Home / Types of cystitis
Back
Published: 08/07/2020
Reading time: 12 min
0
48
- Cystitis - what is it?
- How to determine cystitis
- Why does cystitis develop during lactation?
- Reasons for the development of cystitis in nursing mothers
- First symptoms: what to look for
- Nature and forms of the disease Acute
- Chronic
- Features of disease diagnosis
- Drug treatment Antibiotics
- The feasibility of traditional therapy
Cystitis - what is it?
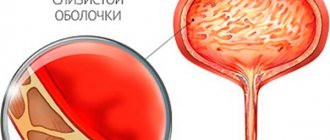
Cystitis is a disease caused by various infections in the bladder and urinary tract. Due to the anatomical features of the female body, representatives of the fairer sex are more likely than men to encounter a similar problem. And after the birth of a child, the likelihood of developing inflammatory processes in the urinary system increases.
Depending on the complexity of the course, there are 2 types of cystitis.
- Uncomplicated. In this case, only the walls of the bladder are affected, sometimes the course of the disease is accompanied by urethritis.
- Complicated type. In this case, the disease spreads upward, and in addition to the bladder, one or two kidneys are affected.
Pathogenetic therapy
Many women ask: “How to treat cystitis with herbal remedies?” With this treatment of cystitis, it is best to follow the recommendations of doctors. Although herbal medicine is very effective, it should be used with medical prescription. Today, there are many herbal remedies for cystitis, but they should be used with the prescription of an appropriate specialist.
- high efficiency;
- safety;
- availability;
- utility.
However, to ensure the safety of the health and well-being of their newborns, breastfeeding women should consult with their doctor before using such treatment.
Many doctors recommend treating cystitis with Canephron. This drug is highly effective and safe for the body. In the production of Canephron, exclusively extracts obtained from medicinal plants are used. If a nursing mother is not allergic to this drug, then it can be safely used as prescribed by a doctor to combat the manifestations of inflammation in the bladder.
In addition to Canephron, cystitis can be cured with Phytolysin. The unique composition of this drug helps create a powerful anti-inflammatory effect in the body, which eliminates inflammation in the bladder within a short time. Phytolysin is also endowed with excellent antiseptic properties, thanks to which it can be used without antibiotics. Regular use of this medicine relieves unpleasant pain, thereby restoring normal renal activity.
Taking herbal medicines promotes the manifestation of a slight diuretic effect in the body, due to which microbes will begin to leave the body. The more often a woman visits the toilet, the more pathogenic particles will be removed from her body. In addition to the pathogenic bacteria themselves, toxic compounds formed by them also leave the body along with urine. The latter are especially dangerous, as they lead to poisoning of many cells in the body.
On average, the duration of taking herbal medicines is determined by the attending physician. Usually this is about twenty days. Herbal medicine is also effective for preventive purposes, the use of which should also be under the supervision of the attending physician.
Thus, cystitis in nursing mothers can be overcome, you just need to follow all the recommendations and prescriptions of your doctor. Self-medication of cystitis while breastfeeding is dangerous for both the mother and her breastfed baby!
Remember this and avoid experimenting with your own health, as they often end badly.
The process of delivery creates certain conditions that provoke the development of cystitis. In addition, a woman’s body, weakened after childbirth, is an accessible target for various types of infections. Considering that the causative agents are pathogenic microflora, treatment of cystitis in hepatitis B is impossible without the use of antibacterial drugs.
To select adequate therapeutic measures, you will need a consultation with a urologist, a speculum examination by a gynecologist, and urine culture to identify microorganisms and their sensitivity.
When drawing up a treatment regimen for cystitis, doctors take into account the properties of the active components to be redistributed into breast milk to varying degrees. Most often, nursing women are prescribed penicillin antibiotics - Amoxicillin and its combination with clavulanic acid (Flemoclav Solutab, Augmentin).
The choice in favor of these medications during lactation is dictated by their low toxicity and low concentration in breast milk. Consumption does not exclude feeding, but requires careful monitoring of the child’s condition.
Cephalosporins are used with extreme caution in women who are breastfeeding for the treatment of cystitis. Some of the latest generation drugs lack relevant clinical studies. A relatively safe remedy from this group is Cedex. They can treat cystitis during breastfeeding.
Fosfomycin, better known by its trade name Monural. Realizes its wide spectrum of antibacterial action in a minimally short course. Breastfeeding will have to be interrupted for only 1 day.
Severe forms of inflammation of the bladder with an increase in temperature to febrile values, and blood in the urine require the use of potent medications from the fluoroquinol group (Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Ofloxacin). Active treatment of cystitis during lactation will require temporary abstinence from breastfeeding. The same precaution applies to the prescription of nitrofurans, nitroimidazoles, and lincosamides.
Treatment during breastfeeding with pharmacological products that have antibacterial potential destroys beneficial intestinal microflora. To minimize the negative effects of synthetic substances, probiotics Bifiform, Baktisubtil, Linex are introduced into the medication course.
Since the disease is caused by an infection, antibiotics are required. A nursing woman should not take many medications that are most often used to treat cystitis. Therefore, the doctor must choose the drug. After analyzing the urine and identifying the causative agent of the disease, the specialist prescribes medication. Most often, these are antibiotics of the penicillin group. They penetrate into milk least of all and do not harm the baby. The most common are “Amoxicillin”, “Amoxiclav”, “Augmentin”.
Antibiotics from the cephalosporin group are also prescribed: Cefazolin, Cefuroxin or Zinnat. If chlamydia or mycoplasma are found in the urine, you need to take stronger drugs: Nitrofuran, Monural, Erythromycin or Ofloxacin. But in this case, breastfeeding will have to be suspended. Sulfonamides, for example Bactrim, and drugs of the quinolone group, for example Nitroxoline, are completely prohibited during lactation.
It is very important to take antibiotics in the correct dosage for the required number of days. Treatment should not be stopped when symptoms have disappeared. The infection may return. Therefore, the duration of taking antibiotics should be at least 5 days.
How to determine cystitis
Cystitis occupies one of the leading places in the list of urological diseases.
It is an inflammatory process localized in the wall of the bladder. The problem is typical for women. Women during menopause, pregnancy, and lactation are at particular risk. You can suspect cystitis based on the characteristic symptoms:
- discomfort (stinging, burning) when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- general malaise (fever, weakness, nausea);
- change in urinary sediment (turbidity, admixture of blood, protein “flakes”).
If such signs appear, you should consult a doctor. Additional laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. These include a general blood and urine test, a urine test according to Nechiporenko, bacteriological culture of urine, ultrasound of the urinary tract, and examination by a gynecologist.
Antibacterial therapy
Cystitis, and especially its complicated form, requires treatment with antibiotics. A young mother is prescribed drugs only after identifying the causative agent of the disease and determining its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents.
For bacteriological culture of urine, an average morning portion is required, collected in a sterile container immediately after toileting the external genitalia and inserting a tampon into the vagina to prevent natural secretions from entering the urine.
To treat cystitis in a nursing mother, antibiotics from the penicillin or cephalosporin group can be used. In this case, it is not necessary to interrupt feeding. Antibacterial agents from the nitrofuran group, for example, such a popular antimicrobial drug as monural, and from the macrolide group are prescribed when chlamydia and mycoplasmas are detected in the urine. This treatment requires a break from breastfeeding and pumping milk.
Attention! All antibacterial drugs must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
If there are no results of a urine test for the sensitivity of the causative agent to antibiotics, then the urologist usually prescribes penicillin or cephalosporin drugs, for example, cephalexin or cefazolin. This is due to the fact that the most common causative agent of cystitis is Escherichia coli. Among the most effective medications are amoxicillin and amoxiclav. Take them strictly according to instructions for five days. It is possible to prescribe drugs from the group of quinolones - ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin.
For uncomplicated acute cystitis, doctors often prescribe monural at a dosage of three grams per day after urinating at night. This is the antibiotic fosfomycin trometamol from the nitrofuran group, which is taken once, but this is not enough for postpartum cystitis. Treatment of cystitis after childbirth with monural requires interruption of breastfeeding.
Cystitis is considered completely cured only after normalization of blood and urine tests. Premature discontinuation of medications can lead to the development of a chronic process and the acquisition of antibiotic resistance by bacteria.
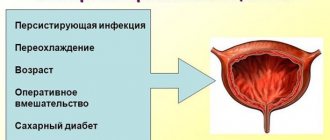
Why does cystitis develop during lactation?
It is believed that 25% of women have cystitis or bacteriuria after childbirth. For some, these conditions have accompanied them since the time they were pregnant. Pregnancy and childbirth themselves suppress the immune response. There are also mechanical reasons:
- impaired circulation of the bladder due to compression by the fetal head;
- excretion of urine through a catheter;
- applying cold to the abdomen in the postpartum period.
Also, after delivery, the vaginal flora changes. The anatomical proximity of the urethra facilitates the penetration of harmful microorganisms from the genital tract into the urinary tract. With the onset of lactation, the mother's body depletes its defenses. Now the first priority is to produce milk for the newborn. The mother gives the child antibodies against viruses and bacteria, depleting her own resource.
Against the background of emerging immunosuppression, infections affect the female genitourinary system. And even the usual flora (E. coli) becomes pathogenic for the body.
What medications to treat cystitis while breastfeeding?
The choice of antibiotics is limited to Amoxicillin, cephalosporins, macrolides and nitrofurans.
- Amoxicillin , according to the American Food and Drug Administration, can pass into breast milk. However, it does not harm the child. This antibiotic is used, if necessary, in pediatrics and neonatology from the first days of a child’s life. As a side effect, the baby may experience loose stools. However, when you stop taking amoxicillin, the diarrhea will also go away. It is necessary to interrupt therapy and replace the antibiotic if the child develops a rash. It must be said that the ideal solution for the period of breastfeeding is to replace milk with formula. At the same time, the woman must pump. However, in practice, pumping and weaning your baby for at least a week will result in decreased milk production. In addition, not every baby will be able to exchange the breast for a bottle, especially if he does not suck on the pacifier. Therefore, if the baby has no adverse reactions, it is possible to combine breastfeeding and amoxicillin, provided that the child is on mixed feeding or is already receiving complementary foods.
- Cephalosporins may also be used during breastfeeding. How to treat: the duration of therapy does not exceed 7 days. The drugs can be taken in the form of tablets or injections. How to treat: for hepatitis B, 2nd and 3rd generation medications are used: cefuroxime axetil, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone.
- The drug Monural can be taken once only according to strict doctor's instructions. Since fosfomycin is prohibited for use in children under 5 years of age, it is prohibited to feed a child with such milk for two days until the substance leaves the mother’s blood.
Reasons for the development of cystitis in nursing mothers
The source of the disease is opportunistic bacteria. They are constantly present in a woman’s body, but when the immune system is weakened, which is observed in the postpartum period, they are activated. The development of cystitis can be triggered by:
- Escherichia coli;
- Enterobacteriaceae;
- Saprophytic staphylococcus.
Much less often, chlamydia, mycoplasma, and various fungi become causative agents of the disease.
The urethra becomes the road to the lining of the bladder for bacteria.
In medicine, there is such a thing as “postpartum cystitis.” The reasons for its occurrence can be various factors.
- Poor circulation of the bladder due to labor. While passing through the birth canal, the child presses the bladder very tightly against the pelvic bones, which provokes this disorder.
- The inflammatory process can be caused by the application of cold ice after childbirth, as well as the installation of a catheter.
- After childbirth, the immune system is very weakened, which becomes a favorable environment for the development of bacteria.
Cystitis during breastfeeding can also be provoked by traditional reasons characteristic of this disease, first of all, poor personal hygiene, hypothermia, incompletely cured gynecological diseases, wearing tight clothing and much more.
Add to this the unreasonable use of a diet after childbirth, when you are worried about the baby, eat only rice and buckwheat, exclude all fruits and are afraid to expand your diet. The body is weakening.
Causes of problems after childbirth
- The reasons for the inflammatory process are complex. During pregnancy, the immune system weakens. This occurs both from the increased consumption of nutrients and from the action of hormones. Childbirth does not improve the situation; after it, the body returns to normal gradually, and most often a new special condition arises - lactation. You need to pay enough attention to yourself, avoid hypothermia, and eat right. Often, a young mother does not have the opportunity to notice and recognize the symptoms of cystitis in time due to general discomfort in her own body.
- In late pregnancy, the enlarged uterus and fetus put pressure on the surrounding internal organs. Frequent urination at this time occurs for natural reasons. After childbirth, the pressure suddenly stops and a false sensation of an empty bladder appears; there is no urge to empty it, but the need remains. Stagnation of urine provokes inflammation; you should get rid of it in time, remembering that you need to visit the toilet.
- During childbirth, various injuries are possible. As the baby's head moves toward the exit, it can further damage the excretory organs. The microflora of the vagina and urethra is completely disrupted during the treatment of ruptures and suturing.
- During childbirth, other manipulations are performed that increase the likelihood of cystitis. Typically, a catheter is used to hygienically dispose of urine on the chair. It slightly injures the urethra, and the penetration of infection is facilitated.
- The development of cystitis can also be provoked by the consequences of long-term hypothermia from ice on the abdomen, which is placed to contract the uterus.
If you have ever suffered from cystitis, or at the time of childbirth there was a hidden inflammatory process in the body, an exacerbation and resumption of the disease is very likely. Conditionally pathogenic microflora, which normally does not create any problems, can become more active against the background of decreased immunity.
First symptoms: what to look for
Cystitis has its own specific characteristics. It can be identified by the following symptoms:
- frequent urination with severe pain;
- feeling after urination that the bladder is not completely empty;
- general weakness of the body;
- elevated temperature;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- change in urine color, it becomes cloudy.
Simple cystitis does not cause an increase in temperature. The following symptoms may also occur:
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
At the initial stage, cystitis can be cured in a few days. And serious medications may not be required. Therefore, in order for treatment of cystitis during breastfeeding to be safer for the baby and mother, it must be started on time. To do this, a woman must know what symptoms accompany the disease:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning in the urinary canal;
- bladder pain;
- small volume of urine, it is cloudy and dark;
- possible fever and general malaise.
Manifestations of cystitis:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- urine comes out in small portions, the process is painful;
- pain, pain in the lower abdomen, especially when the bladder is full;
- the temperature may rise;
- feeling of weakness, lethargy.
Weakness, lethargy and frequent urges indicate the presence of cystitis.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms, you should consult a doctor. The doctor will order an examination:
- Clinical blood test. With cystitis, the number of leukocytes is increased, the ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is increased.
- General urine analysis. Inflammation is characterized by leukocytes from 10 units, red blood cells, protein appears in the urine, and bacteria can be detected.
- To identify the pathogen, urine culture is performed. As a result of the study, in addition to the pathogenic microorganism, its sensitivity to drugs is determined.
- Ultrasonography. With inflammation, the walls of the bladder thicken.
Cystitis must be treated, otherwise the infection will rise higher. The inflammatory process can become chronic and lead to kidney failure. With adequate therapy, the disease goes away in 3–5 days.
Nature and forms of the disease
Characterized by excessive growth of pathogenic bacteria on the mucous membrane of the bladder, the disease develops much more often in the fair sex and has more pronounced dynamics than in men. That is why the diagnosis and treatment of cystitis in women should be treated with the utmost care, analyzing the possible causes and nature of the disease.
The body of a healthy woman is able to independently control and restrain the growth of pathogenic flora. With a decrease in protective properties, the body loses the ability to independently regulate the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, and they begin to literally attack the walls of the bladder.
Two types of disease progression should be distinguished:
Spicy
Acute cystitis appears suddenly and painfully, however, with adequate treatment it does not recur. Uncomplicated cystitis appears only on the walls of the bladder, without affecting the urinary canal and urethra.
Diagnosis of acute and chronic cystitis
Chronic
Transformation of acute cystitis into chronic is observed with incorrect choice of therapy. As a result, the patient experiences relapses from time to time, and outbreaks of the disease can have varying intensity and vague symptoms.
ethnoscience
Cystitis during breastfeeding is best treated using traditional medicine recipes; this is optimal for both mother and child.
- Red brick is heated in the oven or directly on the fire, placed in a bucket and a couple of drops of birch tar are dripped onto the brick. Then they sit on the bucket, wrap themselves in a blanket and sit there until the warmth from the brick is felt. Then they go to bed. Three or four such procedures are required.
- Pour half a glass of washed millet with three glasses of water overnight and carefully filter. Drink half a glass of the infusion three times a day.
- Medicinal plants used to treat cystitis during hepatitis B are the following:
- cowberry,
- St. John's wort,
- bearberry,
- heather,
- yarrow,
- mountaineer,
- chamomile,
- corn silk.
There are herbal preparations that have diuretic, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The collection is prepared from two or three of the above medicinal herbs. The course of treatment is a month.
lechim-pochki.ru
Methods for diagnosing bladder inflammation
The basis for the diagnosis of cystitis is clinical examination. Patients undergo a general urine and blood test. A general blood test will show signs of nonspecific inflammation. Immature forms of neutrophils will be detected in the blood, and leukocytes will be increased. Clinical urine tests will show a high level of leukocytes, red blood cells and bacteria content in the material.
In addition to the tests, a general examination of the patient is carried out. When palpated, the patient feels pain in the lower abdomen. Additionally, an ultrasound of the bladder may be performed.
Features of disease diagnosis
Treatment of cystitis during lactation is a process preceded by a thorough examination of the woman. It should be carried out by the treating gynecologist and urologist. Even if the diagnosis is confirmed, this pathology does not require hospital treatment.
If a young mother who continues breastfeeding consults a doctor, then the inflammatory process is eliminated within 3 days, preventing it from spreading further.
After acute symptoms are relieved, therapy continues for at least 3 weeks.
There are no difficulties in diagnosing cystitis during breastfeeding. The examination includes:
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood. Necessary to determine the pathogen, as well as confirm the presence of an inflammatory process inside the bladder.
- Ultrasound. The doctor sees thickening of the walls of the organ and structural features.
- Cystoscopy is an examination of the bladder and urethra using special equipment.
These studies are enough to make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment for cystitis.
Prevention of cystitis
Like many other diseases, cystitis can be avoided by following preventive measures. If the disease has already bothered you, these tips will help you protect yourself from relapse after recovery.
- Don't get too cold. Keep your feet and lower abdomen warm. You shouldn't wrap yourself up when it's warm outside. Dress appropriately for the weather.
- Take care of your health. Foci of infection in the body contribute to the development of diseases. Dental caries and chronic tonsillitis do not appear as long as the immune system is strong. But its temporary decrease allows the infection to get out and manifest itself at any “point” of the body. For this reason, cystitis or infectious mastitis may occur.
- Cure sexually transmitted diseases. Chronic genital infections can cause inflammatory processes in nearby organs and tissues. If it was not possible to cure chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, or gonorrhea during pregnancy, the time to do it is now.
- Maintain good hygiene. Sanitary pads should be replaced at least every two hours. After defecation, it is advisable to wash yourself or use alcohol-free baby wipes.
- Avoid constipation. They provoke stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, causing hemorrhoids and cystitis. Eat foods rich in fiber, and if necessary, use safe remedies for constipation (Duphalac, Forlax).
- Watch your diet. Prevention of cystitis - following the correct diet of a nursing mother. Avoid sour, salty, spicy, pickled, fried and alcoholic foods.
These recommendations will allow you to avoid not only cystitis, but also other health problems.
Treatment of cystitis during lactation is carried out with absolutely safe means that are fully compatible with breastfeeding. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid of therapy. The sooner you see a doctor, the more effective the treatment will be. And the disease will not bother you for a long time.
Benefits of instillation during lactation and pregnancy
The method of local treatment of the bladder mucosa is instillation. The procedure involves the introduction of antiseptic solutions into the organ through the urethra. The advantage is a local therapeutic effect without a systemic effect.
In case of acute inflammatory process, instillations are contraindicated.
For pregnant and lactating women with chronic cystitis, this is an alternative to frequent use of antibiotics. But the procedure requires special skill. Therefore, it is carried out only by a urologist after a thorough examination and cystoscopy.
Treatment with herbal remedies
Synthetic tablets for cystitis are not a panacea. Pharmacological products based on plant extracts are an ideal adjunct to traditional medicine. A natural cure for cystitis during breastfeeding will reduce the severity of symptomatic manifestations due to its anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and diuretic effects. The following phytocomplexes have received good recommendations from nursing women:
- Urolesan - a natural antispasmodic enhances blood supply to the kidneys, liver and pelvic organs; increases the release of urea during cystitis, the removal of small stones;
- Canephron - normalizes the tone of the urinary tract, prevents the growth of pathogenic microflora, reduces the amount of protein excreted in the urine;
- Cyston - the antimicrobial activity of the active ingredients reduces irritation of the bladder mucosa, relieves the symptoms of painful urination in nursing women.
Herbal medicine will help cure cystitis during breastfeeding if it does not cause allergic reactions on the part of the baby. At the slightest side effects, breastfeeding is temporarily suspended.
Adapted formulas, similar in composition to mother's milk, will help the child endure weaning without harm to the body. To support the lactation period and painlessly return to the process of breastfeeding, there are effective ways - expressing with a breast pump, daily kneading of the breasts. If the husband doesn’t mind, some functions can be assigned to him.
Features of treatment during breastfeeding
Treatment of cystitis in nursing women requires special attention. Therapy methods can only be prescribed by a doctor. This is due to the fact that many drugs enter the child’s body through milk. Medicines can cause allergic reactions, disorders of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, loose stools in an infant during breastfeeding, and disturbances in the development of the child.
It is important that the medicine for cystitis during breastfeeding is not selected independently; self-medication for such a pathology is unacceptable. Inflammation is most often treated with antibiotics. There are a number of medications that women can take during breastfeeding.
Drug treatment
It is most difficult to choose antibiotics for cystitis while breastfeeding; many of the modern drugs pass into breast milk, which is unacceptable. Read more about antibiotics during breastfeeding.
- Most often, drugs from the penicillin series (Cefazolin, Cephalexin) are prescribed, which affect the source of infection, but do not pass into milk.
- Very often, treatment of cystitis during breastfeeding begins with the prescription of the drug Amoxiclav. This is a modern antibiotic that practically does not penetrate into breast milk, so it is often prescribed to nursing mothers when cystitis is detected. This drug is compatible with breastfeeding.
- There are a number of drugs that are not compatible with breastfeeding: antibiotics from the sulfonamide groups (Co-trimoxazole, Bactrim), nitrofurates (Monural) and macrolides (Erythromycin). Breastfeeding is also unacceptable when prescribing Nitroxoline and Nevigramon.
Treatment of cystitis is impossible without taking antibacterial agents.
Important! The course of drugs should consist of 3-5 days.
It is not safe for your health to stop taking it only if your doctor recommends it. Because if treatment is abruptly interrupted, the disease can progress to the chronic stage.
Cystitis is considered cured if urine and blood tests return to normal.
Antibiotics
Monural is approved for the treatment of cystitis for both pregnant and lactating mothers.
The safest drug that can be taken by both pregnant and lactating women is Monural. Treatment with this drug is approved in different countries of the world.
The medicine enters the child's body in small quantities and is immediately blocked in the intestines by calcium, which is contained in breast milk.
Cystitis during breastfeeding is effectively cured with Zinnat. It contains components that are fully compatible with breastfeeding. The drug passes into mother's milk in small quantities. It does not cause adverse reactions in the child, so it is ideal for newborns.
Treatment of cystitis during breastfeeding women is often carried out using the antibiotic Amoxiclav. The drug practically does not penetrate into mother's milk, and, therefore, it is compatible with breastfeeding. The components of the drug quickly rid the body of bacteria.
Taking all of the above antibiotics does not require stopping breastfeeding.
Compatibility of drugs for the treatment of cystitis during breastfeeding
Drug treatment of cystitis in nursing women can be supplemented by taking various herbal complexes that do not have a harmful effect on the body of mother and child.
How and with what to treat the disease during breastfeeding?
Treatment of cystitis is aimed at combating the causative agents of the disease (systemic therapy) and alleviating the condition (symptomatic treatment).
Medications
If inflammation of the mucous membranes of the bladder is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics will be needed for treatment. Many women are concerned about the need to take such serious medications during lactation. Fears are unfounded: new generation medications are compatible with breastfeeding. Antibiotics of certain groups effectively cope with infection and do not harm the health of the newborn.
Antibiotic therapy acceptable for hepatitis B
During lactation, the following antibacterial drugs are prescribed:
- cephalosporins (Cefalexin, Cefazolin, Zinnat, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime);
- penicillins (Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Amoxicillin);
- quinolines (Ofloxacin);
- phosphonic acid (Monural).
The listed medications are compatible with breastfeeding and do not require interruption of lactation. If treatment requires taking medications based on nitrofurans (Furadonin, Furagin, Nitrofurantoin), then lactation will have to be suspended for the duration of therapy.
Important! Do not prescribe or take medications yourself - the doctor is guided by the test results and the general condition of the patient.
The selection of drugs always occurs individually. You should also strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen.
Candles
Preparations based on NVPS are compatible with breastfeeding , since the active substance penetrates into the blood and breast milk in a small concentration (0.7%).
Anal suppositories Diclovit and OKI are good at reducing temperature and have an analgesic effect.
Symptomatic therapy
Phytocomplexes
To eliminate the discomfort accompanying acute cystitis, urinary and anti-inflammatory medications that are compatible with breastfeeding are used.
Plant-based preparations have proven themselves well:
- Canephron.
- Phytolysin.
- Cyston.
Canephron and Phytolysin should not be taken at elevated temperatures.
Traditional methods
Attention! Some “experts” advise resorting to irrigation of the urinary tract with medicinal decoctions. Please note that such manipulations are contraindicated in case of inflammation. Bladder instillations are performed under aseptic hospital conditions after cystoscopy. It is dangerous to use such treatment methods at home.
At home, you can give enemas with a warm decoction of chamomile and calendula, which is used to irrigate the rectum.
If you need to relieve pain and cramps, you can apply a warm heating pad to the lower abdomen. Please note that this method can be used a month after delivery, otherwise there is a high risk of uterine bleeding .
Herbal and natural remedies
- cranberries (fresh berries, juices and fruit drinks perfectly relieve inflammation, have diuretic and antibacterial properties);
- alkaline mineral water (Kataria, Tsimalon) – changes the acid-base balance of urine, due to which unpleasant sensations are mitigated;
- herbal infusions (based on horsetail, chamomile, calamus, plantain);
- infusion of dill seeds;
- decoction of flax seeds;
- corn silk tea;
- infusion of birch buds;
- teas from medicinal mixtures (with chamomile, agrimony and bearberry).
Diet for cystitis
How can you cope with cystitis using diet? First, we donate urine (urine). Diet No. 6 according to Pevzner will help with urine acidification. When alkalizing, table No. 14 is recommended. If you have kidney disease, you should turn to diet No. 7. The general principles of diet therapy include refusal:
- From alcohol, strong black tea and coffee.
- From sweets and sugar.
- From sour vegetable and fruit dishes (with the exception of cranberries).
- From salinities (limiting salt is a must!).
- From products containing dyes and flavors.
- From vegetables rich in essential compounds (garlic and onions, radishes and basil, parsley and celery);
- From seasonings, sauces, ketchups, mayonnaise.
- From marinades, pickled vegetables and pickles.
- From concentrated broths based on fish, meat or mushrooms.
To “flush” your kidneys and bladder, you should drink plenty of fluids. Especially good are lingonberry and cranberry fruit drinks (juices), as well as birch sap.
You can eat stewed and boiled vegetables, but without tomatoes, fermented milk products (not sour cottage cheese, yoghurts, curdled milk, cottage cheese casseroles). It is allowed to eat boiled eggs (no more than 1 piece per day). Compotes, jelly and jellies made from sweet fruits, fresh fruits. Boiled lean fish and dietary meat casseroles, porridge and pasta are allowed.
Many, especially young mothers, having read various forums and advice, try to get rid of the disease on their own with the help of diets, taking on faith the reviews of “experienced” nursing mothers. To achieve maximum effect, the diet can only be used as a complement to drug therapy.
What can and cannot be consumed if you have cystitis? Eliminate salty, smoked, fried, fatty foods, as well as seafood and alcohol, eat gentle steamed food from vegetables and meat. This menu will not harm small tummies and will help cope with inflammation.
In addition, the nursing diet can be supplemented with cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, rose hip decoctions, raspberry and black currant jams - berries rich in vitamin C. However, for safety reasons, it is worth paying attention to seasonal vegetables and fruits.
As for water balance, a nursing mother with cystitis should drink at least 2 liters of pure still water per day. Drink not sweet drinks - coffee, tea, soda, compotes, but water. The fact is that many bacteria feed on the sweet environment, so drinking drinks will promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
You can drink fruit drinks made from fresh berries - lingonberries, cranberries, black currants, which promote frequent urination, and this, in turn, will help remove pathogenic flora from the body as much as possible and thereby relieve inflammation.
How to treat cystitis with folk remedies
If cystitis is not advanced, then the use of folk remedies gives a very good effect and does not require stopping breastfeeding. Juices and fruit drinks made from cranberries and blueberries work very well. These berries have a pronounced antibacterial effect. But you need to carefully monitor your child, because although not often, these berries can cause allergies.
Traditional medicine advises drinking decoctions of lingonberry leaves, bearberry and rose hips for cystitis. And they actually help well with uncomplicated illness. In addition, you need to switch to a salt-free diet and drink a sufficient amount of alkaline mineral water without carbon.
Drinking regime
Compliance with the drinking regime helps speed up the treatment of cystitis during breastfeeding. It is recommended to increase your daily fluid intake. If a large amount of clean water enters the body, urination becomes more frequent, and, therefore, bacteria are removed from the bladder faster.
During lactation, a woman is recommended to follow certain rules:
- Avoid tea and coffee while breastfeeding and give preference to clean water.
- The daily volume of liquid should be at least 2 liters.
- It is not recommended to drink sweet drinks; sugar creates favorable conditions for the development of negative microflora.
It is best to drink fruit drinks made from natural berries during lactation.
Diet therapy
At the first symptoms of cystitis, it is necessary to follow a salt-free diet, since salt will only increase inflammation and swelling of the bladder mucosa. In addition, it is recommended to limit smoked, spicy, fatty foods and dishes made from them. Drinking alcohol is prohibited. It is useful to include plant foods in your diet that have a beneficial effect on the urinary system: carrots, greens, celery, cranberries, watermelons, lingonberries, asparagus.
You should drink plenty of fluids to actively flush out the infection from the bladder and remove toxins. The recommended amount is no less than a liter, and if possible two or more. You should not drink strong tea and coffee, as well as drinks with flavors, spices and herbs, as they irritate the mucous membrane of the bladder and worsen the taste of breast milk. You should not drink sweet liquids, as sugar is a favorable environment for pathogens.
It is recommended to use rosehip decoction, cranberry juice and lingonberry juice for the treatment of cystitis during lactation. They have diuretic and uroseptic effects, as well as a pleasant taste.
To prepare cranberry juice at home you will need one hundred grams of cranberries, one hundred grams of sugar and half a liter of water. First, the berries are sorted, washed and excess liquid is allowed to drain. Then they are placed in a cup, kneaded, placed in cheesecloth and the juice is squeezed out. Place the berry pulp in a saucepan, add water and bring to a boil. Strain and add sugar to the hot broth. Stir until completely dissolved, pour in the squeezed cranberry juice and mix again. Store this fruit drink in the refrigerator and warm it up slightly before use.
Additional treatment recommendations
When treating cystitis, it is important to follow the prescribed dosage regimen and dosage. Self-cancellation of therapy after the unpleasant symptoms have passed is fraught with chronicity of the process. As a result, the body will not receive the full course of antibiotics and will become a reservoir for the proliferation of resistant species of bacteria. To consolidate the antimicrobial effect, drugs are prescribed to sanitize urine. They should be taken over a long course - from 1 to 3 months. You can't interrupt him for no reason.
You can improve the functional ability of the bladder with the help of special gymnastics at home, Kegel exercises. Regular measures play an important role: physical rest in the first days, a gentle diet, psycho-emotional comfort.
Symptomatic treatment
How else to treat cystitis during breastfeeding, besides antibacterial agents? Symptomatic treatment includes taking herbal preparations: phytolysin or canephron. They contain only natural ingredients that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects, relieve spasms, improve kidney function, have a diuretic effect and prevent the formation of stones. The course of taking these drugs is long and lasts a month.
In order to speed up the treatment process a little, you should take drugs that alkalize the urine. These include ordinary non-carbonated mineral water, table salt solution, as well as calcium or magnesium citrate, which are mineral supplements. They neutralize acid in the urine and prevent the growth of bacteria, soothe itching, burning and other unpleasant and painful sensations that occur during urination.
In addition, mineral water is a source of microelements necessary for the body: iron, potassium, magnesium. It is always better to take it without gas, so as not to irritate the intestines and cause bloating.
Important! If the symptoms of postpartum cystitis do not decrease after two days from the start of treatment, you should immediately seek help from a specialist.
If the disease is not treated, the pathological process will penetrate through the ureters into the kidney. In this case, the nature of the treatment changes radically and the woman will most likely have to stop breastfeeding to prevent strong drugs from entering the child’s body.
Almost all painkillers pass into breast milk and are dangerous for babies. Nursing mothers are recommended to use vaginal suppositories with anesthetics. Antispasmodics are prescribed internally - no-shpu, papaverine. They relieve spasms and have an analgesic effect.
Preventive measures
The development of the disease or the occurrence of relapses can be prevented. To do this, follow the following rules of prevention:
- You can't get too cold. The lower abdomen and legs are kept warm. If it's not cold outside, you shouldn't bundle up too much either. Dress according to the weather outside the window.
- It is advisable to cure sexually transmitted pathologies, as well as infectious foci.
- Adjust your diet to prevent constipation.
- Perform the necessary set of hygiene procedures daily. After visiting the toilet, they wash themselves.
- Wear underwear made from natural materials. It should absorb sweat so that diaper rash and irritation do not appear in intimate places. Underwear should not be tight.
If you follow the necessary preventive measures, exacerbation of cystitis is avoided, which is important for nursing women. If the pathology has made itself felt, a visit to the doctor cannot be delayed. Be healthy!
Sources
- https://uroki4mam.ru/tsistit-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii
- https://UroMir.ru/vospalenie-mochevogo-puzyrya/terapiya/chem-lechit-cistit-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://ipupsik.com/zhenskoe-zdorove/zhenskie-bolezni/lechenie-tsistita-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://MyCistit.ru/lechenie/pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii
- https://CistitStop.ru/pervaya-pomoshch-pri-cistite/cistit-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
- https://krasivayagrud.ru/grudnoe-vskarmlivanie/chem-lechit-tsistit-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
[collapse]
Topical products
Everyone knows that during breastfeeding with mother's milk, the child receives both beneficial and harmful substances that could end up in the woman's body from medications. No mother would want to harm her child, so many women postpone treatment for cystitis until later. When breastfeeding, the peculiarities of therapy are that many drugs are contraindicated.
- be sure to take medications: antibiotics, herbal extracts;
- drink more fluids, especially those with a diuretic effect, to flush out bacteria from the bladder;
- maintain intimate hygiene, take a shower and change your underwear daily;
- it is necessary not to stop treatment after the pain disappears, since in a weakened body inflammation can occur again.
There are many recipes for relieving pain and inflammation in the bladder. But even folk remedies can harm a child. Therefore, they can only be used after consulting a doctor. For example, sage, often recommended to relieve inflammation, reduces lactation. The following folk methods for treating cystitis are recommended:
- decoctions of chamomile, yarrow, echinacea, and corn silk are safe for children;
- the most effective remedies for cystitis are lingonberries and cranberries; it is best to drink fruit drinks made from these berries, but you can brew them as tea;
- pour two thirds of a glass of pure millet into 3 glasses of water and leave for 10-12 hours, take 100 g of infusion 3 times a day;
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves has a diuretic effect and helps with inflammation.
When breastfeeding, taking medications is possible only under the supervision of a doctor. Treatment of cystitis requires medical supervision, since many medications are contraindicated during lactation.
To treat fungal or viral cystitis in a nursing mother, the following drugs are used:
- Helping to strengthen the immune system (Genferon, Viferon).
- Destroying the causative agent of the disease (Ganciclovir or Acyclovir).
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are used for cystitis caused by bacteria. Only a specialist chooses a drug for the treatment of cystitis.
Monural has proven itself well for cystitis. The effectiveness of this drug and safety for infant health explain its popularity among other drugs in many countries around the world. The chemical composition of the drug penetrates into mother's milk in minimal quantities, and its negative effects are neutralized by calcium contained in the milk. Monural costs from 350 to 400 rubles.
Another antibiotic can be safely used during lactation - Zinnat. The drug has proven itself in the treatment of various infections, and is prescribed for the treatment of even newborn children. Zinnat costs, on average, about 300 rubles.
Often, to treat inflammation of the urinary tract, nursing mothers are prescribed Amoxiclav, which helps to quickly get rid of bacteria and germs. The medicine is available in various forms. The price varies from 240 to 450 rubles. To prevent relapse, the drug should be used for another 3-5 days after symptoms have resolved.
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed after the causative agent of the disease has been identified. Most often, doctors prescribe drugs from the penicillin series, less often - quinolones and some nitrofurans. A nursing mother is not allowed to independently select an antibacterial agent without conducting the necessary tests and consulting a doctor.
Such remedies as No-shpa, Drotaverine or Papaverine will help a nursing mother relieve the pain that accompanies cystitis. In order not to harm the baby’s health, it is not recommended to take painkillers for more than two days.
After childbirth, cystitis in a nursing mother sometimes develops due to impaired blood flow in the area of the reproductive organs, which makes it difficult for the active medicinal components to reach the site of inflammation. In such a situation, topical agents are added to the treatment of cystitis during feeding:
- Chlorhexidine - available in the form of a solution for douching and rinsing the bladder, suppositories for vaginal administration; prevents the spread of infection that caused the development of cystitis to the genitals;
- Miramistin – has a pronounced bactericidal effect against many strains of viruses and fungi that are multiresistant to antibiotics;
- Furacilin - treatment for breastfeeding cystitis, an old, but with impressive experience of use, remedy is still relevant; the solution is used for sitz baths; the ointment is inserted into the vagina using a medical tampon or applicator.
The targeted action of bacteriostatic agents does not deprive mothers of the opportunity to breastfeed while fighting cystitis.
One of the local therapy options that allows you to treat cystitis during breastfeeding without risk to the baby is instillation. Medicines are injected directly into the bladder with a large disposable syringe or catheter. After which they are held for 2 – 3 hours. During this time, they manage to maximize their anti-inflammatory effect.
Mothers can be safely treated in this way without stopping breastfeeding. When installed, synthetic components have a local effect on pathogenic microflora, excluding the impact on the biological system as a whole. This characteristic feature allows the use of drugs in very high concentrations, against which infectious agents of cystitis are powerless.
Uncomplicated cystitis in a nursing mother can be treated with folk remedies at home. But with a small caveat: “grandmother’s methods” should not be perceived as independent therapy.
- Place crushed St. John's wort herb (5 g) and 200 ml of boiled chilled water in a small saucepan and close tightly. Heat in any type of water bath for about 20 minutes, filter the broth. Dilute the resulting volume with boiled water to 200 ml. Take 90 ml 20 minutes before meals 3 times a day. In the same way, a medicinal drink from lingonberry and bearberry leaves is prepared and used.
- Mix in equal proportions (1 tablespoon each) cinquefoil rhizomes, plantain leaves and horsetail grass. Place the mixture in a thermos, add 600 ml of boiled water, and leave overnight. In the morning, strain the infusion, drink 100 ml three times a day before meals.
- Water extracts from chamomile, calendula, thyme, pine needles, and nettle are used for sitz baths. Based on body weight, one procedure will require 50–100 grams. vegetable raw materials. Brew the medicinal ingredients in the required amount of water, with the expectation that the liquid will cover the lower part of the female pelvis. After cooling to 37º, strain and pour into a wide container. The residence time in the medicinal decoction is 15 minutes. The procedure cannot be performed if postpartum discharge continues, the menstrual cycle continues, gynecological diseases or neoplasms are diagnosed.
All activities must be coordinated with the attending physician.
Acute cystitis during breastfeeding is often caused by various types of microorganisms: bacteria or fungi. Normally, a woman’s bladder and urethra always contain a certain amount of pathogenic microflora, which does not manifest itself in any way. However, if the immune system malfunctions, microorganisms multiply and inflammation occurs - cystitis. This is the main cause of a disease such as cystitis during lactation after childbirth in women.
Additional factors for the appearance of cystitis during lactation are:
- injuries to the vagina and perineum that occurred during childbirth;
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- stagnation of venous blood in the pelvic area as a result of physical inactivity of the nursing mother;
- hypothermia of the abdominal area, resulting from the application of cold to stop bleeding during childbirth;
- violations of the innervation of the perineum;
- poorly treated cystitis in early pregnancy in a woman.
Cystitis is primarily accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. Similar sensations quite often occur in women after childbirth at the beginning of breastfeeding, and are not associated with any pathology. However, cystitis, in addition to pain, is accompanied by frequent urination, hyperthermia, and deterioration in overall health.