protein foods and the activation of bacteria that break down protein, a lot of ammonia is formed, which gives the feces an alkaline reaction. With a carbohydrate diet and activation of fermentation microflora, the formation of CO2 and organic acids, which give an acidic reaction, increases.
The presence of blood in the stool indicates pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by ulceration of the mucous membrane or tumor disintegration.
Stercobilin is the main pigment in feces, which gives it a certain color.
The absence or sharp decrease in the amount of stercobilin in stool (acholic stool) most often indicates obstruction of the common bile duct with a stone, compression by a tumor, or a sharp decrease in liver function (for example, in acute viral hepatitis).
An increase in the amount of stercobilin in feces occurs with massive hemolysis of red blood cells (hemolytic jaundice) or increased bile secretion.
The detection of unchanged bilirubin in the stool of an adult indicates a disruption in the process of bilirubin recovery in the intestine under the influence of microbial flora. The most common causes of this disorder are: suppression of the vital activity of intestinal bacteria under the influence of large doses of antibiotics (intestinal dysbiosis), a sharp increase in intestinal motility.
Microscopic examination in feces can reveal detritus, food residues, elements of the intestinal mucosa, cellular elements: leukocytes, erythrocytes, macrophages, tumor cells, crystals, helminth eggs, protozoa parasitizing in the intestine, microorganisms. Microscopic examination data can give an idea of the state of the digestive ability of the intestine, the state of the mucous membrane (mainly the large intestine).
Detritus constitutes the main background for microscopy of normal feces; it represents the remains of nutrients, microorganisms, and decayed cellular elements. It has the appearance of amorphous formations of small sizes, predominantly granular in shape.
Mucus in normal stool can be in the form of a thin, unnoticeable shiny coating. During inflammatory processes, it is found in the form of strands, shreds and dense, ribbon-like formations.
Muscle fibers (remnants of protein food) - distinguish between unchanged and modified (undigested, poorly digested, overdigested). Unmodified (or undigested) fibers are yellow, cylindrical in shape with cut ends, and have transverse, less often longitudinal, striations. As muscle fibers are digested, they lose their striations, the surface becomes smooth, and the shape becomes rounded.
Normal stool contains some digested muscle fibers. A large number (creatorrhoea) of muscle fibers, especially undigested and poorly digested ones, are found with pancreatic insufficiency, decreased secretory function of the stomach, and accelerated peristalsis.
Connective tissue fibers have the appearance of grayish, light-refracting fibers, sometimes similar to strands of mucus. Not found in normal stool. Their appearance indicates a deficiency of proteolytic enzymes of the stomach.
Plant fiber and starch are the remnants of the carbohydrate component of food. There are two types of fiber: digestible and indigestible.
Indigestible fiber is supporting fiber (the skin of vegetables, fruits, vessels and hairs of plants, etc.), is not broken down in the intestines and is completely excreted in feces. When microscopying native unstained preparations, it has various sharp outlines, a regular pattern in the form of thick double-circuit cellulose shells of brown, yellow and gray color.
Digestible fiber consists of large round cells with a thin shell and a cellular structure. Under microscopy, digestible fiber differs from indigestible fiber by its delicate contours, the presence of starch grains or coloring pigments. Not found in normal stool. Detected in feces during accelerated evacuation.
Starch is absent during normal digestion, since amylolytic enzymes of the digestive tract and enzymes of bacteria in the cecum break down starch completely. The presence of starch always indicates insufficiency of digestion, which occurs with diseases of the small intestine and associated accelerated evacuation, with pancreatic insufficiency.
Fat and its breakdown products, taken with food in moderate quantities, are normally absorbed almost completely. The detection of a significant amount of neutral fat and its breakdown products indicates a violation of the digestion and absorption of fat. Neutral fat in native stool preparations appears as colorless drops.
Fatty acids and soaps occur in the form of clumps, droplets and crystals. The crystals have the shape of thin needles, pointed at both ends. They are often folded into small bundles, sometimes arranged radially, surrounding clumps of fatty acids with a rim. The detection of colorless drops, lumps and needle-shaped crystals in the native preparation suggests steatorrhea.
Cellular elements (intestinal epithelium, blood cells, macrophages, tumor cells) are found in feces containing mucus.
Single cells of the intestinal epithelium can also be found in normal feces as a result of physiological desquamation. The appearance of these cells in large groups, in layers, reflects the presence of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine.
Leukocytes located in the mucus in significant quantities (accumulation) indicate an inflammatory process in the large intestine. White blood cells in the mucus coming from the small intestine have time to break down.
Unchanged red blood cells are found in stool during bleeding from the large intestine and rectum. When bleeding from higher lying parts of the intestine, red blood cells are either completely destroyed or take on the character of shadows, and it is very difficult to recognize them.
Macrophages are found in some inflammatory processes, especially in bacterial dysentery.
Malignant tumor cells can get into the stool when the tumor is located in the rectum. Of diagnostic significance is the finding not of single cells, but of tissue fragments, groups of cells distinguished by characteristic atypia.
Crystalline formations. Tripelphosphate crystals are found in sharply alkaline feces when putrefactive processes intensify. Calcium oxalates are found when eating large amounts of vegetables or when the acidity of the gastric juice decreases.
Charcot-Leyden crystals in the form of an elongated diamond are often found in mucus in combination with eosinophils, indicating allergic inflammation of the intestines, amoebiasis, balantidiasis, and helminthic infestation.
Hematoidin crystals are detected after intestinal bleeding in ulcerative colitis.
Source: https://www.cmd-online.ru/vracham/spravochnik-vracha/koprogramma/
What diseases provoke this?
The causes of steatorrhea can be a variety of diseases. The following can lead to disruption of fat metabolism in the body and, accordingly, the appearance of fatty acids in feces:
- Disease of the intestinal tract. Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, enteritis, Whipple's disease, amyloidosis, diverticulosis, lymphoma (a type of tumor).
- Liver diseases. Hepatitis (alcoholic, chronic or acute), cystic fibrosis, cirrhosis.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts. Cholangitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis in acute and chronic form, giardiasis.
- Diseases of the pancreas. Pancreatitis in acute and chronic forms, Solinger-Ellison syndrome (formation of a tumor that causes loose stools, heartburn, pain, internal bleeding), narrowing of the Wirsung duct (through which pancreatic juice enters the duodenum).
- A number of skin diseases. For example, with eczema and psoriasis, the tissues of internal organs are also affected, which can cause a certain dysfunction of the latter.
- Cholestasis.
- Sclerosing cholangitis.
- Congenital defect of the organ/organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pancreatic insufficiency.
- Alcoholic chronic pancreatitis.
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Cardiospasm.
- Celiac disease.
- Hemochromatosis. A hereditary disease in which iron accumulates in the body.
- Excessive colonization of the small intestine by bacterial microflora.
- Biliary dysfunction.
- Wilson-Konoval disease. Hereditary pathology in which copper metabolism is impaired. It manifests itself already at an early age of the patient.
- Enterokinase deficiency.
- Pancreatogenic malabsorption syndrome.
- Condition after resection of the small intestine.
- Cysts, tumors of various origins, localized in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Taking laxatives, medications, all kinds of weight loss products.
Tripelphosphates in stool analysis
Food consumed by a person passes through the entire gastrointestinal tract, and the result of its processing is feces. By its composition, color, and smell, you can learn about the presence of pathology in different parts of the intestines, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, and stomach.
Stool examination is prescribed in combination with other methods to obtain a complete information picture of a person’s health status in order to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. They are microscopic crystals consisting of magnesium ammonia phosphate. The shape resembles hexagons elongated lengthwise.
They can be detected by microscopic examination. Tripelphosphates are formed when the intestines have a sharply alkaline pH of 8.5–10.0. They should not be present in the stool of a healthy person.
The presence of these crystals indicates that increased protein decay occurs in the large intestine due to the activity of putrefactive bacteria.
When the acidity of the stomach is low, its mucous membrane does not produce enough bactericidal mucus, and therefore harmful microorganisms quickly multiply in the intestines. In addition, tripel phosphates indicate that bilirubin, the bile pigment entering the colon, does not have time to turn into stercobilin. This occurs due to impaired motility, intestinal contents are evacuated very quickly. Often the cause is profuse diarrhea.
Protein intake from food is vital, as new cells are formed from them. Therefore, you need to include proteins of different plant and animal origins in your diet. In order for proteins to perform their role, they must be broken down into amino acids. This process begins in the stomach under the influence of hydrochloric acid, then continues in the duodenum and small intestine. After this, amino acids are absorbed into the blood through the intestinal walls.
But due to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, some amino acids enter the large intestine. The microorganisms located there break them down to form toxic substances.
Thus, the protein rots. The breakdown products of this process enter the venous bloodstream and then into the liver. Over time, this gland is unable to neutralize the toxic products of protein decay. Then some of these poisons are carried through the blood throughout the body, causing: nausea, colic, a feeling of heaviness, rumbling in the stomach, bad breath, headache. Also, the process of decay intensifies due to dysbiosis, when the ratio between beneficial and harmful bacteria is disrupted in favor of the latter.
This can cause diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain, general intoxication, allergies, and deterioration of the skin and nails. When proteins rot, ammonia is formed, which is absorbed into the blood. As a result, there is a negative effect on the central nervous system. Oxygen starvation sets in. In this case, weakness, depression, and depression are observed.
The presence of tripelphosphate crystals also indicates increased motility in the intestinal tract. Normally, part of the bilirubin entering the colon should be converted into stercobilinogen, which should subsequently be oxidized to stercobilin. This is what turns the stool brown. With profuse diarrhea, the movement of intestinal contents accelerates and bilirubin does not have time to be converted into stercobilin. The human body becomes dehydrated and loses many essential microelements.
A stool coptogram examination is performed. It can be used to determine the composition of the intestinal microflora, chemical and physical indicators, microscopic material, the presence of helminths, and blood. Microscopic examination is necessary to detect tripelphosphates. A chemical analysis will show the presence of bilirubin, stercobilin, blood, as well as the pH reaction. In order for the analysis result to be as objective as possible, a number of requirements must be met:.
First of all, you need to contact a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe a comprehensive examination to identify the cause of the inflammatory process and its location, as well as concomitant diseases.
Having a complete picture of the development of the disease, the doctor will determine which treatment plan will be optimal. In addition, you need to fight for the restoration of beneficial microflora in the large intestine, as it plays an invaluable role: it destroys putrefactive bacteria, destroys toxins, stimulates the immune system, produces vitamins folic and niacin, B1, B2, B6, B12, K from dietary fiber. .
If profuse diarrhea is diagnosed, the main thing is to prevent dehydration. Drink water after every bowel movement. You can replenish the loss of sodium and potassium salts using the drug Regidron.
When trying to keep your digestive tract in working order, you shouldn’t go to extremes when it comes to diet: eating just one type of food. Different products are needed, the main thing is quality.
Choose those that do not contain preservatives, nitrates and other chemical additives. It is important not to overuse antibiotics and hormonal drugs, since they destroy not only harmful, but also beneficial microflora in the intestines. And in all cases, try to avoid stress and emotional overload. Tripelphosphates in feces - what does this mean? Diagnostics A stool examination (coptogram) is performed.
In order for the analysis result to be as objective as possible, you need to fulfill a number of requirements: A few days before donating stool, do not take any medications. Avoid vegetables and fruits with bright colors (beets, tomatoes, greens), do not drink tea, coffee, or alcohol.
Stick to a gentle diet of porridge, pureed vegetables, and dairy products. Do not use laxatives. In the morning before bowel movements, it is important to wash yourself thoroughly. Prepare in advance a dry, clean container with a lid and a spatula, put about 20 grams there. On the same day, the analysis must be submitted to the laboratory, since the next day it is no longer suitable. What to do and how to be treated First of all, you need to contact a gastroenterologist.
For this purpose they use: Probiotics, which contain live microorganisms of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, etc. Taking root in the large intestine, they quickly multiply, suppressing the growth of pathogenic bacteria. This group includes drugs: Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, etc. They contain lactulose, which is food for beneficial bacteria and activates their growth, helps normalize intestinal motility.
This group includes the drugs Dufalak, Lactusan, Laktofiltrum, etc. It is necessary to adjust your diet: If you have diarrhea, it is better to avoid foods that promote fermentation, such as sweet pastries, bread, sour fruits and vegetables.
Minimize the intake of spicy and fatty foods, as they inflame the intestinal mucosa and provoke the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
Consume lactic acid products with a short shelf life. They contain live bifidibacteria and lactobacilli, kefir, acidophilus milk, and fermented baked milk. Refuse industrially processed meat products (frankfurters, sausages, dumplings, etc.) Introduce into your diet products with vegetable fiber and pectin, bran, carrots, cabbage, beets, pumpkin, apples, grapes. No ratings yet. Did you like the article? Share with friends:. You may also be interested.
Diagnostics 0. The human immune system is a gift of nature that is difficult to overestimate. Thanks to the protective function of the body. Kidney biopsy is a specialized kidney diagnostic procedure, the purpose of which is to obtain biological material. During pregnancy, monitoring the health of the woman and child is important. Urine tests are quite informative studies that help detect changes in the urinary systems.
Concerning. In modern medicine, a number of diagnostic tests can be used to identify various diseases. When clinical. Every person has had to undergo tests in their life.
Most often a urine test is prescribed. Allergies Blood Medicines Heart disease Tests.
Features in children
Steatorrhea in children develops somewhat differently than in adults. To a greater extent, the causes of this condition in a child are a lack of pancreatic enzymes and the general immaturity of the enzyme system.
Enzymes that take part in lipid metabolism in a newborn begin to be produced in sufficient quantities only when the child reaches 3 months. Until this time, there will be inadequate digestion of fats. What is not considered pathological.
But at the same time, salts of fatty acids in the feces of an infant can be detected even if the liver is not functioning properly. This is in most cases due to genetic disorders. They can be both metabolic and structural in nature.
As for weakened infants, their normal metabolism (metabolism, including fat) is established a little later - by 4-5 months of life.
Kidney stones and their types
Kidney stones are microliths that are formed from minerals and organic substances present in urine with subsequent deposition in the renal pelvis. Their size, structure and shape can be arbitrary, and their weight can vary from several grams to 1 kilogram. Diagnosis of the chemical composition of dense formations allows the doctor to obtain a complete picture of the pathology and choose the most effective treatment regimen. Modern medicine distinguishes four main groups of kidney stones.
Oxalate stones. They are considered the most common group, which includes formations of inorganic origin. They are found in 70% of patients diagnosed with urolithiasis. A prominent representative of this group is wewellite - calcium oxalate monohydrate.
Struvite and ammonium phosphate stones. They are often called infectious due to their origin. Stones are formed as a result of the development of inflammatory processes in the urinary tract. This type is diagnosed in 20% of patients.
Urats. The cause is considered to be excess uric acid and some pathologies of the digestive tract. Deposits are found in 10% of patients.
Cystine and xanthine stones. A rather rare species, found in only 5% of patients. It is believed that their formation is caused by genetic disorders and congenital pathologies.
It is quite difficult to identify microliths that are pure in composition, since most patients develop formations of a mixed type. But determining membership in any one group is an important task, since it allows you to prescribe the optimal type of nutrition and treatment.
Symptoms
With steatorrhea, a person, accordingly, suffers from the symptoms of the disease that caused this condition. But steatorrhea itself manifests itself with independent symptoms. In addition to loose stools with various inclusions of fat, this may include the following:
- Dry cough.
- General weakness, increased fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Bloating.
- Belching.
- Constantly dry condition of the mucous membranes - nose, mouth, etc.
- Rumbling sounds in the intestines.
- Constant thirst (due to dehydration due to illness).
- In some cases, painful sensations in the upper abdomen.
- Frequent stools.
- Liquid sticky feces (due to the increased content of fatty acid salts, neutral fat).
- There are visible spots of fat in the feces. The color of the discharge is grayish, light, with a characteristic shine.
Symptoms, treatment
The symptoms of the presence of oxalates in feces in children are not very pronounced; rather, it is similar to the general clinical picture of stomach diseases with low acidity. The manifestations are:
- General loss of appetite;
- Frequent belching;
- Possibly bad breath;
- Constipation;
- Intestinal disorders, in which the consistency of the stool may be dense;
- The appearance of nausea, vomiting immediately after eating;
- Bloating, flatulence;
- The presence of undigested food remains in the stool.
Important! It is difficult to distinguish symptoms in small children, but if the baby cries after eating, this may mean pain, heaviness in the stomach - such symptoms may also indicate a lack of free hydrochloric acid, which leads to the formation of oxalate crystals.
If the disease is not treated, it can lead to some complications affecting the gastrointestinal tract, in particular:
- Slowing down the breakdown and digestibility of products, which increases the risk of infection and the development of fungal and viral pathologies.
- The formation of crystalline fractions indicates the destruction of cells, and this is a signal of insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body.
- Impaired absorption leads to allergic reactions and decreased immunity.
Important! Treatment for oxalate crystals in feces is prescribed only by a specialist! Under no circumstances should you resort to unauthorized forms, try diets, or introduce animal products into your child’s diet (if the reason is vegetarian food). Such decisions will lead to the development of many pathologies.
Standard oxalate crystal healing therapy includes:
- Selection of the optimal diet, which will have to be followed constantly;
- Prescribing medications;
- Possibly herbal medicine, alternative methods (folk).
As for traditional healing options, they are used as an aid. Most often these are herbal bitters, infusions of secretory-gastric herbs and other herbs. Honey and butter in equal proportions, taken half an hour before meals, helps very well. Plantain, honey water, wormwood - there are a lot of options. However, their choice depends entirely on the amount of oxalates, the state of the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of complications and pathologies.
Oxalate crystals in a child’s stool are a reason to consult a doctor to identify possible gastrointestinal diseases. Despite the fact that crystals do not have diagnostic value, exceeding the normal amount indicates the development of pathologies. Therefore, it is necessary to treat the baby, but only a specialist can tell you what diet to prescribe, medications or choose folk remedies.
Complications of the disease
Complications of steatorrhea occur in case of improper treatment or its complete absence. The following may develop:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system, heart, genitourinary, endocrine, and nervous systems.
- Increased intestinal barrier permeability.
- Disturbance of protein metabolism, which leads to weight loss, ascites, and a decrease in the amount of total protein in the body.
- Hypovitaminosis. It, in turn, is accompanied by frequent dizziness, pain in the joints and spine, swelling, convulsions, dryness, pallor of the mucous membranes, itching, decreased visual acuity, splitting of the nails, fragility and dullness of the hair, stomatitis, glossitis, looseness of the gum surfaces.
Diagnosis of the condition
If you find characteristic symptoms of steatorrhea, you need to contact a physician or gastroenterologist. First of all, the specialist will perform diagnostic procedures:
- Visual examination of the patient.
- Questioning the patient about the symptoms that have appeared, their duration, nutrition, lifestyle, and hereditary factors.
- Submission of blood, stool and urine tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the peritoneal organs.
- Colonoscopy.
- Research on radioisotope technology.
The most important diagnostic procedure for steatorrhea is a lipogram. A laboratory test in which stool is tested for the presence of fat, fatty acids and their salts (soaps). This analysis allows us to identify pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (in particular, the pancreas). According to the results of the study, the patient can be diagnosed with:
- Pancreatitis.
- Tumors of the gastrointestinal tract - benign and malignant.
- Malabsorption syndrome.
- Intestinal tuberculosis.
- Violation of the secretory functions of the pancreas.
- Disruption of normal lymph outflow.
- Increased intestinal peristalsis.
The results of the analysis are also influenced by the correctness of material collection. It is prohibited to do this earlier than 2 days after the X-ray examination with a contrast agent. Three days before collecting stool, stop taking medications that affect the composition, color, and peristalsis of feces.
The stool should be natural, without enemas or laxatives. On the eve of submitting the material for analysis, foods that color stool and contribute to excessive gas formation, constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea are excluded from the diet.
Before collecting the material, empty the bladder and perform genital hygiene. To do this, you need to use soap without dyes, fragrances, or foaming additives.
The material is collected in a dry and clean vessel, from where 20-25 g of feces are separated into a special container. Its contents can be stored in the refrigerator before being submitted for analysis at a temperature of 3-7°C for 24 hours.
Rules for preparing for urine analysis and collection
For biochemical analysis, 24-hour urine will be required. Before carrying out it, it is not recommended:
- alcohol consumption;
- eat fried, smoked, fatty foods;
- take diuretics;
- eat vegetables and fruits with a pronounced pigment.
It is not advisable for women to take the test during menstruation.
Urine is collected during the day in one container, mixed, and poured into a sterile container purchased at the pharmacy up to 200 ml. The first morning portion of urine is not used for collection. A container with ready-made material for laboratory research can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 2 hours. It indicates the amount of urine collected, the weight and height of the person being examined.
Necessary diet
Treatment will be prescribed to the patient in accordance with the identified disease. If fat, fatty acids and their salts are detected in feces, a special diet is required:
- Exclusion from the diet of fatty, hot, spicy, smoked and salty foods.
- Limit intake of pure fat per day to 50 g. It is best if it is butter.
- Exclusion from the menu of alcoholic and sweet carbonated drinks.
- Switch to lean meat - turkey, rabbit, etc.
- Excluding fatty fish from the diet.
- Reduce consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates.
- Consuming reduced-fat (or low-fat) dairy products.
- Exclusion of vegetable fats from the diet. Dishes made from legumes and a number of semi-finished products are especially rich in them.
- It is recommended to give preference to low-fat fish, vegetable dishes, and fermented milk products.
- Taking vitamin complexes.
Small meals with 3-hour breaks between meals are recommended. The weight of one serving should not exceed 200 g.
Nutrition
If amorphous phosphates are detected in the urine, then the appropriate products must be present in the daily diet:
- cereal porridge;
- grains and legumes;
- lean fish and meat;
- vegetables in limited quantities;
- drink plenty of fluids, which should be at least 2.5 liters per day;
- preferably sour berries;
- weak coffee or tea.
If the doctor prescribes a diet for amorphous phosphates in the urine, then the following ingredients must be excluded from the menu:
- alcoholic drinks;
- pickles;
- smoking;
- various sweets;
- marinades;
- bakery and confectionery products;
- dairy products;
- cocoa;
- fatty foods.
Daily calorie content should not exceed 2500 kcal, proteins account for 700 grams, fats - 800 grams, and carbohydrates - 400 grams. Poor nutrition has serious consequences, so every patient must take high-quality multivitamins to restore the body. Comprehensive treatment is also carried out, in which drug therapy, proper drinking regimen and dietary nutrition play an important role.
Drug treatment
The treatment regimen is drawn up by the doctor individually for the patient, depending on the disease that caused the steatorrhea. The symptom itself (fat in stool) is eliminated with the following medications:
- Enzyme agents that improve digestion. “Pancreatin”, “Creon”, “Pancitrate”.
- Absorbent drugs. "Enterosgel", "Smecta", "Atoksil".
- If there is a high content of fatty acids in feces, anticidal agents are prescribed. They neutralize gastric juice and improve the effect of enzyme medications on the body. These are “Almagel”, “Gastal”, “Phosphalugel”.
- Maalox tablets. The instructions for use for the product say that this is a combination drug for discomfort, heartburn, stomach pain, sour belching, a feeling of heaviness, diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. It is available in the form of a suspension and chewable tablets. The required form is selected individually. The instructions for use of Maalox tablets also state that the drug should be taken only after consultation with a doctor.
Steatorrhea is the content of fatty salts, their acids and/or neutral fat in feces. As you have seen, there are many reasons for this. The specific one is revealed only through a comprehensive diagnosis. Based on its results, the doctor draws up a treatment plan for the patient.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
Feces are formed from the remains of the bolus of food in the large intestine. It consists of detritus, dietary fiber, epithelium, water, bile and enzymes. Their number and type depend on nutrition and other factors. By analyzing all the research data obtained, the doctor will determine in which part of the intestine the pathological changes occurred and whether there is an enzyme deficiency.
Thick, dense-textured stool is considered normal. This indicates a sufficient amount of liquid in it. When plant foods with a high fiber content predominate in the diet, intestinal motility increases, and feces take on a mushy form. If an increase in the frequency of bowel movements is noted with liquid stool, then they speak of diarrhea (diarrhea).
Hard stools are a consequence of slow peristalsis and dehydration of feces. This condition occurs with constipation or hemorrhoids. These disorders appear due to poor nutrition, as well as in men with prostatitis, in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
The smell of feces changes with the abuse of protein foods. Fetid occurs during putrefactive processes in the lower intestines, with cholecystitis or pancreatitis. The sour smell is the result of fermentation.
The color of the stool is determined by a pigment called stercobilin, and changes depending on the diet and the use of iron-containing drugs (for example, Maltofer). Colorless stool indicates a violation of the outflow of bile due to stones in the biliary tract (often with cholelithiasis), occurs with cirrhosis of the liver, jaundice. With hepatitis A and C, the level of pigment also decreases. A light color is possible when taking antibiotics or consuming fatty foods, as well as in pregnant women due to increased stress on the digestive organs.
Too dark stool is due to excess stercobilin. Dark brown occurs with pleiochromia (high content of bile pigments in bile). Black feces can appear after taking certain medications, in particular De-Nol.
A pH level below normal with an acidic reaction occurs due to problems with the metabolism of fatty acids, as well as an increase in fermentation microflora. The increase in pH (alkaline reaction) is due to the large amount of meat protein in the diet. In this case, rotting of the protein elements occurs. A sharply alkaline reaction is characteristic of putrefactive dyspepsia.
Fatty acids should not be observed in the stool. In a healthy person, they are absorbed by the body. If the number of fats is several times higher than the reference values, then steatorrhea is diagnosed. As a rule, it is observed in cases of problems with the flow of bile, such as cystic fibrosis. Soaps in the coprogram speak of pancreatic dysfunction.
The detected native protein means the development of inflammation in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, enteritis, gastroduodenitis, duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, cancer). Be sure to take into account the presence of symptoms. If a person experiences pain in the hypochondrium and bloating, then increased protein indicates acute pancreatitis.
Normally, only altered muscle fibers are detected. If a scatological examination shows unchanged muscle fibers, the gastroenterologist will prescribe an additional examination of the pancreas, since this indicator indicates problems with the breakdown of proteins.
Red blood cells in the stool indicate inflammatory processes in the digestive tract or damage to it by tumors. Moving through the intestines, fecal lumps injure the inflamed areas, causing bleeding of varying intensity. Another reason why stool contains blood cells may be helminthic infestation. If occult blood is detected, its quantity will be determined as + for a weakly positive reaction, ++ for a positive reaction.
Mucus is produced by the intestinal epithelium as a protective reaction to irritating factors. In the event of inflammation of an infectious or non-infectious nature, the amount of mucus increases. This occurs, for example, with intestinal tuberculosis, cholera, ulcerative colitis, IBS or Crohn's disease. Bacteria that can cause fermentation in the intestines (dyspepsia) form iodophilic flora. Their determination is made using an iodine test: pathogenic organisms differ in the resulting color.
Extracellular starch indicates a decrease in the function of specific enzymes (amylase) that are responsible for its breakdown. Leukocytes and macrophages indicate the presence of any inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, including those found in large numbers during acute intestinal infection (AIE).
Iodophilic flora
Not detected - Normal intestinal flora should consist of more than 90% lacto and bifidum bacteria. Iodophilic flora is not detected in feces.
Discovered – Iodophilic intestinal flora are bacteria that are stained dark with iodine preparations. These are cocci, rods, yeasts, which are responsible for the processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines. Normally, they make up less than 10% of the intestinal flora. When the ratio of lactobacilli, bifidumbacteria and iodophilic microorganisms changes, the digestive processes in the intestine are disrupted. This is manifested by bloating or intoxication. Changes in bacterial composition may be related to dietary composition. Excessive amounts of simple carbohydrates support bacteria, which obtain energy through fermentation. Excess protein provokes the development of putrefactive flora.
Iodophilic flora was detected, muscle fibers were changed, the reaction was alkaline, the color was dark brown - Insufficient activity of the digestive glands leads to the fact that incompletely digested chyme enters the intestines, which creates favorable conditions for the development of iodophilic flora. Excess animal protein in the diet and insufficient digestion provokes the development of putrefactive flora.
Iodophilic flora, digestible fiber, starch, acidic reaction were detected - The processes of carbohydrate breakdown were disrupted as a result of insufficient activity of the pancreas.
Undigested or partially digested fiber and starch, and excess simple carbohydrates create an environment for the proliferation of iodophilic flora. Crystals in the stool of an adult
Charcot-Leyden crystals in feces: causes, methods of analysis, necessary treatment
An informative way to study the condition of internal organs is a copogram. With the help of this examination, it is possible to identify disorders of metabolic processes, intestinal and stomach functioning, and then prescribe the necessary treatment. The copogram makes it possible to detect salt crystals, in particular oxalates.
Crystals are fragments of cellular formations that have been destroyed during digestive activity. There is a possibility of fixing special crystals in the stool, which are usually found in sputum in case of bronchial asthma. In medicine they are known as Charcot-Leyden crystals.
What are Charcot-Leyden crystals
Charcot-Leyden crystals are smooth, colorless, diamond-shaped particles found during microscopic examination of sputum in patients with bronchial asthma or asthmatic bronchitis.
Also characteristic of allergic conditions, eosinophilic infiltrates in the lungs, pulmonary fluke.
These formations are recorded in cases where there are many eosinophils in the stool, which is associated with the presence of amoebic dysentery, some helminthiasis or the intestinal form of Loeffler's syndrome. These crystals were first discovered in patients with leukemia.
Types of crystals
Feces are formed in the area of the large intestine and contain mainly the remains of consumed food, bacteria, water and other impurities.
To study this biological material, an analysis is carried out - a coprogram.
Decoding the data obtained as a result of the examination allows us to identify the presence of several groups of formations, which are particles of cells destroyed during the digestive process.
There are several types of crystals:
- Epithelial. This type of crystals is the remains of epithelial cells that are broken down under the influence of enzymes of the digestive tract. A small accumulation of these formations does not cause concern; an increased level indicates inflammation of the colon mucosa.
- Charcot-Leyden crystals in feces. This type of crystals is formed from cells involved in an allergic reaction and indicates the presence of helminthic infestation. Intestinal parasites are accepted by the body as a foreign object, so the immune system directs its forces to eliminate the abnormal factor with the help of eosinophil cells.
- Tripelphosphates. These particles appear as a result of an accelerated reaction of excretion of intestinal contents, mainly found during massive bleeding of the digestive tract, when bilirubin loses the ability to convert into stercobilin due to the rapid evacuation of intestinal contents.
- Hematoidin crystals. This type consists of fragments of red blood cells broken down under the influence of hydrochloric acid of the stomach. They appear with massive bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract, and, as a rule, appear in combination with tarry, black stools called melena.
- Oxalates. Crystals in feces of this origin do not have diagnostic value and are detected against the background of low acidity of gastric juice, as well as due to prolonged consumption of vegetarian food.
In the absence of free hydrochloric acid, calcium oxalate is transformed into calcium chloride and is detected by the formation of crystals that fall into the feces.
The reasons for the appearance of oxalates in feces can be:
- prolonged use of plant foods;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- decreased acidity of gastric juice.
Symptoms and manifestations
The clinical picture in the presence of Charcot-Leyden crystals in the feces of a child or an adult is not very pronounced and is mainly similar to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to low acidity.
The patient may complain of lack of appetite and frequent belching, unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth, and periodic constipation.
Signs of a pathological condition include intestinal disorders (the consistency may be dense), nausea, and vomiting after eating.
Increased flatulence and digestive tract disorders may be a concern. Undigested elements of ingested food are found in the stool.
Possible complications if left untreated
The presence of oxalates and Charcot-Leyden crystals in stool indicates serious diseases that require treatment. The formation of crystalline fractions indicates the ongoing process of cell destruction, which indicates a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Neglect of the condition can lead to the development of viral and fungal infections. Pathology increases the likelihood of infection, since the process of breakdown and absorption of food taken in the body is slowed down.
Impaired absorption leads to allergic reactions and decreased immunity.
Diagnostics
If Charcot-Leyden crystals are detected in the stool, the treatment tactics and further course of therapy should be determined by the doctor based on laboratory and instrumental studies. Self-medication, various folk methods and diets can aggravate the condition and lead to serious consequences.
Stool examination is an informative way to identify a number of diseases, the symptoms of which the doctor discovers in the patient after a personal examination and consultation. A copogram or stool examination allows you to identify diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, ureter, liver, and detect the presence of oncological pathologies.
The study makes it possible to identify:
- failure of acid-forming and enzymatic activity of the stomach, pancreas and intestines;
- disruption of the process of evacuation of juice from the stomach and intestines;
- pathological changes in the microflora of the intestines and stomach;
- inflammatory processes of internal organs and systems.
Using this analysis, it is possible to clarify whether there are Charcot crystals in the feces, what type they are, and what causes their appearance. Treatment is prescribed based on the results of a stool test.
How to properly take stool for analysis?
If there are suspicions of crystals in the stool of an adult, then in order to accurately determine them, the patient must adhere to certain rules.
The patient needs to adhere to a diet for several days before donating stool.
From your daily diet you should exclude meat, fish, fatty and spicy foods, foods that change the color of stool (beets, carrots, paprika), as well as foods with a high iron content, and carbonated drinks.
You should also find out whether the patient has taken antiparasitic drugs, for example, Carbarson, Tetracycline, Paromomycin, Metronidazole and Diiodohydroxyquin (iodoquinol) within the last 15 days.
For analysis, feces are taken after a spontaneous act of emptying into a transparent and clean vessel. The required amount for the study is approximately 5 g. The analysis must be carried out no later than 8-9 hours after defecation.
You are not allowed to get tested after using rectal suppositories, castor oil, certain medications, or enemas. Stool contaminated with menstrual fluid and urine is not suitable for testing. Before taking the test, it is necessary to carry out perineal hygiene procedures.
To accurately determine crystals in the feces of infants, it is not allowed to take material for research from the surface of diapers or the skin.
Stages of the survey
First of all, before diagnosing the body for crystals, stool analysis begins with a visual assessment. Define:
- Quantity. The indicator depends on the composition of the food taken and on the contractions of the intestinal walls. With enteritis, when one of the parts of the small intestine is inflamed, an increase in the amount of excreted feces is recorded.
- Consistency. Density depends on the presence of fats and plant fiber. The chair can be formed or unformed. Thick consistency occurs with constipation, cancer of the large intestine, loose stools - with cholera.
- Stool color. The stool may have shades of brown. The indicator is affected by food colorings and drugs. With prolonged use of iron medications, the stool turns black.
- Smell. Shouldn't be harsh.
- Form. Basically, feces have a cylindrical shape.
- Slime. The presence of mucus in a small amount is considered normal.
- Blood impurity. The indicator often indicates cancer.
Afterwards, a microscopic examination is carried out using fecal emulsion. The feces are mixed with saline until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Then the laboratory assistant prepares 4 preparations.
The first of them is designed to detect pathogenic particles and helminth eggs, the second - to detect starch, the third - with Sudan, to determine the presence of neutral fats, and the last, fourth - to differentiate fats. Contents are assessed using a microscope. Crystalline formations occur during helminthic infestations.
Treatment of pathology
If crystals are detected in a child’s stool, treatment is prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis after determining the cause of the formations.
Drug therapy is used. Drugs are prescribed based on the cause of the pathological condition. Herbal medicine and diet therapy are effective and should only be used with the permission of a doctor.
Remember, the detection of Charcot-Leyden crystals in feces indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body. It is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures and identify the cause of the condition. This will allow you to properly organize treatment therapy, avoiding further complications.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/459913/kristallyi-sharko-leydena-v-kale-prichinyi-metodyi-provedeniya-analiza-neobhodimoe-lechenie