One of the problems of the human urinary system is anomalies in the location of the kidneys. This pathology is called kidney rotation. The problem is the displacement of the urinary organ from its usual anatomical bed and its rotation on the vascular pedicle around its axis. It is worth noting that such a condition is not always classified as pathological, especially if the patient with a rotated organ does not experience physiological problems, and the kidney itself functions without failures. Most often, a person is not even aware of the mobility of his urinary organ. The anomaly is detected during ultrasound examination for other diseases.
Important: even in the absence of identified parallel problems, patients diagnosed with rotation of the right or left kidney should undergo a follow-up examination at least once a year, including general blood and urine tests, as well as ultrasound diagnostics.
Classification of the disease
There are unilateral and bilateral pathological position of the kidneys. The disease can affect both the right and left kidney, while the first case is more common and about 10% are anomalies of both excretory organs at once. When the organ is displaced to the opposite side, homolateral dystopia . Cross or heterolateral dystopia is observed when both kidneys move to different parts of the peritoneum, or move them to one side, often connecting with each other and functioning as a single organ.
Depending on the anatomical location of the kidney, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Lumbar (occurs more often than other anomalies) - the organ is located below normal, with the pelvis forward and is often confused with a tumor during examination
- Pelvic - in men it is characterized by the location of a paired excretory organ between the rectum and bladder, in women - between the rectum and uterus. The length of the ureter is shorter than normal. During examination, the pathology may be confused with an ectopic pregnancy.
- Iliac – characterized by the location of the organ in the iliac fossa. During examination, it can be mistaken for a cyst in the ovary.
- Subphrenic (thoracic) – the organ is located above normal. The ureter and vessels are longer than usual. During the examination, it can be confused with a tumor formation on the lung.
Stages
The ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) kidney rotation code is Q61. The symptoms of this condition largely depend on the level of movement, which can be divided into several degrees. The anomaly can be anything: there may be rotation of the right kidney, its left lobe, or both organs at once.
- The first stage is characterized by a descent of the lower border of the kidney by 1 or 2 vertebrae. In this case, the patient may be bothered by a nagging pain syndrome in the lumbar region, which intensifies during physical activity.
- The second stage is characterized by a descent of the organ by 2 or 3 vertebrae. The pain haunts the patient even in a state of complete rest, radiates to the abdominal area and intensifies when the person is in an upright position.
- At the third stage, the lower border of the kidney moves more than 3 vertebrae. In this condition, the patient experiences renal colic, disrupted functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and a constant feeling of pain and discomfort in the lower back. The work of paired organs undergoes disruptions, dysuric phenomena appear, as well as pain when urinating.
Causes
Due to the fact that the disease is characterized as congenital, the main causes are associated with disruptions in embryogenesis. During the development of the fetus, the kidneys are initially located in the pelvic area, subsequently they move higher and take on a normal position.
When negative factors influence the developing fetus, the normal development of paired organs is disrupted. As a result, the kidney takes an abnormal position and dystopia occurs.
There are certain reasons that may influence abnormal renal migration:
- Alcohol abuse.
- Addiction to smoking.
- Addiction to drugs.
- Intoxication with toxic substances.
- Stressful conditions.
Sometimes the cause of renal dystopia is a genetic predisposition.
Forecasts
In general, with early detection of pathology and correctly selected treatment tactics, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. However, if the patient does not consult a doctor in time and independently treats the existing symptoms with improvised means, one can expect the development of renal failure, which will subsequently lead to serious complications with the heart, blood vessels and lungs.
Kidney rotation is a condition characterized by a rotation of the organ around its longitudinal axis and some displacement from its usual bed. This phenomenon cannot be classified as a pathology or disease; rather, it is one of the physiological norms. In most cases, rotation is detected completely accidentally during ultrasound of the retroperitoneum.
Clinical picture
Symptoms depend on the anatomical form of the pathology.
The lumbar version of this pathology may not show any signs, or slight pain is felt in the lower back.
Pelvic dystopia is characterized by pain in the rectum and appendages. As a result, the patient suffers from constipation and frequent urination. With the development of pathology in the expectant mother, she suffers from toxicosis and there is a risk of difficult childbirth.
Patients with ileal dystopia complain of pain in the ileum and abdomen. Pain increases in females during menstrual periods. As a result, the anomaly leads to constipation, nausea, vomiting, and gastralgia.
Thoracic dystopia is characterized by chest pain caused by eating.
The general clinical picture observed in all varieties of this pathology includes:
- Weakness, lethargy, apathy.
- Decreased appetite.
- Blood in urine.
- Lumbar pain after physical activity.
- Colic in the kidneys.
- Pelvic pain.
Kidneys affected by this pathology are most susceptible to the development of diseases such as nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis and tuberculosis.
Symptoms of kidney prolapse (nephroptosis) or increased mobility
Nephroptosis of the kidney is a disease in which the kidney moves from its anatomical bed. Women are most predisposed to this disease, especially during pregnancy. In men, this disease occurs less frequently - in 0.1% of cases. What is kidney nephroptosis, what are the causes of the pathology, symptoms and treatment methods will be discussed later in the article.
Concept and causes of the disease
What is kidney nephroptosis? There are acceptable limits within which any organ can move from its place. Increased mobility of the kidneys in medicine is called nephroptosis, in which organs are displaced into the small pelvis or change position relative to their axis. Nephroptosis on the right is often found, which is explained by the physiological structure of the body: the liver is located above the right kidney, which can put pressure on it, the muscle fibers that hold the right organ are weaker than on the left side.
The root causes of kidney nephroptosis:
- Low pressure in the abdominal cavity. Develops against the background of decreased muscle tone in the abdominal region. The main causes are frequent constipation and diarrhea. In women, weakness of the abdominal wall can be a consequence of multiple pregnancy.
- Depletion of fatty tissue. It is a consequence of infectious diseases or a sharp decrease in body weight.
- Pathological structure of the muscular system.
- Injury to the lower abdomen and back and the formation of internal hematomas.
- Excessive regular physical activity, participation in strenuous sports.
- The process of rapid growth of an organism, which leads to imbalances in the structure and location of internal organs (An organ is a separate set of different types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism). Nephroptosis most often occurs in children during the period of active growth.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal imbalances.
Excessive mobility of the kidney occurs in people whose professions require prolonged standing (surgeons), heavy loads and regular lifting of heavy objects (loaders), and prolonged sitting, which may be accompanied by vibrations (drivers).
Stages (Stage, Stages (Greek) and signs
Nephroptosis of the kidneys in its development goes through 3 stages, which are accompanied by different symptomatic pictures. Degrees (In mathematics Exponentiation Cartesian degree Root of the nth degree Degree of a set Degree of a polynomial Degree of a differential equation Degree of mapping Degree of a point - in geometry) of nephroptosis (kidney (moving kidney, drooping kidney) - a kidney disease expressed in its abnormal mobility) are expressed level of organ prolapse.
Stage 1
The pathological condition of the kidney of 1st degree is characterized by a slight shift of the organ when the patient is in a standing position. In a sitting position, the kidney is located in its anatomical bed. At this stage, it is difficult to diagnose the pathology, since palpation of the kidney can be done during inspiration and in patients with insufficient body weight. Kidney prolapse symptoms of stage 1 are difficult to determine due to the slight feeling of pain that may appear during intense exercise.
Stage 2
Nephroptosis of the 2nd degree is accompanied by the following symptoms (one of the individual signs, a frequent manifestation of any disease, pathological condition or disruption of any vital process) of kidney prolapse:
- Increased pain during activity and even while walking.
- Impaired blood flow to the organ.
- Stagnation of urine in the kidney, which leads to an increase in protein content.
- The development of inflammation, which is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication (fever, weakness, fatigue) and severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Nephroptosis of the right kidney of the 2nd degree is most often diagnosed. During diagnostic procedures, palpating the kidney in a vertical position is not difficult; in a horizontal position, this cannot be done. Nephroptosis of the 2nd degree on the right leads to a decrease in the volume of arterial blood that flows to the organ, which can subsequently lead to a lack of nutrients and atrophy. Stage 2 nephroptosis is also accompanied by increased pressure in the renal vein.
Impaired blood flow leads to strangulation of the urethra and the development of obstacles to the outflow of urine from the bladder. Congestion in the urinary organs leads to a gradual accumulation of harmful compounds and breakdown products. Pyelonephritis gradually develops.
Stage 3
Nephroptosis of the 3rd degree is characterized by the kidney coming out of the hypochondrium and moving into the pelvis. At stage 3, chronic pyelonephritis and a number of other vascular pathologies and diseases of the genitourinary system are added.
Signs of nephroptosis (kidney (mobile kidney, drooping kidney) - kidney disease, expressed in its abnormal mobility) 3 degrees (In mathematics, Exponentiation of a Cartesian power, Root of the nth degree (In mathematics, Exponentiation of a Cartesian power, Root of the nth degree, Degree set Degree of a polynomial Degree of a differential equation Degree of a mapping Degree of a point - in geometry) Degree of a set Degree of a polynomial Degree of a differential equation Degree of a mapping Degree of a point - in geometry):
- Constant pain at rest, which becomes unbearable during physical activity.
- Against the background of pain, the patient develops a depressive state and a state of depression, lack of mood.
- At stage 3, the symptoms of nephroptosis are accompanied by disruption of the digestive organs: appetite decreases or completely disappears, vomiting and diarrhea appear.
- Increased pressure.
- Renal colic, which occurs when the urethra is strangulated, becomes frequent.
- Chronic pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis develop.
Danger of disease
A wandering kidney can be accompanied not only by unpleasant symptoms of the disease, but also cause the development of other diseases and complications that affect all organs (An organ is a separate set of different types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism) of the genitourinary system. Kidney mobility in 20 out of 100 cases can lead to serious complications and cause temporary or permanent disability.
The greatest danger is the increased mobility of the right kidney, as it can lead to a large number of complications that affect the organs of the urinary system and the liver.
A moving kidney leads to the following complications:
- Hydronephrosis develops when the urethra is bent and pinched, resulting in a disruption of the outflow of urine and its stagnation. This is a disease in which there is a rapid increase in the size of the collecting system.
- Acute and chronic pyelonephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease, which is characterized by stagnation of urine and the accumulation of harmful waste products, which is a good breeding ground for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Secondary arterial hypertension is an increase in blood pressure due to impaired blood circulation in the kidneys. If left untreated, a stroke or heart attack may develop.
- Urolithiasis occurs against the background of stagnant processes, which lead to the accumulation of salts and sand, which cannot be released with urine.
- In women in the early stages of pregnancy, a wandering kidney can cause spontaneous abortion.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of nephroptosis includes primary and secondary studies. The first option involves examining and interviewing the patient. Interviewing the patient is necessary to determine symptoms, their duration, and the presence of other diseases. During the examination, the doctor palpates and determines the stage of the disease by the accessibility of the organ (An organ is a separate set of different types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism).
Secondary research for nephroptosis involves laboratory and instrumental studies. Laboratory tests involve a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test and a bacteriological study of urine.
Kidney mobility is determined using the following instrumental methods:
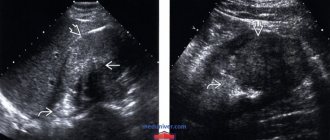
- Ultrasound examination provides an opportunity to study the direction of kidney movement. During the procedure, the patient must be in an upright position - this helps to obtain a more complete clinical picture.
- X-ray diagnostics using a contrast agent allows you to study the condition of the organ and determine the extent of the disease.
- X-ray diagnostics of renal vessels using contrast allows one to obtain data on the condition of the vessels and the presence of pathological processes in a vein or artery.
- The radioisotope diagnostic method involves the intravenous administration of a special dye, which is absorbed by the kidneys and excreted in urine. Diagnosis is carried out in upright and sitting positions. Radioisotope research allows you to obtain information about the performance of organs.
Kidney prolapse in pregnant women
What is nephroptosis and what are its features during pregnancy? Women are much more likely to suffer from nephroptosis. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the female body and is characterized by:
- Larger renal bed and lower location than in men.
- Increased elasticity of the muscle tissue that supports the kidney.
- Wider adipose tissue.
- Slight development of the abdominal muscles, which increases the likelihood of a decrease in intra-abdominal pressure.
Pathological mobility of the organ is diagnosed in women in the postpartum period - the fetus during intrauterine growth leads to stretching of the abdominal muscles and a decrease in pressure. The risk of developing pathology increases with subsequent pregnancies.
Nephroptosis symptoms in women during pregnancy: pain in the abdominal and lumbar regions, disruption of the urination process and deviations from normal urine and blood parameters. If any signs appear, the woman is sent for a repeat urine and blood test and an ultrasound.
Nephroptosis can lead to complications: pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, inflammatory diseases of the urinary system and bladder prolapse in women.
Disease in children
What is renal nephroptosis (Kidney (anatomy) is an organ of the excretory (urinary) system of animals and humans) in children, and what are the main causes and symptoms? In children, kidney prolapse may be accompanied by an asymptomatic clinical picture, manifest or complicated. In the first variant of the development of pathology, there are no symptoms and detection of the disease is random.
The manifest clinical picture is manifested by lower back pain, disruption of the urination process, and the neurological and psycho-emotional development of the child may also be affected.
Complicated nephroptosis is characterized by severe pain in the lower back and abdomen, which increases during activity, and disruption of the process of urination and defecation.
A wandering kidney in a child is diagnosed together with a curvature of the spine. The main causes of childhood nephroptosis (kidney (mobile kidney, drooping kidney) - kidney disease, expressed in its abnormal mobility):
- weakness of the abdominal wall and low intra-abdominal pressure;
- underdevelopment and weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of organs.
Conservative treatment
When choosing treatment methods, it is important to maintain the relationship between the symptoms (one of the individual signs, the frequent manifestation of a disease, pathological condition or disruption of any vital process) and the treatment that is carried out to eliminate the unpleasant signs and consequences of the disease. For this purpose, two methods are used - conservative and surgical therapy.
Treatment of nephroptosis with a conservative method is applicable if it is right-sided nephroptosis of the 1st degree or nephroptosis of the 1st degree on the left. For this purpose it is recommended:
- Wearing a special support device.
- Massage of the lumbar and abdominal area, which is carried out only by specialists, as it can cause even greater harm to health.
- Exercise therapy aimed at strengthening the back and abdominal muscles.
- Proper nutrition.
- Elimination of loads.
The use of medications will not help return the organ to its place, even if it is grade 1 nephroptosis on the right or left. Taking medications is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory consequences in the organs of the urinary system).
Bandage
The bandage must be worn strictly as recommended by a doctor. Today you can purchase a ready-made support device, which will be selected specifically for the physiological characteristics and symptoms of the patient. To treat nephroptosis of the right or left kidney, you can select a special support device, which must be worn throughout the day, following the wearing rules. The bandage should be put on while lying down while exhaling.
Exercise therapy
Treatment of left-sided and right-sided nephroptosis of the 1st degree is effective if special exercises are regularly performed, which are performed in the supine position. This complex helps strengthen the abdominal muscles and serves as a good prevention of nephroptosis:
- Carry out breathing exercises in a lying position with your legs bent at the knee joints. While inhaling, you should protrude your abdominal muscles, and while exhaling, retract them.
- Raising legs in a straightened state 5-10 times.
- Bend your legs alternately and press as much as possible towards your stomach. Repeat similar actions 7 times with each leg.
- The favorite “bicycle” from childhood, lying on your back, is also effective for strengthening the abdominal muscles. Perform the exercise for about two minutes.
- For the next exercise you will need a small ball. Lying on your back, bend your knees and squeeze the ball between them, putting pressure on it. Perform 5 sets of 10 seconds.
- Lying on your back, raise your legs up, while inhaling, and while exhaling, slowly lower them.
- Exercise “scissors”: raise your legs up and spread them apart, inhale, cross your legs as you exhale. Repeat the exercise up to 10 times.
Nephroptosis of the left and right kidneys is a contraindication to complex physical exercises, weightlifting, cardio training, stretching exercises, parallel bars, and jumping. Non-fast walks on flat terrain are acceptable.
Diagnostics
In case of lumbar or iliac pathology of the kidney, the examination is carried out through the abdominal wall. Pelvic dystopia is diagnosed using a rectal examination in males and a bimanual gynecological examination in females. The intrathoracic type of kidney anomaly is identified during fluorography or chest x-ray.
Also, when making a diagnosis and determining the type of pathology, methods of ultrasound examination, urography, and kidney renography are used.
Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude diseases characterized by symptoms similar to renal rotation: nephroptosis, tumor formations of the kidneys and intestines.
What is kidney rotation
Many patients, having heard about the diagnosis of “rotation of the kidneys,” for example, during an ultrasound, are interested in what it is. This is a reversal of the organ with a displacement of more than 2-3 cm.
Most often, kidney mobility occurs when a person assumes a vertical position. In normal condition, the kidney moves by a maximum of 25-30 mm; this occurs during the operation of the respiratory system.
Rotation itself is a type of pelvic dystopia or, less commonly, a manifestation of nephroptosis.
In some cases, when the kidney is fully ascended, the rotation is not complete; the renal gates are positioned in such a way that excessive displacement causes pain and prevents the outflow of urea, pinching the canal.
Renal rotation is diagnosed in 2.8% of newborns, and it can also appear in adults. The organ can be moved to the pelvic area, closer to the chest or to the lumbar region.
Treatment
In the absence of discomfort and unpleasant symptoms, any type of dystopia does not need to be treated.
But if discomfort occurs, you should contact a medical facility. A course of treatment can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist; in this case, self-medication is dangerous. Treatment is prescribed depending on the diagnosis, the level of the pathological process and the presence of complications.
The initial stages, as a rule, are aimed at restoring the functioning of the kidney and preventive measures. It is expected to use a support bandage, monitor your diet and limit unnecessary physical activity.
If inflammation occurs, antibiotics must be prescribed.
If the pathology is complicated by urolithiasis, the doctor, depending on the size of the stone, prescribes lithotripsy or surgical removal.
Also during the treatment process, surgical intervention occurs, during which the kidney is fixed in the renal bed. After surgery, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to avoid complications.
Complications
“Mute kidney”, in the literal sense of the word, is not a disease. This pathological process is a consequence that arises due to the occurrence of congenital or acquired diseases in the body.
When a patient is diagnosed with one “dumb kidney”, but the other turns out to be fully capable, there is no threat to the patient’s life. A functioning kidney “takes over” the functions of its “dead neighbor” and successfully copes with all tasks.
However, a patient who has only one functioning kidney needs to be more attentive to his health. There is a risk of developing an infectious process that can penetrate into the cavity of a dead organ.
As a rule, diseases such as pyelonephritis or cystitis can be dangerous for the patient, since when they enter the cavity of a non-functioning kidney, they can provoke an inflammatory process with the release of a large amount of pus.
Sometimes the kidney tissue completely melts with pus, which leads to the formation of a huge abscess. This extensive suppuration can rupture at any moment. If this occurs, then the area and all organs of the retroperitoneal space become infected with pus, and to save the patient’s life, immediate surgical assistance is required.
The doctor decides whether to remove the dead organ or not. If the risk of infection is minimal, the kidney remains in the body. In cases where the level of infection is very high, the non-functioning kidney is removed from the body through surgery in order to prevent the development of complications.
How to live with dystopia
Dietary nutrition is indicated for patients with dystopic renal anomaly, regardless of the nature of the therapeutic tactics. The diet requires a complete abstinence from smoked foods, alcoholic beverages, fried foods, spicy seasonings, etc. Moreover, such a diet is lifelong.
In addition, it is necessary to protect yourself from pathologies of colds and hypothermia. Doctors especially highlight tonsillitis, the causative agent of which is hemolytic streptococcus, which negatively affects renal function. It is extremely important to maintain a drinking regime and not overuse mineral water to avoid the formation of stones.
Prevention measures
Since renal dystopia has a congenital etiology, preventive measures should be carried out even before the birth of the child.
It is necessary to undergo a medical genetic consultation to exclude the possibility of such an anomaly in future offspring. During pregnancy, you should not drink alcohol, smoke, or eat poorly. It is necessary to avoid radiation or chemical exposure in every possible way, since these substances can lead to various pathologies in the fetus.