The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Irina's question
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Tell me, is there a general difference between a urologist and a nephrologist? Or is a urologist a male specialist, and a nephrologist a female specialist? I'm completely confused!
Doctor's answer
Hello Irina.
Initially, there was no such division into female and male doctor priority in these areas.
Urologist - deals with the treatment of the kidneys and urinary system, which in general is simply a broader profile than that of a nephrologist. In addition, urology also involves surgical intervention, if necessary, whereas if a nephrologist concludes that surgery is likely, he must transfer the patient to a urologist.
A nephrologist deals exclusively with drug treatment of the kidneys.
What does a urologist do?
The genitourinary system of a modern person is fragile and often fails. It is not surprising that almost every one of us is forced to encounter a doctor such as a urologist at least once. However, many patients see a urologist only when the disease has reached an advanced stage. The reason for this may be embarrassment or ignorance of the symptoms of urological diseases. As a result, the treatment process becomes more complicated, it becomes longer, more difficult and unpleasant.
To prevent this from happening, you need to understand who a urologist is, what problems he deals with, and how he differs from other doctors with a similar specialization - andrologist, gynecologist, nephrologist, and so on.
How is the appointment, what does the doctor do?
An appointment with a urologist includes several procedures. First, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, clarifying complaints and collecting information about the medical history. Then the patient's body temperature is checked.
Many male urological pathologies are accompanied by an increase in body temperature, so this symptom should not be ignored.
After examining the patient, the doctor gives several recommendations and prescribes medications. The patient gets dressed and listens to the doctor. This concludes the reception. It lasts no more than 15 minutes
and rarely exceeds this time.
If the doctor finds it difficult to make a diagnosis, additional diagnostic methods
:
- General blood analysis.
- Urethroscopy.
- Biopsy.
- lower abdomen.
After carrying out these methods, the doctor looks at the results and prescribes treatment based on them.
. These are modern, effective methods that allow you to quickly establish a disease, or assess the patient’s health and make sure there are no pathologies.
Typically, boys, unlike adult men, are prescribed fewer tests: only blood and urine tests. Other methods are used extremely rarely, only in the presence of a serious illness
.
Reception of a boy is actually not much different from reception of an adult man. If the child is very small, one of the parents can come with him. The urologist asks the child about pain and discomfort and collects information for the medical history.
Then the child’s genitals are examined and, if necessary, sent for blood and urine tests. After the examination, the child can get dressed. The doctor gives some recommendations on how to deal with pathology
and prescribes treatment.
Who is a urologist
The human genitourinary system includes: kidneys, bladder, genital organs (female and male), prostate gland (in men). Diagnosis and treatment, conservative and surgical, of related diseases are carried out by urologists. Diseases of the genitourinary system have no age restrictions, so urologists can work with both children and the elderly.
A urologist is a doctor who you should contact immediately if you notice the following symptoms:
- pain, stinging, burning when urinating;
- incontinence or poor urinary control, frequent urge;
- pain in the lumbar area, lower abdomen;
- blood in the urine, change in its color;
- discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse;
- infertility, difficulty conceiving;
- pathologies of the genital organs.
All these signs may indicate the development of a serious disease that needs to be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Doctor for male diseases - what kind of doctor is this (venereologist, urologist or andrologist)
A doctor specializing in men's diseases is called an andrologist.
However, this is far from the only specialist dealing with the health of the stronger sex.
Let's talk about the main doctors that men turn to if they have problems with localization below the waist.
Andrologist for men's diseases
This is the main doctor treating men's diseases.
He is a highly specialized urologist.
The doctor deals with problems of male fertility, sexual function, and hormonal profile.
At the same time, it usually does not treat prostate pathologies.
They are directly related to urinary function, and are usually under the competence of a urologist.
The main diseases that an andrologist diagnoses and treats:
1. Hypogonadism.
This is insufficient production of male sex hormones at a young age.
It develops both with damage or underdevelopment of the testicles, and with pathology of other organs (hypothalamic-pituitary system).
2. Disturbance of sexual development in boys.
It can be either premature or delayed.
The second option is often observed with hypogonadism.
3. Age-related androgen deficiency.
The same as hypogonadism, only observed in older men.
This condition is considered physiological - just like menopause in women.
However, it causes discomfort and is associated with certain health risks.
Therefore, an andrologist may prescribe hormone replacement therapy to such patients.
4. Infertility.
It occurs due to a huge number of different diseases and conditions.
The andrologist’s task is to find out the origin of the pathology and eliminate it.
If the underlying disease cannot be eliminated, the doctor prescribes treatment that improves sperm quality.
Andrologists often see patients in reproductive centers.
Together with reproductive specialists, they use assisted reproductive technologies to overcome infertility in married couples.
5. Gynecomastia.
A disease in which a man develops female breasts.
6. Varicocele.
Enlargement of the veins of the scrotum is one of the most common causes of infertility.
An andrologist can treat this disease surgically.
7. Androgenetic alopecia (baldness).
8. Erectile dysfunction.
An andrologist determines the cause of erectile dysfunction and, if possible, eliminates it.
But usually only psychogenic dysfunctions can be completely eliminated.
While with organic ones it is necessary to prescribe situational or supportive therapy.
9. Disorders of sexual desire, body, ejaculation.
Some of these conditions (retrograde ejaculation) can be treated surgically by an andrologist.
10. Hormonal disorders.
11. Lesions of the male reproductive system due to somatic diseases.
It is often involved in the pathological process in liver cirrhosis, diseases of the nervous system, autoimmune and other pathologies.
12. Urinary incontinence in men.
Urologist for male diseases
A urologist can treat everything the same as an andrologist.
Because this is the same doctor, only with a wider profile.
There are relatively few andrologists.
Not every man can find this specialist near his place of residence in order to make an appointment with him.
Therefore, many go to a urologist for treatment.
In addition to the listed pathologies, he also deals with the health of the prostate, bladder, and kidneys.
A urologist identifies and treats:
- urolithiasis
- cystitis
- urethritis
- orchiepididymitis
- pyelonephritis
- abnormalities in the development of structures of the reproductive and urinary system
- phimosis and paraphimosis
- hydronephrosis
- tuberculosis, syphilis and other specific ones with localization of inflammatory foci in the genitourinary system
- mechanical damage to the genital organs
- priapism
- Peyronie's disease, etc.
A urologist much more often treats male sexual diseases with surgical methods.
He performs operations for testicular torsion, urolithiasis, benign hyperplasia or prostate cancer.
A urologist operates on patients with developmental abnormalities of the urinary system.
It treats kidney cysts, bladder diverticula, acute infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs (abscesses, empyemas, boils).
Fertility doctor for men
A reproductive specialist is a highly specialized gynecologist.
That is, he mainly deals with issues of women's reproductive health.
But infertility is seen as a problem for the couple as a whole, and not for one spouse in particular.
Therefore, both spouses come to see a fertility specialist at once.
This doctor prescribes the necessary tests not only for the woman, but also for the man.
He studies their results.
In this case, he often does not refer the patient to an andrologist, but carries out the interpretation independently.
If the quality of the sperm is high, the level of hormones is normal, and there are no sexually transmitted infections, this is where the participation of a reproductive specialist in assessing the state of men’s health usually ends.
Such patients are not subject to further examination.
But sometimes a man may have abnormalities in his tests.
In such a situation, it is highly likely that the reproductologist will refer the patient to an andrologist for further examination and treatment.
However, very often the fertility specialist himself directly guides such men.
This is due to the fact that different doctors cannot always adequately coordinate their actions aimed at achieving pregnancy in a married couple.
It is more convenient when one doctor monitors the reproductive health of both spouses.
Therefore, a reproductive specialist can select hormonal treatment or a scheme for stimulating spermatogenesis for a man.
He independently examines him, monitors the results and adjusts therapy if necessary.
Venereologist for male diseases
In many cases, a man should go to an appointment with a dermatovenerologist if problems arise.
This specialist is not an exclusively male doctor.
However, it treats pathological processes of the reproductive system of an inflammatory nature.
In addition, she deals with venereological (sexually transmitted) diseases that have extragenital manifestations.
If signs of male sexually transmitted diseases appear, the doctor:
- examines the patient
- takes swabs and other tests from him, which he sees as necessary, based on the identified symptoms
- interprets test results and makes a diagnosis
- prescribes etiotropic treatment
The task of a venereologist in the process of treating diseases of the male organs is to destroy the causative agent of the pathology.
That is, to achieve etiological recovery.
Pathologies dealt with by a venereologist:
- syphilis
- gonorrhea
- chlamydia
- anogenital warts
- herpes
- trichomoniasis
- candidiasis
- gardnerellosis
- ureaplasmosis
- mycoplasmosis
Treatment of male diseases can be carried out by other specialists if extragenital structures are involved in the pathological process.
For example, neurologists often take part in the fight against syphilis if the structures of the central nervous system are affected, or cardiologists if syphilitic damage to large vessels and the heart is involved.
A rheumatologist takes part in the treatment of Reiter's disease developed against the background of chlamydia.
In the case of the formation of urethral strictures due to gonorrhea, the urologist is engaged in further treatment of such a patient after the destruction of gonococci.
Diagnosis of a man's health by a doctor
What tests and procedures will be used for diagnosis depend on the reason for the patient’s visit and objective research data.
Diseases of the male reproductive system are very diverse in origin and clinical course.
Most often used:
- spermogram – allows you to assess reproductive function
- blood test for hormones (prolactin, gonadotropins, androgens)
- smears for genital infections
- general clinical tests (general analysis of urine, blood, biochemical urine analysis, coagulogram)
- Ultrasound of the prostate, scrotum, kidneys
The doctor has at his disposal many other tests, clinical tests, and instrumental methods that allow him to assess the structure and function of the genitourinary organs.
Treatment of male prostate diseases
Prostate diseases are among the most common diseases in men.
Very common:
- benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma) - affects most elderly patients, often manifests in middle age
- chronic prostatitis - various types of this disease can occur in men of any age, including young people, especially if they are promiscuous (the risk of prostatitis caused by STDs, most often Trichomonas, increases)
Another common problem is prostate cancer.
This pathology is one of the most common cancer diseases in the world.
It develops mainly after 60 years.
Different prostate diseases are treated differently.
In most cases, conservative methods are used.
For prostatitis the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microflora
- vascular drugs to improve blood supply to the prostate
- prostate massage, physiotherapy
Prostate adenoma is treated with two groups of drugs:
- antiandrogens – to slow down the growth of the prostate gland
- alpha-blockers - to eliminate symptoms associated with urinary disorders
Herbal remedies that provide 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are sometimes prescribed, but they are less effective.
When the prostate reaches a large size, or when the structures of the urinary system are compressed, surgical intervention is performed.
Part of the prostate is removed.
Typically, operations are performed with access through the urethra, without incisions in the skin.
Vacuum in the treatment of male diseases
Vacuum is used for LOD therapy.
This is local negative pressure treatment.
This procedure is used to treat psychogenic and vasculogenic (vascular) erectile dysfunction.
A flask is placed on the man's penis, from which the air is pumped out.
Negative pressure is created, so blood rushes to the genitals.
As a result, an erection is achieved even in the absence of sexual arousal.
For psychological infertility, the use of LOD therapy allows a man to regain self-confidence and avoid the fear of failure.
In case of vascular infertility, vacuum helps to achieve an erection in situations where the patency of blood vessels is impaired.
What is the difference between a urologist and an andrologist?
Andrology is one of the areas of modern urology, which studies male anatomy and physiology. Unlike a urologist, an andrologist works exclusively with male patients. The following issues are within his area of expertise:
- acquired or genetic pathologies of the male genital organs;
- difficulty conceiving;
- violation of potency;
- other sexual problems and deviations.
The diseases that this doctor deals with are typical for representatives of the stronger sex. If a urologist makes sure that a person does not have diseases related to the genitourinary system, then an andrologist ensures that a man is successful in life. You can often find urologists-andrologists combining the functions of these specialists. For example, such a doctor sees in a medical clinic. You can contact him for any reason related to these two areas, which is very convenient for patients.
Diagnostics and treatment in the Department of Urology "Alan Clinic"
The clinic provides treatment for male and female urological diseases, as well as sexual disorders in men. All diagnostic and treatment procedures are carried out within the walls of our clinics - our patients do not have to go to pharmacies or look for where in the city they can undergo additional medical procedures. The cost of a course of treatment includes absolutely everything necessary: a set of procedures, medications (tablets, suppositories, ointments, etc.), additional ultrasounds and tests during treatment and after its completion, follow-up with the attending physician after treatment. Payment in installments is possible.
You can find out more by calling or leaving a request on the website. We will be happy to help you restore your health!
What is the difference between a urologist and a nephrologist?
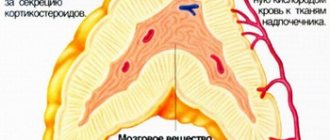
A nephrologist is a specialist who diagnoses and treats kidney problems. His patients are people with the following diseases:
- renal failure;
- polycystic kidney disease;
- urolithiasis disease;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis.
Unlike a urologist, a nephrologist practices exclusively drug therapy. Patients usually come to him on the referral of a urologist when hospital treatment is required.
Is this treatable?
All acute forms of urological diseases are treated with antibiotics, herbal remedies with the addition of probiotics and prebiotics. The chronic course of diseases is controlled with drugs, reducing the frequency and risk of relapses.
Be careful: independent and uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs disrupts the microflora of the intestines and vagina. At the same time, insufficient doses of drugs and self-cessation of taking drugs “as soon as it gets better, because antibiotics are harmful” form resistant bacteria and deprive the patient of the possibility of a full recovery using conventional means.
Complications
The inflammatory process will not go away on its own. It may weaken, the symptoms will go away for a while, but will return with renewed vigor. Long waits and lack of drug therapy lead to complications. Most at risk:
- women with anatomical disorders of the genitourinary system;
- patients who have recently undergone surgery;
- patients recently treated with antibiotics;
- people with diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression;
- elderly people;
- pregnant women.
The lack of medical care and treatment gives the infection a head start - it spreads throughout the genitourinary system, capturing new areas. So, urethritis flows into cystitis, pyelonephritis into acute renal failure, nephrosclerosis.
The University Clinic has a urology department for women - consult our doctors today. Don't give illness a chance to affect your life!
What is the difference between a urologist and a venereologist?
Often, patients of a venereologist become patients after visiting a urologist or gynecologist, when the diagnosis is established. This specialist diagnoses and treats STDs. People come to him with the following problems:
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- uroplasmosis;
- trichomoniasis;
- genital herpes;
- HIV infection;
- genital warts and so on.
If such diseases are not treated, various serious consequences are possible, for example, infertility.
What is the difference between a urologist and a gynecologist?
Only women become patients of a gynecologist, since he diagnoses and treats diseases that are familiar only to the female body. Whereas a urologist works with problems of the genitourinary system of both sexes. You can see a gynecologist with the following problems:
- uterine fibroids;
- cervical erosion;
- adnexal tumor;
- ovarian diseases;
- candidiasis and so on.
Sometimes the areas of activity of doctors overlap, since gynecological, nephrological, andrological diseases can be a consequence of urological infections. And sexually transmitted infections can be accompanied by urological diseases.
So, as follows from the above, if you notice signs of urological problems, you must first contact a urologist. If the problem requires the help of a “narrow” specialist or you happen to see a urologist by mistake, this doctor will give you a referral to the right office.
You can get acquainted with the diseases treated by a urologist in our Urology section.
What tests are performed by a female urologist?
Laboratory tests for a woman (a smear from the urethra, cervix, or vagina can be taken from the urologist directly during the appointment and a microscopic examination can be performed) include:
- blood test (for hormones, infections, tumor markers, sugar, general to detect inflammatory changes and biochemical with assessment of kidney and liver function);
- cytological examination of a cervical smear (PAP test);
- general analysis of urine, a three-glass sample to determine the location of the pathological process (in the urinary canal, bladder);
- inoculation of bacterial biomaterial (urine, secretions, etc.) on a suitable medium with determination of resistance to antifungal and antibacterial drugs);
- serological studies;
- ELISA;
- PCR testing of blood, urine, secretions, etc.
Read also: Oral STDs
Instrumental studies include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, pelvic organs, mammary gland;
- endoscopic methods - urethro-, colpo-, cystoscopy (according to indications);
- CT, MRI;
- urography (x-ray method for assessing the function and anatomical state of the organs of the urinary system);
- urodynamic studies (uroflowmetry, cystometry, urethral profilometry, electromyography), etc.
Who is a urologist?
Urology is a branch of clinical medicine that deals with the treatment and prevention of diseases of the genitourinary system and retroperitoneal space. She studies the causes of diseases, their pathogenesis and develops diagnostic methods. As a surgical specialty, urology is primarily based on surgical treatment methods.
The urologist is responsible for:
- infectious and non-infectious diseases of the urinary structures in men and women (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra);
- pathology of the genital organs in men (testicles, penis).
Among urologists there are specialists who deal with specific problems, for example, an oncourologist (treats malignant tumors) or an andrologist-urologist (treats diseases of the genital area in men).
Information: who is a urologist and what does he treat in children?
In childhood the following may appear:
- Cystitis;
- Balanitis;
- Phimosis;
- Not descent of the testicle into the scrotum;
- Incorrect placement of the sexual flesh;
- Injuries to the urinary organs;
- Hypospadias, the location of the urethra at the bottom of the sexual organ;
- Varicose veins of the spermatic cord;
- Anomalies and inflammation of the ureters in girls.
A pediatric urologist examines and treats the reproductive system, urinary canal, testicles, appendages, and urethra. After birth, the boy must be examined by a urologist, who will determine the presence or absence of anomalies. During infancy, it is necessary to bathe the child frequently. To avoid infections, girls should be washed towards the backside. Boys should wash their penis and scrotum with soap at least once a week.
Who is a gynecologist?
Gynecology is a medical field that studies diseases of the female body, mainly the reproductive system. Gynecologists observe a woman in the following situations:
- at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, during gestation, during childbirth and during lactation;
- in the presence of genital tract infections;
- if there are acute or chronic diseases of the reproductive sphere;
- selection of contraceptives is necessary;
- there are benign neoplasms of the reproductive organs.
Many gynecologists are also obstetricians.
Fundamental differences
A urologist treats the urinary system in patients of both sexes and is responsible for the condition of the genital organs in men. A gynecologist deals exclusively with the treatment of the female reproductive system and pathological conditions of the body that are associated with its changes.
If you don’t understand how to write “gynecologist” or “gynecologist,” then you should analyze this noun and use various dictionaries. Let's address them together.
At an appointment with a urologist: how to prepare for the examination
Any symptoms of abnormalities in the genitourinary area require immediate treatment; the main thing is to find a good specialist who will pay attention to the problems of concern. It is better to use the services of a recommended doctor. If this is not possible, you can easily find clinics on Internet sites, look at photos, experience and patient reviews of this specialist.
An appointment with a urologist takes place according to standard procedures: questioning, examination, palpation, testing and research. Before visiting a specialist, you need to prepare. Simple procedures will help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
- Avoid sexual intercourse the day before your appointment. Sometimes spermogram or smear tests are required.
- It is advisable to empty your bowels and bladder.
- Keep your genitals clean, but do not use antiseptics before visiting the doctor.
- Be morally attuned to issues of an intimate nature. Sometimes a young guy or teenager does not answer the questions asked, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
If there is no opportunity or desire to come to the clinic, a specialized doctor can provide services at home. As a rule, these are paid medical services from private centers. To do this, you need to contact a medical clinic and order a urologist to visit your home. When visiting a patient, the doctor will perform an examination, palpate the prostate and kidneys, and, if a portable device is available, perform an ultrasound.
Which rule applies
There are two spelling difficulties in this word. The first root of this compound noun contains unstressed vowels. It will not be possible to check their stress, since the word is a borrowing from the Greek language. The second root (log) is found often among us and means “word”. It is preceded by the connecting vowel “o”; there can be no other options here. But the first root in the same Greek language means a woman and is written like this - gyneka. For this reason, we write “i” in the first syllable, and “e” in the second.