Why does neurogenic cystitis occur?
Often, many people are accustomed to believing that cystitis appears as a result of bacteria entering the bladder area.
But it is not so. The main reasons can be both reduced immunity and constant stress and depression of the patient. When stress appears in a patient’s life, the correct process of transmitting commands from the body’s nerve cells changes.
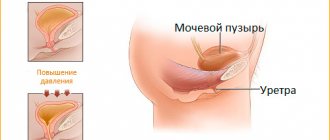
And, as a result, important functions of the bladder are disrupted: storage and evacuation. Bladder dysfunction is accompanied by pain and problems with urination, such as a false urge to urinate.
Now let's look at the main factors that influence the appearance of neurogenic cystitis:
- Fear of the past;
- Reluctance to accept yourself as you are;
- Unexpressed strong resentment towards another person;
- Disappointment in something or someone.
Under the influence of severe stress, the correct process of transmitting commands from the nerve centers of the body is disrupted. By distorting the urination reflex, stress provokes pathological changes in the organs of the excretory system, in which changes in the important functions of the bladder—storage and evacuation—begin to be observed.
Pain and urinary dysfunction are always present in a neurogenic disorder.
Who is at risk
Neurogenic cystitis appears only if it is provoked by certain factors.
These include:
- Childbirth. At the time of the birth of a child, a woman experiences severe stress, sleeps little and is tired.
- Surgery on female organs. Because of worries about its outcome, a woman can easily be “visited” by cystitis.
- Nervous work. An unfriendly team, a boss who constantly shouts and humiliates subordinates, working under tight deadlines - all this can easily provoke chronic stress and lead to prolonged depression.
- Family problems. Mentally unbalanced parents or a spouse who treats the patient with disrespect, illness of a loved one, divorce from a husband, death of a loved one - all this leads to prolonged depression and, as a result, the appearance of cystitis.
- Mental disorder. Some people, due to unpleasant life situations, are accustomed to “denigrating” everything and do not see anything good in life, and sometimes they withdraw into themselves for the whole day to live in the head of a negative situation again and again. Cystitis is especially actively provoked by various fears, sensopathy and mental disorder.
Important. If blood clots appear in the urine during cystitis, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Causes of nervous cystitis
The autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of internal organs, glands and secretion processes, also controls the activity of the bladder. The urinary system is susceptible to the negative influence of psychological problems and mental disorders. The main trigger for failure is stress. The result may be increased frequency or difficulty urinating.
A person’s emotions and his health are inextricably linked. Systematic stress provokes serious disorders in the urinary canal. Long-term negative emotions are no less dangerous. Conflicts based on sex complete this list. All these negative factors provoke cystitis, frequent relapses, and then make the disease chronic.
Any quarrel can provoke a bladder disorder, because each person perceives stress individually. For some, a slight misunderstanding is enough, while others are not exhausted even by constant conflicts.
Brain injuries, multiple sclerosis, and diabetes mellitus make a person less resistant to stress, so in such patients the risk of developing a neurogenic form of cystitis is very high. If the body already had tumors of the urethra and bladder, then neurosis can provoke increased catarrhal inflammation. There are also other initiators of a negative state.
Cystitis has many reasons for its development. This could be a herpes infection, ataxia, Parkinson's disease, diabetes or stroke.
The process of urine excretion is regulated by the nervous system, and disruption of its activity is one of the main causes of the disease. In addition, cystitis develops with mental problems and psychosomatics.
In this case, frequent urination develops, accompanied by pain. A similar condition can develop in men, but is more often diagnosed in women with an unstable emotional background.
Additionally, problems in the sexual sphere, problems at work, difficult relationships in the family and other emotional upheavals.
Exacerbation
Patients often wonder whether cystitis can worsen due to nervousness. Complications of the disease are characteristic of the chronic type, into which an untreated disease can develop. In addition, the mental factor is often not the only indicator of the disease.
A psychosomatic cause gives impetus to disruptions in the body, but further disturbances in the functioning of the system have physical properties. Advanced cystitis can be aggravated by hypothermia, as a result of decreased immunity, overload, and gynecological problems in women.
Cystitis due to nervousness after stress has a positive dynamics of treatment after reducing the level of nervousness and solving psychological problems. The main thing is to find the cause in time and provide the necessary help to the body by turning to specialists.
Reasons for the development of cystitis due to nerves
Cystitis, provoked by a neurotic disorder, can appear in any person if certain negative factors are present.
People in our country very rarely think about nervous balance and calm psychological state. Many of them are so carried away by their problems and experiences that they do not notice how it affects their body. People don’t even realize that nervous conditions can cause cystitis.
Neurogenic cystitis occurs regardless of gender or age. The problem may be for people going through difficult stages in life that cause psychological stress. The state of nervous imbalance has always had an impact on the body and well-being of a person.
In order for the disease to go away forever, it is necessary not to be nervous, not to worry, not to resort to aggression, stress and other destructive emotions. It is recommended to take sedatives if the patient cannot achieve this on his own.
You need to surround yourself with people you enjoy being with. If possible, change your place of work to a more comfortable one.
Treatment of neurogenic cystitis should take place in a calm environment to prevent exacerbation of the disease. If it so happens that the patient has exposed himself to unwanted stress or emotions, he needs to relax, attend a massage session, visit a psychologist, listen to soothing music, and do something that gives him pleasure.
It is recommended to wear comfortable and not tight clothing, as well as underwear. Hypothermia of the genital organs should not be allowed.
It is very important to undergo a full examination and treatment, to get rid of all harmful viruses and bacteria that can lead to the appearance of neurogenic cystitis. It is imperative to monitor genital hygiene.
Prevention
The basis for the prevention of neurogenic cystitis is maintaining mental health. To do this, follow a number of recommendations:
- Creating a comfortable psycho-emotional background. This is the key to psychological health. To do this, eliminate the effects of stress or reduce them to a minimum. Such conditions are created in all spheres of life: at home, at work, in society. It is also important that a person must be part of society. Thus, the risk of developing depression and hypochondria is reduced.
- Eliminate excessive stress and create conditions for rest. Providing rest and psychological relaxation is an important point in the prevention of neurogenic pathologies. Prevention is aimed at reducing the impact of negative factors on the body. You should avoid hypothermia, maintain personal hygiene and include the necessary foods in your diet.
Are women and men equally susceptible to the disease?
Women are often affected by neurogenic cystitis. The disease begins in them after some turning point in their life. Moreover, according to the test results, they do not have an infectious process in the body. Inflammatory processes develop due to the characteristics of the nervous system’s reaction to a number of negative emotions, changes in living or working conditions, and other circumstances.
Men can suffer from cystitis of a nervous nature already in adulthood. At this time, the risk of developing inflammatory processes in the prostate gland increases. This negatively affects the psychological state of the stronger sex.
The nervous form of cystitis often affects women and men who do not know how to discuss existing problems and hide them within themselves. In this case, prolonged negative emotions and a nervous breakdown can provoke the appearance or recurrence of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area.
Cystitis is a painful problem for many people. It occurs very often, but many do not associate the symptoms with this disease and are not aware of its existence.
So what is cystitis? What are the causes, symptoms and treatment? Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man?
Symptoms of cystitis
Neurogenic cystitis develops against the background of stress or mental factors. Its symptoms are no different from other forms. The disease consists of a combination of general intoxication syndrome and urination disorder.
Dysuric syndrome has the following manifestations:
- Frequent urination
- Burning and cutting along the urethra
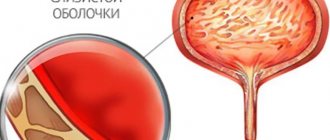
- Blood in the urine
- Flakes of pus in urine
- Appearance of sediment
- Change in urine odor and color
The syndrome of general intoxication manifests itself in the same way as in other inflammatory diseases. In the first hours of illness, body temperature can rise to 39 degrees.
Over time, the temperature remains at the same level (in the absence of treatment), or decreases (if adequate treatment is carried out). In addition to hyperthermia, patients are concerned about general malaise, weakness, body aches, and loss of appetite.
The intensity of these symptoms depends on the type of inflammation, as well as the etiological factor. It is worth noting that with neurogenic cystitis, subjective symptoms will be very pronounced, as they depend on the psycho-emotional background.
Under the influence of stressful situations, the mechanism of urination changes and patients notice an acute urge to go “small”. It is so strong that apart from it, the patient cannot think about anything else. Nervous cystitis appears only in cases of prolonged depression and everyday stressful situations.
Symptoms of neurogenic cystitis depend on the type of disease. The following types are distinguished:
- Hypotonic type. The patient experiences a feeling of heaviness in the bladder area and a weak urge to urinate. Thanks to these symptoms, a decent amount of urine accumulates in the bladder - up to 1.5 liters. These symptoms appear due to a lack of pressure inside the bladder.
- Hypertensive type. Pain when urinating, a small amount of urine produced, a frequent urge to urinate - all this is characteristic of this type, due to the appearance of intravesical pressure.
The main symptoms of this form of bladder inflammation:
- Increased urge to urinate.
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, pubic area and perineum.
- Slight increase in body temperature.
- Changes in the composition of urine, the appearance of blood, pus and an unpleasant odor in it.
- Painful sensations in the urethra during miction.
Against the background of acute intoxication, patients may experience a sharp rise in body temperature to 39 degrees and a sharp pain in the abdominal area. Patients experience severe pain during sexual intercourse.
| Form of the disease | Characteristic signs |
| Hypertensive | Frequent urge, but the amount of urine produced is extremely small |
| Characteristic soreness | |
| Due to high intravesical pressure, the urge to urinate does not stop | |
| Hypotonic | Heaviness in the bladder area, the urge is weak |
| Up to 1.5 liters of urine accumulates, but due to the reduced pressure inside the bladder, the body does not feel the need to urinate |
Clinical picture
The first signs of the disease appear gradually, usually arising from nervousness or against the background of prolonged depression. Typically, the patient experiences mental lability, increased excitability or anxiety, and frequent urge to urinate. Sometimes, on the contrary, against the background of mental disorders, the sensitivity of the urethra decreases, and the urge becomes rare.
According to this principle, two forms of neurogenic cystitis are distinguished:
- Hypertonic – the organ is in constant tone, which reduces its volume. This option is characterized by frequent urge and increased urine output. Patients often complain of pain when urinating, which appears later.
- Hypotonic cystitis - the muscles of the organ are relaxed, which leads to stagnation. This creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and provokes the development of inflammation. Urinary incontinence is sometimes noted.
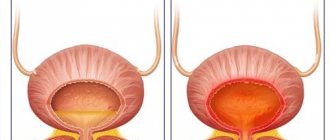
In the chronic course of any form of the disease, pain is characteristic, which indicates inflammation of the mucous membrane. Like all variants of cystitis, the pathology requires mandatory examination and treatment.
Diagnostics
The signs of neurogenic cystitis are practically no different from ordinary inflammation of the bladder caused by the “work” of harmful microorganisms.
Only a qualified urologist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Most likely, you will be asked to undergo the following studies:
- urine tests;
- ultrasonography;
- cystoscopy;
- radiography.
Most often, when contacting a urologist, procedures such as a general urine test, bacteriological culture and ultrasound of the pelvic organs are prescribed. With non-infectious cystitis, pathogens are detected in urine only during secondary infection; most often, pathogens are not detected.
Ultrasound results allow one to suspect the localization of the pathology: the doctor sees that the walls of the bladder are thickened. Doppler ultrasound may reveal a decreased or increased (depending on the nature of the disorder) volume of residual urine.
To clarify the diagnosis and condition of the patient, a urine test according to Nechiporenko can be used. The procedure allows you to identify relatively small deviations from the norm.
With neurogenic cystitis, a slight increase in the concentration of leukocytes (more than 2000) may be observed, which indicates inflammation. Due to the blurred clinical picture, specialists often perform an endoscopic examination - cystoscopy.
The procedure is performed only during remission, because can lead to damage to the mucous membranes and deterioration of the patient's condition.
The information obtained as a result of a comprehensive examination allows us to suspect neurogenic disorders, however, to confirm the diagnosis, the urologist will issue a referral to a psychotherapist. After the conversation, the specialist will refute or confirm the suspicions.
For cystitis, patients are prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- urine tests - general and bacteriological;
- general blood analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- examination of the organ mucosa using a cystoscope;
- determination of the pathogen (polymerase chain reaction is the most accurate);
- ultrasound examination;
- X-ray examination (a contrast agent is used to increase accuracy).
How to treat cystitis?
To treat neurogenic cystitis, psychological help should be used along with the use of drug therapy.
The first thing that is recommended to do is strengthen the nervous system. Since neurogenic cystitis cannot be treated with medications, you should mentally prepare for recovery. It is necessary to remove all stressful situations, avoid conflicts, and try to get out of depression. Internal mood plays a key role in the treatment of cystitis.
With such an illness, psychiatrists recommend throwing out any emotions, freeing yourself from grievances and burdens on the heart, expressing your opinion, trying to ignore evil people who cause fear or anger. Of course, it is not always possible to put your feelings in order on your own (especially if the nervous disorder is so severe that it affects the organs). It is worth contacting a psychologist or psychosomatic therapist.
With timely treatment of neurogenic cystitis, the disease can be completely cured. Medication is aimed at relieving painful symptoms and preventing complications. The main components of the process are physiotherapy and psychoanalysis. Sometimes exercises are added, but the approach to each case of illness must be individual.
To relieve inflammation, antibacterial drugs and adrenergic blockers are prescribed. Sometimes injections are added to the list. At the end of treatment, you should take special vitamins to maintain immunity and eliminate the last aggressive effects of drugs.
Among the best physiotherapy procedures for the treatment of neurogenic cystitis are those aimed at stimulating muscles (warming, ultrasound, electrical signals). Consultations with a psychologist are required, especially for depression, stress, low self-esteem or sexual dissatisfaction. Psychotherapeutic manipulations may be prescribed.
The initial stage of cystitis can be treated with homeopathic medicines and traditional methods (herbal remedies and herbs). In extreme cases, surgery to expand the organ is required.
Treatment of the disease is impossible without normalization of the mental state. In order for treatment measures to be effective, experienced therapists first refer their patients to a psychologist. It is extremely important to learn how to deal with negative emotions, depression, and bad thoughts.
Psychologists recommend that their clients get rid of all negative emotions using any methods available to them. It is extremely important to combat low self-esteem.
At the initial stages of progression of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs, homeopathic medicines are used. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and calming effect.
The herbal preparations included in their composition help restore the functioning of the bladder mucosa.
To combat cystitis, various manipulations are used - for example, ultrasound procedures, warming, vibration massage, magnetophoresis, electrophoresis. All these procedures have a beneficial effect on the condition of the mucous membrane. Ultrasound has a particularly active effect: it has pronounced antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity.
They fight anxiety and negative emotions with:
- water procedures;
- auto-training;
- relaxing massage;
- sanatorium and resort treatment.
Drug treatment for a nervous disease does not begin without laboratory tests. Ultrasound, X-ray, cystoscopy, urine collection are the most common tests and procedures that are performed by the patient before the doctor makes a final diagnosis. To get rid of “nervous” cystitis, treatment is prescribed with several procedures at once.
| pharmachologic effect | Prescribed drug |
| Eliminating pain | “Nurofen”, “Spazmalgon”, “Noshpa”, “Paracetamol” |
| Relieving inflammation | "Voltaren" |
| Calming effect | "Persen", "Glycine", "Novo-Passit" |
Psychosomatic diseases are not amenable to traditional drug treatment. No antibiotic will relieve you of the cause of urinary dysfunction if cystitis is neurogenic in nature. Therefore, only the patient himself can correct the situation by accepting and realizing his problems.
Psychologists who deal with pathologies of this kind recommend that their patients show fear and anger without holding back or fearing the judgment of others. There are many techniques that allow you to get rid of negative emotions, thereby eliminating the symptoms of cystitis due to nervousness.
Antidepressants and mild sedatives can be auxiliary agents in the treatment of such pathology. Of course, it is best to seek help with such a problem from an experienced psychologist who will prescribe effective therapy, including taking medications.
But if this is not possible, then try to find a way to “pour out your soul” by getting rid of negative emotions and experiences on your own. Scream, hit a pillow, write all your grievances on paper and burn the list, or just cry “into your friend’s vest.”
After the doctor has carried out all the necessary diagnostic measures, treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the disease. Under no circumstances should treatment be delayed, as this can lead to a chronic development of the process.
Therapy
Along with neurogenic cystitis, inflammation often occurs due to mechanical irritation of the bladder walls, hypothermia, and exposure to the bacterial flora of the sexual partner.
Treatment of the disease is planned individually and carried out comprehensively.
- Drug therapy. Diuretics (Furosemide), antidepressants, antibiotics (Monural, Urolesan), and vitamins are prescribed.
- Homeopathic treatment. If complications are not identified, medications such as Cystoit, Canephron are prescribed.
- Herbal medicine (folk remedies). The use of herbal teas that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. To treat cystitis, lingonberry leaf, knotweed, and bearberry are used. But before taking herbal infusions, you need to consult a specialist.
- Physiotherapy:
- ultrasound treatment - eliminates inflammation, normalizes blood circulation;
- electrophoresis - has an anti-inflammatory effect, eliminates swelling of the inflamed organ, relaxes and soothes;
- magnetophoresis - the drug is delivered to the bladder using the magnetic field of a special device;
- thermal heating;
- vibration massage.
In the absence of timely and competent treatment, complications may develop, and chronic cystitis may recur.
Phytotherapy
Of the medications for this disease, those that are primarily prescribed are those that will relieve involuntary spasms of the bladder (Papaverine and Drotaverine have good reviews in this regard).
As well as antibiotics and vitamin complexes. Recommended physical therapy will help strengthen specific muscle groups and improve blood circulation.
Sometimes homeopathic remedies are recommended for people with this problem. Special operations to expand the bladder are very rarely performed.
The symptoms of nervous cystitis are similar to the standard symptoms of bladder inflammation. Moreover, a combination of two problems is very likely: a bacterial attack and a stress factor. Or hypothermia and stress, or the consequences of surgery plus the same stress.
To combat inflammatory processes, antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Properly selected therapy can quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms and normalize the condition of the genitourinary organs. In some cases, adrenergic blockers are indicated for patients. Additionally, injections are prescribed.
Of the antibiotics, the most effective and safe are Monural, Ofloxacin, Palin, Redil, Norbactin, Furagin, Furadonin. Among NSAIDs, patients are most often prescribed Amidopyrine, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, and Indomethacin.
Diuretics are used to combat congestion. Long-term accumulation of urine is dangerous because it promotes the spread of the inflammatory process and the formation of clots from pus and blood. These clots can cause acute urinary retention. Chemical and herbal preparations are used as a diuretic.
Drug therapy always ends with taking vitamins. They help increase your defenses and remove all the negative effects of taking medications.
Treatment
To treat neurogenic cystitis, psychological assistance is used using drug therapy. Medicines from the following groups are used:
- Antibiotics. Since bacteria are present in cystitis, antibacterial agents are the mainstay of treatment for cystitis. There are special complex drugs for the treatment of urinary inflammation. These drugs are called uroseptics. They have a wide spectrum of action and destroy bacteria that affect the genitourinary system.
- Diuretics. Stagnation of urine in the bladder during cystitis is a dangerous condition, as this leads to the spread of the process, the formation of blood clots or pus. Such processes cause blockage of the urethra and acute urinary retention. Both chemical preparations and herbal analogues are used. Increased urine output leads to mechanical removal of bacteria and cleansing of the bladder.
- Anti-inflammatory. To eliminate painful sensations that are a consequence of the inflammatory process, non-steroidal drugs are used, but in severe cases, adrenal hormones are used. Non-steroidal drugs (NSAIDs) with an ulcerogenic effect, which can cause gastritis, duodenitis or ulcers. Patients who already have these diseases are allowed to use NSAIDs only in the form of rectal suppositories.
- Painkillers. Painkillers are prescribed in cases where the pain syndrome is pronounced. With cystitis of neurogenic origin, the pain is intense. This is due to the fact that the perception of pain depends on the psychological state.
Psychotherapeutic assistance to patients is provided individually. This is due to the fact that each person, as an individual, requires an individual approach from a psychotherapist.
The number of sessions that a patient needs to deal with the problem varies.
To treat cystitis that appears due to stress or depression, several sessions will be required.
But to eliminate the pathology that appears from the fear of sexual intercourse, which is caused by rape, a long course of psychotherapy will be required.
In some cases, patients receive care for several years. Treatment methods also differ.
The goal is to completely eliminate the psychological factor, but this is not always possible to achieve. In such cases, measures are taken to ensure that the patient abstracts himself from it.
Diagnostic procedures
Neurogenic cystitis, as it turned out, can include several causes of manifestation - mental disorders and infections, so treatment cannot be one-sided. Diagnosis of the cause of the disease should be carried out not only by a qualified urologist or gynecologist (for women), but also a consultation with a psychotherapist will not hurt.
The specialist will prescribe the patient to undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, a general urine and blood test, bacteriological analysis, and cystoscopy. Based on laboratory tests, the doctor will make a diagnosis and prescribe medication for the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
Many patients themselves understand what causes the appearance of cystitis. However, you should definitely check with a urologist. The doctor prescribes a urine test, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and an x-ray of the bladder, and also examines the bladder using an endoscope. After the studies, if the infection has not been identified and there are no pathologies, the urologist refers the patient to a doctor who deals with diseases of the nervous system. The latter asks the patient whether he has problems in the family or at work, then refers the patient to undergo an electroencephalogram and tomography, and also gives a referral for a spinal examination.