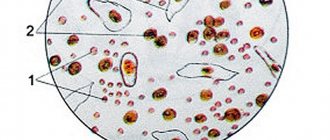
All glands and mucous membranes in various human organs are covered by the epidermis lining the surface, consisting of various types of cells.
In individual organs it is classified into different types - squamous (flat) or other various structural types of various configurations characteristic of certain organs of the body. Detection of squamous epithelium in urine in a standard general laboratory study of urine is a very common occurrence.
Human urine, passing along its route, washes many vessels and organs included in the urinary system. And the discovery of one epithelial cell type, or several, during its examination helps the doctor to specify the pathological processes.
After all, it is the type of epithelial cells found in the urine sediment that determines what further direction in the diagnosis the doctor will determine.
Squamous epithelial cells cover the surfaces of all serous membranes of internal organs. Certain sections of the renal tubules of the nephron and the small excretory ducts of the glands consist of its cells. As urine passes through the urethral system, individual coating particles or entire layers are washed out or exfoliated, which are deposited in the urine sediment.
- Normal squamous epithelium in urine in women and men
- Why is there increased squamous epithelium in the urine of women?
Reasons for increased squamous epithelium in pregnant women
What is squamous epithelium?
Flat epithelium is a layer, a single layer of cells that lines the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system, digestive tract, and respiratory system. Almost all endocrine glands in the human body consist of these cells. The cells of this layer themselves are small in size and flattened in shape. In the genitourinary system, they are found in the lower sections in men (ureters) and in the ureters, in women - in the vagina. Flat epithelium is found in the urine of women, getting there directly from the vaginal cavity.
Types of epithelium
The presence of squamous epithelium is inherent in all serous membranes of human internal organs. It is because of such cells that the sections in the renal tubules and small ductal glands are composed. As urine moves through the body, urine exfoliates or washes away epithelial particles, sometimes even in large layers that settle as sediment.
According to its location, as well as the composition of the cells, the epithelium consists of one layer (flat, cubic or prism-shaped cells) or several. Its multilayer type can be keratinizing (in the case of the gastrointestinal mucosa or corneas of the eyes) or not. In the case of human skin, the epidermis, the type will be non-keratinizing.
Epithelial mucus in urine can be divided into three categories:
- flat – the cells are colorless, have a rounded nucleus, and are flat. In analyzes they are found in small quantities, but they can also be in layers. If the norm is exceeded, this indicates an infection that has entered the urethra;
- polymorphic or transitional - characterized by the shape of the cells in the form of a cylinder, they can also be round. There may be several nuclei. If the norm for the number of cylinders is violated, this indicates cystitis or pyelonephritis;
- renal epithelium in urine - part of the renal parenchyma. In a baby, its amount can reach up to 10 units, which often happens in newborns due to adaptation of the body systems and excretory system. The norm for adults is the complete absence of cells of this type in a urine test.
At the same time, the detected leukocytes in the urine of a baby cannot be due to the development of the body in new conditions for it. Typically, this indicates an infection or inflammation in the kidneys that is indolent and without symptoms.
The renal type (epithelial) lines the inside of the kidney tubules in the parenchyma area, and its sediment in urine indicates kidney damage and disease. This often occurs with renal ischemia, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis and diabetes mellitus. Also, the renal type can be found in urine sediment during rejection of renal implants.
The transitional cell type is present in urine in small quantities. If there is a sharp increase in their number, then experts diagnose prostatitis, pyelonephritis or cystitis. The amount is not divided for patients of different ages; children and adult patients are equally susceptible to diseases accompanied by the appearance of a precipitate with a transitional cell type. The transitional type should normally be no more than 3 cells in the field of view of the microscope.
Squamous epithelium in urine - what does it mean?
Three types of epithelial cells can be detected in excreted urine under microscopy:
- squamous epithelium;
- transition;
- renal.
Squamous epithelial cells are present in the urine in single quantities. Passing through the kidneys and ureters, other parts of the system, urine comes into contact with these cellular structures, some of which peel off and come out. In men, flat epithelial cells are normally absent from the urine (in rare cases, they leave the urethra in low concentrations). In women, single cells of squamous epithelium are always present in urine analysis, since they can partially come here from the vagina.
General instructions and precautions
If the doctor doubts the accuracy of the analysis, then a repeat test will be prescribed. This is the right decision, if the result for some reason turns out to be incorrect, and the patient is completely healthy, then the use of medical therapy is harmful to the body in the absence of a reason. The body receives an unnecessary dose of the chemical and this can affect its health in the future.
If an examination is carried out and the content of epithelium in the urine is increased, then sometimes this is a mistake, the specialist will refer you to retake the test to determine the exact result. Sometimes the reason is that the urine was collected incorrectly. This occurs due to poor hygiene of the genital organ, as well as if urine was collected in an unclean container.
If both tests are identical, then the patient is referred to a doctor for consultation. Which, after complex examination techniques, identifies the exact cause of such a deviation from the norm and prescribes measures to restore the normal state. When squamous epithelium is detected, there is no cause for alarm, since this group does not have any special diagnostic value. Most likely, the cause of formation is the presence of infectious bacteria in the system, which can be easily eliminated with the help of medications. If a specialist discovers another type of cell, a more thorough examination is prescribed in order to prescribe special treatment using drug therapy.
The use of medications is always prescribed only by a specialist; self-medication can only aggravate the situation and provoke the formation of a serious disease. If symptoms develop, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. You should go for a consultation to determine the cause and maintain your health. If you correctly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, as well as use the prescribed therapy, you can eliminate the cause of the deviation from the norm in a fairly short time, as well as restore your health. An epithelial urine test is the best way to establish the norm and condition of the body.
Urinalysis - squamous epithelium
Flat epithelium in the urine of women does not have much diagnostic value - it is always present. However, a significant increase in the concentration of these cells in urine samples often indicates an inflammatory or infectious process in the genitourinary system. In such cases, women are prescribed a comprehensive examination to determine the possible cause of the increase in the number of these cells in the sample. It is worth considering that the objectivity of the studies is often determined by compliance with the rules for collecting urine.
How to properly take a urine test for women?
Knowing how to properly take a urine test, a woman can save herself from the need for repeated examinations.
To obtain objective data, you must:
- Before collecting a urine sample, toilet the external genitalia (wash yourself).
- Prepare a dry, clean jar (preferably a special sterile container for tests from a pharmacy).
- For the study, it is necessary to collect an average portion of urine (at least 50 ml).
- Once collected, the sample must be transported to the laboratory within 2 hours.
- The analysis is not performed during menstrual flow.
To prevent flat epithelial cells from penetrating into the urine from the vaginal cavity, experienced gynecologists advise patients to use a little trick. Before collecting urine, after washing, thoroughly wiping the perineum, you need to insert a hygienic tampon into the vagina. At the end of the procedure it is removed. This simple manipulation helps to exclude even a single squamous epithelium in the urine and eliminates the need to retake the test.
Flat epithelium in urine is normal in women
As noted above, women always have squamous epithelium in their urine, the norm of which does not exceed 10 units. When microscopying a sample of material, a laboratory technician counts the number of cells present in the field of view of the microscope. Exceeding the concentration of these cells in urine is a symptom of a pathological disorder and requires additional examination.
Age and epithelium
In women, the rate of squamous epithelium in the urine changes with age, and quite significantly. Before the girl reaches 1 year, the optimal indicator is 1-3 units, and an increase in the norm by 3-5 units is a reason for additional examinations and treatment. Over the next 17 years of life, a female representative may have 1-3 cells, which characterizes the optimal functioning of the genitourinary system.
From the age of 45-50 years, the rate of epithelial excretion in urine rises to 1-6 units, without any significant reason. Most often, this indicates the beginning of a restructuring of the body before menopause, and sometimes – about some gynecological diseases. In this case, the woman’s life is not in danger, but her health may be seriously compromised.
Recommended topic:
Decoding urine analysis in children
If these indicators are already exceeded by 4-5 units, additional diagnostics are required, since such an analysis result may indicate the following:
- problems with kidney function;
- pathologies of the cervix, appendages and ovaries;
- the presence of polyps or cysts in the vagina (rarely).
Increased squamous epithelium in urine - causes
If squamous epithelial cells in the urine are elevated, doctors prescribe a set of diagnostic measures aimed at establishing the cause of the disorder. Often such a deviation from the norm can be:
- The result of exposure to the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract of viruses, fungi, infections (nephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis).
- A metabolic disorder in the renal tissues, which is provoked by a failure of metabolic processes leading to renal dysfunction, salt diathesis (crystalluria).
- The result of long-term use of medications.
- Urethritis of any etiology.
It is worth noting that often the increase in the concentration of squamous epithelial cells in the urine is temporary. Before starting therapy and further diagnostics, doctors often conduct a repeat analysis. The presence of two negative results is an indication for active diagnostic and therapeutic measures, the nature of which depends on the presumptive diagnosis.
Types and reasons of education
According to its norms, squamous epithelium is different in men and women. As a rule, in males its presence is identical, and sometimes it is completely absent. And in the female sex it is identical only in the visual field or is absent. It is very important to correctly collect urine for examination. If the rules are not followed, the result may very well be incorrect. Urine is usually collected in special containers; they must be sterile and clean. In cases where this is not possible, they resort to using a container, but thoroughly wash it in advance and rinse it with boiling water to kill all bacteria. Careful hygiene of the genital organs is necessary.
The samples are collected in the morning after careful hygiene. Experts consider the average portion of urine to be the most informative norm. Examination always reveals squamous epithelium. Doctors consider this manifestation to be the norm, which does not affect the system and cannot cause any harm to the health of the body. But, if renal epithelium is detected in urine, it is necessary to take action, since this manifestation is not the norm. Perhaps this is the result of a lesion in the parenchyma. When these cells are found in urine, this indicates that:
- general intoxication of the body;
- pyelonephritis develops;
- failure in the urinary system;
- cessation of kidney function.
The reason for the formation is often the formation of a dangerous process in the system, which requires surgical intervention by several categories of doctors to eliminate the disease. If the formation of transitional epithelium is detected in urine, this means that there are stones in the system, and cystitis or pyelonephritis is developing. The manifestation of this type of epithelium is quite rare in medical practice. But still, when it manifests itself, specialists take the right measures to eliminate this deviation from the norm.
Epithelium in urine - treatment
The treatment plan directly depends on what caused the increase in the number of epithelial cells in the analysis. A lot of squamous epithelium in the urine is often found in infectious diseases of the urinary system. In such situations, the basis of treatment is antibacterial drugs, which are selected according to the type of pathogenic agent. Among the antibiotics commonly used in urology:
- Azithromycin;
- Clarithromycin;
- Cefazolin;
- Ceftriaxone.
To maintain the body's defenses and increase local immunity, doctors prescribe immunostimulants:
- Immunal;
- Immunomax.
The following are also used as part of complex therapy for diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Canephron;
- Cyston;
- Phiolysin.
What to do
If you begin to worry about problems with urination, pain in the lower back, abdomen or groin area, you should not hesitate, you should urgently see a doctor. Tell him about how you feel, this will allow you to determine the most appropriate treatment and make it possible to establish the specific cause of the illness.
For this purpose, the patient will need to undergo a number of necessary diagnostic procedures and wait for the test results. Further, if assumptions about the presence of the disease turn out to be positive only in this case, the doctor begins to look for the most suitable ways to solve existing ailments.
The importance of this approach lies precisely in timeliness. Independent measures are inappropriate here; such an attitude towards one’s health can lead a person to an extremely dangerous state. As for absolutely any disease.
Therefore, it is also worth behaving prudently if, in addition to feeling unwell, suddenly the color of your urine also seems very suspicious to you. For example, its composition has become more cloudy, with a specific odor. Such signals may indicate the presence of serious illnesses. There is no need to hesitate; it will be better if you immediately seek help from your doctor.
Squamous epithelium in urine during pregnancy
Doctors pay special attention to this parameter during gestation. During the period of bearing a baby, a woman’s urinary system works in an intensive mode, and all the changes that occur in the body are reflected in its functioning. This period is characterized by frequent urination, which provokes additional desquamation of the squamous epithelium. In addition, the enlarging uterus puts pressure on the organs of the urinary system, changing their usual topography. As a result of these changes, the squamous epithelium in the urine is often physiologically increased.
Doctors allow the presence of no more than 5 squamous epithelial cells in a urine test. An increase in this indicator causes concern among doctors. They conduct periodic urine tests and monitor the condition of the pregnant woman. Increased squamous epithelium in the urine may indicate pathologies such as:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis.
Normalization Tips
Don't panic if your urine test shows an increased number of squamous epithelial cells. It should be borne in mind that such a condition may also indicate changes in the body that are not so harmful:
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra.
- Hormonal imbalance - it can be triggered by menstrual irregularities, as well as a decrease in immune abilities.
- Genetic predisposition - in this case, the increased level of epithelium will remain throughout life.
To protect yourself as much as possible from such violations, it is recommended to play sports and do everything possible to improve your immune abilities.
Nutrition is no less important - it must be comprehensive, complete and correct. When the first signs of a problem with the genitourinary system appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. Also, do not forget to get your urine tested from time to time.
— 3 031
Red blood cells in a general urine test - characteristics and norms
The blood microelements in question supply all cells of the body with oxygen. These bodies are red in color and are the most numerous, but their presence in the urine is not normal.
When testing urine sediment for the presence of red blood cells, the patient should be asked about the presence/absence of menstruation.
The presence of these elements in urine is allowed, however, in very small quantities:
- In men, the norm is 0-1 red blood cells in the urine.
- For women and children – 0-3.
The appearance/increase in the level of red blood cells in urine sediment is often associated with a violation of the integrity of the organs of the genitourinary system, inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract:
- Malfunctions of the kidneys: the presence of stones, malignant formations, kidney infarction, inflammatory phenomena, injury.
- Incorrect selection of anticoagulants.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the urinary tract: cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis.
- Increased blood pressure, which affects the blood vessels of the kidneys.
- Poisoning with chemicals, heavy metals.
We suggest you read: How to increase sperm count?
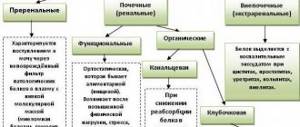
Cylinders in general urine analysis - characteristics and norms
The place of formation of the bodies in question are the renal tubules. The structure of these elements may vary, which is determined by the nature of the constituent components: red blood cells, protein, renal tubular cells.
The appearance of the cylinders is also different, due to which it is customary to divide them into granular (the basis of the structure is erythrocytes, cells of the renal tubules), hyaline (the leading role in the structure belongs to the cells of the renal tubules), erythrocyte, waxy (granular hyaline bodies), epithelial (as a consequence epithelial detachment).
The presence of almost all of the above groups of cylinders in the urine is not the norm.
An exception is hyaline casts, the number of which in the urine of men, adults, and children cannot exceed 20 per 1 ml. urine.
Hyaline casts
The source of their formation is protein. Their presence in urine is possible in the following diseases:
- Treatment with diuretics.
- Inflammatory phenomena that occur in the kidneys.
- Pathologies in the functioning of the kidneys, which are caused by urolithiasis, malignant tumors, injury.
- High blood pressure.
- Exhausting physical work.
Grainy cylinders
Their formation is associated with deformation of the cells that make up the kidney tissue. There may be several ailments that often provoke the appearance of granular casts in the urine:
- Intoxication due to lead poisoning.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys.
- Infection of the body.
Waxy cylinders
Their presence is the result of pathologies that deeply affect the kidneys during processes of a chronic, acute nature:
- Renal failure (chronic/acute).
- Malfunctions of the kidneys that are associated with amyloidosis, nephrotic syndrome.
Red blood cell casts
The formation of this type of cylinders is a consequence of numerous penetrations of red blood cells into the renal tubule, which provokes its blockage. The presence of red blood cell casts (even a negligible amount) in the urine is a defective phenomenon that can cause several diseases:
- The presence of blood clots in the cavity of the renal veins.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys.
- Heart attack/kidney cancer.
Epithelial casts
The presence of epithelial casts in the urine is evidence of serious malfunctions in the kidneys:
- Destruction of kidney tissue.
- Infection of the body.
- Intoxication as a result of poisoning with heavy metals and chemicals.
Causes and symptoms of increased epithelium in men, women and children
The presence of epithelial cells in the urine is not an independent disease, but a symptom of an inflammatory process. Disorders of the urinary tract are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, hyperthermia, and disturbances in the urination process. In severe cases, renal failure develops. If the cause of the appearance of epithelium in urine is prostatitis, then the man is worried about frequent urination, especially at night, and impaired potency.
Treatment is prescribed based on what pathology is identified during a urine test. For infectious pathologies, antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy and diuretics are prescribed. In addition, chronic diseases of the genitourinary system can be treated using traditional medicine methods. Therapy is carried out under the control of urine analysis.
As a rule, the female half of the population in most cases shows an increased content of flat epithelial cells. This is due to the anatomical location of the urethra: it is very close to the anus, so it becomes easily accessible for the penetration of infectious microorganisms.
We suggest you read: Pain with prostatitis - how to relieve symptoms in men
Very often this indicator increases in pregnant women. This is caused by severe stress on the kidneys and weakened immunity during pregnancy. The most common diseases are:
- Cystitis is a disease in which inflammation of the mucous membranes of the bladder walls occurs.
The main symptoms are: As a rule, if cystitis is not advanced, its treatment takes about 2-3 weeks. In the future, it is recommended to monitor your health so as not to cause a relapse. - An increased amount of cylindrical (transitional) epithelium is characterized by the development of nephropathy, in which the filtration capacity of the kidneys is impaired. At the very beginning, the disease does not show any symptoms. With further spread of the infection, the patient may experience symptoms such as severe pain in the lumbar region; foam in urine; increased renal pressure; swelling of the limbs.
In the male half of the population, an increase in the number of epithelial cells in the urine occurs due to inflammatory processes in the urethra or after prostate massage. It is worth noting that an increase in this indicator in men is very rare. Among the diseases that are caused by an increase in the epithelium, it is worth highlighting:
- Urethritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the urethra. The most striking symptoms are: pain during urination, swelling on the head of the penis. If timely treatment is not started, purulent discharge and complications such as prostatitis may appear.
- Prostatitis is an inflammatory process in the prostate gland, which is a complication of untreated urethritis. It can be in acute and chronic form. The main symptoms: pain in the groin and when going to the toilet, increased body temperature, a feeling of constant fullness of the bladder. As the condition worsens, it becomes difficult for the patient to go to the toilet.
- Stones, polyps and tumor formations, viral hepatitis - these diseases can be caused by long-term use of certain medications or infection of the patient’s body.
As a rule, a slightly elevated content of renal epithelial cells is considered normal for children. By the end of the first year of life, this indicator returns to normal. In a healthy person, this type of cell should be completely absent.
Children have a genetic predisposition to increased renal epithelium, so parents prone to such diseases need to constantly monitor the situation to prevent complications. If a general urine test reveals an excess, this indicates infection of the parenchyma in the kidneys, namely:
- Severe infection in the patient's body. The most striking symptom is fever (above 38.0) and pain in the lower abdomen when urinating.
- Rejection of a donor organ after transplantation. In this case, the filtration functions in the kidneys are disrupted, and the processes of urine excretion worsen.
This video talks about the reasons for the appearance of epithelium in the urine and diseases that lead to the appearance of squamous, transitional or renal epithelium.
Rules for collecting urine for analysis
There are certain rules that must be followed when collecting fluid for analysis. This is due not so much to the convenience of the patient, but to the importance of obtaining the required starting material without impurities, which will guarantee an accurate result.
More on the topic: What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Sequence of actions for collecting urine:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | one day before collecting fluid for analysis, you must stop taking foods that can color the secreted fluid. These include beets, carrots, and all types of citrus fruits. It is necessary to exclude spices and salt from the diet, and not to take diuretics. As part of drug treatment, you need to stop taking nitrofuran drugs for a day, which color urine bright yellow. |
| 2 | Immediately before collection, you need to carry out thorough hygiene of the genitals, possibly without using chemicals. It will be enough just to wash with clean water |
| 3 | urine is collected in a volume of 100 ml in the morning on an empty stomach. The container used is plastic or glass, it must be clean, it is better to sterilize in boiling water or use containers from a pharmacy |
| 4 | the collected analysis must be delivered to the laboratory or clinic as soon as possible, since bacteria may form when stored in a warm place for more than 2 hours |
| 5 | Women during menstruation should avoid taking tests to avoid bloody discharge in the fluid, which will be perceived by research doctors as a symptom of the disease. If the need is urgent, you should use a tampon |
Reasons for the formation of flat cells in urine
The presence of flat cells in urine always indicates inflammation in the body. Why are they being released? The reasons why it was detected may be the following:
- inflammation due to viruses or fungal parasites, if there are bacteria in the urine that have affected the bladder area;
- impaired metabolic processes in the kidneys, which arise from metabolic disorders and lead to kidney dysfunction and crystalluria, salt diathesis;
- due to taking medications that cause destructive disorders in the kidneys and their dysfunction;
- disease of the lower organs of the excretory system, urethritis of various etiologies;
- urological diseases in men, in which the prostate becomes inflamed.
The presence of flat cells in minimal quantities in patients of different sexes is assessed differently by doctors. For female urine this indicator is normal, but for men it indicates genitourinary diseases.
Mucus in a general urine test - characteristics and norms
The substance in question is created due to the functioning of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system.
The presence of a small amount of mucus in the urine of children and adults is allowed. If the recorded amount of mucus in the urine is quite extensive, the doctor prescribes repeated testing to eliminate possible errors during the collection of this biological material.
Due to inflammatory phenomena that occur in the organs of the urinary system and other pathological phenomena, urine stagnation occurs, which provokes increased mucus production. This process complicates the drainage of mucus, which leads to its excretion in the urine.
The most common causes of increased mucus levels in the urine are:
- Venereal diseases.
- Infection of the body.
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules.
- Delaying the process of urination.
- Presence of stones in the urinary organs.
Salts in general urine analysis - characteristics and norms
When studying urine sediment, the salts present in it will be presented in small crystals. The presence of a limited number of such crystals, in the absence of other errors in the testing, is not always the result of violations, but such phenomena should not be ignored.
The presence of these substances in urine, even in small quantities, is not normal.
If crystals are detected in the urine, the doctor must take measures to eliminate this phenomenon: diet, adequate exercise, prescribing diuretics, etc.
Often, factors that provoke the appearance of certain groups of salts in the urine are certain foods, drinking insufficient amounts of fluid, and inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
The most common types of salts present in urine are urates, oxolates, and phosphates.
There may be several factors that can provoke the appearance of these salts in urine sediment:
- Excessive consumption of certain foods (mushrooms, meat, fish), drinks (black tea, coffee, cocoa) and insufficient amount of fluid.
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys (inflammatory phenomena, renal failure).
- Children under 6 months. This is due to the inability (at this age) of the kidneys to fully perform their functions.
- Gout.
- Excessive fluid loss due to vomiting and diarrhea.
- Increased urine acidity.
Oxalates
Their appearance in urine does not depend on its acidity, and may be due to several reasons:
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- The presence of stones in the urinary tract.
- Congenital diseases associated with errors in the metabolism of oxalic acid.
- Diabetes.
- An abundance of foods rich in oxalic acid (beets, sorrel, asparagus, spinach) and vitamin C (red currants, citrus fruits, tomatoes) in the daily diet.
- Chemical poisoning.
Salt crystals (phosphates)
The most popular reason for the appearance of salts of this group in the urine are foods rich in phosphorus (seafood, dairy products, eggs), and gastric lavage.
Other factors (of a pathological nature) that can cause the detection of salt crystals in the urine include:
- Diabetes.
- Constant disruption of bowel function.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the genitourinary organs.
- Liver failure.
Treatment
If a woman feels that her urination pattern has changed, the urge has become frequent and painful, the urine has changed its color, smell, consistency, you should immediately go to a specialized specialist for an appointment. The doctor will conduct an initial examination and also prescribe the necessary tests.
It is important to take a urine test several times to eliminate the possibility of a diagnostic error. Depending on the results obtained, the urologist will individually determine treatment tactics for each patient. If urethritis occurs, then antibacterial treatment is necessary, including taking Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin.
Azithromycin in original packaging. Source: upulmanologa.ru
It is imperative to take medications that help improve immunity. During the entire treatment period, which is within ten days, you should adhere to dietary nutrition. The patient should avoid spicy, fatty, fried and salty foods, as well as alcoholic beverages.
In chronic forms of the pathology, courses of antiseptic therapy are carried out. If there is an active inflammatory process, then antibiotics are indicated. Particular preference is given to Furadonin, Ofloxacin and Levofloxacin. You can also take pills to relieve pain (Canephron, Phytolysin, Cyston).