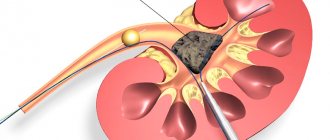
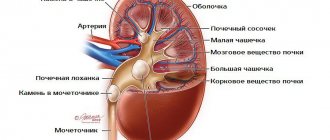
Urolithiasis is one of the most common diseases of the human urinary system. This pathology does not form immediately - the precursor to kidney stones is sand. It is at this stage that the disease should be identified and treated, since if a large number of stones accumulate, there is a high risk of developing renal failure and other severe and life-threatening conditions. According to statistics, this pathology occurs three times more often in men than in women, so representatives of the stronger sex should pay special attention to its first signs.
- 2 Causes and development factors
- 3 Symptoms of sand in the kidneys in men
- 4 Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
- 5 Treatment
5.1 Table: drug therapy for the presence of sand in the kidneys
5.1.1 Photo gallery: drugs for sand in the kidneys in men
- 5.2.1 Video: what to eat and what not to eat for kidney stones and sand
- 7.1 Video: how to prevent urolithiasis
Characteristics and causes of the disease
Don’t wait for serious health problems; start treatment at the stage of sand formation in the kidneys. The risk group includes people from twenty to fifty years of age. Men are more susceptible to the disease than women, so the stronger sex is advised to undergo regular examinations with a doctor and closely monitor their health. Lack of therapy leads to severe discomfort and triggering of the inflammatory process.
Doctors identify several negative factors that influence the formation of sand in the kidneys of the stronger sex. The main cause of the disease is a metabolic disorder in the body. As the pathology progresses, the amount of toxins in the blood increases.
See a selection of effective methods for treating bladder stones in women.
Read about the causes and treatment of pain after urination in women on this page.
Metabolism is influenced by many factors:
After contacting your doctor, re-read this list; there is a high probability that the factors described above led to the formation of sand in the kidneys. Before starting therapy, eliminate the root cause of the disease, and then follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Features of the disease during pregnancy
In pregnant women, urolithiasis is a fairly common problem. This is due to the fact that the body endures a large load, exposing itself to the development of other diseases.
Sand in the kidneys can cause complications during pregnancy due to fluid retention in the body, accelerating the process of inflammation. This entails treatment with antibiotics, which negatively affects the health of children. Painful sensations during urination cause discomfort not only for the expectant mother, but also for the fetus.
Women carrying a fetus have a weakened renal system, so sand in the kidneys is common during pregnancy. This state of affairs causes many complications for the expectant mother.
For those carrying a fetus, the formation of sand and kidney stones is a serious process, since with possible stagnation of urine, a favorable environment is created for the development of microorganisms that cause inflammatory processes.
As it develops, inflammation can become chronic. In this case, you will have to take antibiotics for treatment, which is undesirable during pregnancy and can negatively affect the fetus.
When a pregnant woman has urolithiasis, formations can begin to come out - this is a very painful process. The following manifestations indicate that there is sand in the kidneys of pregnant women:
- swelling;
- pain during bowel movements;
- increased pressure in the arteries;
- aching sensations in the lower back;
- pain in the right side and above the pubic area;
- urge to vomit;
- increase in temperature;
- pain in the kidney area.
Signs and symptoms
At the beginning of the formation of sand in the kidneys, the patient may not feel any symptoms. Salts accumulate not only in the kidneys, but also in other organs of the urinary system. Symptoms of the disease appear as a result of a large amount of salt formations or under the influence of low temperatures, stress, during its passage through the urinary tract.
Attacks of acute pain resemble sensations during an exacerbation of appendicitis. The cause of the trouble is the passage of grains of sand through the urinary tract. Grains of sand irritate the mucous membranes, and blood impurities are often found in the urine. After the sand comes out, the patient complains of nagging pain in the lumbar region.
You can suspect the presence of sand in the kidneys based on characteristic clinical signs:
- disturbance of the urination process. Urinary canals irritated by sand lead to a difficult process of emptying the bladder. Many men complain of incomplete emptying of the bladder; patients note frequent, intermittent urination;
- abnormal urine consistency. Visually, you can notice changes in the secreted fluid (urine includes impurities of blood, pus, becomes thick, and has a sharply unpleasant odor). A urine test reveals an increased content of leukocytes, an abundance of salts, and protein;
- During a painful attack, the patient may be accompanied by other symptoms: increased body temperature, increased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting. Often, impaired fluid excretion leads to swelling of the face;
- at the beginning of the development of the disease, sand can come out of the kidneys painlessly; the only sign of pathology is a change in the color of urine.
How to find out about sand in the kidneys?
To understand which symptoms are characteristic and which are indirect, you need to have an understanding of the process of sand formation. This condition has an individual formulation in medicine – urolithiasis. Sand is a suspension consisting of proteins, salts and phosphates. The particles are small and have not yet formed into a single stone, but there is a high probability that over time they will form into stone.
It is widely believed that the reason for the formation of sand lies in disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system. However, it has long been recognized as erroneous. The real reason for the formation of suspended matter and calculi is a disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
Women may suspect that they have salts and sediment in their kidneys by the appearance of their urine. In order to carry out self-diagnosis at home, you will need a sterile transparent container. After performing hygienic procedures, you need to cover the vagina with a clean napkin or cotton pad so that the discharge does not get into the container, and urinate. Collected urine normally has a straw color and does not have an unpleasant pungent odor. The biological fluid is transparent and does not contain foreign impurities.
If the morning portion is cloudy, and tiny particles float in it, then we can assume that there is sand in the woman’s kidneys. However, this does not always become a reliable symptom. In order to verify your assumption, you need to leave the collected urine for half an hour. If the sediment has separated from the clear liquid, then with a high degree of probability the process of stone formation can be suspected.
Specific clinical signs
In the early stages of urolithiasis, there are no pronounced clinical manifestations. Since the grains of sand are small in size, they do not impede the outflow of fluid from the filtering organ, just as small stones do not cause serious complaints in the patient. When particles of salts, phosphates and proteins stick together and form a calculus. A neoplasm larger than 3 mm in diameter may cause renal colic in a woman. This condition is accompanied by a violation of the outflow of urine through the ureters, as a result of which one of the filtering organs is seriously damaged. With renal colic, severe pain occurs in the abdomen and back, and blood circulation in the organ is disrupted. Women can compare renal colic with contractions in terms of the intensity of the pain syndrome.
With sand in the kidneys, minor damage to the ureters occurs with small but coarse particles. Because of this, a woman experiences a burning sensation and dull pain during urination. In the same way, stones injure the epithelium of the urethra. Often women, experiencing a burning sensation when urinating, talk about an exacerbation of cystitis. But this is a misconception.
The appearance of bloody impurities in the urine or urine turning orange is also a sign of urolithiasis. Blood is released due to injury to the epithelial tissue of the urinary system.
Features in women
Symptoms of sand in the kidneys have particular manifestations in women. In the pelvic area of the fairer sex there is not only the urinary system, but also the reproductive system. The uterus and appendages undergo monthly changes, which affects the woman’s well-being. Various pathological processes in this area may have similar symptoms as with urolithiasis:
- nagging pain in the abdominal area is caused by microtrauma of the ureters (or inflammation of the ovaries, fallopian tubes);
- pain when urinating is caused by inflammation of the urethra - urethritis (or speaks of cystitis);
- an increase in body temperature occurs during acute inflammation caused by the formation of stones and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms (or occurs with a cold);
- headaches appear with increased blood pressure and intoxication due to impaired renal function (or occur from overwork).
It is not always possible to understand that the existing symptoms indicate problems with the kidneys. If you continue to refer to other causes of the disease and refuse examination, then over time stones will form from grains of sand. The progression of urolithiasis is dangerous to health and threatens to result in surgical treatment. Regular medical examinations will help prevent the disease and promptly find out about its onset.
Diagnostics
Sand in the kidneys is quite difficult to determine if the patient does not complain of unpleasant symptoms. Often, pathology is diagnosed accidentally during a blood test for other diseases.
If you suspect the presence of sand in the kidneys in men, a number of diagnostic procedures are performed:
An important role is played by the external examination of the patient and the presence of complaints from the patient. The doctor can also prescribe a comprehensive examination of the body to identify the root cause of the disease (sand is always formed during the course of any pathologies or after exposure to negative factors).
Conservative therapy: how urolithiasis is treated in men
Treatment of urolithiasis and the subsequent removal of stones from the excretory tract is a long process that requires urgent monitoring by specialists. If there is sand in the kidneys, the course of therapy and the necessary medications are prescribed according to the individual indicators of each patient.
Treatment includes diet and special medications, which are prescribed based on tests. For latent periods (outside the exacerbation phase of the disease), physiotherapy is also prescribed.
Important to remember! The process of sand release is compatible with the risk of urinary tract inflammation. It is imperative to establish the chemical composition of the sand accumulated in the body. Such procedures cannot be performed independently at home, so the help of specialists is irreplaceable.
Urologists identify a special group of people who are prone to the formation of sand in the kidneys. As a rule, we are talking about genetic predisposition (hereditary factor - transmission from parents). The disease can be avoided by following preventive measures.
Effective treatments
How to remove sand from the kidneys? Therapy for urolithiasis includes several stages:
- removal of sand from the urinary tract,
- relief of unpleasant symptoms,
- prevention of relapses.
To do this, the doctor prescribes special medications and diet for the patient. Changing your lifestyle for the better plays an important role.
This aspect of therapy is prescribed to all patients who have excessive amounts of salts and other elements in their urine. Cleansing the kidneys is important when sharply unpleasant symptoms appear; if the sand is completely removed from the urinary tract, the signs of the disease disappear. Getting rid of grains of sand is much easier than removing formed stones.
Medicines and special physical activity are suitable for cleansing the organs:
- active mode. Constant movement is the key to getting sand out of the kidneys. Patients are asked to run, jump, squat, and race walk. Changes in body position will cause salt crystals to move towards the exit. Dynamic loads are combined with drug therapy. This method is mandatory for obese patients;
- diuretics. All drugs with a diuretic effect are made from natural ingredients and can reduce the period of removal of sand from the kidneys. Doctors consider popular medications from this group: Canephron, Trinephron, Fitolit, Fitolysin, Urolesan, Marelin. Due to the absence of synthetic components, the likelihood of side effects is minimized. If taking one medication does not give the expected result, replace it with another remedy.
How to get rid of sand in the kidneys? Modern medicine offers a method of electrical stimulation to quickly get rid of salt crystals in the urinary tract not only for men, but also for the fair sex. The principle of physiotherapy is simple: the device increases blood flow, enhances peristalsis, promoting the removal of formations. Thanks to electrical stimulation, you can get rid of sand in the kidneys in just 4 days.
Read useful information about the symptoms and treatment of cystitis in women after intimacy.
The features of treatment for hydronephrosis of the right kidney during pregnancy are written on this page.
How to treat sand in the kidneys? An important role is played not only by getting rid of salt crystals, but also by preventing the recurrence of the problem.
Change your diet, follow a diet for sand in the kidneys:
- the amount of protein should not exceed 15% of the total weight of the products. Replace some meat products with beans and soy. Steam, simmer, boil foods, avoid frying;
- drink at least two liters of clean water per day. Dehydration has a detrimental effect on all systems and organs in the human body;
- Load up on fruits, vegetables, and various cereals. The specific list of products depends on the chemical composition of the salts. Your doctor will help you choose the right diet.
Natural remedies are used as an auxiliary therapy, used to strengthen the immune system and cleanse the body of accumulated toxins.
Effective recipes for treating sand in the kidneys using folk remedies:
- warming up the lumbar region. Warm water and other sources will help start the blood circulation process and reduce pain. For sand in the kidneys, it is recommended to take hot baths (three times a week);
- diuretic herbs and decoctions from various plants (oregano, horsetail, nettle, centaury). You can make medicine from one plant or prepare an herbal mixture. Pour 100 grams of raw material with a liter of boiling water and leave for several hours. Drink the resulting product throughout the day. Prepare a fresh potion every morning. The course of therapy can last up to one month.
Drug treatment
Traditional therapy for urolithiasis is prescribed after laboratory tests of the composition of urine and ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder and varies depending on the type of salts (oxalates, phosphates, urates, xanthine or cystine stones) and the reasons for their appearance.
The prescription of drugs for the treatment of stone formation is carried out on a strictly individual basis (depending on the volume of microliths and the composition of salts in the urine, as well as the characteristics of the patient).
The main methods of treating sand in the kidneys include:
- taking drugs of synthetic and herbal origin;
- shock wave method - lithotripsy (performed without surgical intervention);
- compliance with the diet (table No. 6) for the period of therapy and general nutritional correction on an ongoing basis;
- drinking plenty of water;
- surgical intervention.
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed if there is a focus of inflammation and infection. At the same time, diuretic drugs (Cyston, Canephron, etc.) and medications that break down stone crystals are used. In the presence of urethritis and cystitis, anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Remember that self-medication of the kidneys can provoke unforeseen complications, therefore all treatment methods (folk and traditional) must be agreed upon with the treating doctor.
Review of medications used for sand in the kidneys
Drugs for sand in the kidneys are used to reduce kidney colic and speed up the elimination of stones. If there is a high likelihood of renal failure, antibiotic therapy and parenteral hydration should be urgently prescribed.
Most small stones in patients with relatively mild hydronephrosis can be treated with acetaminophen. More severe cases require drainage with a stent or percutaneous nephrostomy.
Uncomplicated kidney stones do not require drug therapy. The patient is advised to take enough fluid (2.5 - 3 liters) and maintain bed rest.
The main list of drugs that are used to treat sand in the kidneys:
- opioid analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids;
- calcium channel blockers;
- alpha-blockers;
- xanthine oxidase inhibitors;
- alkalizing agents;
- antibiotics;
- antiemetics.
Narcotic analgesics act on opioid receptors in the central nervous system (CNS) and are used to treat renal colic. Side effects include excessive sedation, respiratory depression, smooth muscle spasm and the formation of mental as well as physical dependence. Narcotics can be purchased at a pharmacy strictly with a doctor's prescription.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit pain and inflammation by reducing the activity of cyclooxygenase, which is responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins. Both effects are useful in the treatment of renal (ureteral) colic. The price of NSAIDs varies widely: from 200 to 4300 Russian rubles.
NSAIDs are less effective than narcotic analgesics, as has been shown in numerous randomized controlled trials. They have now become the recommended standard of care for acute colic pain, although they should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment. NSAIDs cause less nausea and sedation than opioid analgesics. They also do not depress breathing and do not have abuse potential. Medicines in this group have adverse effects on renal function, gastrointestinal mucosa and platelet aggregation. List of common pain medications for sand in the kidneys:
Glucocorticoids are systemic or local steroid agents that reduce inflammation of the ureter. They also have profound metabolic and immunosuppressive effects. Corticosteroids are not included in current guidelines for the treatment of kidney stones. They should not be taken in case of severe cystitis or diabetes mellitus.
Time-release kidney sand tablets simplify treatment and help improve the condition of patients. The medication can be used for no more than 10 days. Sometimes the course of therapy can be extended to 15 days after consultation with a doctor.
Terazosin tablets are indicated for the treatment of essential hypertension. These drugs, which remove excess sand from the kidneys, help lower blood pressure. In this case, it is also recommended to use only short-term therapy (no more than 10 days).
Oral alkalizing agents are used to treat metabolic acidosis. They are also prescribed if long-term maintenance of alkaline urine is desired. Potassium citrate is absorbed and biotransformed into potassium bicarbonate, acting as a systemic base substance. Its effects are mainly due to chlorides (prior to absorption) and then bicarbonates. Less than 5% of potassium citrate is excreted unchanged in the urine. It is very concentrated and, when used after meals and before bed, helps maintain an alkaline urine pH for about 5-7 hours. At the recommended dosage, it alkalinizes urine without the risk of systemic alkalosis.
Infected hydronephrosis requires intravenous antibiotic therapy in addition to drainage or placement of a urethral stent. Typical pathogens causing
infections are aerobic gram-negative intestinal microorganisms: Escherichia coli and Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterobacter and Citrobacter. Candida albicans sometimes occurs in patients with diabetes or immunodeficiency. Initial empiric antimicrobial therapy should cover common bacterial pathogens.
Patients with acute renal colic often experience severe nausea or vomiting. Along with analgesics, antiemetics are often prescribed: phenothiazines and butyrophenones. German-made drugs are recommended.
conclusions
Although sand in the kidneys is not considered a diagnosis, this phenomenon is not considered harmless. When microliths form, symptoms appear that significantly reduce a woman’s quality of life. Since it is not always possible to immediately identify sand, you need to undergo a thorough examination. Sometimes there is a need for differential diagnosis. Pathology therapy is complex and is selected individually for each woman. The prognosis depends on following the doctor's orders.
Exit of sand from the kidneys: symptoms
The release of sand can be accompanied by very severe pain, arising from the side and radiating to the front and back of the body. More than 50% of patients experience nausea and vomiting. Some patients report signs of infection or hematuria.
In very rare cases, the release of sand ends in the death of the patient. Therefore, only a doctor can remove and treat all medical symptoms (especially in pregnant women).
Location and characteristics of pain in nephrolithiasis:
- Stones blocking the ureter: mild to severe deep lateral pain without radiation to the groin, increased frequency of urination, dysuria, stranguria.
- Stones inside the ureter: sharp, severe pain in the side and lower abdomen, pain radiating to the testicles or vulva area, intense nausea with or without vomiting.
- Crystals in the upper part of the ureter: irradiation to the flank or lumbar areas.
- Distal ureteral stone formations: irradiation of pain to the groin or testicle (men) or labia (women).
- The stones have passed into the bladder: mostly asymptomatic.
The best and worst drugs, according to doctors and patients
You should not try to treat kidney stones at home using folk remedies. Dissolution and removal of stones must be done under the supervision of a physician.
Sand in the excretory system is a fairly common disease that interferes with the normal functioning of the genitourinary system. Signs of sand leakage can occur to the same extent in both women and men. However, statistics show that sand appears in the kidneys in men much more often than in women. This is due to physiological characteristics.
It is worth noting that a person’s age does not affect the occurrence of this disease. It can occur in both older and younger people.
As a rule, the onset of sand formation goes unnoticed, and only an increase in its quantity leads to the appearance of minor, at first, discomfort that needs to be paid attention to.
Prevention
Sand in the organs of the urinary system is easier to prevent than to treat. For this purpose it is recommended:
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports,
- Healthy food,
- to refuse from bad habits,
- treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner,
- drink enough fluid (at least 2 liters per day).
Doctors advise not to abuse diets, especially radical ones. The diet should be balanced. You need to eat food of both plant and animal origin.
Compliance with these recommendations ensures improved metabolism, as well as normalization of the urinary system.
Characteristic symptoms
Doctors identify several characteristic symptoms that determine the presence of sand in the kidneys in men:
- Sharp and nagging pain in the lumbar region. May be permanent or intermittent.
- Unpleasant sensations when urinating are caused by sand moving through the bladder. The process of passing urine becomes difficult, and the urge to urinate occurs more and more often.
- Increased body temperature. The main reason is inflammatory processes in the walls of the pelvis, ureters and bladder. When moving, crystalline formations injure the mucous membrane of the urinary system, which leads to its inflammation, and as a result, an increase in body temperature.
- Changes occur in the composition of urine. It changes color and becomes cloudy or dark. Blood may appear in it in the form of clots. Blood stains may also appear on underwear.
- High blood pressure.
- Nausea and vomiting;
- The appearance of swelling on the face and lower extremities.
Symptoms of urolithiasis
Symptoms of urolithiasis in men can be subtle, and there are often similarities with other ailments. Therefore, if you experience any unpleasant sensations, it is better to immediately undergo an examination and make sure that there is no potential danger.
The main signs of the formation of kidney stones:
- Attacks of pain with possible exacerbation;
- Temperature increase;
- Painful sensations in unexpected cases;
- Pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
A stone in the ureter touches its walls. This is what leads to pain, by which the disease is recognized. You should not take painkillers, as they will not bring the desired result. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes
Sand in the body can form under the influence of many reasons, but one of the main ones, according to the unanimous opinion of urologists, is metabolic disorders.
Disorder of the functions of natural chemical processes in the body leads to disruption of the water-salt balance. Over time, the concentration of salts in the blood and urine increases significantly, which contributes to the formation of sand, and then kidney stones.
The disease can also be caused by indirect causes, for example:
- hot climate, especially in combination with the above factors;
- bone fractures;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- physical overload;
- stress.
Causes of kidney stones
As a rule, urolithiasis in men is accompanied by terrible pain in the lower back, but the approach of the stone to the exit from the ureter is felt throughout the entire abdominal cavity.
The causes of urolithiasis in men can be divided into two groups:
- External factors;
- Internal.
Men can easily put up with pain, so at first they are not even aware of the formation of foreign particles. The first signs of urolithiasis are often detected late, when no means can destroy the formed sand.
External factors
Bladder stones are removed in various ways, but you should not bring yourself to this state. External influences are difficult to eliminate, although you can resort to some preventative procedures. They will reduce the harmful effects and maintain health.
- Dry climates are the main cause of dehydration;
- The soil composition spoils food, affecting the entire body;
- If there is an excess of salts in the water, the water-salt balance is disrupted;
- An incorrect daily routine disrupts the functioning of the bladder;
- Lack of water affects the development of the disease;
- Excessive content of meat products in the diet.
Stones in the ureter in adult men form for various reasons. Often this is an incorrect diet or drinking regimen, and an incorrect lifestyle.
Intrinsic factors in the formation of kidney stones
Bladder stones can also be a consequence of certain diseases. Moreover, they develop in a latent form, which significantly increases the risk of untimely detection:
- Infectious diseases of the ureter;
- Disorders of the digestive tract;
- Abnormal development of the ureter and digestive tract.
In such cases, sand gradually forms in the bladder of men, “combining” into stones. At first there are no unpleasant sensations, and everything becomes clear in the later stages, when kidney stones cause pain.
Treatment methods
Under no circumstances should you treat yourself! Therapy must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. If symptoms appear, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible.
There is no point in delaying your visit, since early diagnosis allows you to prescribe an appropriate course of treatment, thereby preventing the development of the disease, reducing the possibility of the occurrence of side diseases in the short term, and without consequences for the male body. Delay threatens impaired potency, reproductive function and other complications.
A set of therapy methods is selected by the attending physician individually for each patient and is carried out, at an early stage, on an outpatient basis. Its main task is as follows:
- the release of all crystalline formations from the male kidneys;
- elimination of inflammation;
- restoration of the water-salt balance of the entire body as a whole.
At the early stage of treating sand in the kidneys, conservative methods are used:
Medicines are prescribed to remove sand from the kidneys in men and restore basic functions:
- diuretics, remove sand in a timely manner, which prevents the formation of stones;
- stimulating the breakdown of sand and stones, which reduces pain when urinating,
- anti-inflammatory, preventing possible complications.
A diet for sand in the kidneys is prescribed based on a urine test, which helps to identify which salts are present in excess in the body. It is selected individually for each patient.
As a rule, the following foods are completely excluded from the diet or significantly limited:
- strong tea;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- alcohol;
- canned food;
- fried and spicy foods;
- smoked products.
It is recommended to consume meat boiled and in small quantities. You also need to spend fasting days, consume dairy products, vegetables, fruits and be sure to drink a lot of clean water.
Dietary nutrition according to the presented scheme helps to establish water-salt balance and metabolism. The diet for sand in the kidneys is prescribed individually, and it is necessary to follow it. If you ignore your doctor's recommendations, the treatment may not be effective.
An active lifestyle involves regular physical activity, within reasonable limits, for example:
- walking;
- visiting the gym.
In some cases, physical therapy may be used to treat sand in the kidneys. Studies have shown that the use of this method in combination with other components of treatment helps reduce the time it takes to remove sand from the body. The main condition under which a doctor can prescribe this method is the absence of inflammatory processes.
When treating, you can also use folk remedies, but in no case independently. It is imperative to consult a doctor.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the fact that folk remedies are used only in combination with basic drug treatment.
In the treatment of this disease, folk remedies use herbal teas that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect. They can be bought at a pharmacy, on the recommendation of your doctor.
They must be prepared and consumed strictly according to the instructions indicated on the packaging. The components of such fees are:
- dog-rose fruit;
- parsley leaves;
- strawberry leaves;
- birch buds;
- flax seeds;
- lingonberry leaves.
There are quite a few recipes for kidney preparations. A specialist will help you decide which one is right for a particular patient. Watermelon and freshly squeezed grapefruit juice also have a significant diuretic effect.
Complex treatment allows, in a relatively short time, to establish the body’s protective functions and remove sand from the genitourinary system.
Treatment of sand in the kidneys at home with folk remedies
An ultrasound can detect sand in the kidneys. Treatment at home is possible only if there are no stones that can block the ureteral duct if the location changes.
The most popular methods:
1. Watermelon + black bread. Watermelon fasting day or watermelon cleansing is the most common and effective folk remedy for sand in the kidneys. Throughout the day, the patient is asked to include watermelon pulp (up to 2 kg) and rye bread in the menu. During the period of highest kidney activity (from 15-00 to 19-00), it is recommended to take a warm bath.
During the procedure, you should eat most of your daily portion of watermelon. This procedure promotes abundant urination and cleanses the body of sand. Also, this technique eliminates tissue swelling and helps to lose up to 3 kg.
2. Rosehip. The rhizome of the plant (the shrub must be at least 3 years old) is successfully used in folk medicine to remove sand.
Dried and crushed roots, collected in early spring or early winter, are brewed like regular tea in a thermos (1-2 teaspoons per liter of water), leave for 4 hours. Take 100 ml 4 to 5 times a day.
The course of treatment is 2 weeks, after a month's break it can be repeated.
3. Treatment fee No. 1. A diuretic herbal mixture of birch buds, cornflower, bearberry and dried parsley root, taken in equal proportions, helps remove sand from the kidneys.
A tablespoon of plant material is poured with hot water and simmered in a water bath for about a quarter of an hour. The strained decoction is taken 100 ml twice a day, and the first portion should be drunk between 4-00 and 5-00. The therapeutic course is 14 days.
4. Treatment fee No. 2. Another option for a medicinal diuretic: combine crushed lingonberry leaves (dry), knotweed herb, peppermint and dill seeds, taken in equal quantities.
Steam 2 tbsp in a thermos. spoons of raw materials per ½ liter of boiling water, leave for 12 hours, filter and take 1/3 cup 3-4 times a day.
5. Oil + lemon. An effective way to remove sand is to take olive oil and lemon juice. In a glass bowl, mix 85 ml of high-quality extra virgin olive oil and freshly squeezed lemon juice.
The resulting composition is drunk every evening before bed until the sand stops coming out. To increase diuresis and quickly get rid of crystalline stones, drink at least 10 glasses of clean (melt or spring) water throughout the day.
Diet for sand in the kidneys
Regardless of whether you use conservative therapy or use folk remedies, nutritional adjustments are required. The therapeutic diet is prescribed individually depending on the patient’s metabolic characteristics, concomitant pathologies, and salt composition.
A nutritious and varied diet is recommended that saturates the body with all the necessary substances. Foods rich in compounds that provoke the formation of crystals in the kidneys are completely excluded from the menu.
The use of table salt in the diet is minimized; a doctor will help determine the daily portion for each specific case.
The following products are definitely contraindicated:
- canned food;
- sausages;
- pickles and marinades;
- smoked meats;
- alcohol;
- fried foods;
- fatty food;
- animal fats;
- spices and seasonings;
- margarine;
- mayonnaise;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- strong coffee;
- legume vegetables.
In case of urate stones, in addition to the listed dishes, meat of young birds and animals, as well as decoctions from them (broth), offal, fatty fish and caviar, salted cheeses, mushrooms, sorrel, spinach, cauliflower, rhubarb, are completely excluded from the menu.
Boiled lean meat should be present in the diet no more than three times a week. It is useful to use first cold-pressed vegetable oils for dressing salads, especially olive, flaxseed, walnut, corn, soybean, sunflower, and sesame.
Every day you should eat a variety of fruits, raw and after heat treatment, with the exception of those prohibited. Cranberry, lingonberry and viburnum juice are good for removing sand.
Causes
The causes and mechanism of sand formation in the kidneys and organs of the urinary system are not fully understood. There are three theories of the development of the disease:
Physicochemical theory considers an imbalance between crystalloids and colloids, which leads to the onset of sand formation. The reasons for this are damage to the urethral wall of various natures, infections caused by bacteria in the urinary tract, insufficient presence of vitamin A in the body, endocrine system disorders, pathologies of the thyroid gland, sedentary lifestyle and weakening of muscle function, previous injuries to the musculoskeletal system, dysfunction digestive system, periodic delays and stagnation of urine.
Stones are divided into two main types: calcium- and non-calcium-containing. In 70% of cases, stones consist of calcium, in 5% they are mixed, and in 25% they are not calcium (uric acid salts).
Risk factors include:
- abnormal structure of the organs of the urinary system;
- heredity;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- gout;
- urinary tract infections.
Why do kidney stones form?
Reasons for appearance
First you need to figure out what sand is. Salt deposits deposited in the kidneys have a crystalline structure. Gradually accumulating, they form small particles up to 0.8 mm, reminiscent of sand. They pose a particular danger due to their tendency to increase in size, become overgrown with new deposits, and turn into stones. In women, the formation of sand in the kidneys can cause severe complications, including complete blockage of the ureters and death.
There are several reasons why sand forms in the kidneys:
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- drinking excessively hard water;
- unbalanced drinking regime;
- alcohol abuse;
- metabolic disease;
- infectious diseases and pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle;
- deficiency or excess of certain vitamins and microelements;
- thyroid disease.
Symptoms
The classic symptom of kidney stones is renal colic, a sudden, severe pain in the lower back that radiates to the abdomen and bladder. It manifests itself with intense walking, running, shaking in transport, eating disorders or drinking too much. About 50% of patients experience nausea and vomiting. At the initial consultation, patients report the presence of infection and the presence of blood in the urine. Main types of symptoms:
- pain when urinating;
- urinary disturbances;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- the appearance of pus in the urine;
- excretion of sand and small stones along with urine;
- nausea, vomiting, fever up to 38 degrees Celsius.
The presence of sand in the kidneys and small stones may not appear for a long time or cause easily controlled symptoms.
The clinical picture depends on the location of grains of sand and stones:
- in the kidney - dull, aching pain in the lumbar region;
- in the ureter - pain in the groin area, radiating to the corresponding thigh;
- in the bladder - pain in the lower abdomen radiates to the perineum, becoming more intense with movement.
The pain is accompanied by dysfunction of the digestive tract: constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal muscle deflation.
The need to urinate increases with any shaking, including traveling by transport, playing sports and fast walking. During urination, the stream of urine may suddenly be interrupted due to the displacement of the stone.
Main symptoms in men and women
- Oh, it’s okay, there’s no need for an ambulance! It’s probably just sand gone... - you’ve probably already been “brushed aside” in a similar way.
Full content
THE CONTENT OF THE ARTICLE
There are many reasons why sand accumulates in the kidneys and bladder. Their consideration is the topic of another article. Here we are interested in the removal of these third-party substances, which can have an extremely negative effect on the human body.
Treatment with folk remedies for sand in the kidneys begins only after symptoms are identified.
That is, a woman must understand that she has exactly this problem, and not some other one.
It should be noted that due to the structural features of the female urinary system and the pelvic organs in general, the symptoms of sand in the kidneys in representatives of the fair half of humanity may be different than in men. This must also be taken into account.
- Expert opinion: Today it is one of the most effective remedies in the treatment of kidney diseases. I have been using German drops in my practice for a long time...
The function of the kidneys is to cleanse the blood and remove toxic compounds and metabolites. One of the main signs of the development of urolithiasis (urolithiasis) is the presence of sand in the kidneys, which can be detected using ultrasound. I will discuss the causes and treatment of sand in the kidneys in detail in simple words in this publication.
What is sand in the kidneys?
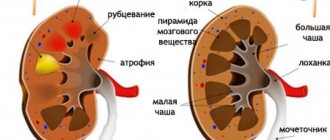
In some cases, undissolved crystal particles or sand form in the lower part of the kidney calyces. Most of these small stones are excreted from the body in urine through the urinary ducts.
When water-salt metabolism in the body is disrupted, existing particles are covered with new layers, which leads to the formation of stones.
Also, the presence of sand can provoke the development of inflammatory processes and the appearance of an ascending infection, and this poses a threat to the functioning of the human body.
Causes of sand in the kidneys, risk factors
Symptoms of sand in the kidneys in women, photo
First of all, the appearance of solid crystals in the kidneys is associated with metabolic disorders. Changes in the chemical composition of blood plasma provoke the formation of microlites in urine.
Sand from the buds is a crystalline formation. They are formed from compounds dissolved in urine. When there is sand in the kidneys, this is manifested by characteristic processes. There are primary and secondary manifestations. The first include:
- Change in the shade of urine - it becomes cloudy and dark, and has a pungent odor.
- Painful sensations appear. They are sharp, aching in nature and cover the abdominal area and groin. This is often evidence of sand coming out. When it moves through the urinary canals from the kidneys, it injures them.
- Disturbances in the process of urination - frequent urge and pain. Sometimes there is blood in the urine.
The second group includes the following manifestations:
- vomiting and nausea;
- the temperature increases and swelling appears;
- hypertension;
- malaise, increased sweating;
- formation of gases in the body;
- sleep disorders.
Symptoms in women are practically no different from the symptoms of sand in the kidneys in men. Both sexes suffer from severe pain in the lower back, abdomen and genitals. An important point is that the presence of sand in the kidneys in women is a contraindication to pregnancy, since during such a period the renal system is most vulnerable.
Treatment for renal pathology will take a long time and carefully. This is due to the fact that there is a risk of the onset of inflammatory processes, since stone crystals damage the internal surfaces where microbes enter. For this reason, at the level of general therapy, medications that have an enveloping and softening effect are prescribed.
It is necessary to treat sand in the kidneys depending on the type of formation and its chemical components. The most common are oxalates, urates and phosphates.
Possible complications
If a patient does not consult a doctor for help in a timely manner, complications arise that are associated with damage to the organs of the urinary system:
- Chronic pyelonephritis is a constantly recurrent inflammation of the renal pelvis of infectious etiology, which leads to kidney dysfunction.
- Acute obstructive pyelonephritis - blockage of the urinary tract with a stone occurs, which disrupts the flow of urine and creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of various bacteria, which can subsequently enter the blood with toxins and cause shock in the patient.
- Pyonephrosis or purulent kidney - urgently needs to be removed surgically.
- Purulent paranephritis is inflammation of the tissue surrounding the kidney.
- Nephrosclerosis is the replacement of renal functional tissue with connective tissue.
- Chronic renal failure is kidney dysfunction.
- Acute renal failure - observed when two or only kidneys fail.
A man who has a tendency to develop sand and stones should contact his doctor or the nearest clinic for medical assistance in case of pain on the right or left side, as well as in the presence of red urine.
Diagnostics
With primary signs of the disease, the patient usually consults a general practitioner or surgeon. The doctor interviews the patient, studies his medical record and taps the lumbar region - a positive Pasternatsky symptom indicates kidney disease.
After a physical examination, the doctor transfers the patient to the urology department, where the urologist refers him for laboratory and instrumental studies. Laboratory tests include a complete blood count (CBC) and a complete urinalysis (UCA).
The CBC determines an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and an increased number of leukocytes in the presence of an infectious agent.
OAM determines micro- or macrohematuria, changes in acidity, bacteria and salt in the urine.
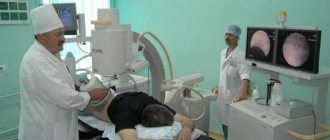
Instrumental diagnostic methods for nephrolithiasis:
- X-ray examination - helps determine the location of sand/stone;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) - allows you to see the size of the kidney, pelvis, which can be dilated, swelling of the parenchyma, the presence of sand/stone;
- excretory urography - assesses the functional state of the kidneys;
- CT (computed tomography) with contrast - helps to find out the density of stones, their location and the anatomical and functional state of the kidneys;
- mineral study of sand/stone.
If the patient is sent for a CT scan, then X-ray diagnostics are not performed.
A complete examination of the patient gives the urologist an idea of:
- localization of sand/stone;
- affected side;
- number of stones;
- shape, size, surface of the stone;
- sand/stone composition.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at removing sand conservatively or surgically and simultaneously treating the underlying disease.
Non-operative treatment is divided into 2 types: medication and herbal medicine. There are two types of drug therapy aimed at removing sand/stone:
- Stone-expelling therapy - drugs from the terpene group are used that stop the crystallization of salts.
- Stone-dissolving therapy - acts on uric acid stones, dissolving them. Doctors use citrate mixtures (citric acid, potassium bicarbonate).
To eliminate pain with drug therapy, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In folk treatments aimed at crushing stones, decoctions of flax seeds, infusions of knotweed grass, horse sorrel seeds, dandelion roots, peas, radish juices with honey, lemon, carrots and beets, pumpkin, barberry, berries, onions and garlic are used. For pain, use an infusion of dill seeds.
Diet therapy
After removing the sand/stone from the kidney, you need to visit a nutritionist to create the right diet.
The patient must:
- reduce the consumption of alcohol, pickles, spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- divide daily meals into 5 meals;
- do not overeat;
- drink 2-3 liters of water per day;
- drink green tea or coffee beans;
- eat green vegetables and fruits;
- reduce sugar and salt intake;
- Avoid taking medications with calcium or vitamin C.
Diet therapy depends on the composition of the stone. For stones consisting of phosphates, eating meat, fish, eggs, peas, legumes, apples, quinces, lingonberries, and grapes is encouraged. Dairy products, vegetables, and fruits are excluded from the diet.