Along with menopause come unpleasant changes in the body. Such changes affect not only the organs of the reproductive system. One of the influences on a woman’s body during menopause is considered to be difficulty with urinary incontinence. Most women are convinced that this is an inevitable age-related change that can only be tolerated by using sanitary pads and not leaving home for a long time. However, even with this, as it seems at first glance, irreversible phenomenon, such as urinary incontinence during menopause, therapy is very acceptable and has its fruits.
Urinary incontinence during menopause - what should a woman do to eliminate such an ailment?
When menopause occurs, a number of problems arise related to the functioning of the body. Hormonal changes also affect the functioning of the genitourinary system. Sometimes women develop urinary incontinence, accompanied by physical and psychological discomfort. There is a misconception that the disease cannot be corrected. In fact, with proper treatment, the pathology gets rid of quite quickly.
Personal hygiene
Personal hygiene during this period has some peculiarities. Often, women have a feeling of uncleanliness during incontinence treatment. But frequent washing leads to the fact that the mucous membrane becomes even more dry, as a result of which the condition can worsen. You need to wash yourself no more than 2-3 times a day, and not always with the use of cosmetics.
It is necessary to use urological or ordinary pads of high absorbency. It is very important to change them as often as possible to prevent irritation of the mucous membranes and skin with urine.
Smell
Urine odor becomes a serious problem with incontinence. How to reduce it? Many pads contain odor-absorbing elements, but these may not be very effective. Therefore, it is recommended to carry spare underwear with you. It is important that it is not synthetic, as this may increase the smell. You can use wet wipes for intimate hygiene.
The main problems with urination during menopause
During menopause, this problem is caused by hormonal changes. Estrogen levels decrease, so the muscles in the pelvic area become less elastic. The following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Urgent incontinence is characterized by a pronounced urge to deurinate when the bladder is not full enough.
- The stress type of incontinence develops under the influence of certain factors. These include sexual intercourse, lifting heavy objects, active physical activity and banal sneezing or laughing.
- A painful form of pathology is provoked by infectious diseases. It is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and pain during urination.
- The mixed form of incontinence is distinguished by a combination of symptoms. The urge to deurinate does not depend on the degree of bladder fullness and predisposing factors.
Involuntary release of urine is a physiological and psychological problem for women. The disease prevents you from fully enjoying life. The urge can occur at any time, which leads to awkward situations. With an advanced form of the disease, a woman loses the opportunity to attend work and public places.
Factors in the development of incontinence during menopause
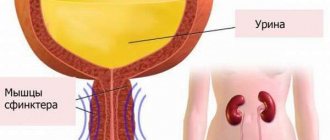
The main reason for the inability to hold urine is the lack of control over the sphincters. During menopause, the problem can arise even if the woman has not previously encountered genitourinary diseases. Most often, pathology is provoked by a combination of different factors. Pelvic floor dysfunction occurs for the following reasons:
- weakening of the pelvic muscles;
- decreased elasticity of the bladder;
- dryness of the genital mucosa;
- overweight.
Decreased pelvic floor muscle tone
With age, the muscular system weakens. During menopause this is felt most acutely. The reason is a decrease in the amount of estrogens, which are involved in the production of collagen. Due to muscle weakness, control over the organs of the genitourinary system is lost. In advanced cases, prolapse of the reproductive organs is observed. If measures are not taken in time, the problem can only be solved through surgery.
Decreased bladder elasticity
Menopause is accompanied by hormonal changes that affect the condition of all organs. During this period, as a result of a decrease in natural elasticity, the bladder becomes rigid. This leads to increased sensitivity of the organ. It contracts even with minor movements. As a result, the urge to urinate appears if the volume of accumulated urine does not exceed 100 ml when the norm is 400 ml.
Vaginal dryness
The functioning of the excretory system is related to the amount of estrogen in the body. During menopause, hormone levels decrease, which causes vaginal dryness. A lack of mucus is also observed in the urethral area. Organs become more vulnerable to infections. Their structure becomes thinner, and their protective function weakens. Ultimately, all this leads to urinary incontinence.
Excess weight
Metabolism is interconnected with hormonal status. During menopause, many women gain weight faster. A significant increase in body weight affects the functioning of internal organs, which cannot withstand the resulting load. As a result, the bowels and bladder become weaker. It becomes more difficult for a woman to hold urine when she urges.
Causes
Let's look at the reasons why frequent urination may occur during menopause. This is a fairly common problem, although it is not talked about as often. Of course, women who have previously had infections of the reproductive system or kidney diseases are at greater risk.
The changes that occur in the body during menopause are very serious, therefore they affect not only the reproductive system, but also everyone else.
Due to a decrease in estrogen, tissue elasticity deteriorates. This also applies to bladder tissue.
All reasons for frequent urination during menopause:
- Deterioration of elasticity. The loose tissue cannot hold urine as well as it used to. Plus, organs can change their location. The intestines also weaken.
- Overweight. If you gained weight during menopause or were obese before, your organs will also work worse under the pressure of weight.
- Dry mucous membranes. This is a common occurrence during menopause. Irritation and burning can cause infections, which can make urination difficult to control during menopause.
- Changes in bladder tissue. During menopause, the walls become stiffer and do not stretch well. Urine may pass even if it is not completely full.
Due to weakened immunity, kidney disease, diabetes and thyroid diseases can occur. These are other, more serious reasons why incontinence may occur.
Treatment
If symptoms of incontinence appear, you should consult a urologist as soon as possible. The effectiveness of therapy depends on the speed of taking measures to eliminate the disease. No diagnostic procedures are required. If an infectious disease is suspected, a woman may be prescribed a blood test for laboratory testing. In the initial stages of pathology, medicinal methods are used to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required.
Medicines
When choosing a medication, the doctor takes into account the cause of the disease. If incontinence is caused by psychological factors, sedatives are prescribed. Among them are Duloxetine and Cymbalta. Spasmex, Driptan, Detrusitol and Vesicare have a strengthening effect on the sphincters. In some cases, tonics are prescribed: Neuromidin, Ubretide, Proserin and Aksamon.
Most problems caused by menopause occur as a result of decreased estrogen levels. Therefore, to normalize the condition, women are prescribed hormonal drugs. Some of them have a contraceptive effect. They turn off the function of the ovaries, delaying the natural process of wasting eggs. For menopause, the following medications are used:
Surgery
Surgical intervention is required if gymnastics and medications are insufficiently effective. This treatment method is considered low-traumatic. The recovery period takes 2-3 weeks. There are several ways to perform the operation:
- Colporrhaphy is the process of tightening the vaginal walls surgically. As a result, pressure on the bladder is reduced.
- Applying a loop to the urethral area that fixes the position of the organ is called a sling. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Disadvantages include the likelihood of relapse.
- Colposuspension involves tightening the tissue of the urethra to the area of the inguinal ligaments. The operation is considered the most complex of those presented.
Gymnastics
This is a mandatory stage of complex therapy. Kegel exercises are performed to strengthen the pelvic muscles. They not only eliminate urinary incontinence, but also increase a woman’s libido. Before performing gymnastics, you need to feel the muscles responsible for holding urination. The most effective exercises include the following:
- It is necessary to quickly squeeze and relax the muscles for a minute.
- They contract and are fixed in this position for 4 seconds, then relax. If possible, the contraction time is gradually increased to 20 s.
- Fast muscle contractions are replaced by slow ones. In total, up to 40 contractions are performed in one approach.
Treatment by reason
The main direction of treatment for urinary incontinence is changing the daily routine, using medications, as well as physical training of the pelvic floor muscles. Injection methods of treatment have become widespread, in which a special gel is injected into the sphincter area. The substance creates a mechanical barrier to the outflow of urine from the bladder.
Surgical methods involving sphincter plastic surgery are also used. When surgery is contraindicated, doctors resort to using special pads that absorb urine and eliminate unpleasant odors.
Disease of the urinary system
For diseases of the urinary system, specialists use broad-spectrum antibiotics (Azithromycin, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin), as well as antiviral and antifungal drugs. After completing the course of treatment, in most cases the symptoms disappear.
A mandatory component of therapy is diet, reduction of physical activity, and exclusion of tobacco products and alcoholic beverages.
Stress urination can also be treated with medication. In the initial stages, drugs are used that improve tension in the sphincter and urethra (Proserin, Reminil, Aksamon). Medicines that improve the elasticity and firmness of the pelvic floor muscles are also prescribed. Sedatives are indicated (Novo-Passit, tincture of valerian or motherwort, Persen, etc.).
Cardiovascular pathologies
Often menopause is a trigger for the development of cardiovascular pathologies. A reduction in estrogen levels provokes the development of atherosclerosis, which impairs blood circulation. As a result, internal organs suffer and do not receive the necessary nutrition. Impaired oxygen transport to the bladder leads to disruption of its functionality.
As preventive measures aimed at preventing morphological changes in blood vessels, women are advised to take products containing hormones (Klimonorm, Klimen). Timely use of such drugs will help avoid many problems.
Diseases of the female genital organs
Often, urinary incontinence is provoked by inflammatory processes in the female genital organs. Drugs with an anti-inflammatory effect are a group of drugs that relieve pain, swelling and other symptoms. The effectiveness lies in the suppression of the transfer of arachidonic acids.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are represented by antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, antimycotics, non-steroidal drugs and biological stimulants.
Endocrine disorders
Some representatives of the fairer sex do not require additional therapy, since urinary incontinence is eliminated through hormonal drugs (Ovestin, Angelique, Femoston). They are used to correct hormonal levels during menopause.
Features of hygiene during menopause
When menopause occurs, special attention is paid to caring for the genitals. Both lack of hygiene and excessive cleanliness pose a danger to the health of the genitourinary system. The abundance of pathogenic bacteria provokes the development of infectious diseases. The use of aggressive cleansers to wash the genitals leads to dry mucous membranes. Until the problem of urinary incontinence is eliminated, a woman is recommended to use specialized urological pads.
Prevention
The unpleasant consequences of menopause can be avoided if you prepare your body for the changes in advance. How she will tolerate hormonal fluctuations depends on the initial state of health and lifestyle of a woman. Doctors recommend thinking about prevention after the age of 40. Preventive measures include the following principles:
- It is recommended to do yoga or stretching to generally strengthen the muscle corset.
- You should not visit the ladies' room unless absolutely necessary. Forced deurination when the bladder is not full has a negative effect on its elasticity.
- It is advisable not to abuse foods and drinks that have a diuretic effect.
- Kegel exercises can be done at any age. Trained pelvic floor muscles will become unusable later.
- Hypothermia of the genitals should be avoided. This will prevent inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Medicines and drugs
The drugs are the first-line treatment for incontinence. If a woman has only recently been diagnosed with incontinence, then it would be more logical to first try using conservative methods to treat it. And only if they are ineffective, doctors will recommend surgery to the patient. On the other hand, if surgery is contraindicated for some reason, then medications may be the only reliable means that can help the patient.
However, medications are not the only way to treat incontinence. It is also important to follow a proper diet and perform physical exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which will help to hold back urine when you urge to go to the toilet. In some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures can also help.
You should also remember that medications cannot help instantly. Some medications need to be taken for many years.
What drink?
Only the attending physician can answer this question. The fact is that for different types of disease, the range of drugs used may not coincide at all. Self-medication for incontinence is dangerous and can lead to worsening of the condition. And some medications simply will not be given to the patient at the pharmacy without a prescription.
Types of medications used to treat incontinence:
- Antidepressants,
- Nootropics,
- Sedatives,
- Antispasmodics,
- M-anticholinergics,
- Estrogens,
- Adrenomimetics,
- Vasopressin analogues.
Mixed incontinence is also often observed, in which signs of urgent and stress forms are observed.
Most often, medications are effective for urgent and mixed forms of incontinence, enuresis, and less often for stress.
M-anticholinergics
Substances of this type act on the M-cholinergic receptors of the bladder. Anticholinergics help reduce tone and relax the muscles of the bladder, increasing its available volume. Effective for urgent forms of incontinence. Taking anticholinergic drugs reduces the frequency and severity of the urge to urinate. The bladder becomes less likely to overflow, and therefore the frequency of urges decreases.
Popular anticholinergic drugs based on tolterodine: Detrusitol, Urotol, Uroflex, Roliten. The course of treatment with medications of this series is at least a month. The drugs Vesicare and Enablex use other substances - solifenacin, darifenacin. The effect of these drugs can be noticeable after just a week. Contraindications for anticholinergic drugs are pregnancy, narrowing of the ureters, and stones in the bladder.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics have a similar scope of application to anticholinergics. They fight bladder muscle spasms and increased excitability. Reduce urinary instability and the number of urges. Indicated for mixed and urgent forms of incontinence. From this group of drugs we can note Spazmex (trospium chloride), Betmiga (mirabegron). Also popular are drugs based on oxybutynin (Driptan).
Antidepressants, nootropics and sedatives
The mechanism of urination is regulated by the brain and spinal cord. Therefore, neurological and mental disorders can disrupt this mechanism. Some antidepressants, sedatives and nootropics can help with incontinence of a neurogenic and psychogenic nature.
Very often, among antidepressants for incontinence, doctors prescribe Imipramine, Duloxetine, Melipramine. Nootropics, such as Pantocalcin, Pantogam, Phenibut, Picamilon, have an auxiliary effect, strengthening the nervous system. Sedatives and tranquilizers relieve nervous tension and normalize sleep.
Antidepressants should not be taken if you have hypertension, pregnancy, liver disease, or glaucoma. Also, antidepressants often cause side effects, such as seizures, and can negatively affect the condition of the heart, liver, and blood.
Hormonal drugs
The doctor may prescribe analogues of female hormones if incontinence is caused, among other reasons, by a lack of these hormones in the body. This is due to age-related changes in women during menopause. Lack of estrogen leads to weakness of the pelvic muscles, which support the urethra and bladder neck in the desired position.
When treating incontinence (most often stress-type incontinence), estriol-based drugs are used, such as Ovestin, Microfollin, Presomen. They can be used both in the form of tablets and in the form of vaginal suppositories. Many urologists, however, question the effectiveness of hormones for incontinence in women.
Adrenergic agonists
This group of drugs are synthetic analogues of adrenaline and act on the alpha-adrenergic receptors of the bladder neck, helping to increase its tone. Adrenergic agonists are prescribed for stress incontinence. However, the effect of use is not always observed. Popular drugs in this group are midodrine (Gudron), ephedrine.
Incontinence tablets
Let us describe some popular drugs used for incontinence in women. Most of them come in the form of tablets or capsules. These dosage forms are very convenient for oral administration. Of course, in order for medications to have an effect, you must carefully follow your doctor’s recommendations for taking them.
Detrusitol
Available in capsules containing tolterodine as the active substance. This medicine belongs to the class of m-anticholinergic drugs. The drug helps relax the muscles of the bladder, increasing its available volume. The medicine must be taken once a day, 1-2 capsules. It doesn’t matter when you do it - before or after meals, it doesn’t affect its effectiveness. Contraindications: age over 18 years, urinary retention, ulcerative colitis, megacolon.
Vesicare
The active ingredient is solifenacin. The drug belongs to the class of new generation anticholinergics. Prescribed for urgent forms of incontinence, helps to relax the bladder. Take Vesicare 5 mg once a day; if necessary, the dose can be increased to 10 mg. Contraindicated in case of urinary retention, severe renal failure, and in childhood (under 18 years).
Spazmex
Spazmex contains trospium chloride. The medicine is indicated for mixed and urgent types of incontinence, bladder spasms and increased excitability. The average daily dose is three 15 mg tablets. Tablets can only be taken before meals. Contraindications – age under 14 years, urinary retention, tachycardia, severe renal failure.
Imipramine
The drug belongs to the class of tricyclic antidepressants. The drug is able to normalize the functioning of the urinary tract. It is especially effective for nocturnal enuresis, when urine is released involuntarily. The course of treatment with the drug can last several months. The dosage is determined by the doctor. Usually 1-3 tablets per day are prescribed. This dose should be taken before bedtime. Contraindicated in children under 6 years of age, with dysfunction of the liver, kidneys, hematopoietic organs, heart failure and myocardial infarction, and bladder atony.
Ovestin
Contains a natural analogue of female sex hormones – estriol. Under the influence of the drug, the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs are restored, their blood circulation improves, and their resistance to inflammation increases. The course of therapy with the drug in tablet form is at least a month. 2-4 tablets are prescribed per day.
Minirin
Minirin contains desmopressin, a synthetic analogue of vasopressin. The function of vasopressin in the body is to regulate urination. Therefore, due to the use of desmopressin, urine is excreted by the kidneys in a smaller volume.
Desmopressin is often used for nocturnal enuresis. The dosage is individual and varies between 10-40 mg per day. Minirin is taken only after meals. Contraindications: severe thirst, anuria, heart failure, stagnation of fluid in the body, sodium deficiency.
Midodrine
A medicine belonging to the group of alpha-agonists. Available in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous administration. Midodrine helps to increase the tone of the bladder sphincter. Contraindicated for people with hypertension or vascular spasms. The standard dosage is 2.5 mg 2 times a day.
Hygiene rules
Constant contact of the genitals with urine residue causes irritation, burning, and itching. When it gets on laundry, urine causes the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and odors. What needs to be done to prevent health problems and improve the quality of life in society.
- It is recommended to carry out hygiene procedures after each trip to the toilet. Wash with clean, warm water or wipe the perineum with special wipes.
- After a shower, you can treat your genitals with a moisturizer to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Use special hypoallergenic pads or make them yourself from natural fabric, cotton wool, gauze.
- For severe incontinence, disposable panties and diapers are used. At night, use special moisture-absorbing diapers.
The most important thing is to ensure the cleanliness of the genitals and prevent the development of infection. There are a huge number of special intimate hygiene products on sale. Please note that it is recommended to use them 1-2 times a day. Their too frequent use causes an allergic reaction and dries the skin of the genital organs.
What should the elderly drink?
Incontinence occurs more often in older women than in middle-aged women. This is due to age-related degradation of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic floor. The urologist should select the right drug. After all, not all forms of incontinence can be cured with the same medications.
Most often, older women are prescribed drugs such as Driptan, Vesicare, Spazmex, Betmiga, drugs containing estrogens, Duloxetine. When taken systematically, they are able to neutralize age-related changes in the urinary system. A drug such as desmopressin is prescribed to elderly people with caution due to their high risk of developing hyponatremia.
Drugs for the treatment of incontinence in the elderly
For age-related incontinence in older women, anti-incontinence medications are used.
Since test indications are individual, only a specialist prescribes the method and medication:
- A group of antidepressants is used for stress enuresis. Duloxetine, Imipramine regulate urination, promote relaxation, and significantly reduce toilet visits;
- Antispasmodic medications Spazmex, Oxybutynin, Driptan remove inflammation, increase the time period for filling the bladder, and regulate nerve signals. The most easily tolerated drugs.
- Hormone modeling methods . Reduce atrophic disturbances in the integrity of the bladder walls. Desmopresin is a representative of drugs in this pharmacological group. Only the attending physician prescribes and regulates the intake of pills.
- Anticholinergic methods . The drug Driptan, due to its healing characteristics, is equally optimal for girls and older women.
Causes of the pathological condition during menopause
Permanent urinary incontinence develops due to weakening of the sphincter muscles. This can happen for various reasons.
- Rupture of tissue in the vaginal area. This may occur as the baby passes through the birth canal;
- Pelvic injuries;
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic organs, especially removal of formations on the uterus;
- Excess body weight;
- Pregnancy. The increasing size of the uterus begins to squeeze the bladder. The larger the fetus becomes, the more often the woman experiences the urge to go to the toilet;
- Stress;
- Overactive bladder syndrome;
- Frequent constipation.
Stress is one of the causes of urinary incontinence during menopause
If we talk about the menopause period, then during this period women often encounter this problem. In this case, in addition to the listed factors, the following can provoke urinary incontinence:
- Loss of elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles due to a sharp decrease in produced hormones, namely estrogen;
- Flabbiness of the pelvic tissues, which can also occur due to ordinary physiological aging;
- Urinary tract infections. They can occur at any other age, but during menopause the body is most susceptible to various types of pathogenic pathogens.
Urinary incontinence in women during menopause must be treated. You should not think that the irreversible processes of decline of reproductive functions and their consequences cannot be controlled. The right approach to the problem will allow you to quickly return to normal life.
Types of violations
Experts have divided urinary disorders into several types.
- Stressful. In this case, due to tension in the abdominal muscles, the sphincter relaxes and urine cannot be retained. This happens when you sneeze, cough, laugh, or lift heavy objects.
- Sudden. In this case, there is no connection with external factors. Everything happens due to processes occurring in the body. And at some point urine is released. Usually a woman knows about such leaks and wears special pads.
- Frequent trips to the toilet. Problems with the bladder during menopause can be endless. A woman goes to the toilet both day and night. Little urine comes out.
As already mentioned, if itching or pain occurs, you should consult a doctor.
Types of urinary incontinence and their characteristics
For middle-aged and older women, 3 types of urinary incontinence may be characteristic. These are: stressful, urgent and mixed.
Stress urinary incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence, despite its name, is not associated with constant stress, but with a weak state of the pelvic floor muscles, in other words, flabbiness. If a woman is at rest, then she has nothing to fear, but if any sudden physiological change occurs, for example, a strong sneeze, an unexpected fit of laughter, lifting an object that is too heavy, then involuntary urination may occur. In this case, the patient’s brain does not receive a preliminary signal about this.
How does the problem manifest itself?
There are 3 types of problems:
With stress urination, the problem may occur during laughter.
- Stress urination. Incontinence occurs during physical activity, when the abdominal muscles tense, for example, while laughing or coughing.
- Sudden urination. The pathology is not controlled and occurs due to internal changes in the body, and not external stimuli. In this case, the patient does not have time to get to the restroom.
- Frequent urination. There is a constant urge to urinate at any time of the day.
In general, the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- uncontrolled urination during exercise;
- involuntary loss of urine before reaching the toilet;
- frequent inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract;
- frequent urges at night;
- urination immediately after the urge occurs.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis of urinary incontinence can be made based on a complete examination of the patient and her complaints. In order to determine the severity of the pathology, the doctor may prescribe the following instrumental examination methods:
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder;
- X-ray of the bladder;
- Cystoscopy. This is an endoscopic procedure to evaluate the inside of the bladder.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder - a method for diagnosing urinary incontinence during menopause
In addition, the woman is prescribed laboratory tests in the form of a general urine test and sometimes microflora cultures.
Treatment options
It is impossible to treat urinary incontinence during menopause without conducting a full examination and diagnosis. There are different approaches to solving the problem: from conservative-medicinal to radical-surgical. It all depends on the nature of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Medication
Drug treatment is most effective for the urgent type of urinary incontinence, since it is associated with a violation of internal processes. In the case of a stressful condition, the emphasis must be placed on strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, in which gymnastics and surgery play a major role.
In order to select suitable medications, the doctor initially establishes the cause of the pathology. For urgent type of incontinence, the patient may be prescribed:
- Drugs that reduce the activity of bladder muscle tissue. Example: Spazmex, Pantogam;
- Drugs that relax the muscle tissue of the bladder. Example: Detrusiol;
- Antidepressants. They allow you to stop false urges to urinate. Example: Imipramine.
Ideally, after drug therapy, the bladder muscles should become more relaxed, and therefore able to accumulate a larger volume of fluid. In addition, the patient’s brain must learn to distinguish real urges to go to the toilet from false ones.
Absolutely all of the listed and other medications, as well as their exact dosage, should be prescribed only by the attending physician. Otherwise, you can worsen the existing situation.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is the most radical method of solving the problem of urinary incontinence. Surgery may be prescribed if conservative treatment does not produce results for a long time, which is more typical for older patients.
There are various methods of surgical treatment. The surgeon chooses the most suitable one in each individual case, depending on the cause of incontinence and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
The most popular method is the free loop method. It is also known as a sling. This procedure is one of the most minimally invasive and therefore safe. The woman is given a special strip of synthetic material that creates a loop effect. It is she who begins to support the neck of the bladder, which solves the problem.
Surgeries quickly and effectively eliminate urinary incontinence, but there are contraindications to them. Thus, surgical intervention may be prohibited for the following patients:
- Those who have acute infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Pregnant;
- With diagnosed serious diseases, such as: diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, heart failure;
- Having scars in certain areas of the vagina and bladder.
Pregnancy is a contraindication to surgery for urinary incontinence
In general, the final decision to perform an operation can only be made by the attending physician, who will first assess all the existing risks.
Additional non-surgical methods
To treat pathological urinary incontinence, doctors, in addition to medications and surgeries, can prescribe various exercises and physical therapy procedures.
Since incontinence develops as a result of relaxation of muscle tissue, regular training of them can allow them to return to their former elasticity, which will be enough to fully control urination. Today, there are many different techniques for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, but probably the most famous are “Kegel exercises.” In fact, it is not difficult to master them even at home, but when it comes to regular incontinence associated with a specific problem in the body, then it is better to do this in the company of a doctor or a certified trainer.
Physiotherapy procedures also include quite effective methods for treating incontinence, for example:
- Electrical muscle stimulation;
- Microcurrents;
- Warming up.
But these procedures are usually used as additional measures to the main therapy. If we are talking about rare cases of incontinence and a younger body, then perhaps they will be enough.