Urinary incontinence after prostate cancer removal ● All treatments ●
Problems with urination occur in more than half of men who have had a prostatectomy.
Surgical treatment is prescribed when pathological formations are detected in the prostate gland, as well as for complications caused by prolonged inflammatory processes. With advanced prostate disease, tissue is replaced with connective tissue. Currently, experts consider the prostatectomy method to be the most effective for malignant lesions of the gland. After its resection (TUR), urinary incontinence may develop. If such a disorder occurs, the patient should consult a urologist.
When is therapy required?
Unpleasant symptoms that appear after prostate surgery most often disappear within a year. With correct treatment and the doctor prescribing effective medications, the time for complete restoration of the function of the urinary system is 6 months.
You should know that signs of urinary incontinence after resection of the gland appear in many representatives of the stronger sex. TUR is considered a serious surgical method that contributes to the appearance of tissue swelling and dysfunction of nerve cells and blood vessels.
During resection, the surgeon removes part of the urethra and sphincter tissue associated with the gland. As a result of such intervention, damage to these areas occurs, which leads to urinary incontinence. Treatment of malignant tumors is often carried out using radiation, which also leads to problems with urination.
What is radical prostatectomy
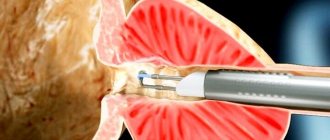
Radical prostatectomy is the most effective operation for removing tumors from the prostate and fighting cancer. It represents the complete removal of the seminal vesicles, glandular tissue and its capsule.
If there are indications, the iliac lymph node systems are removed. This type of surgical intervention, in addition to many advantages, has one drawback - incontinence, which occurs in every patient after the operation.
Today, problems with urination due to prostatitis can be eliminated using alternative and medicinal methods.
Treatment tactics for each patient are determined depending on the stage of development of the disease. Tumor removal is most often performed in one of the following ways:
- Radical prostatectomy - the most effective way to treat severe adenoma and cancer is the complete removal of the prostate gland.
- Transurethral resection is the excision of part of the prostate by inserting a special mini-instrument through the urethra.
Radical prostatectomy, today, is the most famous method of treating cancer in the field of urology
Prostatectomy should never be performed if:
- the patient constantly takes medications to thin the blood;
- there are acute inflammatory processes in the body;
- patient age over 70 years;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular failure, which is in the stage of decompensation.
The effectiveness of surgical treatment of prostate diseases has been clinically proven. Soon after surgery, patients experience relief and improvement, and most patients with cancer manage to extend their life by at least 2-3 years, to a maximum of a decade.
Recovery methods
After resection of the prostate, the rehabilitation period begins. On the first day, patients require catheterization. Men should exercise caution after installing the device. By following all the doctor’s recommendations, the risk of complications is significantly reduced.
After removing the catheter, blood often appears in the urine, and a man may feel a burning sensation when urinating. Patients also often experience an increased urge to empty the bladder. Such symptoms are considered normal after TURP of the prostate .
To speed up recovery, doctors recommend that patients follow the following rules:
- Do Kegel exercises. It helps restore the muscle fibers of the pelvic organs. The exercise involves tensing and relaxing the anus and perineum area.
- Stick to a diet. Pickled dishes, spicy foods, and alcoholic drinks should be excluded from the menu. It is also advisable to drink tea and coffee as rarely as possible due to their diuretic properties.
- Get physical therapy. Electrical muscle stimulation allows you to get rid of urinary incontinence and frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Use special pads to protect linen and hygiene.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Bladder catheterization procedure in men and women
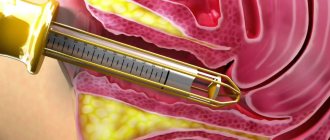
Bladder catheterization is a procedure that is prescribed if the natural outflow of urine is disrupted for pathological reasons.
There are two types of urinary catheter: metal (hard) and rubber.
Urine can be removed catheterally and the inside of the urethra can be disinfected with antibacterial agents by rinsing (the procedure is prescribed in case of infection).
The bladder catheterization procedure itself is absolutely painless when performed correctly. This procedure has been carried out for a long time and still many patients are frightened by such manipulations performed by medical personnel.
Sometimes you can encounter misunderstanding on the part of patients and refusal to catheterize the bladder, which makes further implementation of this procedure difficult.
All this happens due to a lack of information among people about catheterization, which is quite easy to fix.
What does bladder catheterization look like? This procedure involves inserting a catheter tube into the inside of the bladder. Carrying out the procedure correctly will require experience and skill on the part of medical professionals.
It will not be a bad idea to establish trust between the patient and the doctor, since during the procedure it is necessary to completely relax and accurately follow the doctor’s commands so that no complications or painful sensations arise.
Indications for bladder catheterization are:
- disturbance of urine outflow;
- complications resulting from an infectious disease;
- taking urine for diagnostic purposes.
There are many reasons why the outflow of urine may be impaired, and all of them can develop hydronephrosis (a disease that occurs in the kidney cavity due to excess fluid). The most common causes of urine retention include the following diseases:
Treatment
After a correct diagnosis, the doctor can prescribe specialized, adequate treatment.
- Urethritis. For urethritis, antibiotics or other antibacterial drugs are prescribed depending on the pathogen. With acute urethritis and early treatment, complete recovery is possible. Sluggish chronic processes are more difficult to treat and require additional measures (stimulants, restorative drugs, adaptogens).
- Urolithiasis disease. For urolithiasis, the ultrasonic crushing method is widely used. When stones are localized in the bladder, it is sometimes difficult to aim the apparatus when crushing directly at the stone due to its high mobility. In this case, an endoscope and special instruments are used - lithotripters, which are inserted directly into the bladder.
- Prostate pathologies. When treating chronic prostatitis, an integrated approach is required. In addition to antibacterial drugs (antibiotics, nitrofurans), restoratives, physiotherapy, and prostate massage through the rectum are recommended. In case of severe inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antispasmodics (papaverine, no-spa) are prescribed. Electrical stimulation and magnetic therapy help well. The effectiveness of the measures taken strongly depends on the stage of the process and the degree of its severity.
- Urethral stricture. Laser correction is widely used in the treatment of urethral strictures with accompanying pain during urination. Urethroplasty is also effective, in which donor tissue from the patient himself (parts of the buccal mucosa or foreskin) is transplanted into the affected area of the urethra. The tissues take root well and restore urine flow.
- Consequences of catheterization. Cutting and pain after insertion of the catheter, as a rule, does not require additional treatment and goes away on its own. But you need to be completely sure that there is no infection and the cause is related only to catheterization. Sometimes a short course of nitrofurans (5-noc, nitroxaline) is additionally prescribed to prevent infection.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease and the man’s complaints. Next, he examines his genitals for rashes and discharge.
The next step is a rectal examination of the prostate. The contours of the organ, its soreness and boundaries will help in making a diagnosis. The doctor then orders a series of tests.
Urine is examined for the presence of leukocytes and protein. Bacteriological culture is also done. A secretion is taken from the gland and a smear is taken from the urethra. In some cases, if cancer is suspected, an organ biopsy is performed.
Incontinence with prostatitis
Problems with urination often develop with acute inflammation of the prostate. The chronic form of the disease is rarely accompanied by incontinence. Most often, with low-grade inflammation, men suffer from pain that occurs when the bladder is emptied.
When problems arise with urine retention due to prostatitis, doctors prescribe a set of diagnostic measures, including laboratory testing of biomaterials for infections and transurethral ultrasound.
Treatment for inflammation in the prostate
With proper therapy, problems with frequent urination usually disappear completely. By eliminating inflammation in the tissues of the gland, the symptoms of irritation of the nerve endings of the urethra are reduced.
The course of treatment includes the use of antibacterial drugs, alpha-blockers, and analgesics. To reduce swelling of the prostate tissue, special massage and physiotherapy are performed. With the approval of the urologist, patients perform prostate massage procedures at home. They are performed with a special device or finger.
Kegel exercises help strengthen muscles and improve microcirculation in the pelvis. It is also useful to squat and cross your legs while lying on your back. Exercises must be done regularly.
To eliminate problems with urine retention, traditional medicine methods can be used.
The following methods have a good effect:
- An infusion containing valerian, St. John's wort, hops, and knotweed. The product is prepared from 2 tbsp. collection and a glass of boiling water. Drink 1/3 cup twice a day.
- Dill seed infusion. Taken several times a day.
- A decoction of bird cherry bark collected during flowering. The drink is taken in a glass 2-3 times a day.
- Carrot juice. Drink a glass 30 minutes before breakfast.
- Drink made from plantain leaves. Taken 4 times a day on an empty stomach.
- An infusion consisting of birch leaves, St. John's wort, and yarrow. Drink three times a day.
Preventative measures to help avoid problems with urine retention include:
- regular bladder emptying;
- exclusion of harmful foods from the menu;
- regular exercise;
- visiting a urologist 1-2 times a year.
The problem of urinary incontinence occurs in many patients who have undergone TURP of the prostate. In most cases, it goes away within 6-8 months after surgery.
If symptoms persist, drug treatment is carried out. Compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions, hygiene rules, and the elimination of physical inactivity can help you get rid of urinary incontinence forever.
You might be interested
Postoperative enuresis during removal of prostate adenoma
Prostate adenoma is a pressing problem of not only medical but also social significance. If earlier it bothered mature and elderly men, today it is easy to identify in young people. The most effective way to combat male pathology is surgery.
After complete or partial resection of the prostate gland, the urinary process is disrupted in most patients. The likelihood of developing uncontrolled bladder emptying is determined by many factors. According to various data, its frequency ranges from 3% to 80%. Since this pathology is a problem of social maladaptation, its correction is an important task of modern medicine.
Urinary incontinence in men can occur after removal of the prostate by any surgical method. Experts identify several types of this disorder, each of which appears as a result of a specific exposure factor.
- Stressful. Characterized by droplets or small amounts of urine, it occurs due to sudden tension in the abdominal muscles during sneezing, coughing, laughing, and other types of physical activity.
- Orthostatic. Episodic incontinence that occurs regardless of the time of day, body position and intensity of physical activity. Develops due to frequent imperative urge to urinate.
- Total. Periodic or constant leakage of urine in large volumes. Develops against the background of spinal cord and urinary tract injuries during surgery.
A mixed type of incontinence is often observed, combining several varieties with the same severity of characteristic signs or with a predominance of one of them.
Urinary incontinence after a TUR of prostate adenoma is considered a common occurrence. In this case, the mechanism of occurrence of pathology can be determined by a wide variety of factors.
- Postoperative catheterization. Removing the tube provokes the involuntary release of urine.
- Secondary infections. They develop against a background of weakened immunity.
- Detrusor hyperactivity.
- Loss of urinary control due to spinal nerve injury.
- Removal of the bladder sphincter during surgery.
- Damage to the pelvic organs.
- General intoxication of the body.
In some cases, uncontrolled urination occurs due to shock.
Since incontinence in medicine is considered a symptomatic complex, experts divide all factors into two groups: intraoperative, discussed above, and preoperative. The latter includes:
- patient's age;
- prostate size;
- presence of urinary disorders;
- PSA level in the blood;
- body mass.
Considering the nature and intensity of uncontrolled urination, it is the last indicator (extra pounds) that doctors pay great attention to. They believe that with adequate physical training, the patient’s weight decreases and pelvic muscle tone is observed, which reduces the likelihood of developing incontinence or shortens the recovery process.
Urinary incontinence after radical robotic prostatectomy
After robot-assisted prostatectomy, the urethral catheter is removed on days 4-7. Before removing the catheter, an X-ray examination (retrographic cystography) is performed, the results of which determine the integrity of the vesicourethral anastomosis. Removing the catheter takes 10-15 seconds and is a painless procedure.
After removal of the urethral catheter, symptoms of stress urinary incontinence may occur, which will decrease day by day. Urine leakage may last from several days to several weeks. In the first days after surgery, some patients may not feel the urge to urinate, while others, on the contrary, note an excessively frequent urge to urinate both during the day and at night. You should not give in to anxiety; most likely, these symptoms will go away in the coming days. The first day after surgery, it is necessary to keep a urination diary indicating the time of urination and the volume of urine released. When dripping urine, you should stock up on special urological pads that will add confidence to you.
Examination to determine the cause
Frequent urge to defecate at night, urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction after removal of prostate cancer disappears on its own within a year. Otherwise, the patient is recommended to undergo examination. First of all, a consultation with a neurologist is carried out. It is necessary to determine the degree of preservation of sensitivity in the perianal region and perineum, to exclude diseases of the spinal cord and to assess the likelihood of damage to peripheral nerves.
Next, laboratory tests are prescribed, among which the main ones are:
- general urine analysis;
- Nechiporenko test to exclude the inflammatory process;
- culture for the pathogen if infection is suspected;
- blood test to determine glucose levels.
The latter is performed in order to exclude diabetes mellitus, which is characterized by the production of large amounts of urine, which increases the frequency of the urge to defecate.
Instrumental diagnostics includes a list of the following procedures.
- Ultrasound. The condition of the pelvic organs is assessed, as well as the amount of residual urine is determined after the act of urination.
- Cystoscopy. Allows you to identify damage to the bladder mucosa and its etiology.
- Uroflowmetry. The evacuation function of the bladder during the natural act of emptying is assessed.
- Cystometry. Helps determine intravesical pressure and assess detrusor overactivity.
The patient performs a cough test to visually assess the degree of urinary incontinence. In addition, he is asked to keep a diary, the readings of which will help control the quality and volume of urine excreted, as well as the frequency of urination.
Postoperative period
After bladder surgery, they must resort to rehabilitation methods. The postoperative period is divided into two stages: inpatient rehabilitation and recovery at home. The hospital uses the following methods:
Rules that the patient must follow at home after surgery and discharge from the hospital:
- Systematically clean the area where the catheter was inserted. Doctors recommend using warm water and soap for these purposes.
- To quickly restore the bladder, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
- For 2 months after discharge from the hospital, it is prohibited to engage in active physical activity and lift heavy objects.
- He is allowed to start intimacy only after a month.
- Avoid consumption of fried, fatty and spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, and coffee.
3 days after surgery, patients often complain of pain in the bladder area, as well as a frequent desire to go to the toilet. These unwanted reactions leave people within a week. If the patient follows all rehabilitation recommendations, recovery is quick and takes a month.
Why is a urine test taken through this device?
Urine collection with a Foley catheter is indicated after internal surgery or after a cesarean section to ensure that bladder surgery was successful. Bladder catheterization can be used to determine whether there are inflammatory processes in the internal organ (prescribed if blood is detected in the urine).
In addition, urine catheter testing is more accurate than regular urine testing. This is due to the fact that urine does not pass through the urethra. In this way, the condition of the kidneys and bladder can be accurately determined. You need to provide urine with a catheter with the help of a medical professional.
A pregnant woman may encounter a catheter several times during her special condition: during a urine test, when the fetus is too low (it can pinch the ureters), immediately before and after childbirth.
What is bladder catheterization, what is it for, consequences
According to statistics, every second man in old age and every third on average are faced with diseases of the genitourinary system. Prostatitis is considered the most common; in addition, there are a number of diseases that seriously complicate the process of urination and are also difficult to diagnose in the laboratory. To facilitate the examination process, bladder catheterization is used in men.
In general, the bladder catheterization algorithm involves inserting a small silicone tube into the bladder cavity through the urethra. For certain indications, a catheter can be inserted not through the urethra, but by penetrating the peritoneum. Also, such a procedure involves not only helping the patient, but also helping specialists in determining the origin of a particular illness, after which the correct approach to therapy is possible.
What is this procedure and why is it performed?
Bladder catheterization is one of the ways to maintain the functions of this internal organ during the period of treatment and recovery of the patient. There are a number of diseases of the genitourinary system, as a result of which a man is unable to empty the bladder on his own, or the process of urination causes him severe pain and discomfort. In this case, the catheterization technique is an indispensable procedure.
The main goal of this procedure is to completely empty the bladder, as well as administer medications prescribed by a doctor and wash this internal organ if necessary. This procedure is actively used in the treatment of urological problems in men and women, and bladder catheterization in children is also acceptable.
Indications for the procedure
In order for the procedure to benefit the patient and also help the specialist in determining the etiology of the problem and making a diagnosis, it is necessary to use it only for specific reasons.
Indications for bladder catheterization are as follows:
- stones in the bladder, tumors, and adenoma;
- inflammatory process (cystitis);
- state of coma or shock;
- recovery period after surgery;
- for diagnostic purposes;
- for the purpose of administering drugs during treatment.
Preparatory stage
The preparatory stage should always begin with the health worker explaining the procedure to the patient and obtaining her consent. Next, a nurse or paramedic wearing sterile gloves should treat the external genitalia.
This will help protect the urethra from infection. Next, you need to process all the tools that will be used. The catheter is lubricated with Vaseline. In addition, it is necessary to prepare a container into which urine will be drained.
It is imperative to place a moisture-absorbing diaper (or at least a towel) under the patient. The medical worker must ensure that the procedure is carried out under sterile conditions. If the action is performed at home, then the person must do this entire procedure himself. The preparation methods are the same for men and women.
Indications for catheterization
Placement of a urinary catheter is a common medical procedure that is performed to normalize the flow of urine in various conditions.
Bladder catheterization is indicated for patients undergoing abdominal surgery.
Indications for staging:
- Obstruction of the urinary tract. This process is associated with pathologies: prostate adenoma, tumor of the lower bladder, anaphylactic shock, trauma. In women, urethral obstructions are much less common.
- Surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity. Indications for catheterization are those operations that are performed in the pelvis in women. This is done in order to provide the doctor with access to the uterus and appendages. For men, this manipulation is necessary for surgical treatment of the rectum and sigmoid colon through the abdominal approach.
- Minor gynecological operations. Manipulations performed by a gynecologist, which require the introduction of instruments into the uterine cavity, are carried out exclusively with an empty bladder. One such operation is the treatment of uterine bleeding by curettage. Before the procedure, a catheter is placed so that during the intervention, urine does not accumulate in the bladder of women.
- Hospitalization in the intensive care unit. Patients undergoing treatment in intensive care are subject to catheterization. This is so that medical personnel monitor the amount of urine excreted. In severe illnesses, urine production is often disrupted, which causes complications. It is of great importance for those patients undergoing forced diuresis.
Flexible catheter
The procedure is carried out quickly, and if the medical personnel are sufficiently qualified, no problems arise.
Today there are two types of catheters: flexible and metal. Flexible ones are made of polyvinyl chloride, a hypoallergenic polymer. Used for bladder catheterization in men without prostate disease.
Metal
If a man has prostatitis or prostate adenoma, then a metal one is used to pass through the section of the urethra near which the gland is located.
Postoperative cystitis.
Often, after gynecological and obstetric operations, patients develop cystitis, which can cause bladder dysfunction of various types. According to E. S. Tumanova (1959), of 593 patients who underwent various gynecological operations, 70 (11.8%) had cystitis in the postoperative period.
The disease develops as a result of insufficient asepsis or injury during catheterization, which is forced to resort to due to urinary retention in the postpartum or postoperative periods. Infection of the bladder is facilitated by anatomical changes in it that occur during pregnancy and childbirth, as well as suppurating ovarian cysts, pelvioperitonitis, endometritis, etc. Embolic transfer of infection to the bladder is possible. The infection enters the bladder in various ways: ascending, hematogenous and lymphogenous. Especially often, the infection enters the bladder from the urethra, which constantly contains microflora.
Anatomical and physiological features also contribute to the development of cystitis; short and wide urethra, proximity of the vagina and anus.
From a pathological point of view, catarrhal, hemorrhagic, follicular, ulcerative-necrotic, gangrenous and many other forms are distinguished.
In the pathogenesis of the disease, great importance is attached to local circulatory disorders. The greatest danger is the removal of the uterus for cancer or fibroids, since during these operations the bladder is detached. Embryogenetically, this is due to the common formation of the vagina and bladder triangle, as well as the presence of vascular anastomoses between the uterus and the bladder.
Cooling plays a role in the development of cystitis. There are also antibacterial cystitis caused by taking concentrated medications or erroneously introducing chemicals into the bladder (hydrochloric, acetic acid, alcohol, etc.).
Control of pelvic functions after stroke
Helping a patient with urinary incontinence
Patients with severe brain damage often experience dysfunction of the pelvic organs. In some cases, paralysis of the bladder develops, in which the feeling of its filling and the ability to empty it voluntarily are lost. Lack of bladder control often causes severe depression and feelings of helplessness in people who have had a stroke.
One way to overcome these negative feelings is to remove the ban on discussion from the topic, to deprive it of the “shameful” component. Urinary incontinence is the same body reaction to illness as any other, like pain, like a fracture, like a fever. Information about the disease and methods of its treatment and correction is what people who are faced with the disease or its complications need. Knowing treatment is the first step to symptom relief. Therefore, in the “Communication” section there are no taboo topics, no “shameful” topics, it was created so that you can exchange experiences in overcoming the consequences of a stroke, the experience of living with complications, so that you can get support and advice from those who know first-hand how much labor and emotional stress are hidden behind the dry words “recovery stage”.
In addition, if the bladder is paralyzed, the urine in it may become infected. The infection can spread from the bladder to the kidneys, and then there is a risk of impairment of their function. This significantly complicates the early rehabilitation period.
How to restore urination after a catheter
An indwelling catheter in the bladder can be installed for various reasons, but most often it is due to urinary problems.
If the patient's health improves, the urologist may decide to remove the catheter. After the catheter is removed, doctors will evaluate how the patient empties the bladder without the catheter.
In the following days, you need to monitor your urination patterns yourself.
Discomfort during urination is the most common complication of bladder catheterization. The patient may also complain of frequent urination. These symptoms usually disappear on their own within a few days. In this case, the patient is recommended:
- continue to take the antibiotics prescribed by your doctor (during treatment, do not forget about probiotics, which will help avoid dysbiosis);
- continue taking alpha blockers - drugs that improve urination;
- drink enough fluids;
- Ask your doctor for the results of a urine culture that was taken shortly before discharge from the clinic (if the results are poor, you may need to replace the antibiotic with a more effective one);
- use painkillers (Voltaren, Acamol).
In some cases, patients discover blood in their urine after removing the catheter. As a rule, this indicates damage to the urethral mucosa. This phenomenon disappears on its own within a few days. However, if the bleeding intensifies, you should inform your urologist.
Urinary incontinence
Quite often, patients experience urinary incontinence after bladder catheterization. This phenomenon disappears gradually on its own. Initially, cases of enuresis will be quite frequent, but gradually the frequency of such episodes will decrease and eventually disappear altogether. As a rule, patients note a significant improvement in the situation at the end of the second month after the removal procedure.
To avoid bedwetting, doctors advise drinking enough fluid in the first half of the day and minimizing it in the second half. Tea, coffee and alcohol should be excluded.
During the recovery period, it is not recommended to use urine retention devices such as a penis clamp or condom catheter. If the patient does this, his muscles designed to control urination will not strengthen and enuresis will not disappear.
To regain control over urine retention, experts advise performing Kegel exercises. Their essence is that the pelvic floor muscles need to be alternately tensed and relaxed, and perform pushing movements with them.
At first, the exercise should last 3 seconds, but over time, their duration can be increased to 20 seconds. You can do Kegel exercises several times a day. To feel the pelvic floor muscles, the patient must stop the stream of urine during urination.
To improve the quality of life, the patient can use special pads or diapers. They are sold in every pharmacy. However, you should not abuse them. Some patients continue to wear diapers after their urination has returned. This is done just in case, to be on the safe side.
In such a situation, you can experiment and walk around the house without a diaper to make sure that there is no problem. Many patients have the sensation of leaking urine, although they eventually find that their underwear is completely dry.
Gymnastics
To restore urination after a catheter in men and women faster, the patient can perform the following exercises:
- Take a supine position. Raise your legs one at a time, and then simultaneously for 3 minutes.
- Sit with emphasis on your heels and place your fists in the bladder area. As you exhale, you need to bend forward all the way, and as you inhale, return back. Repeat 8 times.
- Get on your knees, place your hands behind your back. While exhaling sharply, you need to bend over 6 times.
It is worth saying that restoration of urination after a catheter is only possible if the patient performs the exercises regularly.
After class, you need to lie on your back, stretch your legs forward and arms along your body. You need to start relaxing from your toes and further up. Having reached maximum relaxation, you need to lie down for a few minutes.
Quite often, during the rehabilitation period, patients begin taking diuretics. Doing this is contraindicated.
Before starting any exercises, the patient should consult with their doctor, as in some cases they may be contraindicated.
You should seek medical help after removing the catheter in the following cases:
- increase in body temperature to 38° C or more;
- difficulty urinating (especially if the problem gets worse); absolute retention of urine.
It is important to remember that postponing a visit to the doctor until later and doing it on your own can lead to serious consequences. Only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of the problem and explain to the patient how to restore urination after a catheter.
Urinary incontinence after catheter in men: what to do
If the patient was given a catheter to drain urine according to indications, after its removal, fluid may leak for a short time. As he recovers, the situation will stabilize.
To improve your condition, you should follow the recommendations:
- regularly perform therapeutic exercises;
- reduce the amount of liquid you drink at night;
The patient should exclude spicy foods from the diet, as they irritate the bladder receptors. You should avoid eating salty, pickled and smoked foods.
For patient comfort, absorbent pads are used.
Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles
Before surgery, it is necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. After removal of the urethral catheter, you must continue to perform these exercises. During urination, you should try to stop the stream of urine several times and resume urination. Try to tense the muscles around the anus. With these exercises, the rectum is pulled inward, while the abdominal muscles, gluteal muscles and thigh muscles should be relaxed.
Don't overdo it with exercise!! Frequently performing these exercises can cause spasm of the pelvic muscles, which will lead to acute urinary retention. This situation can be resolved by installing a urethral catheter.
There are other types of correction of urinary disorders after radical prostatectomy. Among them are biofeedback exercises, magnetic and electrical stimulation, and surgical correction. You can discuss these types of urination correction with your doctor.
With prostatitis, a man’s quality of life is significantly reduced, since pain in the lower abdomen, decreased potency and libido, and urinary incontinence cause a lot of inconvenience and create psychological discomfort.
Frequent urge to go to the toilet is caused by a narrowing of the urinary canal due to an inflamed organ.
It is impossible to ignore the symptoms for a long time, since as the disease progresses, the man experiences complete urinary incontinence, and cystitis, pyelonephritis and other urological ailments join them.
Treatment options for urinary incontinence
option of surgical intervention for urinary incontinence
Treatment of urinary incontinence after surgery for prostate adenoma always begins with gentle methods. Drug therapy is complemented by physical therapy, through magnetic stimulation of muscle fibers and organs of the pelvic area. A special course of physical therapy is also prescribed. They mainly affect the pelvic floor muscles, which is why they practice Kegel exercises, designed specifically for representatives of the stronger half of the globe.
Since one of the main links in the disruption of the urination process is a disruption of neuromuscular transmission, this process is corrected with medications. It is necessary to take those medications that promote the release of acetylcholine from the endings of nerve synapses. Most often, the drug Neuromidin is prescribed for this purpose.
This medication normalizes the process of impulses passing through the receptor network to the desired part of the brain. This occurs due to the blockade (closing) of potassium channels in the membrane membranes. Neuromidin enhances not only the effect of acetylcholine on muscle fibers. Adrenaline, serotonin, histamine and oxytocin also enhance their effect. You can often see drugs such as:
- Solifenacin.
- Oxybutynin.
- Trospium hydrochloride.
These drugs reduce the excitability of the bladder, thereby reducing the number of visits to the toilet. If conservative treatment in combination with physiotherapy and exercise therapy is not effective, then surgical methods are resorted to.
To do this, some artificial systems are sewn in (slings, loop systems, artificial sphincter, etc.). Slings and loops allow you to increase the angle between the neck of the bladder and the rectum, thereby increasing the ability to retain urine inside the bladder. Sewing in an artificial sphincter is practiced more often than other autoimplants.
The system is modeled from several components:
- Cuff.
- Water pump.
- Tubes, several pieces.
After installing such a system, a man has the opportunity to independently control the process of urine discharge. If the cause of impaired urination lies in the narrowing of the bladder neck, then dissection is indicated to normalize the process. Implantation of a rubber ring or balloon expansion of the lumen of the urethra gives a good effect.
Often the cause of impaired urination is associated with the formation of scar tissue on the operated prostate. In this case, ultrasound or microwaves can help, thanks to which the scarred areas are crushed.
Our readers recommend! To increase POTENTIALITY and treat PROSTATITIS, experts recommend regularly taking Ureferon. The product not only stimulates the activity of the prostate gland, but intensively rejuvenates the entire reproductive system, restoring high sexual activity. The drug helps cleanse blood vessels and fully fill the cavernous bodies. Find out more..."
The prostate gland and its effect on urination
The prostate gland prevents pathogenic bacteria from entering the bladder from the urethra through the urinary canal.
It acts as a valve that blocks their passage. The inflamed organ increases in size, compresses the canal, preventing the normal outflow of urine.
The stream of liquid becomes weak, it accumulates in the bladder and causes urine incontinence and spontaneous emptying.
| Author of the article: Bezrukov Evgeniy Alekseevich, head of the department of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova, professor, doctor of medical sciences |