Indications for surgery
Surgery can only be recommended if the benefits from it are greater than the risks from the surgery itself:
- The patient has a clear violation of the outflow of urine. In very advanced cases, urine may not be released at all.
- The kidneys are unable to function properly.
- Presence of chronic renal failure.
- This organ often becomes inflamed.
- The presence of severe pain that complicates the patient’s life.
Quite often, the kidney can be saved and its functionality restored. Only in the most advanced cases do doctors have to resort to complete or partial removal of these organs. Also, during the treatment process, you will definitely need to take medications that will destroy bacteria and relieve spasm and inflammation.
Restrictions and contraindications
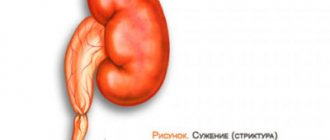
Stenting has a number of limitations that are taken into account when choosing methods for treating urological diseases. Artificial dilatation of narrowed ducts is not resorted to when:
- exacerbation of genitourinary infections;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- renal failure;
- tendency to internal bleeding;
- allergies to PVC, silicone or other materials.
Ignoring contraindications is dangerous due to internal bleeding and hematuria (blood in the urine).
Preoperative preparation
The preparation period depends on the patient’s condition and how the disease progressed. If a large amount of nitrogenous bases was found in the blood, then the doctor first prescribes a diet and medication, and only after the condition has normalized can surgery be performed.
But first of all, doctors need to assess the performance of the kidneys and ureters. It is necessary to submit urine for bacterial culture. If bacteria are found in urine, then in mild forms of hydronephrosis, antimicrobial drugs may well cope with the problem, and surgical intervention will not be necessary. You will also need to do a kidney x-ray, an ECG and some other tests, depending on the patient's general health. The day before surgery, you can only eat liquid food. In the evening, the patient is given laxatives or an enema.
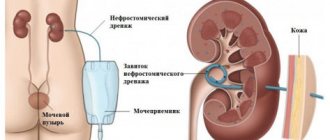
Next, the kidney is drained. This is a manipulation in which urine is removed from the kidneys into a urinal using rubber tubes. In surgery, there are two methods of performing this procedure: open nephrostomy and percutaneous puncture nephrostomy.
In the first case, the doctor makes an incision in the lumbar region, then in the kidney, and through it inserts a catheter into the pelvis. Then it is sewn to the skin, and after the wound is sutured, it is attached to a urinal.
In the second case, an ultrasound machine is required. The patient is given local anesthesia, then a puncture is made in the kidney area, and when the needle reaches the pelvis, it is filled with a contrast agent. Next, a special conductor is inserted into the needle, the needle is removed, and a tube is passed through the conductor, through which urine will flow. It is attached to the skin. All this takes an experienced doctor no more than half an hour.
Installation of drainage is necessary if:
- The patient has chronic renal failure.
- There is severe inflammation of the kidneys.
- Hydronephrosis grade 3.
- The patient is in serious condition.
- In addition to drainage, you also need to cleanse the blood. This can be done in the following ways:
- Hemodialysis is a procedure in which blood is removed from the body, purified, and then returned back.
- Peritoneal dialysis is the purification of blood inside the body.
Are there ways to predict the course of hydronephrosis in a newborn?
There is currently no method to determine how hydronephrosis will develop in a newborn. Therefore, the most correct approach is to monitor the condition of the kidney over time by an experienced urologist. The main method of assessment during dynamic observation is ultrasound. The difficulty of predicting the development of hydronephrosis in a newborn is determined by unstable water metabolism, changing kidney function, as well as the possibility of ripening (maturation) of its organs and tissues. These processes can lead to the disappearance of the expansion of the pelvis or stabilization of its size. At the same time, with long intervals between examinations (more than 2 months), you may miss the onset of deterioration in the kidney’s condition and be late for surgery.
Types of surgical intervention
Pyeloplasty for hydronephrosis is the preferred type of operation, since it does not remove the kidney, but simply changes the structure of the damaged pelvis. It comes in the following types:
Open surgery
This type of plastic surgery is performed under general anesthesia. It is carried out subcostally. The patient is placed on his back or on his healthy side, if possible. Next, the doctor makes a small incision in the area of the damaged kidney, opens its lower part and removes the damaged areas along with the diseased pelvis. The wound is then sutured. You need to make sure that there are no leaks after the operation, otherwise complications may arise.
If the pelvis is located inside the kidney, then after removing the sections, the healthy end of the ureter must be inserted and sewn directly into the kidney.
Endoscopic methods
The entire process occurs through the urethra. Initially, a camera is inserted there, with the help of which the entire further procedure for removing damaged areas is controlled. During the operation, the integrity of the skin and soft tissues is not compromised, so patients quickly return to normal. There are two of them:
- Bougienage. A rod (bougie) with an increased diameter is inserted into the ureter through the urethra. Due to its action, the lumen of the ureter becomes larger and the outflow of urine is normalized.
- Balloon dilatation. In order to remove the narrowing through the urethra, a camera and a lighting device are inserted, as well as a catheter with a balloon. When the balloon hits the painful area, it inflates and remains there for two minutes, causing the ureter to expand.
Laparoscopy
It is performed under anesthesia. The patient lies on his side, he is fixed with elastic bandages and bolsters. During surgery, the patient's position may change.
A pair of incisions about 1 cm long are made on the stomach, side or back of the patient (depending on where the affected area is located). A camera and a flashlight are inserted into the first incision, through the remaining instruments necessary for the operation. To make the working space larger, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas. Next, the surgeon removes the enlarged pelvis and sews the ureters into the kidneys. Postoperative incisions of the skin and soft tissues are very small, so no stitches are required, only bandages are used.
Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy is an operation during which an organ is removed.
This type of surgery is performed provided that only one kidney is damaged. It is carried out at the last stage of hydronephrosis, if the kidney is almost completely atrophied and cannot function correctly. It is dangerous to leave it because of the possibility of infection accumulating in it.
Surgical treatment of hydronephrosis in children differs from operations performed on adults.
If this disease was detected in a child during fetal development, and it progresses rapidly, then surgery can be performed even before the baby is born.
Ureteroplasty for hydronephrosis is usually necessary if it was damaged during surgery. It happens:
- Intestinal. The ureter is formed from part of the small intestine.
- The ureter is formed from the tissue of the bladder stem.
If the first degree of the disease is detected after birth, then it is quite possible to do without surgery and cope with the disease with the help of medications.
In the second stage, one of the following types of surgical intervention is used:
- Ureteral stenting - a tube of the required diameter is inserted into the place where the ureter exits through the kidneys, which prevents its collapse.
- Pyeloplasty.
- Nephrostomy - a catheter is inserted into this organ, through which urine will be discharged into a urinal.
- In case of the third degree of the disease in children, the last two types of operations are also performed.
Laparoscopic operations for renal pathology
These are the most effective and least traumatic methods of performing surgery for plastic surgery of a distended pelvis. The same actions are performed as during open intervention (excision of the distended membrane of the pelvis, suturing of the ureter into the kidney), but special instruments are used, inserted through a probe. Operative access is carried out through two small incisions (up to 2 cm). A probe with a camera and lighting is inserted into one, and a special tube with instruments is inserted into the other. It is now even possible to perform nephrectomy (organ removal) using laparoscopy.
Postoperative period
The postoperative period passes, as a rule, without complications if the patient follows the doctors’ recommendations. If the surgical method was chosen correctly, then recovery occurs quite quickly, but, of course, this also depends on what stage the disease was at. It is very important to follow all doctor's recommendations. Rehabilitation takes place in the hospital for another two weeks, the patient regularly has stitches treated and bandages changed.
All necessary tests will also be taken from the patient again. Bad urine tests after surgery do not mean that anything was done wrong. After all, the operated person continues to receive drug treatment for several days. Bacteria in the urine after surgery are well destroyed with the help of antibiotics, and the patient is also given antiviral drugs.
Types of stenting and techniques
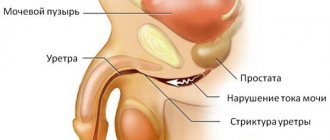
Stent placement is performed using different methods. The choice of technique depends on the anatomical features of the urinary system and the degree of narrowing of the ureter.
Retrograde
Retrograde stenting is the placement of a supporting frame in the narrowed part of the duct in an ascending manner through the urea. Performed in case of severe compaction of the duct walls, pregnancy, urolithiasis, tumors. The following tools are required for the operation:
- cystoscope;
- catheter;
- stent;
- equipment for ultrasonic control of the procedure.
Installation of a stent in the ureter is carried out as follows:
- under anesthesia, a catheter with a stent at the end is inserted into the urethra;
- the surgeon installs an expansion tube into the deformed part of the ureter under the control of a cystoscope.
After the procedure is completed, an x-ray is taken to ensure that the drainage tube is placed correctly.
Antegrade
Antegrade ureteral stenting is recommended for injuries and strictures of the urethra, exacerbation of urethritis. The operation is performed according to the following scheme:
- under anesthesia, an incision is made in the lower back;
- the end of the stent is installed in the renal pelvis;
- the second end is connected to an external urinal.
To avoid negative consequences, the stent catheter is closed for 3 days. During this time, the patient is under the supervision of a urologist.
Forecast
If the disease affects only one kidney, then the outcome is positive, although much depends on how badly it was affected. But, as a rule, if the operation is performed well, and in the future the patient complies with all the doctor’s instructions, then recovery occurs in 90% of cases.
With bilateral hydronephrosis, it is impossible to make an accurate prognosis, since the kidney tissue is inflamed and atrophied, which means there is serious renal failure.
It is much easier to treat the disease if it was detected at an early stage and irreversible changes have not yet occurred. Therefore, as soon as signs of this disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Features of stenting in children and pregnancy
Pregnant women and young children are more susceptible to urinary tract infections, which is associated with:
- immaturity of the immune system in children;
- natural decrease in immunity in pregnant women;
- hormonal imbalance.
To avoid dangerous complications, surgeons resort to retrograde stenting of a narrowed fragment of the ureter. Only elastic tubes made of hypoallergenic materials are used as drainage devices. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Stagnation of urine in pregnant women is dangerous due to gestational pyelonephritis and kidney abscess. To avoid serious complications, long stents up to 50-70 cm in length are placed in the ureter.
When installing an expansion tube into the ureter, the surgeon must make “allowances” taking into account the further development of the fetus. The stent is removed 1-3 weeks after delivery.
How much does a stent and surgery cost in Moscow?
The cost of stenting is influenced by various factors: the type of stent, the need for endoscopic bougienage of the ureter, the length and location of the narrowed section of the duct.
Cost of stent catheters:
| Types of drainage system | Cost in rubles |
| silicone with metal frame | 5000-5900 |
| PVC perforated | 4800-5200 |
| polyurethane two-loop | 2900-3000 |
| with rigid conductor and pusher | 7000-7500 |
| with appliqué threads without conductor | 3500-3800 |
| closed with Teflon coating and conductor | 4500-4900 |
Installation of a ureteral catheter without taking into account the cost of the stent varies between 7,000-10,000 rubles. It is recommended to carry out the operation, replacement and removal of drainage devices in special clinics with modern equipment.
Stenting is a gentle operation that restores the patency of the urinary ducts. It prevents many urological diseases - hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, kidney necrosis. If the rehabilitation rules are followed, complications after the procedure are extremely rare.
Consequences
Stenting is an operation that is sometimes accompanied by early or late complications. In the first days after the procedure, a third of patients complain of:
- burning in the urethra;
- discomfort in the suprapubic area;
- pain when urinating.
In 76% of cases, symptoms go away on their own within 1-3 days.
If you have lower back pain and high fever, you should consult a urologist. Blood clots in the urine sometimes indicate damage to the walls of the urinary canals by the stent catheter.
Complications with a stent in the ureter:
- pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- migration (displacement) of the stent;
- fouling of the tube with salts;
- fistulas in the ureter;
- reverse flow of urine.
If the technology for installing the drainage tube is not followed, its destruction is possible. Therefore, it is recommended to perform the procedure under X-ray control.
Rehabilitation after installation of a urological stent
After installation of the drainage device, a recovery period follows. To prevent complications, patients should:
- Eat properly. To prevent irritation to the ducts, avoid spices, marinades, spicy foods, preserves, and sauerkraut. Ban on citrus fruits, mushroom broths and alcoholic drinks. During the first 1.5-2 weeks you need to drink more fluid. Suitable drinks include cranberry juice, still mineral water, weak tea, and rose hip decoction.
- Take antibiotics. The stent catheter is a foreign body that the body is trying to get rid of. After surgery, local immunity decreases, which increases the risk of infectious inflammation. Therefore, to prevent complications, they take antimicrobial agents and uroseptics - Nolitsin, Nitroxoline, Monural.
- Get checked regularly. On the recommendation of a urologist, urine and blood tests are taken once every 2-3 weeks. Hematuria indicates damage to the ureteral wall by the stent. According to indications, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the excretory system and urography.
Pregnant women should be constantly monitored by a urologist. As the fetus grows, the ureter stretches, and its individual parts are compressed. To prevent inflammation and pain, herbal uroseptics are prescribed - Canephron N, Fitolysin. Before giving birth, patients must undergo an ultrasound examination and laboratory tests. The stent is usually removed after delivery.
After installation of a ureteral stent, many have a high concentration of leukocytes and proteins in the urine. But in 75% of cases this is due solely to the presence of a foreign body in the body.