Every man in his life has encountered such a phenomenon as discharge from the urethra. They can be clear or yellowish, white or bloody, with or without an odor, abundant or minimal, and are not always a cause for concern. This is why it is so difficult to track the onset of the disease in time - if a person is not used to monitoring his health, he may not notice that the process has crossed the border of the norm and has become pathological.
To prevent this from happening and the patient does not have to deal with the consequences of a completely advanced disease, every man should know which discharge from the urethra is normal and which should cause concern.
Normal urethral discharge in men
In some cases, discharge may appear from the external opening of a man’s urethra, which does not indicate a pathological process, but, on the contrary, indicates the normal state of the man’s body.
- During strong sexual arousal, a small amount of mucous transparent discharge (literally a few drops) can be detected on the head of the penis. This fluid is secreted by the urethral glands and is designed to protect the inner surface of the urethra. It is important to remember that we are talking about discharge in a state of strong arousal or during a physiological morning erection.
- The release of sperm, both during sexual intercourse and outside of it (emission).
- Defecational prostatorrhea is the appearance of discharge from the external opening of the urethra during strong straining during defecation. This can be explained by the peculiarity of the location of the internal organs in the male pelvis. The prostate is adjacent to the anterior wall of the rectum and during the passage of feces is somewhat compressed, which leads to the release of its secretions.
- Victory prostatorrhea – discharge of prostate secretion after urination (in a small amount).
There are still disputes about the last two cases in some medical circles, but provided that the gland is in a normal state (as confirmed by ultrasound and analysis for the content of prostate-specific antigen), they do not indicate the presence of a pathological process in the male genitourinary system.
As you can see, all the above reasons are not a frequent and long-lasting phenomenon. Rather, they can be called episodes. Therefore, doctors believe that the external urethral meatus in healthy men should always remain dry and clean.
Prevention
There are a number of preventive recommendations. First of all, you should take care of your personal intimate hygiene. A negligent attitude can result in the development of many dangerous diseases. It is necessary to wash the head of the genital organ daily with laundry soap, removing accumulated smegma from the surface. The procedure should be performed twice a day (morning and evening). To avoid contracting sexually transmitted diseases, you should use contraception when having sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner. In addition, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive medical examination at least once a year, which will help to promptly identify and eliminate possible health problems.
What should be a cause for concern?
Men, in most cases, know their bodies well and are able to quickly understand that something is not happening as usual. This is facilitated by the male anatomy - the external genitalia are clearly visible and accessible to inspection by the patient himself. As soon as the discharge changes in quantity, consistency, color or smell, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis. It is better to spend a few hours and make sure there is no cause for concern than to allow the situation to worsen.
- Pathological discharge may be gray, white, green, yellow or even brown.
- The presence of blood is always a serious cause for concern and an immediate visit to the doctor.
- An unpleasant odor coming from the penis may indicate bacterial activity.
- In most cases, pathological discharge is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the urethra: pain, burning, discomfort. All manifestations are especially intensified during and immediately after urination.
- In some cases (chlamydia, for example), the discharge is practically no different from normal. Due to this, they may not be noticed by the patient for a long time, which poses a threat of the disease becoming chronic.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis in men is not as common as in women, and it indicates, first of all, that the stronger sex has a reduced immune system. In most cases, this occurs due to taking high doses of antibiotics or chemotherapy. The reasons for its appearance must be sought in the man himself, through diagnostics of the body.
If there is discharge, a man should in any case consult a doctor. Having considered the patient’s complaint, the doctor will first of all direct him to undergo tests, which will be examined in a special laboratory. It is the laboratory method that can detect infectious agents such as Trichomonas or gonococcus. Often tests confirm the presence of yeast fungi.
In addition to tests done using a microscope, men culture the secretions in a nutrient medium, which is how some types of infection are determined. All this helps to choose the right therapy.
Antibiotics are the main method of treatment for discharge. If the diagnosis is not established, antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action are used. When the cause of thrush is identified, the urologist prescribes specialized medications. It is important not to self-medicate after the appearance of discharge, because it still will not give a good result, but will only aggravate the symptoms and illness.
What should alert the patient to the presence of discharge?
The patient cannot always immediately pay attention to changes affecting his genitourinary system. Of course, if their urethra secretes fluid or mucus throughout the day and in large quantities, then the man will notice it very quickly. Also, the detection of discharge is accelerated by its color other than transparent, and the presence of unpleasant sensations, pain and stinging.
However, more often there are situations when only a small amount of liquid or mucus is released during the day, which is difficult to notice. At the same time, everything is also complicated by periodic urination, during which the discharge is removed along with the urine and it may seem that there is less of it than there is.
- You need to be especially careful in the morning, because during the night a man normally does not visit the toilet, and the discharge manages to accumulate in quantities sufficient to be detected.
- If you press on the urethra in the direction from the base of the penis to its head, you can squeeze out a certain amount of liquid out.
- The sticking of the sponges of the external opening of the urethra or the formation of crusts on them may indicate the slow release and drying of some fluid.
- Underwear can also carry a lot of useful information. Even if during the working day one drop of mucus is released from the urethra, it will definitely have time to dry and leave a noticeable mark on the tissue.
- Sometimes discomfort or discharge is provoked by a certain error in the diet - drinking alcohol, eating food with a lot of spices.
- Casual sexual intercourse should force a health-conscious man to monitor his condition more closely in the following weeks, since most sexually transmitted diseases manifest themselves in this way.
You can also carry out the following test yourself: the first portion of urine is collected in a transparent container and carefully examined. If the patient has a discharge, threads or flakes will be found in the urine that are not normally present in the urine.
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient needs to contact a medical center. During the initial examination of the penis, the doctor will assess the condition of the penis, foreskin, and identify the presence of a rash, deformation of the organ, swelling and other signs.
The urologist will also assess the condition of the lymph nodes using palpation. The size of the prostate and the presence of an inflammatory process in the glandular tissue is indicated using a rectal examination.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Finger examination. Used to assess the condition of the prostate gland. Rectal penetration is sometimes used as a method of treating prostatitis. The doctor feels the presence of lobes, tissue density and size.
- Laboratory research. General tests are prescribed. Elevated white blood cell counts are a sign of infection.
- Smears for microscopic examination and culture. At the same time, the accuracy of the study is high; mycoplasma, candida fungi and other pathogens can be detected on the mucous membrane.
- PCR method (polymerase chain reaction). The study helps to detect sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), pathogens such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, and detect gonorrhea, herpes or syphilis.
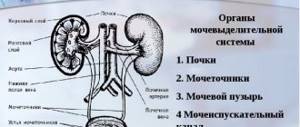
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Helps detect inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Ultrasound reveals the exact size and condition of organs and the presence of tumors.
- CT scan. It is prescribed to confirm or refute an existing diagnosis. Usually indicated for complicated and severe diseases.
- Biopsy. It is prescribed if a neoplasm has already been detected on the prostate gland or other organ. The study helps determine whether cells are malignant or benign.
Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed. The more serious the problem with men's health, the more procedures you will have to undergo. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations in order to identify the disease in time.
What could the discharge indicate?
In urology and venereology, discharge is one of the most obvious, important and first symptoms of the disease. Doctors can get a lot of information by studying the fluid released and even make a diagnosis without additional examinations.
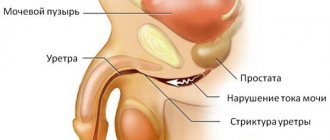
- The most common cause of this phenomenon is inflammation of the urethra - urethritis. At the same time, the mucous membrane of the urethra tries to protect itself and produces a significantly increased amount of mucus with the help of its glands. Urethritis can be of either infectious etiology or non-infectious (with severe hypothermia, for example).
- Specific infectious agents are bacteria that cause sexually transmitted diseases and are sexually transmitted. This group includes pathogens of gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis.
- Nonspecific bacteria - can be introduced into the genitourinary tract from other organs under certain conditions (the presence of a powerful inflammatory focus in the pelvic cavity, weakened immunity, injury, non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene by a man).
- Urethritis can be caused by chemicals and crystals that appear in the urine when stones form in the kidneys. In response to mechanical or chemical irritation of the urethral mucosa, an inflammatory reaction is likely to develop.
- Oncological pathology of the prostate is a serious disease that can cause discharge mixed with blood.
- Penile cancer can also cause inflammation of the urethra.
Associated symptoms
Excretory processes accompanied by an unpleasant odor or the appearance of other symptoms may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted or inflammatory diseases. You can suspect trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, balanoposthitis, gonorrhea or urethritis.
Associated symptoms:
- difficulty urinating,
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder,
- the appearance of pain syndrome,
- unpleasant smell,
- the appearance of pus and blood,
- itching and burning in the urethra, on the head or in the foreskin,
- erectile disfunction.
If you experience difficulty urinating, lack of sexual desire, increased urge to go to the toilet and a feeling of incomplete emptying, prostatitis can be suspected. Pain, burning and itching are common symptoms characteristic of any disease. The smell indicates the proliferation of microorganisms on the mucous membrane of the penis.
What affects the color of discharge in men?
The transparency and color of the discharge directly depend on what processes are occurring in the man’s body. In any discharge from the urethra, three fractions can be distinguished: fluid, mucus and cells. The turbidity of the discharge depends on how many cells it contains. The cells also give the discharge a certain color.
- A large number of epithelial cells causes high viscosity and gray color of the discharge.
- Leukocytes rush into the inflammatory focus in large numbers when microbes multiply and color the discharge yellow or green.
- White and dense masses, sometimes resembling cottage cheese, speak in favor of male candidiasis (thrush).
- It is important to understand that the same disease at different stages can manifest itself with discharge of different nature. At the initial stage, the patient is likely to experience clear or slightly cloudy discharge. Afterwards, the body has time to react and sends leukocytes into the inflammatory focus, which change color towards yellow or green.
Passing the examination
If a man notices the appearance of atypical discharge, he should consult a doctor. Typically, the examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The specialist examines the penis, perineum, glans and foreskin. The purpose of the procedure is to identify deformation of the genital organs, signs of injury, rash, discharge or signs of inflammation.
- Palpation of the lymph nodes in the groin and assessment of their condition. Enlarged, painful, inflamed lymph nodes indicate the course of the pathological process.
- Prostate examination. The specialist massages her through the rectum, and also obtains secretions for microscopic examination. Before the massage, it is recommended to refrain from urinating for one to two hours. If prostate adenoma is present, the increase in lobes is approximately the same. Dense strands can be felt. If a man is diagnosed with a malignant tumor, it usually grows evenly. During palpation, blood with clots may be released from the urethra.
- Smears are collected for microscopy and culture. During the examination, blood cells, fatty inclusions, and sperm are visible in the stained smear. The procedure can also help identify a number of pathogens. If there is an increase in the number of white blood cells, this may indicate the presence of chronic inflammation or urethritis. If too many eosinophils are detected, the man may have an allergy.
- Taking a general clinical blood and urine test.
Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed. If there is not enough information to establish the pathology, the doctor may refer the patient for an ultrasound scan of the prostate, bladder and kidneys. Additionally, urography or CT may be performed.
Does the discharge fully reflect the nature of the disease?
Although doctors can immediately guess the cause of the discharge, they will never be able to make a diagnosis based on an external examination. It is necessary to analyze the secretions, examine them under a microscope, and culture them on a nutrient medium. The color, smell, quantity and consistency may be the same for different diseases. Previously, many pathologies were characterized by a rather specific clinical picture, but now there has been a loss of many of these features. Consequently, the symptom that several decades ago made it possible to make a correct diagnosis with 100% probability today only gives us the right to speculate.