Every third woman experiences bladder inflammation, regardless of age. There is an opinion, and it is widespread, that cystitis is easily treated. Unfortunately, medical statistics refutes this. According to various sources, cystitis does not go away after antibiotics in every fourth of the sick, and this is only according to official information. While up to 60% of patients do not seek medical help, preferring to be treated independently. There are several reasons why cystitis does not go away after treatment, and to correct the situation it is necessary to exclude them all.
Why does it occur?
Symptoms of cystitis are pain when urinating, a feeling of fullness in the bladder, a frequent desire to go to the toilet, burning and stinging. It has already been proven that the main cause of cystitis, including chronic cystitis, is an infection that has begun to spread in the patient’s genitourinary system. But even after treatment, when the disease should have gone away, there is a risk of exacerbation. Especially in the following cases:
- During menopause in women over 40 years of age.
- Against the background of other ailments: endometritis, urethritis, adnexitis, prostatitis, tonsillitis and even caries, which, at first glance, is not related to bladder diseases. The fact is that any “old” disease can become an “Achilles heel” for a person and strike in the most unexpected way. For example, the return of cystitis.
- Hypothermia, swimming in cool water can also cause a relapse if the immune system is impaired or weakened (during the off-season).
Who is cystoscopy recommended for?
This examination should be done for those whose cystitis does not go away and treatment does not produce results. Quite often, people with chronic cystitis undergo the procedure, which, even with treatment, causes persistent exacerbations.
When cystoscopy should not be performed:
- For acute symptoms of cystitis;
- For urinary tract infection;
- If the patient is diagnosed with poor blood clotting.
Cystoscopy is of rigid type and flexible type. In the first situation, the specialist prefers a regular cystoscope: its tube more accurately examines the urinary tract and the bladder itself. But this procedure cannot be called painless.
The flexible type involves the use of a flexible tube, the insertion of which is more delicate. But the information obtained from this study will not be clear enough.
During the examination, the patient lies on the couch - his perineum is treated with an antiseptic before inserting the instrument. The doctor fills the urinary canal itself with liquid, and a cystoscope is inserted there, so the doctor learns about the condition of the walls of the organ. Cystoscopy is done for both diagnosis and therapy.
When the disease persists
Cystitis can worsen for other reasons:
- There is a latent sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the body.
- The treatment was interrupted: the patient stopped taking the medication ahead of time prescribed by the doctor.
- Medicines were unable to suppress pathogens.
- The immune system turned out to be very weak.
- The lumbar region turned out to be overloaded, for example, during physical activity (sometimes it is enough for a woman to lift an overly heavy bag to “break” her lower back).
Cystitis can worsen for many reasons
- Hormonal levels have changed. For example, before menstruation, due to pregnancy or, on the contrary, abortion.
- Relapses occur after injury or injury.
- Metabolism has changed. This phenomenon is typical for women who prefer heavy, filling foods with an abundance of fats (cheese, lard, salads with mayonnaise, industrial sauces).
- The thyroid gland failed.
- The functions of the central nervous system (CNS) are impaired.
- Due to individual intolerance to certain medications.
It happens that treatment is useless if a tumor appears in the body. That is why it is important to identify (or exclude) the presence of any tumors from a qualified oncologist.
Medical indications
The pathology in question may not go away for a long time with constant hypothermia. If cystitis does not stop due to low body defense, then a course of immunomodulators and vitamins is indicated. A purulent process or failure to comply with hygiene rules can also lead to infection.
Provoking factors for long-term cystitis include infectious processes associated with staphylococcus and streptococcus. These bacteria are the cause of the chronic form of the pathology. This is explained by the fact that when symptoms of cystitis appear, the patient carries out its therapy, but after another decline in protective forces, he notices a relapse.
The reason for such a clinic is inflammation, which can easily spread throughout the patient’s body. Therefore, if cystitis does not go away for a long time, it is recommended to be examined and identify a hidden source of the infectious process.
How to properly treat cystitis?
The golden rule for successful treatment of any infectious disease is systemic administration of drugs. Any medications - be they uroseptics, herbal remedies, and even more so antibiotics - must be taken strictly in courses and in the dosage prescribed by the doctor. Bacteria, viruses or fungi die if the medicine is chosen correctly and the patient is not allergic to individual components of the medicine.
Some patients are guilty of listening to advertising and starting to change pills if they do not feel immediate relief. This behavior can be called a huge mistake - after all, many medications are cumulative in nature and the therapeutic effect occurs “slowly but surely.” Unsystematic use causes the body to develop a stable immunity to the drugs, treatment becomes useless, and the disease becomes chronic.
Medicines should be prescribed ONLY by a doctor
An alternative to traditional tablets is the drip route of drug administration, when medicinal solutions are injected into the bladder through a catheter. Despite all the advantages of this method, it is worth remembering: it is not suitable for everyone. Only a practicing urologist can say for sure how necessary such a procedure is for a patient with cystitis.
Herbal medicine and traditional medicine - baths, douches, decoctions and poultices are very loved by patients for the absence of chemicals and their gentle effect on the body. But plants can be basically useless, and even worse - cause allergies. So you have to treat two diseases at once.
All kinds of food additives, vitamins, teas for cystitis can cause irreparable damage to health. The thing is that their influence has not been fully studied by doctors and is not confirmed by medical statistics. While you take them in the hope of a speedy recovery, pathogenic organisms continue to multiply, “taking over” other vital systems of the body. Don't experiment on yourself, don't hope for a miracle! Trust only experienced doctors with good practice.
Anatomical features of the body
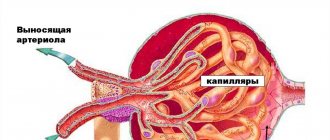
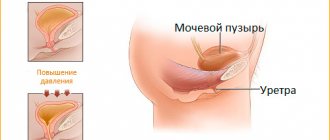
The structure of the female genitourinary system, as already mentioned, is itself a predisposing factor to the development of cystitis. A short and wide canal without any bends, proximity of the anus and vagina, small volumes of the bladder.
But besides this, the female body sometimes has some abnormal features. These cases are not so common, but they are also diagnosed during the examination.
Anatomical pathologies:
If you avoid visits to the doctor, then you may not even know about your anatomical features. And cystitis, which is treated only on the basis of complaints and tests, will not respond to therapy. Although the listed cases are rare, they are not so rare that people with persistent cystitis cannot suspect they have them.
Repeated tests
What tests should a person who has already undergone treatment for cystitis do?
- A prerequisite for examination is bacterial culture, which identifies the causative agent of infection in the urethra or vagina. It allows you to determine the type of bacteria (virus or fungus) and select the best antibacterial drug.
- A rapid test is performed for the presence of nitrites, red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine. During the inflammatory process, the number of leukocytes can be up to 10 units.
- A urine test is taken according to Nechiporenko, which is considered one of the most important for making a diagnosis specifically in the urological part.
- Blood is examined for the presence of hepatitis of all types.
- A smear is taken (doctors call this test polymerase chain reaction or PCR) to check for sexually transmitted infections. Most often, the presence of diseases such as toxoplasmosis, mycoplasma genitalium, herpes, chlamydia and gonorrhea will be checked.
- The vaginal microflora is examined for dysbacteriosis.
- An ultrasound of all organs of the genitourinary system is performed.
- If necessary, a study is carried out for possible hormonal disorders.
- In some cases, a biopsy and cystoscopy are performed to exclude (or confirm) the likelihood of developing cancer.
Bacterial culture plays a big role in prescribing a new course of therapy against chronic cystitis. To obtain correct data, bacterial culture is carried out 3 times, and only then can the doctor judge with complete confidence the presence of certain harmful microorganisms in the body. That is why you need to be very well prepared for submitting urine for bacterial culture.
It is important to properly prepare for urine testing
Collect urine only after thorough genital hygiene. Prepare a sterile container (it is advisable to purchase it in advance at the pharmacy) and start collecting early in the morning immediately after sleep. You need to take urine in the middle of urination, but not at the very beginning, much less at the end. Remember: no more than 2 hours should pass from the moment of collection to the time of analysis, otherwise bacteria can multiply and the result can be significantly distorted.
Treatment methods
If cystitis symptoms persist, the doctor re-examines the patient, prescribing new medications. To recover, a person must complete the full course of therapy without stopping the prescribed medications. Premature cessation of treatment may lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Any treatment regimen for protracted cystitis includes bed rest. If necessary, the patient is admitted to the hospital. Prolonged chronic inflammation can be treated for several months. In addition to taking medications, it is recommended to eat properly (avoiding spicy and salty foods, canned food, carbonated water). It is more difficult and longer to treat cystitis that occurs against the background of dysfunction of the endocrine system and neurovegetative disorders. These pathologies are difficult to diagnose.
If 30 days have passed after taking the medication, and the symptoms of cystitis do not subside, then the doctor reconsiders the treatment tactics. Experts highlight the following rules that must be followed if there is a tendency to relapse:
- Self-administration of antibiotics is contraindicated.
- Medicines are taken after identifying pathogenic flora.
- Medicines taken in low dosages create resistance to active substances, which complicates therapy. If there is no effect within 7 days, then the treatment regimen is revised or antibiotics of a different pharmacological group are selected.
Chronic inflammation cannot be treated with herbs and douching. Otherwise, more serious pathologies may develop. It is prohibited to take various supplements. You can increase your immunity with a course of microelements. These medications should only be prescribed by a qualified physician.
How are recurrent cystitis treated?
- The first thing urologists focus on is selecting a new antibacterial drug, taking into account all the research.
Bed rest is recommended
- The disease that caused the relapse must be treated. To do this, the patient may need to be monitored by several specialists at once.
- To support antibiotics, they can prescribe herbal medicines, uroseptics and advise the necessary beneficial herbs.
- Diet, rest, and proper drinking regimen are considered mandatory for the successful treatment of recurrent cystitis.
- Sometimes it is allowed to use warm baths, heating pads, lotions and other home treatments.
- Modern physiotherapy, treatment with mineral waters, and therapeutic exercises are often included.
Remember: treatment of advanced cystitis always requires time and patience from the patient. However, you cannot ignore the doctor’s advice, just as you cannot rush things. Don't want cystitis to come back again and again? Treat yourself thoroughly!
Prevention measures
It is known that it is better to prevent a disease than to undergo long-term treatment. What is important to know to prevent exacerbation of cystitis?
Follow simple rules of prevention
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Don't sit in one place for a long time, take dynamic breaks.
- Go to the toilet on time, little by little. Better - at the first urge.
- Maintain hygiene, paying special attention to the genitals.
- Do not use deodorants on your intimate area.
- Pee all the way - it is important to empty the bladder completely.
- Choose only high-quality contraceptives.
- Even if the stinging, burning and pain have disappeared, take the entire course prescribed by your doctor.
- Don't indulge in spicy foods, caffeine, or alcohol.
Remember that six months after successful re-treatment you will need to take a urine test to make sure that you have finally recovered. It is advisable to do another ultrasound examination and, if necessary, do a smear to check for infection or dysbacteriosis. Only attention to yourself and vigilance will help avoid new relapses. Take care of yourself, see doctors on time and never get sick!
Recommendations from doctors for patients prone to relapse of the disease
Basic requirements for preventing recurrence of cystitis are control of fluid intake, diet, and hygiene.
How to treat cystitis? What to do if you suffer from cystitis? First, take all the above measures. Secondly, you should start carefully monitoring your fluid intake. Both simply still water and natural juices, compotes, teas and herbal decoctions will be beneficial. Thirdly, it is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene and wear only cotton underwear. You can take herbal baths yourself to reduce irritation of the skin of the external genitalia. Herbal decoctions are also useful to drink; they can strengthen the body's defenses.
Urologists often say that one of the most common complaints that patients come to them with is that they cannot cure cystitis. Of course, the doctor asks about how you are being treated, who you contacted, etc. More often, the answer lies in the plane: “I am being treated myself, there were no tests.”
Unfortunately, patients’ attitude towards cystitis is not always responsible. Many people perceive this disease as a mild cold that can be cured with cranberry juice and tablets like Furadonin.
But if cystitis does not go away, you have to go to the doctor: and it turns out that the treatment will not be easy. Is it only in the frivolity of the approach to treatment that a protracted illness lies? Or are there other reasons for this?
Are you sure you really understand what cystitis is? This is the medical name for inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. About 90% of all cases of cystitis are infectious in nature. This is a common disease that is much more often diagnosed in women due to its anatomical condition.
With cystitis, the bladder wall and mucous membrane become inflamed. Potential pathogens live in our bodies. According to various sources, from 85 to 95% of all pathogens are E. coli.
Cystitis happens:
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation with sharp symptoms and pain, burning, itching and even fever. Chronic cystitis manifests itself to a greater extent in laboratory indicators. For the time being, the chronic disease is asymptomatic, but an exacerbation again reminds of inflammation - and it goes away with all the symptoms of acute cystitis.