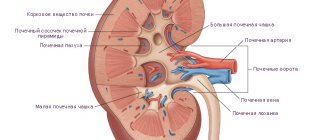
Many people face various inflammatory diseases. The kidneys are one of those organs that are often affected by disease. These include pyelonephritis, paranephritis, glomerulonephritis. To find out the nature of inflammation and its causative agent, it is necessary to conduct a series of laboratory and instrumental studies.
If the inflammation is infectious and caused by bacteria, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. The range of medications for kidney treatment is very wide. The choice of drug cannot be made at random, but take into account the nature of the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Therefore, the prescription of medications for renal inflammation should be individualized.
Inflammatory kidney diseases
The urinary system performs very important functions in the body. It is through it that impurities and toxins are removed, and metabolism is also regulated. The kidneys are constantly under stress. Disruption of their work and inflammatory diseases affect the condition of the entire body.
Inflammation of the kidneys is called nephritis. This group of pathologies includes pyelonephritis, nephrosis and renal tuberculosis. These diseases manifest themselves as severe pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, difficulty urinating, weakness, and high fever. In addition, glomerulonephritis also occurs. This disease is associated with autoimmune disorders, but is also accompanied by a serious inflammatory process.
If inflammation affects the bladder, cystitis develops. The symptoms of this disease are also unpleasant: severe pain and pain when urinating, impaired urine flow. The cause of all these inflammatory diseases is most often an infection. It enters through the urethra due to poor hygiene or through the blood. That is why antibiotics for such diseases are the main method of treatment.
Complications of therapy
Antibiotic-induced acute interstitial nephritis is a rare childhood disorder. You should be concerned if your kidneys hurt 2-4 weeks after taking a beta-lactam antibiotic. Patients develop acute renal failure with fever. Glomerular filtration rate decreases. The study answers the question of whether antibiotics can cause kidney damage. Symptoms of damage: fever, difficulty urinating, weakness.
An increase in morbidity associated with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria causes the development of severe forms of pyelonephritis.
An E. coli infection begins with a urinary tract infection and causes fever, lower back pain, and vomiting. About half of patients require hospitalization.
The study showed that approximately 12-20% of nephritis are resistant to fluoroquinolones. Ciprofloxacin and its generics belong to a class of drugs. A certain strain of E. coli begins to produce new beta-lactamases, which protects bacterial cells.
The development of bacterial resistance confirms the need for preliminary identification of nephritis pathogens. Treatment with antibiotics without prior consultation with a urologist or nephrologist is not recommended. Kidney recovery from inappropriate therapy may require probiotics or dialysis depending on the severity.
Rules for antibiotic treatment
Antibacterial drugs can have a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect. Bactericidal antibiotics cause the death of microorganisms that are sensitive to their effects. When using bacteriostatic drugs, the growth and reproduction of bacteria stops. Typically, antibiotics act selectively on certain types of microorganisms, so they should be used after testing. But there are also broad-spectrum drugs; they are used less frequently, as they are more toxic to the kidneys.
Such medications are taken in the form of tablets, suspensions or injections. For mild to moderate infections, you can take tablets. Suspensions are indicated for children and weakened patients, as they are easier to dose. In the most severe cases, antibacterial drugs are best administered by injection. This way they penetrate the blood faster and spread throughout the body.
How do antibiotics work?
When kidney inflammation is diagnosed, antibiotic treatment is the basis for correct and effective therapy. How do antibacterial drugs work in the patient’s body?
Antibiotics are potent drugs that selectively act on a certain type of pathogenic bacteria that provoke inflammation of the bladder and kidneys. At the same time, such medications do not have a toxic effect on the patient’s body, especially this factor applies to the latest generation of antibacterial agents.
They are introduced into the patient’s body in several ways:
- In the form of tablets or suspension (if the drug is not destroyed in the body by gastric juice or enzymes of the digestive system);
- In the form of injections (for severe inflammation or when you need to achieve maximum effect as quickly as possible).
Antibacterial agents have important properties:
- Bactericidal effect - death of pathogenic microorganisms;
- Bacteriostatic effect - inhibition of the growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Side effects of antibiotics
These drugs destroy bacteria. This has a beneficial effect on the patient's condition. But the peculiarities of their chemical composition mean that they often cause side effects. First of all, it is dysbacteriosis. Antibiotics act not only on pathogenic microorganisms. They can also destroy beneficial bacteria living in the intestines. This disruption of the microflora leads to abdominal pain, heaviness, flatulence, and intestinal upset.
The second most common complication after taking antibiotics is damage to the gastric mucosa. This is manifested by nausea, slow digestion, and heartburn. Women often develop thrush during this treatment. In addition, allergic reactions are common side effects. This could be a rash, hives, itchy skin, watery eyes, or runny nose. A particularly severe allergic reaction occurs when drugs are injected.
Wrong choice of antibiotics, exceeding or decreasing the recommended dosage, early cessation of treatment or frequent unauthorized use before this can lead to the development of resistance in bacteria. As a result, chronic inflammation can develop, which is very difficult to cure.
Will antibiotics help?
There are many reasons why an inflammatory process in the kidneys can begin, but the disease itself usually occurs against the background of decreased immunity. Very often, pyelonephritis is observed in pregnant women precisely for this reason. The most effective method of treatment in this case is treatment with antibiotics; their choice is quite wide. Antibiotics for inflammatory processes in the kidneys are the most effective treatment method.
During pregnancy, not all medications are allowed to be taken, so the attending physician prescribes a treatment regimen based on the patient’s health condition and after carefully studying the risks. The problem is that the antibiotic can have a negative effect on the formation and growth of the fetus. Inflammatory processes in the kidneys are dangerous due to their complications. Any kidney disease can become chronic if not treated correctly, and subsequently, in a particularly unfavorable course, lead to the destruction of kidney tissue.
The cause of kidney inflammation is enterococci and staphylococci that enter the body. Less commonly, kidney inflammation can be caused by other pathogens.
Inflammation of the kidneys is more common in women than men; this is caused by the specific structure of the female genitourinary system. But the approach to antibiotic treatment in patients of both sexes is almost the same. Medicines in tablets do not have the desired effect.
Inflammation of the kidneys is usually accompanied by symptoms such as a sharp increase in temperature against the background of active sweating. The patient begins to feel chills. From the genitourinary system, the disease is manifested by difficulty urinating. Attacks of nausea, dizziness, and general weakness may occur. Against the background of kidney inflammation, blood pressure may increase and appetite may decrease. The most striking manifestation of the inflammatory process in the kidneys is cloudiness of the urine, which, upon examination, reveals a high content of protein and leukocytes.
In the acute form of inflammation, intense manifestation of most of the symptoms is observed. With chronic inflammation, the symptoms are almost the same, but the temperature may rise slightly, and rarely above 38 °C. In patients with chronic kidney inflammation, the skin usually has an sallow tone.
Purely anatomically, you most often encounter inflammation of the right kidney. Treatment of the disease can be started only after an accurate diagnosis has been made and confirmed by laboratory tests. Only after identifying the pathogen that led to the inflammation can antibiotics be selected that will have the most effective effect and suppress the growth and reproduction of pathological flora. The dosage of any drug in the treatment of kidney inflammation depends on the patient’s condition. If the inflammatory process is intense, taking pills is replaced by intravenous administration of drugs.
How to use antibiotics for kidney pathologies
The main goal of such treatment should be to eliminate the infection. Therefore, when choosing a dosage, it is necessary to ensure that the concentration necessary to kill bacteria is achieved in the kidney tissues. Sometimes, at the beginning of treatment for kidney disease, antibiotics are prescribed in a loading dose, then it is reduced. In any case, the dosage is selected strictly individually.
Usually the duration of treatment is 7-10 days. But this is only if the bacteria are sensitive to this drug. Therefore, broad-spectrum antibiotics are first prescribed for kidney and urinary tract diseases. And they take urine tests to determine the causative agent of the infection. If no improvement is observed after a couple of days, the drug is discontinued and a specific drug is prescribed that acts specifically on these bacteria. Sometimes it is also necessary to use several drugs at the same time.
You should take antibiotics only as prescribed by your doctor. If negative reactions occur, you must immediately inform him about this in order to change the drug in time. It is also important to take additional probiotics to restore disturbed intestinal microflora.
Possible complications
Unfortunately, taking antibiotics is fraught not only with the death of pathogenic bacteria, but also with side effects that the drugs cause:
- dysbacteriosis;
- thrush;
- resistance of pathogenic microflora to antibiotics if used incorrectly;
- allergic reaction (before taking the drug you need to do allergy tests).
The key to a successful treatment outcome for kidney inflammation is timely assistance from a specialist and properly selected therapy. In most cases, kidney infections cannot be treated without the use of antibiotics. Each of them has its own spectrum of action and certain contraindications. Under no circumstances should you take antibiotics on your own! It is important to seek help from a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
Video. A specialist from the Moscow Doctor clinic on the rules for using antibiotics for kidney inflammation:
Names of antibiotics for kidney diseases
The list of antibacterial drugs is quite long. According to the chemical composition of these drugs, several groups are distinguished. In addition, there are several generations of antibiotics. They may differ in effectiveness and toxicity. The new generation of drugs will not always be more effective; for some pathologies, already tested, time-tested drugs are more often used.
Antibiotics for kidney and urinary tract diseases should be prescribed by a doctor. After all, not all of them are effective against the causative agents of such diseases, in addition, many of them can damage the kidneys. Usually, drugs from several groups are used, and not all drugs from them are indicated. Most often used:
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- penicillins;
- fluoroquinolones;
- carbamazepines.
It is impossible to decide on your own which antibiotic is best for kidney disease. Only a doctor can determine this based on tests and the patient’s condition.
How to understand if your bladder is suffering
Antibiotics for the kidneys and genitourinary system are generally the same. Just like the initial symptoms. The causes of diseases are different. Often, a person suffering from cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) independently begins to look for the cause in a completely different place from where it was localized. Everything is attributed to the kidneys or reproductive organs. Over time, the inflammatory process will spread to them, but it is best to start therapy immediately, without delay.
To recognize the onset of problems, you do not need any special knowledge in the field of medicine:
- pain going down from the lower back;
- increased fatigue and frequent morning gag reflex;
- changes in urine consistency, color and smell;
- possible appearance of blood in urine;
- increase in body temperature to 37.8 degrees;
- pressure and frequent urge to urinate.
Even if the patient decided that this is how the kidneys are making themselves known, which is also quite possible. Antibiotics used for kidney disease will give a positive result in any case. It is believed that the inflammatory processes are interconnected. But there is one “but”. It is worth considering the gender of the person who has kidney and bladder problems. This is important, since the manifestations of ailments may differ:
| signs | man | woman | General characteristics for wallpaper floors |
| Problems with urine output | Since the urethral canals differ in length and width, urine is discharged less actively. But at the same time, the fullness of the bladder affects the patient’s well-being. | Desire for frequent bowel movements. Urine flow is much lower. | Burning in the urethral canal, mainly at the end of bowel movement. Increased temperature, dry mucous membranes (oral and groin cavity), discharge |
| Nervous system | Drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness | ||
| Gastrointestinal organs | Pain, constipation | Bloating, diarrhea (common) | |
| Other organs | Prostate pain, cardiac arrhythmia | Gout, renal colic, enlarged lymph nodes | The inflammatory process spreads to the reproductive system, weak sexual desire, pain during sex |
Need to know! The inflammatory process in the kidneys and bladder often occurs in childhood. Characteristic features of inflammation are high fever and severe pain in the groin area or lumbar region. Contractive attacks make the child cry and lead a passive lifestyle.
Cephalosporins
Judging by the reviews of doctors and patients, these are the most effective antibiotics for kidney diseases. The names of such drugs are unfamiliar to many people, since they are prescribed less frequently for other pathologies. But they are most effective against bacteria that cause inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract. Already on the second day of treatment, most patients feel relief. Cephalosporins have low toxicity and are well tolerated by most patients, but they cannot be used in chronic renal failure. These are effective antibiotics for kidney diseases; the patient feels relief after just a couple of days of treatment.
The most commonly used drugs are: Cephalexin, Ceforal, Tsiprolet, Klaforan, Tamycin, Cefoperazone. Judging by the reviews, they are effective against a large number of microorganisms, prevent the development of purulent complications and quickly relieve inflammation.
Diagnosis and symptoms of the disease
There are several types of inflammatory process:
- pyelonephritis means damage to the parenchyma and pyelocaliceal region;
- glomerulonephritis is diagnosed with glomerular pathology;
- pyonephrosis indicates the formation of a purulent abscess and melting of organ tissue;
- Tuberculosis is diagnosed when Koch's bacillus is detected.
The main task of a nephrologist is to identify the localization of the lesion, the causative agent of the infection, and differentiate the pathology of the kidneys and urinary tract.
The following symptoms will help recognize kidney disease:
- nagging dull pain on the right or left side of the lumbar region;
- urinary disturbance;
- chills and fever;
- weakness and dizziness;
- nausea and loss of appetite;
- cloudy urine;
- swelling;
- high blood pressure.
The main symptom is pain in the kidneys, which does not subside when changing body position and even lying down.
Inflammation of the kidneys can be acute with a sharp development of symptoms, tachycardia and sweating, poor urine output, as well as chronic - with a change in skin tone, an increase in temperature up to 38 degrees. Dangerous is purulent inflammation associated with urolithiasis, a sharp deterioration in health and severe pain. What to do in each specific case is suggested by taking an anamnesis, ultrasound, urine and blood tests. In almost 90% of cases, kidney inflammation has to be treated with antibiotics.
Any pathology of the urinary tract that interferes with the outflow of urine increases the chances of infection:
- blockage of the urinary tract due to kidney stones or enlarged prostate;
- incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- structural problems such as narrowing or pinching of the urethra;
- Vesicoureteral reflux, or urine flowing back into the kidneys.
Women, due to the short length of the urethra and the characteristics of the genitourinary system, are more likely to develop pyelonephritis. The infection enters the organ in two ways:
- ascending - against the background of a genitourinary infection;
- descending - due to an infectious focus in the body.
The risk of infection increases as a result of disruption of the innervation of the bladder as a result of lumbosacral injuries or surgical interventions.
Due to inflammatory dysfunction of the prostate gland, the outflow of urine is disrupted. Using a urinary catheter increases the risk of infection. Weak immune system due to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
Aminopenicillins
These are the most famous and low-toxic antibiotics. For kidney disease in women, they are used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. But they are not very effective in the presence of complications, so their use is advisable only in mild cases of the disease. They are especially effective against enterococci and E. coli.
There are several broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs from the aminopenicillin group, which are most often used for kidney inflammation.
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Penicillin";
- "Ampicillin."
Features of prescribing antibiotics in the treatment of kidneys in women and men
It should be noted that due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the urinary organs, women suffer from inflammatory kidney diseases much more often. In young and middle-aged men, this pathology practically does not occur, but in older men, against the background of stagnation of urine as a result of mechanical compression of the urethra by enlarged prostatitis or prostate adenoma, kidney inflammation may develop. Unlike women, inflammatory processes in the urinary organs in men are more often chronic in nature, and the manifestations of the disease are often erased. Based on this, approaches to treatment for representatives of different sexes will differ.
In men, inflammatory kidney diseases usually occur against the background of prostate pathology, have a chronic course, and should be treated like chronic diseases
Since in men, pyelonephritis most often develops against the background of E. coli, the drugs of choice for them are usually semisynthetic penicillins in combination with clavulanic acid (Flemoclav, Amoxiclav, Panclave), as well as cephalosporins of the second and third generation.
For women, it is preferable to prescribe hydroxyquinolone drugs, which have a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity, are effective against fungi, and are well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, the drugs of choice for them are fluoroquinolone derivatives (Nolitsin, Cifprofloxacin), the effect of which occurs quite quickly, while side effects are usually minimal.
Aminoglycosides
These antibiotics for kidney and bladder diseases are used in cases of renal failure or other chronic pathologies. They are less toxic than other drugs, they can be used even during pregnancy, but they are also less effective. Judging by the reviews of doctors, aminoglycosides are most active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, therefore they are good at preventing purulent complications. Improper use of such drugs can lead to damage to the kidneys and hearing organs.
Aminoglycosides are most often used in a medical setting in the form of injections. The most common drugs are Amikacin, Gentamicin, and Netilmicin. Sometimes in difficult cases they are combined with antibiotics from the penicillin group.
Antibacterial agents
In medicine, there are quite a large number of groups of various antibacterial agents; their main classification depends on the chemical component of the drug. In addition, each group has several generations.
- Ampicillin, Amoxicillin (penicillin group) - drugs suppress the activity of E. coli and are actively used in the treatment of inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Zinnat, Cephalexin, Claforan (a group of cephalosporins) - drugs are active against pathogens of the inflammatory process, while they do not negatively affect the patient’s body. This group of medications helps prevent the possible progression of the disease to the purulent stage;
- Amikacin, Gentamicin (group of aminoglycosides) - drugs have excellent bactericidal properties, they are prescribed for kidney inflammation, accompanied by various complications;
- Ciprofloxacin, Pefloxacin, Ofloxacin (a group of fluoroquinolones) are drugs with bactericidal properties; they are prescribed if the patient is suffering from pain;
- Sumamed, Vilprafen (group of macrolites) - very effective for inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, they have a particularly strong pathogenic effect against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- Furadonin, Furamag (group of uroseptics) - prescribed for moderate severity of the disease.
All of the above drugs are effectively used in treatment, but it is important to remember that each of the groups of these drugs has individual contraindications. For example, most of them are strictly prohibited for young mothers during lactation and women during pregnancy. The group of macrolites is prohibited for children under 14 years of age. Antibiotics for men are selected individually; in this case, it is important to monitor the presence of possible chronic diseases and complications of the inflammatory process.
Only the doctor, after examining the patient, conducting the necessary medical tests and after confirming an accurate diagnosis, determines which antibiotics to take.
Carbapenems or beta-lactams
These antibiotics are rarely prescribed for kidney diseases, only in cases of severe disease and the presence of a large number of complications. After all, a contraindication to their use is renal failure, so they try to prescribe them when other drugs have proven ineffective, as well as in cases of chronic inflammation with many complications. This group includes little-known drugs: Meropenem, Carbonem, Imipinem. Judging by the reviews, they are effective in cases where bacteria develop resistance to penicillins or cephalosporins.
Treatment of pathology with antibiotics
Antibiotics are among the main drugs used as part of complex therapy for inflammatory infections of the genitourinary system. There are several groups of antibiotics that can effectively cope with infectious inflammation.
Aminopenicillions
As a rule, treatment is started with aminopenicillins. These include amoxicillin and penicillin. They are effective against Escherichia coli and Enterococcus. A significant disadvantage is that they do not act against the main pathogens of pyelonephritis. Penicillins are allowed to be used during pregnancy and lactation.
Cephalosporins
These are low-toxic drugs that are effective against bacteria that cause pyelonephritis and other nephritis. Medicines prevent the acute form of inflammation from becoming chronic. Already on the third day of using a cephalosporin antibiotic, relief of the symptoms of the disease can be observed. Antibiotics should be prescribed with caution to pregnant women and people with kidney failure.
Drugs of the cephalosporin group:
- Cephalexin;
- Zinnat;
- Cephalothin;
- Cefaclor;
- Clarofan.
Fluoroquinolones
Prescribed for acute forms of inflammation, severe pyelonephritis, in cases where there is a danger to the patient’s life.
1st generation fluoroquinolones:
- Ofloxacin;
- Fleroxacin;
- Ciprofloxacin.
Important! The above drugs should not be taken in case of renal and liver failure, epilepsy, atherosclerosis and cerebral circulatory disorders, or during pregnancy.
For chronic kidney inflammation that progresses to the acute stage, it is recommended to take 2nd generation fluoroquinolines:
- Spaofloxacin;
- Levofloxacin.
They are effective against pneumococcal infections.
Second-line antibiotics
The doctor prescribes some antibiotics only for severe forms of inflammation; they can only be used in a hospital setting. There are several groups of such drugs.
Aminoglycosides:
- Gentamicin;
- Amikacin;
- Sizomycin;
- Amikacin;
- Tobramycin.
The doctor selects the dosage of each antibiotic depending on the patient’s tolerance, general condition, and severity of clinical manifestations.
Taking aminoglycosides may be accompanied by side effects:
- hearing impairment;
- reversible renal failure.
They are not prescribed for renal failure, damage to the auditory nerve, uremia, elderly people and pregnant women.
Additionally the following can be used:
- 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins (Cefpirom, Ceftriaxone);
- carbamazepines (Imipenem, Meropenem).
See a selection of effective methods for treating pain when urinating in women.
The list and characteristics of tablets for bladder inflammation can be seen in this article.
Go to https://vseopochkah.com/mochevoj/mocheispuskanie/rezi-u-muzhchin.html and learn about the probable causes and methods of treating pain at the end of urination in men.
Fluoroquinolones
These drugs are also toxic and have a large number of contraindications and side effects. They are also used only in the most serious cases, when there is a threat to the patient’s life due to complications. Fluoroquinolones are bactericidal drugs that destroy infection in the urinary system.
In the chronic form of kidney pathologies, when a serious exacerbation occurs, Levofloxacin or Sparfloxacin is started.
If the inflammation is severe, there are complications and the risk of death is high, stronger medications are prescribed: Ciprofloxacin, Tsifran, Moxifloxacin, Ofloxacin. These drugs are also used in cases where other antibiotics have not worked.
Consequences of self-medication
Medicines are not suitable for self-treatment. This rule applies to all medications. Taking into account side effects, contraindications, age, body weight, diagnostic data - all this information is the key to successful treatment and is necessary for the correct choice of drug. The consequences of uncontrolled use of antibiotics include allergic reactions, addiction syndrome, and the development of bacterial resistance, which complicates subsequent stages of treatment and limits the doctor’s choice of medications. In the treatment of diseases of the urinary system, improper use of medications threatens the pathology becoming chronic.
Other means
If the patient does not self-medicate and consults a doctor on time, most often it is possible to quickly stop the infection and inflammation. Experts know better which antibiotics to take for kidney disease.
In some cases, the use of other groups of drugs is justified. For example, nitrofurans are sometimes used. These remedies have long been known and were often used for cystitis or pyelonephritis before. These are “Furadonin”, “Furazolidone”, “Furamag”.
Sometimes, if there is intolerance to penicillins and cephalosporins and the condition is mild or moderate, drugs from the macrolide group are prescribed. These are “Vilprafen”, “Sumamed”, “Erythromycin”, “Clarithromycin”, “Azithromycin” and others. Judging by the reviews, they are most often used for glomerulonephritis, as they have a mainly bacteriostatic effect.
Kidney dysfunction
Treating the kidneys with antibiotics is not always beneficial. Therefore, in case of any problems, they should not be used. As for the inflammatory process in them, the factors that provoked it are very different, which means that treatment with only one type of pills or other medications is pointless.
A healthy person knows about the presence of such an organ as the kidneys only from a short school course on anatomy. Anyone who is faced with kidney problems will know not only how much they hurt and what consequences such a “meeting” will result in, but also where exactly the left or right kidney is located without an ultrasound examination. The worst thing is when the disease, especially the kidney disease, becomes chronic. And then the natural human filter malfunctions. If the cleansing function does not occur, then all organs suffer, not just the urinary system.
Renal dysfunction
What types of kidney diseases can there be? There are quite a few of them and they all begin with an inflammatory process:
- renal failure and metabolic diseases;
- cancerous tumors and hydronephrosis;
- polycystic disease and nephroptosis;
- nephrolithiasis and glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis and stones.
Each symptom has its own characteristics. If a course of treatment aimed at eliminating inflammation has not begun in a timely manner, then sooner or later, one of the diseases presented will certainly appear. How to determine that inflammation has begun and begin the search for a suitable medicine for kidney inflammation? It’s better not to diagnose it yourself and not go into searches. But the initial stage, some kind of hints, are worth knowing:
- morning swelling of the face and limbs;
- sudden changes in blood pressure. Horse racing;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- lack of sleep and chronic fatigue.
It is worth paying attention to lower back pain, which can spread below the kidneys, into the groin and between the thighs
Then everything goes on and on. And a person is simply not able to cope with the pain that is constantly present. But often, in conditions of weakened immunity, the symptoms are blurred for a long time. This is extremely unfavorable, since it is not entirely clear what is happening. At the same time, the chronic process comes into full force and all that remains is to support yourself with medications.
Drug rating
Antibiotics can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. They are chosen individually, but there are several that are used most often. In accordance with the frequency of their use, we can rank the most effective antibiotics:
- "Tsifran";
- "Furadonin";
- "Doxycycline";
- "Nolitsin";
- "Amoxicillin."
They combine high efficiency, good tolerability and low price. These are broad-spectrum drugs, so they help in most cases.
What antibiotics are prescribed?
In the treatment of kidneys, aminopenicillins are primarily used. Drugs in this group have proven themselves well in the fight against enterococci and in cases where the inflammatory process in the kidneys arose due to E. coli. These drugs are the least toxic of all antibiotics, so their use is also allowed if the patient is pregnant. The use of these drugs is indicated in the initial stages of the inflammatory process. This group includes:
Next in frequency of use is the group of cephalosporins. These antibiotics also have a low level of toxicity. But their use is most justified if there is a high risk of developing a purulent form of inflammation. Positive dynamics in treatment are observed starting from the 3rd day of taking the drugs. The group of cephalosporins includes:
Principles of treatment
Therapy is selected based on diagnostic results that determine the condition of the genitourinary system and the pathogen that causes the disease. Before starting a course and prescribing antibiotics, the doctor must conduct research, including:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis and urinary tests;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography or tomography.
Self-selection of antibiotics is dangerous. This can transform the disease into an acute or chronic form with the appearance of complications.
Types of antibiotics depending on the form of release
Antibiotics for the treatment of kidney inflammation are available in both tablet and injection forms. Both have their advantages and disadvantages. Tablets are easier to give to children, they can be used without problems for outpatient treatment, and there are no systemic side effects when used. On the other hand, as a result of taking tablets, dysbiosis may develop, and the effect of their use does not occur as quickly as when using injection forms.
Tablet antibiotics include fluoroquinolone derivatives (Levofloxacin, Nolitsin, Norfloxacin), a combination of semisynthetic penicillins with clavulanic acid (Flemoklav Solutab, Augmentin, Amoxiclav), macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin).
Antibiotics in the form of tablets or capsules can be taken outside a hospital setting; they are easier to give in childhood
Injectable forms of antibiotics
A number of drugs are released only for parenteral (intramuscular or intravenous) administration. These include benzylpenicillin, gentamicin, carbapenems. The advantage of these medications is the rapid onset of the therapeutic effect, the absence of dysbacteriosis, and a more pronounced effect compared to tablet forms. On the other hand, the use of injectable forms in most cases requires a hospital stay, and if a child is ill, it is much easier to persuade him to take a pill than to give an injection.
The vast majority of mothers are faced with issues of child illness and the use of antibacterial drugs for their treatment. At one time, a real revolution for me was the release of polysynthetic penicillins in the form of solutions or sweet suspensions (Ospamox, Amoxil, Flemoxin). They are very convenient to dose; the child happily agrees to try the pleasant-smelling sweet liquid. If the disease required the use of injectable forms, then the positive effect of the drug was almost completely offset by the psychological trauma of the child.
In most cases, kidney inflammation requires the use of antibacterial drugs. In a situation where it is impossible to determine the causative agent of the disease, treatment begins with the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, the safest of which are semisynthetic penicillins in combination with clavulanic acid. Antibiotics in the form of solutions for infusion act faster and more effectively, however, in some cases (pregnancy, childhood), treatment still begins with dosage forms for oral administration.
Treatment of pregnant, lactating women and children
safe medicines for mother and child
Due to physiological changes in women during pregnancy, their kidneys very often hurt: this may indicate that they have inflammation, which is a complication of cystitis, an exacerbation of pyelonephritis, etc. Of course, they try to treat pregnant women without prescribing antibiotics, but sometimes this is not possible. In urgent cases, when the process progresses and the kidneys hurt more, women can be administered Cefazolin and Ceftriaxone.
Penicillin is used to treat cystitis and other inflammations. In addition, this same drug can be confidently used during lactation, since it penetrates into milk in low doses that are not capable of harming the baby. But it was noticed that during lactation, after taking Penicillin, thrush, diarrhea, and rash in women can develop. Thus, taking any antibiotics during a critical period of pregnancy is undesirable - you should avoid any hypothermia, which can cause the development of cystitis and, as a consequence, pyelonephritis and kidney failure.
Rules of application
Safe treatment is only possible with preliminary diagnosis and receipt of doctor’s recommendations:
- Antibiotics should be taken in the dosage prescribed by the doctor at a strictly defined time. Features of the action are associated with the need to maintain a certain concentration of the active component to effectively destroy pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure a uniform supply of the drug to the body throughout the entire treatment period.
- When treating with antibiotics, it is important to understand that part of the natural intestinal microflora inevitably dies when exposed to drugs. At the active stage of anti-inflammatory therapy, you should start taking natural prebiotic and probiotic drugs in order to reduce the consequences of taking antibacterial tablets.
- Manifestations of mild intoxication are considered normal, but increased side effects indicate excessive toxicity of the chosen drug.
Deterioration of the condition while taking antibiotics indicates incorrect tactics or the addition of a secondary infection. Dosage adjustment, selection of another drug, and repeated laboratory diagnostics are required.
Auxiliary treatment
The drug treatment regimen depends on the cause of the disease. If a bacterial infection spreads to the urinary tract, causes intoxication or fever, symptomatic drugs are prescribed.
- non-narcotic analgesics – Diclofenac, Ibuklin;
- detoxification agents – Reamberin, Ringer’s solution;
- antihistamines - Astemizole, Clemastine;
- antispasmodics – Platiphylline, Drotaverine.
At the remission stage, immunostimulants and vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed - Centrum, Alphabet, Doppelherz. They stimulate the immune system, preventing relapses of inflammation in the kidneys.
Urine provides a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms. Entering the urinary tract from the outside or through the blood, pathogenic bacteria are able to multiply unhindered and lead to infectious damage to the kidneys, which can lead to the development of chronic processes and subsequent renal failure. In this regard, antibiotics play a significant role in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory kidney diseases. Since inflammatory processes of the urinary system are more common in women, they are the main patients in need of antibacterial therapy.
Antimicrobials for kidney treatment
To find out which antibiotics to take for kidney inflammation, the sensitivity of bacteria to different groups of drugs is determined. To combat pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, the following types of antimicrobial agents are used:
- carbapenems;
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- fluoroquinolones.
Based on pharmacological activity, antibiotics are divided into 2 groups - narrow and broad spectrum. The former target specific types of bacteria, while the latter destroy most known pathogens in the kidneys.
Antibiotics should be selected only by a urologist or nephrologist, taking into account the results of laboratory tests of blood and urine.
Penicillins
To destroy pneumococci, streptococci, and E. coli, low-toxic penicillin antibiotics are prescribed. Their advantages include:
- wide spectrum of action;
- low toxicity;
- bactericidal activity.
The penicillin group includes semi-synthetic and natural antibiotics that are produced by mold fungi. To treat a kidney infection, doctors prescribe:
- Oxacillin is a beta-lactamase-resistant drug that is used to treat cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- Ampicillin is an antibiotic in tablets that exhibits bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli, streptococci, and enterococci;
- Penicillin is a low-toxic antibiotic used in the complex therapy of pyelonephritis;
- Amoxicillin is an oral suspension that destroys uncomplicated kidney infections;
- Azlocillin - a solution for injection into a muscle or vein, eliminates urogenital infections of a bacterial nature.
Penicillins are the first-line medications used to treat kidney infections. In case of an allergic reaction to their components, cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones are prescribed.
Cephalosporins
This group of drugs includes semi-synthetic and natural antibiotics. Their spectrum of action is wider than that of penicillins. The components of the drugs are excreted by the kidneys, so they quickly destroy the infection in areas of inflammation. For the treatment of pyelonephritis the following are used:
- Kefzol is an injection powder that destroys infection in the bile and urinary tract;
- Cephalexin is a bactericidal capsule that disrupts the synthesis of cell membranes of pathogenic bacteria;
- Klaforan is a semi-synthetic antibiotic that eliminates bacterial flora in the renal parenchyma and urinary tract;
- Cefamandole is a bactericidal solution for intramuscular administration, which is prescribed for infectious lesions of the kidneys, ureter, and genital organs in women;
- Keiten is an injection powder that eliminates abscesses in the organs of the urinary system.
Antibiotics for kidney diseases are taken in courses of 7-10 days. Kidney injections are given into a vein or muscle once a day. Cephalosporins are much more toxic than penicillins, but they are less likely to provoke allergic reactions.
Fluoroquinolones
Broad-spectrum drugs exhibit bactericidal activity against most pathogens of pyelo- and glomerulonephritis. Fluoroquinolones are prescribed for complicated or indolent inflammation of the kidneys.
Names of antibiotics for kidney pain:
- Pefloxacin is an antimicrobial agent that blocks the production of protein components of bacteria. Used in the treatment of bacterial infections in the bladder, prostate, kidneys.
- Ciprofloxacin is a bactericidal tablet that eliminates inflammation in the kidney tissue (parenchyma). They act selectively on pathogens, preventing the synthesis of bacterial DNA and the proliferation of microorganisms.
- Ofloxacin is an effective remedy that eliminates inflammation in the lower and upper urinary tract. Destroys most pathogens of pyelonephritis.
- Sparfloxacin is a tablet antibiotic that inhibits the proliferation of more than 80% of pathogenic bacteria. Effectively fights pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis and prostatitis.
- Levofloxacin is a drug for the treatment of kidney infection complicated by bacterial inflammation of the ureter. Quickly relieves pain and prevents the formation of ulcers in the urinary system.
Fluoroquinolones are not prescribed to pregnant women and children under 18 years of age, due to the high toxicity of this group of drugs.
Carbapenems
To quickly cure inflammation in the kidney tissue, carbapenems are prescribed. They are resistant to beta-lactamases, which destroy penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics.
In the treatment of kidneys the following are used:
- Ertapenem is an effective antibiotic that is suitable for the treatment of nosocomial and community-acquired bacterial infections;
- Meropenem is a broad-spectrum medicine that is used in the treatment of indolent pyelonephritis;
- Imipenem is a drug that exhibits antibacterial activity against most pathogens of kidney infections;
- Jenem is an injection powder suitable for the treatment of severe kidney diseases;
- Mepenem is a potent antibiotic that destroys complicated infections in the kidneys.
Long-term use of carbapenems is dangerous due to intestinal dysbiosis and vitamin deficiency. Most drugs are nephrotoxic, that is, they have a toxic effect on the kidneys.
Aminoglycosides
Compared to carbapenems, aminoglycoside antibiotics are more toxic. But they have a pronounced bactericidal effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacteriaceae, and Proteus. For kidney diseases, the following are often used:
Antibiotics easily penetrate into the extracellular spaces, destroying the infection around the kidneys. Their effectiveness depends on the peak concentration of active substances in the blood. Therefore, when treating kidney problems, you must strictly adhere to the dosage determined by your doctor.
An overdose of aminoglycosides leads to disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Reserve drugs
To prevent inflammation from passing into a purulent-destructive form, therapy begins with the most effective medications. For complicated forms of pyelonephritis in adults, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The most effective drugs are those that are not destroyed by beta-lactamase, a bacterial enzyme.
The list of effective medications includes:
- Clindamycin;
- Lincomycin;
- Tetracycline;
- Doxycycline;
- Azaktam.
Antibacterial therapy is a mandatory stage of drug treatment for inflammation in the kidneys. Most drugs are highly toxic, but without them it is impossible to eliminate the bacterial flora in the affected areas.
Reasons for the development of inflammation
Kidney inflammation can occur at different ages. At risk are:
- Small children;
- women 18-30 years old;
- men over 50 years of age (due to a tendency to develop prostate adenoma).
The main cause of inflammation is the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the kidneys from other organs, through the blood and lymph. More often these are streptococci, which come from foci of infection in the respiratory system (tonsillitis, pharyngitis).
Predisposing factors:
- pregnancy;
- hypothermia;
- diabetes;
- urolithiasis disease;
- heart diseases;
- genitourinary system infections;
- surgeries on the pelvic organs;
- weakened immunity.
Find out the instructions for using Palin for cystitis and other urological diseases.
Read about how to prepare cranberry juice and how to use it for kidney ailments at this address.
What antibiotics treat nephritis?
If the patient is diagnosed with nephritis, then benzylpenicillin is prescribed for a course of 10 days. In this case, the dose is 1 million units, which are administered up to 6 times within 24 hours. If the cause of kidney inflammation is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, then the treatment regimen is selected taking this fact into account. In this case, the choice falls on penicillins that can fight this pathogen, for example, Pipracil and Securopen. If these drugs are not suitable for any reason, they are replaced with Gentamicin or Amikacin.
If the patient had kidney problems before the inflammatory process, he is prescribed Ciprofloxacin with monitoring of a biochemical blood test.
Cephalosporin antibiotics are effective in the treatment of both pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. This type of antibiotics is eliminated from the body primarily by the liver, so they can be used for any kidney disease. Most antibiotics exclude alcohol consumption.
It is worthwhile to dwell separately on the list of antibiotics approved for use in pregnant and nursing mothers. It includes cephalosporins, protected penicillins and macrolides. All these drugs successfully inhibit the growth and development of microorganisms and at the same time belong to low-toxic drugs. Macrolides have the weakest effect on pathogens and are prescribed during pregnancy if the use of drugs from the other 2 groups for some reason becomes impossible. Most often, drugs from this series are prescribed to pregnant women during exacerbation of the chronic form, when the course of the disease is not so intense. When breastfeeding, preference is given to Amoxicillin, Cefoperazone, Cefobid. These drugs are quickly eliminated from the body and do not accumulate in organ tissues.
The standard treatment plan for pyelonephritis includes several drugs: with anti-inflammatory, uroseptic and antibacterial effects. What role do antibiotics play in kidney inflammation? In our review, we will consider the principle of action and features of the use of common antimicrobial agents for the treatment of urinary tract infections.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys, in which this organ often hurts. It occurs due to various bacterial or viral infections of other organs and can lead to the development of kidney failure. For this disease, antibiotics are prescribed only in cases where studies have proven the bacterial nature of its occurrence. Since glomerulonephritis most often develops after a sore throat, purulent skin lesions or pneumonia, patients are prescribed a drug active against streptococcus. Thus, antibiotic therapy is carried out with the help of Erythromycin, Ampicillin, Erythromycin or cephalosporins. When prescribing them, it should be remembered that penicillin drugs and Erythromycin cannot be used if the patient has renal failure.
For all other pathologies, when the kidneys are painful and inflamed, antibiotic therapy rarely differs from that given above. All medications are prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis . When making this choice, the specialist must take into account the type of microorganisms that caused inflammation, their sensitivity to various substances, and the presence of concomitant diseases, such as cystitis or renal failure.
What antibiotics to take for kidney inflammation
Basic therapy for diseases of the urinary system is carried out over a course of several days to two weeks. If the disease progresses slowly and the clinical picture is characterized by low intensity, antibiotics for the kidneys are prescribed in tablets. Otherwise, preference is given to antibacterial agents in solutions for injections or droppers. To suppress bacterial flora, the following groups of drugs are used:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides;
- carbapenems;
- aminoglycosides.
Penicillins
Antibiotics for the kidneys of the penicillin series are prescribed in cases where the diagnostic results showed that inflammation occurred due to the penetration of gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria into the body: Escherichia coli, staphylo- or streptococci, enterococci. The drugs block the synthesis of a special protein, peptidoglycan, which takes part in the construction of the cell membrane, as a result of which microorganisms die.
Penicillin antibiotics are characterized by low toxicity, due to which they can be used for urinary tract diseases in pregnant women and nephrotic syndrome. This group of drugs includes:
- Augmentin. This is a combined antibiotic containing two active components - amoxicillin trihydrate and clavulanic acid. It is available in the form of tablets of 20 pieces. packaged. The dosage regimen is selected depending on the age and body weight of the patient. The minimum course of taking an antibiotic is 5 days. Augmentin is used with caution for liver diseases. The drug can cause diarrhea, nausea, and headache. Amoxiclav is a complete analogue of Augmentin.
- Trifamox. This multicomponent antibiotic contains a combination of amoxicillin and sulbactam pivoxil as active substances. The drug has several forms of release: tablets, suspension, solution for injection. The recommended daily dosage is 750 mg (3 tablets). Duration of treatment – 14 days. The medicine is not prescribed to patients with mononucleosis and ulcerative colitis. Trifamox can cause allergic reactions, stool disorders, and cholestatic jaundice.
If Pseudomonas aeruginosa is detected in tests, penicillins are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at combating this pathogen. These medications include: Pipracil, Securopen. The effect of these antibacterial agents is enhanced with the help of 2nd or 3rd generation aminoglycosides - Gentamicin, Amikacin. If you are intolerant to aminoglycoside drugs, use the fluoroquinolone Ciprofloxacin.
Cephalosporins
Drugs in this group are usually prescribed if there is a high risk of complications. Cephalosporins prevent the transition of the acute form of inflammation to a purulent one and effectively destroy the causative agents of pyelo- or glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys involving interstitial tissue). Improvement in the well-being of severely ill patients is observed already on the third day after the start of antibacterial therapy.
Cephalosporin antibiotics for kidney pain are not recommended for patients with an allergy to the active ingredient or for pregnant women in the first trimester. The drug group includes:
- Ceftriaxone is a powder for the preparation of a solution for parenteral administration. The standard dosage of the medicine is 1-2 grams 1 time/day. In severe cases of kidney inflammation, the dose is increased to 4 g. The drug can cause chills, urticaria, vomiting, diarrhea, and intestinal dysbiosis. A complete analogue of Ceftriaxone is the drug Rocephin.
- Cefotaxime – solution for injection. For intramuscular administration, the standard dosage is 0.5 grams, for intravenous injections - 1 g. The drug often causes allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, swelling), dyspeptic disorders (vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, dysbacteriosis).
- Kefadim is a solution for injections with the active ingredient ceftazidime. For kidney problems, the initial dose of the drug is 1 gram. An antibiotic can cause itching, cramps, headaches, and intestinal upset.
- Cephobid. The active ingredient is cefoperazone. The drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, 2-4 grams every 12 hours. In severe cases, the dosage is increased to 8 g. Side effects are minor: urticaria, diarrhea, pain at the injection site.
This drug group has low activity against enterococci, staphylococci, and E. coli, but is effective against streptococcal flora. Macrolides do not destroy bacteria, but stop their growth, stimulating the immune system to fight infection. More often they are prescribed for glomerulonephritis. The following drugs are considered the gold standard of treatment:
- Erythromycin - tablets with the same active ingredient. For kidney diseases they are prescribed in a dosage of 1 piece. (250 mg) every 4-6 hours. In difficult cases, 2 tablets (500 mg) with the same time interval. Erythromycin is contraindicated during breastfeeding and with hearing impairment. The drug can cause candidiasis of the oral cavity and vagina, tinnitus, and diarrhea.
- Vilprafen – capsules based on josamycin. For streptococcal infection, 1-2 g per day is prescribed for a course of 10 days. The only contraindication for Vilprafen is severe liver disease. Side effects from the antibiotic are associated with the digestive tract: loss of appetite, heartburn, nausea, diarrhea.
Carbapenems
These antibiotics with a beta-lactam ring are similar in principle to penicillins. Carbapenems are active against many types of pathogenic microorganisms, including aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Due to the high risk of developing dyspeptic disorders, this group of medications is used only for the treatment of severe forms of inflammation of the urinary tract and kidneys. Among the wide range, the following stand out:
- Tienam. The active ingredient is cilastatin imipenem. The medicine is administered intramuscularly or intravenously in dosages of up to 4000 mg. When using Tienam as an anti-relapse solution, the dose is reduced to 1000 mg. Possible undesirable effects include: changes in taste perception, confusion, and epileptic seizures.
- Jenem. The active substance is meropenem. The antibiotic is administered only intravenously at 500 mg every 8 hours. Jenem is strictly contraindicated during lactation. It causes serious side effects very rarely; nausea, diarrhea, and skin rash appear more often.
Aminoglycosides
These antibiotics for kidney disease are often used in combination with penicillins or cephalosporins. Aminoglycosides inhibit the synthesis of proteins necessary for the construction of the cell membrane of the bacterial cell. They are active against aerobic gram-negative bacteria, staphylococci, Escherichia coli, enterobacteria, and Klebsiella. Aminoglycosides are highly toxic and increase the risk of neuromuscular blockade, damage to the vestibular system, and hearing loss. The preferred drugs are:
- Amikacin. It is administered intramuscularly or in a stream (drip) dose of 5 mg every 8 hours. The drug is contraindicated in cases of acoustic neuritis (inflammation of the inner ear and auditory nerve), severe kidney disease with uremia (poisoning of the body with toxins) or azotemia (increased levels of nitrogenous metabolic products in the blood).
- Sizomycin. For kidney infections, it is prescribed at a dose of 1 mg/kg of the patient’s weight, but not more than 2 mg/kg per day. The drug is contraindicated for disorders of the vestibular apparatus, traumatic brain injuries, and diseases of the hearing organs.
- Gentamicin. The dosage regimen of the drug is selected for each patient individually, focusing on the severity of the disease. The standard course of treatment is 7-10 days. Gentamicin is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity of the body to antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group.
- Tobramycin. For moderate infections, this solution is administered intramuscularly or intravenously at 0.002-0.003 g/kg body weight three times a day. Tobramycin is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women. In addition to neurovestibular disorders, the drug can provoke a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, platelets and leukocytes in the blood.
Many people face various inflammatory diseases. The kidneys are one of those organs that are often affected by disease. These include pyelonephritis, paranephritis, glomerulonephritis. To find out the nature of inflammation and its causative agent, it is necessary to conduct a series of laboratory and instrumental studies.
If the inflammation is infectious and caused by bacteria, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. The range of medications for kidney treatment is very wide. The choice of drug cannot be made at random, but take into account the nature of the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Therefore, the prescription of medications for renal inflammation should be individualized.