Cystitis in women - inflammation of the bladder - is a disease that is characterized by such a clear clinical picture that making a diagnosis does not cause difficulties for either a doctor or a person with sufficient life experience.
Frequent painful urination, sometimes accompanied by severe pain and the appearance of blood in the urine, are its characteristic symptoms.
To prevent cystitis from becoming chronic, a woman should not self-medicate; first of all, she should consult a urologist who will conduct a detailed diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. If the clinic at your place of residence does not have such a specialist, then you need to contact a therapist.
Signs of cystitis
Those who have already experienced all the negativity of the disease know its symptoms: frequent urination is most likely the most unpleasant manifestation of cystitis.
A person can go to the toilet more than thirty times a day, but the act of urination gives relief literally for a minute. And then the patient again has the feeling that the bladder is full and it becomes more and more difficult to contain it.
Symptoms of cystitis include:
- Stinging and pain during urination;
- Discomfort in the perineal area;
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Increase in general body temperature;
- Rashes (if it is, for example, herpetic cystitis).
Not all women consider cystitis to be a disease that requires seeing a doctor. But this is a mistake: taking a pill from the medicine cabinet and sitting warm is not enough. There is a high probability that such half measures will lead to chronic cystitis.
Symptoms of the disease
The question of which doctor treats the disease should arise when the first signs of pathology appear.
You should go to the doctor if the following symptoms appear: too frequent urination, pain when urinating, pain in the lower abdomen, dark urine (sometimes with traces of blood), fever, general weakness.
Such signs appear if there is an acute phase of cystitis.
With chronic cystitis, characteristic symptoms are also observed: an excessively frequent desire to empty the bladder, sharp pain at the end of urination, traces of blood in the urine, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen.
Such symptoms are not to be joked about: if treatment is not started in a timely manner, serious complications can arise, and an advanced disease is much more difficult to cure.
When you can't put off visiting a doctor
First, assess your condition. If you have acute cystitis, the disease has manifested itself for the first time, you need to go to a medical facility as quickly as possible.
Delay can result in a rapidly developing chronic form of cystitis.
Acute cystitis manifests itself:
- Hyperthermia or a slight increase in values on the thermometer;
- Asthenia;
- Stitching pain in the very bottom of the abdomen;
- Cutting pain during urination;
- Nausea (and even vomiting);
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- Change in urine color.
Unfortunately, the pathology of the urinary system often affects the functioning of a woman’s reproductive organs. Therefore, to make sure that in your case cystitis develops in isolation and the genitals are not affected, you should go to a gynecologist. Moreover, this is the first doctor to treat cystitis. Or rather, the first specialist who needs to be visited by a woman with a prognosis of cystitis.
But many patients first visit a therapist, and this is also correct. Especially in acute cases of the disease, it is better to first come to the local physician: he will probably open a sick leave.
Which doctor should you go to for cystitis? Which doctor treats cystitis in women?
The essence of cystitis is the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the bladder, which leads to pain and the inability to urinate normally.
This disease is considered female, but sometimes occurs in men.
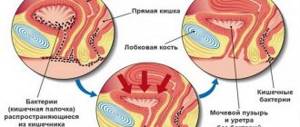
This situation is due to the fact that women have a shorter and wider urethra, which allows pathogenic bacteria to freely enter the bladder and multiply there, causing an inflammatory process.
Causes of cystitis
This disease can reveal itself in all its glory when:
- severe hypothermia or sitting for a long time on a cold surface;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- inaccurate sexual intercourse;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- untimely urination.
Each of these factors can be the last straw that will lead to inflammation, so you need to take all measures to prevent this.
Symptoms of cystitis
With this disease, a woman feels severe pain in the area above the pubis, and when urinating, it feels as if broken glass is passing through the urethra. The patient begins to run to the toilet very often; due to frequent urination, a very small amount of urine is released every 10-15 minutes. The situation may be complicated by fever and general poor health.
If recovery does not occur for a long time
Simple, uncomplicated cystitis does not last more than 5-7 days. If symptoms of inflammation are observed for a longer period of time, then it is necessary to exclude specific inflammation, deep damage (for example, interstitial cystitis). In this case, the patient will be referred to a specialist (urologist, urogynecologist, phthisiatrician, etc.).
When is the best time to see a nephrologist?
You cannot self-medicate - complications may arise. The infectious and inflammatory process will spread to surrounding tissues. This can lead to kidney problems and the development of pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis). Pyelonephritis can occur due to normal hypothermia. If a woman has complications, she should consult a nephrologist.
A nephrologist deals with the following issues:
- glomerulonephritis (damage to kidney tissue);
- amyloidosis (failure in the interaction of carbohydrates and proteins);
- changes in the body due to long-term use of medications;
- kidney stones;
- urinary tract infections;
- pyelonephritis (tissue damage of a bacterial nature).
A visit to a nephrologist is mandatory if there is pain in the lower back, painful urination, or change in the color of urine.
How is the inspection carried out?
A timely diagnosis and proper treatment can quickly get rid of the problem and bring the organs of the urinary system back to normal.
To be examined by a nephrologist, you need to prepare:
- it is advisable not to take diuretics and other drugs;
- do not drink alcohol;
- reduce fluid intake in the evening;
- Skip breakfast in the morning.
If this is the first time, the doctor will ask about complaints, the nature of work, daily routine, and the presence of kidney disease in relatives. He will analyze the sounds when tapping the back and abdomen, and listen to noises with a stethoscope. He will feel his lower back with his fingers. He will be interested in the condition of the eyes and oral mucosa, pressure and temperature.
Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidney that occurs due to hypothermia or intoxication of the body. Kidney problems can also occur due to high blood pressure. The kidneys produce the hormone renin, the adrenal glands produce aldosterone. These hormones are responsible for normal blood pressure. If there is a problem in the functioning of organs, the balance of hormones is disturbed, and hypertension appears.
After the initial examination, the doctor will prescribe examinations: x-rays or ultrasound of the kidneys to rule out damage to the vessels and arteries of the organs.
Advantages and disadvantages
A nephrologist diagnoses and treats kidney diseases. He selects not only drug treatment, but also prescribes phytoprophylaxis. And if kidney function decreases, he sets a diet and gives recommendations regarding changes in diet and lifestyle.
Such a specialist provides therapeutic treatment. His area of expertise is conservative methods.
Help from a urologist
It is a mistaken belief that this is not a women’s specialist; only men can be treated by him. Among doctors, this specialist helps both sexes.
Problems that a urologist solves:
- Deviations and pathologies of the urinary systems.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands.
The bladder is the main organ of the human urinary system. Contact a urologist, he will be the one who will correct the situation and select the correct treatment regimen. Consulting a doctor can cancel a trip to the therapist. Based on external manifestations, he will be able to determine whether cystitis is developing or whether it is a disease with similar symptoms.
What the urologist will do:
- prescribe general tests;
- will refer you for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- prescribe a biochemical urine test;
- will study the rate of urine flow and its exit from the body;
- cystoscopic examination.
The attending physician will choose a complex of therapy. These will not only be pills for cystitis, but also maintain the health of the entire body as a whole.
A urologist rarely works with women alone; more often he will refer the patient to a gynecologist, especially if the disease is in the form of a chronic pathology. Medicines remove all causes of a urological and gynecological nature.
Which doctor treats cystitis in women?
When a woman encounters symptoms of a disease such as cystitis, which doctor to contact becomes the most pressing question. And many girls have a fear of the diagnostic procedure. This disease is located between two medical specializations - gynecology and urology.
First of all, you should visit a therapist. After analyzing the patient’s complaints, he will most likely refer him to a specialist who treats cystitis - a urologist. Women will additionally be advised to visit a gynecologist, since quite often among representatives of the fair half of humanity the cause of the disease is various diseases of the genital area.
A urologist is a doctor specializing in the treatment of the human genitourinary system, who is thoroughly trained in this area.
His areas of expertise include diseases of the kidneys, bladder and urinary system as a whole. For him there is no division by gender and age.
Therefore, the doctor treating cystitis is a urologist, since cystitis in all its forms falls within the scope of interests of this specialist.
To fully clarify the reasons that led to the development of the disorder, the woman is prescribed certain studies:
- general urine analysis;
- bacteriological urine culture;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- blood analysis;
- analysis for vaginal dysbiosis;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- cystoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- PCR research.
Only after identifying the pathogen or cause of cystitis, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
As a rule, it involves taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, along with physiological procedures. Diet is also an important factor in the treatment of cystitis.
The doctor will advise you to give up spicy, smoked and fatty foods, alcohol and drink more than 8 glasses of water a day. Cranberry juice or fruit drink will also be useful.
Gynecological measures
More often, when asked who a woman should go to for help, the answer is to a gynecologist. It's easy to explain. The infection affects the genitals. Vivid symptoms come from the area where the genitourinary system is located. A woman with cystitis is associated with pain in the pelvic area. But doctors warn that external manifestations are often erroneous.
Diseases of the genital organs can lead to cystitis. But their treatment has its own scheme. If the symptoms, rather than the cause, are treated, the disease may subside and then manifest itself in a more severe form.
Diseases that can lead to the development of cystitis:
- vaginosis;
- candidiasis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea.
A gynecologist identifies the predisposition of a girl’s and woman’s body to the disease. You can refuse to visit a therapist and immediately contact a gynecologist. Specialization allows the doctor to carry out the same medical diagnostic actions.
Doctor's orders are often completed with a transvaginal ultrasound. It is not cystitis itself that needs to be cured, but the cause of its development. One of the reasons that a gynecologist can determine is inflammation of the bladder. It is pronounced after sexual intercourse is completed. The abnormal location of the urethra opens it up to infection. Another doctor can change this situation.
Visiting the family doctor
Which doctor should you go to first with cystitis? The first link will be the family doctor at the outpatient clinic. It is the starting point in the difficult process of diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis will begin with collecting an anamnesis of life and illness. This is necessary to determine the root cause of the disease and differential diagnosis with other ailments. It is necessary to reliably find out exactly the time and circumstances when the disease first occurred.
The survey is followed by palpation and auscultation, checking the Pasternatsky symptom. For better diagnostic results, laboratory diagnostic methods are used.
At the outpatient clinic you can undergo a general clinical set of tests, these include:
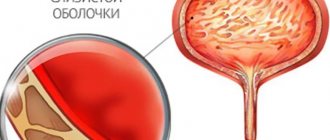
- A general blood test - an increase in the number of leukocytes, neutrophils and an acceleration of ESR indicates a suspected infectious lesion of the bladder.
- General urine analysis - an increased number of leukocytes, red blood cells, casts, squamous epithelium, mucus and bacteria can serve for differential diagnosis of diseases at different levels of the genitourinary system.
- Biochemical analysis - determination of indicators of the renal complex.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko - determination of formed elements in urine.
- A smear from the urethra and bacteriological culture of urine - determination of the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Source: https://bolezn.info/ginekologiya/k-kakomu-vrachu-nuzhno-idti-s-tsistitom-kakoj-vrach-lechit-tsistit-u-zhenshhin.html
Should a woman take a voucher to see a urologist?
Who to go to with cystitis is a urologist. If for some reason you have doubts about contacting a therapist or gynecologist, then be sure to visit a urologist. A urologist is a doctor whose specialty is the genitourinary system of the body. He deals with kidney pathologies (partially), bladder problems, and pathologies of the urinary system.
What examination can a urologist prescribe:
- OAM – cystitis is rarely treated without a general urine test;
- Urine culture tank;
- Urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- Vaginal smear for flora;
- PCR;
- Ultrasound of the urinary organs;
- Cystoscopy.
In extremely rare cases, the patient has to undergo this entire list of tests and studies. If the doctor has compelling reasons for such a comprehensive examination, then the patient will probably have to go to the hospital to speed up the process.
Which doctors will help a woman with cystitis?
- 1 Therapist
- 2 Urologist
- 3 Nephrologist
- 4 Gynecologist
Cystitis is a specific disease, when the first symptoms appear, patients do not always know which doctor to contact. Traditionally, inflammation of the bladder is treated by a urologist, but due to the structural features of the genitourinary system, women may need to consult a gynecologist.
Traditionally, bladder inflammation is treated by a urologist.
Therapist
Often women who first encounter an inflammatory process in the bladder turn to a therapist with complaints of:
- frequent urination;
- pain when urinating;
- burning and stinging when emptying the bladder;
- pain in the lower abdomen, lumbar region;
- the appearance of blood or pus in the urine;
- weakness;
- frequent urges.
Being a multidisciplinary specialist, the doctor will help identify the cause of the pathology (listen to complaints, collect anamnesis, examine the patient, give directions for tests).
The cause of the disease can be pathogenic microorganisms, so the doctor, after identifying the pathogen, prescribes treatment. If necessary, refers the patient to a specialist doctor.
Urologist
It is generally accepted that a urologist is a specialist who treats diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems in men. However, this is also a doctor who treats cystitis in women and children.
The bladder is an organ of the urinary system, so if cystitis occurs, you can contact this doctor, bypassing the therapist. The urologist may prescribe:
- urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the urinary organs;
- bacterial sowing;
- biochemical urine analysis;
- cystoscopy.
An integrated approach is important: after assessing the condition of the body, it is necessary to discover the causes of the pathology and select the correct treatment.
Nephrologist
Nephrologist's specialization is diagnosis and treatment of kidney pathologies:
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney stone disease;
- renal failure;
- neoplasms in the kidneys.
The kidneys belong to the urinary system, so a nephrologist is able to help patients suffering from cystitis.
The bladder, like the kidneys, belongs to the urinary system, so a nephrologist is able to help patients suffering from cystitis.
If cystitis is not treated in a timely manner or is treated incorrectly, the risk of the infectious process spreading to the kidneys increases, so patients with complications of cystitis are referred for consultation to a nephrologist.
If a girl has cystitis, it is important to exclude diseases of other organs of the urinary system.
The nephrologist prescribes blood and urine tests, ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys. After assessing the degree of inflammation and the danger to the urinary organs, the nephrologist will prescribe treatment and give recommendations to prevent complications.
Gynecologist
This doctor diagnoses and treats diseases of the female reproductive system, so patients often turn to him at the first symptoms of bladder inflammation.
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats diseases of the female reproductive system.
Pathology can occur in connection with diseases of the genital organs such as:
- candidiasis;
- vaginosis;
- thrush;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia.
As a result of untimely treatment of these diseases, chronic cystitis may develop. The gynecologist examines the patient, takes smears (for flora and STDs). Effective therapy may require simultaneous treatment by a gynecologist and a urologist.
The gynecologist can detect another cause of bladder inflammation - an abnormally located urethra (close to the vagina). In this case, acute cystitis can occur frequently, especially after sexual intercourse. Treatment is surgical.
During early pregnancy, changes in hormonal levels in women increase the risk of infection. At the same time, the immune system weakens, and the incidence of inflammatory processes in the urinary system increases.
When the first manifestations of the disease appear, you should contact the gynecologist who is seeing the woman. He monitors the tests, manages the pregnancy and will definitely select drugs that will act on the causative agent of cystitis and will not harm the unborn child.
If the diagnostic results do not reveal diseases of the reproductive system, a consultation with an immunologist may be required.
Based on an immunological blood test and other studies, the causes of cystitis can be detected and the necessary treatment prescribed.
If interstitial cystitis or cystalgia is suspected, it may be necessary to consult a neurologist or endocrinologist.
Source: https://cistit.expert/diagnostika/vrach/zhenshhin
Why do you need to consult a gynecologist?
What other doctor treats cystitis? As already mentioned, this is a gynecologist. Very often gynecological pathologies lead to problems with the bladder - vaginosis, colpitis, candidiasis, sexually transmitted diseases. In this case, we are talking about cystitis of a bacterial nature, and such cystitis accounts for about 70% of all cases of inflammation of the bladder walls in women.
How are gynecological pathologies diagnosed:
- An examination in a chair is a standard procedure; a doctor can detect a problem based on external signs, and an examination using special gynecological instruments will also help;
- Transvaginal ultrasound - allows you to detect what an examination cannot;
- Flora smear - such a smear is taken not only when diagnosing cystitis, it is a mandatory point in a traditional gynecological examination;
- Testing for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases - it may be carried out in another office.
Many people know that women are many times more likely to suffer from cystitis, because the anatomical location of organs in their body literally contributes to this. The infection occurs in a bladder from the urethra or urethra infected with bacteria.
If in men this path is narrow and long, it is simply difficult for pathogenic agents to reach the bladder, then in women it is wide and rather short.
Features of the course in men
Women are more likely to develop cystitis due to its structural features. The acute form is more common among them, especially occurring after hypothermia or sexual contact.
If cystitis is chronic, symptoms will definitely appear during pregnancy. This condition is dangerous because it is impossible to choose antibiotics because of the unborn child. Therefore, at the first signs of exacerbation, you should see your doctor. Women are also more likely to experience relapses of the disease.
In men, cystitis occurs much less frequently. Usually they develop a chronic form, occurring against the background of other diseases of the genitourinary system. Often these are other inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
First aid at home
Severe pain is a good reason to go to the clinic or call the local doctor or ambulance. While waiting for doctors, try to alleviate the condition:
- Intense pain requires mandatory bed rest.
- It is allowed to take tablets: Ketorol, No-shpa, Pentalgin.
- Two liters of fluid per day is the required minimum. It is better if it is lingonberry, cranberry, blueberry fruit drinks, a decoction of lingonberry leaves, St. John's wort, and yarrow.
- Carbonated drinks, tea, coffee, juices - citrus, tomato - are prohibited.
- To relieve pain and burning, it is recommended to add a little soda to your drink, which reduces acidity.
Structure and function of the bladder
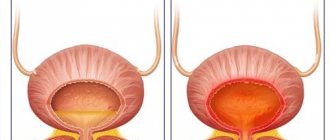
The bladder is a hollow organ, which is a bag whose walls consist of three layers (the inner layer is the mucous membrane lining the cavity of the bladder, the middle layer is the muscular layer, and the outer layer is serous). When filled with urine, it takes on a round shape, and after emptying it resembles a triangular sac.
Located in the pelvic area. The rectum is adjacent to the bladder at the back, and the pubic bones are at the front. In women, the uterus is located above and behind the bladder, and in men, the seminal vesicles are adjacent to it from the sides and below, and the prostate gland is located under the organ. On the right and left in the area of the bottom of the bladder is the confluence of the ureters, two thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the cavity of the bladder, from where it is discharged out.
The capacity of the bladder is on average 250 ml. It is with this volume of urine that a healthy person has the urge to urinate. Urine puts pressure on the receptors located in the wall of the bladder, from which the impulse is transmitted along the spinal cord to the brain, where the desire to empty the bladder is formed. In response to this signal, the person goes to the toilet.
The muscle of the bladder, which seems to envelop the organ, is called the detrusor. It contracts, reducing the capacity of the latter and expelling urine from it. At the same time that the detrusor muscle relaxes, another muscle called the sphincter relaxes. It is located in the neck of the bladder (its narrow part, which is connected to the urethra) and is always in a contracted state. It is thanks to it that a person’s urine does not leak spontaneously. Thanks to the relaxation of the sphincter and the contraction of the detrusor, the act of urination occurs.
A healthy person is able to regulate the functions of both muscles, the sphincter and the detrusor. This happens at the level of a reflex during sleep. During the daytime, a person controls his urination consciously. At about three years of age, the child gains control over the act of urination. Between the ages of 3 and 5 years, the nervous system matures.
Medicines
When treating cystitis, a number of drugs are used to help fight infection, pain and inflammation. Several groups of drugs are used, they can be combined. Various remedies come in the form of tablets, suppositories, and topical creams.
- Antibiotics. Antibiotic treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor if the nature of cystitis is bacterial, otherwise they can be harmful. After a course of these drugs, urine culture tests are performed again to determine the results of treatment. Examples of antibiotics: Monural, Nolitsin, Palin, Furagin, Rulid and others.
- Herbal medicines. Used as part of complex therapy to relieve symptoms. They usually have no serious contraindications, but consultation with a specialist is recommended. Examples of herbal remedies: Cyston, Monurel, Canephron and others.
- Antispasmodics. They are often necessary for severe pain during exacerbations. Examples of antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine.
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers based on ibuprofen.
- Probiotics. Sometimes used to restore microflora after treatment with antibiotics, to prevent relapses of cystitis. Before using them, it is advisable to consult a gastroenterologist. Examples of probiotics: Acipol, Bifiform, Hilak Forte and others.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods are aimed at quickly treating cystitis at home, but at relieving symptoms; they do not treat the problem that caused the inflammation. Therefore, home-prepared medications can be an addition to therapy; drug treatment is mandatory in any case.
Warming up
Heat therapy is one of the safest traditional methods. However, you should definitely consult a doctor; in some types of cystitis, heating is prohibited, since heat can promote the growth of bacteria. If there are no contraindications, a heating pad can be an effective remedy for pain and speed up recovery.
You can use a heating pad with water or a millet bag heated in a frying pan, depending on which method is more convenient. You can warm yourself up with sitz baths based on chamomile, hop cones, and mint.
Morse and jelly
Cranberry is an extremely useful berry for cystitis. It can remove inflammation and has a diuretic effect, which speeds up recovery. You can make fruit juice based on cranberries. To do this, take a glass of frozen berries per liter of water, cook for about 10 minutes, then strain. You can add mint to the drink to taste.
It is better to replace sugar in fruit drinks with honey. You can simply stir it in a glass of drink in the required amount when the fruit drink has cooled. If honey is added to hot liquid, it will lose its beneficial properties.
It is not forbidden to drink cranberry jelly during cystitis. You can prepare it yourself from fresh or frozen berries or buy ready-made powder at the pharmacy.
Healing herbs
Based on medicinal plants, you can make decoctions for oral administration for a diuretic or uroseptic effect. Infusions and decoctions are an excellent means for auxiliary therapy, if there are no allergies or other contraindications.
- Camomile tea. You need a tablespoon of dried plant per glass of hot water, brew for 15-20 minutes. Take a third of a glass orally three times a day before meals.
- Cowberry. A tablespoon of dried plant is poured with a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour. Take half a glass three times a day before meals.
- Also, decoctions and infusions can be made based on parsley, juniper fruits, sage, and rose hips.
When taking herbal decoctions and infusions, you should remember several rules - the principles of herbal medicine, the observance of which leads to a good result.
You should not take the same decoction or infusion for more than a month; you need to take a break for 2-3 weeks, then it is better to change the remedy. It is better to take decoctions in the afternoon, since some herbs have a sedative effect.
Folk remedies can be taken during remission with chronic cystitis, then the likelihood of the disease returning and a new exacerbation is reduced.
Will a nephrologist help?
As a subspecialty specialist, a nephrologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of all diseases affecting the kidneys. Kidney stones and benign or malignant neoplasms, nephritis and renal failure in a woman - all of them, to a certain extent, can provoke the appearance of cystitis, when the help of a nephrologist is required.
The kidneys, bladder and urethra are an integral system of the urinary system, and therefore a specialist such as a nephrologist also consults and, if necessary, prescribes treatment for patients diagnosed with cystitis.
It is important to remember that you should not start treatment, just as you should not practice making an independent diagnosis and prescribing one or another drug for yourself.
Incorrectly selected treatment or untimely completion of the course can provoke the spread of the infectious process both in the bladder and its transfer to the kidneys, and therefore you should definitely undergo an examination and consultation with a nephrologist.
Urolithiasis disease
Another name for the pathology is urolithiasis. Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, the process of stone formation begins in the bladder. They can be either single or multiple. In women, stones in the bladder most often have spines, which easily injure the walls of the organ. These stones are called coral stones.
The etiology of the disease is currently not fully understood. However, the following factors are known to be provoking:
- Congenital pathologies of the urinary system.
- Obesity.
- A lifestyle that does not involve physical activity.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Frequently being under stress.
- Disturbance of calcium metabolism.
- Frequent consumption of meat in large quantities.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Pain. Over time, its intensity increases. The calculus changes position or increases in size, resulting in tissue injury. This is why women have bladder pain.
- Presence of blood in urine. This symptom also indicates tissue damage.
- Frequent urge to urinate or, conversely, lack thereof.
- Signs of general intoxication of the body.
- During the emptying of the organ, the stream of urine suddenly stops.
Regarding which doctor to contact for pain in the bladder caused by stones. In this case, the urologist also deals with the treatment of the pathology. Based on the results of laboratory tests and ultrasound diagnostics of the bladder, the doctor chooses the tactics for managing the patient. Treatment of urolithiasis can be either conservative or surgical.
Other reasons
Most often, pain in women occurs for the reasons described above. But in rare cases, discomfort may result from:
- Apoplexy of the ovary.
- Endometritis.
- Adnexitis.
- Endocervicitis.
- Para- or perimeter.
In any case, when the first alarming signs appear, you should consult a doctor or, if you feel unsatisfactory, call an ambulance. Even the slightest delay can result in all sorts of complications, and if the bladder ruptures, the lack of medical intervention can lead to death.
Women visiting a gynecologist
If the family doctor discovers a pathology related to the genital organs or the root cause of inflammation of the bladder is a sexually transmitted disease, an additional consultation with a gynecologist will be scheduled.
Initially, a repeated medical history will be collected. A gynecological examination of the genitourinary system was performed using mirrors and a bimanual examination.
To verify the pathogen that could cause the disease, additional tests may be required.
Such a set of analyzes are:
- vaginal smear;
- urethral smear;
- scraping of the cervical canal;
- hysteroscopy;
These methods will also help to exclude or confirm suspicion of pregnancy. Depending on what pathogen is detected, there will be appropriate treatment.
The most common sexually transmitted diseases are:
- Chlamydia is the most common localization of the pathogen in the cervical canal, urethra and rectum. Further, through contact, it can infect nearby organs.
- Gonorrhea - the causative agent is gonococcus, damaged areas of the mucous membrane begin to burn strongly, and pus is released along with urine.
- Trichomoniasis - the disease can occur with only a small amount of mucus secretion.
This group of diseases also includes vaginal candidiasis, which manifests itself in the form of white discharge from the urethra.