Adrenal glands
is a paired organ of the endocrine system, which is a gland located at the upper pole of each kidney.
The adrenal glands are formed by two structures: the medulla (inner) and the cortex (outer). Both substances are regulated by the central nervous system. Each type of substance functions as an independent gland, although anatomically they are combined into one organ. Cortex
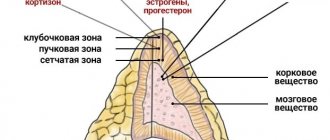
. Steroid hormones produced in the cortex control the body's metabolism and energy. There are three zones of the cortex, in each of which specific hormones are synthesized:
- Aldosterone is synthesized in the zona glomerulosa, which affects water-salt metabolism
; - glucocorticoids are synthesized in the zona fasciculata, which regulate the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
, as well as
the exchange of nucleic acids
; - In the reticular zone, sex hormones are formed, primarily androgens, which affect the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Brain matter
produces catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine). Adrenaline is synthesized only in the adrenal glands. Catecholamines affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system (increase blood pressure, change the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle), cause an increase in blood glucose and stimulate the breakdown of fats, which is necessary for their absorption by the body. This variety of functions of the hormones produced by the adrenal glands shows how important it is for this organ to function correctly. Disturbances in its functioning affect the general condition of the body. Depending on the type and location of the pathology, the manifestations of disorders may be different.
Symptoms of adrenal gland diseases in women
The adrenal glands are small paired glands that are located in the abdominal cavity directly above the kidneys.
These are tiny organs, however, they secrete hormones that affect the condition of the entire body. Any problems in their work immediately affect a person’s health. In most cases, diseases are associated with a decrease or, conversely, an increase in the production of hormones. Let's look at the symptoms of the most common adrenal gland diseases in women.
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome
The development of this disease is associated with an increase in the level of adrenal hormones in the body; this condition develops in most cases due to tumors of the adrenal cortex of various natures.
Signs of the disease:
- increased blood pressure;
- obesity, and the localization of fat is observed on the stomach and shoulders, the outline of the figure resembles a male physique;
- absence of menstruation or cycle irregularities;
- problems with conception and pregnancy;
- bruises appear easily on women’s bodies and heal slowly;
- depression, decreased mood;
- increased bone fragility;
- headache;
- dysfunction of sexual desire in women;
- muscle weakness;
- a moon-shaped oval of the face is formed.
Treatment of this disease can be either therapeutic or surgical; it is prescribed by an endocrinologist after a thorough diagnosis.
Overgrowth of the adrenal cortex
Congenital pathology associated with a genetic mutation. Excessive enlargement of adrenal cortex tissue leads to a significant increase in the level of adrenal hormones.
Symptoms of the disease
So, the main signs of the disease are as follows:
- early appearance of hair under the arms and in the genital area;
- pigment spots in the external genital area;
- sexual dysfunction: late onset of the first menstruation;
- profuse acne on the skin of the face.
Treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist. Unfortunately, this pathology cannot be completely eliminated, but with properly selected therapy the condition can be stabilized.
Lack of adrenal hormones
This pathology can be reflected in the background of injuries or tumor lesions of the organ cortex, and can also be a complication after infectious diseases.
Symptoms of the disease
The signs of the disease are as follows:
- decreased blood pressure;
- drop in body weight, sometimes sharp to critical, life-threatening levels;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of performance, chronic fatigue, weakness;
- abundant appearance of pigment spots on the skin;
- frequent urination, especially at night;
- decrease in blood sugar levels.
Neoplasms in the adrenal glands
In most cases, the adrenal glands are affected by benign neoplasms. The causes of tumors are still poorly understood, however, they appear to be related to the level of hormones of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, and genetic predisposition also plays a role.
Symptoms of adrenal cortex tumors
The signs of this disease are very diverse:
- problems with the stomach and intestines: regular nausea, vomiting;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- arrhythmia;
- muscle atrophy;
- frequent urge to urinate, especially at night;
- feeling of dry mouth.
Treatment of tumors of the adrenal cortex is carried out jointly by oncologists and endocrinologists.
Addison's disease
This pathology is quite rare compared to other diseases of the adrenal glands. The disease and its symptoms develop for a number of reasons:
- hereditary factors;
- damage to the adrenal cortex by toxic substances;
- infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis.
Symptoms of the disease
This disease is characterized by a number of characteristic symptoms:
- increased fatigue, decreased performance;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- lowering blood pressure;
- female sex hormones decrease;
- lack of sexual desire.
Treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist, and hormonal levels are corrected.
Nelson's syndrome
This condition develops against the background of a sharp decrease in the level of adrenal hormones in the blood. Most often, we are not talking about a simple decrease, but about the total absence of these vital substances in the human body.
The syndrome can occur as a reaction to surgery to remove the adrenal glands during surgical treatment of Cushing's disease, due to injuries and hemorrhage into the organ.
This condition requires urgent hospitalization; treatment can only be carried out in a hospital, since aggravation of the condition can lead to coma or death.
The task of doctors is to check the patient’s hormonal background in order to find out the true cause of his condition.
Symptoms
This syndrome is characterized by a number of symptoms:
- profuse sweating;
- confusion or loss of consciousness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vomit;
- weakness;
- decrease in blood glucose.
Hyperaldosteronism
This disease is characterized by excessive secretion of aldosterone. This disease develops in women for a number of reasons:
- severe liver disease;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- heart failure.
Symptoms
This disease is characterized by a number of symptoms:
- menstrual irregularities;
- regular headaches;
- tachycardia;
- night cramps of the calf muscles;
- sleep disorders.
Treatment of this disease in women can be carried out both in a hospital setting and on an outpatient basis.
Adrenal gland disorders in women: on the verge of normality and pathology
Of course, serious disorders in the functioning of the adrenal glands are difficult to ignore, because their manifestations seriously affect the patient’s well-being. However, there are many cases where patients endured symptoms for years without contacting doctors, although the cause was precisely a malfunction of the adrenal glands.
The inability to conceive and bear a child is a common problem faced by modern women. Often the cause of infertility is precisely a deviation in the functioning of the endocrine glands, in particular the adrenal glands. Treatment will not have the desired effect if hormone levels are not corrected. If you experience the following symptoms, you should seek help from an endocrinologist:
- increased photosensitivity: after exposure to the sun, pigment spots appear on the skin;
- reduction in the size of the mammary glands and uterus;
- painful sensations in the mammary glands;
- clitoral enlargement;
- menstrual irregularities or complete absence of menstruation;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- profuse acne on the face.
Women's diseases are closely related to the functioning of the endocrine system. Doctor's intervention is necessary at the first symptoms of the disease in order to prevent further aggravation of its symptoms.
Doctors diagnose most women with adrenal pathologies as infertile. If pregnancy does occur, it is constantly under threat of failure.
Therefore, a woman suffering from abnormalities in the functioning of the adrenal glands must be constantly under the supervision of doctors during the period of bearing a child; the task of doctors is to check and constantly monitor the patient’s hormonal levels.
Source: https://azbukapochek.ru/bolezni/drugie-bolezni/simptomy-zabolevanij-nadpochechnikov-u-zhenshhin.html
Treatment of paired glands
If your adrenal glands hurt and other symptoms of their poor functioning appear, then you should not delay visiting a doctor. Failure in them can negatively affect a person’s overall health. Treatment of the adrenal glands primarily depends on the type of pathology that caused their damage and the degree of functional damage. The first priority here is to eliminate the root cause.
Drug treatment
When a patient is being treated, this process must be supervised by a specialist. The basis of drug therapy is to normalize hormonal levels, for which synthetic hormonal drugs are used. They will make up for the lack of hormones or eliminate their excess. The second goal is to treat or completely eliminate negative factors that aggravate the course of the disease. To do this, patients take:
- vitamin complexes;
- antibacterial agents;
- antiviral tablets.
Surgical intervention
If the patient has not cured the pathology with complex therapy, then the specialist may suggest that he undergo surgery to remove one or two glands. There are two types of operations:
- cavitary - a serious procedure that requires long-term rehabilitation afterward;
- endoscopic is a gentle method that requires only a few incisions, special medical equipment and a short rehabilitation period afterwards.
Adrenal gland diseases in women: alarming symptoms and treatment
The adrenal glands are paired endocrine glands located above the poles of both kidneys. The shape of the right adrenal gland is close to pyramidal, the left - to hemispherical, the mass of each gland is about 14 g.
The adrenal glands consist of a cortex and a medulla, which differ greatly in the nature and functions of the hormones they produce. The cortex makes up approximately 90% of the organ's mass.
Adrenal hormones take part in the processes of regulation of plastic metabolism and provide some forms of immune defense of the body. The starting material for the synthesis of many hormones is cholesterol.
The main symptoms of adrenal gland diseases in women, how to check whether the signs of the disease are dangerous, what to do for treatment? Let's sort it all out!
Hormones
The adrenal cortex consists of three active layers that differ in structure and function: glomerular, fascicular and reticular.
About 30 different active substances are synthesized in the adrenal cortex.
Cortical hormones or corticosteroids are divided into three groups:
- Glucocorticoids (zona fasciculata hormones).
- Mineralocorticoids (hormones of the zona glomerulosa).
- Sex hormones (hormones of the reticular zone).
Glucocorticoid hormones are involved in the vital processes of protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Some glucocorticoids can stimulate fluid retention in tissues. This group includes cortisone, hydrocortisone, and corticosteroids.
The mineralocorticosteroid hormones aldosterone and dehydrocorticosterone regulate water-salt metabolism and maintain normal kidney function.
During pregnancy, the level of progesterone in women's blood increases, which is necessary for normal gestation.
This is a temporary physiological norm; some time after childbirth or artificial termination of pregnancy, the concentration of progesterone decreases to its original level.
The medulla produces catecholamines, better known as stress hormones, norepinephrine and adrenaline. Catecholamines are involved in almost all regulatory processes involving the nervous system.
Frequent illnesses
Adrenal gland diseases are more common in women . Presumably, this is due to natural cyclicity and fundamental hormonal changes during pregnancy and lactation.
Pathologies in these glands can lead to their secretory hypofunction or hyperfunction.
Changes in the type of hyperfunction often indicate tumor processes in different areas of the gland. It can be:
- pheochromocytoma affecting the medulla;
- glucocorticosteroma localized in the zona fasciculata;
- corticoestroma or androsteroma, developing in the reticular zone;
- Aldosteroma, tumor of the zona glomerulosa.
Hyperfunction also develops with hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, which occurs as a result of dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Benign tumors in most cases are not hormonally active and can develop indefinitely without affecting the woman’s well-being.
A specialist will tell you how to recognize Itsenko-Cushing's disease:
Hormonally active tumors
Tumor processes in the tissues of the adrenal glands lead to hormonal imbalance; patients develop symptoms characteristic of excess of one or another group of hormones.
Associated symptom complexes are named after excess hormone :
- hypercortisolism;
- hyperestrogenism;
- hyperandrogenism;
- hyperaldosteronism.
With cortical dysplasia or a mixed tumor, symptoms of excess of several hormones appear simultaneously.
Pheochromocytoma
Tumor processes in the adrenal medulla can develop against the background of dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
Symptoms of excess catecholamines:
- tachycardia;
- hypertension with increased pressure to crisis level;
- sudden mood changes, causeless fear;
- nervousness;
- weight loss;
- patients also complain of severe fatigue.
About the types of adrenal tumors in this video:
Glucocorticosteroma
When the zona fasciculata is damaged, glucocorticosteroma develops, producing an excess of glucocorticoids.
Metabolic disturbances occur in the body , which may be indicated by:
- muscle and general weakness;
- stretch marks (stretch marks) on the torso and abdomen;
- hypertension;
- weight gain for no apparent reason;
- apathy;
- joint pain;
- thirst.
Among the manifestations of hypercortisolism are decreased libido, excessive blushing and multiple caries.
Aldosteroma
The tumor affects the glomerular layer and is accompanied by characteristic signs of impaired water-salt metabolism.
In addition, it is possible:
- headache;
- paralysis and paresis;
- convulsions.
When is surgery necessary for an adrenal tumor?
Androsteroma and corticoestroma
Tumor formations in the reticular zone lead to an imbalance of sex hormones. Androsteroma intensively produces androgens - male sex hormones.
At the same time, women experience male-type changes in appearance:
- the timbre of the voice decreases;
- Excessive body and facial hair appears;
- body proportions change (in adults – slightly).
In patients with this pathology, the menstrual cycle is disrupted and infertility develops.
Corticoestroma produces an excess of female sex hormones. Reproductive function disorders are accompanied by female-type weight gain. Patients have decreased libido, dysmenorrhea, and often infertility.
Adrenal insufficiency
The pathology occurs with signs of weakened function of the cortical layer of the glands.
Primary deficiency develops as a complication of autoimmune or infectious diseases that destroy the glandular tissue of the glands.
Secondary disorders are associated with insufficiency of pituitary hormones that regulate the secretory activity of the adrenal glands.
Acute
Acute adrenal insufficiency can be primary or secondary.
This condition is life-threatening and is a reason for immediate hospitalization of the patient.
The disease develops as a consequence of hemorrhage in the adrenal tissue or abrupt withdrawal of glucocorticoid drugs used in the treatment of systemic diseases.
Sharp exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease due to severe stress are also possible.
Acute adrenal insufficiency has three clinical forms :
- Vascular.
- Neuropsychic.
- Gastrointestinal.
Symptoms of the gastrointestinal form resemble acute surgical diseases. Patients complain of lack of appetite, abdominal pain, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Flatulence and diarrhea are possible.
The course of the neuropsychiatric form clinically resembles meningeal lesions. Patients suffer from severe headaches, complain of weakness, and possible seizures.
In the cardiovascular form, blood pressure is low, the pulse is weak, and signs typical of circulatory disorders are observed:
- cyanosis;
- pale skin;
- cold extremities.
Patients lose the ability to urinate independently.
Chronic
In chronic adrenal insufficiency, symptoms increase gradually over a long period.
Patients experience decreased appetite and digestive disorders, leading to weight loss.
Sustained hypotension, general and muscle weakness develop, memory and other thinking processes deteriorate.
With hormone deficiency, the following are possible:
- body hair loss;
- libido disorders;
- sweating;
- nervousness;
- increased frequency of urination.
What is Bronze disease and how to recognize it, your doctor will tell you:
The clinical picture of secondary failure is characterized by a lesser degree of digestive disorders, pigmentation of the mucous membranes and skin remains within normal limits.
Each symptom of a hormonal disorder may also indicate non-endocrine diseases. But a combination of two or three signs and the lack of effect from appropriate therapy is a fairly serious reason for a visit to an endocrinologist.
However, you should not wait for a pronounced clinical picture.
The first alarm bells are changes in skin color and body weight with a normal diet and diet.
The first symptoms of some forms of adrenal dysfunction in women may appear in childhood and worsen during puberty. It can be:
- cardiac arrhythmias;
- underdevelopment of the internal genital organs and mammary glands;
- hypertrophy of the external genitalia (false hermaphroditism)
- delayed puberty;
- profuse acne;
- early pubic hair growth.
In girls with adrenal dysfunction, the formation of a normal menstrual cycle is delayed over time and may be accompanied by obvious symptoms of hormonal hypo- or hyperfunction.
Diagnostics
Due to the wide variety of symptoms that develop as a result of dysfunction of the adrenal glands, a comprehensive examination will be required .
Additionally, instrumental diagnostics may be needed. Depending on the expected diagnosis, the patient’s condition and the technical capabilities of the clinic, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound;
- computed tomography and multislice computed tomography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
If tumor processes are suspected, radiation semiotics is performed. The complex of examinations also includes radiography to determine probable osteoporosis and assess the size of the pituitary gland.
Drug treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the type of disorder. For benign and malignant tumor processes, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
Patients with severe symptoms of hormonal deficiency are prescribed lifelong hormone replacement therapy .
To correct concomitant disorders from other body systems, vitamin D, calcium supplements, diuretics, and drugs that normalize digestion are additionally prescribed.
Patients with identified pathologies of the adrenal glands are prescribed special diets and are advised to avoid stress.
Source: https://beautyladi.ru/zabolevaniya-nadpochechnikov-u-zhenshhin/
Causes
Adrenal adenoma in women or men is not recorded very often. Why does the disease develop at all? There may be several reasons for this:
- some patients have a genetic predisposition to this type of tumor;
- the patient does not struggle with his excess weight;
- some hormonal changes may explain the appearance of adrenal adenoma in women;
- addiction to alcohol or smoking;
- the presence of other somatic diseases associated with problems in the body’s hormonal system (hypo- and hyperthyroidism, damage to the pituitary gland, diabetes mellitus).
Identified adrenal adenoma in men or women should be classified. First of all, the doctor classifies the pathology as a hormone-producing or non-producing type.
Tumors that do not produce hormones are more common. They are also called "silent".
If the growing tissues release any substances, it is necessary to determine their nature. Based on the detection of the secreted hormone, they are distinguished:
- corticosteromas, which produce various glucocorticosteroids;
- corticoesteromas producing estrogens;
- aldosteromes, which produce mineralocorticoids;
- androsteromes, which, in contrast to corticoesteromes, produce male sex hormones;
- mixed, highlighting several different products at once.
Additionally, all adrenal adenomas are divided into pigmented, oncocytic or adrenocortical adenomas.
Altered adrenal glands: symptoms of the disease in women
Symptoms of adrenal diseases are associated with a deficiency or excess of hormones - cortisol, aldosterone, catecholamines and sex hormones. A glandular cyst may be asymptomatic, but if it grows rapidly, it causes abdominal pain and hypertension. To make a diagnosis, ultrasound, tomography, and blood tests are prescribed.
If a hormone-producing or large tumor is detected, its removal is indicated. Conservative therapy is based on suppressing excess hormone synthesis or replacing it with a drug in case of adrenal insufficiency. Herbs are not used for hormonal imbalance due to a tumor.
The main symptoms of adrenal disease in women
Diseases of the adrenal glands lead to the development of several sets of symptoms in women, which are associated with excess or insufficient production of hormones - from changes in figure to severe pain and deterioration of general condition.
Hypercortisolism
Caused by increased production of cortisol by the cortex. Manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- fat deposition in the face (moon-shaped) and torso;
- thin and dry skin with purple-purple stretch marks;
- pinpoint hemorrhages;
- acne;
- hair growth on the face and limbs, thinning of the scalp;
- disturbance of the cyclicity of menstruation, cessation of menstrual flow;
- osteoporosis with a tendency to bone fractures;
- increased blood pressure, rapid pulse, rhythm disturbance;
- frequent colds, pneumonia;
- abdominal pain, alternating constipation and diarrhea, intestinal or stomach bleeding;
- secondary diabetes - increased thirst, frequent urination, bouts of hunger;
- pain in the lumbar region, swelling of the legs and lower eyelids with the addition of nephrotic syndrome, renal colic;
- neurological disorders - impaired coordination of movements, swallowing, slurred speech, memory loss, lethargy, depression.
We recommend reading the article on adrenal fatigue. From it you will learn about the causes of adrenal fatigue, symptoms in women and men, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of the syndrome.
And here is more information about adrenal gland diseases.
Hypocorticism
With adrenal insufficiency with cortisol deficiency, the pigmentation of the skin is disrupted. First, parts of the body exposed to the sun darken, the areola of the nipple, the perineal area, and the palmar folds. Then the change in skin color becomes widespread and spreads to the mucous membranes. There are also variants of the disease with spotty coloring or weak pigmentation.
In addition, women are found to:
- weight loss;
- general weakness;
- increased irritability;
- depressive states;
- low blood pressure;
- fainting with a sudden change in body position;
- low sex drive;
- nausea, weak appetite, abdominal pain;
- craving for salty foods, even to the point of eating regular salt in its pure form;
- 2 hours after eating, patients feel severe weakness, lethargy and drowsiness.
Hypoaldosteronism
Lack of aldosterone leads to progressive weakness and exhaustion. Patients complain that it is difficult for them to even get out of bed; they experience fainting and dizziness. Blood pressure is low, heart rate is slow. Impairment of the conduction of cardiac impulses can reach complete blockade and cardiac arrest.
Due to the increased excretion of fluid and salts, dehydration, convulsive syndrome, and confusion are observed. Hypoaldosteronism is characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation with vascular collapse. A long-term disorder of water-salt metabolism leads to impaired cerebral circulation with memory loss, impaired speech, motor function and sensitivity of the limbs.
Violation of the formation of sex hormones
The adrenal glands produce female and male sex hormones. Clinical manifestations in women appear with an excess of estrogen and androgen imbalance. The following signs are considered typical:
- hyperestrogenemia (increased estradiol) - accelerated puberty in girls, heavy bleeding in women;
- hyperandrogenism (many male sex hormones) - cessation of menstruation, growth of facial hair, rough voice, acne, enlargement of the clitoris and reduction in the size of the uterus and mammary glands, increased libido; hypoandrogenism (lack of testosterone) – depression, tearfulness, brittle nails and hair, low exercise tolerance, low sexual desire.
Increased catecholamine levels
Most often, excess adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine are caused by a tumor of the adrenal cortex - pheochromocytoma. It is characterized by hypertensive crises. Blood pressure can rise sharply to 200-250 mm Hg. Art. and higher. A severe headache, dizziness, feelings of unreasonable fear, and panic appear.
Catecholamine crises are accompanied by:
- pallor of the skin with a marbled pattern;
- rapid and increased heartbeat;
- pain in the heart area;
- muscle tremors;
- increased body temperature;
- bouts of vomiting;
- copious urine output.
Such conditions can occur after eating, physical exertion, stress, or deep palpation of the abdomen. The sudden onset is followed by a rapid spontaneous cessation of the crisis with the restoration of blood circulation parameters.
There are also forms of the disease with constant hypertension and inter-crisis high blood pressure.
Symptoms of adrenal cysts in diseases in women
Adrenal cysts in women are usually detected by chance, since such formations do not have hormonal activity, that is, there are no obvious symptoms. Patients may not be aware of their existence throughout their lives. Clinical symptoms appear when the cyst grows rapidly:
- pain in the abdomen, back;
- heaviness in the hypochondrium, lumbar region;
- increased blood pressure resistant to conventional antihypertensive drugs.
Heaviness in the lumbar region or right hypochondrium
Diagnosis of adrenal gland diseases in women
In order to study the structure of the adrenal glands, ultrasound, computed tomography and MRI are used for diagnosis in women.
If changes are detected, then to clarify the diagnosis it is recommended:
- selective arterio- and venography – administration of contrast into the vessels of the adrenal glands;
- Doppler scanning - study of blood flow in the glands;
- scintigraphy – intravenous injection of a radiopharmaceutical followed by scanning;
- excretory urography – study of kidney function with an iodine-containing contrast agent.
It is mandatory to determine the content of cortisol, estradiol, testosterone, aldosterone and catecholamines, potassium. To clarify the level of hormonal imbalance, stimulating tests are performed.
Treatment of symptoms and diseases of the adrenal glands in women
The vast majority of symptoms of adrenal diseases are caused by tumor formations - adenomas that produce adrenal hormones, therefore, if they are highly active, treatment in the form of removal is indicated. For “silent” formations, dynamic observation is carried out. Conservative treatment methods are used less often.
Medicines
Depending on the type of hormonal changes, the following may be prescribed:
- hypercortisolism – Mitotan, Orimeten;
- hypocorticism – Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone;
- hyperaldosteronism – Veroshpiron, Kapoten;
- hypoaldosteronism – Doxa, Cortineff;
- deficiency of sex steroids – Nandrolone;
- excess androgens - contraceptives with antiandrogenic action (Diane, Logest), Clostilbegit, Veroshpiron.
Symptomatic therapy includes drugs for high blood pressure, diuretics, hypoglycemic agents, vitamins, potassium salts, calcium salts (if indicated).
Folk remedies for symptoms of adrenal disease in women
The use of plants from folk remedy recipes for tumor processes in the adrenal glands in women is strictly contraindicated. This is due to the fact that they contain biogenic stimulants, which can lead to rapid growth of the tumor.
Although there are herbs that have hormonal activity, their effect on the imbalance of cortisol and aldosterone and catecholamines is extremely difficult to predict. Therefore, when a diagnosis of excess or deficiency of adrenal hormones is established, only drug therapy or surgery is prescribed.
Watch the video about the adrenal glands and folk remedies:
Prevention of the development of pathologies
A number of diseases have a hereditary predisposition. Therefore, it is important, in case of known cases of adrenal gland damage in the family, to undergo a comprehensive examination, including a medical geneticist, even at the stage of pregnancy planning.
Disturbances in the formation of hormones lead to:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of contraceptives in tablets;
- stress;
- unbalanced diet - lack of vitamins and minerals (berries, vegetables, fruits), unsaturated fatty acids (found in avocado, fish, nuts, vegetable oil), amino acid tyrosine (turkey, soy, lentils, peanuts, cheese);
- refusal of salt or its excess in the diet;
- lack of a daily routine, sufficient duration of night sleep;
- smoking;
- abuse of alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks.
Correcting eating habits and giving up nicotine and daily alcohol intake is a prerequisite for treating the adrenal glands. Dosed physical activity, swimming, yoga, meditation, and relaxing massage help restore hormonal levels.
We recommend reading the article on how to test your adrenal glands. From it you will learn about the reasons for examination, which doctor to see, how to check the structure of the adrenal cortex and what diseases can be detected.
And here is more about the adrenal glands and blood pressure.
Symptoms of adrenal gland disease in women can manifest as pain, changes in the body, or even be without any signs at all, as in the case of cyst formation. Treatment is predominantly medicinal; in some cases surgery is necessary. If you suspect the presence of diseases, you should consult a doctor rather than use traditional medicine.
Source: https://endokrinolog.online/nadpochechniki-simptomy-zabolevanija-u-zhenshhin/
Diagnostics
Modern medicine has a huge arsenal of ways to recognize gland diseases in a short time. After collecting anamnesis and examining the patient, the doctor decides on diagnostic methods. The main laboratory methods for determining malfunctions of the adrenal glands are:
- general blood and urine tests;
- hormone tests (cortisol, aldosterone, ACTH, DHEA-c, testosterone).
Diagnosis of the disease can be made by instrumental methods, the most used of which are:
- X-ray of the skull to determine the size of the pituitary gland;
- computed tomography or MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- x-ray of the skeletal system to detect osteoporosis;
- X-ray examination for a complete picture of the condition of the organ;
- phlebography.
Adrenal diseases - what are the symptoms?
Diseases of the adrenal glands are considered serious disorders, because they lead to serious deviations in the functioning of the human body.
The adrenal glands are an irreplaceable organ, and the hormones they produce are vital to the body.
The main causes of adrenal diseases are most often associated with increased production or lack of hormones directly from the adrenal glands or pituitary hormones.
What are the adrenal glands and what are their functions?
The adrenal glands are paired glands located in the cavity behind the peritoneum above the kidneys.
They perform many important functions :
- Take part in metabolic processes;
- Produce hormones;
- Stimulates reactions to stress;
- Produce adrenaline and norepinephrine.
In the human body, the functions of the adrenal glands play a very important role, as they are responsible for the production of hormones. Adrenal adenoma is a common disease among people suffering from adrenal dysfunction. You will find more detailed information in our article.
How to recognize adrenal diseases?
The most common diseases :
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- Addison's disease;
- Hyperaldosteronism;
- Adrenal tumors;
- Nelson's syndrome;
- Adrenogenital syndrome.
Cushing's syndrome
Increased influence of adrenal hormones on the body.
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome has no different manifestations from the disease.
It is determined in cases of a tumor of the adrenal gland or a tumor of another organ.
Main features :
- High blood pressure;
- Excess weight according to the male type;
- Moon-like face;
- Impaired glucose metabolism;
- Muscle atrophy and weakness;
- Amenorrhea;
- Hirsutism;
- Osteoporosis;
- Depression;
- Headache;
- Furunculosis;
- Circulatory disorders;
- Decreased potency;
- Bruises due to increased capillary fragility.
Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism is a disorder in which there is an increased production of aldosterone by these glands.
reasons for this failure:
- Serious liver disorders;
- Chronic nephritis;
- Heart failure.
In case of insufficiency of the cortex, an immune disease occurs, which turns into a complete disorder of the entire organism.
The reasons for the process are:
- Necrosis after childbirth;
- Damage to the pituitary gland;
- Malignant tumors;
- Long-term infection.
Signs of all forms of hyperaldosteronism:
- Muscle weakness;
- Migraine;
- Attacks of tachycardia;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Polyuria;
- Convulsions;
- Hypervolemia;
- Edema;
- Constipation.
Adrenal tumors
Adrenal tumors include the following:
- aldosteroma;
- glucocorticosteroma;
- corticoestroma;
- glucoandrosterome;
- pheochromacytoma - local increase in the number of gland cells.
Most of these formations are benign, and they appear extremely rarely.
The causes of organ tumors are unknown. Most likely, they are hereditary .
The adrenal glands produce hormones that control metabolism, blood pressure, and sex hormones.
The main symptoms of this disorder depend on what hormone it produces excessively.
Organ tumors have the following symptoms :
- Increased pressure;
- Feeling of heart rhythm failure;
- Muscle weakness;
- Frequent urge to urinate at night;
- Headache;
- Sweating;
- Panic;
- Irritability;
- Dyspnea;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Pain in the abdomen, chest;
- Pale or red face;
- Disorder of sexual development;
- Changing the appearance of men and women;
- Blueness of the skin;
- Convulsions;
- Aches in the joints;
- Blood sugar imbalance;
- Shiver;
- Chills;
- Dry mouth.
Complications include retinal hemorrhage, pulmonary edema, and cerebral circulatory disorders.
Adrenogenital syndrome
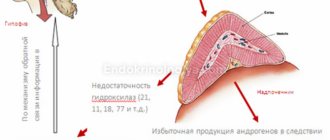
Congenital hyperplasia of the glandular cortex combines a complex of congenital disorders caused by mutations at the genetic level .
The disease occurs due to a disruption of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme system.
Signs of the syndrome:
- Virilization;
- Increased potassium content;
- Early pubic hair growth;
- heart rhythm disturbances
- Acne;
- Late first menstruation;
- Violation of water balance;
- Hirsutism;
- Menstruation disorders;
- Reduction in the size of the breasts, uterus and ovaries;
- Enlargement of the clitoris.
This disorder is the cause of infertility.
A fatal outcome cannot be ruled out.
Increased production of male hormones in women causes a change called “hyperandrogenism.”
An excess of male hormones in the weaker sex affects the ability to conceive and bear a child.
A woman in a position with such a disorder should be under the supervision of a gynecologist due to the threat of pregnancy failure.
It is necessary to monitor the level of male hormones in her body in order to adjust the treatment regimen.
Most often, hyperandrogenism is treated with artificial cortisol analogues. These drugs are prescribed to neutralize the influence of the pituitary gland on the glands.
When a large amount of adrenal hormones is produced, serious manifestations occur.
Excessive production of cortisol causes Cushing's syndrome, and too much male hormones in women causes masculinization.
Normally, cortisol neutralizes the production of adrenocorticotropin, which is secreted by the pituitary gland.
Chronic lack of cortisol is manifested by adrenogenital syndrome.
As for the symptoms of adrenal gland diseases in women, they correspond to the general symptoms described above.
Prevention
Problems with the adrenal glands can be prevented if you know the main preventive recommendations:
- it is necessary to minimize the number of stressful situations;
- improve the microclimate in the family and immediate environment;
- give preference to proper nutrition and exercise;
- timely treat any pathologies to which the body is exposed;
- Periodic testing and medical examinations are the key to timely detection of dysfunction of organs and systems.
There is no need to ignore the symptoms of adrenal gland diseases; they can indicate quite serious abnormalities, which can be corrected simply and quickly. You should not get carried away with self-medication; it is better to entrust your health to an experienced doctor. After all, only a doctor can find the true cause of the disease and cure it safely for the body.
Primary deficiency: Addison's disease
Addison's disease is caused by a lack of hormone production, namely cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens. What is the threat of such problems from these bodies?
There are complaints about the following symptoms:
- severe asthenia, fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss with a tendency to exhaustion, desire to eat salty foods;
- nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal area of different locations, sometimes diarrhea;
- Menstruation may be disrupted in women;
- weight loss of varying degrees, atrophic changes in muscles, decreased muscle strength;
- staining of the skin and mucous membranes. In this case, the skin becomes tan or sharply brown with a hint of bronze. Pigmentation appears first on open areas of the body (limbs, face, neck area), then on closed areas.
From the organ systems:
- cardiac system: decreased blood pressure, slow heartbeat, muffled heart sounds;
- gastrointestinal tract: during an exacerbation, constipation, vomiting may occur, the liver increases in size;
- urinary system: decreased glomerular filtration rate;
- reproductive system: atrophic changes in the genitals, secondary sexual characteristics become less pronounced;
- neurological changes: aggression, irritability, depression, convulsive syndrome (as a result of potassium deficiency).
In women, as a result of impaired androgen production, in addition to menstruation disorders, infertility may occur.
Patients with secondary deficiency develop almost the same symptoms as patients with Addison's disease, but there are no skin manifestations.
How our clinic will help you
The most reliable method of treating adrenal adenoma is surgical removal of the tumor.
- If the adenoma has reached a very large size or has a bilateral localization, then it is removed in the classical way through a large incision in the lumbar region.
- Laparoscopy is considered a more gentle method. Removal is performed using an endoscope through small incisions in the skin.
After a successful operation, the doctor selects the most optimal option for hormone replacement therapy. The entire rehabilitation period takes about a week.
Deficiency or excess of hormones
Diseases of the glands occur both with and without hormonal dysfunction.
The lack of hormones that cause pain and other symptoms is provoked by adrenal insufficiency of the primary or secondary type, acute or chronic.
Excess hormones usually occur for other reasons, including:
- various tumors of the brain zone;
- neoplasms of the zona fasciculata, glomerulosa and reticularis;
- mixed type tumors;
- dysfunction and hypertrophy of the adrenal cortex.
In other cases, pathologies of the glands occur without significant problems on the part of the endocrine system due to the formation of tumors that do not have hormonal activity.
Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome and disease
Itsenko-Cushing's disease is a hypothalamic-pituitary disease characterized by excessive production of corticotropin with hyperplastic changes in the adrenal glands and their excess production (hypercortisolism).
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome is a series of diseases of the adrenal cortex, accompanied by their hyperfunction.
Women with this disease have the following list of complaints:
- poor sleep, headache, fatigue;
- red stripes appear on the body, mainly in the thighs and abdomen;
- progressive weight gain with the onset of obesity;
- excess hair growth on the body and face, dry skin;
- decreased libido, menstrual irregularities;
- constant pain in bones and muscles;
- hair loss on the scalp.
External changes in such women are also characteristic. The face becomes moon-shaped, fat mainly accumulates on the abdomen, chest, and buttocks, but the limbs remain thin. Marble skin, dry. A lot of pimples appear all over the body. Excessive facial hair (mustache, beard) is visible. There are many small bruises on the body.
From the organ systems:
- cardiac system: increased blood pressure, which is accompanied by pain in the occipital region of the head, decreased vision;
- respiratory system: tendency to inflammation of the lungs and bronchi;
- digestive system: gum inflammation, gastritis;
- urinary system: the occurrence of urolithiasis, kidney inflammation;
- reproductive system: in women – inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, reduction in the size of the uterus, absence of menstruation;
- osteoarticular system: manifestations of osteoporosis, which affects the spine.
Complications of Itsenko-Cushing's disease (syndrome): profound disruption of the heart, osteoporosis with primary involvement of the spine.
Changes in function during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, hormonal changes occur in the female body. The endocrine system responds to pregnancy by increasing the production of all types of adrenal hormones, with the exception of androgens.
To determine the level of physiological changes in the functionality of the adrenal glands during pregnancy, women are recommended to donate blood for hormones - this analysis is recognized as the most informative.
Diagnostic procedures
The manifestation of symptoms due to adrenal dysfunction can often be observed when the pathology has long passed the initial stage of its development.
So, to diagnose a disease, you will need a whole range of research procedures. The attending physician prescribes the diagnosis.
As a rule, to make a correct diagnosis, the patient will have to:
- Be tested for hormones to determine which substances predominate in the blood and which are deficient;
- Undergo ultrasound screening of the kidneys and adrenal glands, which can detect the presence of tumors;
- To recognize their nature, the patient may be prescribed an MRI or CT scan.
The results of the study allow the doctor to obtain a detailed picture of the disease and make attempts to determine the causes of the disease.
If disturbances have occurred in other systems of the body, treatment is tailored taking into account this factor. Conservative therapy or surgical intervention is carried out in accordance with the symptoms of adrenal diseases.
Adrenalectomy
Surgery is resorted to only in extreme cases when hormonal therapy has not brought the desired results. Taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, one or both adrenal glands may be removed. Surgeons use two approaches:
- Traditional. Abdominal surgery is performed, a small incision is made, if the tumor is small - on the back, in the lumbar region. For large tumors, a large incision must be made in the abdomen.
- The endoscopic approach involves surgery using endoscopes that are inserted through a small hole in the abdomen or back. This method has its advantages:
- The patient can go home after a few days.
- Minimal injury.
- Working capacity is restored in 2-3 weeks.
- There are no scars left after surgery.
- Bed rest - just one day.
If one adrenal gland is removed, then most often you can forget about the symptoms of the pathology, but if both are ectomized, you will have to take hormonal medications for the rest of your life.
Endocrine glands are very important in the normal functioning of our body. Any of their pathologies must necessarily undergo adequate therapy under the supervision of a competent specialist. This is the only way to ensure the normal functioning of all organ systems.
Source: fb.ru
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Unusual shape
Hello. I recently had an ultrasound, where the specialist told me in detail where the adrenal gland is located and why they are needed, but I was alarmed that they were of different shapes. This is fine?
Good afternoon. This phenomenon is absolutely normal and there is no need to worry. In every person, the right adrenal gland is triangular in shape, and the left is in the shape of a crescent. So don't worry, it's not scary.
To find out where a person’s adrenal glands are located, just look at the photo, but what their role is in the body or what the functions of the adrenal cortex are are more complicated questions.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
Despite the small size of this organ (the length of each side is only about 1 cm), its importance for the body is enormous. What is he responsible for and what functions does he perform?
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>