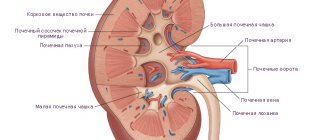
Renography of the kidneys is a method of x-ray examination of the kidneys using radioactive components. Such diagnostics are organized after intravenous administration of a radioactive substance that accumulates in the kidneys and helps to identify pathologies of the organ.
This diagnosis makes it possible to assess kidney function and urine flow rate. The method is used to monitor the condition of the kidneys after a transplant operation, as well as to assess the dynamics of the process. All patients with suspected kidney damage are allowed to undergo renography. Due to the introduction of a small dose of radioactive substance, this method has no contraindications, it also does not require special preparation and takes approximately thirty minutes. In this regard, renography is also performed for seriously ill patients.
It is important!
Often, radioisotope renography is used for the timely detection of complications, such as thrombosis of the reconstructed vessel in the period after surgery.
Ultrasound research methods
Ultrasound echography (synonyms: echography, echolocation, ultrasound scanning, sonography, etc.) is a diagnostic method based on differences in the reflection of ultrasonic waves passing through tissues and environments of the body with different densities. Ultrasound is acoustic vibrations with a frequency of 2x10 4 - 10 8 Hz, which, due to their high frequency, are no longer perceived by the human ear. The possibility of using ultrasound for diagnostic purposes is due to its ability to propagate in media in a certain direction in the form of a thin concentrated beam of waves. In this case, ultrasonic waves are absorbed and reflected differently by different tissues depending on the degree of their density. The reflected ultrasonic signals are captured, transformed and transmitted to a reproducing device (oscilloscope) in the form of an image of the structures of the organs being examined.
In recent years, the method of ultrasound diagnostics has been further developed and, without exaggeration, has made a real revolution in medicine. It is used in the diagnosis of diseases of almost all organs and systems: heart, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, thyroid gland. Any congenital or acquired heart defect is reliably diagnosed by ultrasound echography. The method is used in neurology (study of the brain, ventricles of the brain); ophthalmology (measurement of the optical axis of the eye, the magnitude of retinal detachment, determination of the location and size of foreign bodies, etc.); in otorhinolaryngology (differential diagnosis of the causes of hearing damage); in obstetrics and gynecology (determining the timing of pregnancy, the condition of the fetus, multiple and ectopic pregnancy, diagnosis of neoplasms of the female genital organs, examination of the mammary glands, etc.); in urology (study of the bladder, prostate gland), etc. With the advent of Doppler systems in modern ultrasound machines, it has become possible to study the direction of blood flows inside the heart and through the vessels, identify pathological blood flows due to defects, study the kinetics of valves and heart muscles, conduct a chronometric analysis of the movements of the left and right parts of the heart, which is of particular importance for the assessment functional state of the myocardium. Ultrasound devices with color images are being widely introduced. Under the pressure of ultrasound research methods, X-ray methods are gradually losing their relevance
Radioisotope examination of the kidneys (scintigraphy) is nowadays a fairly simple and accessible diagnostic method. It is performed not only in the hospital, but also on an outpatient basis using a device called a renograph.
Such an examination is more informative than even a traditional ultrasound, and its harm to the body is less than from an x-ray. However, there is a contraindication to its use
– and breastfeeding. We’ll find out why later in the article.
Indications for examination
Patients with various kidney diseases are recommended to undergo regular renography
. It is often carried out repeatedly without harm to the person in order to determine the effectiveness of the prescribed one. It can also be performed in combination with x-rays.
However, you need to remember that x-rays are taken no more than once a year.
Scanning of the kidneys using the radioisotope method is indicated in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Vascular diseases of the parenchyma: glomerulonephritis, nephritic syndrome, amyloidosis.
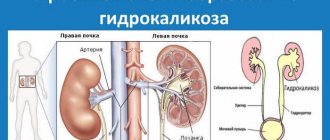
- Hydronephrosis.
- Malignant hypertension.
What is being studied?
The majority of patients examined using a renograph have pathologies of the urinary system
.
Radioisotope renography will help the doctor perform the following manipulations:
- record the excretory functions of the proximal tubules;
- check kidney blood flow;
- detect the presence of vesicoureteral reflux;
- determine the condition of kidney tissue in the largest and smallest segments of the kidneys;
- consider the ability of the kidneys to function after transplantation.
Renography in children
In children under one year of age, radioisotope testing of the kidneys is not used; the same is true for pregnant women, because even small doses of radiation can negatively affect the fetus
and the baby’s fragile body.
Instead of renography, the doctor will prescribe a screening ultrasound for children of this age to examine their kidneys.
However, if the child has a pathology, then in this situation the attending physician assesses the need to use this research method.
Children under 3 years old are given a sedative
so that the child is calm and the scintigraphy result is objective and of high quality.
Small patients are given preliminary iodine intake in small quantities as necessary preparation. For three days before renography, adults should give the child 3 drops of Lugol's solution orally or 3-5 drops 3 times a day of 5% iodine tincture
to block the reactive functions of the thyroid gland.
Renography for children
For children under one year of age, renography is not used. Some sources indicate other age limits - they do not recommend using radioisotope methods in children under 4 years of age. We are inclined to the first opinion. Up to a year, during the first month and a half, the child undergoes a mandatory screening ultrasound - examination of the kidneys. No one will prescribe isotope renography to a baby in the absence of pathologies. But if they are present, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
Interesting! The dose of radiation that the body receives during an examination is 1/100 of the dose received when using a conventional x-ray.
Carrying out the procedure
Isotopes demonstrate the appearance of the kidneys, evaluate their functional abilities, and help detect pathologies appearing in them at an early stage. This is especially important in oncology.
For renography, a new generation radioisotope study, the drug Hippuran
. It helps to obtain a view of the affected areas of the kidneys, while ultrasound is useless in this case. It is administered in doses calculated in relation to body weight.
The kidneys have the ability to capture the radiopharmaceutical in the required quantities and remove it from the body. Hippuran can disintegrate quickly, so the body’s exposure to radiation is minimal.
Renogram
– this is a record of isotope radiation that appears over the organs under study at the moment the Hippuran passes through them. The renogram displays all the changes occurring in the internal organs.
The patient is examined in a static state, sitting. Seriously ill patients are examined lying down. The drug is injected into the vein of the subject, and special renograph sensors, which are installed on the patient’s body, record its accumulation, passage and excretion from the kidneys.
Thus, the renogram is divided into 3 parts for each kidney:
- Vascular, which depicts the placement of a radioisotope in the vessels of the kidneys.
- Secretory, shows the accumulation of Hippurin in the kidney.
- Evacuation room, where the exit of the drug from the kidneys is recorded.
Radiologists analyze the resulting result using mathematical analysis and use it to identify the effectiveness of the cleansing functions of the kidneys
, the rate of filling of its vascular system, the period of elimination of the drug from the kidney, the features of its accumulation in the urinary system.
A radiologist will tell you all about scintigraphy in children in this video:
Radioisotope diagnostics of the kidneys is a method of visualizing pathological processes using pharmaceuticals containing a radioactive nuclide in their molecule and evaluating the results with radiodiagnostic equipment.
If the structure and structure of the kidneys can be assessed using ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography, then the radionuclide method makes it possible to determine tubular secretion, glomerular filtration, blood supply to the kidney, urological dynamics, the state of the kidney parenchyma, the topography of the entire organ and its individual sections. All this is important when diagnosing the disease in its early stages, when other methods are still uninformative.
Radionuclide compounds can be used in patients with high sensitivity to radiocontrast agents.
Renography result
More details about isotope testing can be found in the video
What is MSCT with contrast?
The finished renography chart displays three main segments that help the attending physician in making a diagnosis, namely:
- excretory and excretory functions, reflect the output of radioactive compounds in urine;
- tubular and secretory, reflects the secretion of O-iodinated acid with the help of epithelial cells of the canals from the blood;
- vascular and vascular functions reflect the presence of radioactive compounds in the kidneys.
The time threshold for removing a radioactive substance from the human body is determined by the rate of secretion, as well as the state of urine output. If the patient has deviations, the renograph graph displays them in a certain area, which makes it possible to identify their location and the cause of formation.
For information! Renography does not make the diagnosis 100% accurate, however, with its help the doctor is able to determine the level and degree of complexity of existing disorders in the renal system.
Indications for radioisotope scanning of the kidneys
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of kidney development.
- Acute and chronic renal failure in the stage of compensation and subcompensation.
- Assessment of kidney viability after trauma.
- Hypertension of vasorenal origin with assessment of renal function.
- Preoperative preparation with determination of renal function.
- Visualization of a functionally inactive kidney.
- Acute and chronic kidney infections with detection of scar damage to the cortex (pyelonephritis)
- Determination of the degree of obstruction of the renal arteries.
- Preparation for kidney transplantation.
- Renal infarctions.
Contraindications for the study
The radionuclide indication method is quite simple to carry out, not burdensome for patients, has high reproducibility and the ability to monitor over time, but there are also contraindications for scintigraphy:
- Intolerance to a radioactive drug.
- Pregnancy in the first trimester, lactation period.
- Children under 1 year of age.
- The patient's weight is more than 125 kg.
- Taking antihypertensive drugs.
- Acute mental disorders.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Emergency conditions that threaten the patient's life - increasing cardiovascular and respiratory failure, coagulopathies, gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Presence of metal prostheses and plates.
Preparation
- Three days before the proposed study, it is necessary to exclude the use of alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks, narcotic and psychotropic drugs.
- 5-6 hours before the procedure you need to cancel any meals.
- 1 hour-30 minutes before the examination, you need to drink 500 ml of water. The water must be clean, non-carbonated, non-mineral. Drink in small sips.
- Be sure to discuss taking medications with a specialist. Some medications may affect the outcome of the procedure.
- Immediately before the examination, remove all metal objects/jewelry from the body (rings, chains, earrings, cufflinks, watches, etc.).
- If you have metal prostheses, you must notify the specialist in advance about this.
Excess body weight of the patient (weight over 120 kg) may become an obstacle to the examination.
General principles of preparation for radioisotope diagnostics
The patient needs to be explained the importance of preparing for the study and the essence of the study itself, and be sure to warn about the possible complications of this diagnostic method.
Three days before the study, you should stop taking narcotic, psychotropic substances and alcohol. Consult a doctor about the medications the patient is currently taking to avoid distortion of the study results. Pregnant women, children and patients with thyroid diseases are prescribed to take potassium iodide an hour before. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be light and occur 6 hours before.
Emptying the intestines and bladder is mandatory within 2-3 hours of the study. An hour before the procedure, you need to drink 1 glass of pure still water.
Progress of the procedure and subsequent patient care
- To obtain a picture in the posterior projection, the patient is placed on his stomach; if a picture in the anterior projection is needed, he is placed on his back. It is prohibited to move during the study. For patients with severe psycho-emotional agitation, it is recommended to prescribe mild sedatives.
- The patient is attached to special sensors in the kidney area, which will capture the radiation of the injected substance and transmit it to the monitor.
- A calculated amount of radioactive substance is injected intravenously, and fast-frame photography is performed within 1 minute to assess renal blood flow. After administration of the substance, side effects such as nausea, hot flashes, dizziness, and lack of air are possible, but after a few minutes these phenomena disappear on their own.
- Next, the isotope passes through the functional units, 1 image per minute is recorded for 20 minutes. This concludes dynamic scintigraphy.
- After 3.5 hours, the isotope reaches the renal pelvis, this makes it possible to conduct static scintigraphy and evaluate the topography and pathological changes in the shape and size of the kidney. Subsequently, the isotope is excreted from the body along with urine within three days.
After the examination, you need to re-treat the puncture site with an antiseptic to avoid infection. A hematoma may form; to eliminate it, heparin ointment should be used within two to three days.
Bed linen should be changed every time bedridden patients urinate to avoid contact with radioactive urine. The procedure should be carried out using disposable rubber gloves.
With this diagnostic method, the patient does not need hospitalization in a hospital, but every day for a week, on an outpatient basis, the general condition, acid-base and water-salt metabolism, creatinine and urea levels in the blood should be assessed. In order to accelerate the removal of the isotope, it is recommended to consume large amounts of liquid with natural adsorbents (Polifepam, Activated carbon, Filtrum).
July 13, 2020
Radioisotope examination of the kidneys is very popular in urology and nephrology. It is safe even for children, and the results obtained are of higher quality than those of CT and MRI. There is no need for special preparation for the examination; it is carried out on an outpatient basis. This type of diagnosis is suitable for searching for any renal pathologies, allowing you to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Radionuclide (radioisotope) diagnostics is a modern technique that evaluates signals from a special radioactive drug that is injected into the tissues of internal organs. Simply put, to perform a radioisotope examination of the kidneys, a contrast agent is injected into the body, and its passage through the blood vessels of the organs is monitored using x-rays. After a certain period of time, the substance is excreted in the urine without any residue.
Why is the use of special drugs required? It is difficult to accurately recognize the internal structure of the kidneys on a regular image. “Illumination” of tissues with contrast agents makes it possible to perfectly visualize the structure of the kidneys, even when performing simple radiography. Even at an early stage, when other methods are not very informative, radionuclide diagnostics will provide the necessary data to a specialist. The contrast agent does not harm the body, the risk for the patient is minimal, so the technique is also performed in children.
There are several diagnostic methods:
- Renography. Allows you to evaluate the speed of urine flow, but does not show the structure of the internal organs. Helps to identify disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system using sensors placed on the human body. The dynamics of the movement of the introduced isotopes is recorded by a radiograph, which draws information in the form of graphs.
- Scanning. This technique is more informative, as it reflects the structure and function of the kidneys, shows their shape, size, layers, any lesions - tumor, destructive, inflammatory. The study is carried out using a scanner, which records the movement of the injected drug.
- Scintigraphy. Images, according to this technique, are taken using a gamma tomograph at certain intervals. This type of examination is the most accurate, but also more complex.
X-ray of the kidneys with a contrast agent: preparation and how to do it
Kidneys are vital paired organs that perform regulatory, filtering and many other functions. Many toxins and wastes constantly pass through them, and often because of this, organs malfunction.
Sometimes it is asymptomatic, and in some cases it is accompanied by intense symptoms.
In both cases, an instrumental examination of the kidneys and urinary tract is necessary, which includes the ureters, bladder and urethra.
Despite the development of radiation technologies and the emergence of modern methods, the use of x-ray diagnostics of kidney diseases remains quite in demand. This is the technique preferred by most doctors.
With its help, you can identify almost all deviations in the anatomy and functioning of organs, as well as find the causes of kidney symptoms.
For many patients with pathologies of the urinary system, x-ray remains the only available way to identify the problem and begin timely therapy.
Why are kidney x-rays done: indications
Classical radiography of the kidneys is a fairly accurate and cheap method for diagnosing diseases of the excretory system. Despite the fact that the name only mentions the main paired organs, the procedure involves an x-ray of the entire urinary system. It includes direct examination of the kidneys, each ureter and bladder, as well as the structures adjacent to them.
In diagnostic practice, radiography can be survey or targeted. In the first case, the entire urinary tract is visible in the image, and in the second, the doctor focuses on its individual elements or processes. To conduct a survey radiography of the kidneys, it is necessary to have symptoms that indicate problems with blood purification, synthesis and excretion of urine. These include:
- noticeable change in urine odor;
- the presence in the urine of impurities of blood, pus or mucus, sand and other atypical elements;
- recurring pain in the lower back or bladder;
- urinary retention while the urge persists;
- pronounced swelling of the legs and eyelids.
Also, a survey x-ray of the bladder and other parts of the urinary system is carried out when bacteria, blood, protein and elements appear in laboratory urine samples, or an increase in creatine and urea in the blood.
Important! Deviations in tests are indications for X-ray diagnostics, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
In addition, x-rays of the kidneys are indicated for acute conditions and in situations where regular monitoring of the course of pathologies of the urinary system and monitoring the results of therapy are necessary:
- congenital or acquired anomalies of organs - doubling of the kidney, aplasia and hypoplasia, enlarged kidney (all degrees of hydronephrosis are clearly visible on the pictures), doubling or tripling of organs (horseshoe kidney), their prolapse, etc.;
- congenital and acquired anomalies of the ureters - aplasia, doubling or tripling of the ureter, ectopia or dystopia, urethrocele, ureteral separation, diverticula, etc.;
- congenital or acquired anomalies of the bladder - diverticulum of the bladder, duplication of the organ, contracture of the neck of the bladder;
- injuries of the urinary system;
- urolithiasis, in which stones can be located both in the organ cavity and in other parts of the urinary system;
- neoplasms - polycystic or single kidney cyst, malignant tumors, bladder polyps;
- inflammatory diseases - abacterial or infectious pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to evaluate urodynamics and identify in more detail the internal cavities of the urinary organs. An x-ray with a contrast agent is used for this. It will show a slightly clearer picture, and will also allow you to track the process of urine production and excretion.
Important! A contraindication to x-rays of the kidneys with contrast is considered to be acute renal failure (abbreviated as ARF).
An x-ray of the bladder is also taken using a contrast agent. Unlike studies of other parts of the urinary system, diagnosis of pathologies of this organ is possible even with acute renal failure. Contrast enhancement is carried out by instilling a solution with iodine through the urethra. In this case, the contrast agent is removed immediately and cannot harm the internal organs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uNMnG6NbtLk
The main source of information about the state of the urinary system is the comparison of the obtained images with the anatomical norm.
Despite the fact that the x-ray anatomy of the kidneys is extremely flexible (indicators depend on the gender, age, complexion of the patient and other factors), an experienced specialist can always identify pathological changes.
He will determine why the pelvis is enlarged, what caused dysuria (lack of urination), and at what stage the inflammation or tumor process is.
If a doctor prescribes an x-ray of the bladder and kidneys, do not hesitate and refuse the procedure. This type of diagnosis is no more dangerous than other modern methods, and its accuracy is comparable to high-tech research.
Kidney examination: performance and results of x-rays and alternative methods
X-rays of the kidneys are prescribed to diagnose diseases or pathologies in the organs. However, the examination must be carried out with caution, especially with the use of contrast. Before resorting to this procedure, it is worth considering existing alternative research methods.
If the patient’s tests do not provide a comprehensive picture, an x-ray is prescribed. At the same time, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and his ability to undergo the procedure.
Symptoms for which it is recommended to do kidney x-ray:
- pain in the urethra;
- mucus in the blood;
- strong smell of urine;
- lower back pain;
- blood in urine;
- swelling.
Valentina Sheveleva talks about kidney examination. taken from the channel “CENTER FOR RADIATION DIAGNOSTICS FSBI LRC of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation”.
What does an x-ray show?
X-rays are used to diagnose:
- polycystic disease;
- renal hypertension;
- urolithiasis;
- hydronephrosis;
- nephritis;
- tumor.
Also, the x-ray shows:
- bone injuries;
- pathologies of development of the genitourinary system;
- organ shape;
- stones and sand.
Methods for performing kidney x-rays
With radiation diagnostic methods in the early stages, the doctor sees changes in the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system. The results obtained from the study will allow him to decide on treatment and make a more accurate diagnosis.
X-ray
During the examination, an iodine-based contrast agent is injected into the patient’s body, which fills the organs and channels, it helps to “highlight” them in the image.
The urologist prescribes an analysis taking into account:
- patient's condition;
- the radiation exposure he has already received;
- possible consequences.
Before conducting the study, the doctor must check for allergies to contrast.
Survey radiography
The analysis is carried out without a contrast agent.
It is prescribed for the diagnosis of diseases:
- Bladder;
- kidney;
- ureters.
Images are also taken to check the integrity of the bones:
X-ray with contrast
X-rays with contrast show a detailed picture of the urinary system:
- changes in the functioning of organs;
- pathologies;
- the appearance of neoplasms.
Intravenous urography
The analysis is carried out for diagnosis:
- kidney function;
- cancer;
- pathologies.
This is an effective study that allows you to identify:
- renal failure;
- nephritis;
- problems with other organs of the urinary system.
Excretory urography
When performing excretory urography, more contrast is administered.
This is one of the most dangerous and informative studies showing the condition:
Retrograde urography
During the study, contrast is injected into the urethra and advanced against the flow of urine.
With this contrasting method, look:
Source: https://diagnost-mk.ru/rentgen/kontrastnyj-pochek.html
Indications for radioisotope diagnostics
Renography, as the simplest diagnostic method, is an indication for detecting any diseases of the urinary system. It is used when urolithiasis is suspected - when detecting abnormalities in laboratory tests, for renal colic, and so on.
Renography will help clarify the diagnosis in case of renal failure, acute and chronic pyelonephritis, in case of an unsuccessful operation with the development of complications. Other possible indications for implementation:
- atherosclerosis of the renal arteries;
- chronic glomerulonephritis;
- hypertension of renal origin.
Radioisotope scanning is indicated to identify serious autoimmune kidney pathologies, to differentiate and clarify the size of cysts, adenomas, hemangiomas, lipomas, and malignant tumors. Using scanning, you can determine the size of the organ, its position, congenital and acquired structural anomalies, as well as the consequences of injury. Since renal function is not specified with this technique, it is advisable to carry it out in combination with renography.
Scintigraphy provides the most complete and accurate information. If there is a technical possibility, it is prescribed for any of the above problems. It is this technique that will help detect small stones, tumor metastases or kidney tumors in the initial stages. The technique is used to evaluate the effectiveness of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery.
Indications
- The presence of acute and/or chronic inflammatory diseases of the renal pelvis apparatus (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis).
- The need to assess the degree of kidney damage in trauma.
- Assess possible renal dysfunction due to prolonged disruption of the outflow or stagnation of urine.
- Monitoring the dynamics of work and survival of an organ after transplantation (transplantation).
- Suspicion of the development of urolithiasis (urolithiasis).
- Development of "renal colic".
- Suspicion of the presence of tumor formations, cysts, hemangiomas.
- Examination of the kidneys to determine the structure, congenital or acquired developmental pathologies, position and size of the organ.
- The need to assess the blood supply to the kidney.
- Monitoring of treatment, use of radiation/chemotherapy, surgery.
The range of indications for isotope studies of the kidneys is extensive. It can be prescribed for changes in tests, unclear symptoms, and so on. The specialist can refer the patient for examination if any diseases of the urinary system develop.
Contraindications
The dose of X-ray radiation during such a study is minimal, but it still exists. Therefore, during pregnancy, radionuclide diagnostics are prohibited. The exception is cases when this is vitally necessary and pregnancy develops in the 2-3 trimesters. Lactation is not a strict contraindication, but it is recommended to stop breastfeeding for 1-2 days. Temporary contraindication - acute period of infectious diseases.
Kidney studies using radioisotopes are prescribed for children, because the dosage of radiation is 30-100 times less than conventional radiography. Doctors do not recommend radioisotope testing of the kidneys for children under one year of age. If the procedure is vital, children from 2 months of age are given potassium iodide before the procedure, which will reduce the effect of the radioisotope on the body.
Preparation and execution of the procedure
3 days before the radionuclide diagnosis, it is important to stop taking alcohol and psychotropic drugs. You do not need to eat before the session (4-5 hours), and before the study (half an hour before) you need to drink 500 ml of water. Be sure to remove all metal jewelry before placing it in the cabinet.
Stories from our readers
“I was able to cure my KIDNEYS with the help of a simple remedy, which I learned about from an article by a UROLOGIST with 24 years of experience, Pushkar D.Yu...”
A special drug is introduced into the bloodstream by intravenous injection. Next, for renography the person is sitting, and for other techniques - lying down. Sensors are attached to the body to record the level of radiation. The scanners of the devices move in the projection of the kidneys, taking pictures. At the end of the procedure, which lasts from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours, you need to drink more to quickly remove radioisotopes from the body.
Diagnostic results
Based on the photographs, the specialist will evaluate:
- symmetry of the location of the kidneys;
- organ size and function;
- clarity of structure;
- ureteral patency;
- absence or presence of darkening, spots.
A vascular rheogram will help analyze the work of the veins and arteries in the kidneys, a secretory rheogram will reflect the accumulation of contrast, and an evacuation rheogram will show the rate of its removal. This information will help make a final diagnosis.
Decoding indicators
The result of the half-hour procedure is graphs in which the horizontal axis indicates time in minutes, and the vertical axis indicates radioactivity as a percentage.
The kidney function graph is a curve that can be divided into three fragments:
- vascular - the graph curve goes sharply upward: this reflects the appearance of a radioactive drug in the blood;
- tubular - this fragment of the graph shows the work of the glomeruli to cleanse the blood of hippuran;
- excretory - the radioactive substance leaves the blood along with the urine, the curve graph goes down.
Indicators are considered normal when maximum estrus is reached in 3-4 minutes, and the hippuran excretion time is up to 12 minutes. A difference between the indicators of two kidneys is allowed, but it should not be more than 20%.
Evidence of impaired glomerular filtration is mainly the curvature of the second fragment of the graph. The closer this line is to the horizontal, the longer this period lasts, therefore, the rate of blood filtration is reduced and kidney function is impaired.
Tired of fighting kidney disease?
SWELLING of the face and legs, PAIN in the lower back, CONSTANT weakness and fatigue, painful urination? If you have these symptoms, there is a 95% chance of kidney disease.
If you don't care about your health
, then read the opinion of a urologist with 24 years of experience. In his article he talks about RENON DUO capsules.
This is a fast-acting German remedy for kidney restoration, which has been used all over the world for many years. The uniqueness of the drug lies in:
- Eliminates the cause of pain and brings the kidneys to their original state.
- German capsules eliminate pain already during the first course of use and help to completely cure the disease.
- There are no side effects and no allergic reactions.
The use of nuclear physical phenomena in medicine has become very common in recent years. One such example is radioisotope testing of the kidneys. It has significant advantages compared to ultrasound, MTR or CT and is included in the mandatory complex of urological studies.
Radioisotope research of the kidneys provides the most accurate results today for further treatment or prevention of diseases.
The essence of diagnosis, goals and advantages
Radionuclide diagnostics is a study of the functioning of human internal organs and tissues, based on recording the radiation of a radioactive pharmacological drug. It is characterized by high sensitivity, a wide and accurate range of data obtained during the study. This makes it possible to detect diseases already at the initial stages, when other methods are still uninformative. Its role in monitoring the effectiveness of drug or surgical treatment is also very important.
Radioisotope testing of the kidneys involves the introduction of a special substance into the blood, which allows one to examine the structure of the kidneys.
The essence of the method is to analyze the information obtained after the introduction of a special radioactive substance into the blood, which is distributed throughout the body depending on the functioning of its organs and systems. The radiation is detected using special equipment. The administered drug tends to accumulate quickly and is quickly eliminated from the body, without causing any harm to the patient. Based on the characteristics and speed of movement of radiopharmaceuticals with the blood, as well as their heterogeneous concentration in organs and tissues, one can judge the presence of a particular disease. The most commonly used isotopes of iodine. At the accumulation stage, they make it possible to “see” the functional and structural state of the kidneys, and the rate of excretion characterizes the state of the urinary tract.
The simplicity of the process, minimal risk to the patient and the lack of specialized preparation for the procedure make it a very popular and effective diagnostic tool. It is also important that radionuclide compounds can be used in patients with increased sensitivity to radiocontrast agents. And the main advantage of such methods was the ability to study physiological functions in parallel with the determination of topographic and anatomical parameters.
What is kidney renography
Radioisotope research methods are very popular. They allow you to assess the functional state of parenchymal organs. To understand what kidney renography is, you need to decide on the methodology and evaluation of the results.
The essence of the method
Intravenous administration of a radioisotope substance leads to its accumulation in the renal tissues. The method is based on the ability of the kidneys to extract hippuran from the blood and excrete it in the urine. It is detected using scintillator sensors that are installed above the kidneys. The result is displayed as two curves.
With this method you can:
- evaluate the evacuation function of the tubules;
- determine the state of renal blood flow;
- identify reflux from the bladder into the ureters;
- assess the condition of organ tissues;
- assess kidney function after transplantation.
Indications
The study is indicated to assess the functional state of the renal glomeruli in patients with the following pathologies:
- arterial hypertension;
- kidney pathologies of any origin;
- diabetes;
- swelling of unknown origin;
- causeless increase in temperature;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- condition after organ transplantation;
- any kidney surgery.
As a primary diagnostic method it is used for pathologies:
- urolithiasis disease;
- amyloidosis;
- chronic glomerulonephritis;
- pathology of the renal arteries;
- kidney hydronephrosis;
- renal failure.
Contraindications
The procedure is absolutely safe and does not produce a large radiation load. The administered labeled substance is quickly excreted from the body in the urine. The procedure does not cause complications. The only condition for which it is not recommended is pregnancy. The study is safe even in childhood.
The method is simple and universal and does not require special training. There are certain conditions under which it is better to carry out it. The patient must be fed. Before the test, it is recommended to drink a glass of water without gases.
For those taking diuretics, they are canceled the day before the study. They have a diuretic effect and can distort the analysis.
The preparation of children has some peculiarities. In order to prevent the thyroid gland from using radioactive iodine, they are given a solution in drops. For these purposes, you can use Lugol's solution 3 drops per day. For young children, an iodine grid is applied to the skin in the form of a game.
Methodology
The examination is carried out in a sitting position. The exception is severely ill patients who cannot sit and children. The study is not carried out on people under the influence of alcohol or drugs and who have metal objects with them. The main condition for obtaining an accurate result is the stationary position of the subject.
Sensors are installed in the projection of the kidneys on the back, recording radioactive rays of labeled iodine. The location is determined based on topographic anatomy data. In obese patients and people with a migrating kidney, an x-ray is taken to clarify the location.
131 I-hippuran is administered intravenously and its appearance in the kidneys begins to be recorded. The amount of the drug is calculated individually depending on the age and weight of the patient. A gradual increase in concentration and excretion of the drug is recorded in the form of a curve, for each kidney separately. The study takes 20-25 minutes.
Result evaluation
The curve recording is conventionally divided into 3 parts:
- The vascular part reflects the time of appearance of hippuran in the vessels of the parenchyma.
- Secretory (tubular) - secretion of a substance from the blood by the tubular epithelium.
- The excretory component is the removal of the labeled isotope from the kidneys.
The curve is placed between two axes. On the abscissa there are time marks in minutes, on the ordinate axis there is concentration in percentage.
The following indicators are recognized as the norm:
- the time during which the maximum concentration of the substance appears is 3-4 minutes;
- the time during which the curve decreases by half - half-life, 10-12 minutes;
- The difference between the two kidneys in these two indicators normally does not exceed 20%; such a renogram is called symmetrical.
Glomerulonephritis is an autoimmune kidney disease that affects both organs simultaneously, unlike pyelonephritis. Therefore, changes in the curve will be noticeable on the right and left results. The changes for amyloidosis are relatively similar to glomerulonephritis, also bilateral. In this case, the excretion of hippuran will be slowed down, but the period of maximum concentration of the substance will be maintained. As the disease progresses, the amplitude of the curves decreases and they become flat.
In hypertension caused by damage to the renal artery, the left and right curves will be asymmetrical. On the affected side, the time it takes for the concentration to reach its maximum will be increased. But at the same time, the ability to concentrate and output at the same speed for both sides will remain.
The method allows you to determine renal failure even before the appearance of clinical symptoms. The curve will show a noticeable increase in the time it takes to clear the blood of the radioisotope substance.
Some types of research results are specific and have their own names:
- Afunctional type - there is a vascular segment and a smooth decrease in the line.
- Isosthenuric curve - the line rises to a certain level and throughout the study runs parallel to the x-axis, which is typical for chronic renal failure.
- The obstructive type occurs when there is an obstruction to the outflow of urine - a stone, tumor, adhesions. There is a vascular and secretory segment, but there is no excretion of substances (the curve gradually rises upward).
- Parenchymatous - the height of the line decreases, other indicators slow down, characteristic of glomerulonephritis.
Although renography uses a radioactive drug, this study has a very low radiation dose, unlike X-ray or CT. Therefore, it can be carried out several times. In some cases, an assessment of the treatment performed and the degree of recovery of renal function is required.
After organ transplantation, there is a need to evaluate the function of the new kidney, how functional it is and whether damage has occurred. This method, combined with ultrasound, will be indispensable.
Radioisotope renography is an x-ray method for detecting pathologies using a radioactive marker. A special radioisotope substance is injected intravenously, which has the ability to accumulate in tissues.
The difference between pathological cells and healthy ones is clearly visible in the image. The kidneys are able to extract this substance from the blood and remove it from the body without causing any harm to the patient. This occurs in the renal tubules, in epithelial tissue.
After the drug is administered, scintillation sensors are attached to the kidneys, the data of which is displayed in the form of two curves. The left and right kidneys are determined separately.
Using sensors, you can trace the entire path of urine formation and excretion, evaluate the evacuation function of the tubules, the condition of the vessels, and identify pathologies of the ureter and bladder.
What is isotope renography? It has several types of research. Their use depends on the characteristics of the pathology. All of them display a complete picture of the organ’s work:
- Renography allows you to assess the severity of disorders of the entire urinary system. Show quantitative indicators of blood filtration, the rate of urine formation and its excretion. Highlight small deviations and establish dynamics.
- The statistical view (scanning) helps determine the location, shape of the kidneys, and placement relative to other organs. Get a schematic representation of the organ. A special scanner is used that tracks and captures the contrast agent, which is administered 45 minutes before the procedure.
- Scintigraphy is performed using special equipment. The method helps to obtain a high-quality image of all internal organs. The computer program generates an image after processing the information. The pictures are of high quality. They show the slightest changes in the organs, which makes it possible to establish the onset of the development of the disease.
Indications
Such studies are carried out to confirm or establish a diagnosis of diseases of the urinary system. Prescribed in the following cases:
- formation of stones in the kidneys and excretory system (urolithiasis);
- enlargement of the renal pelvis (hydronephrosis);
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis in chronic form;
- renal failure;
- pathology of the renal artery;
- amyloid dystrophy.
The method is prescribed to evaluate the functioning of the organ and the effectiveness of treatment after:
- surgical operations on the organ;
- identifying obstruction;
- kidney transplantation.
The procedure may be prescribed for certain diseases that negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys, to determine their consequences:
- high blood pressure (hypertension);
- diabetic nephropathy;
- severe swelling;
- febrile conditions of unknown origin.
It should be taken into account that patients with malpositioned kidneys may have inaccurate results. The method has a low radiation dose and is performed on patients with severe pathologies.
Contraindications
Renography is one of the most accurate and safe diagnostic methods. It has virtually no contraindications. The procedure cannot be performed in the following cases:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children under three years of age;
- allergy to intravenously administered radioisotope;
- for alcoholism and drug addiction;
- obesity with a weight of more than 120 kg;
- mental illness.
The price of the radionuclide procedure is not high and is available to everyone, unlike nephroscintigraphy. It is considered an objective research method.
Preparation
There is no special preparation for diagnosis. There are necessary conditions that must be met for the procedure to be carried out efficiently:
- several days before renography you should not drink alcohol;
- you should give up unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, fatty, salty), carbonated drinks;
- do not take diuretics the previous day;
- In the morning, have breakfast and drink 500 ml of clean water without gas.
There should be no metal objects on the patient’s body (earrings, rings, piercings).
The essence of the method
Research is carried out in a special room. In a sitting position. If this is a child or a seriously ill person, you can do the procedure while lying down. The patient is given an intravenous drug (hippuran).
Methods for radioisotope research of the kidneys
Depending on the nature of the indications that need to be obtained during the study, there are several methods of radionuclide diagnostics of the kidneys. Each of them has its own characteristics in conducting and interpreting the results obtained. Their totality gives the most complete picture of the functioning of organs.
Renography
Radioisotope renography of the kidneys is a method that is based on external recording of the degree of radioactivity using a special installation. It does not visualize internal organs, but is used to quantify the function and flow rate of urine. Renography allows you to determine the condition of each kidney separately. It is worth noting that kidney X-ray is one of the tools for a comprehensive analysis of the human urinary system. Based on the data obtained, it is impossible to make a final diagnosis, but it is possible to identify disturbances in work and assess the dynamics of renal processes. Renography is performed in a sitting position. The patient is injected with a low-radiation marker. Sensors are placed in the area of the kidneys, heart and bladder. The dynamics of the movement of isotopes is recorded by a radiograph, which displays information in the form of two curves. The procedure takes no more than half an hour and has almost no contraindications.
Scanning
Scans or static renal scintigraphy provide schematic visualization. This method is used to determine the shape, size, and position of the observed organ. Scanning can identify lesions, destructive processes and developmental pathologies. The study is carried out using a scanner that records the radiation of the drug injected into the patient’s blood. The procedure can take one to two hours, since research begins 40-60 minutes after the marker enters the body.
Scintigraphy
Dynamic scintigraphy is carried out in a gamma tomograph, which records radiation and forms an image based on this data. Pictures (scintigrams) are taken at certain intervals. Compared to scanning, the resulting images are more accurate and detailed. They make it possible to assess the functioning of the urinary system at all stages of the movement of the isotope.
The essence of the method
At the beginning of the study, the patient is injected intravenously with a radioactive drug, hippuran.
Intravenous administration of the drug hippuran based on a radioisotope (ionic salt of the O-iodinated group labeled 131I) leads to its accumulation in the renal parenchyma. It is then extracted from the blood by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. During renography, this process is recorded by scintillator sensors installed above the organs. The result of the study is recorded in the form of two curves (graphs) showing the functioning of the right and left kidneys. Each curve consists of three parts:
- vascular - shows the time of entry of hippuran into the renal parenchyma;
- tubular (or secretory) - reflects the secretion of a radioactive label by the tubular epithelium into the blood;
- excretory – reflects the excretion of hippuran from the kidneys in the urine.
Curves are drawn between two axes. The vertical axis shows the concentration of hippuran in percentage, and the horizontal axis shows the time in minutes. Studying the graphs obtained during radioisotope renography makes it possible to obtain the following data:
- characteristics of renal blood flow;
- assessment of the evacuation function of the renal tubules;
- condition of the renal parenchyma;
- the presence of reflux from the bladder into the ureters;
- condition of the operated or transplanted kidney.
Indications for examination
Radionuclide diagnostics of the kidneys has a very wide application; depending on the nature of the disease, one of the methods described above can be chosen:
Radioisotope examination of the kidneys is appropriate for urolithiasis, tumors, cysts or inflammation in the genitourinary system, and oncology.
- Isotope renography of the kidneys is prescribed for urolithiasis, renal failure, chronic pyelonephritis and any suspicion of a disease of the urinary system, as well as to identify possible consequences of surgical intervention. The procedure is prescribed for chronic glomerulonephritis, damage to the renal arteries, amyloidosis and arterial hypertension. This method allows you to study the functioning of each kidney separately.
- Scans are used to detect tumors and cysts and to diagnose abnormalities in the development, location and shape of organs. This type is of particular importance for determining the side of the lesion. Since the method itself cannot detect disturbances in the functioning of the body system being studied, it is very often prescribed in combination with renography.
- Scintigraphy provides the most comprehensive range of indications compared to other types of diagnostics, so it is used in all the cases described above. The method is also used in oncology to detect metastases in the kidneys and after chemotherapy to evaluate its effectiveness. If scanning can only determine the presence of neoplasms, then scintigraphy determines the nature of this formation, which is very important in the timely diagnosis of malignant tumors.
Preparation for the procedure
Radioisotope examination is a procedure that does not require any lengthy or special preparation. However, a few days before the examination it is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol, any narcotic and psychotropic drugs. You should not eat immediately before the diagnosis, your last meal should be 4-5 hours ago, and 30-60 minutes before the procedure you should drink half a liter of clean still water. If you are taking medications, it is best to check with your doctor to see if they will affect the results. Due to the use of special equipment, the patient should not have metal objects or jewelry on his body. Failure to comply with these rules may distort the objectivity of the information obtained. Radioisotope examination of the kidneys is painless, except at the time of injection of a special substance.
Research is carried out in the radioisotope diagnostics department, in a specially designated room, which must be equipped with all the necessary radiodiagnostic equipment. Since diagnosis is based on recording the radiation of a radioactive drug injected into the blood, the only unpleasant sensation will be the injection of the isotope.
Depending on the chosen research method, the procedure is carried out sitting (RXR of the kidneys) or in a lying position (static or dynamic scintigraphy). With isotope renography, special sensors are attached to the patient, which record radioactivity in specified areas and display information in the form of two curves - a rennogram of the left and right kidney. When scanning, a special scanner is used, which gradually moves in the projection of the kidneys and, reacting to the radiation of the radiopharmaceutical, forms a static image. To perform scintigraphy, the patient is placed in a gamma tomograph. The principle of its operation is the same as that of other procedures, but the resulting images are more detailed and reflect the dynamics of the organs. After the examination, the injected radioactive drug is quickly eliminated naturally through the urinary tract. To speed up the process of cleansing the body, you need to drink plenty of fluids.
How is the research performed?
Radioisotope renography is performed in a specially equipped room. During the examination, the patient is in a sitting position. Children or patients in serious condition are allowed to perform the procedure in a lying position.
To obtain data, sensors are attached to the patient’s back (in the area where the kidneys are projected) and in the heart area, recording the entry of the radioisotope into the kidneys. In overweight patients, the location of the organs can be clarified using a previously taken x-ray.
After preparing the patient for the study, hippuran is injected into a vein (the dose of the drug is calculated individually and depends on the weight and age of the subject). The curve is plotted by a radiograph recorder. The procedure lasts about 20-25 minutes.