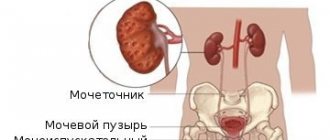
What types of microorganisms can cause inflammation?
The inflammatory process in the walls of the bladder can be caused by different types of pathogens: bacteria (opportunistic, pathogenic and specific), viruses and fungi.
When the cause of a disease is bacteria
In the presence of predisposing factors, inflammation of the bladder can also be caused by opportunistic microflora, which is constantly present in the human body. In this case, the trigger for the development of inflammation can be:
- Gross neglect of the basic rules of personal hygiene, in particular, improper toileting of the genitals, which can lead to the entry of microorganisms living in the rectum into the lumen of the urethra, and from there into the bladder. Intestinal flora is the most common causative agent of bacterial cystitis.
- Carrying out instrumental therapeutic or diagnostic manipulations. Very often, cystitis develops after catheterization of the bladder, bougienage of the urethra, or cystoscopy.
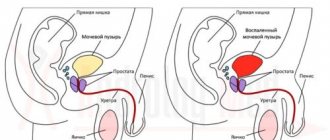
- Concomitant inflammation of the prostate in men, which leads to an increase in local body temperature and the creation of conditions favorable for the development of pathogenic flora.
- Diabetes mellitus, leading to changes in the chemical composition of urine and a decrease in the barrier function of epithelial tissue.
- Pregnancy. The development of cystitis can be facilitated by both compression of the bladder by the pregnant uterus and changes in the chemical properties of urine due to impaired excretory function of the kidneys.
- Urolithiasis disease. Mechanical closure of the urinary tract contributes to stagnation of urine and the creation of conditions favorable for the activation of opportunistic flora.
- Diseases of the upper urinary tract and urethra. They increase the risk of infection entering the bladder cavity.
Bladder inflammation is most often caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Klebsiella, Enterococcus and Proteus.
Bacterial cystitis is not usually classified as infectious, since in this case there is no transmission of the infectious agent from one sick person to another. Therefore, when a conditionally pathogenic flora is detected in the urine, a urologist often makes a diagnosis of non-infectious cystitis.
If the infection came from outside
Bacterial cystitis can also be caused by sexually transmitted bacteria. This type of cystitis is called infectious. Most often, inflammation of the bladder is caused by the following types of microorganisms:
- Gonococcus. Most often, gonococcal cystitis occurs in female patients, with a low level of the immune system, suffering from inflammation of the urethra, external genitalia and vagina.
- Chlamydia. This type of microorganism causes a decrease in the protective properties of the mucous membrane of the bladder and activation of opportunistic microflora. Therefore, with chlamydia, non-infectious cystitis often occurs, but its cause was the invasion of chlamydia.
- Ureaplasma and mycoplasma. These intracellular parasites are often found in patients suffering from long-term chronic inflammation of the bladder.
The inflammatory process can also be caused by protozoa, in particular Trichomonas. However, the existence of Trichomonas cystitis is denied by many experts.
Cystitis caused by sexually transmitted microorganisms has the most malignant course and can lead to the development of chronic inflammation and damage to the genital organs. Often such inflammatory processes take an asymptomatic course, leading to the development of serious changes in the walls of the bladder.
It has been reliably established that inflammation of the bladder walls is also caused by certain types of viruses. Most often, viral cystitis occurs due to penetration of adenoviruses, papillomaviruses and herpes viruses into the bladder. As a rule, this type of inflammation is detected in children with a low level of the immune system.
A pronounced weakening of the immune system leads to the development of another type of cystitis – fungal. The inflammatory process in the bladder is most often caused by actinomycetes, blastomycetes and candida.
The bladder is also quite vulnerable to specific bacterial infections. Thus, inflammation of the mucous membrane of this organ can develop due to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and tuberculosis affecting the kidneys and genital organs.
Reasons for the development of chlamydial cystitis
This is one of the most common cystitis caused by infection with Chlamydia trachomatis. About 5% of the population is affected by chlamydial infection, and the number of patients is constantly increasing. Infection is possible both sexually and through household contact. Chlamydia is very often asymptomatic and does not bother the patient in any way. This leads to the development of a urinary tract infection, which affects the condition of the entire body.
Chlamydia infection most often occurs during sexual intercourse. This is why using a condom is so important. Chlamydial infection affects not only the genitals, but also rises upward. Personal hygiene products and towels used by an infected person can be contagious. In the future, this infection causes changes in the organs of the reproductive system, which can cause infertility.
Distinctive signs of inflammation
As a rule, the symptoms of different types of cystitis are the same. Basically, they are of the nature of pain that occurs during the process of urine excretion and at rest. Associated symptoms include:
- small portions of urine released;
- increased frequency of urination;
- urgent urination (unbearable urge to urinate);
- feeling of a not completely emptied bladder;
- low-grade body temperature;
- chills;
- weakness and fatigue;
- lower abdominal pain.
The physical and chemical characteristics of urine change, which outwardly manifests itself as its atypical color and smell. Sexual intercourse is disrupted, and severe pain may occur during it.
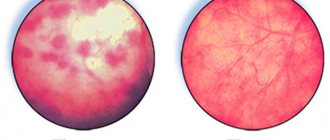
Bacterial infections often cause flocculation and cloudiness in the urine. However, this is not a reliable sign of a bacterial process.
The nature of the existing inflammation and its most likely causes can be judged from the history of the disease. If, on the eve of the appearance of signs of cystitis, new sexual intercourse took place, a slight burning sensation was observed in the urethra or vagina (in women), and atypical vaginal or urethral discharge was noted, suspicion falls on the infectious nature of the disease.
In the case where, before the appearance of clinical signs, there was hypothermia, a stressful situation, a cold, and the signs themselves appeared unexpectedly or against the background of minor aching pain in the groin area, the most likely cause of inflammation is a banal microflora. The likelihood of its activation increases in the presence of concomitant diseases of the urinary system, pregnancy, and old age.
Other causes of the disease
The bacteria that cause cystitis are very susceptible to a course of general-spectrum antibiotics, for example, Monural, Nolitsin. The frequency of administration and dosage should be selected by the attending physician, taking into account test data and the specific clinical picture. To relieve severe pain and reduce burning sensation when urinating, any non-narcotic painkillers, for example, Ibuprofen, are prescribed.
Good results are shown by the use of the drug No-shpa and other drugs aimed at relieving spasms of smooth muscles. As a local disinfection, you can use rinsing the perineum with a weak solution of furatsilin.
After sexual intercourse, you should definitely treat the entrance to the urethra with an antiseptic, because damaged and irritated mucous membranes may be susceptible to any other pathogenic microorganisms.
During treatment and for another month after cystitis, you should adjust your diet, avoid drinking alcohol, large amounts of caffeine, hot, spicy and salty foods. You can, in agreement with your doctor and in the absence of allergic reactions, drink herbal teas according to traditional medicine recipes.
But only after a diagnosis has been made and drug treatment has been prescribed, because medicinal plants themselves have little effect against pathogenic microflora of the bladder.
Teas based on bearberry and rose hips, the so-called kidney collection, have a weak disinfectant effect on the bladder mucosa. After the exacerbation is relieved, you can take a hot bath and visit the bathhouse and sauna.
During the period of illness when urination causes acute pain, hot compresses and warming procedures are strictly contraindicated. It is important to understand that the infection spreads through the blood and lymph flow and is able to circulate freely throughout the body, creating a bacterial focus anywhere. Increasing body temperature has a stimulating effect on blood and lymph flow, so the patient can become significantly worse in a short time. If bacteria were not in the kidneys, they will definitely appear, which threatens chronic pyelonephritis. Treatment of cystitis in children should be especially considered. All measures to help young children should be discussed with their doctor. A very common mistake patients make is that they stop treatment as soon as the pain goes away. The marker of the end of treatment is not the absence of pain, but tests that do not contain cystitis pathogens.
Basic principles of therapy
To select the most effective therapeutic regimen for an inflamed bladder, it is necessary to carry out such diagnostic measures as:
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical urine test;
- bacteriological urine culture;
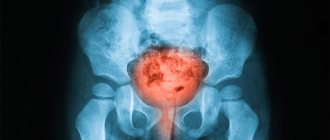
- ultrasound and x-ray examination of the bladder;
- cystoscopy;
- urine testing using polymerase chain reaction.
Based on the test results, the nature and degree of the inflammatory process is determined, and the specific type of pathogen is determined. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the nature of the disease.
Of particular importance is the selection of drugs that have the ability to destroy the infectious agent.
In addition, prescribed drugs must be used in optimal doses. Violation of this rule leads to the formation of stable microflora and chronicity of the process.
When fighting chronic forms of the disease, treatment is carried out against the background of immunomodulatory therapy.
Inflammation of the bladder is called cystitis. In the organ, it is most often caused by an infection that occupies the walls and the entire mucous membrane. The disease is widespread among the population due to many provoking reasons.
Women get sick much more often than men. This occurs due to differences in the structure of the genitourinary system. The incidence of pathology levels off by age 65 in both sexes.
Cystitis during pregnancy
Cystitis is very common among women expecting a child. There are many prerequisites for bladder inflammation during pregnancy, here are the main reasons:
- compression of the pelvic organs, which causes problems with the outflow of urine;
- slow functioning of the intestines and internal organs;
- hidden urological infections, or chronic diseases, especially those that manifest themselves during pregnancy, for example, pyelonephritis;
- hypothermia or cold;
- improper hygiene of a pregnant woman, rare change of underwear;
- dehydration, rare urination.
To avoid cystitis, a pregnant woman must take a shower at least twice a day, change her bottom often, avoid getting too cold, and also drink enough fluids every day. Under no circumstances should you be dehydrated - this increases the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the bladder. If you notice that your urine has become concentrated (has acquired a strong odor and dark color), this is a signal that your body does not have enough fluid.
Etiology of cystitis and main symptoms
The etiology of the disease studies the occurrence of the disease, the causes and conditions of its provocation. The systematization of these factors constitutes the content of various classifiers, which facilitate diagnosis.
The combination of reference book positions allows us to create a descriptive model of cystitis. By backing it up with laboratory tests and examinations, the disease can be accurately identified.
Typical signs of pathology cannot be confused with other diseases. In a situation with cystitis, the following symptoms develop:
- The urge to urinate is uncontrollable and frequent. In this case, the volume is released in small portions, almost drop by drop - 10-15 ml.
- Cutting in the urethra and burning when urine comes out, especially at the end.
- Spasmodic pain in the pelvis, pubis, lower abdomen.
- Increased body temperature, weakness and signs of intoxication, causing nausea and vomiting.
- Urine darkens, becomes cloudy, sediment, clots of pus, and blood appear.
Video on the topic
Briefly and clearly about the causes, symptoms and methods of treating cystitis in the TV show “Live Healthy!” with Elena Malysheva:
To diagnose cystitis, a special and general urine test, a smear from the vagina, urethra, and rectum are used. Treatment is carried out using a conservative method, using herbal remedies, uroantiseptics and antibiotics; if necessary, painkillers are used. A healthy lifestyle, constant support of a high level of immunity, sufficient hygiene care and moderate sex life will be the key to preventing the occurrence of cystitis.
Infectious cystitis and its causative agents
The physiological structure facilitates the path of cystitis pathogens in women into the urethra and bladder. The rectum, vagina, intestines, anus and genital area are the main sources of pathogens.
The following factors play a positive role in the penetration of pathogens:
- The urethra in women is short and wide.
- The close location of the beginning of the urethra to the anus, which helps bacteria from the intestines to spread into the bladder.
- Sexual intercourse is highly likely to cause infection in the urethra. A woman is infected with pathogenic flora from the vagina. A man can provide infectious agents from the genital area.
- Menopause, hormonal disorders, and decreased local immunity can cause bacterial cystitis.
- Infection can be transmitted to the urinary tract from any inflamed organ of the woman’s reproductive system.
Infections that cause cystitis in women are grouped into categories:
- opportunistic microorganisms;
- vaginal microflora;
- microflora of the gastrointestinal tract;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- respiratory viruses.
Opportunistic microorganisms.
The body of a living being is inhabited by opportunistic microorganisms. They live in places of direct contact with the environment and serve to maintain the constancy and resistance of the microflora to aggressive manifestations.
The microflora of a healthy person is at rest and is not subject to pathological processes.
Any favorable reason, especially a decrease in immunity, provokes the activation of pathogens and their reproduction.
Vaginal microflora
The natural protection of a woman's genitals is in the vaginal area. Its healthy microflora consists of lactobacilli in an amount of up to 90%, bifidobacteria about 10% and 1% of a group of key cells. Their totality includes:
- fungus of the genus Candida;
- mobiluncus;
- gardnerella;
- leptothrix and other bacteria.
All bacteria are in balance. This is monitored by the immunity of the vaginal wall, correcting minor deviations from the norm. But it cannot cope with serious imbalances in the ratio and cannot even out the balance.
The pathogen can be not only from key cells, but also from a completely different type: from sexually transmitted infections, saprophytic bacteria.
Any microbe that causes the development of vaginal dysbiosis can lead to inflammation, which is called vaginitis or colpitis. These bacteria, causative agents of pathology of the vaginal mucosa, can provoke the disease, each individually or as a whole association:
- Trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- candida.
Microflora of the gastrointestinal tract
The digestive tract has a variety of microflora representatives. They are necessary for healthy digestion and maintaining the immune system.
Infectious cystitis is provoked by:
- Gram-positive bacteria:
- enterococci;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci.
- Gram-negative bacteria:
- E. coli or Escherichia coli;
- Klebsiella;
- enterobacteria;
- Proteus.
Escherichia coli is the most common causative agent of cystitis in women. A significant danger also comes from Klebsiella. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is the last one in this trinity.
Sexually transmitted infections
Sexual intercourse with frequent changes of partner, unprotected sex (insufficient hygiene) can give rise not only to pleasure, but also to unpleasant diseases. A young girl more willingly and more often allows herself this joy of life, without thinking about the consequences.
The first signs of sexually transmitted diseases have symptoms similar to those of cystitis. The person is trying to get rid of them. Thus, it triggers the true disease.
If, as a result of the developed pathology, pathogenic bacteria enter the urethra, then cystitis will also join the venereal disease. An acute process, the treatment of which is not started in time, will turn into a chronic one.
Vaginal microflora
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xDPa1y_3mU8
Various microorganisms are constantly present in our body. They are present on the skin, in the gastrointestinal tract, the genitourinary system, in a word, in organs that are in direct contact with the external environment. The microflora in these organs is necessary for full functioning. In addition, UPF has an antagonistic effect against pathogenic flora, which protects the body from the excessive proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
But if immunity decreases for some reason or external factors influence, bacteria begin to multiply rapidly. When their number exceeds the maximum permissible norms, they become pathogenic and cause various infections.
The main representatives of the natural microflora of the vagina, Candida fungi, are capable, under certain conditions, of causing cystitis. It is the yeast-like fungi of the river. Candida causes thrush in women. Inflammation of the bladder develops as a complication of vaginal candidiasis. With weakened immunity, fungi can be spread by blood to all organs, which causes general candidomycosis.
Candidal cystitis is diagnosed when more than 1000 colonies of fungi are detected in 1 ml of urine.
Ureaplasma is a virus-like bacteria classified as mycoplasma. This type of microorganism has the ability to attach to leukocytes and change their functioning, which reduces the body’s defense response. In such cases, cystitis is especially difficult, often becoming chronic with frequent relapses.
In people of puberty, cystitis is often caused by a urogenital infection. The most common cause is chlamydial infection. About 10% of people in Russia are infected with chlamydia. Chlamydia has no symptomatic manifestations, and can only be detected if a complication has already appeared - some chronic disease of the genitourinary system.
Chlamydia can be present in the body in the form of atypical forms. This significantly complicates treatment and often causes frequent relapses of the disease. Another bad thing is that after treatment, stable immunity is no longer formed.
The body of every woman is inhabited by opportunistic microorganisms. They live on organs and mucous membranes that have direct contact with the environment, for example, the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, and all skin. The presence of such diverse representatives of microflora helps maintain the constancy of the internal environment and make the body more resistant to environmental factors.
E. coli is the most common cause of cystitis
In the body of a healthy person, opportunistic microflora is at rest. It does not cause pathological processes. But as soon as the body’s immune status decreases, bacteria begin an active reproduction process. As a result, the development of infectious diseases, including infectious cystitis.
The gastrointestinal tract is the richest in the presence of representatives of various flora. They contribute to the process of normal digestion, participate in the synthesis of vitamin complexes, and, of course, are responsible for the body’s immune defense.
Infectious cystitis is caused by gram-positive (staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci) and gram-negative bacteria (enterobacteriaceae, Proteus, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella).
Escherichia coli occupies a leading position in the development of acute inflammatory process in women. Next comes Klebsiella, and Staphylococcus saprophytis closes the top three.
Fungi of the genus Candida and ureaplasma are representatives of the female microflora, which are responsible for the development of infectious cystitis.
Candida is the main causative agent of vaginal candidiasis (thrush), and if it is not treated, then cystitis also follows. In patients with weak immune defenses, the infectious process is distributed with the bloodstream throughout all organs and systems, and, as a result, general candidomycosis and candidal cystitis.
Candida often causes fungal cystitis in women
Ureaplasma belongs to the subspecies of mycoplasma and has virus-like properties. Ureplasmas have the ability to attach to leukocytes, disrupt their functional abilities and reduce the protective-inflammatory response. As a result, chronic cystitis develops.
In sexually active women, cystitis occurs due to urogenital infection. Chlamydia occupies a leading position among sexually transmitted infections.
In the initial stages, chlamydia does not manifest itself in any way; it can be detected after complications of the genitourinary system have developed. In the human body, chlamydia exists in atypical forms. It is this fact that complicates the diagnosis. Unfortunately, immunity to this infection is not developed.
Chlamydia can cause not only cystitis in women, but also more serious diseases of the genitourinary system
Cystitis in pregnant women
The frequency of cystitis in pregnant women is associated with the functioning of the body during gestation. They appear as follows:
- During this period, the immune system supports the development of the fetus, but ceases to fully protect the mother’s body.
- The hormonal background is transformed. This changes the balance between healthy and pathogenic flora, which contributes to disruptions in the functioning of the genitourinary system.
- The child grows in the womb. It begins to put pressure on nearby organs, including the bladder. Blood supply deteriorates, local immunity decreases.
- Blood supply disruption occurs under the influence of progesterone, a hormone that promotes stagnation and proliferation of pathogens.
Risk factors:
- The use of diaphragms and spermicides that can affect the microflora of the female urethra;
- Weakened immune system (HIV infection, antitumor treatment);
- Difficulty emptying the bladder (enlarged prostate gland. Bladder stone);
- Pregnancy (due to dramatic changes in anatomy and physiology);
- Poor personal hygiene;
- Diabetes;
- Older age. During menopause, changing hormonal levels are often associated with genitourinary tract infections.
How to make an accurate diagnosis
The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the completeness of the information provided to the doctor. This procedure is called taking an anamnesis. In addition to what the patient himself tells the doctor, the specialist will ask leading questions regarding the following points:
- Urine and urinary process:
- color, transparency, strong odor of urine;
- intermittency and frequency of urination;
- burning, pain, itching during urination;
- blood in urine;
- purulent, bloody discharge from the urethra.
- Hygiene and its means.
- Sex:
- intensity of sexual life;
- duration of breaks in intimate relationships;
- the presence or presence in the past of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Other pathologies:
- urolithiasis;
- oncological diseases of the genitourinary system;
- chemical and radiation therapy.
A medical history alone is not enough for an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, tests are prescribed, and as the inflammation process becomes clearer, instrumental studies are offered.
- general urine analysis;
- bacterial culture;
- “two-glass” test for women.
A little-known fact: a diagram developed by doctors in Ohio illustrated the dependence of urine color on the presence of pathologies in the body.
Instrumental methods:
The completeness of information obtained through all these methods allows for the correct diagnosis of cystitis. This will subsequently make it possible to determine in the patient management protocol how to effectively treat the pathology.
Complications
With proper and adequate treatment, bladder infections rarely lead to complications. But if left untreated, they may include the following complications:
Pyelonephritis . Both children and older adults are at greatest risk for kidney damage because their symptoms are often unnoticed or not taken seriously. Hematuria (blood in the urine). Cystitis with manifestations of hematuria is called hemorrhagic. During inflammation, blood cells enter the urine, which sometimes can only be seen under a microscope (microhematuria) and which disappear in the urine after treatment. If blood cells remain after treatment, the real cause has to be found out. Blood, which can be seen with the naked eye in the urine, rarely appears with bacterial cystitis, and more often accompanies inflammation caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Treatment and prevention of infectious cystitis in women
The results of urine culture for microflora will indicate the type of bacteria and the list of antibiotics that can cope with it. For this reason, self-medication is dangerous to health.
Without analysis, the patient does not know his enemy by sight. The medications are selected by the doctor and you must adhere to his treatment regimen.
Since we are talking about the infectious nature of cystitis, the main therapy consists of taking a set of medications:
- antibiotics;
- immunomodulators;
- diuretics.
Prevention and alleviation of the disease is accompanied by the use of immunomodulators. The ascending path for infection is blocked by the complex mechanism of their activity.
In addition to the use of medications, preventive measures include simple lifestyle rules. Colds, hypothermia, freezing, poor intimate hygiene, and synthetic underwear can cause infection in the urethra. To maintain bladder health, you need to pay close attention to these factors.
Infectious cystitis is accompanied by specific uncomfortable pulling sensations in the pelvic area combined with pain when urinating. Treatment is based initially on identifying the pathogen. To achieve a lasting result, complex therapy is required to remove not only the clinical manifestations, but also the source of infection.
What does the structure of the male genitourinary system look like?
The structure of the male genitourinary system has a number of features that are closely related to the risk of developing certain diseases. Moreover, the presence of pathologies in it affects the health of other organs and the body as a whole.
Let's take a closer look at the anatomy of the genitourinary system and what functions it performs.
Diagram of the structure of the male genitourinary system
The male genitourinary system, depending on its functions, is divided into two main components: the reproductive and urinary systems. However, some organs can be classified as both systems, since they perform several functions simultaneously.
Sexual
The organs of the reproductive system (see photo below) are divided into internal and external.
Internal ones include:
- Prostate gland – usually called the prostate. The main function is the release of a special alkaline secretion, which is responsible for sperm motility. The gland looks like a nut.
- The seminal vesicles are a kind of storage of seminal fluid in men. Located next to the prostate gland. When they ejaculate, they release semen, which passes through the prostate and is mixed there with an alkaline secretion. As a result, sperm is formed.
- Testicles (testes) are the organ in which the synthesis of spermatozoa for seminal fluid occurs. The hormone testosterone is also produced here.
- The vas deferens are channels connecting the testicles and seminal vesicles.
- The epididymis is a place for the maturation of sperm. They are located next to the testes and have an elongated shape in the form of a tourniquet.
The external genitalia include:
- Penis (sexual member) is an organ for sexual intercourse. From it, seminal fluid is released into the woman, which ensures possible fertilization.
- The scrotum is a kind of leather bag that has muscle tissue. It interferes with the testes, protects them from external influences and provides the optimal temperature for sperm maturation (34 ° C).
Also used for urination. Consists of a base, trunk and head. Inside is the urethra, which connects to the bladder. Its length is about 18 cm. There is a slit on the head through which sperm or urine comes out.
What sexually transmitted infections cause cystitis?
Infectious cystitis can be caused by sexually transmitted pathogens. During unprotected sexual intercourse, if one of the partners has an STI, then in 80% of cases infection occurs with the development of infectious cystitis.
Urologists and gynecologists have identified the main STIs that can lead to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder wall.
| Pathogen | Peculiarities |
| Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) | The most common infectious disease, in most cases it is asymptomatic. Or with the presence of nonspecific implicit signs: |
· in women – scanty vaginal discharge, periodic itching;
· in men – low-grade fever, pain along the urethra (urethritis).
In the presence of the HLA B-27 gene, arthritis and uveitis (inflammation of the uvea of the eye) can join urethritis and cystitis with the formation of Reiter's triad.
· purulent discharge from the vagina, urethra;
· burning sensation that occurs during sexual intercourse;
· constant discomfort, itching.
Prevention
Prevention of viral cystitis is to strengthen the immune system. This is achieved through hardening, balanced nutrition and an active lifestyle.
Take precautions during sexual intercourse. This is important for women, because a short urethra makes them susceptible to cystitis.
In proper nutrition, as in the prevention of viral cystitis, it is important to have vitamins, which are an integral component in the production of interferon. Important B vitamins and vitamin C (except citrus fruits).
Viral cystitis can cause severe disturbances in the functioning of the bladder. In addition, inflammation can cause the development of defects that threaten serious complications.
Treatment of the disease requires systemic intervention, because viruses can spread throughout the body and cause other foci of pathology.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor; starting treatment ensures recovery.
What hidden infections cause cystitis?
In addition to sexually transmitted infections, there are additional pathogens that cause infectious cystitis - Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, and staphylococci. They all belong to the group of opportunistic pathogens, that is, they are present even in an absolutely healthy body. But with a decrease in the general protective properties, their activation and subsequent infection occurs.
The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli. It can enter the urethra and bladder through the ascending route if personal hygiene rules are neglected. Additional factors of infection are:
- disruption of the normal vaginal microflora;
- hormonal imbalance due to taking hormonal drugs, endocrine diseases;
- high-carbohydrate diet with a minimum amount of protein and natural fiber (vegetables, fruits);
- local hypothermia;
- physical inactivity that accompanies office work.
In addition to the ascending route of infection, a hematogenous or lymphogenous route is possible, that is, through blood or lymph.
Methods of infection penetration
If inflammation is a consequence of exposure to bacteria, then the type of cystitis is bacterial.
If it is caused by: viruses, fungi, parasites, consequences of a tumor process - this is non-bacterial cystitis. This difference plays an important role in determining the treatment method. Bacterial pathogenic flora affects the bladder in one of the following ways:
- hematogenous;
- lymphogenous;
- ascending or contact;
- descending.
In the contact route, the infection can be introduced into the bladder during catheterization or cystoscopy.
Infectious cystitis in women
Women are 6 times more likely to suffer from infectious cystitis than men. This fact is explained by the structural features of the body, and in particular the urethra.
| Gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) | Unlike chlamydia, it is accompanied by clinical manifestations, on the basis of which the doctor may suspect an infectious nature: |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Characterized by watery, foamy discharge from the vagina or urethra. Itching is always present, and the appearance of ulcerative defects on the surface of the mucous membranes is additionally noted. |
| Mycoplasma genitalium | Conditionally refers to the causative agents of STIs. Just like chlamydia, mycoplasmosis is not distinguished by the presence of specific symptoms. |
| Options | Men | Women |
| Length | up to 22 cm | no more than 5 cm |
| Diameter | up to 8 mm | up to 1.5 cm |
| Presence of bends | there are 2 bends | smooth running |
The female urethra is significantly shorter in length and with a larger diameter than that of men. Therefore, infectious agents from the external environment penetrate into the bladder cavity along the ascending path almost unhindered.
Due to the fact that the external opening of the urethra and the anus are located very close, E. coli easily penetrates in the absence of proper hygienic care.
What infections cause cystitis in women?
Three large groups of causes of infectious cystitis in women are considered:
- Sexual infections (chlamydia, trichomonas, gonococci). This group is also called specific pathogens, since the changes caused have a unique clinical and laboratory picture.
- Opportunistic pathogens. These mycobacteria are found even in a completely healthy body. In a certain amount they are part of the normal microflora. But under the influence of external or internal factors leading to a violation of immunological defense, their numbers increase, and, accordingly, infection occurs.
- Gynecological diseases. Inflammatory changes in the reproductive system can trigger a relapse or aggravate the course.
Due to the fact that infectious cystitis can be caused by different types of pathogens, treatment is carried out not only by urologists, but also by gynecologists.
Gynecological infections causing cystitis
If there is a focus of infection in the pelvic area, infectious agents can enter the bladder through the blood (hematogenous route).
The main provoking gynecological diseases are salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes), oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries).
Infectious cystitis in women: symptoms and treatment
Regardless of the reasons leading to infectious cystitis, the clinical picture is quite specific:
- In the first place, urologists place dysuric disorders in the form of frequent and painful urination in small portions, and false urges are possible.
- Sometimes accompanied by an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels.
- Externally, urine becomes cloudy due to impurities and flakes. The appearance of blood is an extremely undesirable sign and has a difficult prognosis.
Infectious cystitis is characterized by a rapid onset with a peak of clinical manifestations in the first day. Complaints may persist for a week.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, hospitalization is not required. To determine the treatment regimen, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests: a general blood and urine test, a smear for microflora. Based on the data obtained, an antibiotic is selected, and in order to relieve pain, an anesthetic drug is selected.
Such complex treatment gives a positive effect within a few days. If complaints persist, then you should seek repeated consultation.
The main signs of a bacterial type of disease
The severity of symptoms and the duration of inflammation divide the forms of cystitis into acute and chronic. If a specific area of the bladder is damaged, the pathology is called focal. If the process is total in nature, the entire organ is affected, this type of cystitis is diffuse.
Depending on the nature of the inflammation of the walls, cystitis occurs:
- catarrhal;
- hemorrhagic;
- granulation;
- fibrous;
- ulcerative;
- gangrenous;
- allergic.
Hardware examination (cystoscopy) will help determine the specific type of wall damage. This clarification is necessary to determine treatment tactics. There is also the concept of postcoital cystitis. This type of inflammation can be experienced by a girl who has become sexually active. It appears immediately or a few days after intimacy.
Bacterial-type cystitis occurs most often and is characterized by the ingress of various bacteria onto the surface of the bladder. The infection enters the tissue through the urethra, sometimes “descending” through other organs, for example, the kidneys.
In women, infection through the urethra is a common route of infection due to the structural features of the urethra; it is meek and relatively wide compared to men.
Many provoking factors can provoke the development of bacteria. The main causes of bacterial inflammation of the urinary tract include:
- Development of gynecological and venereal diseases of the genital organs.
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene, which also leads to the spread of bacteria from the rectum.
- Dysbacteriosis, disorders of the vaginal microflora.
- Decreased immunity. This affects the protective functions of the mucosa, which loses its natural ability to resist bacteria.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse. There is a risk of not perceiving other flora and direct infection.
More precise reasons, and there may be several of them, can be determined by a specialist after conducting diagnostics, examining urine, smears, and blood.
With acute bacterial inflammation, typical symptoms of cystitis appear. They are felt especially intensely after sexual intercourse, during urination. The main features include:
- Pain when urinating, especially at the beginning and at the end of the process.
- Itching and burning. This tissue reaction is typical when bacteria spread on the surface of the genital organs, irritated not only by inflammation of the urinary tract, but also by current gynecological diseases, for example, the development of ureplasma.
- Blood, mucus, clots of pus in the urine.
- Change in urine color, presence of a specific unpleasant odor.
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
If the infection was caused by the gastrointestinal tract, then constipation and diarrhea may occur. In acute stages, fever, nausea, and chills are observed.
The difference between non-bacterial cystitis lies in the factor that provokes inflammation. These are not bacteria, but simple microorganisms, fungi, viruses, parasites, and neoplasms in the form of tumors.
In some cases, there is a mild pain syndrome.
Infections that cause cystitis in men
The incidence rate in men is 5 cases per 100,000 population, which is significantly lower than in women. Escherichia coli, which is the most common cause of the nonspecific form of the disease in women, rarely causes this pathology in men.
The most common pathogens are genital infections (chlamydia, gonococci), staphylococci, fungi, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
For men, the hematogenous route of infection is more typical, for example, with prostatitis, pyelonephritis, and kidney tuberculosis.
In terms of clinical manifestations, infectious cystitis in men is similar to women. There is also frequent and painful urination, accompanied by pain and burning. The urine becomes cloudy due to impurities of the inflammatory component or hemorrhagic (blood).