Excludes: renal pelvis (D41.1)
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
A urethral polyp is a benign neoplasm of the urethra. The ICD10 code is N34.2. Women suffer from urethral polyps approximately 1.5 times more often than men. This is explained by the anatomical features of the urethral mucosa. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose the disease using modern research methods.
Urologists take an individual approach to the choice of surgical method for removing polyps in the urinary canal. Before surgery, antibacterial therapy is carried out with the latest generation antibiotics. Complex cases of urethral polyps are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. The medical staff is attentive to all the wishes of patients.
Description
Urethral polyp.
A benign, round, pedunculated neoplasm arising from the epithelial layer of the wall of the urethra. Clinically manifested by pain, burning in the urethra, a feeling of mechanical obstruction when urinating, sometimes bloody or purulent discharge, acute urinary retention. Diagnosed by examination and palpation of the genital organs. If a urethral polyp is suspected, but it is not in direct visibility, urethroscopy, ultrasound, and urethrography are performed. Treatment is predominantly surgical: transurethral resection, cryodestruction, radio wave excision, electrocoagulation.
Additional facts
Polyps are the second most common (after papillomas) benign neoplasms of the urethra in male patients and the most common in women. According to statistics, about 4% of all urological patients, or 400 people per 10,000 population, consult doctors with this pathology. With age, the risk of morbidity increases. The peak occurs at 55-60 years of age, which is facilitated by previous urogenital infections (chlamydia, mycoplasmosis), deterioration of blood supply to the urethral wall during genital atrophy. The incidence of polyps in women is 1.5 times higher due to the anatomy of the female urinary system and the general tendency to develop epithelial tumors, especially against the background of hormonal disorders after menopause.
Urethral polyp
ethnoscience
As an effective addition to the main treatment, some traditional medicine can be used. They are often aimed at strengthening the immune system and suppressing the inflammatory process. Before using homemade products, you should consult your doctor.
Celandine
Celandine juice is often used to treat various neoplasms (benign). This medicine is also believed to be effective for urethral polyps.
Alcohol mixture
For preparation you need freshly squeezed plant juice and vodka. Liquids are taken in equal proportions and mixed thoroughly in a glass container (vial, jar, bottle). The finished mixture is taken 20 drops before meals 1-2 times a day, for 40-45 days. Then you need a week's break and then repeat the course.
Tampons with celandine juice
If the neoplasm is located at the entrance to the urinary opening, you can use sterile swabs moistened with plant juice to apply to the polyps. The procedure should be performed with caution, avoiding tissue injury.
Infusion
A dried suspension (finely or coarsely ground) of celandine in the amount of 30 grams (1 tablespoon) is poured with 200 grams of boiling water. Cover the container with the mixture with a lid and let it brew for 40 minutes. Then, the infusion is placed in a water bath and slowly heated for 30 minutes. The finished product is used for healing baths. You can use it every other day for 7-10 days.
Celandine juice gives a cauterizing effect, so the use of any product based on this medicinal plant should be carried out strictly according to the instructions, after consultation with the doctor.
Causes
The main mechanism for the development of urethral neoplasms is increased proliferation of mucosal cells, which occurs as a response to the effects of damaging agents. Provoking factors for the formation of polypous growths are chronic stress, poor diet, sleep disturbances, and bad habits. The main causes of polyps are: • Damage to the urethra.
Pathology develops under the influence of physical and mechanical factors.
In urology, damage to the urethra is possible as a result of operations on the genitourinary system or injury from stones due to urolithiasis, in gynecological practice - during termination of pregnancy, difficult childbirth, complicated by perineal rupture of varying degrees of severity. • Urinary tract infections.
The infectious process is always accompanied by an inflammatory reaction, which leads to a decrease in the function of damaged cells.
Mediators and components of inflammation enhance carcinogenesis, initiating the formation of tumor cells and increasing their survival and ability to penetrate neighboring tissues. The main infections that cause the formation of polyps include gonorrhea, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, and chronic urethritis of nonspecific etiology. • Hormonal imbalances.
According to observations, persons with endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism) and women in menopause are more susceptible to the formation of benign urethral tumors.
The postmenopausal state is characterized by a gradual decrease in the function of the female reproductive glands and a decrease in the production of estrogens, which have a stimulating effect on the antitumor immunity of the genitourinary system. • Hereditary predisposition.
The human genetic apparatus contains areas responsible for normal cell division and differentiation. When the genes of these areas are mutated, the production of regulatory proteins of irregular structure is stimulated and are unable to perform their functions of controlling the cell population. Pathological changes in the genome are passed on to offspring, so a history of urethral polyps in parents increases the risk of morbidity in children.
Preventive measures
Even benign tumors cannot appear out of the blue. Therefore, disease prevention should be done. The rules that doctors have developed are as follows:
- It is necessary to use only high-quality barrier contraceptives.
- You should have one sexual partner.
- It is necessary to limit salt intake.
- You need to eat right, especially reduce your intake of fatty foods.
- Protein foods should also be reduced, and emphasis should be placed on plant foods - fruits and vegetables.
- Every year you should undergo a routine examination with doctors of different specializations, as well as take the necessary tests. This will protect you from many ailments, including the formation of polyps in the urethra.
If a person is diagnosed with urethritis and prescribed a course of antibiotics, then this treatment should not be ignored, even if the symptoms have become less noticeable. Remember that chronic urethritis often provokes the formation of polyps. If you ignore antibacterial therapy, the inflammatory process will not disappear, but will grow with renewed vigor. All this affects the growths that appear in the urethra and other areas of the genitourinary system.
Pathogenesis
At the moment, there is no consensus on the mechanisms of polyp development. Most often, the process manifests itself as a result of inflammatory, traumatic, trophic damage to the urethral mucosa against the background of impaired humoral and cellular antitumor immunity. This leads to active tissue proliferation, a decrease in the degree of cell differentiation and their immunity to apoptosis (physiological death). Additionally, the relationship between the mucous membrane and the underlying layers of the urethra is disrupted, and the effectiveness of the regulatory mechanisms of the endocrine and nervous systems decreases. Polyp tissue contains more actively dividing cells (up to 40%) than normal tissue (5%), which causes rapid growth of the tumor. As the tumor increases, the percentage of undifferentiated, genetically damaged cells increases, which under unfavorable conditions can lead to malignancy - the development of urethral cancer.
Classification
Urethral polyps are divided into several types depending on etiology, quantity, and tissue structure. Determining the type of polypous lesion is an important point when choosing further treatment tactics. In men, polyps are usually localized in the distal part of the urethra or at the exit from it and are pedunculated formations no larger than 0.5 in size. In women, tumors more often form on the posterior wall of the urethra, often spread to the vaginal tissue and are large in size - from 1 to 10 Based on the type of cellular structure, there are 2 types of polyps: • Fibrous.
The tumor consists of dense connective tissue with a minimal number of vessels and glandular cells.
More often this is a single formation that develops against the background of infectious, inflammatory processes or when the trophism of urethral tissue is disrupted. There is a slow growth of the polyp, rare cases of germination into adjacent layers, and a low risk of malignancy. A subtype of fibrous polyp is the urethral caruncle in women, also consisting of elastic connective tissue, but well vascularized. • Ferrous.
It is a nodular neoplasm consisting of glandular tissue into which blood vessels profusely grow. Histological examination also reveals cysts - cavities filled with serous fluid or secretion. A glandular polyp often develops with hormonal imbalance, is characterized by rapid growth and a tendency to infiltrative penetration into the underlying layers of the urethra. According to the etiology of the process that caused the formation of a pathological focus, inflammatory, neoplastic (from atypical cells), and hyperplastic (due to the proliferation of healthy tissue) polyps are distinguished. Regardless of the type of neoplasm, it is necessary to monitor its dynamic development. The risk of a benign polyp turning into a malignant one always exists, especially with rapid growth and a large size of the tumor focus.
Reviews
Only a doctor can choose the right course of treatment. He will be able to carefully analyze the situation based on the test results. Self-medication will not only not give results, but can also lead to serious complications.
Feedback from patients who underwent treatment:
Victoria, 50 years old “I was discovered to have a polyp in my urethra measuring 0.1 mm. The doctor decided to monitor his further development. I used sea buckthorn suppositories to relieve inflammation. After the course, the formation came out in the form of a blood clot. The polyp is gone. However, after 2 years, at the next study, its size was already 0.5 mm. I refused cryodestruction, so the operation was performed.”
Victor, 45 years old “Due to constant inflammation, a polyp has formed in the urethra. I had to have surgery. It was performed under general anesthesia. I walked away from him easily. To eliminate the inflammation, I had to undergo a course of IV drips. 5 years have passed and there have been no relapses.”
Oksana, 35 years old “A polyp in the urethra formed as a complication of chronic kidney inflammation. It was decided to carry out electrocoagulation. The intervention is practically painless and is performed under local anesthesia. After finishing the procedure, I went home 4 hours later. I’m waiting for histology and selection of a course of treatment.”
Symptoms
Benign urethral tumors, including polyps, develop more often after 45 years. In the initial period, manifestations are completely absent or insignificant: there is a slight burning sensation when urinating, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Patients often mistake symptoms for another disease of the genitourinary system with a similar clinical picture, for example, cystitis or urethritis. As the size of the polyp increases and inflammatory changes occur, the symptoms increase, which forces the patient to consult a doctor. The main signs of the pathology are difficulty urinating, pain, burning in the urethra during sexual intercourse, and when walking. Possible urinary incontinence during coughing, sneezing, laughing, and the appearance of blood when the tumor grows into the submucosal layers of the urethra. In the later stages, an infection may occur, which, rising up the urinary tract, leads to pyelonephritis and the appearance of purulent discharge from the urethra. Cough. Malaise.
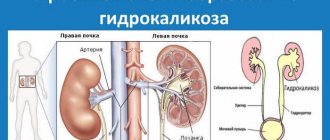
Bladder polyp: ICD-10 code, signs and treatment
Any formations on the mucous membrane of the bladder organ that rise and enter its cavity are called polyps of poor etiology.
Often bladder polyps have a very thin stalk, but there are types without it. The international classification of the disease ICD 10 has defined a special code for this disease - D41.
4 in the section of formations of unknown etiology or uncertain nature in the urinary organs, category D41.
What is a polyp called?
In some cases, mucous tissue in the membranes of the organ can grow, expanding its area and forming growths.
Polyps in the bladder in women, as well as in men, are dangerous, since they often degenerate into tumors of malignant etiology and develop oncology, and also in the case of proliferation of mucous tissue at the entrance to the ureter (ureteral polyp), a barrier is formed to the natural outflow of urine, formed by the kidneys.
Loading …
If a polyp is detected in the bladder, diagnosis and treatment require knowledge of its shape and size, as well as its exact location.
Why do growths form inside the bladder?
Polyps often form inside the walls of the bladder in women, children and men for the following reasons:
- the patient’s genetic predisposition to the occurrence of this disease;
- failure of metabolism and processes in organs and their tissues, especially in the bladder, the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the body;
- long-term use of tobacco, which provokes the development of polyps;
- poor environmental conditions in the place where a person lives.
Of these factors, the most significant is genetic predisposition, while patients who have information about a similar disease in the family need to use this information as an indication for action and be examined by doctors as often as possible.
When examined, polyps in the bladder in men are most often tied to the patient’s age. In the case of hereditary diseases, it is necessary to understand that if such a pathology appears in relatives at the age of 40, the patient must also undergo regular examination upon reaching this age.
More on the topic: What causes increased protein in the urine?
Symptoms
The resulting polyps in the bladder usually do not show symptoms, so the patient does not know about the development of the disease in his body. Treatment of concomitant diseases and their diagnosis accidentally reveal these growths. When they degenerate into oncological ones or acquire a large pathology, the destruction of the formations begins, while the patient notes a number of signs:
- The urine released becomes pink, which indicates bleeding at the site where polyps are attached to the walls of the bladder. The blood may be visually invisible to the patient himself, but during laboratory testing, specialists detect the manifestation of hematuria;
- When the growth is localized on the ureter, a problem arises with the movement of urine from the kidneys to the bladder, which is felt by patients as discomfort and problems with urination, as well as pain during deurination. (These symptoms are often mistakenly perceived as cystitis);
- Patients note frequent inflammation in the bladder with its accompanying symptoms.
What diagnostic methods are needed to detect polyps?
To identify polyps, the following methods of examining the patient’s body are used:
No. Useful information
| 1 | ultrasound examinations that determine the pathology itself, its size, shape and structure of polyps |
| 2 | The patient’s urine is collected for laboratory testing for many indicators that identify problems in the genitourinary area |
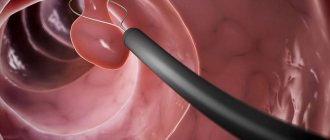
| 3 | Cystoscopy, an endoscopic method, is performed to clarify information about the growths, while the manipulation determines the etiology of the formation and excludes oncology. Specialists insert a small camera into the cavity of the bladder through the urethra, transmitting an image of the inside of the organ to the monitor. Thus, the doctor receives maximum information about the size and other parameters of the growths. Part of the tissue is also taken for biopsy. |
| 4 | Cystography can also serve as a method for diagnosing polyps. An examination using X-ray equipment involves the use of a contrast agent, which is injected into the bladder. After it is filled, an examination takes place, during which, thanks to the strong contrast, any formations on the internal walls of the organ become visible. |
More on the topic: How is bladder cystostomy performed?
How are polyps in the bladder treated?
If the growths are not very large, they do not interfere with the functioning of the bladder; in this case, they can not be removed promptly, but simply observed regularly, monitoring the change.
Surgical treatment
Indications for surgery are usually the following:
- an increase in pathology, multiple formation of growths, changes in their size during observations. In this case, the neoplasm begins to penetrate into the organ cavity;
- discharge of blood in the urine, which indicates bleeding or necrosis of the polyp at the site of its connection with the walls of the bladder;
- the formation of growths interferes with the natural removal of fluid from the body; located at the entrance to the ureter, they close the lumen;
- in the case when the neoplasm degenerates into malignant and threatens the development of oncology.
Conservative treatment
At the moment, traditional medicine has not developed methods for drug treatment or conservative treatment of neoplasms in the form of growths on a stalk in the bladder.
All patients who are trying to monitor their own health must adhere to the recommendations of specialists on changing their diet and habits in order to maintain health and prevent relapse after undergoing surgery to remove benign tumors.
To do this, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods with chemical components that form mucus in the body, as well as carry out comprehensive treatment of all inflammatory processes that have arisen. Traditional medicine specialists recommend taking celandine tinctures, increasing the amount of parsley and dill in your daily diet, and also trying to drink herbal infusions instead of tea and coffee.
How do surgeons remove polyps?
Removal of bladder polyps and similar benign formations is performed using endoscopy and a cystoscope. A diathermocoagulator is a special device inserted through the urinary canal into the cavity of the bladder organ.
The surgeon performs the operation with this device because there is a small loop at the end of the device. The entire operation takes place under strict control of equipment and video surveillance. The polyp in the bladder is wrapped in a loop, heated to a temperature determined by specialists, after which the formation is cut off from the place of its attachment in the wall.
Due to the increased temperature, the vessels of the injured tissue are sealed and the tissue of the walls in the bladder remains intact. For the patient, these actions remain only the stories of specialists, since at the time of the manipulation he is under general anesthesia.
More on the topic: What is the bladder sphincter?
The surgical intervention takes place with little bleeding, since the vessels are sealed and bleeding does not open. After such removal, the patient must be examined and observed by the attending physician for a long time.
Recovery after endoscopic operations for patients is characterized by a short period, while the usual active life begins very soon. Experts recommend that after such manipulations, regular examinations are carried out once every six months, eventually moving to a frequency of once a year.
Disease prognosis
In clinical practice, it has been proven that in one case out of 10 in patients with growths in the cavity of the bladder organ, they transform into a malignant formation. This can be avoided if the polyp is removed in time.
In some cases, re-formation of growths is possible, which depends on their type in the body of a particular patient. In some cases (9%), there are specific growths that recur after successful surgery; in general, tissue regrowth occurs in 70% of patients with such an identified disease.
BLADDER PROBLEMS? Folk remedies will help!
Rate this post: Loading…
Source: https://onefr.ru/organy/mochevoj-puzyr/kak-lechatsya-polipy-v-mochevom-puzyre-u-muzhchin.html
Possible complications
The main danger of a benign tumor process is its possible malignancy. The risk increases with a hereditary predisposition or the presence of other tumor foci. Another complication is the development of chronic cystitis, urethritis or inflammatory kidney damage. A urethral polyp reduces the immunity of the urinary system, making it more susceptible to infections. Tumor growth into blood vessels leads to disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane and bleeding - hematuria syndrome. In men, hematospermia (blood in the ejaculate) may occur. Long-term chronic blood loss leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Prevention
It is not possible to prevent the development of a congenital polyp, but the risk of its occurrence is reduced if pregnancy takes place in favorable conditions, without exposure to aggressive factors on the expectant mother and fetus.
Measures to prevent acquired urethral polyp are:
- avoiding injury to the urethra, and if it occurs, adequate treatment;
- prevention, detection and treatment of infectious and congenital pathologies that can provoke the development of this neoplasm;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely emptying of the bladder;
- regular preventive examinations with a urologist.
Diagnostics
A small urethral polyp in the absence of a urological infection does not produce pronounced symptoms, and the existing manifestations in the form of slight pain or burning in the urethra are nonspecific. It is discovered by urologists or gynecologists by chance at a preventive appointment or during an examination for another pathology with similar symptoms. Diagnosis of urethral polyp includes: • Objective examination.
A history and existing complaints are collected, information about previous diseases of the excretory system, genetic predisposition is identified, and the genital organs are examined.
Visually and by palpation, the polyp of the urethra has a smooth surface, soft structure, pink color without dark areas. • Laboratory methods.
General clinical examinations include blood and urine tests to identify signs of inflammatory processes in the body.
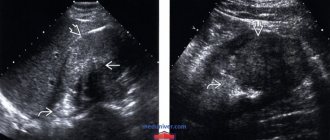
Biomaterial is collected from the urethra and vagina, followed by bacteriological analysis. Histological examination of the tumor site (biopsy) helps to identify the type of polyp and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one. • Ultrasound of the urinary system.
A simple, safe, fast method for the early diagnosis of urethral polyps.
Detects tumors of the urethra and bladder due to their different echogenicity from healthy tissue, as well as the degree of blood supply. Ultrasound machines with elastography function additionally evaluate the microstructure of the tumor, which makes the study more accurate. • Cystourethroscopy.
The diagnostic procedure allows you to visually determine the condition of the excretory tract, bladder, and identify the presence of polyps, clearly visible against the background of the unchanged canal wall.
It is also possible to collect material for histological examination and perform simple therapeutic manipulations (removal of stones, irrigation of foci of infection with antiseptics). • Urethrography.
A modern research method in which the urethra is filled with a liquid or gaseous X-ray contrast agent. After a few minutes, a series of x-rays of the urethra is taken, allowing one to assess the diameter of the lumen of its various parts and the presence of narrowings, the condition of the mucosa, the size and localization of tumors.
Preparatory activities
Before prescribing surgical intervention, a whole range of diagnostic measures must be carried out.
Among the effective research methods are the following::
- General clinical tests (blood, urine, feces);
- Echocardiography or ECG to assess the functions of the heart and blood vessels;
- Examination by a gynecologist or urologist;
- Carrying out urethroscopy (endoscopic diagnostic method);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Considering that polyps form against the background of existing pathologies, mandatory treatment of infectious processes takes place, with the exception of cases requiring emergency surgery due to stagnation of urine.
Based on the totality of the data obtained, they formulate the tactics of the treatment process, the type of intervention and assess the degree of risk of various postoperative complications.
Treatment
In the presence of concomitant diseases, small size of the formation without a clear clinical picture and the elderly age of the patient, treatment is limited to observation and treatment of the local inflammatory process or correction of hormonal disorders. Surgical intervention is necessary if the urethral polyp bleeds, obstructs the passage of urine, or grows rapidly. The main methods of performing operations are: • Surgical removal.
When performing surgical interventions for polyps, wedge-shaped excision of the tumor with a conventional scalpel within healthy tissue is most often used.
The manipulation is performed under general anesthesia followed by suturing. If the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach place or at the base of the urethra, endoscopic techniques can be used. In this way, mainly large (from 1 cm) or potentially malignant polyps are removed. • Physical destruction.
Several types of effects on polyp tissue are used. With the radio wave method, the tumor is destroyed under the influence of directed high-frequency radio radiation, the impact of which leads to a thin tissue incision. Damaged vessels instantly coagulate and do not bleed. Radio wave removal is a modern painless method that does not leave scars and ensures rapid tissue restoration. Electrocoagulation, laser removal, and cryodestruction of polyps are also used. These methods make it possible to use local anesthesia, accurately adhere to the boundaries of the tumor, and minimize damage to healthy tissue. After the operation, the patient is fitted with a urinary catheter for two days so that the aggressive environment of urine does not damage the surgical wound and slow down regeneration. The excised polyp tissue is sent for histological examination to exclude tumor malignancy. The patient is incapacitated for 4-5 days after the operation, after which he can fully return to work.
Cost of removing urethral polyp in women
The operation is performed only by experienced ON CLINIC specialists. Laser or radio wave equipment of the latest modifications is used. The highest qualifications of our doctors and the most advanced equipment allow us to exclude any complications.
You will be able to undergo all the necessary tests in the shortest possible time, since ON CLINIC has all the necessary diagnostic equipment, including its own modern laboratory, and we never have queues.
If necessary, you can use a hospital, which is called one of the most comfortable in Moscow.
The final cost of an operation in our medical center depends on the category of complexity of each specific case, the number of necessary studies, the wishes of the patient, etc.
ON CLINIC provides world-class medical services at reasonable prices and guarantees an absolutely transparent pricing policy that excludes the imposition of unnecessary services.
Trust your health to professionals! ON CLINIC