The adrenal glands are paired organs whose main task is to produce hormones in the quantities a person needs. For little-understood reasons, a malfunction occurs in and activity, resulting in the formation of a cavity in the tissue. Subsequently, it is filled with liquid contents and gradually increases in size. This neoplasm is called an adrenal cyst.
Types of adrenal cysts
Modern science has identified several types of cystic formations that affect the adrenal glands. All of them have been studied in detail and have their own treatment methods:
- Epithelial cyst - a neoplasm consists predominantly of epithelial cells with the inclusion of segmental cells.
- Endothelial cyst - forms in places where the diameter of a vein or artery increases.
- A parasitic tumor is the result of damage to the body by echinococcus that has entered the human body.
- A pseudotumor is a blood clot that appears as a result of physical trauma. This neoplasm is not a tumor and cannot be classified as a cyst.
Classification
Adrenal cysts come in various sizes. A case was recorded when the formation reached 10 cm. It is the size of the cystic cavity that determines the symptoms and further treatment regimen.
Based on morphological characteristics, experts distinguish several types of cysts:
- true epithelial form. The cystic formation is lined with columnar epithelium of the adrenal cortex;
- true endothelial form. The cyst is formed against the background of expansion of the blood and lymph nodes;
- parasitic cyst. A cystic formation is formed due to damage to the adrenal glands by various infectious diseases;
- pseudocyst. It is a hemorrhage into healthy adrenal tissue or a malignant tumor of the pancreas. Such a cavity does not have an epithelial base and can exceed 10 cm in size.
Course of the disease
The cyst itself does not cause any pain to a person. But as it increases in size, it can block nearby blood vessels and compress nerve fibers. This leads to the patient’s blood pressure increasing and the blood supply to some pelvic organs being disrupted.
Constant pressure on the nerves causes spasmodic pain in a person's back and reduces his mobility. And when blood circulation in the adrenal gland itself is disrupted, areas of tissue death occur, which reduces the performance of the organ.
An adrenal cyst itself cannot cause serious pathological changes in the body. However, with concomitant diseases, such as hypertension, heart failure or disruption of the endocrine system, the patient's condition worsens sharply.
Symptoms
The tumor in the area of the adrenal glands varies in size, ranging from several millimeters. Small tumors in most cases do not cause inconvenience or discomfort. That is why the patient rarely goes to the doctor for diagnosis. As the capsule size increases, the following signs appear:
- There is an aching pain in the lower back. It may radiate to the side where the compaction is localized,
- Kidney activity is impaired. This symptom appears when the tumor increases to several centimeters in diameter and begins to put pressure on the internal organs,
- compression may be felt in the abdominal cavity,
- If kidney function deteriorates, problems with urination arise. It becomes rare and urine is difficult to excrete by the body,
- pressure rises. This happens if the cyst begins to put pressure on the renal artery,
- there is also an increased feeling of anxiety, increased stress,
- arrhythmia and taicardia join the symptoms,
- In some cases, the activity of the gastrointestinal tract will deteriorate.
Cyst in children
Adrenal cysts in children are diagnosed during the fetal development of the baby. During this period, it cannot influence the formation of the body, so the pregnant woman does not undergo any special treatment. After birth, the baby is again examined to assess the size and growth rate of the cyst. If the measurement results show that the tumor is not growing and does not pose a danger to the organ, then it is left without treatment until the situation changes for the worse or until the child grows up.
Sometimes it happens that the cyst of the left adrenal gland resolves, but remains on the right or vice versa. This is a normal situation, since this type of neoplasm most often affects only one organ - the left or right adrenal gland.
Causes and factors influencing the formation of cysts
There are two types of prerequisites for the formation of an adrenal cyst: genetic predisposition and the consequences of an acquired disease. The exact causes of this pathology have not yet been established due to the small number of clinical cases.
Most often, a cyst occurs during the embryonic development of the body, in particular, during gastrulation, if, as a result of a genetic failure during the laying of the germ layers, a fluid-filled cavity is formed.
Symptomatic manifestations
Symptoms of an adrenal cyst appear when the tumor reaches a significant size - approximately 3-5 cm in diameter. There are cases when the tumor reached 10 cm.
In this case, the first sign of a cyst is pain. It is localized on the right or left side opposite the kidney or reflected in the lower back.
Blood pressure also increases. This phenomenon is also accompanied by pain, but in the head.
The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is often disrupted, accompanied by abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Hormonal imbalance caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland leads to a variety of symptoms, for example, tachycardia, arrhythmia, and pain in the retrosternal space. For the same reason, the patient’s mental state changes
General information about the disease
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that are located on top of the kidneys. They are responsible for the production of hormones that regulate carbohydrate metabolism, increase blood pressure, are responsible for heart rate, and also affect the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
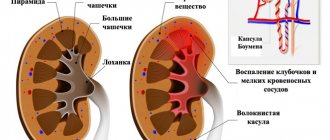
An adrenal cyst is a benign formation that looks like a cavity containing fluid.
It can be localized in any part of the organ and, as a rule, does not affect changes in the human hormonal system.
The size of the cyst depends on several factors: the location, the contents of which it consists and the age of its formation.
Diagnosis of pathology
Treatment of adrenal cysts begins with diagnosis. This process includes a whole range of laboratory and instrumental studies.
First of all, the patient donates blood for analysis. It determines the level of hormones in the body.
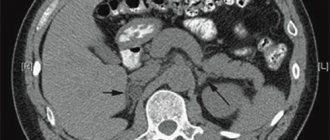
The presence of a cyst can be determined using ultrasound examination of the adrenal gland. However, the exact location of the tumor, its size and density are determined only with the help of magnetic resonance imaging.
The cyst can be found in unborn children. For this, ultrasound or computed tomography is used.
After birth, the baby is regularly examined for several months for growth and increase in education. Removal of an adrenal cyst is indicated only if it is rapidly increasing in size.
Why is a cyst dangerous?
What will happen to the patient if you do not get rid of the rapidly growing formation:
- With large capsule sizes, a state of adrenal insufficiency crisis occurs;
- Cutting pain in the stomach and intestines;
- Bloating;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Arrhythmia and tachycardia;
- High blood pressure;
- Meningitis;
- Psycho-emotional disorders;
- Endocrine disorders.
In addition, the cyst can fester, leak and even burst, which is dangerous due to severe internal bleeding and the development of peritonitis. The latter threatens human life.
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment of an adrenal cyst is not aimed at eliminating the tumor, but at suppressing its manifestations or consequences. If the tumor causes back pain, the patient is prescribed a painkiller that suits his body.
If the tumor is accompanied by inflammation, the patient takes a course of antibiotics.
With high blood pressure caused by a tumor, it is normalized with antihypertensive drugs.
Clinical picture
The capsule may be endothelial in nature or parasitic. In the first case, dilation of lymph nodes and blood vessels is diagnosed. The second form occurs due to the action of infection. Tests for adrenal cysts will help identify the pathogen. The parasite that causes the growth is often hydatid echinococcosis.
The epithelial form of the disease is characterized by the formation of a cortical layer on the surface of the organ. The cavity can be formed from the cells of the secretory areas of the kidney. An epithelial formation arises from the lymph nodes.
Pseudoformation may also occur on the surface of organic structures. The appearance of a cavity provokes hemorrhage from a neighboring vessel. In congenital pathology, a growth is formed in the embryo as a result of improper development of the fetal sections.
The disease can be provoked by any negative factor - maternal smoking, alcohol or drug abuse, autoimmune processes and gene reactions. Under the influence of negative factors, a growth develops on one of the kidney assistants.
The disease is asymptomatic and only with large growth of the capsule does pain in the lower back appear.
It is important to pay special attention to the following changes:
- the kidneys stop functioning perfectly;
- difficulty urinating;
- urine color changed;
- abdominal discomfort;
- lower back pain.
Surgical treatment
Surgery for an adrenal cyst is indicated only if it has degenerated into a malignant tumor. Surgery is also necessary if the size of the tumor begins to interfere with blood flow in the organs next to the kidneys.
How to treat an adrenal cyst surgically is decided by a specialist, based on the severity and form of the disease, as well as the general condition of the patient. In some cases, not the entire cyst is removed, but only dead tissue. But most often, of course, it is removed completely.
The operation can be performed laparoscopically or openly. Laparoscopy is performed using special instruments in the form of tubes with microcameras and instruments installed in them. The tubes are inserted through the skin directly to the adrenal gland. This type of operation is not accompanied by heavy bleeding, and after it the patient recovers faster, since there are no surgical sutures on his skin. However, only a highly qualified doctor with extensive experience can perform this type of procedure. This type of operation lasts no more than 1 hour and the patient can go home the next day, where he continues outpatient treatment.
A sample of the removed cyst must be sent for histological examination to exclude kidney cancer.
The open method of surgery involves removing the cyst through an incision made in the skin and soft tissue around the kidney. This method eliminates accidental damage to blood vessels or nerve fibers, but has a longer rehabilitation period. After the operation, the patient remains in the hospital for several days or even weeks under the constant supervision of doctors.
Conclusions about laparoscopic treatment of adrenal cysts
Thus, laparoscopic surgery of the adrenal glands has a number of advantages (reducing the invasiveness of the operation, pain and the number of complications, rapid rehabilitation, better cosmetic effect, higher quality of life, etc.) - partial adrenalectomy has taken its rightful place in the treatment of benign adrenal lesions , increasing the quality of life of patients in the postoperative period - to reduce the number of relapses it is necessary to more carefully examine and select patients in the preoperative period - during surgery it is necessary to use modern electrosurgical systems and additional methods of hemostasis.
Treatment with folk remedies
As is the case with drug treatment, herbal medicine cannot rid a person of a cyst, but it can relieve pain and relieve inflammation. This type of therapy should be carried out only with the permission of the attending physician. This will reduce the risk of the cyst growing and transforming from a benign tumor to a malignant one.
Symptoms and treatment of cysts in the adrenal glands have been known for a long time; accordingly, medicinal herbs were selected that can alleviate human suffering.
Decoctions are usually prepared from currants, lungwort, knotweed, geranium, nettle or horsetail. As a rule, these herbs are brewed with boiling water and infused either individually or as a collection, that is, 1 tablespoon of each herb. Water should be poured at the rate of 200 g per 1 tbsp. collection spoon.
Another very effective herbal mixture includes lungwort, string, viburnum flowers and currant leaves. The proportions for its preparation are the same - 1 tbsp. spoon for 200 g of boiling water. The product should be infused for no more than 30 minutes.
It is also recommended to drink more water, fruit drinks or eat watermelons and seaweed. This will force the kidneys to work better and, therefore, the adrenal glands will be supplied with fresh blood and microelements.
Inflammation of the adrenal gland is relieved with a decoction of licorice root, parsley and juniper.
Adrenal adenoma in men: symptoms, treatment, useful recommendations
The adrenal glands are paired organs located in the retroperitoneal cavity. These are endocrine glands that synthesize hormones that are involved in the normal course of many processes in the body. When the functionality of the adrenal glands is impaired, the functioning of other organs occurs. One of the most common problems of the adrenal glands in men is adenoma.
Adrenal adenoma is a benign formation with clear boundaries, filled with fluid, which can occur in the cortex (75% of cases) or medulla (25% of cases) of the organ. In men, these types of tumors develop 2-3 times less often than in women.
More often they are diagnosed after 35 years of age. For a long time, a man may not even be aware of the presence of an adenoma. The danger of formations is that in some cases they transform into malignant ones.
It is important to promptly identify adenomas and carry out all therapeutic prescriptions from the doctor.
Types and forms of education
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), adrenal adenoma has code D35.0. These formations can have different sizes and differ in functionality (synthesize or not synthesize hormones). But only adenomas weighing up to 100 g are considered benign. If they are larger, then they are classified as malignant and must be removed.
There are 3 main types of adrenal adenomas in men:
- Adrenocortical is the most common, in most cases it is benign. Externally, this node is in the form of a capsule.
- Pigmented is not often diagnosed; it measures no more than 2-3 cm. It has a dark purple hue due to the presence of dark cells in it. Common in people with Cushing's syndrome.
- Oncocytic consists of large cells, the structure is granular. The most rare adrenal adenoma.
Based on the nature of hormone synthesis, adenomas can be hormonal-producing or hormonally inactive. Based on the location of the tumor, adenomas of the cortex or medulla are distinguished.
Find out the instructions for using Melaxen tablets for disorders of melatonin synthesis in the body.
How and how to reduce insulin in the blood with elevated levels of the hormone? Read the answer on this page.
Cortical layer:
- corticoestroma,
- corticosteroma,
- androsterome,
- aldosteroma,
- corticoandosteroma.
Adrenal medulla:
- ganglioneuroma,
- pheochromocytoma.
Reference! About 95% of adenomas in men are unilateral, that is, they affect one adrenal gland, usually the left one.
Causes
The immediate causes of the formation of adrenal adenomas in men are not fully understood. According to some expert opinions, tumors are a response to increased load on the glandular tissue of the organ. Hereditary factors play an important role in the development of adenoma.
Risk factors for adenoma in men:
- age over 35 years,
- obesity,
- chronic high blood pressure,
- diabetes mellitus type 2,
- unhealthy diet
- smoking,
- regular stress,
- surgical interventions on the adrenal glands or organ injuries,
- weakening of the immune system due to past infections and chronic diseases,
- overproduction of hormones by the endocrine glands.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of adrenal adenomas may differ, depending on their nature, size, and hormonal activity. Tumors that do not synthesize hormones are usually asymptomatic. If the formations are small and do not affect the functioning of the body, they are not removed.
Hormone-producing formations can express their presence in different ways. This depends on the amount of hormones synthesized and their nature.
Corticosteromas provoke disruptions in the metabolic process of fats, causing obesity. This causes high blood pressure in men and other characteristic symptoms:
- muscle atrophy,
- thinning of the skin,
- excessive sweating,
- increased blood glucose,
- emotional instability,
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Aldosteromes synthesize increased amounts of aldosterone, causing Conn's syndrome. Sodium is retained in the body and potassium is intensively excreted.
Men experience characteristic symptoms:
- increased pressure,
- convulsions,
- muscle weakness,
- deterioration of orientation in space.
Impaired metabolism causes calcium to be removed from the bones. They become fragile and can often break. Due to increasing muscular dystrophy of the legs, it becomes difficult for the patient to get up and move around. The hernia of the anterior abdominal wall bulges (frog belly).
Androsteromes produce androgens, male sex hormones. This type of formation may not cause pronounced symptoms and may manifest itself latently. This makes them very difficult to diagnose. It is worth paying attention to the strengthening of male characteristics: deepening of the voice, muscle development, increased hair growth, skin rashes.
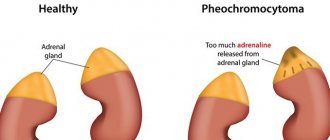
Pheochromocytomas produce a lot of catecholamines and cause the following symptoms in men:
- high pressure,
- increased fatigue,
- dizziness with a sudden change in body position,
- tachycardia,
- anxiety,
- visual impairment.
In more severe cases, cerebral hemorrhages and heart attacks are possible.
If the adenoma synthesizes female sex hormones in excess, the man experiences characteristic changes:
- breast enlarges,
- body hair falls out,
- female type obesity develops,
- voice changes (becomes higher pitched),
- the functioning of the reproductive system is disrupted (erection disappears, libido decreases, penis becomes hypotrophied).
Diagnostics
To identify an adenoma in the adrenal gland, it is necessary to carefully examine it.
Often formations are detected accidentally during instrumental diagnostics of the abdominal organs:
- CT scan,
- MRI,
- Ultrasound.
To find out the hormonal activity of the tumor, you need to undergo laboratory tests:
- daily urine to determine cortisol levels,
- blood test for hormones,
- dexamethasone examination (to diagnose Itsenko-Cushing syndrome),
- blood plasma examination to detect the breakdown of catecholamines.
Laparoscopy and collection of material for histological examination are carried out in case of active growth of adenoma and if a malignant process is suspected.
Effective treatments
If benign neoplasms are small, then treating them is inappropriate in most cases. A man needs to undergo regular examinations to monitor the condition of the adenoma. If it does not increase in size, then clinical observation should be continued further.
If education somehow affects the functioning of the body, then treatment is necessary. His tactics will depend on the size of the adenoma and its hormonal activity. More often they resort to surgical removal if the tumor rapidly increases in size and is characterized by hyperactivity in terms of hormone synthesis.
Surgical intervention
There are several ways to remove adrenal adenomas in men:
- Laparoscopy is the insertion of a laparoscope and surgical instruments into the abdominal cavity through small incisions to remove the tumor. Thanks to the built-in camera, you can monitor the entire operation process. This method of intervention allows you to remove small benign formations.
- Abdominal surgery makes an incision in the abdominal wall to access the affected adrenal gland, after which the tumor and nearby affected tissue are removed. This method is used for large adenomas, as well as for their bilateral location. Abdominal surgeries are more painful than minimally invasive ones. The rehabilitation period lasts longer, the likelihood of complications is higher.
The postoperative period should include the use of restorative hormonal therapy, depending on the hormone-producing characteristics of the adenoma.
If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent the development of infection. If the malignant nature of the adenoma has been identified, men undergo courses of chemotherapy after surgery.
The most commonly used drugs are Mitotan, Methotrexate, and Cisplatin.
Look at a selection of effective methods for treating colloid thyroid nodules in women and men.
The rules for preparing for the pancreatic ultrasound procedure and the specifics of its implementation are described on this page.
Go to https://fr-dc.ru/vneshnaja-sekretsija/slyunnye/sindrom-shegrena.html and find out what Sjogren's syndrome is and how to treat the disease.
Folk remedies and recipes
As an additional treatment method to stop the growth of adenoma, at the initial stage you can resort to traditional medicine that will help normalize hormone levels and strengthen the immune system.
Proven recipes:
- Pour boiling water over the mulberry leaves (2 tablespoons per glass of water). Cook for 20 minutes. Drink a decoction instead of tea.
- Mix knotweed, nettle, pikulnik, and horsetail in equal quantities. Take 2 tablespoons of the mixture and cook them in 0.5 liters of water for 10 minutes. Take 70 ml 2 hours after meals.
- Pour snowdrop flowers into a jar. Pour alcohol over them and let it brew for 5 days. Take 15 drops of tincture before meals.
Prevention measures
There are no specific measures to prevent adrenal adenoma in men.
You can reduce the risk of a tumor or prevent the growth of an existing one if you follow these recommendations:
- quit smoking,
- regularly visit an endocrinologist to check the health status of men at risk,
- Healthy food,
- avoid emotional and physical overload.
Adrenal adenoma responds well to treatment, especially in the early stages of development.
To prevent possible complications that a neoplasm may entail, a man needs to regularly monitor his health.
If symptoms appear that indicate metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and take appropriate measures to stabilize the condition.
From the following video you can learn traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of adrenal adenoma in men:
Source: https://fr-dc.ru/gormony/harakternye-simptomy-adenoma-nadpochechnika-u-muzhchin-metody-lecheniya-i-udaleniya-novoobrazovanij
Prognosis and complications
In general, an adrenal cyst may not cause problems for a person throughout his life. This is the case if it does not increase in size and does not transform into a malignant tumor.
If the situation worsens, complications are possible. First of all, constant pain affects the patient’s psyche. Hormonal imbalance caused by a tumor negatively affects the functioning of the human cardiovascular system.
It is also possible to develop meningitis and other inflammations in the brain.
In this regard, the prognosis may be unfavorable, especially if the cyst was discovered too late, at the stage of its transformation into a malignant tumor.
Causes
Among the causes of cystic lesions, experts highlight abnormal fetal development. It is often said that cysts begin to form at the embryonic stage. It may not bother a person all his life; it is also possible that it will make itself felt already in adolescence and even childhood.
The exact cause of deviations in fetal development is not always possible to establish, therefore, during pregnancy, all women should follow the doctor’s recommendations for the prevention of various lesions, including cystic neoplasms.
Adrenal cysts are divided into several types. Each of them has its own characteristics. Any cystic lesion is divided into true and false. The true one is a closed cavity of the skin epithelium in which fluid is located. There is no epithelial layer in a false cyst.
When it comes to adrenal cysts, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- epithelial true;
- parasitic;
- endothelial true;
- false.
A parasitic infection is usually caused by a parasite. Very often the infectious agent is echinococcus. Penetrating the tissue, it causes the growth of an uncontrolled tumor with fluid inside. The parasitic form is quite rare.
Preventive actions
Only one thing can be classified as preventive measures - regularly undergo medical examinations, especially using ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands. This will allow you to detect pathology in the early stages and prevent its growth. This procedure must be carried out at least 2 times a year. No other preventive measures have yet been developed, since the causes of the cyst are not yet known to science for certain.
An adrenal cyst often does not pose a health hazard, but it is necessary to monitor it in any case. If a tumor grows on the face, then treatment must be carried out without fail. Therapy in most cases has a positive prognosis and the patient returns to a normal lifestyle as soon as possible.
Key aspects of surgical treatment
If a cyst is detected that is larger than 4 cm in diameter, the patient is indicated for surgical treatment. The following surgical methods are practiced today:
- Cystectomy (remove the cyst along with the capsule);
- Partial adrenalectomy (a fragment of the adrenal gland and the cyst itself must be removed);
- Laparoscopy (in a similar way, only a tumor that is benign and has not reached a large size is removed).
Most often they try to resort to cystectomy surgery. It is completely justified if you need to remove a large tumor. The formations are simply excised followed by suturing. However, the technique can be considered as a rather stressful method of treating adrenal pathology. After the operation, the patient will undergo a long period of hormonal therapy.
Partial adrenalectomy is a more gentle surgical procedure. The method is relevant in a number of situations when only part of the tissue is subject to excision. In this way, the threat to life and health disappears, and it is also possible to avoid excessively negative reactions of the body in response to the surgeon’s intervention.
Surgeries to remove cystic formations of the adrenal glands laparoscopically carry some risks. They are low-traumatic, there is no need to go through a long rehabilitation period, but there is always a danger of relapse. This is due to the fact that during laparoscopy, the surgeon may not notice a small fragment of the tumor and simply not remove it.
General rules and methods of treating the disease
The choice of therapy depends on the type of incidentaloma. There are several ways to solve the problem:
- all large adrenal gland formations (regardless of their nature) (more than 60 mm) must be removed. There are many surgical methods to prevent relapses; doctors recommend removing the tumor through an open incision;
- observation in dynamics. Tactics are used for formations less than 30 mm in diameter that are benign. It is recommended to conduct preventive examinations every six months. The absence of mutation or increase in formation is a good sign, which can increase the amount of time between observations from 6 to 24 months;
- even small formations that affect the production of hormones must be removed. The patient will have to use special means to maintain hormonal balance in the body for the rest of his life.
Therapy of malignant tumors
If a malignant tumor is detected, treatment involves removing not only the tumor itself, but also the affected adrenal gland to prevent relapses. If the tumor is inoperable, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is used. During treatment, constant monitoring of the patient's blood pressure is necessary.
Adrenal incidentaloma is often diagnosed in people over 55 years of age. Recently, the disease has become “younger”, be vigilant, take care of your health from a young age.
Self-medication in such a situation is strictly prohibited! Folk remedies and painkillers will not have any effect on tumors, especially malignant ones. Trust your health to professionals and follow their recommendations.
What antibiotics should I take for kidney inflammation? Look at the drug review.
Read about how to take Palin capsules for urological problems in this article.
Go to the address and learn about the rules for treating pain when urinating during pregnancy.
Adrenal adenoma: symptoms, treatment, removal in women and men
In women, adrenal gland disease is diagnosed more often. In men, the tumor is less common. The pathology is benign. There are several types of the disease, differing in course and symptoms.
The tumor is formed from glandular tissue without metastases spreading throughout the body. Despite its benign nature, the adenoma must be treated. The tumor does not resolve on its own, so doctors carefully monitor the patient and the tumor.
The patient needs to undergo regular medical examination.
Characteristics of the disease
The kidneys in the human body perform an important function in removing toxic substances. Above the kidneys are endocrine glands that independently produce the corticosteroid hormone - the adrenal glands. The organ consists almost entirely of the cortex and forms three sections.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hCJcQS1OMOo
The adrenal glands are responsible for cell ion exchange, protein breakdown and carbohydrate synthesis. The organ's cortex produces androgen. When an adrenal adenoma forms, the hormone is produced in large volumes. Therefore, in women, the disease is often accompanied by external changes associated with the production of male hormone in increased quantities.
Adrenal adenoma is a tumor that forms in the cortex or medulla of an organ from glandular tissue.
The disease is accompanied by the active production of hormones that cause certain changes in the body. The tumor can occur in one organ or affect the areas of the left and right adrenal gland.
Adenoma can occur in any part of the organ - this affects the level of hormone produced.
Education is diagnosed mainly in adults after 30 years of age. The disease is a benign tumor, but requires urgent treatment. The nodule cannot resolve on its own, so the doctor selects an adequate course of therapy to eliminate the adenoma.
The ICD-10 code for the disease is D35.0 “Benign neoplasm of the adrenal gland.”
Types of pathology
Depending on the area of the adrenal cortex affected, the adenoma may or may not produce the hormone.
The type of adenoma depends on the type of hormone produced by a specific area of the organ.
Corticosteroma (produces cortisol), androsteroma (produces androgens), aldosteroma (produces aldosterone), and mixed species (can produce multiple hormones) are common.
Based on location, there are two types of adenoma - unilateral and bilateral. The formation of a tumor in the left adrenal gland does not affect the activity of the right organ. The principle of formation of adenoma in the right organ is the same. The bilateral type affects two organs at once.
The disease is also classified depending on its structural composition:
- pigmented adenoma contains a large volume of dark-colored pathogens;
- the adrenocortical form resembles a capsule or node in appearance;
- oncocytic is a small-grained tumor;
- the clear cell form consists of clear cells;
- microadenoma can only be detected by random examination using the latest equipment with high kidney magnification.
Each type causes hormonal imbalance in the body and certain disturbances in the functioning of the organ. Slow-growing tumors affect people less, but they still need to be treated.
Causes of the disease
The reason that causes the growth of adenoma in the tissues of the adrenal glands is not exactly known to doctors. Research into this pathology is still underway. Experts identify a number of factors that can provoke the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- active production of hormones;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- being in a stressful state for a long time;
- high blood pressure;
- previous heart disease - heart attack, stroke;
- metabolic disorders;
- injury or surgical intervention of neighboring tissues or organs;
- endocrine system disease – diabetes mellitus;
- excess body weight;
- abuse of nicotine and alcoholic beverages;
- age after 30 years.
Signs of pathology
At the initial stages of adenoma formation, men and women usually have no symptoms. It is difficult to identify the disease at this stage.
It is discovered by chance when examining another organ for pathologies.
The first signs appear when the tumor enlarges, when compression of nearby tissues occurs and active production or, conversely, deficiency of hormones occurs. Symptoms may depend on the type of adenoma.
The formation of a tumor in the medulla of an organ - pheochromocytoma - can occur in the presence of a hereditary predisposition. This type produces symptoms:
- muscle weakness and early onset of fatigue with little physical activity;
- dizziness is noted with a sudden change in body position;
- blood pressure remains high on an ongoing basis;
- the skin acquires a characteristic pale tint;
- regular pain in the head;
- heart rate increases to 100 beats per minute;
- increased sweating;
- vision decreases sharply;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system - an anxiety state.
Pheochromocytoma is dangerous due to serious consequences - retinal detachment, stroke and myocardial infarction.
Androsteroma is characterized by the production of increased levels of androgens, exhibiting symptoms:
- increased endurance and strength;
- increased hair growth;
- young men experience early puberty;
- increased muscle mass;
- rapid skeletal growth;
- rashes on the skin.
The aldosterome produces a large volume of aldosterone, which actively removes potassium, but sodium remains intact. This type is manifested by the following symptoms:
- weakness in the body;
- presence of muscle cramps;
- blood pressure rises to critical levels;
- accumulation of excess fluid in soft tissues;
- pain in the heart area;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system - irritability, short-term memory loss;
- regular dizziness;
- decreased vision;
- shortness of breath for no apparent reason.
Corticoestroma is responsible for the production of estrogens, which leads to the following symptoms:
- erectile function decreases in men;
- formation of excess body weight;
- hair loss;
- voice change;
- frequent urination;
- There may be blood in the urine.
Corticosteroma actively produces cortisol, which shows signs of:
- accumulation of adipose tissue;
- fragility of skeletal bones;
- the dermis becomes thin and dry;
- decrease in muscle tissue;
- men experience erectile dysfunction;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- pain in the head area;
- high blood pressure;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- excessive sweating;
- skin rashes;
- dry mouth and dental problems.
Diagnosis of pathology
To prescribe the correct treatment, you need to undergo an extensive examination of the body. Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- CT can determine the density of the tumor, size, location and boundaries;
- MRI provides a visual image of the tumor with precise boundaries and dimensions;
- a dexamethasone test reveals the presence of cortisol in the blood;
- urine is collected during the day for detailed study for the presence of hormones;
- blood and urine are examined to determine the type of adenoma.
Tests and CT scans for adenoma are the most effective methods for diagnosing pathology. After receiving the results, the doctor determines how to remove the tumor.
Treatment of adenoma
A small tumor that develops without dangerous symptoms usually does not require treatment. The patient is under close medical supervision. The patient undergoes regular examinations - computer and magnetic resonance imaging and blood and urine tests. This allows you to monitor the development of adenoma over time.
It is possible to use drug therapy for small adenomas. To restore the activity of the adrenal glands, the patient is prescribed a course of hormone-based medications. The medicine is selected depending on the type of tumor.
To stimulate the body's protective functions, it is necessary to take a vitamin complex and immunostimulants on a homeopathic basis. This will boost the functioning of the immune system and speed up the healing process.
Benign neoplasms up to 30 mm in size are removed by surgery. Before the operation, the patient undergoes medication preparation.
A course of immunostimulants and antibacterial drugs to reduce the production of hormones - Metyrapone and Ketoconazole - are prescribed.
To restore blood pressure, you need to drink sodium nitroprusside, Phentolamine or Esmolol.
Surgery to remove a tumor can be performed using the following methods:
- Traditional abdominal surgery is used more often due to accessibility, but is considered the most traumatic method. An incision is made in the abdominal cavity, diaphragm and chest area to access the lump. This method is used for unilateral damage to the body. The length of the suture after excision of the adenoma can reach 30 cm.
- Laparoscopy refers to endoscopic techniques with a gentle process of tumor removal. Access to the node is made using punctures of the abdominal wall. Through the holes, air and a special instrument are introduced into the cavity, which will be used to excise the adenoma.
Laparoscopic surgery
- The retroperitoneoscopic method is a modern method of tumor removal. The instrument is inserted through the lumbar region using special incisions. This is the most gentle method - the patient is discharged on the second day after surgery.
Treatment of adrenal adenoma with folk remedies is not recommended. Doctors advise contacting a clinic at the first suspicious symptoms. You should not warm up the back or massage the lumbar region - this is dangerous for the patient’s well-being. This can provoke active growth of the tumor and transformation of atypical cells into malignant ones.
After the operation, unpleasant consequences may be present:
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract;
- disruption of the genitourinary system;
- abnormalities in the structure of the blood, which are manifested by thrombosis or internal bleeding.
It is also recommended to monitor blood pressure and hormones at first. To restore hormonal balance, a course of Fludrocortisone and Hydrocortisone is prescribed.