Representatives of the stronger sex often do not pay due attention to their health, and consult a doctor only when unpleasant symptoms interfere with normal life. Redness of the urethra in men is an alarming sign that should not be ignored.
Such symptoms indicate inflammation of the urethra. The process of urination causes severe pain and discomfort to a patient with such a disease. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease will progress and lead to serious consequences.
Inflammation of the urethra. Source: cistitstop.ru
Redness around the urethra in men can be easily noticed when going to the toilet or performing intimate hygiene. The urethra consists of several parts, and each of them can become inflamed. Most of the urethra is located outside, so infections can easily enter it. The great advantage of the inflammatory process is the pronounced symptoms that appear in the first hours or days after infection.
Doctors identify several of the most common causes of infectious inflammation in the urethra. Provoking factors include:
- Bacterial damage. Infection occurs during intimacy with an infected partner. If the patient experiences additional burning and itching in the intimate area, chlamydia, gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted diseases can be suspected.
- Virus infection. Bubbles may appear on the patient’s penis and intimate area, which burst and turn into wounds. This causes severe pain to the patient and takes a long time to heal.
- Male thrush (candidiasis). Fungal microorganisms live in the body of every person, but in a latent state they are not dangerous. The manifestation occurs if the patient's immunity decreases. Additionally, the patient may be bothered by discomfort during urination and a white coating on the genitals.
- Poor hygiene. E. coli, streptococcus, and staphylococcus can provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
- Allergic reaction.
- Injury to the urethra during a medical procedure or during the advancement of stones.
- Prolonged exposure to cold.
Redness of the urethra due to STDs
Sexual infections are the most likely cause of redness.
There are many diseases that can provoke such symptoms.
It could be:
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis;
- herpes;
- candidiasis;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- papillomavirus;
- gardnerellosis.
Some diseases have characteristic manifestations by which they can be suspected.
Gonorrhea manifests itself in men with a sharp onset and profuse purulent discharge from the penis with an unpleasant odor.
But in women, discharge can be scanty.
And in 50% of cases they have no significant symptoms at all.
Trichomoniasis in male patients is manifested by inflammation of the urethra and liquid discharge from it.
In women, the disease is almost always combined with vaginitis.
- Urethritis in men: diagnosis of inflammation of the urethra, prevention of the disease
Vaginal discharge appears.
They are abundant, gray or yellow in color, foaming, with an unpleasant odor.
Upon contact with the skin, pinpoint hemorrhages and red spots appear.
Chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma infections do not have characteristic manifestations.
They occur with mild symptoms in more than half of the patients.
In addition to redness around the urethra, the following are noted:
- itching;
- slight clear discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Gardnerellosis usually causes balanoposthitis in men, and less commonly, urethritis.
This is an anaerobic infection.
It develops mainly due to immune deficiency.
- Urethral diverticulum
Other reasons
Redness around the urethra in men can also be caused by other, less common causes. Their comparative lack of prevalence does not mean that they are safe. As in the cases described above, all measures will need to be taken to eliminate the following factors:
- allergic reactions to low-quality lubricants or contraceptives. In this case, you need to reconsider your “arsenal” of love devices;
- allergies to medications, especially topical ones;
- allergies to cosmetics and detergents;
- mechanical injuries of the urethra - for this it is not necessary to hit the penis, it is enough to insert a catheter or allow foreign bodies to enter the urethra;
- urolithiasis - particles of stones are often excreted along with urine. Considering that these are abrasive substances, it is not surprising that they irritate and damage the urethra.
Urethritis, regardless of its form, various viral and fungal diseases, mechanical injuries and other problems that can provoke beauty around the urethra require a responsible approach to their treatment. It is very rare that something can go unnoticed for your health. Considering that we are talking about the reproductive system, if a characteristic symptom appears, you should immediately contact a specialized specialist to carry out the required diagnostic procedures and prescribe effective therapy.
Regardless of the reason that caused the redness around the urethra, a man should take all necessary measures to protect himself from possible complications, as well as further spread of infection (if any). It is strictly forbidden to continue living an intimate life; it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
After curing a discovered problem, it is advisable to thoroughly reconsider your lifestyle in order to prevent its recurrence in the future.
Source: pochke.ru
Redness of the urethra due to herpes
Herpetic infection begins with a prodromal period.
1 week after infection, the patient feels a slight tingling or burning sensation in the area where the rash will appear the next day.
It arises quickly, literally overnight.
Many blisters appear on the skin.
They are filled with clear liquid.
- Narrowing of the urethra in men and women: causes, symptoms, treatment
The pathological process primarily affects the external genitalia.
Bubbles appear on the penis, vulva, vagina, pubis, perineum, scrotum.
In 30% of patients, inflammation of the urethra develops.
Rashes appear inside it.
The person feels a burning sensation.
Urination becomes painful.
On examination, redness of the urethral sponges is noted.
Transparent discharge is possible.
Herpes infection is characterized by a recurrent course.
Once infected, a person becomes a carrier of herpes for life.
From time to time he experiences exacerbations.
As a rule, they are not as severe as with the primary infection.
How to treat urethritis in men
Treatment of this pathology is aimed at getting rid of infection and inflammation, but therapy depends only on the cause of its occurrence .
Based on this, treatment is selected for each patient individually.
The basis of drug therapy is the use of antibiotics, the most common of which is Monural, which is prescribed for bacterial, infectious and inflammatory forms of the disease.
But in addition to this, additional drugs are prescribed:
- antipyretic.
- anti-inflammatory.
- painkiller.
- medications aimed at improving the functioning of the kidneys and urinary tract.
If the disease is detected at the initial stage, then it can be treated at home , but if the pathology is in an advanced form, then hospitalization cannot be avoided.
In this situation, only a doctor can tell you how to treat urethritis in men.
During treatment, the patient must adhere to a special diet and avoid sexual intercourse.
In order to defeat the infection, it is absolutely forbidden to use general antibiotics, since it is important to take into account the strain of the bacterium.
Based on this, for the treatment of urethritis in men, drugs are prescribed individually ; the following can be used for these purposes:
Antibiotics of the nitroimidazole group:
- Metronidhol, which is effective for trichomonas urethritis, is available in the form of tablets, suppositories and injections.
- Secnidazole, produced in the form of granules, is effective in the fight against Trichomonas.
Antibiotics of the tetracycline group:
- Doxycycline, effective for gonococcal non-gonococcal urethritis, is available in the form of tablets, capsules and solutions that are taken orally or by injection.
Fluoroquinolones:
- Moxifloxacin, available as tablets or solution for infusion.
- Ofloxacin, like the previous drug, affects a large number of bacteria and is suitable for any type of disease .
- Levofloxacin, available as infusion solutions or tablets.
Triazoles:
- Fluconazole, which helps in case of candidiasis. This drug is available in the form of tablets, capsules, solution and syrup.
Quinoxalines:
- Dioxidin, which is indicated if there is no effect after treatment with other drugs.
Medicines for treatment
Macrolides:
- Erythromycin, this drug is safe and highly effective, is used orally and intravenously.
- Clarithromycin, which is a derivative of erythromycin.
But before starting treatment, you need to read the instructions for use , since most drugs have acute contraindications in the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment of urethritis in both men and women is carried out using conservative therapy, in which the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs - antibiotics. In addition, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapy is carried out simultaneously. If a patient is diagnosed with diseases of the genital area, these inflammatory foci are also eliminated in parallel. Women may additionally be recommended warm sitz baths using herbal remedies: chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus or a weak solution of potassium permanganate. As for sexual contacts, their number must be limited, or even better, temporarily stopped. In severe cases, the patient may be recommended to be hospitalized.
An indispensable component of successful treatment of urethritis should be a gentle diet. From the patient's diet it is necessary to exclude fried, spicy, salty, smoked, spicy foods - in a word, everything that irritates the urinary tract. It is also necessary to ensure that the amount of fluid you drink per day is at least one and a half to two liters. It is better if it is clean water or cranberry juice, which has excellent antibacterial properties and is recommended by experts as an additional means of combating urinary tract diseases.
During the acute phase of the disease, it is also advisable to avoid drinking coffee, alcohol and carbonated drinks.
What can be considered a criterion for recovery? Of course, your well-being will improve and there will be no symptoms of the disease. But if you want to protect yourself from the transition of urethritis to the chronic stage, you need to do tests after treatment and perform a control culture to make sure that it is the cause of the disease that has been eliminated, and not its symptoms. It should also be remembered that when certain infectious pathogens of urethritis, for example, gonococcus, are detected, both sexual partners are treated, regardless of whether symptoms of the disease are present in the second of them.
As measures to prevent the disease, you can use the recommendations of traditional medicine, which offers diuretics, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents: decoctions of lingonberry and currant leaves, linden tea, cranberry juice.
Redness of the urethra due to candidiasis
Candida is an opportunistic fungus.
It lives on the skin, intestines and genitals.
Candidiasis is the inflammatory process caused by this fungus.
In people with good immunity, such phenomena are rarely observed.
The disease is not severe.
Local antifungal agents are sufficient for treatment.
Most often the penis is affected in men, and the vulva and vagina are most often affected in women.
Much less often the urethra is involved in the pathological process.
This usually occurs when the clinical course of the fungal infection worsens.
In women, urethritis is observed only in combination with vulvovaginitis.
In male patients, inflammation of the urethra mainly develops against the background of balanoposthitis.
But sometimes isolated candidal urethritis also occurs.
Causes of this disease:
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- decreased immunity;
- HIV;
- hypothermia;
- weakening of the body due to serious illness;
- lack of adequate genital hygiene.
If redness of the urethral sponges is noted against the background of candidiasis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
This suggests that the disease is of moderate severity.
It can progress and cause complications.
In the absence of timely medical care, painful erosions and cracks in the genitals often occur.
They bleed, secondary bacterial flora joins.
Pustular elements (ulcers) appear.
A characteristic accompanying symptom of candidiasis is white thick plaques that are easily removed and have a sour odor.
Prevention of urethritis
For those men who want to prevent such unpleasant moments in their own lives, doctors give recommendations.
- Sexual relations should become safe. So either use condoms or stop messing around with your body. A larger percentage of patients received urethritis after a night with strangers. Remember that women do not have obvious signs of inflammation that can be examined before contact;
- Maintain personal hygiene. Don't share washcloths and underwear with your best buddies;
- Do not weaken your immune system by smoking, drinking alcohol or eating fatty foods;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Treat genitourinary diseases in a timely manner and undergo routine examinations with a urologist at regular intervals;
- Remember that even caries and sore throat can lead to inflammation of the urethra, so take care of your overall health;
- Avoid stressful situations, or try not to be in them for a long time. Hormonal disruptions can lead to imbalances in the functioning of internal systems and allow opportunistic pathogens to develop.
Redness of the urethra in Queyre's disease
Oncological diseases of the urogenital system include Queyr's disease. This is cancer of the mucous membranes.
Main localizations:
- penis head
- prepuce
- vulva
A red plaque appears. It has clear boundaries and a velvety surface. This is a non-invasive cancer and does not spread beyond the mucous membrane.
But if left untreated, it becomes invasive. It transforms into squamous cell carcinoma.
Redness of the urethra with urethritis
Urethritis is the name given to inflammation of the urethra of any origin.
We just discussed the many sexually transmitted infections that cause redness, pain, swelling, and discharge.
All of them occur in the form of urethritis.
In addition, this disease can be caused by representatives of nonspecific bacterial microflora.
Many bacteria live on the genitals or in other parts of the body (intestines, nasopharynx).
If they enter the urethra in large quantities, especially a damaged one, they can provoke nonspecific urethritis.
It manifests itself as redness and purulent discharge from the urethra.
Probable pathogens:
- coli;
- streptococcus;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella;
- staphylococcus and others.
Provoking factors:
- urethral injuries;
- insufficient genital hygiene;
- the presence of asymptomatic forms of sexually transmitted infections;
- local use of medications (antibiotics, glucocorticoids).
The disease is very dangerous.
Inflammation can spread to the overlying parts of the reproductive system.
Adequate therapy
The disease can be cured only with a complex of drugs, with additional vitamin support and traditional medicine methods. Several groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antibiotics against bacterial pathogens;
- Medicines that restore normal microflora;
- Immunostimulants – to support the immune system;
- Antihistamines - to avoid allergies and swelling;
- Antiviral drugs;
- Vitamin complexes;
- Herbal baths and compresses with anti-inflammatory and tanning effects.
The urethra is a unique organ in structure. All therapeutic instructions must be followed in full to avoid complications.
Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules
Unfortunately, this reason also occurs quite often. For some reason, many men do not understand that the cleanliness of their genitals must be monitored very carefully. Ideally, you should wash your pride at least once a day, and twice in the hot season. But in reality, basic hygiene procedures are performed much less frequently in many cases.
What does this lead to:
- to the appearance of saprophytic staphylococci,
- streptococci,
- Proteus,
- coli.
It is known that in normal quantities these microorganisms do not cause any changes in the tissues of the penis. However, a sharp increase in the number of their colonies is already fraught with serious problems. This is expressed in the appearance of characteristic diaper rash, an unpleasant odor and, accordingly, redness of the urethra.
The easiest way to deal with this reason is to regularly observe hygiene, namely, do not neglect the need to take a shower often (or even wash the genitals directly), regularly change underwear, wear panties only made from natural materials and ideally suited to their size.
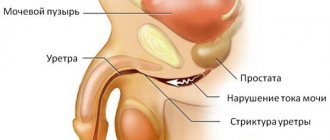
Redness of the urethra with prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland is most often caused by E. coli.
Less commonly, these are pathogens of sexually transmitted infections.
But most of them parasitize the prostate without causing significant symptoms.
The infection enters the prostate in various ways.
Its source may be the urethra.
This suggests that the man initially developed urethritis.
If he does not pay attention to the redness of the urethra, pain and swelling, and does not go to the doctor, then after a few weeks the infection will spread upward.
It ascends the urethra and reaches the prostate ducts.
The urethra is anatomically connected to this organ.
There are also the opposite situations, when prostatitis develops initially, and then the infection penetrates the urethra, causing its redness.
Bacteria enter the prostate gland from other sites in the body through the blood or lymph.
These lesions can be located anywhere, including in areas of the body distant from the prostate.
To identify prostatitis, the doctor palpates the organ through the rectum.
If necessary, he performs a transrectal ultrasound.
Inflammation of the urethra
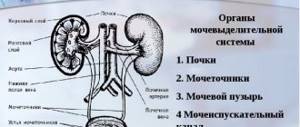
In men, the urethra is a long, hollow tube through which urine is drained from the bladder. The canal consists of three sections, and inflammation can begin in each of them. It is the external location of most of the tube that is already a favorable factor for infection. Any signs of an infectious lesion in men are clearly visible, practically from the first days of infection. Most often, the longest section running along the length of the penis is affected - spongy or spongy.
- The spongy section is a movable segment of the urethra, from 10 to 15 cm. It ends with an opening for urine excretion;
- The membranous or membranous section is the narrowest section, about 2 cm long, located between the base of the penis and the prostate gland;
- Prostate – It’s easy to guess that this section of the urethra is located in the prostate gland.
Sometimes a man may notice redness on the head near the urethra. Even if there are no other symptoms or pain, pathology is already suspected.
The reasons lie either in neglect of the rules of personal hygiene, or in an introduced infection. Urethritis manifests itself very quickly, although there are exceptions to this rule (we will talk about them later). Let's move on to consider the reasons.
Redness of the urethra with urethritis
Typically, redness around the urethra indicates inflammation of this organ.
This pathology is called urethritis. It can be caused by a significant number of etiological factors. These are injuries, tumors, burns, allergies, etc. But the most common cause is infection.
They can be nonspecific - when inflammation is caused by transient or resident microorganisms. That is, those that live permanently on the genitals, live in other areas of the body, or from time to time colonize the structures of the urogenital tract. In addition, redness of the urethra is caused by the genital infections we just discussed.
The cause cannot be determined by the symptoms. This requires laboratory tests. But assumptions can be made based on clinical signs.
Redness of the urethra and purulent discharge most likely indicate gonorrhea. Especially if the discharge is copious. But if it is scanty, nonspecific urethritis may be the cause.
It can cause enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes. Redness of the urethra and mucous discharge indicate chlamydia, mycoplasmosis or ureaplasmosis.
The appearance of an unpleasant odor may indicate gardnerellosis or trichomoniasis. Redness of the urethra due to inflammation of the paraurethral glands
The paraurethral glands, as well as their passages, may also be involved in the pathological process. In this case, the symptoms of dysuria intensify. There is pain when urinating. The discharge becomes abundant. Complications may develop.
Most often they occur against the background of gonorrhea or nonspecific infectious processes. Abscesses of the paraurethral glands appear. Urethral diverticula may develop.
Nonspecific chronic form of urethritis
This form is not as easy to cure as the infectious form. Accompanying diseases are often added to the chronic pathology, and the symptoms of urethritis are not pronounced or are absent at all. Treatment should begin with the use of immunostimulants. They will help stimulate the body's defenses and quickly cope with the disease. Later, individually agreed antibacterial agents are used. A feature of the treatment of nonspecific urethritis is that the second half does not need to be treated.
Redness of the urethra with cystitis
Bladder inflammation is mainly diagnosed in women.
Male patients are usually spared this disease.
The main causative agent of acute cystitis is Escherichia coli.
It initially enters the urethra.
Basically, bacteria penetrate there from the intestines.
Then it rises upward and provokes cystitis.
This is favored by the special structure of the urethra in women.
They have it short and wide.
Symptoms appear:
- frequent and very strong urge to urinate;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain in the pubic area.
Symptoms are also noted from the urethra.
There is redness and pain.
What is the difference between specific and nonspecific urethritis?
Diseases that arise due to infection, at an early stage of their development, occur with symptoms of a non-infectious disease, after which signs of an infectious complication appear. Among the pathogens there can be specific and nonspecific species, and in the case of the latter, pus is formed.
Nonspecific bacterial urethritis is caused by streptococci or Escherichia coli, as well as staphylococci and similar infections. Specific urethritis is caused by gonorrhea, fungi, trichomonas, chlamydia, miplasmosis. Infection occurs through the reproductive tract, hematogenous or lymphogenous.
If it spreads through the lymph flow or blood, the infection enters the urinary canal through lymph or blood, especially if the body already has chronic diseases. Most often, infections affect the tonsils, which leads to sore throat, as well as the teeth, which can lead to caries.
More on the topic: How is an ultrasound of the bladder performed?
Classification
Acute and chronic urethritis in women is classified according to several criteria. So, according to etiology they distinguish:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
The infectious form of the disease occurs:
- nonspecific urethritis - most often provoked by Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci;
- specific - sexually transmitted, trichomonas urethritis is more often diagnosed in women;
- viral - provoked by HPV or herpes virus.
According to the nature of the pathological process, it can be acute or chronic. Urethritis is classified as either complicated or uncomplicated by cystitis. The latter is very rare. Even if everything points to urethritis in women, it is highly not recommended to independently compare symptoms and treatment. Such actions can only aggravate the course of the pathological process.
Redness of the urethra with balanoposthitis
In men, the head can become inflamed as a result of:
- candidiasis;
- gardnerellosis;
- nonspecific bacterial infections.
The urethra is very close.
Therefore, inflammation spreads to it quite often.
In various infectious processes, the urethra is involved in 30-50% of cases.
Symptoms noted:
- redness of the head;
- sticky deposits on it with an unpleasant odor;
- itching or pain;
- elements of the rash - papules, spots;
- swelling;
- accumulation of pus in the preputial sac;
- redness of the urethra;
- discharge from it.
The signs of urethritis are the same.
The only difference is that they are combined with the clinical symptoms of balanoposthitis.
Editor
Update date: 10/11/2018, next update date: 10/11/2021
Redness of the skin or mucous membranes is a sign of inflammatory changes.
Redness of the urethra is no exception.
Since most of the urethra in men is not visible to the eye, only sticking and redness of the urethral sponges can be visually alarming.
However, other signs may also indicate lesions of the urethra.
Redness around the urethra
Characteristic symptoms
Urethritis is characterized by pronounced unpleasant symptoms. The patient is concerned about:
- Painful sensations during urination;
- Burning sensation in the genitals;
- Feeling of itching and discomfort in the intimate area during intimacy;
- Swelling of the genital organ;
- The appearance of blood in the urine or seminal fluid;
- Unpleasant odor and pus in the urethral discharge;
- Redness of the urethra extends to the head of the penis.
- The urethra in the morning is covered with a dried purulent crust.
If you experience at least a few of the symptoms listed above, you should definitely contact a medical specialist. The doctor will conduct diagnostics, make an accurate diagnosis, and find out the cause of the development of the pathology.
Stages of treatment
- Before treating pathology, it is necessary to conduct a complete diagnosis, which is one of the most important stages. Initially, the doctor examines the man and also collects anamnesis. The patient also needs to submit a urethral swab and urine for laboratory tests. In order to determine the infectious process, it is necessary to conduct a blood test.
- After receiving test results and assessing the clinical picture, a medical specialist prescribes medications for the treatment of urethritis. The selection of medications is carried out in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as the degree of development of the disease. To exclude an external factor that contributes to the development of the disease, the patient is recommended to reconsider his lifestyle.
- At the third stage of treatment of the pathological process, a repeat examination is carried out. With timely diagnosis of the disease and the appointment of objective treatment, complications of the disease are excluded.
Attention. After treatment of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the possibility of hypothermia. The patient is also advised to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene.
If a man shows the first signs of the disease, he should urgently seek qualified help from a medical specialist. This is explained by the fact that if the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the patient may experience quite serious complications that will be very difficult to cure.
The most common treatment for the disease is the use of drugs. In order to eliminate the cause of the disease, it is necessary to use antibiotics. Tablets are selected taking into account the characteristics of the pathogen. Antibiotics are selected according to the state of the microflora. Before treating a disease with these medications, it is necessary to conduct a sensitivity test to them. Also, to treat the inflammatory process, it is necessary to use medications whose action is aimed at restoring the microflora.
If the cause of inflammation of the urethra in men is ureaplasma, then the disease is treated with drugs that belong to tetracyclines, for example, Doxycycline. Quite often in this case, fluoroquinols are prescribed in the form of Levofloxacin or Ofloxacin. Doctors can also prescribe macrolides to patients in the form of Clarithromycin and Erythromycin.
If the cause of the disease is chlamydia, then in most cases it occurs in a chronic form. In this case, it is necessary to use azithromycins. If the urethra is affected by the herpes virus or adenovirus, the use of antiviral drugs is necessary. If the patient is prone to allergic reactions, then he needs to take antihistamines. With their help, the fight against unpleasant sensations is carried out. A very effective drug in this case is Tavegil.
In order to support the microflora, it is recommended to use drugs that are developed based on lactobacilli. To ensure quality treatment of the disease, men are recommended to take vitamin complexes. With a weakened immune system, it is necessary to use immunostimulants and immunomodulators. To increase the body's defenses and improve the functioning of the immune system, it is recommended to take Polyxidonium.
In order to ensure the effectiveness of therapy, it is necessary to use medications that have a local effect. To wash the urethra, it is recommended to use hydrocortisone, which has excellent antiseptic properties. Also, the penile area must be lubricated with antiviral ointment Acyclovir.
Treatment of urethral inflammation in men is highly effective only with the correct selection of drugs. That is why this procedure must be performed by a qualified doctor.
ethnoscience
In order to ensure the highest possible effect of traditional drugs, it is recommended to use traditional methods. They are characterized by the presence of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, which can significantly speed up the process of treating the disease. The most effective folk medicines include:
Cranberry. The plant is characterized by the presence of anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. During the treatment of the disease, patients are recommended to drink cranberry juice, which will have a positive effect on the effectiveness of treatment.
Black currant. The foliage and berries of this plant have a positive effect on relieving the inflammatory process. To prepare the medicine, you need to take the raw material, pour boiling water over it and take it in the form of ordinary tea. It is best to take the medicine in the evening.
Parsley . The above-ground part of this plant is crushed, mixed with milk and simmered in the oven for one hour. A single dose of the medicine is one tablespoon. It should be taken every hour. This medicine has a diuretic and antibacterial effect.
Phytocollection. It contains plants such as horsetail, St. John's wort, wheatgrass, lingonberry, and black elderberry. All components must be crushed and mixed in equal quantities. The resulting raw material is poured with a glass of boiling water in a ratio of 1:10. After boiling the medicine, it is infused for 8 hours. The decoction must be taken at least 4 times a day, 1/3 cup. The course of treatment with this drug should be at least 3 months.
Hemp milk. This medicine is used for baths. That is why it must be diluted with water before use.
Herbal collection. Its preparation is based on plants such as horsetail, St. John's wort, caraway, wheatgrass, and sage. All plants must be crushed and mixed in equal proportions. After this, you need to pour boiling water over them and leave for several hours. The infusion can be used orally or for baths, which will ensure effective fight against microbes.
Treatment with folk remedies is effective. Despite the safety of the drugs, the patient should consult a medical specialist before using them.
Redness of the urethra with condylomas
Condylomas may form inside the urethra.
They are red or pink in color.
Formed only in the distal part of the urethra.
They can often be seen with the naked eye, as they protrude outside the canal.
Symptoms:
- redness of the urethra;
- itching;
- splashing urine when urinating;
- sometimes – pain;
- if the condyloma is damaged, there is bleeding.
Possible inflammation of the condyloma as a result of the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
Intraurethral formations should be removed in a timely manner.
Otherwise, they may increase in size and disrupt urodynamics.
What is male urethritis?
Among the male population, urethritis is the most common disease. In women, this pathology is much less common, and less pronounced pain syndromes are noted. This is logically explained by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the body of men and women. In particular, the male urethral canal is about 22 cm and consists of several bends.
In women, the canal is wider and much shorter. That is why, when an infection enters the male body, it lingers in the bends and causes inflammation, the mucous membranes begin to swell and problems occur with the outflow of urine.
Redness due to traumatic inflammation of the urethra
Redness of the urethra is not always caused by infections.
This may be a temporary phenomenon that occurs as a result of:
- chafing of the penis;
- local use of drugs;
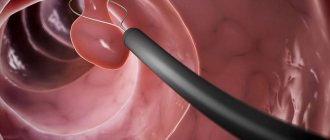
- urethroscopy - a study in which a tube with a camera is inserted into the urethra;
- cystoscopy - a similar diagnostic procedure, supplemented by examination of the bladder;
- taking urethral smears and scrapings;
- instillations - the introduction of drugs deep into the urethra using a catheter;
- catheterization of the bladder for urinary retention due to prostate diseases.
Any mechanical damage to the urethral mucosa causes an inflammatory reaction.
But this inflammation is not dangerous in most cases.
It goes away quickly.
Often this redness is accompanied by pain.
It intensifies as urine passes through the canal.
Classification of urethritis
Inflammation and redness of the urethra can be of different types. If the infection enters the body during intimacy, the disease is classified as specific.
A nonspecific disease develops with the activation of opportunistic microorganisms. Primary pathology occurs in the urethra, and secondary pathology passes through the blood or from nearby internal organs. If treatment for urethritis is not started in a timely manner, the disease can quickly turn from acute to chronic.
The following microorganisms can cause inflammation of the urethra in men:
- Gonococcus. It is transmitted during sex or through the use of contaminated personal items.
- Virus. Microorganisms penetrate through the mucous membrane.
- Bacteria.
- Candida fungus.
- Trichomonas. Symptoms appear only after a week, and the disease can quickly become chronic.
- Tuberculosis bacillus. The most dangerous cause of urethritis.
The treatment method is selected individually, after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Specific urethritis
This definition refers to a complex of diseases that are caused by various viruses and bacteria penetrating the body:
- gonococci;
- ureaplasma;
- chlamydia;
- Trichomonas;
- mycoplasma;
- herpes;
- human papilloma virus.
This is not a complete list of external infections that can cause redness of the urethra in men. Bacteria and protozoan microorganisms in the vast majority of cases manifest themselves in the appearance of characteristic mucous or purulent discharge directly from the urethra itself. They cause persistent irritation of the urethra and the entire head of the penis. Such common symptoms of sexual diseases appear as itching and burning in the urethra, pain when emptying the bladder, intermittent urination, the presence of pus and even blood in the urine.
Today, specific urethritis is the most common cause of inflammation of the urethra in the stronger sex. However, viruses and bacteria can provoke not only the development of this disease, but also a disease such as balanoposthitis. It is characterized by damage to the external tissues of the penis, especially the foreskin, as a result of which ulcers and even purulent melting appear on them.
The herpes virus and human papillomavirus are characterized by the formation of vesicles filled with clear liquid. This process is accompanied by severe burning and painful sensations. Unlike protozoa and bacteria, getting rid of such viruses will be much more difficult. It is likely that a person will have to live with them all his life, taking the necessary measures to reduce the risk of activation of the pathogen.
Redness of the urethra after Miramistin
Patients often use this drug for self-medication.
It is advertised as a means to prevent STDs.
Therefore, Miramistin is often injected into the urethra and the genitals are treated with it.
But this is far from the safest drug.
It does have a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity.
But at the same time it often has an irritating effect on the urethra.
It can call:
- chemical irritation;
- redness of the urethra;
- burning;
- allergic reactions that appear some time after using the drug.
Miramistin should be used only in extreme cases.
For example, if a condom breaks.
It should not be considered a panacea.
It does not prevent genital infections 100%, but only reduces the risk of infection.
To protect against sexually transmitted diseases, you should use barrier contraception.
If you have not used a condom, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
He will carry out effective prevention of sexually transmitted diseases with more gentle and safe drugs.
In addition, with an almost 100% guarantee of results.
Diagnostics
In order to cure urethritis as quickly and effectively as possible, you need to find out the exact cause of the development of the inflammatory process. Specialists can identify the pathogen through laboratory testing of biological fluids and additional instrumental techniques. Comprehensive diagnosis of patients with the symptoms listed above includes:
- Biochemical laboratory blood test.
- Examination of a patient's urine in the laboratory.
- Examination of urethral discharge under a microscope. A smear is taken by a physician during the initial examination.
At the initial stage, the symptom in the form of purulent discharge from the urethra may not appear. To make an accurate diagnosis, a physician may prescribe special testing for such a patient. For the appearance of discharge, medication, heat exposure is prescribed, or a special probe is used. Recently, the PCR method has been increasingly used to diagnose urethritis. The causative agent of the disease is detected in the liquid environment of the patient's DNA.
Sources used:
- https://www.venerologia.ru/pokrasnenie-uretry
- https://onvenerolog.ru/uretrit/pokrasnenie-uretry.html
- https://doktora.guru/polovaya-sfera/uretrit-u-muzhchin-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
- https://moninomama.ru/pochki/pokrasnenie-vokrug-uretry-u-muzhchin-o-chem-eto-mozhet-govorit
- https://onefr.ru/organy/mochevoj-puzyr/pokrasnenie-vokrug-mocheispuskatelnogo-kanala-u-muzhchin.html
- https://uran.help/diseases/pokrasnenie-mocheispuskatelnogo-kanala-u-muzhchin.html
Diagnosis of urethritis
It is possible to find out which pathogenic microorganism causes inflammation of the urethra. To do this, you will have to undergo laboratory tests, as well as check the internal condition of the urinary urethral tube. We list the tests that are mandatory:
- Blood for biochemistry and general analysis (to check for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases);
- Urinalysis - general and three-glass;
- A smear from the urethra (discharge) for microscopic analysis.
If the disease is detected at the initial stage, discharge is usually not yet observed. Then the hole is “irritated” on purpose:
- Chemical test - involves taking a drug that accelerates the release of pus;
- Thermal test - irritation of the hole occurs through increased exposure temperature;
- Physical test - involves the use of a special probe for these purposes.
The discharge is examined under a microscope, but sometimes this is not enough, then a colony of microorganisms is grown to identify it (bacteriological method). Nowadays, a very popular PCR test is the isolation of inflammatory DNA from human fluids. If there is an assumption that the patient has suffered a microtrauma, then an additional X-ray examination is prescribed.