Non-infectious cystitis occurs and develops without the penetration of infectious agents into the bladder cavity. It is most often diagnosed in young and mature women. It has a chronic progressive nature. Periods of remission alternate with exacerbations, which occur several times a year.
Non-infectious cystitis is most often a chronic disease.
Urination with cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder today is a fairly common problem, characterized by a lot of unpleasant sensations, such as impaired urination, pain due to cystitis, etc.
If the disease is not treated, it can lead to very serious consequences. If you look at the statistics, in most cases, namely, in 60-70%, representatives of the fairer sex are affected; the disease develops much less often in men and children, however, it is not an exception. Why do women get sick so much more often? This is explained by the fact that their urethra is much shorter and wider, which provides direct access for bacteria to enter. In most cases, it is from the vagina that pathogenic microorganisms enter the bladder through the urethra, and after 12-48 hours, the first symptoms of the disease can be observed. As a rule, this time is enough for microorganisms to multiply and create unfavorable microflora in the organ.
Urination during cystitis, as a rule, becomes more frequent, causing discomfort and pain to the patient. Naturally, if this symptom is present, you should immediately contact a specialist who will conduct an appropriate examination and prescribe adequate treatment. Concomitant manifestations of the inflammatory process, depending on the form of the disease, may be:
- fever;
- general exhaustion of the body;
- weakness;
- feeling of “ache” in the joints;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
If you let the disease take its course or self-medicate, there is a high probability that the disease will become chronic and will constantly torment you with systematic exacerbations. In order to prevent cystitis with blood at the end of urination, you should know the main causes of the disease and the factors predisposing to its development.
Causes of discomfort
After an acute attack of cystitis, the patient still had unpleasant sensations, although the disease, in his opinion, went away. These patient complaints will tell the doctor about the persistence of inflammation and the transition of cystitis to a chronic form.
Treatment of cystitis is not difficult; with the right course of therapy, the symptoms go away without a trace. The discomfort may pass, but the inflammatory process persists longer than the pain.
Patients feel relief and calm, so they often stop therapy after the pain disappears, which should not be allowed!
With proper treatment with antibiotics, the bacterial flora is completely destroyed within five to seven days. When taking the drugs for about three days, the entire bacterial flora is not destroyed; bacteria remain, which adapt to antibiotics and become resistant to them.
The appearance of a painful sensation after treatment indicates the continued spread of bacteria and the progression of inflammation in the bladder. Repeated treatment with antibiotics may not be effective, and discomfort will persist, since the bacteria are no longer susceptible to the drugs.
Consultation with doctors and strict implementation of their prescriptions and recommendations are very important!
If treated incorrectly, not only does the infection multiply and spread, but also the structure of the organ, its mucous and muscular membranes changes - the bladder shrinks, decreases in size, its sensitivity changes and pain appears.
What can cause cystitis?
If we talk about the reasons for the appearance of the disease in the body, there can be a lot of them, but still experts identify the most common:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- use of chemical products for intimate hygiene;
- frequent and promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- hypothermia, which can almost immediately provoke cystitis without pain when urinating. Painful sensations in some cases may occur a little later;
- infection, namely bacteria, fungi, viruses that penetrate the organ through the vagina, intestines, kidneys;
- protracted chronic diseases that reduce the body’s defenses, such as oncology, HIV, tuberculosis.
As can be seen from the above, there are a huge number of factors contributing to the development of the disease, so every person should monitor their health as responsibly as possible, adhere to preventive measures, so that later they do not have to endure pain when urinating during cystitis and other unpleasant symptoms.
Symptomatic manifestations of the inflammatory process in the bladder
The clinical picture of the disease can be different, namely, each human body can cope with the inflammatory process differently. In some women, for example, the symptoms will be pronounced with blood when urinating due to cystitis, pain, and so on. For others, on the contrary, only slight discomfort will be felt. It also happens that the disease very quickly becomes chronic, so it is very important to know the earliest signs of the disease in order to be able to recognize them in time and begin treatment immediately. The main symptomatic manifestations of cystitis include:
- frequent urge to go to the toilet “in a small way”;
- the amount of liquid released during the process is minimal;
- urine acquires an unpleasant specific odor;
- becomes cloudy;
- the patient feels discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen;
- There is difficulty urinating with cystitis; a person wants to urinate, but simply cannot.
Treatment of cystitis and frequent urination with blood in it
Inflammation of the bladder must be treated at its earliest stage in order to avoid complications and a chronic form. Therefore, with the first signs, you should immediately go to the doctor and not self-medicate. The disease can be caused by various microorganisms, and, as is known, many drugs affect only certain groups of them. Accordingly, the medicine you choose incorrectly at the pharmacy may not only not cure the disease, but also aggravate its course. Therefore, if excessive urination and pain due to cystitis in women have been detected, you should contact a competent specialist. He will take the necessary tests and, based on their results, prescribe adequate treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of acute and chronic cystitis and urethritis is carried out only by a doctor, who must conduct a complete diagnosis and identify treatment or diagnostic errors. Drug therapy is required, which is difficult to select due to the complexity of the course.
Do not self-medicate, especially with sluggish processes and pain.
In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to ensure a balanced diet and drinking regimen:
- Drink at least 14 glasses of pure plain water per day.
- Limit intake of salty, peppery, spicy, fried, fatty foods.
- Limit the consumption of foods containing calcium and phosphates.
- Maintain personal hygiene!
- Avoid sexual intercourse during and after cystitis.
- If sexual intercourse has taken place, then after it empty your bladder and carry out hygiene procedures.
- Wear cotton and breathable underwear, change it often, and do not wear tight clothing.
- Always empty your bladder completely to avoid stagnation of urine.
When the course of treatment is completed, the patient must continue to treat his health as carefully as he did during treatment, so that repeated suffering does not occur! Take care of your health!
What drugs are used in the treatment of cystitis - this will be discussed in the video:
urogenital.ru
Symptoms and treatment of cystitis in women. Cystitis and sex: how are they connected?
Cystitis in women is a fairly common phenomenon that can lead to very unpleasant consequences. How to identify the symptoms of cystitis, what are the preventive measures and the treatment process for cystitis, says gynecologist at the Be Healthy clinic Ekaterina Krasilova.
Cystitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. This disease is caused by bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder. The most common causative agents of cystitis are opportunistic flora (Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, Proteus) and sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, trichomonas, some viruses and fungi).
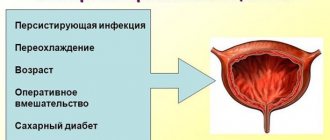
There are a number of factors that increase the “chances” of cystitis, including poor personal hygiene, promiscuity, diabetes, old age, pregnancy, obesity, hypothermia, and rare urination. Prolonged presence of urine in the bladder creates optimal conditions for the development of infection: the temperature is maintained at a constant level, a sufficient amount of organic substances are dissolved in the urine, and there are nearby sources of microflora.
What is “honeymoon cystitis”? They say it occurs in women due to frequent sex. Is it so?
“Honeymoon cystitis” is cystitis that can occur after a woman’s first sexual intercourse. This happens if the microflora of the vagina or intestines is “thrown” into the urethra: in women it is short and wide, and bacteria penetrate into it quite easily.
The cause of “honeymoon cystitis” can be infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, a violation of the vaginal microflora - bacterial vaginosis or vaginal dysbiosis. Another cause of cystitis may be failure to maintain hygiene by a woman or man before intimate relationships.
It should be noted that today “honeymoon cystitis” has come to be called cystitis associated with any sexual intercourse, and not just the first. This can have a serious impact on the sexual life of the sick woman and her psychological state.
As for physical health, cystitis can lead to such unpleasant complications as ascending pyelonephritis (inflammatory process in the kidneys), ulceration of the wall and a decrease in bladder capacity, narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, which leads to difficulty urinating.
What symptoms of cystitis should women pay attention to in order to notice the disease at the very beginning?
Cystitis is manifested by frequent urination with pain, the appearance of a small amount of urine during the day and night, and a frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty. Urine with cystitis may become cloudy or bloody, have a pungent odor, pressure or cramps in the lower abdomen, and sometimes low-grade body temperature (for a long time in the range of 37.1-38°C) may also appear.
If a woman seeks medical help when she first experienced acute symptoms, then, as a rule, it is easy to help her.
Do I need to get tested to detect cystitis? What is used to treat cystitis?
Diagnosis of acute cystitis is rarely difficult. The disease is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints, medical history, clinical picture, and urine analysis. If necessary, a study is carried out for sexually transmitted infections to diagnose a possible pathogen and select adequate therapy.
As a rule, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and painkillers are used in the treatment of cystitis. As a supplement, herbal remedies are prescribed that have a bactericidal effect and are also aimed at increasing the volume of daily urine.
How to protect yourself from cystitis? 5 rules
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene: try to wash the external genitalia after each visit to the toilet, but at least twice a day, using hand movements from front to back and in no case vice versa. Use specialized soap based on lactic acid (it is better to purchase it at the pharmacy).
- Use ironed underwear made from natural fabrics of the “correct cut” (thongs are not recommended). If possible, replace tampons with pads, since tampons can mechanically compress the urethra and be a source of infection in the immediate vicinity of the external opening of the urethra.
- Practice monogamous safe sex, before and after which it is also necessary to toilet the external genitalia. Do not allow oral sex if your partner has pathologies such as stomatitis, tonsillitis, oral candidiasis and other infections, since saliva can transfer pathogenic bacteria to the external genitalia and the urethra.
- Carefully monitor your health - treat colds, sore throats, chronic inflammatory diseases (caries, tonsillitis, urological or gynecological pathologies) in a timely manner.
- Consume the optimal amount of fluid; in the hot season it should increase by 1-1.5 liters. Do not restrain yourself when you want to go “small”, since prolonged retention of urine in the bladder contributes to the development of infection. And, of course, avoid stress and hypothermia so that your immune system always guards your health.
Main symptoms of cystitis
- The urge to empty the bladder frequently;
- Decreased volume of urine excreted during urination;
- Weak stream of urine;
- Increased body temperature;
- The urine smells unpleasant, sediment has appeared in the urine and its color has changed.
Cystitis without pain when urinating is most often determined by constant passive combinations of symptoms. This medical phenomenon is called polyuria, with which people most often turn to specialized specialists - urologists and gynecologists.
Only on the basis of this complaint, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics, which includes studying the patient’s medical history, referral for a general urine test, as well as blood for biochemistry, culture of urine bacteria in a nutrient laboratory medium, and ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
These examinations are necessary to exclude the patient from other urinary tract diseases and renal stone pathologies that have the same symptoms. For example, diabetes mellitus is often accompanied by the same symptoms as cystitis; the smell of urine is just as unpleasant.
Urinary incontinence during cystitis
Among urological diseases, cystitis is the most common urological problem in the world. Develops as a result of infectious and inflammatory damage to the mucous lining of the cavity of the bladder reservoir. It is accompanied by such unpleasant and annoying symptoms that it is simply impossible to ignore. The neglect of the disease and its chronicity often causes the development of the most unpleasant symptom - urinary incontinence with cystitis.
Introduction
Modern diagnostic methods and a professional approach to the treatment of various pathologies of the genitourinary system make it possible to successfully cope not only with the acute form of cystitis, but also with the manifestations of latent clinical manifestations of chronic cystitis with periodic outbreaks of exacerbations. The only way to avoid the unpleasant consequences of the disease is to consult a doctor in a timely manner if characteristic signs of the disease appear, such as:
- frequent urge to urinate (urination), combined with the difficulty of their implementation, or with short acts of urination that do not relieve the urge;
- suprapubic cutting, cramping pain, which manifests itself regardless of the act of urination, either during voiding or during imperative urges;
- changes in the consistency and composition of urine (possible inclusion of blood clots);
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- intoxication symptoms, weakness and fever.
Inflammatory processes in the mucous structure of the walls of the bladder cavity usually occur suddenly. In most cases, as practice shows, both cystitis and incontinence (incontinence with cystitis) are noted simultaneously when the doctor diagnoses complications caused by the inflammatory process, which suggests that urinary incontinence itself is a consequence of the neglect of cystitis.
Prevention
A few tips that will really help prevent urinary incontinence when cystitis occurs:
- Drink more fluid.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol). Nicotine and alcohol can irritate the bladder.
- Watch your weight. Excess weight means extra urinary pressure.
- Carry out exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and strengthen the bladder.
- Prevent cystitis.
In case of exacerbation of cystitis, you should visit the toilet at the first urge. Overfilling the bladder can cause bladder irritation and lead to relapse of the disease.
Even if the disease reappears and the symptoms are similar to the previous one, contacting a doctor should be done immediately and without fail. The diagnosis may reveal completely different causes of this disease.
Causes and types of pathology
All processes occurring in the human body are thought out to the smallest detail by nature itself. And any violations in this complex mechanism are due to certain reasons. Up to 38% of our compatriots with cystitis are faced with the problem of uncontrolled urination, but only 4% of such patients seek medical help. The rest ignore the disease, considering this manifestation of cystitis to be a natural phenomenon, thereby aggravating their condition.
The etiological process is determined by more than one factor. Among them:
- Dysfunction of the neuro-reflex control of the urinary act.
- Congenital and acquired changes in the anatomical structure of the urinary system and adjacent organs.
- Long-term inflammatory processes in the structure of the bladder.
Development mechanisms
Control of the nervous system over the contractility of the detrusor (muscle tissue of the bladder) does not allow the manifestation of involuntary movements. Inflammatory reactions in the cavity of the bladder lead to failure of the process, regardless of the genesis of the development of cystitis. Against the background of prolonged inflammation in the bladder tissues, the integrity of the mucous membrane of the reservoir cavity is disrupted and the immune defense mechanism is reduced, which causes the development of bladder hyperactivity.
Inflammatory reactions cause irritation of nerve receptors, which give false signals to frequent urination.
Even a slight accumulation of urine in an inflamed bladder can deform the walls of the bladder and become a catalyst for irritation of receptors. Receiving distorted information about the need to urinate, the brain issues a command to muscle contraction of the detrusor muscle. The urge is sometimes so intense that it is simply impossible to control the process of reservoir emptying.
Cystitis and urinary incontinence (UI) can provoke:
- pregnancy, against the background of which the circulatory functions in the bladder walls are disrupted due to compression by the enlarged uterus;
- violation of reflex functions in the process of trauma to the bladder during childbirth;
- thinning of the bladder walls caused by an age-related decrease in estrogen secretion (during menopause);
- pelvic floor incompetence and vaginal prolapse.
Treatment of frequent urination in men
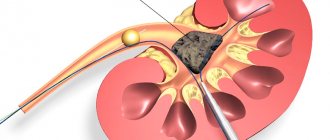
Treatment methods for pollakiuria depend on what disease is causing it. In case of urolithiasis, procedures are carried out to crush or remove stones. Infectious inflammations are treated with antibiotics selected in accordance with the results of sensitivity testing.
For chronic cystitis, auxiliary therapy methods are effective:
- Electrophoresis. Ions deliver the active substances of medications to the mucous membranes of the bladder and enhance their effectiveness.
- Inductothermy is the heating of the body by electromagnetic waves. The procedure improves blood and lymph flow, relieves swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Magnetotherapy.
- EHF therapy is the effect of high-frequency electromagnetic pulses on tissues. The procedure has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Ultrasound therapy.
Drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB)
To normalize urination in hyperplasia, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors and alpha-blockers are prescribed. If necessary, surgical methods are used: transurethral resection or open prostatectomy.
For the treatment of prostatitis, in addition to antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating suppositories are prescribed: Vitaprost, Prostatilen, Prostopin, Longidaza, ichthyol.
See also: 7 approaches to treating prostatitis.
Vitaprost suppositories are a drug of animal origin used for diseases of the prostate gland and bladder. Price from 930 rub.
In case of diabetes, the first step is to stabilize blood glucose levels. To normalize urination, M-anticholinergics and lipoic acid are prescribed. For diabetes insipidus, take Minirin and Carbamazepine.
We have reviewed the best pills for treating frequent urination in men.
At home
At home, the bladder can be “calmed” with decoctions of medicinal herbs: orthosiphon stamen, chamomile, sage, lingonberry leaf. Standard preparation scheme: pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water, leave until it cools. Beekeeping products have a good anti-inflammatory effect: propolis, honey with royal jelly, dead bee tincture.
A course of taking the “Fitolysin” paste solution helps relieve inflammation of the genitourinary tract. It enhances the effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemic drugs, stimulates urination, removing microbes from the bladder.
Phytolysin is a combined herbal preparation that has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effect. Price from 421 rub.
Warming up is allowed only with the permission of a doctor. In some cases, such procedures provoke the proliferation of pathogens.
Elderly people are recommended to perform Kegel exercises and squats to strengthen the pelvic floor as part of the treatment for frequent urination.
What are the types of NM?
There are several types of such violations, specifically reflecting each specific case. But their most complete classification, which has become a priority in medical practice today, is the classification proposed by the International Continence Society. It includes:
Imperative type of NM
Urgent or imperative. It is characterized by the patient’s inability to hold urine at the very peak of the imperative urge to micturate. The reason is due to increased muscle activity of the bladder walls, provoked by pathologies of the spinal cord or brain, hormonal imbalance, inflammatory processes, or damage to the bladder walls.
Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment
The diagnostic search is based on a comprehensive examination, including:
- Methods of clinical and anamnestic nature - questioning and identifying anamnesis, gynecological examination with taking smears.
- Examination using instrumental techniques - using ultrasound of the urethra and bladder, muscle examination, ultrasound with Doppler, cystometry, uroflowmetry and sphincterometry, electromyography of the bladder and sphincter, laser Doppler flowmetry of the bladder.
For each type of urinary incontinence, the doctor selects the appropriate drug therapy or surgical intervention according to the indications (sling operations, colporrhaphy with plastic surgery and perineolevatoroplasty, etc.).
For example, patients with the most common manifestation of imperative cystitis, UI, are recommended to undergo complex treatment, including a three-month course of medication with the following medications:
- Antimuscarinic group - "Vesicare" or other drugs with the active substance - "Solifenacin" with a morning dose of 10 mg.
- A drug that improves blood circulation in the muscle tissues of the MP and mediator (mediated) therapy - “Picamilon” at a dosage of 50 mg 3/day.
- Vitamin complexes with group “B” vitamin – 1 mg/day, to improve muscle tone.
- To reduce resistance to urine flow and normalize voiding, use the adrenergic blocker “Setegis” (2 mg before bedtime) with mandatory blood pressure monitoring.
- To strengthen the pelvic muscles, a two-week course of exercise therapy (15 min 3/day) is recommended.
Diagnostics
Activities carried out as part of the diagnosis of frequent urination:
- Anamnesis collection, analysis of a pre-filled urination diary.
- General and Nechiporenko urine analysis, uroflowmetry.
- General blood test, sugar, hormones.
- Urethral smear, prostatic juice test using PCR.
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary organs.
- Survey and excretory urography (x-ray of the kidneys after administration of a contrast agent).
- Cystography (bladder x-ray after contrast).
- Urethrography (x-ray of the urethra with contrast).
- CT, MRI.
Urologist and dermatovenereologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin tells us what diseases can be detected by taking a urine test in men
Based on the diagnostic results, the patient can be redirected to a nephrologist, neurologist, and in some cases to a psychotherapist.
How to prevent UI with cystitis
A number of very simple recommendations will really help prevent the development of this pathology during inflammatory processes in the bladder.
- Maintaining increased fluid intake.
- Exclusion from the diet and lifestyle (alcoholic drinks and smoking) of factors that irritate mucous tissues.
- Carry out constant monitoring of weight, thereby eliminating pressure on the bladder walls.
- Exercise regularly, strengthening the MP and pelvic muscles.
- Treat in a timely manner and prevent chronicity of infectious and inflammatory pathologies.
Uncomplicated processes of voluntary urination with cystitis respond well to therapy. With timely elimination of inflammatory processes in the bladder tissues, the problem with urine incontinence is eliminated independently. Difficulty in treatment is caused by UI, accompanied by concomitant causes. You cannot solve this problem on your own. It is very important not to start the disease and start treatment on time.
Sources:
https://tsistit-lechenie.ru/mocheispuskanie-pri-tsistite/ https://www.7ya.ru/article/Chastoe-mocheispuskanie-bol-cistit-u-zhenwin-Kak-lechit-2017/ https:// mycistit.ru/diagnostika/nederzhanie-mochi