- Ultrasound of the kidneys can reveal the expansion of the pyelocaliceal system, enlargement of the kidney, and determine the thickness of the renal parenchyma.
- X-ray examination is the basis for diagnosing renal hydronephrosis. Using plain radiography, you can determine the size of the kidneys and identify stones. With contrast intravenous urography, a series of pictures are taken and the nature of the rate of formation and excretion of urine is determined. With hydronephrosis, the flow of contrast into the renal pelvis system slows down. The pelvis and calyx are dilated and have rounded contours. In later stages, the contrast agent may not reach the kidney affected by hydronephrosis at all. Sometimes it is possible to identify the level and nature of urinary tract obstruction.
- Radioisotope urography allows you to more accurately determine the nature of dysuric phenomena and characterize the degree of damage to each kidney individually.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging, as well as angiography are used in unclear cases to clarify the diagnosis.
Urolithiasis of the kidneys
Among the most indolent pathologies in the field of urology, urolithiasis of the kidneys ranks first. For a long time, the patient does not realize that he has stones. Only due to their mobility and the appearance of concomitant symptoms is it possible to learn about the development of the disease. At the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor, undergo an examination, and receive the necessary treatment.
What it is?
Urolithiasis (UCD) of the kidneys, or urolithiasis, is a disease whose development takes more than six months.
Initially, sand forms, then, if the patient continues to lead an unhealthy lifestyle, stone-like deposits form. Concretions (their second name) can be single or multiple.
Depending on the chemical composition, they are divided into oxalates, urates, phosphates, xanthines, cystines and struvites.
Localization of stones inside the kidney is the most dangerous of all types of urolithiasis, since damage to the organ occurs and problems with the outflow of urine. Factors predisposing to the development of urolithiasis are varied, but are associated with the patient’s lifestyle. Therefore, minimizing the development of urolithiasis is within his competence.
Causes of stone formation
The likelihood of stone formation increases if the patient:
- Abuses sour, spicy, salty foods
- Leads a sedentary lifestyle
- Does not eliminate inflammatory and infectious processes in the organs of the urogenital tract
- Has a hereditary predisposition to the development of urolithiasis
- Drinks unfiltered water
Other predisposing factors are disorders of protein metabolism, enzyme deficiency, problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and dehydration.
Symptoms
The development of urolithiasis occurs asymptomatically. Only a change in the position of the solid conglomerate leads to the appearance of signs. The condition is defined as renal colic and is accompanied by characteristic phenomena, including:
- Pain syndrome. Localization – lumbosacral back, with transition to the groin, suprapubic region
- Dyspeptic phenomena. Nausea and prolonged, repeated vomiting are constant manifestations of an attack of renal colic.
- Increased body temperature. Caused by the onset of complications (for example, inflammatory processes of the urogenital tract) or psycho-emotional arousal
- The appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria). The symptom is caused by damage to the kidney tissue by stony deposits during its mobility
- Reducing daily diuresis. A reduction in urine volume is caused by a stone blocking the ducts.
- Neurological disorders. Irritability, short temper, and general restlessness are explained by pain. The patient cannot assume a certain body position
Other symptoms depend on the location of the stone inside the pelvis, its size and composition, and the age of the colic. Of no small importance is the presence of concomitant pathologies and complications in the patient that resulted from urolithiasis. Physical activity and bumpy riding can trigger colic.
Possible complications
The following complications may develop as a result of urolithiasis:
- Pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pyelocaliceal system). The condition is caused by the stone remaining in an unchanged position for a long time, which contributes to the accumulation of pathogenic microflora around it
- Hypertensive crisis. The pathology is associated with an increase in blood pressure due to compression of the renal artery by stone-like deposits
- Paranephritis. An extremely serious condition in which the parenchyma melts due to a purulent process. The reason for its development is complicated pyelonephritis
- Iron-deficiency anemia. Refers to the effects of constant blood loss during urination
The occurrence of any of these complications can be avoided if you promptly seek qualified medical help. Only by using proven, competent methods can you save a kidney with a calculus inside.
Urolithiasis during pregnancy
KSD, worsened during pregnancy, poses a threat to the development of pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system never resolves on its own and always requires drug treatment.
It is this fact that is incompatible with the period of pregnancy and aggravates it. Regarding the use of medications, gynecologists do not object to administering an injection of No-shpa directly during renal colic.
But other medications are strictly contraindicated for pregnant women.
The second risk that women with urolithiasis are exposed to during pregnancy is a violation of the outflow of urine (if the canal is blocked by a stone). This creates problems with urination and causes pain in the lumbosacral back. Also, stagnation of urine contributes to the attachment of pathogenic microflora and the development of inflammatory and infectious processes.
The presence of a calculus and its movement inside the pelvis do not directly affect the course of pregnancy. The operation is not performed during pregnancy; women are recommended to treat stones with medication only after childbirth.
Disease in children
The following factors contribute to the development of urolithiasis in children:
- Hormonal problems that cause disturbances in calcium metabolism in the body
- Predominance of sour and salty foods in the diet
- Limited mobility
- Drinking contaminated water
- The presence of inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract, in which a change in the chemical composition of urine occurs
- Hereditary predisposition
If the child does not have signs of hydronephrosis - hydronephrosis of the kidneys, and purulent damage to this organ, crushing the stones is carried out in a conservative way.
Which doctor should I contact?
As with the elimination of other pathologies related to the urinary system, treatment of urolithiasis is carried out by a urologist. You can contact a specialist in this profile without first visiting a therapist. The urologist prescribes diagnostic procedures and, based on their answers, prepares the necessary treatment. It comes down to removing stones using a conservative or surgical method.
Diagnostics
To confirm the presence of urolithiasis, assess the general condition of the paired organ, determine the parameters of the stone (size, location), the following is carried out:
- Biochemical, clinical examination of blood and urine. An increase in ESR and leukocytes in the blood are signs of inflammation, but with urolithiasis they indicate an ongoing complication. A decrease in hemoglobin levels indicates the need to compensate for the iron removed from the body during hematuria.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. A quick and simple method for confirming the presence of stones, clarifying their parameters, and localization.
- Excretory urography. A solution containing iodine is administered intravenously to the patient. Then a series of x-rays are taken (often after 15 and 40 minutes). An iodine-containing solution fills the ureters, making it possible to visualize the condition of the urinary system as a whole.
- Survey X-ray examination. Provides a general clinical picture, including the relative position of the kidneys. This type of diagnosis is carried out simultaneously with excretory urography.
Other research methods are prescribed only when there is doubt regarding the size, type of stones, or their location; blood supply and general condition of the kidneys.
Treatment
The scope of therapeutic intervention depends on the diagnostic results. Stones are removed conservatively or surgically. In the first case, physiotherapy is additionally used. The number of procedures is prescribed taking into account the size and composition of the stone.
Conservative therapy
The table shows the drugs that are prescribed for conservative therapy, their dosages, and the regimen of use.
| Pharmacological group and name of the drug, scheme of its administration | Destination purpose |
Antispasmodics:
| Improving overall well-being by eliminating pain and spasms. Relaxation of the ureters and unhindered movement of stone deposits outward. |
Analgesics:
In order not to cause damage to the veins, it is better to administer intravenous drugs only after dissolution with sodium chloride. | Elimination of pain, relaxation of the walls of the urogenital tract, which helps the stone leave the kidney. |
Medicines that help eliminate urolithiasis and suppress pathogenic microflora:
Since the Urolesan solution has an unpleasant taste, it can be placed on a piece of sugar and consumed in this form. | Suppression of the inflammatory and infectious process that has arisen inside the urogenital tract. Destruction of the stone into small fragments. |
| Diuretic drugs: Furosemide (administer 4 ml intramuscularly) or Lasix (4 ml intramuscularly). | Stimulation of urine production and increased excretion. Together, these properties contribute to the leaching of stone. |
When is surgery needed?
The need for surgical intervention is considered only in the absence of a positive result from conservative therapy.
A surgical approach is a necessary measure in a condition where urolithiasis is complicated by a purulent process and destruction of the parenchyma.
The operation is also prescribed to eliminate large stones that cannot be crushed by a laser beam or ultrasonic vibrations.
Diet
Nutrition for urolithiasis has its own characteristics. The consumption of salty, sour, spicy foods and dishes is contraindicated. It is forbidden to drink coffee or drink alcohol. The doctor prepares a diet based on the chemical composition of the rocky sediment:
- With phosphates, in addition to the basic recommendations, the consumption of legumes, potatoes, herbs, nuts, eggs and confectionery is contraindicated.
- Eliminating urates involves eliminating the presence of cheese, mushrooms, broth, herbs, sausage, fish and smoked meats in the diet.
- If you have oxalates, you should not eat chocolate, all foods containing vitamin C, broths, spices, and offal.
- The presence of xanthines suggests avoiding salty cheese, fatty meats and fish, greens, marinade, and canned food.
- When treating cystines, there is a ban on the consumption of fruit drinks, lettuce, cherries, fruit juices and all dishes enriched with spices.
Recommended diet - no more than 5 rubles. per day, in small portions, provided that the water balance is increased to 1.5 liters per day.
Stone crushing methods
There are several types of their destruction - through the use of ultrasound, laser or through abdominal surgery. The choice of a specific method depends on the individual equipment of the clinic where the intervention is planned; size and location of the stone.
Characteristics of each operation:
- Ultrasonic lithotripsy (stone crushing). Provides standard preliminary preparation - cleansing the intestines with an enema, refusing to eat food on the eve of the operation. Involves the use of ultrasonic vibrations. Allows you to crush the tumor into the smallest fragments, and then wash it out of the body with saline solution. The risk of damage to the parenchyma is eliminated.
- Laser lithotripsy. Preparation involves refusing to eat food (the evening before the operation) and water (on the day of the intervention). The tumor is crushed using a high-precision beam. In this case, the image of the kidney condition is transmitted to the monitor screen of the laser unit. This type of lithotripsy provides a favorable outlook. The possibility of injury to the organ is excluded.
- Abdominal surgery (open). It is a traditional surgical procedure (with tissue dissection). It is carried out only for large, multiple neoplasms. It involves a long recovery period, restrictions on physical activity and nutrition.
In modern urology, the method of open surgery is used only when there are serious reasons. Abdominal surgery is not the primary option for eliminating urolithiasis.
Only a urologist can prescribe a specific method of lithotripsy. The specialist takes into account the diagnostic results and factors related to the patient’s health status.
Prevention
Not every person develops stony deposits during their lifetime. Their formation requires a long-term unhealthy lifestyle. The following will help reduce the risk of developing urolithiasis:
- Normalization of nutrition and drinking regime. It is not recommended to consume sour, spicy, salty snacks, fast food, carbonated drinks, and unfiltered water.
- Increasing the volume of physical activity.
- Timely elimination of inflammation of the urogenital tract.
- Regular medical examinations and a more attentive attitude to health if there is a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis.
It is also important to stop dysfunction of the digestive organs, normalize body weight, avoid a monotonous diet, and stop drinking alcohol.
Conclusion
Urolithiasis of the kidneys is a pathological condition that is characterized by the formation of stones of various sizes and composition. The pathology is treated conservatively or through surgery.
But even after prompt removal of stone-like deposits, there is no guarantee that they will not form again. Especially if the patient has a hereditary predisposition and eats foods unfavorable to the body.
Early contact with a specialist increases the likelihood of treating urolithiasis using a conservative method.
: Urolithiasis - removal of stones and treatment of renal colic
Source: https://GuruSpa.ru/mochekamennaya-bolezn-pochek/
How is the operation performed?
The stent is inserted through the urethra and passes into the renal pelvis. The tube is attached directly to the kidney tissue thanks to a special spiral end, twisted in the shape of a pig's tail.
Using a cystoscope, the doctor finds an abnormally narrowed area of the ureter and places a mesh called a balloon there. The mesh expands and the duct is thus opened again.
Depending on the complexity of the situation and the expiration date of the tube itself, the period for removing the implant from the body is set. The operation may be canceled if acute inflammation begins again immediately before installation. Then suitable antibiotics are prescribed, and the operation is postponed to another time.
Kidney block. Treatment of kidney block
When the kidney is blocked, it changes in such a way that its calyces and pelvis expand and difficulty in the outflow of urine occurs. Increased pressure begins to build up inside the kidney, the blood supply to the kidney is disrupted, the underlying tissue atrophies, and the kidney functions stop working.
As a result, the tissue becomes very thin, the calyx and pelvis greatly increase in size, and under the influence of gravity the kidney falls down and a blockage occurs. A kidney block occurs when there is some obstruction in the path of urine, due to which urine does not enter the bladder .
Urine remains in a certain place, which causes the kidney to overfill.
Stopping the functioning of the kidney is very dangerous for the body , as inflammation begins, which very quickly spreads throughout the entire circulatory system; often other organs important for the life of the body begin to fail (stump, lungs, etc.
) - all this can lead to serious complications for the patient, and sometimes death. Most often, kidney block is diagnosed with hydronephrosis. Hydronephrosis is a disease during which one or both kidneys become stretched and greatly increase in volume.
Causes of hydronephrosis
The main causes of congenital hydronephrosis:
- Urinary tract dysthenesia;
- Congenital anomaly of the renal artery;
- Pathologies of valves and ureter;
- Compressive ureter;
- Ureterocele;
- Retrocaval location of the ureter;
- Obstruction of the lower urinary tract.
The main causes of acquired hydronephrosis:
- Urological diseases;
- Inflammatory changes in the urinary system;
- Narrowing of the urinary system as a result of injury;
- Kidney stone disease;
- Tumors of the urinary tract;
- Prostate tumors;
- Tumors of the cervix;
- Metastases in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes;
- Infiltration of the retroperitoneal tissue of the pelvis;
- Spinal cord injuries;
- Impaired urine flow.
Very often, the cause of a kidney block is an additional vessel that goes to the lower pole and compresses the ureter (at the point of origin from the pelvis).
In connection with this process, kinks and compression of the ureteropelvic segment are formed, and scar tissue is also formed, which causes a narrowing of the lumen of the ureteric canal. Obstacles to the outflow of urine can also be valves, spurs, stones and diverticula in the mucous membrane of the ureter.
Symptoms of kidney block
The symptoms of hydronephrosis will directly depend on the manifestation and form of this disease (acute or chronic form). In the case of the acute form, kidney blockage occurs very quickly , all symptoms develop within a few hours. The main symptoms of acute hydronephrosis:
- Severe pain in the back, side, or between the ribs;
- Renal colic;
- Pain on the side of the affected kidney;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Bloating;
- Fever;
- Frequent urination;
- Urinary tract infection;
- Pain when urinating.
in the photo - urologist-oncologist V. Shaduri consults a patient
In this case, the kidney blockage develops gradually, and symptoms may not appear for several weeks or months. Symptoms will directly depend on the location and duration of blockage of urine flow in the kidney.
The severity of symptoms will also depend on the degree of distension of the kidney.
With a slowly increasing blockade of the urinary tract, the patient experiences the same symptoms as with the acute form of hydronephrosis; sometimes the patient feels a dull, prolonged pain in the side.
Treatment of kidney block
When the first symptoms of kidney block appear, immediately contact the urology and oncology center to identify the cause of hydronephrosis and for timely treatment of this pathology.
Treatment for kidney blockage will directly depend on the cause and extent of the urinary tract blockage.
The goal of treatment is to remove accumulated urine and reduce pressure in the kidney, as well as completely eliminate the causes of hydronephrosis in order to prevent irreversible consequences for the body as soon as possible.
In the acute form of hydronephrosis, accumulated urine must be removed before the kidney is damaged . To do this, a special catheter is inserted into the bladder or directly into the kidney itself.
This drainage allows you to get rid of urine and reduce pressure in the kidney.
If hydronephrosis develops slowly, then urgent treatment is not required, but the accumulated urine must still be removed; for this, a tube is inserted into the ureter.
After the pressure in the kidney has stabilized, highly qualified doctors at our urology and oncology center begin to eliminate the cause that caused the blockage of the kidney. The method of removal also depends on the individual cause, but most blockages require immediate surgery.
Surgery may be needed to remove a stone from the ureter or to remove a pathologically abnormal part of the urinary tract. Sometimes surgical transfer of the ureter to another part of the bladder is required. As medical statistics show, most patients fully recover after treatment if the disease is diagnosed in the early stages.
If you suspect a kidney block, immediately seek medical help at our urology and oncology center . We employ a huge number of highly qualified specialists with extensive experience in this field of medical activity. They will help to accurately determine the causes of the disease and, as soon as possible, prescribe the correct individual course of treatment.
This might be interesting:
- Hydronephrosis
- Kidney cyst
- Kidney tumor
- Kidney prolapse
- Nephroptosis
Source: https://www.urolog-onkolog.ru/blok-pochki.htm
17th century diet
-What are these rules?
– Firstly, in order to keep your kidneys healthy, you need to eat right. The most healthy diet is the diet of the 17th century, when even salt was difficult to obtain, so people ate only fresh foods. In the production of fast food and shelf-stable products, a huge number of different reagents are used, which must undergo decontamination in the human body. And in order to destroy them and make them safe, the kidneys must work to the limit of their capabilities. Secondly, you need to be careful when taking antibiotics, analgesics and antiviral drugs. These rules need to be known not only to patients of nephrologists, but also to people at risk.
Click to enlarge
- Who is included in it?
– These are patients with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, and chronic diseases that require painkillers. Among them there are especially many patients with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. People at risk include people who were born with low body weight (particularly premature babies), and those who abuse nutritional supplements and follow diets with a high protein load.
Article on the topic
A capricious couple. Which kidney diseases are deadly and how to avoid them
Kidney block: Characteristics, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
In medical practice, a condition often occurs in which a so-called kidney block occurs. This phenomenon occurs due to acute disruption of the outflow of fluid from the paired organ as a result of blockage of the urinary tract. The blocked kidney ceases to perform its functions, in a short period of time it fills with filtered fluid and increases in size.
The likely cause of the development of kidney block is hydronephrosis. This serious condition is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the collecting apparatus of the kidney. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that if the outflow of urine is not restored in a timely manner, the paired organ becomes overfilled with fluid, which can result in kidney rupture.
Characteristics
Speaking about the fact that this is a kidney block, and what structural and functional changes are accompanied by this disease, we can say that when this pathology occurs, increased fluid pressure is created inside the paired organ, the blood supply to the organ is disrupted, and atrophic changes are formed in the parenchyma. With the development of a renal block, the tissue of the paired organ becomes thinner, the boundaries of the pelvis and calyces expand, and the kidney itself moves downward and ceases to function.
Rice - kidney hydronephrosis and healthy kidney
The accumulation of fluid inside the kidney (hydronephrosis) is not a separate disease, as this mechanical problem occurs due to blockage of the urinary tract.
Disruption of the natural process of excretion of urine from the body is a serious condition that leads to the development of autointoxication, local inflammatory reaction, as well as other serious complications, including death.
Causes
In urological practice, multiple congenital and acquired factors are identified that lead to the development of hydronephrosis and kidney block.
Acquired hydronephrosis
The acquired form of renal hydronephrosis occurs under the influence of such negative factors:
- Benign and malignant tumors of the prostate gland in men.
- Urolithiasis, followed by blocking of the lumen of the ureter with a calculus.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, leading to the formation of connective tissue strictures in the urinary tract.
- Previous injuries to the kidneys and urinary organs.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms in the area of the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra.
- Foci of metastasis in the area of retroperitoneal lymph nodes in cancer.
- Various neoplasms in the cervix in women.
- Spinal cord injuries.
- The presence of foreign bodies in the urinary tract.
Along with acquired factors for the development of hydronephrosis and kidney block, there are factors leading to the development of congenital hydronephrosis. These factors include:
- Retrocaval localization of the ureter.
- Mechanical compression of the ureter.
- Congenital anomalies of the artery that supplies blood to the paired organ.
- Dyskinesia of the urinary tract.
- Blockage of the lumen of the urinary tract with single or multiple stones due to urolithiasis.
- Ureterocele.
Important! A common cause of hydronephrosis and renal block is the presence of a so-called accessory vessel extending to the lower renal pole and compressing a segment of the ureter located near the renal pelvis.
In the presence of an additional vessel, compression of the ureteropelvic segment is observed, followed by the formation of a connective tissue scar, disrupting the process of natural drainage of fluid from the paired organ.
Less common factors in the development of the block are pathologies of the urinary tract valves, as well as diverticula in the ureter.
Author
Ganshina Ilona Valerievna
Source: https://uran.help/diseases/blok-pochki.html
Indications and contraindications for installation
Installation of a stent in the kidney is carried out strictly according to medical indications.
Indications in medicine are:
- stenosis (stricture) of the ureter;
- urethrohydronephrosis;
- kidney cancer;
- swelling of the ducts due to a long-term inflammatory process in the bladder;
- narrowing of the ureter due to the growth of the uterus in a woman during pregnancy;
- in men, stenosis occurs due to prostatitis;
- kidney stone getting stuck in the canal.
A stent may be placed after removing a kidney stone if sand or smaller stones are still found in the kidneys.
Contraindications are 2 factors: if there is an injury to the urethra or an acute inflammatory process in the pelvis is diagnosed.
Kidney block symptoms – Kidney block: Characteristics, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
In medical practice, a condition often occurs in which a so-called kidney block occurs. This phenomenon occurs due to acute disruption of the outflow of fluid from the paired organ as a result of blockage of the urinary tract. The blocked kidney ceases to perform its functions, in a short period of time it fills with filtered fluid and increases in size.
The likely cause of the development of kidney block is hydronephrosis. This serious condition is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the collecting apparatus of the kidney. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that if the outflow of urine is not restored in a timely manner, the paired organ becomes overfilled with fluid, which can result in kidney rupture.
Congenital hydronephrosis
Along with acquired factors for the development of hydronephrosis and kidney block, there are factors leading to the development of congenital hydronephrosis. These factors include:
- Retrocaval localization of the ureter.
- Mechanical compression of the ureter.
- Congenital anomalies of the artery that supplies blood to the paired organ.
- Dyskinesia of the urinary tract.
- Blockage of the lumen of the urinary tract with single or multiple stones due to urolithiasis.
- Ureterocele.
Important! A common cause of hydronephrosis and renal block is the presence of a so-called accessory vessel extending to the lower renal pole and compressing a segment of the ureter located near the renal pelvis.
In the presence of an additional vessel, compression of the ureteropelvic segment is observed, followed by the formation of a connective tissue scar, disrupting the process of natural drainage of fluid from the paired organ.
Less common factors in the development of the block are pathologies of the urinary tract valves, as well as diverticula in the ureter.
Diagnostics
In addition to the symptoms and treatment of kidney block, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the main options for laboratory and instrumental diagnosis of this serious condition. To identify kidney block due to hydronephrosis, the following diagnostic measures are used:
- An ultrasound technique for examining the kidneys, which allows you to determine the size of the organ, measure the thickness of the parenchyma, and also identify the expansion of the pyelocaliceal apparatus. In addition, the ultrasound method is able to recognize the presence of kidney stones, determine their exact location and size.
- General clinical examination of blood and urine. A general blood test is not the main method for diagnosing renal block, but thanks to this study, it is possible to identify specific markers of inflammation. A general examination of urine may reveal blood fragments, leukocyturia, and protein fragments.
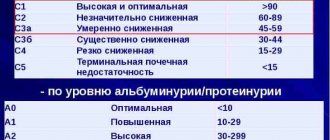
- Laboratory blood test for creatinine level. An increase in this marker indicates the development of structural damage in the kidney area. The higher the creatinine level, the greater the percentage of renal parenchyma involved in the pathological process.
- A pyelography technique that allows you to identify the location of a renal calculus (if present).
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the kidneys.
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis): causes of formation, symptoms and treatment of kidney stones
In the literature there are other names for the problem - nephrolithiasis. The pathology affects both men and women. The disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which makes it relatively easy to diagnose.
Types of stones
Kidney stones in men and women may differ depending on the causes of the development of the pathological process. The chemical composition of clots of insoluble salts plays a key role in the classification of stones.
Types of kidney stones:
- Calcium - 70% of all clinical cases. The stones gradually grow with partial or complete blockage of the urinary tract.
- Uric acids - 15% in general statistics.
- Infected – 10-15%. A prerequisite for this type of stone is the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the structure of the stone.
- Cystine – 2-3%. The rarest type of kidney stones.
The chemical composition of insoluble particles in the urinary tract cavity has little effect on the clinical picture of the disease. It is possible to determine the structure of the stones only after removing the stones from the lumen of the urinary tract.
Features of pain
Urolithiasis is a disease that is accompanied by pain in 99% of cases. Characteristic complaints and features of the clinical picture allow the doctor to accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
Features of pain in nephrolithiasis:
- Paroxysmal character. Pain occurs when the stone moves through the urinary tract. When the stone stops, the discomfort subsides.
- Expressiveness. Renal colic is one of the most severe discomforts, second only to ear pain.
- Change of localization, depending on the advancement of the stone. If the stone is located near the exit of the kidney, the patient complains of lower back pain. The advancement of the stone into the ureter area provokes discomfort in the lower abdomen with transition to the thigh. If the stone approaches the exit from the urethra, then the pain additionally migrates to the genitals.
- Weakening when drinking alcohol and performing thermal procedures. The reason is temporary relaxation of smooth muscles and easier passage of stones through the urinary tract. For renal colic, it is recommended to take a hot bath to reduce the severity of the main symptom.
- The appearance of cloudy impurities in the urine at the peak of the pain syndrome. The reason is mechanical damage to the wall of the excretory tract, which is accompanied by the rapid addition of a secondary infection.
Patients suffering from renal colic note a frequent desire to go to the toilet. Urination is painful with the release of a small portion of liquid.
Symptoms
The symptoms of kidney block will directly depend on the cause of the pathology, as well as on the form of the disease. In case of acute obstruction of the urinary tract, clinical symptoms increase over a short period of time, leading to severe complications within a few hours from the moment of obstruction of the urinary tract. The main symptoms of acute kidney block include:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Acute pain syndrome (renal colic).
- Feverish condition.
- Frequent painful urge to empty the bladder, which is accompanied by the release of minimal portions of urine or its complete absence.
- Increased gas formation in the intestines (flatulence).
- Pain in the lumbar region on the left or right, as well as girdle pain, which can radiate to the left or right iliac region, as well as to the perineum.
- The appearance of clinical symptoms of infectious inflammatory damage to the urinary system, which is typical for the addition of a secondary infection against the background of stagnation of urine.
If the disease develops gradually, the intensity of clinical manifestations may increase over several weeks or several months. The severity of pain and the nature of urination disorders will depend on the degree of increase in the volume of the blocked kidney, and on the level of capsule stretching. Patients with a sluggish growing kidney block may complain of nagging pain in the lower back, increased urge to urinate, general malaise and an increase in body temperature to low-grade levels.
Complications
- Infections of the urinary system: acute and chronic pyelonephritis, suppuration of the retroperitoneal space (fatty tissue in which the kidneys are located), urosepsis, etc.
- Hydronephrosis. Long-term partial obstruction of the ureter by a stone leads to chronic overstretching of the renal pelvis, which in turn causes atrophy of the kidney tissue. As a result, the kidney actually dies, turning into a bag of urine (see kidney hydronephrosis).
- Chronic renal failure. An increase in urine pressure in the urinary tract caused by stones, in combination with chronic infection, causes destruction of the filtering apparatus of the kidneys and sclerosis of its tissues. As a result, the kidneys cease to cope with their functions, up to the complete cessation of urine formation.
Causes
The following risk factors predispose to the disease:
- decreased intra-abdominal pressure against the background of decreased muscle tone of the abdominal wall due to complications resulting from multiple pregnancy;
- abnormalities in the fixing ligamentous apparatus of the kidney;
- depletion of the fatty capsule of the organ after urinary tract infections or poor diet;
- injury to the pelvic area with rupture, sprain, and formation of perinephric hematomas;
- external influences in the form of vibration, shaking, heavy physical activity, power sports;
- in adolescence due to spasmodic growth and sudden changes in body weight;
- genetic predisposition - rarely recorded.
Therapy methods
Treatment tactics depend on the stage of development of nephroptosis in the right kidney; conservative and surgical methods are most widely used.
Conservative treatment
Before complications develop, at the first stage of the disease, conservative therapy consists of following several rules:
- to fix the kidney, orthopedic treatment is prescribed using bandages, belts, corsets made according to individual parameters;
- the patient needs a special course of exercise therapy to strengthen the muscle corset, which will restore muscle tone, normalize intra-abdominal pressure, and limit organ hypermobility;
- the patient needs to avoid heavy physical activity;
- sanatorium treatment with hydrotherapy is indicated;
- complete balanced nutrition, with the appointment of a high-calorie diet with low body weight.
Medications are prescribed if the patient has developed chronic diseases as a result of organ prolapse.
For example, if you have high blood pressure, you need to take antihypertensive drugs. Antibacterial therapy is indicated for exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis.
Monitoring by a urologist with regular examination is recommended. Every six months you need to take a urine test, do a biochemical blood test, undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, and radioisotope renography. The essence of observation comes down to confidence in the absence of negative dynamics.
If conservative treatment does not give the expected effect and the disease progresses, the patient is prescribed surgery.
Surgery
The purpose of the operation is to fix the kidney in the physiological bed and eliminate its hypermobility.
The indication for the surgical method - nephropexy - is the prolapse of the organ by 3 vertebrae or more.
This is the third phase of the development of the disease, there are signs of decreased blood flow in the renal vessels, functional impairment, and relapses of urinary tract infections.
Nephropexy is performed using the classic lumbotomy method, or laparoscopy is used, a minimally invasive method.
Traditional surgery is accompanied by increased blood loss, trauma and a long postoperative period.
Laparoscopy is preferable due to the short recovery period. During the operation, safe polypropylene mesh implants are implanted; they hold the organ in a physiological bed. The effect of the method is 95%, relapses are extremely rare.
Postoperative rehabilitation within 3 months, the patient is prescribed a special regimen. It is necessary to wear orthopedic aids and avoid lifting heavy objects. Medical supervision consists of examination, monitoring the results of laboratory tests, undergoing ultrasound and urography procedures every three months.
ethnoscience
The goal of using alternative medicine is to strengthen the body's defenses, reduce the intensity of pain symptoms, and prevent complications of nephroptosis.
They are used in the initial stages of the disease in parallel with conservative treatment.
It is advisable for patients to use natural preparations continuously throughout the course of their illness. Here are some proven folk recipes:
- Sprinkle lightly moistened flax seeds with husks with powdered sugar and fry in a dry frying pan. Consume in small portions 3-4 rubles. in a day. Flaxseed can be replaced with peeled sunflower and pumpkin seeds.
- Crushed stems of Kochia coronata (summer cypress) in the amount of 2 tbsp. pour 1.5 cups of boiling water into a thermos and leave overnight. Drink the infusion 3-4 r. per day before meals, 50 ml. It contains oils and enzymes that are beneficial for the kidneys.
- Pour three teaspoons of crushed onion peel into 500 ml of boiling water, strain after 30 minutes. Drink one spoon four times a day.
- To 100g honey add 15g butter, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of coffee made from acorns, 4 yolks from domestic chicken eggs. Mix the ingredients. Take 2 hours a day. spoons after meals.
Baths will help prevent further development of the disease and alleviate the patient’s condition:
- Pour 1 kg of chopped oat straw into 20 liters of water, bring to a boil, and simmer for 60 minutes over low heat. Add the strained infusion to the bath. Take the procedure for half an hour 2 times a day with an interval of 10 hours, repeat every other day.
- An infusion of crushed Jerusalem artichoke leaves and flowers in a proportion of 3 tbsp. add spoons per 1 liter of boiling water to a sitz bath. The procedure is carried out daily before bed for 15 minutes. Instead of Jerusalem artichoke, you can use horsetail.
It is important to note that the temperature of the water in the bath should be maintained at 38 degrees.
Therapeutic baths remove excess fluid from the body, thereby relieving stress and pain from the kidneys.
Courses of 10 procedures with a break of 1 month are recommended.
In addition, many other procedures are effective: honey applications, kidney teas, turpentine baths, they should be carried out according to the instructions of A.S. Zalmanov.