In some cases, parasites can be found in a person's bladder. Parasitic infestations are often found in countries in Africa, East Asia or South America. There are two groups of parasites. The first group is true, that is, those that live in the organs of the genitourinary system. The second is false parasites, that is, those helminths that ended up in the bladder by chance, for example, pinworms. In most cases, it is not helminths that are found in the urine, but only their eggs or tissues. Moreover, this disease can be found at almost any age.
The bladder is a “comfortable” place for parasites to live and reproduce.
Worms in the human bladder, symptoms and treatment
Helminthic diseases are caused by worms (helminths) - parasitic worms that can appear in the bodies of both humans and animals.
Receiving at the expense of the host all the substances necessary for existence, helminths deplete the body and poison it with the products of their own metabolism.
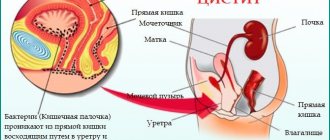
Helminthic diseases are widespread throughout the world and affect various organs, so worms are often found in the bladder, which can cause serious health problems: endocrine diseases, kidney stones and cystitis.
Parasites that cause diseases in the urinary system
Infestation by parasites is a common phenomenon even in civilized countries. Often, even the cleanest people living in prosperous conditions cannot be protected from such guests entering the body. There are many different types of parasites, so let’s take a closer look at which ones cause diseases of the urinary system.
Schistosomes
These parasites are especially common in countries with tropical climates. Much of Africa's population is infected with schistosomes, and they have also become a major cause of increased mortality in South America, Asia and the Middle East.
Where schistosomes enter the body, the skin becomes inflamed and turns into red dots that resemble an allergic rash. As the parasite develops inside the body, new, more serious symptoms appear.
After a few months, the parasite reaches the veins of the bladder. An inflammatory process begins to develop, and at first it spreads only in the upper layers of the mucosa, and over time, many ulcers appear throughout the bladder, causing its walls to thicken and deform.
Schistosomes often cause a huge number of common human diseases, for example, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, pollips, all kinds of cysts, menstrual irregularities and many others.
Filaria
Worms of the genitourinary system also appear due to parasites such as filaria. These are large threadworms that can reach 10 centimeters in length. They parasitize, among other things, the organs of the urinary system and exist in “balls” in which individuals of both sexes are present, actively reproducing.
Filaria living in the lymphatic system cause physical harm to the part of the body in which they live, and the fruits of their vital activity cause intoxication.
If in the first stages this can only cause an allergic rash, then after a couple of years the lymph begins to enter the urine.
Due to the fact that the passage of lymph is disrupted, tissues expand and elephantiasis may develop .
Trichomonas
The simplest single-celled organism, such as Trichomonas, can live only in the urethra, and therefore rarely affects other body systems. This parasite causes a disease called trichomoniasis. As a rule, these parasites live in the vagina in women and in the urethra in men, but they often settle in the upper parts of the genitourinary system.
Pinworms
This is the most common type of parasite in our country. These helminths are active not only in the rectum, but also, spreading through the bloodstream throughout the body, they enter the bladder. This can cause bladder inflammation, severe pain, and blood in the urine.
How does infection occur and who is susceptible?
Schistosomes, for example, are found in huge quantities in water bodies of countries with tropical climates. They most often enter the human body through water - when a person simply drinks contaminated liquid. The parasite can also enter through the pores of the skin, so even walking barefoot in such bodies of water can be very dangerous.
Infection with parasites can also occur through the bite of a mosquito that carries the infection. This is how they become infected, for example, with filaria.
Parasites such as Trichomonas are transmitted sexually from an infected person.
Infection through household contact is also possible, but in the case of Trichomonas it is much less likely, since they die very quickly while outside the body.
But helminths such as pinworms are most often transmitted in this way. An infected person leaves parasite eggs on all household and personal hygiene items, and they are easily transmitted to other family members.
Worms can be detected in the urine of both children and adults, regardless of what socioeconomic group they live in and how carefully they monitor hygiene.
Symptoms and diagnosis
As a rule, the presence of parasites in the urinary system is accompanied by a number of symptoms that can be a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Symptoms
The main and most common symptoms of worms in the bladder are as follows:
- severe headaches and sleep disturbances;
- chronic fatigue, fatigue, weakness and nervousness;
- loss of appetite, frequent constipation or, conversely, diarrhea;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, renal colic;
- discomfort or pain during urination;
- allergic skin rashes and itching;
- blood in urine.
All these symptoms actively signal to a person that something wrong is happening to his body, and he needs to see a doctor.
If you continue to tolerate and ignore these signs, then worms in a person’s bladder can lead to very serious consequences, including oncology.
Diagnostics
Worms in the urethra and bladder can only be detected 5-6 weeks after infection. The following methods are used to diagnose parasites:
- culture of blood and urine for helminths;
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- cytoscopy of the genitourinary tract;
- use of intradermal allergy test;
- other laboratory and instrumental studies.
All this helps to identify parasites before they cause serious damage to the body and get rid of them through treatment.
Treatment
The necessary treatment is prescribed by a doctor and depends on the location of the disease, as well as its stage. First of all, special medications are prescribed, however, if the disease is “advanced,” then surgical intervention is necessary.
The dosage is selected very carefully, because you need to kill the parasite without harming the person himself. The patient is also prescribed a special diet that limits vitamin-rich foods to deprive the parasite of additional nutrients.
The patient is often prescribed drugs such as Biltricide (Praziquantel) and Metrifonate.
After the course of treatment, the patient takes tests again and, if they do not satisfy the doctor, the therapy will have to be repeated.
Worms in the bladder may not be such a terrible phenomenon and may not lead to serious consequences if you pay attention to the symptoms in time and consult a doctor. The earlier the infection is detected, the faster and easier it will be to treat.
Source: https://glisty24.ru/parazity/glisty-v-mochevom-puzyre/
Filariasis
Filariasis is the general name for diseases caused by extraintestinal nematodes of the Filariata species. Filariasis affecting the human lymphatic system is wucheriosis and brugiosis. The disease is common in Africa, South America, and Asia. Cases brought by tourists are being observed in other countries. According to WHO, there are about 140 million infected people in the world. Lack or improper treatment leads to the development of elephantiasis.
Filaria are filamentous, round-shaped worms that belong to the category of nematodes. The size of the female is 10 cm, the male is 4 cm. Filaria have a complex life cycle. Intermediate carriers are blood-sucking insects that ingest microfilariae in human or animal blood. In the insect, the parasite reaches maturity, and subsequent bites lead to infection of the final host, a human. In the human body, microfilariae migrate in the subcutaneous blood vessels and cause severe itching. Mature macrofilariae settle in lymphoid formations, blocking the lumen of the lymph nodes. The presence of worms causes inflammation and enlargement of connective tissue, thickening of the walls of blood vessels. Microfilariae can live for 3 years, and some macrofilariae remain viable for 20 years or longer. The incubation period in humans lasts 18 months, with primary infection up to 6 months.
Worms in the urine and bladder: can there be
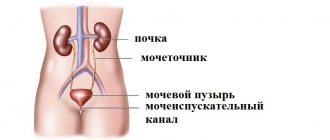
Parasites in the human body are able to travel through the bloodstream. Affecting the entire body, helminths are most often found in feces, but sometimes parasites appear in the bladder. What kind of worms are localized in the genitourinary system, what are the dangers of the diseases caused, and how to treat parasites - everyone should know this.
What parasites are found in the human bladder?
The usual place of localization of worms is the intestine. Here the helminths find the necessary nutrition and develop, laying eggs, as well as poisoning the host’s body with waste products.
Detection of worms in urine is much less common - due to the large accumulation of liquid, it creates an unfavorable environment for parasites.
However, there are types of worms that can breed in the genitourinary system:
- Filaria. While establishing their residence, worms cause mechanical injuries, which provokes a lot of diseases. Infection is a mosquito bite.
- Echinococcus. They are dangerous due to the fusion of the wall of the parasite cyst with the wall of the genitourinary organ. The larva provokes the development of an inflammatory infection. Infection - lack of hygiene.
- Trichomonas. Cause damage to the bladder and enlargement of the ureters. Localization in urine or vaginal lubrication (in women). Infection – infection from a sexual partner.
- Pinworms. Small worms up to 10 mm in length. Infection – lack of hygiene, improper washing. They provoke an inflammatory process in the system and often cause bedwetting.
- Schistosomes are a parasite that settles in the genitourinary system and causes infectious inflammation of the organs.
It is extremely rare to find roundworms in urine. As a rule, these parasites appear in the human bladder in the most advanced cases, when there is no adequate therapy for a long-term illness.
Causes of parasitic diseases
Worms in urine are a consequence of non-compliance with hygiene rules. The most likely route of infection is fecal-oral. For example, pinworms and roundworms are detected in the urine due to the fact that the patient does not wash himself properly and introduces worm eggs from the perianal area into the genitourinary system.
The second route of infection is unwashed vegetables, fruits, and contaminated water. And although helminthic infestations affect the intestines, they spend part of their life in parenchymal organs. One of these is the kidneys.
For example, echinococcus settles in one of the kidneys, creating a cyst, and develops inside the formation. Filaria do not need the intestines; their localization area is the urinary tract and the entire genitourinary system.
In this case, filariae cause irreparable damage to the entire lymphatic and circulatory systems of the body.
Fact! Infection with filaria is possible only through the bite of mosquitoes. As a rule, people bring the disease from hot countries. In our latitudes, the likelihood of infection is extremely low.
Parasitic diseases of the genitourinary organs
Depending on the type of parasites, the following system pathologies develop:
- The helminth Schistosome causes schistosomiasis, called snail fever and bilharzia. Infectious pathology most often affects adults employed in agriculture and fishing. Children are affected by lack of hygiene and bathing in contaminated sources. There is intestinal and genitourinary schistosomiasis. Worm waste causes toxic poisoning of the body. If left untreated, the patient is at risk of lymph entering the urine and tissue expansion. And this leads to elephantiasis.
- Echinococcosis. Damage to the kidneys by worms leads to the development of inflammation of the renal parenchyma. After the larvae develop in a cyst attached to the kidney tissue, the worms may appear in the urine.
- Trichomonas urethritis, caused by Trichomonas, smoothly flows into trichomoniasis of the bladder. Painful urination and enlarged ureters are only a small part of the problem. It is extremely difficult to cure Trichomonas, and relapses are common. Therapy is required for both sexual partners.
Regardless of the type of pathology, treatment should be immediate and complete. Parasites of the genitourinary system are extremely difficult to remove, so therapeutic procedures should not be disrupted.
Treatment of parasites in the genitourinary system
Let us immediately note that only a specialist makes a diagnosis, and he also prescribes treatment. Diagnosis is carried out by taking tests that will determine not only whether the patient may have worms in his urine, but also the type and dynamics of the invasion. The proposed drug treatment is prescribed for both children and adults. The most effective are considered:
- Praziquantel. Taken three times a day. The course of treatment is one day.
- Metrifonat. The dose is determined by the doctor and taken in three doses throughout the day.
After treatment, samples are taken to identify parasites in the genitourinary system. If the result is positive, a repeat course is prescribed.
In case of critical development of the disease, for example, the formation of multiple cysts, resection of part of the organ may be prescribed. Surgery is a last resort, as cases of profuse bleeding are common. Today there is an alternative method - echinococcectomy. The contents of the cyst are removed with a thin needle inserted into the affected area under ultrasound guidance.
Important! Advanced cases of pathology can lead to removal of the organ along with the cysts. The traumatism of the operation is high, so you should be careful about your own health.
Schistosomiasis and filariasis require conservative methods, so anthelmintic medications are sufficient. After therapy, the specialist must prescribe rehabilitation medications and also recommend prophylaxis to reduce the risk of relapses and re-infection.
Folk remedies are used as adjuvant therapy. If worm eggs are diagnosed in the urine, then it is good to take decoctions of bitter herbs: wormwood, tansy.
Having an anthelmintic effect, decoctions help only at the initial stage. When worms multiply in the genitourinary organs, treatment with decoctions and infusions is useless and dangerous.
Such therapy can provoke aggravation of the process and cause complications in the treatment of the patient.
Source: https://parazitron.ru/simptomy/glisty-v-moche.html
Prevention
Experts say that it is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat its consequences later. To avoid infection with worms, you must follow simple rules that will protect your body:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap: before eating and after visiting the toilet;
- wash vegetables, fruits and herbs thoroughly;
- regularly worm your pets;
- purify or boil water;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- consume quality products;
- do not eat raw meat or fish.
Such simple preventive rules will effectively protect the body from helminths. By following them, every person can improve their quality of life and maintain personal health.
Infections of the genitourinary system by other types of helminths are recorded extremely rarely, that is, they account for less than 5% of the total number of calls.
Worms in urine - can they be detected in tests, reasons
Diseases classified as parasitic are those that are caused by the invasion of helminths into the body.
They infect people and animals; during the process of colonization, they receive nutrients from the host to carry out life activities, while simultaneously depleting and poisoning the body with metabolic products.
Helminthiases are actively distributed throughout the world and can be diagnosed in various organs, including the bladder. Such an invasion more often than others leads to serious health problems and complications.
Can they be in urine?
They are usually not found in urine. Therefore, if you suspect the presence of parasites, it is not logical to first take a urine test. First of all, a study of blood and stool is required, since this is the most representative material. Only after establishing the absence of characteristic signs will it be necessary to take other tests.
There are several reasons why helminths are rarely detected in urine:
- Most often, worms settle in the small intestine, less often in the muscles or brain. The urinal is an unsightly place for them, because there is little food there.
- Helminths rarely live in a liquid environment. It's uncomfortable for them.
- Urine undergoes thorough filtration in the body - through the kidneys, which retain even the smallest excess particles in their pelvis. As a result, the liquid comes out purified, so helminths are occasionally detected in the urine even if they infect the urinary tract.
First of all, worms are looked for in other human systems and organs.
But there are always exceptions to the general rules, but they are not so frequent as to include urine tests in the list of mandatory tests.
Types of parasites in the human genitourinary system
Most helminths live in the digestive tract, where all the necessary conditions are there for them. But rarely can a parasitic organism be diagnosed in urine. This environment is unfavorable, because there is a lot of liquid.
But some species are not subject to these rules, and therefore worms are excreted along with urine. Such a problem can cause irreparable harm to the human body in the absence of adequate treatment, leading to dangerous complications.
Typically detected in urine:
- pinworms,
- schistosomes,
- filariae,
- Echinococcus.
Enterobiasis
Enterobiasis is caused by roundworms from the group of nematodes, simply pinworms. They usually live in the intestines, and infection occurs after ingestion of mature parasite eggs. The eggs hatch in the duodenum and then travel down the small intestine. Pinworms usually parasitize in the cecum, but if the body is heavily infested, they are diagnosed in the small and large intestines.
During the breeding season of helminths, the female with the eggs ceases to attach to the intestinal walls and descends into the rectum along with the feces. At night, she lays eggs in the anus, which can also end up in the vaginal area, and therefore in the urine, which is collected for testing.
Filariasis
Worms are also excreted in urine when the body is infected with filaria. These are large thread-like worms up to 10 cm in length. They also settle in the genitourinary system, living in the form of balls, where there are individuals of two sexes at once, leading an active reproduction process.
Filariae in the lymphatic system physically harm the body; waste from their vital activity provokes severe intoxication.
At first, in the first stages of invasion, a simple rash develops, but subsequently lymph enters the urine, its flow is disrupted, tissue expansion occurs and elephantiasis develops.
Schistosomiasis
Worms of this type are more common in tropical countries, so most of the population of Africa is infected with them. They are also the main cause of high mortality rates in Asia, the Middle East, and South America.
At the site of schistosome invasion, the skin becomes inflamed and red rashes appear, reminiscent of an allergy. As the disease progresses, increasingly intense symptoms develop.
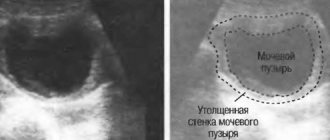
After a few months, the parasite attacks the venous system, the bladder, inflammation is activated - first only on the surface of the mucous membranes, but then throughout the bladder, where many ulcers form, leading to thickening and deformation of the walls.
Protozoa in urine can lead to the development of many diseases, for example:
- polyps,
- varicose veins,
- haemorrhoids,
- cysts,
- problems with menstruation, etc.
Echinococcosis
Echinococci are worms that provoke the disease of the same name, echinococcosis. Parasites enter the body in the following ways:
- through raw meat, fish,
- through dirty fruits, vegetables,
- if personal hygiene is not observed,
- after swimming in dirty ponds,
- after contact with pets.
Helminths quickly spread throughout the body through the bloodstream, also affecting the bladder and kidneys. The infected person complains of weakness and loss of strength, constant itching of the skin, and pain in the kidneys.
How does infection occur and who is susceptible?
The route of infection may differ for different worms. For example, schistosomes live in large numbers in bodies of water in tropical climates. They usually enter the body through water, but also through skin pores. Even being barefoot in water in such reservoirs is extremely dangerous.
Invasion of parasites into the human bladder can occur after the bite of an insect that carries the infection. This is a common route of infection with filaria.
Pinworms are most often transmitted through household contact. The patient leaves worm eggs on hygiene and household items. They are easily transmitted to other people who communicate closely with him.
Worms are diagnosed in the urine of both adults and children; the frequency of infection does not depend at all on the socio-economic group of the patient. Personal hygiene alone is not always enough to prevent parasitic pathologies.
Symptoms of the disease
Doctors identify the basic symptoms of the presence of parasites in humans.
They allow us to make an assumption about helminth infestation:
- sleep problems,
- nervousness,
- headaches,
- diarrhea and constipation,
- loss of appetite,
- itching and papular rash on the skin,
- chronic fatigue,
- pain in the lower abdomen, lumbar area,
- blood in urine
- local redness on the skin,
- pain during urination.
The listed symptoms should be a reason to urgently visit a doctor. Long-term presence of helminths in the body will cause inflammation of the urinary tract, kidneys, and adrenal glands.
When pathology is detected in females, in the absence of timely treatment, helminthiasis affects the organs of the reproductive system. This provokes vaginal bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse, and the formation of nodes and growths.
In men, worms also cause a lot of discomfort. Invasion leads to prostatitis, diseases of the seminal vesicles, and infertility. With timely treatment, it is possible to protect the genitourinary organs.
How is infestation diagnosed?
Symptoms of parasite damage should alert a person and a doctor.
These can vary, but the most common include:
- mechanical intestinal obstruction,
- inflammation of the bile ducts,
- stabbing pain during urination,
- swelling of the eyelids, face,
- muscle pain,
- increase in the size of the spleen, liver,
- rash,
- increase in the size of lymph nodes.
When a woman's genitals are infected by parasites, redness, increased mucus secretion, bleeding, and an unpleasant odor are noted.
The disease causes constant discomfort, causeless weight loss, and pain.
Even with the slightest suspicion of helminthiasis, it is necessary to immediately go for diagnostics. Sometimes urine tests help diagnose the problem when other methods and studies do not show results.
Methods of drug treatment
Helminths have a very negative effect on the organs of the genitourinary system. Invasion ultimately leads to dangerous diseases. Treatment needs to begin as quickly as possible.
Medicines are prescribed not only to the patient, but also to his sexual partner. With helminthiasis, there remains a high probability of developing additional diseases. The patient must be tested for HIV, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Worms are rarely detected in urine, but this type of analysis is considered the most dangerous. These parasites can destroy their own protective barrier, causing damage to the genitourinary organs with dangerous infections. Even a few suspicious symptoms are a reason to visit a doctor for examination and diagnosis.
Treatment should be prescribed only by a specialist in accordance with the location of the pathology and the stage of the lesion. First, medications are selected, but if it gets worse, surgery may be required.
The dose of drugs is selected carefully in order to kill the parasite and at the same time not further harm the patient’s health. At the same time, a special diet with many restrictions and a sufficient amount of vitamins is required to deprive the helminths of the opportunity to obtain nutrients.
Most often, medications such as Metrifonat and Biltricide are indicated. After completing the full course, additional tests are required to obtain treatment results. It happens that it needs to be repeated.
Worms found in the urine will not be a big threat to health and life only if treatment is started in a timely manner. Every person should be attentive to their own health and consult a doctor in a timely manner. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier and faster the treatment.
Prevention of infection
To prevent worm infestation, constant adherence to simple rules is required:
- do not include raw fish, meat in the menu,
- always ensure timely hand washing after using the toilet, interacting with pets, before and after eating,
- choose only high-quality and fresh products for your diet,
- wash vegetables, herbs, fruits thoroughly before eating,
- boil and filter water for drinking,
- organize regular deworming of pets.
The listed rules are easy to follow; they will help protect the entire body from uninvited guests, minimizing the risk of invasion of the bladder.
Source: https://rvdku.ru/parazity/diagnostirovanie-glistov-v-moche-simptomy-porazheniya-vidy-gelmintov-i-sposoby-ih-ustraneniya
Treatment of the disease
Trichomoniasis affects the genitourinary system. Such a disease can provoke the occurrence of more serious pathologies. It is recommended to begin its treatment as soon as possible. Medicines should be taken not only by the patient, but also by his sexual partner. If you have trichomoniasis, the risk of infection with other diseases increases. That is why the patient is also examined for the presence of HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, etc. If not only trichomoniasis is present in the body, the patient needs specially selected treatment. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
Worms in urine are extremely rare. However, they are considered the most dangerous. Such helminths can destroy the protective barrier and provoke the occurrence of other infectious diseases. That is why if you have at least a few symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Urine analysis will be discussed in the video:
peptic.ru
Types of worms parasitizing the bladder, symptoms and treatment of infestation
Worms in the bladder: types, symptoms, treatment, complications that a parasitic invasion of such a localization can cause - all this is the subject of numerous scientific studies.
Domestic scientists are also studying them, despite the fact that worms in the bladder are considered more common in countries of Asia, Latin America or Africa.
However, they are also detected in patients living in temperate latitudes. Infection usually occurs during a person’s stay in the habitat of dangerous parasites.
Worms can be found in any person, regardless of gender, age and nationality, but in any case, treatment should begin immediately.
Can there be worms in urine?
Parasites in urine are an atypical phenomenon in temperate latitudes, if we mean helminths, whose usual habitat is the intestines.
They are usually found in feces in the form of larvae, eggs, or even adults during active reproduction. Therefore, in parasitology there are two conditionally delimited groups.
The first is true parasites, which are characterized by being in an unfavorable environment of liquid secretions. The second group includes helminths that live in mucous membranes or migrate throughout the human body at a certain stage of development.
There is no suitable habitat for them in the bladder, and entry into it occurs accidentally.
Filariasis
In temperate countries, filaria infestation is classified as a disease introduced during migration from Africa, South or Central America, but more often from Asia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGjQnsAWqAg\u0026list=PLVfuNpw4LNyvfUmpxBtAxTSu9SCGOFU7K
Parasites that infect the human body have only one mode of transmission - transmission.
They spread with the blood of a person already infected with nematodes, through blood-sucking insects, to which they penetrate the intestines with biological fluid.
Having undergone molting, the larvae enter the oral cavity from the body cavity of the intermediate host.
Then, when sucking blood, they again end up on human skin and penetrate the body through damage.
The human bloodstream becomes the site of the final molt and transformation into sexually mature nematodes, again with the ability to lay larvae.
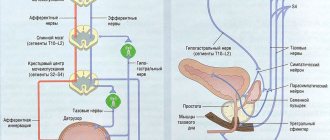
The usual place of dislocation of adult individuals is blood vessels and lymph nodes. Parasitic infestation is indirectly associated with the genitourinary system. Nematodes can block lymph flow and cause elephantiasis of the limbs and genitals.
Complications
Parasitic worms in the human bladder can cause serious diseases of the genitourinary system. In men, a frequent consequence is prostatitis, the chronic form of which is one of the causes of adenoma and prostate cancer.
The degree of organ damage and the likelihood of death depends on the type of parasite.
Schistosomiasis can cause bladder diseases, ultimately leading to cancer.
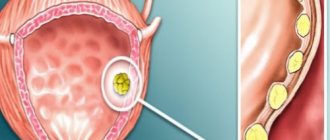
An echinococcal cyst, when ruptured, can lead to seeding and the appearance of numerous new formations. It can grow to enormous sizes and compress internal organs, leading to kidney atrophy.
With wuchereriosis (helminthiasis from the filariasis group), swelling of the scrotum and vulva, rupture of the vessels of the peritoneum, intestines, kidneys and bladder are possible.
Diagnosis of parasitic infection
Parasites can be detected in the body only through special examinations. Initially, a person needs to submit feces and urine for tests - they will detect worms, as well as their eggs. After this, you need to donate blood from a vein, which will show the presence of larvae in the circulatory system.
Diagnosis is supplemented with instrumental examination. The patient must be referred for an ultrasound of the genitourinary system. Such an examination will allow you to accurately see the presence of foreign bodies in the body. In an advanced state, the patient may be prescribed a biopsy procedure, which will be performed under ultrasound supervision. Bladder parasites can form cysts in the kidneys or bladder. Then the patient undergoes a tomography to accurately see the contours and size of the tumor.
Signs
At an early stage, the disease schistosomiasis has symptoms such as redness of the skin, itching and papular rashes. If helminths use human lungs for their migration, a “wet” cough occurs, the lymph nodes, spleen and liver enlarge.
It takes about six months from helminthic infestation to detection of a lesion in the bladder. Below are the symptoms of genitourinary disease caused by worms:
- poor appetite;
- disturbed sleep and headaches;
- fatigue and weakness in the body;
- colic in the kidneys;
- urination is frequent and painful;
- aching pain in the lower back;
- detection of blood in urine;
- fibrosis of the bladder when the disease is advanced.
If the patient was negligent about his health and patiently endured on his feet all the inconveniences caused by worms to his body, then the disease simply moves into the field of oncology, developing into bladder cancer. Women are at risk of vaginal bleeding because their genitals are affected. Intimate life is painful, nodes and polyps form.
Men who develop schistosomiasis will develop seminal vesicle disease, and the prostate gland will also not remain healthy. The disease will simply lead both to infertility.
How is infestation diagnosed?
Helminths in the bladder are detected by instrumental and laboratory tests 1.5 months after invasion. Preliminary diagnosis requires immunological tests confirming the presence of antibodies to parasites. The disease is diagnosed by identifying worm eggs in urine and feces. The first thing the attending physician prescribes is a urine test. Helminths in the bladder cause hematuria, increased protein and leukocyte levels. Typical methods for determining worms are sedimentation, filtration and separation of urine into fractions. Urine for analysis is collected during the period of greatest concentration of larvae - from 10.00 to 14.00. A blood test will show an increase in white blood cells, neutrophils and signs of anemia. For some parasites, the genitourinary system is a temporary habitat, so stool should be cultured for the worm.
Additional information is obtained after undergoing cystoscopy. During the study, the bladder is visualized with a special device, which is inserted through the urethra. This diagnostic method makes it possible to observe schistosomiasis granulomas, amoebic ulcers, and local accumulations of oviworms. A biopsy of pathologically disturbed areas of the bladder is performed. Ultrasound examination reveals disorders of the vessels of the genitourinary system, changes in the outline of the bladder, and the presence of tumors in the kidneys and ureters. Mass examination of the population of endemic regions requires subcutaneous allergy tests with antigens. In addition to infectious disease specialists, the disease is diagnosed by gastroenterologists and urologists.
Complications
- Damage to the lymphatic tissues of the genitourinary system.
- Formation of abscesses, which, when opened out, cause peritonitis.
- Formation of holes in the walls of the bladder, leading to permanent infections.
- Formation of cysts in the bladder and kidneys.
- Infertility.
- Development of elephantiasis.
- Death.
- Men experience swollen testicles, epididymitis, and increased sensitivity of the scrotum and penis. The scrotum in some cases increases to 20 kg or more.
- Women experience vaginal bleeding and may develop cancer of the uterus and appendages.
- In children it leads to severe anemia, developmental delays and decreased mental activity.
Dysenteric amoeba
Amebiasis is a disease affecting the large intestine. Urogenital amebiasis is formed when a microbe penetrates the urinary tract from the intestines. In women, the microorganism from the intestines enters the vagina. Inflammation of the external and internal genital organs occurs. Transmission occurs through sexual and oral routes.
The source of the disease is a single-celled microbe called amoeba. The invasion is characterized by pathological inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. The amoeba exists both in the active phase and in the resting phase, transforming into a cyst. A cyst is a round microorganism measuring 0.015 mm, characterized by a double shell. Life expectancy in feces is 30 days, in water 60-130 days. Microbes enter the body from the carrier of the cysts, usually a person. Often the patient is unaware of the microbes in the body. Cysts enter the environment with feces. The penetration of parasites into soil or water causes infection of the crop, through which human invasion occurs. On the surface of the skin they die within 5 minutes, but under the nails they live for 60 minutes or more. Urogenital amebiasis is expressed by the appearance of ulcers on the head of the penis and in the vagina. The lymph nodes in the groin area become inflamed.
How to avoid infection?
WHO annually organizes preventive activities in countries with the greatest prevalence of parasites. The primary problem is limited access to clean drinking water. In many countries, residents drink water, wash and water animals in the same fresh water body. You can avoid infestation by worms by following basic hygiene rules:
- wash your hands after every visit to the toilet;
- do not drink raw water from suspicious bodies of water, especially near pastures;
- do not swim in unfamiliar fresh water bodies;
- Wash consumed vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
The development of world tourism leads to the spread of parasites from endemic countries. When staying in a foreign country, you should be careful when consuming unfamiliar foods and drink only bottled water. After visiting regions with a high level of parasite prevalence, it is worth taking a urine and stool test for eggworms within 1-2 months.
| Papules and itching appear on the skin where parasites have invaded. Often these symptoms are mistaken for dermatitis. After 5-6 days, the skin becomes smooth and clean. After two to three weeks, a cough begins as the parasites migrate to the lungs. The cough may turn into suffocation. Then pain in muscles and joints occurs. |
| The appearance of blood in the urine, abdominal pain, irregular bowel movements, blood in the feces, alternating constipation and diarrhea. |
Types of helminths
Typically, worms settle in the human intestines, finding in it everything necessary for life. Detection of helminths in the urine of adults or children is much less common. Microorganisms do not like large amounts of liquid. However, there are types of worms that live in the genitourinary system. If you do not pay attention to this and delay treatment, the consequences will be serious illness.
Scientists have identified a worm called the “helminth Schistosoma,” and the disease is called “schistosomiasis.” Medical reference books may call the same disease slightly differently: snail fever or bilharzia.
Schistosomiasis is considered an infectious disease caused by worms. According to statistics, it more often affects adults who have agricultural professions and are employed in fishing. Among those suffering from this disease, there are also children who do not observe personal hygiene when they swim in dirty ponds with an abundance of various worms. There are 2 forms of the disease: genitourinary schistosomiasis and intestinal.
Read about the symptoms of parasites in the intestines here.