Cystitis is a very unpleasant disease from which no one is immune. Most often, pathology occurs in women due to the structure of their body, in particular the pelvis. Expectant and newly-made mothers especially suffer from this, since in their new position their immunity decreases, and they cannot take any medications. Despite this, men are also not immune from the appearance of sores. Cystitis can also affect the stronger sex. Less commonly, the disease appears in children. Today’s article will tell you how to properly take Metronidazole for cystitis and whether such treatment is justified.
Mechanism of action
Metronidazole is included in the list of vital drugs and has targeted antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effects.
Active against anaerobes and gram-positive microorganisms, in combination with amoxicillin it copes with Helicobacter pylori. Available in tablet, capsule and injection form, as well as in the form of gels, ointments and suppositories (suppositories). The mechanism of action of Metronidazole is aimed at inhibiting the synthesis of nucleic acids, which leads to disruption of the reproduction and death of microorganisms, and in the long term to their complete destruction. The effectiveness of the drug is ensured by the bioavailability of the active substance and its ability to create a high concentration in tissues and biological fluids in a short time:
- saliva;
- vaginal secretion;
- seminal and cerebrospinal fluid.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XWS7uaGsBOY
According to patient reviews, within a day after taking Metronidazole, the symptoms of cystitis weaken and with complex therapy a lasting effect is achieved in a short time.
pharmachologic effect
The effectiveness of the antibiotic Metronidazole lies in the specificity of its mechanism of action. When entering the body, the active components have a depressing effect on the DNA of bacteria, which act as causative agents of inflammatory processes. The result of this influence is a gradual inhibition of the development of pathogenic microorganisms and their further destruction.
The drug Metronidazole is rapidly absorbed, and medicinal use does not depend on the main meal. The maximum concentration of the base component in the blood and tissues is achieved 1-2 hours after the first use of the antibiotic. Many gram () and gram (-) microorganisms show increased sensitivity to the action of Metronidazole.
Since there are quite a lot of medicines that contain Metronidazole, such medicines contain various components, but Metronidazole is considered active. It affects the human body as follows:
- It affects the DNA chain, destroying membrane bonds, influencing the process of reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
- The substance also affects the respiratory process of pathogenic microorganisms, significantly inhibiting it.
- As a result, the natural death of infectious agents occurs, and this process proceeds quickly, without any particular complications.
For this reason, given the main property of the medication, it is so often used for cystitis.
The inflammatory process in the walls of the bladder can have a different nature, but if the cause is bacteria, then Metronidazole will help cope with the infection much faster.
Why is the drug so often used for cystitis:
- high efficiency against major pathogens (including E. coli);
- quick results and elimination of basic, inconspicuous symptoms;
- small range of side effects.
But when carrying out drug therapy, there is a high probability of developing resistance.
That is, microorganisms may lose sensitivity to the drug, in which case there is a high probability of therapy being ineffective. Timely antibacterial treatment will help correct the situation. In what cases is there a risk of treatment failure:
- if the course was not brought to its logical conclusion;
- medication was stopped after the unpleasant symptoms disappeared;
- the drug was taken in a high dosage or the dose was deliberately reduced after the condition had stabilized.
Metronidazole is classified as an antimicrobial drug, has nothing to do with antibiotics, and is considered a bactericidal agent.
How does Metronidazole work?
Treatment of cystitis with Metronidazole causes heated debate. Some representatives of medicine are confident in the effectiveness of this method, while others say it is useless. To find out whether a medicine will help or not, you need to understand its principle of action.
The medicine is a derivative of 5-nitromidazole. This drug has not only an antibacterial, but also an antiprotozoal effect. It stops the proliferation of protozoa and anaerobic microorganisms. The drug "Metronidazole" for cystitis will help you only if the disease is caused by the following microorganisms:
- trichomonas;
- entamoebas;
- bacteroids of different types;
- fusobacteria;
- gram-positive bacteria.
After ingestion, the drug immediately begins to be absorbed. The active substance is distributed throughout the body, showing the highest concentration after two hours. The effectiveness and speed of the drug do not depend in any way on food intake.
Features of antibiotic absorption
Metronidazole is taken in the treatment of cystitis only as prescribed by a doctor and in strict accordance with the dosage indicated in the annotation. You should also know the specifics of taking the drug.
- Excess body weight requires an increase in the daily dose of the drug.
- Concomitant pathologies or complicated cystitis may cause a change in dosage.
- In the acute form of the disease, at the beginning of treatment, take a one-time loading dose of the drug (500 mg).
- The drug should not be interrupted, otherwise the effectiveness of therapy will decrease.
- The components contained in the tablet color the urine dark.
- Metronidazole is not used to treat colds and flu.
- In combination with antibiotics, it is not recommended for use in patients under 18 years of age.
Contraindications to taking Metronidazole include:
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- age up to 6 years;
- individual intolerance.
During long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor biochemical blood parameters.
The potent antibacterial drug Metronidazole is prescribed solely for indications and is not used as a prophylactic agent.
The tablet form is most often prescribed by doctors to treat cystitis. Bioavailability with this method of therapy is 80%. This indicator is quite high compared to the penetration abilities of other antimicrobial antibiotics, even though gastric juice sufficiently oxidizes the tablets. This percentage of bioavailability is achieved due to the fact that the basic components of the drug are able to overcome cell membranes and barriers.
About 80% of the half-life products of the Metronidazole tablet are excreted in the urine by the kidneys and 15% by the gastrointestinal tract. For patients with kidney pathologies, doctors reduce the dosage of the active substance due to the fact that they have an imbalance in the natural output of chemical components. As a result, an excessive amount of antibiotic accumulates in the body, which increases the risk of intoxication.
Parenteral administration of the drug Metronidazole allows you to quickly achieve the maximum concentration of the active substance, which is carried through the bloodstream. After 6 hours after the injection, half the volume of the antibiotic is removed. When using medicinal suppositories vaginally, the drug is partially absorbed. About 20% of half-life products are excreted during the natural outflow of urine.
Analogs
There are a lot of drugs based on metronidazole. There are medicines with identical names, but from different manufacturers. These include Metronidazole from, "Avexima Siberia", "Green Oak", "Kelun-Kazfarm".
The most popular products with identical active ingredients, but with different trade names include:
- Trichopolum;
- Flagyl;
- Metron;
- Batsimex;
- Efloran.
Tinidazole has a similar effect, but its composition is different. The main active ingredient is identical to the name. This is an antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drug that is often prescribed to patients with individual intolerance to metronidazole.
For bacterial cystitis, Clindamycin is sometimes prescribed. This is an antibiotic that destroys anaerobic microorganisms. Trichomonas is not susceptible to it. If the analysis reveals this particular pathogen, then there is no point in taking this medication.
Metronidazole is a cheap and effective drug that is suitable for treating cystitis and other infectious diseases. Self-administration is undesirable, because the likelihood of recognizing the pathogen without examination is small, and given that inflammatory reactions often occur due to mixed infections, there is practically no chance of a successful cure. The medicine has many side effects, but this does not mean that they will certainly appear. Each organism is individual, so it is impossible to predict the reaction to treatment.
Contraindications for use
Treatment of cystitis with Metronidazole cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- Individual sensitivity to the drug.
- Breastfeeding period, as the drug will pass into milk.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- Severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
- Blood diseases.
- Diseases of the central nervous system, insomnia.
Metronidazole is not used in children under 6 years of age. Also, the drug should not be used in the treatment of influenza and ARVI, and as a preventive measure. It is not recommended to use the product with other drugs unless recommended by the attending physician.
The use of Metronidazole in any form of release should be avoided if there are the following contraindications:
- pregnancy especially in the first trimester;
- children under 18 years of age;
- individual intolerance to the product or its components;
- hypersensitivity to suppositories or tablets;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- lesions of the central nervous system, organic in nature;
- lactation period in women (breastfeeding);
- leukopenia.
In the presence of such diseases and conditions, the medication is not prescribed; it is used with caution when treating pregnant women in the second and third trimester.
In any case, the prescription is made by a doctor; if there are no indications, then therapy is not carried out, since with subsequent treatment, if cystitis occurs, the treatment will be ineffective.
In what cases should the drug not be used?
Metronidazole is never prescribed for cystitis in women in the first trimester of pregnancy. There is a possibility that the drug may adversely affect the formation of the fetus. Therefore, treatment is replaced with safer herbal remedies, and the use of Metronidazole is postponed until the second half of pregnancy. But even in this case, it is prescribed if the expected benefits outweigh the risks.
Under no circumstances should Metronidazole tablets be used to treat inflammation of the bladder if the patient has hypersensitivity to its components (major or minor). Taking pills during lactation is contraindicated. The medication is also not prescribed under the following circumstances:
- lesions of the nervous system;
- blood diseases;
- liver dysfunction.
It is prohibited to use an antimicrobial agent for children under three years of age.
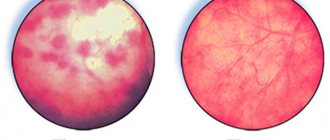
Characteristic symptoms of cystitis and clinical and laboratory tests
To prescribe adequate therapy and treatment for cystitis, the primary task is to identify etiological factors, determine the type and localization of pathogenic microorganisms. The disease is diagnosed based on medical history and the results of laboratory and clinical studies, which include:
- initial consultation, examination by a gynecologist or urologist;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- urine and blood tests;
- culture for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- microscopic examination of a smear from the cervix or urethra.
Considering that the impetus for the development of acute cystitis is bacterial infection, there are standard signs that you should pay attention to.
Main symptoms:
- urge to urinate frequently;
- burning and stinging;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen;
- cloudy urine and the presence of blood clots and flakes in it.
Metronidazole for cystitis: should I take it or not?
Statistics show that cystitis is most often provoked by trichomonas, ureaplasma and mycoplasma, gonococci, chlamydia, E. coli, streptococci and staphylococci. You can determine what exactly you are dealing with through simple laboratory tests in the form of a urine test. Metronidazole will not help with cystitis if the disease is caused by facultative anaerobes or anaerobic microorganisms.
Are you still wondering whether it is worth taking the described remedy to treat bladder inflammation? Then you should consult a doctor, get tested and get answers to all your questions. Only after this can you be sure that the medicine will help or, on the contrary, will be ineffective.
Mode of application
The drug is used in a minimum dosage of 250 mg, 2 times a day. This dosage is considered optimal for adult patients.
If we are talking about vaginal suppositories, they are administered 1-2 times a day.
The dosage can be adjusted by a urologist, but only if indicated. If the effectiveness of therapy is questioned and is absent within 48 hours, then there is a high probability of treatment failure, its adjustment and the prescription of antibiotics are required.
During lactation in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the drug is not used, regardless of the cause of the disease or complications. Because it can affect the process of fetal formation.
During pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, the drug is used, but therapy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor and only if indicated.
Tablets should not be used for patients under 18 years of age. For newborns, therapy with Metronidazole is not carried out.
The attending physician should tell the patient how to take Metronidazole for cystitis.
To achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect, the patient must follow the following rules:
- the drug in tablet form should be taken on an empty stomach before meals, the tablets should not be chewed, but simply washed down with clean water;
- during treatment with antibacterial tablets, a person needs to drink a lot of liquid - fruit drinks, teas, brewed herbal teas, etc.;
- in severe cases of the disease, Metronidazole is prescribed in the form of intravenous infusions, the course of treatment in such cases should not exceed three days, after which the patient should switch to tablets;
- a course of treatment with Metronidazole tablets usually lasts from 3 to 10 days;
- Metronidazole for cystitis in women is often prescribed in the form of vaginal suppositories, suppositories are inserted into the vagina for 7-10 days, while the patient must completely avoid sexual intercourse;
- an antibacterial drug in the form of a gel must be used to treat the genital organs: women inject the gel intravaginally, men treat the glans penis with the drug;
- when using the drug, the patient is prohibited from drinking alcoholic beverages of any strength, since the combination of alcohol and antibiotics can lead to the development of serious side effects;
- when the first improvements appear, patients should not stop using Metronidazole; only a full course of taking the antibacterial drug will help achieve the necessary therapeutic effect and prevent relapses of the disease;
- if any adverse reactions occur (nausea, vomiting, convulsions, etc.), you should stop taking metronidazole and seek medical help;
- After antibiotic therapy, a recovered person should take a course of probiotics, which will prevent the development of dysbiosis in the intestinal tract.
Metronidazole is used for bacterial infections. The drug is taken orally. The dosage is selected based on the patient’s age and the course of the pathology:
- Infants up to one year old are given 125 mg per day.
- Children from 2 to 4 years old are prescribed 250 mg per day.
- Children from 5 to 8 years old are given 375 mg per day.
- Older children and adults are prescribed 500 mg per day.
The dosage is divided into 2 doses. You should take the medicine at the same time every day. In severe cases, the dose is increased and divided into 3 doses. The drug begins to act 2-3 hours after administration. Excreted in urine and feces after 8 hours.
Let's summarize
From the article you learned how to take Metronidazole for cystitis. Dosage, features of the drug and main nuances are presented to your attention. After the course, wait two weeks and take the tests again. If the result shows that the contents of the bladder are sterile, then the treatment has brought a good result. When tests show remains of bacterial flora in the bladder, you must definitely consult a doctor and decide what to do next. If cystitis is not cured immediately and completely, it will turn into a chronic form, which is almost impossible to get rid of. Take care of your health, take antibiotics only as prescribed by your doctor. Best wishes!
Metronidazole is a popular drug used to treat infections of the urogenital system. It is often recommended on forums and prescribed by domestic doctors. But is it really possible to prescribe Metronidazole for cystitis in women and what is its effectiveness - further in the article.
Standard therapeutic methods
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_y235lM8asA
How to take Metronidazole when treating cystitis? Based on the medical history and after laboratory tests, the doctor determines the dosage of the drug.
Intensive therapy involves taking Metronidazole 250 mg/3 times a day, standard cases – 250 mg/2 times. The course of treatment depends on the form of the disease and the severity of the patient's condition. As a rule, complete cure of acute cystitis occurs in 5–7 days, and the chronic form is stopped within ten days. In exceptional cases and only under the supervision of a doctor, the treatment period may be extended for several more days.
Metronidazole is prescribed with extreme caution to elderly patients. To determine the optimal dose of the drug, monitoring the concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma is required. For this purpose, a few days after the start of administration, a blood test is performed and if the concentration increases, the dosage is reduced or alternative forms of treatment are prescribed.
To neutralize the components on the gastrointestinal mucosa, take the tablets with a sufficient amount of liquid: water or milk. During the period of using Metronidazole, you need to drink plenty of fluids. Especially good are herbal decoctions and fruit drinks made from fresh cranberries, lingonberries, sea buckthorn and black currants.
A fundamentally important point in the treatment of any form of cystitis and associated infections is the simultaneous use of Metronidazole by a sexual partner. This measure helps prevent relapses of cystitis and avoid dangerous complications.
The patient needs to consult a doctor before starting therapy. The dosage and duration of treatment is determined based on the results of a comprehensive examination. Patients suffering from obesity and other concomitant pathologies that have a direct impact on the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug are subject to regular observation.
As a standard, you need to take Metronidazole in the amount of 2 tablets per day. In this case, treatment is carried out for at least one week. Daily intake depends on the prescribed form of release:
- Granules - up to 2 pieces per day.
- Suppositories are prescribed only to females, as they are inserted into the vagina. Dose: two suppositories.
- Gel – applied externally or intravaginally.
- Injection solution - its intravenous use is indicated for acute cystitis. Therapy does not last more than 3 days. The medicine is administered by drop method, as there is a risk of disruption of the functioning of the central nervous system.
Before treating a chronic inflammatory process occurring in the bladder, the extent of damage to the entire body is determined. The tablets are taken with water after meals. To prevent possible gastrointestinal upset, Metronidazole is taken with milk.
Food during therapy should be rational, with fiber. The impact on cystitis occurs on the first day of treatment. To do this, the patient is prescribed the drug at the maximum dose. In the following days, it is necessary to gradually reduce the amount of medication.
Incomplete therapy increases the risk of inflammation becoming chronic. This increases the chances of frequent relapses of the disease.
When should Metronidazole be prescribed?
Does Metronidazole help with urological diseases? The drug has not completely lost its importance in the treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system (urethritis and cystitis). It remains a key drug for the treatment of trichomoniasis, a disease that is very similar in symptoms to cystitis. It is caused by a single-celled microorganism that can multiply in the mucous membrane of the bladder. Trichomoniasis is transmitted in most cases through sexual contact.
According to the World Health Organization, this disease is a very common urological pathology, since about 170 million cases of new infections are officially registered every year. Clinically, trichomoniasis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- burning sensation in the genitals;
- discomfort or aching pain when urinating;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet.
As is easy to see, the symptoms correspond to the clinical picture of cystitis. And without specific diagnostics, it is not always possible to draw a line between these diseases.
Overdose
If the volume is exceeded, signs of overdose appear in the form of:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- ataxia;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- development of seizures.
In such cases, the medication is discontinued. To eliminate side effects, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
There have been no clinically described cases of overdose. But if the drug was taken in a high dose, the risk of developing unwanted side effects increases significantly: nausea, vomiting, disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Side effects
A synthetic antimicrobial agent penetrates into all organs and tissues, and therefore causes a variety of undesirable reactions.
The most commonly affected systems are:
- nervous (dizziness, mood swings, sleep problems);
- digestive (impaired defecation, nausea, abdominal pain);
- hematopoietic (abnormalities in tests);
- urinary (inflammation of the bladder, candidiasis, increased amount of urine excreted).
Patients often complain of the development of allergic reactions: rash, itching, redness. You should tell your doctor about all side effects so that he can take action.
Drug tolerance
Taking the drug for any form of cystitis requires constant examination of the patient. The doctor must monitor not only blood counts, but also the composition of urine. The prescribed treatment regimen is followed. Inflammation is characterized by rapid adaptation of the pathogen to the antimicrobial agent. Regular laboratory diagnostics will help identify when Metronidazole is ineffective.
Bacterial resistance to it is observed in some cases:
- refusal of treatment after the symptoms of inflammation disappear;
- long breaks between doses of the drug;
- independent reduction of the prescribed dose.
If the patient has chronic pyelonephritis, the drug is taken in small quantities. Metronidazole and Amoxicillin are an effective regimen for preventing the development of microbial tolerance. In this case, therapy is carried out in low doses.
Metronidazole is a proven and reliable drug that belongs to the group of active antimicrobial agents for the relief of urinary tract infections.
Presented in several pharmacological forms:
- film-coated tablets for oral administration;
- powder intended for the preparation of intramuscular injections;
- ready-made injection solution of Metronidazole in ampoules;
- vaginal suppositories and gel.
The effectiveness of the drug for intravenous and intramuscular administration is due to the immediate biochemical effect on protozoan microorganisms. As a result of the synthesis of the active substance with deoxyribonucleic acid, the proliferation of bacteria is blocked, which subsequently leads to their death. Metronidazole is highly active against pathogens of thrush, giardiasis, gram-positive and aerobic bacteria.
The action of the tablet form of Metronidazole is based on a gradual decrease in the degree of oxidative processes and suppression of the activity of single-celled bacteria. The drug successfully fights genitourinary infections, and in combination with antibiotics exhibits increased activity against bacteria that cause stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Suppositories and gel are forms for topical use. By creating a high concentration at the injection site, within a few minutes they overcome the intercellular barrier and interact with the DNA of microorganisms, disrupting their division processes. The action of Metronidazole in the form of suppositories and gel is aimed at suppressing the pathogens of thrush, streptococcus and trichomoniasis.
In case of acute cystitis, aggravated by concomitant pathologies, intravenous injections of Metronidazole are prescribed in the first three days, then they switch to taking the tablet form. At the same time, treatment is carried out with suppositories, which are inserted into the vagina or rectum twice a day: in the morning after hygiene procedures and in the evening, just before bedtime.
Causes of cystitis
This inflammatory process most often occurs in women, due to the anatomical features of the urinary system. As a rule, cystitis is caused by the proliferation of bacterial microflora. Pathogenic microflora may be constantly present in the urinary tract, but not cause disease. The inflammatory process occurs only when favorable conditions are created for it. In particular, the following phenomena contribute to this:
- hormonal imbalance;
- hypothermia
- failure of the immune system;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
- sedentary lifestyle
- kidney diseases (passage of sand, kidney stones)
As soon as favorable conditions appear, pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply, which causes an inflammatory process in the bladder.
The presence of inflammation manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- acute sharp pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by urination;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, with very little urine coming out.
- general weakness;
- when urinating, the pain intensifies;
- cloudy urine
- blood in the urine;
- increase in body temperature.
If at least a few of these symptoms appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor, get examined and get a treatment plan.
Metronidazole is effective in the treatment of cystitis only if the disease is caused by microorganisms sensitive to this drug.
This antibiotic is widely used to treat a variety of diseases: giardiasis, toxoplasmosis, dysentery, trichomoniasis and other infectious diseases caused by parasitic protozoa. Metronidazole prevents bacterial cells from producing nucleic acids, causing them to die.
The active ingredient of the drug has high bioavailability - 80%, due to which it is quickly distributed throughout the tissues and fluids of the body. The drug is present in all organs of the body, acts on the central nervous system, penetrates into breast milk, and affects the fetus during pregnancy.
Interaction with other drugs
Drug interactions with Metronidazole vary; there are several drugs that are not recommended to be combined with an antimicrobial agent. Because such a “tandem” can lead to undesirable consequences.
Description of drug interactions:
- does not combine well with aluminum and products containing it;
- It is undesirable to combine with indirect anticoagulants (potentiates the effect);
- in combination with disulfiram, there is a high probability of developing irreversible complications;
- when the level of carbamazepine in the blood increases, in combination with metronidazole, the risk of toxic effects of medications on the body increases;
- use in combination with lansoprazole can lead to the development of glossitis, stomatitis and other oral diseases.
Adsorption of Metronidazole from the digestive tract is reduced if the medication is combined with antacids based on aluminum hydroxide. When the antibiotic and disulfirams are used simultaneously, acute psychosis and impaired consciousness occur. When combined with Prednisolone, the process of eliminating Metronidazole is accelerated.
General recommendations for admission
To achieve a positive outcome of an infectious lesion of a hollow organ of the excretory system, certain rules for antibiotic therapy should be followed. During the treatment of cystitis, you should completely avoid the use of alcoholic beverages, which reduce the effectiveness of Metronidazole and can lead to adverse reactions of a psychosomatic nature.
Remember: Without the consent of your doctor, it is prohibited to combine an antibiotic with other medications, as it actively interacts with them.
The drug is not prescribed for acute respiratory viral infections and influenza, so when diagnosing cystitis, doctors select other medications. After the first course of treatment, doctors may prescribe Metronidazole again, but patients should take a break of 3 weeks. This antibiotic has a fairly powerful anti-inflammatory effect and is prescribed strictly as needed. It is not prescribed as a preventive measure for bladder inflammation.
As a rule, when positive dynamics are detected in the first days of taking Metronidazole, patients are given the erroneous feeling that the disease has receded. However, to achieve complete recovery, you must complete the entire therapeutic course. Only under this condition can a subsequent recurrence of cystitis be avoided.
For the entire period of treatment with Metronidazole, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited, since ethanol in combination with the active substance causes intoxication, accompanied by a sudden increase in hypertension, migraine-like pain, cramps in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting.
When treating genitourinary infections in both women and men, doctors recommend giving up intimate life. After a course of therapy, a control blood test is carried out, and biological material from the vagina or urethra is also required to confirm the absence of infection.
Drivers of vehicles and people operating other complex machinery when taking Metronidazole should take into account its side effects.
Diarrhea, skin rashes, dizziness and loss of coordination of movements signal the need to immediately stop taking Metronidazole.
Self-medication is unacceptable; use of the drug requires medical supervision. Only a doctor will select the optimal therapeutic regimen, and if negative symptoms occur, prescribe an alternative course of treatment.
additional information
For treatment to be beneficial, you must take the medication correctly. At the end of the annotation, the manufacturer describes the special conditions for admission. Be sure to check them out.
- During treatment, it is necessary to exclude ethanol in any form. The consumption of even low-alcohol drinks is prohibited, as this can provoke disulfiram-like reactions.
- During therapy, the patient may notice that the urine has become dark in color. Nothing wrong with that. This reaction does not require discontinuation of treatment.
- Both partners should be treated, since after recovery of one, the infection can be transmitted to him again.
- The effectiveness of the medicine may be affected by other medicines. If you are taking any medications, be sure to notify your doctor.
Variety and effectiveness of different forms of medicine
Metronidazole causes the following side effects:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pain in the intestines;
- allergic reactions, rashes;
- insomnia;
- blood clotting disorder;
- kidney dysfunction;
- vaginal dysbiosis, candidiasis.
If side effects occur, you should inform your doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will adjust the dosage of Metronidazole or prescribe another drug with a similar effect.
To reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal upset and vaginal dysbiosis, it is recommended to combine Metronidazole with probiotics. It will also be useful to eat more natural fermented milk products during the treatment period.
Treatment with an antimicrobial drug can cause a number of undesirable consequences; the list of side effects that occur most often includes:
- diarrhea, digestive disorders;
- change in taste sensations;
- the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth;
- dizziness, nausea, vomiting attacks;
- feeling of pain in the lower abdomen;
- brown coloration of urine;
- allergic reactions of various types;
- burning sensation or irritation in the area of the external genitalia.
If the conditions described above occur, it is necessary to urgently interrupt treatment with metronidazole and consult a doctor. Therapy requires correction; instead of antimicrobial agents, preference is given to antibiotics.
Possible consequences of treatment with metronidazole
Being an antimicrobial drug, metronidazole suppresses not only the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms, but also the natural intestinal microflora, contributing to the development of dysbiosis with accompanying symptoms:
- diarrhea;
- sharp pain in the intestinal area;
- constipation;
- nausea.
To restore intestinal dysfunction, the drug taken should be combined with complex means for restoring intestinal microflora:
- Hilak-forte;
- Linux.
The latter can be drunk during antibacterial therapy, as well as for some time after the end of treatment.
The development of candidomycosis (thrush) after metronidazole has a similar mechanism. Suppression of the natural microflora of the mucous surfaces of the body entails the rapid development of fungi of the genus Candida. In order to prevent the occurrence of candidiasis, the antifungal drug nystatin is prescribed simultaneously with metronidazole.