Primary and secondary candidal urethritis - in men and women
The main way of infection with fungal urethritis is unprotected sexual intercourse.
However, the infection in men can also penetrate through the circulatory system, through the intestinal walls or skin. The first signs of change appear a few hours after the pathogen enters the urethra. The incubation period varies from 3 days to 3 weeks, and it is best to take tests 3-7 days after potential infection. In this case, the specific symptoms depend on the type of disease - primary or secondary urethritis, as well as on the duration of the course.
The acute form of fungal urethritis in men manifests itself:
- white coating on the glans penis and foreskin;
- curd-like discharge from the urethra;
- itching, burning and discomfort when urinating;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of bladder fullness.
Expert opinion
Madmuzev Armen Davidovich, specializes in male venereal diseases
In men, the disease is more severe due to the greater length of the urethra.
In women, the presence of candidal urethritis can be suspected by the following signs:
- burning and pain when urinating;
- purulent discharge from the vagina and urethra;
- dry mucous membranes;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
In a chronic course, the disease reminds itself of itself during hypothermia, severe stress or other adverse effects. In such cases, a person complains of general weakness, chills and decreased performance. In the acute form of candidal urethritis, such signs are absent.
Candidal urethritis can be primary (when the infection enters directly into the urethra) and secondary (as a complication of a chronic fungal disease).
Primary occurs more often in men, and is usually the result of sexual contact with a partner who has an exacerbation of vulvovaginal candidiasis (in 85–90%). From the moment the fungus enters the urethral mucosa until the appearance of pronounced symptoms (burning, pain, discharge) can take from several hours (6–12) to 3 weeks (the incubation period during which the fungus gains strength).
- against the background of acute vulvovaginal candidiasis, which lasts up to 2 months without treatment (and then becomes chronic);
- chronic thrush, which occurs in a mild form (symptoms are almost invisible and do not bother), but regularly worsens.
Another source of fungal infection is the intestines; candidal urethritis in men and women equally often appears as a result of poor hygiene due to dysbacteriosis (for example, after long-term antibiotic therapy).
Drugs for the treatment of candidal urethritis can be divided into 3 groups:
- antibiotics;
- antifungal agents;
- immunomodulators.
Antibacterial drugs or antibiotics are rarely prescribed; their prescription is justified if urethritis threatens severe complications.
The antibiotic is selected individually, taking into account the results of the bacterial culture test and drug sensitivity.
Antifungal agents such as Flucostat, Fluconazole, Diflucan, etc. are most often prescribed. Immunomodulators that complement therapy act directly on the root cause of the disease. Such drugs can be combined with vitamins to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sMFo23PsoK4
Symptoms of thrush in men, causes and treatment of the disease
If an antibiotic or antifungal drug does not give the desired effect, then the therapy is adjusted. The drugs are replaced, the treatment of candidal urethritis is continued.
And also as part of therapy, the patient is prescribed a diet:
- recommend giving up alcohol;
- no smoking;
- exercise;
- eat right (exclude unhealthy foods from your diet, include boiled meat, fruits, vegetables, dairy products).
The diet can be followed for a long period of time, it will help avoid relapse of the disease. To do this, it will be enough to take vitamins 2 times a year and adhere to proper nutrition.
White and purulent discharge from the urethra in men is male or gender: how to treat?
Have you been struggling with PROSTATITIS and POTENTITY for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
In men, there is physiological discharge from the urethra, which is considered normal. But there are also a number of specific secretions that alarm representatives of the stronger sex. Typically, such manifestations indicate the presence of inflammatory processes that originate in the genitourinary system. How to determine which urethral discharge in men is natural and which should be examined by a doctor? We will tell you in more detail in this article.
Causes of discharge from the urethra
It is immediately worth noting which discharges are not pathological. The male body, like the female body, has its own structural features of the urinary system. In women, clear, odorless vaginal discharge is the norm; in men, this process is different due to the specific structure of the organ. An organ is a separate collection of different types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism. The following manifestations are considered normal:
- Emission (usually occurs at night). Night ejaculation is normal in a sexually mature person;
- Sexual arousal. During sexual arousal in men, clear mucus is observed on the head of the penis. This is also normal and physiological;
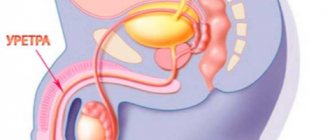
- Defecatory prostatorrhea. With strong straining during defecation, stringy clots may protrude from the urethra. The canal (synonym: urethra, Latin urethra) is an unpaired tubular organ of the urinary (genitourinary) system of humans and other vertebrates, connecting the bladder with the external environment. But they must be odorless.
Slime color
In fact, men should be puzzled if the discharge has a white, yellowish, greenish tint along with a specific odor. These signs indicate that something is wrong with the body. Let's describe in more detail which color says what.
White discharge from the urethra
During urination, in the morning, leucorrhoea may be observed in the mucus. But this rather indicates the presence of smegma under the foreskin or sperm, if there was sexual intercourse. It is worth worrying if, along with such discharge, pain is felt when going to the toilet, the underwear has an unpleasant odor and itching, burning in the organ occurs. Organ Organ - a separate set of different types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism - a separate set of different types cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism. This indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
Purulent discharge from the urethra in the stronger sex
An abscess is usually accompanied by an unpleasant odor and is correspondingly accompanied by pain. Purulent discharge is a polysemantic word: Discharge is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment from the urethra in a man can be yellow, gray or green. The main cause is microbes that have penetrated the genitourinary system. These include gonococci, chlamydia, and trichomonas. Sexually transmitted diseases are often accompanied by purulent discharge from the penis.
Bloody discharge
Blood in urine is also not normal. Hematuria is a consequence of any disease.
Often, blood impurities occur against the background of prostatitis, cystitis, and urolithiasis.
Sometimes it manifests itself during heavy physical activity (specific work or weightlifting).
Types of discharge from the urethra canal Elongated, artificially limited space intended for organizing communication, transferring or moving something Elongated, artificially limited space intended for organizing communication, transmitting or moving something (synonym: urethra, lat. urethra) - unpaired tubular organ of the urinary (genitourinary) system of humans and other vertebrates, connecting the bladder with the external environment: what pathology are they talking about
The nature of highlighting is a polysemantic word: Highlighting is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment directly depends on the source of this state. Discharge from the genital organ due to an STD:
- Mucous. Typically, a viscous transparent mass appears against the background of chronic chlamydia. Often appears with ureplasma urethritis;
- Mucopurulent. The source is acute chlamydia, as well as mycoplasmosis. If it is chlamydia, then the existing mucus “sticks” to the head (the name of a number of rounded individual objects or the ends of objects of a more complex shape of the penis (it is difficult to wash off);
- Purulent discharge is a polysemantic word: Discharge is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment from the urethra canal (synonym: urethra, lat. urethra) - an unpaired tubular organ of the human urinary (genitourinary) system and others in vertebrates, the channel connecting the bladder with the external environment (synonym: urethra, lat. urethra) is an unpaired tubular organ of the urinary (genitourinary) system of humans and other vertebrates, connecting the bladder with the external environment in a patient, the presence of gonorrhea is indicated. Such discharge has a bright shade of yellow or green, the consistency is viscous, sticky and thick. If purulent discharge is accompanied by itching and pain when urinating, this is gonorrheal urethritis.
Other factors may also cause specific discharge, namely:
- Candida fungus. Usually formed against a background of reduced immunity. It can also occur if a man has undergone drug treatment with antibiotics. Usually, antifungal agents should be administered along with such drugs, but sometimes the immune system fails;
- Non-gonorrheal urethritis. Inflammation of the urethra is usually accompanied by mucous, clear discharge from the urethra. However, they may have an unpleasant odor;
- Balanoposthitis. With this disease, a white coating usually appears on the head of a number of rounded individual objects or ends of objects of a more complex shape of the penis and under the foreskin. Often accompanied by white or clear discharge;
- Prostatitis. This pathology is also marked by the presence of certain secretions. In the acute phase, white clots are possible after urination. In the chronic form, clear mucus is released more against the background of the inflammatory process;
- Tumors. Typically, with malignant oncology, brown and even burgundy discharge is observed. You can also see large clots of mucus with blood. But if the patient has undergone surgery on the genitals, such discharge may indicate that the wounds are healing, so brownish clots form.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
Important: pus from the urethra canal (synonym: urethra, Latin urethra) is an unpaired tubular organ of the urinary (genitourinary) system of humans and other vertebrates, connecting the bladder with the external environment in representatives of the stronger sex, indicating the presence of a venereal disease. Less often, they indicate that the patient has an advanced form of pathology of the genital organ. An abscess is more difficult to treat than an acute or chronic form of the disease, so you should not delay treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
If the patient sees unpleasant discharge with a specific odor, this is a disease that needs to be diagnosed.
Treatment is carried out by a urologist or andrologist.
If a sexually transmitted disease is detected, the patient is referred to a venereologist.
To begin with, the patient is examined by a doctor, and in particular the urethral canal. For an accurate diagnosis, the following tests are prescribed:
- Urethral smear (bacteria culture for pathogenic microflora);
- Blood and urine analysis;
- PCR analysis to identify the pathogen;
- Urethroscopy if the patient complains of painful urination.
With a microexamination of urine, doctors can study in detail what microorganisms are in the system (gonococci, yeast, epithelial cells), etc. Without a thorough diagnosis, correct treatment is excluded. It is for this reason that you should not try to improve your health on your own.
Pathological discharge is a polysemantic word: Discharge is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment from the urethra in men: treatment methods
Any person of male gender or gender that is alarming to a man. Emphasis is a polysemantic word: Emphasis is a polysemantic word: Emphasis is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment - the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it with In order to focus the reader's attention on this fragment from the urethra, it should be examined by a specialist, even if aggravating symptoms are not observed. Treatment directly depends on the etiology of the disease. It is worth immediately noting that caustic discharge is a consequence of pathology, but cannot act as an independent disease. Treatment methods include:
- Taking antibacterial agents. If the cause lies in a pathogenic microorganism (infection), antibiotics are prescribed. They are also different, so only a doctor can prescribe an adaptive option;
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. Inflammation after injuries or damage leads to certain types of diseases, so taking anti-inflammatory, gentler drugs is appropriate in this case;
- Antiviral drugs are prescribed if the cause is a virus;
- For pathologies such as prostatitis, adenoma, and cystitis, complex therapy is prescribed, which includes taking not only oral medications, but also injections and rectal suppositories.
Prevention of urethral discharge
Since there are more than enough reasons for specific discharges, it is almost impossible to determine preventive measures. But there is a set of basic rules that can help prevent the development of most pathologies in men.
Doctors' recommendations are:
- Always use condoms. The fact that 70% of men have a sexually transmitted etiology of discharge is an ambiguous word: Emphasis is the use of a different font style when printing text for some fragment of it in order to focus the reader’s attention on this fragment. And this, in turn, indicates that men, male or gender people, male or gender people neglect contraceptives;
- Maintain hygiene. Under the foreskin there is smegma, in which pathogenic microorganisms “love” to multiply. Therefore, hygiene procedures must be performed at least twice a day;
- Preventive agents against parasites. It is worth taking special medications once a year that prevent the proliferation of worms in the body. But they contribute to the formation of many pathologies;
- Visit a urologist once a year.
Specific discharge should be immediately examined by your doctor to avoid serious consequences.
Read more
Smegma is a fat-like substance that accumulates under the skin of the foreskin, which covers the head of the penis. It is formed from the secretion of her sebaceous glands, mixed with naturally exfoliated epithelial cells. Smegma also contains normal microorganisms (mycobacteria) that have the ability to use fats in their own metabolism. It begins to form in newborn boys, its quantity increases significantly during puberty and decreases only in old age.
Physiological role
Smegma is secreted normally and has a number of properties that ensure the normal functioning of the male penis.
Basic:
- facilitating the process of sliding the head of the penis;
- prevention of microtraumas and cracks when the head emerges from the foreskin;
- preventing the development of local infections, thanks to the bactericidal components included in its composition.
Normally, smegma is a mixture of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture, which, due to insufficient genital hygiene in Russia in the 19th and early 20th centuries, accumulates in the sac of the foreskin in uncircumcised men, and in the mixture of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture, which, due to insufficient hygiene of the genital organs in uncircumcised men, a male or gender person accumulates in the foreskin sac, and looks like a white coating at the base of the head, the name of a number of rounded individual objects or the ends of objects of a more complex shape, may have a uniform or curdled consistency, as well as a spicy aroma comparable to the aromas of savory cheeses.
Stagnation
When smegma stagnates, dense accumulations are formed, which can calcify and harden. The result is white plaques called smegmolites. When an infection occurs, the color of smegma is a mixture of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture, which, with insufficient hygiene of the genital organs in uncircumcised men, accumulates in the sac of the foreskin, and in the mixture of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture, which due to insufficient hygiene of the genital organs in uncircumcised men, it accumulates in the foreskin sac, and in the case of men it changes, more often to yellow or green, and the smell becomes unpleasant and pungent.
Excessive accumulation of smegma occurs when:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis);
- diseases that are sexually transmitted if specific balanoposthitis (or balanitis) develops.
What does stagnation of smegma lead to and how to prevent it?
Against the background of smegma stagnation, it is possible for microbial flora to join and multiply, which contributes to the occurrence of inflammation of the external genitalia, as well as the development of neoplasms - benign (papillomas) and malignant (cancer).
The narrowing of the foreskin makes it difficult to expose the head of the penis. It can be physiological (observed in boys up to 7 years of age), caused by gluing of the epithelial lining of the head of the penis with the inner layer of the foreskin. In this case, it is necessary to carefully and carefully observe the hygiene of the genital organs, avoiding injury. No special treatment is required unless a secondary inflammatory reaction develops.
In boys 16-17 years old, as well as in adult men, phimosis is a sign of pathology and requires consultation with a urologist. The reason for the development of the disease determines the doctor’s individual prescription of one or another correction method (not necessarily surgical) in each specific case.
Smegma is a mixture of secretion from the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture, which, with insufficient hygiene of the genital organs in uncircumcised men, accumulates in the foreskin sac, and in long-term phimosis it becomes more viscous. Its stagnation in the preputial sac (fold of the foreskin) can lead to the proliferation of banal microbial flora (staphylococcus, E. coli, streptococcus) or fungi, and to the development of inflammatory processes. Most often - balanitis (inflammation of the glans penis) and balanoposthitis, when, along with the head of the penis, inflammatory changes develop in the inner layer of the foreskin.
With a number of diseases transmitted sexually in Russia in the 19th - early 20th centuries - inn servants (STDs), a specific inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system occurs, accompanied by an increase in the production of smegma and stagnation, leading to an increase in its density and a change in odor.
The most common:
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- fungal infections;
- viral (herpes, cytomegalovirus, papillomavirus) infections.
Doctors also consider chronic stagnation of smegma to be one of the predisposing factors in the development of penile tumors. Along with cancer, precancerous formations, as well as local malignant tumors, may occur:
- pointed kandiloma, papillomas;
- Bowen's disease;
- Keir's erythroplasia.
To prevent congestion it is necessary:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- wearing underwear that prevents compression and overheating of the external genitalia in Russia in the 19th - early 20th centuries - a tavern servant of the organs.
Hygienic procedures are of great importance for maintaining male strength, and also ensure the health of the genitourinary system, preventing the development of many diseases. It is necessary to regularly wash the external genitalia in Russia of the 19th - early 20th centuries - tavern servant organs (twice a day), using warm water and products with an alkaline pH (preferably plant-based), maintain intimate hygiene before and after sexual contact, wear comfortable underwear .
Does smegma need to be treated?
As one of the physiological fluids, smegma itself does not require treatment; it has protective properties and helps the male reproductive system function normally. Therefore, the question “how to get rid of smegma?” meaningless.
It is necessary to distinguish between the normal production of smegma and infectious processes, in which a white coating also appears on the penis. Only diseases in which the properties and amount of secreted smegma change are subject to treatment.
The most common are:
- inflammatory processes caused by microbial, parasitic, fungal, viral infections;
- sexual infections.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude damage by fungal flora, the development of which is characterized by:
- the appearance of a cheesy coating;
- itching, discomfort in the genital area;
- pain when urinating;
- pain is physical or emotional suffering, painful or unpleasant sensation, swelling of the head of the penis.
With STDs, along with general symptoms (general weakness, headaches and muscle pain, loss of appetite, and sometimes elevated body temperature), specific signs associated with the route of transmission and the site of infection are identified.
Main manifestations:
- burning, pain in the lower abdomen, as well as along the urethra when emptying the bladder;
- discharge from the penis;
- plaque, swelling, rash on the penis;
- pain, discharge, rash in the throat (usually in the tonsil area), in the rectal area.
If there is a possibility of contracting a sexually transmitted infection, you should consult a dermatovenerologist.
If there is a suspicion of tumor formation, then you should pay attention to possible structural changes in the penis (tissue compaction or disruption of their integrity), as well as the presence of general signs of tumor intoxication:
- body weight loss;
- malaise, general weakness;
- poor appetite or sudden changes in taste preferences;
- periodic (in the evening) increases in body temperature up to 37.5°C.
Conclusion
Thus, smegma is a physiological phenomenon that does not require the use of therapeutic agents. However, if hygiene is not observed and against the background of certain conditions leading to its stagnation, its properties may change, as well as infection. In this case, you need to consult a doctor who will diagnose the disease and select treatment taking into account individual characteristics.
Read on topic: The importance of personal hygiene for men's health
Specifics of the course of the disease
Treatment of candidal urethritis takes place in two stages - eliminating the infection and restoring the walls of the damaged organ. Elimination of the infection occurs with the help of a course of antimicrobial agents. The infectious process should not be treated using only traditional methods. They can only be effective in combination therapy with antifungal drugs.
Antibacterial therapy, selected based on the results of the diagnostic study, is used when a concomitant disease occurs in the genitourinary system. The complex carries out preventive measures for side effects from antibiotics using vitamins and immunostimulating agents. In acute cases of candidal disease, a specialist prescribes urethral lavage with specially developed substances with antimicrobial and disinfectant properties.
The chronic form of candidal urethritis is more difficult to treat. This type of disease requires the use of systemic antifungal medications, antibacterial therapy, and the administration of medications into the urethra is prescribed. During the period of therapy, sexual contact should be completely avoided.
Fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic microorganisms. This is due to the fact that they are normally present in the human body (in the intestines, oral cavity, vagina) and in the absence of provoking factors do not cause tissue damage. But there comes a time when the local immune response weakens and the fungi begin to actively divide. In this case, humidity, temperature and acidity of the environment play a huge role.
Fungal colonies are localized mainly on the mucous membranes, and the internal lining of the urethra is an excellent environment for their life.
In men, the course of the disease occurs with more pronounced symptoms and external manifestations, while in women, fungal urethritis most often becomes chronic due to the blurred clinical picture
The urethra is a narrow duct, one end connecting to the bladder and the other to the external environment. Normally, local immunity is able to fight pathogenic microflora that enters the lumen of the canal. But if for some reason this is not enough, microscopic fungi begin their aggression.
In this case, the upper layer of the mucous membrane is damaged, tissue swelling, redness and possible bleeding occur, the width of the urethra decreases, which causes unpleasant painful sensations during the operation of the canal (urination, ejaculation). The waste products of microorganisms are excreted in the form of whitish or greenish discharge.
If candidal urethritis is left untreated, it can develop into candidomycotic inflammatory process of the bladder, vagina, testicles, vas deferens and prostate.
Treatment of the disease
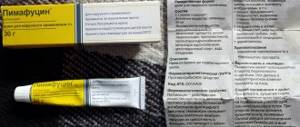
An individual treatment regimen is selected for each patient, which is prescribed based on the person’s physical characteristics and the severity of the disease. Candida urethritis is treated with local and systemic drugs. The main treatment for the disease is antifungal drugs, which help suppress the spread of the fungus and reduce its number. For this purpose, Fluconazole is prescribed, which is used for 14-21 days. It is also possible to use the following drugs:
- "Orungala";
- "Nystatin";
- "Clotrimazole";
- "Lamisil."
The course of treatment with Fluconazole is 14-21 days.
In addition to antifungal agents, fungal urethral disease should be treated with antihistamines, painkillers and multivitamins. Often, the doctor prescribes the patient to wash the urethra using a special catheter. With its help, an antimicrobial agent is introduced into the urethra, which kills pathogenic microorganisms.
Folk remedies
Mycotic urethritis can be cured using traditional medicine, but before using them, you must consult your doctor. The most effective are various tinctures and decoctions prepared with medicinal herbs. Medicines can be applied to the affected area or taken orally. The most effective are:
Complications
The type of complication depends on gender and the origin of the disease. Most often, men are diagnosed with the following types of pathologies that appear due to untreated urethritis:
- Prostatitis.
- Balanitis.
- Orchitis.
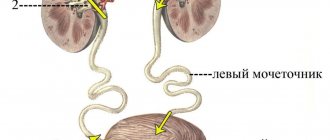
- Narrowing of the ureters.
In women, the lack of qualified medical care leads to cystitis, the transition of urethritis to a chronic form, disruption of the vaginal microflora and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
With severe lesions, infertility may develop in men and women. The disease greatly weakens the general immune system, which causes relapses of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
The immune system is able to stop the growth and development of Candida fungus. But at the same time it can remain in the seminal vesicles, testicles, and prostate gland. Against the background of hypothermia, with weakened immunity and exacerbation of chronic ailments, the fungus becomes active again, and the disease manifests itself again. In addition, the infection can affect other organs and cause the development of diseases such as pyelonephritis, prostatitis, and impotence.
Candida fungus
The greatest danger is candidiasis accompanied by high fever. A fungus can enter the bloodstream, which impairs the functioning of the entire body. As a result, the quality of life decreases, problems with ejaculation and erectile function begin, prostatitis and vesiculitis develop.
Complications in women
One of the complications of this type of disease may be inflammation of the bladder.
Without timely treatment, fungal urethritis in women becomes chronic, which is difficult to completely cure.
In this case, the normal microflora in the vagina is disrupted, resulting in pain during sexual intercourse. With complicated candidal urethritis, women complain of the following abnormalities:
- cystitis;
- inflammatory process in other genitourinary organs.
Types and forms
To make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the type and subtype of urethritis.
A careful history will help classify candidal urethritis.
According to the duration of the flow, they are distinguished:
- acute stage (no more than 2 months passed from infection to the start of treatment. The clinical picture is clearly expressed);
- chronic stage (the disease lasts quite a long time with periodic relapses. Symptoms almost do not appear).
Based on how the infection entered the urethra, candidal urethritis can be primary or secondary. In the first case, the infection began directly from the urethra, and in the case of secondary infection, the fungus got there from other foci in the body.
Also, this disease can be presented in a “pure” form, that is, only fungi are present in the tests, or in a mixed form, when a bacterial infection is also added to the candidal infection.
Prevention
To prevent the development of urethritis, you should avoid negative factors that predispose you to such an unpleasant disease. Avoid chronic inflammation and diseases of the organs in the pelvis. Beware of hypothermia, do not lead a chaotic lifestyle, and do not allow casual intimate relationships. Nutrition should be rational; excessive consumption of fried, hot, sour, pickled and spicy foods should be avoided. Avoid frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely detection and proper treatment, candidal urethritis is completely curable. When the disease becomes chronic, recovery will be lengthy, and the likelihood of complications increases. To avoid the development of pathology, you should follow simple rules:
- No unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Regular preventive examinations.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Proper, balanced nutrition.
- Timely treatment of all chronic diseases.
When the first symptoms appear, you should visit a venereologist, urologist or gynecologist. A specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and relieve the person of discomfort.
Candidal urethritis is completely cured within 14 days (in 50%), less often it takes about 3-4 weeks to get rid of it (in 20%). Chronic forms require patience; such an infection can be treated for up to 2 months.
In men, the disease occurs less frequently than in women (1–2%), but is more acute, with more severe symptoms. The infection usually results from unprotected sexual contact (in 85–90%).
In women, urethritis is a secondary disease, a complication of vulvovaginal thrush (in 75–85%) with weak, blurred manifestations.
The prognosis for recovery is 95% out of 100%, with the exception of candidiasis due to incurable immunity disorders (HIV infection), which turns into a systemic infection and spreads throughout the body.
Relationship between urethritis and cystitis
Many women, having discovered characteristic symptoms, diagnose themselves with “urethritis” and begin treatment with all methods available to them.
Meanwhile, this problem can successfully masquerade as cystitis, which is no less “popular” among women: they are really similar, but if urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra, then cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder itself. Therefore, in general, they need to be treated differently.
Why are we talking about this? To remind you once again about the dangers of self-medication and the need to see a doctor. After all, only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and begin effective treatment.
Causes
The causes that provoke mycotic urethritis can be divided into external and internal. External factors include:
- insufficient hygiene, which contributes to increased humidity and the development of fungi;
- infection from a sexual partner.
Internal causes that can provoke fungal urethritis are:
- high sugar;
- overweight;
- dysbacteriosis;
- taking antidepressants.
But most often candidiasis appears due to the Candida fungus entering the body. This fungus has a huge number of spores and, when exposed to a favorable environment, begins to actively multiply. The fungus penetrates the cells and parasitizes them, poisoning the body.
If Candida gets into a less favorable environment, a protective mechanism is triggered that can preserve its viability. When the opportunity is right, the fungus becomes active and begins the process of reproduction. This possibility may be a decrease in immunity, sexually transmitted diseases, that is, something that reduces the body’s resistance.
On our website you can learn about the following types of urethritis:
- nonspecific;
- non-infectious;
- acute and chronic;
- gonorrheal and non-gonorrheal;
- bacterial;
- trichomonas;
- chlamydial;
- allergic.
The main differences between urethritis and cystitis are described here.
The most common way of infection of the urethra is through sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraceptives.
But infection can also occur in other ways, for example, from peripheral foci (vagina in women and intestines in both sexes). If the disease has become chronic, the fungi can be localized in the Bartholin glands in women and the prostate in men, and when favorable conditions occur, infection passes into the urethra in a descending manner.
Factors that provoke candidal urethritis include:
- sexual intercourse with a carrier of infection;
- the presence of systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, etc.);
- decreased general and local immune response, which can be caused by hypothermia, recent or chronic diseases;
- prolonged or uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- the presence of sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, trichomoniasis).
A person’s lifestyle, as well as adherence to personal hygiene rules, plays a huge role in the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs.
Types of urethritis
In medical practice there is a classification of candidal urethritis. The disease is divided according to the nature of its course into acute and chronic candidal urethritis, and according to its occurrence - primary and secondary candidiasis. Primary candidiasis is an independent disease, secondary candidiasis is a consequence or complication of any disease.
Acute candidal urethritis occurs and resolves with treatment without complications within several months. Urethritis manifests itself quite sharply during the first week and is characterized by itching, burning and pain in the urethral area. There may be purulent or bloody discharge during or after urination.
Depending on the pathogen, some specific forms of the disease are distinguished, for example, gonorrhea, candidiasis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia. Individual treatment is selected for each of them.
Chronic urethritis - occurs in the absence or improper treatment of the acute stage of the disease. In the chronic form, stages of remission occur, but with any provoking factor, for example, a cold, the disease returns to an acute state. In women, this stage of the disease is more severe and directly affects the reproductive system.
Description
Candidiasis is a fungal disease. It manifests itself mainly when immunity decreases and personal hygiene rules are not observed. The causative agent of the disease is fungi of the genus Candida. Most people already have them in their bodies in a “dormant” form – in conditions insufficient for active development.
Thrush in women is less pronounced than in men. This is due to the fact that the urethra, which is affected by the fungus, is much shorter in the fairer sex. Therefore, it has less sensitivity, and women feel almost no pain when they get thrush. This complicates the diagnosis and treatment of the problem, because often patients discover the disease already at advanced stages.
Possible symptoms
When a fungus enters and multiplies on the wall of the urethra, candidal urethritis can occur in the latent stage. The incubation period lasts up to several weeks. After this, the first signs of candidal urethritis appear. These include:
- Severe itching and burning in the urethral area, aggravated by urination.
- Copious discharge from the cervical canal. They are characterized by a yellowish-greenish color and an unpleasant putrefactive odor.
- Cutting pain in the groin.
- Redness in the genital area in women and in the urethra in men.
- Frequent urination.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of candidal urethritis in men and women differ in their external manifestations.
So, women may notice:
- mucous discharge from the urethra is whitish or greenish in color with a specific smell of sour milk, and with a mixed form of the pathogen, the smell changes to a more unpleasant one;
- feeling of burning and stinging when urinating;
- itching in the pubic and perineal area;
- mild pain in the lower abdomen;
- redness and increase in size (due to swelling) of the outer part of the urethra;
- symptoms of sexually transmitted infections, if they were the root cause of decreased immunity.
In most cases, damage to the urethra is accompanied by vaginal candidiasis. Then the clinical picture includes white cheesy discharge from the vagina, a constant feeling of itching and burning.
Candidal urethritis in men is much more pronounced and manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the presence of mucus discharge from the urethra (in the morning, thread-like discharge and sticking of the external opening of the urethra are especially noticeable);
- the skin of the head of the penis around the urethra has an inflamed and swollen appearance;
- discharge from the urethra takes on a green or yellow tint, sometimes with blood stains;
- Often the entire surface of the head is covered with a white-gray coating. Subsequently, this area becomes covered with small ulcers;
- urination causes painful sensations (burning and stinging).
This pronounced clinical picture is characteristic of the acute phase of the disease. In a chronic course, most symptoms disappear, but recovery does not occur; the infection spreads upward, changing its location and affecting other internal organs.
What signs might women and men have?
Signs of such a disease may vary in their external manifestations. Women most often notice the following symptoms:
- White or green coating on the urethra, accompanied by the specific smell of sour milk. If the form of bacteria is mixed, the smell becomes more unpleasant.
- A burning sensation and sharp pains are felt when urinating.
- Itching and burning appear in the pubic and perineal area.
- Pain that is mild in intensity occurs in the lower abdomen.
- The outer area of the urethra turns red and increases in size.
- Signs of sexual illness appear if it has become the primary cause of a weakened immune system.
Most often, infections of the urethra are accompanied by vaginal candidiasis. In this case, the clinical picture contains a whitish, curd-like discharge, and the constant presence of burning and itching.
In men, urethritis is more pronounced, manifesting itself with certain symptoms of candidiasis:
- Mucus is secreted from the urethra, and in the morning the external urethral opening becomes sticky.
- The skin of the head becomes inflamed and swollen.
- The discharge becomes green or yellow in color and may contain blood.
- Quite often, the surface of the head is covered with a whitish-gray coating. Subsequently, this area becomes covered with small ulcers.
- When urinating, pain occurs.
Such pronounced signs of the disease are characteristic of its acute form. If the disease is chronic, then many signs disappear, but this does not lead to recovery. The infection continues to spread throughout the body, changing locations and causing damage to other organs.
To determine an accurate diagnosis, simple examinations performed by a urologist and gynecologist will not be enough. This is explained by the fact that the signs of urethritis are similar to other infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs. To more accurately determine the infectious pathogen and determine the correct treatment course, you should undergo some clinical tests:
- Sowing. This analysis makes it possible to determine the type of bacteria and its sensitivity to the medications used. The material is taken from the urethra using a special instrument. If there is no discharge, then the first portion of urine is suitable instead of biological material. This helps to determine the nature of the fungus by pseudomycelial threads detected in the urine;
- Microscopy. Identification of the fungus confirms the acute stage of the disease, filaments of pseudomycelium indicate the chronic phase. When collecting material, a small spatula is used to collect secretions from the ureteral passage. At the same time, not only the fungal species is detected, but also their number. Several variants of this study are known, but luminescent microscopy provides the greatest accuracy.
Doctors add urethroscopy to laboratory tests. With its help, you can visually determine all changes in the urethra. The procedure is performed by inserting an endoscope into the ureteral canal.
In the case of candidal urethritis, it is covered with a white coating; open inflammatory zones with bleeding may be observed.
All this is accompanied by swelling and a decrease in the diameter of the urinary passage.
As an addition to detecting urethritis, the following are prescribed:
- urine and blood tests;
- biochemistry;
- examinations for hepatitis, syphilis, AIDS;
- culture for infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted.
The whole complex of measures makes it possible not only to identify diseases of a concomitant nature, but also to establish the primary cause of urethritis.
Diagnostic procedures are considered a mandatory step in order to determine an adequate and effective treatment course.
Causes of pathology
Any candidiasis in the body is a kind of signal that the immune defense is weakened and special conditions favorable for the fungus have appeared. Candidal urethritis is no exception; its immediate cause is a weakening of general or local immunity.
What factors can contribute to the development of fungus:
- trauma to the mucous membrane of the urethra (for example, damage by a catheter during medical procedures, stone or sand during urolithiasis);
- unprotected sexual contact;
- the presence of a bacterial infection of the genitourinary system or sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis);
- dysbiosis of the vagina and intestines;
- violation of hygiene standards;
- allergic reaction to any local cosmetics or medications (lubricant, vaginal suppositories);
- taking antibiotics (more than a week), hormonal drugs and contraceptives, cytostatics;
- chronic, acute diseases and metabolic disorders (colds, ARVI, diabetes mellitus, hypovitaminosis, tuberculosis, iron deficiency anemia, etc.)
- stress;
- alcohol abuse and diet violations (predominance of sweets, fast carbohydrates).
And other conditions or diseases that lead (directly or indirectly) to a decrease in the body’s protective functions can trigger the appearance of fungal urethritis.
Components of the human immune system
With candidal urethritis, inflammation occurs in the mucous membrane of the urethra, caused by the activity of fungal flora. This causes discomfort and the appearance of characteristic discharge.
Causes
The disease is caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. They belong to the opportunistic microflora of the body - that is, they live on the mucous membranes of a healthy person without causing diseases.
Their activity increases when local immunity decreases, as a result of which beneficial bacteria cannot cope with fungi and they cause an inflammatory process.
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease are:
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- insufficient personal hygiene.
In such conditions, fungi multiply rapidly. The infection can spread higher up and affect the bladder and kidneys.
The cause of the disease is yeast fungi
Traditional treatment
For candidal (fungal) urethritis, appropriate drug therapy in combination with the use of proven folk remedies and treatment methods gives lasting positive results. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are designed to alleviate the symptoms of candidal urethritis, including relieving discomfort when urinating, reducing pain, they help relieve inflammation and weaken the influence of harmful bacteria, and strengthen the human immune system.
Below are the most effective and affordable folk remedies and methods used for urethritis, namely:
- In order to get rid of unpleasant sensations during urination (itching, pain), a linden decoction is used (a spoonful of the crushed plant is brewed with a glass of boiling water, heated over a fire and infused for at least half an hour). Take a glass before meals twice a day.
- The medicinal plant wheatgrass has diuretic and antimicrobial properties. A decoction is prepared from crushed roots of the plant (pour two spoons into a glass of cold water, leave for a day, drain, then add boiling water and brew). Drink half a glass half an hour before meals twice a day.
- A decoction of crushed blackcurrant leaves brewed with boiling water strengthens the immune system, has an antibacterial and diuretic effect. You can even take this decoction in the form of regular tea; consuming fresh currants will enhance its effect.
- Parsley decoction is effective for maintaining the general condition of the body, and is also a natural diuretic. For greater efficiency, crushed leaves are poured with milk and “simmered” in the oven until the volume is halved. In addition, there is a known recipe where a spoonful of chopped parsley is poured with plain cold water and left for at least ten hours in a warm room. Juice from parsley leaves is also used (to soften the therapeutic effect, it can be diluted, for example, with carrot juice).
- For candidal urethritis, an infusion of cornflower flowers is often used (one spoonful of flowers is poured into a glass of hot water and infused for two hours). The product is taken before meals during the day.
- A good effect in relieving itching and burning is achieved by drinking soothing teas based on medicinal herbs such as mint and lemon balm.
All folk remedies are used after consultation with a doctor, who can also advise the duration of the course of treatment.
How is the disease diagnosed?
If you experience discomfort in the genital area, you should see a urologist or gynecologist. First, the doctor will examine the damaged area, after which he will prescribe diagnostic procedures that will help identify the type of pathogen and the extent of the damage:
- Bacteriological culture of a smear from the urethra. The procedure allows you to identify the fungus and determine its quantitative presence. If there is no discharge, then the first part of the urine is taken for analysis from a three-glass sample, in which the urine is collected in 3 different containers.
- Analysis of urine and feces for the presence of fungi.
- Blood test to determine antibodies to yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
The doctor must carry out a number of diagnostic measures - they allow not only to clarify the diagnosis, but also to identify the true causative agent of the disease. The causative agent can be both a sexually transmitted infection and opportunistic microorganisms, so a man will be tested for infections of both types.
Simultaneously with identifying the true pathogen, the doctor also receives results of its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs - this is the basis for treatment prescriptions.
Medical diagnosis
Examination for the diagnosis of candidal urethritis in women and men includes the following activities:
- Examination by a gynecologist.
- Examination of the urethra using a urethroscope.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Taking a smear to examine pathogenic flora and identify the pathogen.
- Bacteriological culture.
- In some cases, a histological examination is possible, when a scraping is taken from the affected tissue.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs for some indications.
All these measures will help not only to identify the disease, but also the causative agent, and prescribe more correct treatment.
Features and symptoms of the disease
The main reason for the development of candidal urethritis is the activation of fungal growth as a result of a weakening of the body's immune forces. The causative agent of the disease is opportunistic microorganisms (those that do not have a negative effect on the body under normal conditions). You can get urethritis at absolutely any age, but most often the infection affects mature women.
The causative agent of candidal urethritis is the Candida fungus.
Candidal urethritis can begin with an inflammatory process directly in the urethra, but the infection can enter the urethra from any other affected organ of the genitourinary system. The first variant of infection occurs mainly after sexual intercourse with a carrier of the infection. Suppression of the local protective forces of the urethra can occur against the background of the following factors:
- stress,
- alcohol and cigarette abuse,
- overweight,
- dysbacteriosis,
- problems with the immune system (congenital or acquired),
- allergic reactions of the body,
- promiscuous sex life,
- autoimmune processes,
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system,
- while taking hormonal and antibacterial drugs.
How does the disease manifest? These may be the following symptoms:
- itching, burning sensation in the genital area,
- pain when urinating,
- discharge from the urethra.
The discharge may also be cheesy, liquid or even foamy, and have an unpleasant odor. The edges of the urethra gradually become inflamed, and a white coating forms on them.
Unlike other types of urethritis, which can develop without pronounced symptoms, a disease caused by yeast fungi manifests itself with a number of symptoms:
- the appearance of a burning sensation or quite noticeable pain during urination;
- itching in the perineal area;
- the appearance of white discharge on the head of the penis;
- the appearance of pus or cream-colored inclusions in the urine.
When urethritis becomes chronic, body temperature may rise slightly and weakness may appear throughout the body. However, it is highly undesirable to let these symptoms appear. It is better to start treatment much earlier.
To make a diagnosis of urogenital candidiasis, a number of laboratory tests are required. Microscopic examination is aimed at determining the predominant vegetative forms - these can be budding yeast cells and mycelium.
Culture testing helps determine the growth of fungal colonies of more than 100 CFU/ml. In addition to standard tests, your doctor may prescribe additional tests to accurately diagnose the nature of the disease and the presence of parallel developing infections. Additionally, blood and urine tests, testing for HIV, genital herpes, syphilis, etc. may be required. You may also need to consult specialists in another field: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, etc.
In men
So, men experience the following symptoms indicating the presence of a fungal infection:
- When urinating, pain, burning and itching are observed.
- The head of the penis is red and swollen.
- The head itself is covered with a light white coating.
- There may be discharge from the urethra in the form of white mucus.
- Frequent urination, constant feeling of bladder fullness.
- The penis becomes very sensitive.
- During sexual intercourse, sharp pain is observed.
General principles of treatment of candidal urethritis
By prescribing effective treatment, the doctor tries to achieve two goals: eliminating the infection from the urethra and restoring its wall. Most often, antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) are used to get rid of infection - specific drugs are selected individually, taking into account the results of a diagnostic study.
In addition to antibacterial drugs, a man may be prescribed medications that can prevent the development of side effects from antimicrobial treatment, immunomodulators and vitamins.
It will be quite difficult and long-term to treat the disease in question, which occurs in a chronic form - in addition to classical antibacterial therapy, the man is prescribed the injection of drugs directly into the urethra, and also undergoes a course of immunotherapy.
Treatment of acute and chronic forms of pathology
During therapeutic measures, two goals are pursued at once - getting rid of the infection and restoring the affected areas of the walls of the urinary canal.
The infection is eliminated using antibiotics selected for a specific pathogen. The therapeutic course will depend on the level of advanced disease and lasts from seven to ten days. It happens that its duration is about a month.
The patient is treated at home; only those patients who have severe purulent complications are admitted to the hospital. In addition to antibiotics, for the treatment of candidal urethritis, men and women are prescribed vitamin complexes and immune system stimulants.
Treatment of the chronic stage is much more difficult. In such cases, as a supplement, the patient is injected into the ureter with medicinal compounds. You can learn about the treatment of acute and chronic urethritis in men from our material.
The principle of the treatment course for children is practically no different. Only taking into account age can the dosage of medications be reduced. For childhood illnesses, experts recommend using ointments.
What contributes to the development of fungal infection
Infection of the urethra with fungus occurs under the following circumstances:
- decreased general and local immunity;
- active hormonal (including contraceptive) or antibacterial therapy;
- errors in nutrition (abuse of sweets, flour products, foods containing starch, carcinogens);
- the presence of chronic systemic diseases of the endocrine, digestive and hormonal systems (diabetes mellitus, dysbacteriosis, vitamin deficiency, age-related hormonal disorders);
- infection with pathogenic flora (bacteria, viruses, fungi) during sexual intercourse;
- obesity;
- prolonged stressful situations;
- allergic diseases;
- antitumor therapy using cytostatic drugs;
- AIDS.
Diagnostics
Usually, diagnosing urethritis is not difficult, but given the low-symptomatic nature of candidal inflammation, clinical data should be confirmed by the results of laboratory methods. Patients are prescribed the following procedures:
- General urine analysis.
- Two- or three-glass sample.
- Urethral smear (microscopy, culture).
When examining women, material is taken not only from the urethra, but also vaginal mucus is analyzed. In the discharge from the urethra, leukocytes, yeast-like cells, and mycelial filaments are found.
To determine the concomitant pathology, a biochemical blood test and immunogram are performed. It is necessary to differentiate urethritis from other diseases of the urogenital tract, including sexually transmitted diseases.
Characteristic symptoms
During the incubation period (from the moment the infection hits the urethral mucosa until the onset of the disease), the pathology does not manifest itself in any way.
- Women are characterized by mild, mild symptoms (minor discomfort, burning and stinging when urinating, scanty discharge - in 65%), which most often are not even paid attention to (since they appear against the background of vulvovaginal candidiasis with more pronounced symptoms).
- In men, due to the anatomical features of the structure (small diameter of the urethra and inlet) and isolated course (only urethritis, without concomitant diseases), the symptoms appear brighter and more acute, causing noticeable discomfort when urinating.
- The chronic form of candidiasis in men and women is characterized by an almost asymptomatic course with frequent exacerbations (4 or more times a year) and increasing symptoms (with each exacerbation the manifestations become more pronounced).
- swelling, redness of the mucous membranes of the urethra and head of the penis (in men);
- pain, stinging, burning (less commonly, itching) when urinating;
- copious, moderate or scanty discharge (in the form of whitish, grayish or yellowish crusts around the entrance to the urethra, thread-like mucus during urination, cheesy clots from the urethra).
Discharge from candidiasis usually appears in the morning.
Click on photo to enlarge
| Complications in women | Complications in men |
| Candidiasis vulvitis and vaginitis (inflammation of the external labia and vagina) | Candidal balanitis and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin) |
| Fungal cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) | Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland) |
| Impaired renal filtration function | Fungal vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) |
| Candidal orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) | |
| Cystitis |
Complications in womenComplications in men
| Candidiasis vulvitis and vaginitis (inflammation of the external labia and vagina) | Candidal balanitis and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin) |
| Fungal cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) | Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland) |
| Impaired renal filtration function | Fungal vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) |
| Candidal orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) | |
| Cystitis |
How does nonspecific (nongonococcal) urethritis differ from ordinary urethritis and how to treat it?
Nonspecific urethritis (NU) is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra (urethra). According to etiology, the disease is divided into:
Infectious (venereal) form.
These include: bacterial, chlamydial, viral, mycotic, trichomonas, tuberculous urethritis.
Non-infectious form.
Which includes: congestive, metabolic, traumatic, allergic urethritis.
Types and symptoms of nonspecific urethritis
Every year, WHO registers up to 50 million cases of non-gonococcal urethritis. And if we add in urethral syndromes that occur in a latent form, then the figure turns out to be truly impressive.
Thus, according to clinics specializing in diseases of the genitourinary system, for every 100 thousand applicants, 217 cases of N.U. For comparison, gonococcal urethritis (gonorrhea) is 5 times less common.
Types of nonspecific urethritis
Pathogen
Symptoms
| Bacterial | Staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia coli, mycoplasma, corynebacterium, gardnerella. | Itching and burning when urinating, frequent unproductive urges, mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant fishy odor, swelling and redness of the urethral sponges. |
| Tuberculous | Koch stick | Weakness, temperature 37.1-38.0, sweating. In the initial stages, the disease has symptoms of urethritis of the posterior wall - burning, urination with blood. It usually occurs against the background of kidney tuberculosis. The first symptoms may appear several years after infection. |
| Mycotic (candida) | Fungi of the genus Candida (C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. Grabrata) | During urethroscopy, a cheesy white-gray coating is found on the mucous membrane of the male urethra. After its removal, inflamed tissue is visible. The head and foreskin are swollen (balanoposthitis). I am concerned about burning and discomfort in the urethra. Women experience viscous white-pink discharge. |
| Trichomonas | Trichomonas vaginalis | Itching and feeling of “blockage” when urinating, paresthesia, gray-white foamy discharge without pus. Trichomonas nongonorrheal urethritis in men is often accompanied by hemospermia. |
| Chlamydial | Chlamydia trachomatis strains | The disease is transmitted through sexual intercourse and is often asymptomatic (especially in women). The discharge is scanty, glassy, rarely mixed with pus. |
| Viral | Genital wart virus, herpes virus, urethroconjunctivitis virus | Viral non-gonococcal urethritis may be accompanied by conjunctivitis, joint damage (Reiter's disease), and the appearance of keratinized areas on the skin. With herpetic urethritis, numerous vesicles appear on the foreskin and the inner surface of the urethra. Breaking through, they form ulcers. |
Fact for women. In 80% of cases, nongonorrheal urethritis in women occurs latently, without external signs. The reason is the structure of the female urethra. It is 15 times shorter and several times wider than the male one.
Pathogenic microflora does not linger in the urethra, but immediately slips into the bladder, causing its inflammation. Cystitis and nonspecific urethritis in women practically do not occur separately, but occur “in combination,” so to speak.
What if it's gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea or gonococcal urethritis is not as common as, for example, chlamydia, but due to acute symptoms and a high percentage of complications, this disease is known to everyone.
Men.
The incubation period is 2-5 days. Dysuria, swelling of the urethra. At the beginning of urination, men feel a sharp but quickly passing pain. If the infection process has passed through the external urinary sphincter, then pain may also appear at the end of urination. From scanty mucous membranes to abundant purulent discharge it takes only 2-3 days.
Women.
The incubation period is 5-10 days. The disease often occurs in a latent form. Pain may be felt in the side or lower abdomen. The vaginal mucosa swells, pain and inflammation in the throat after oral sex. During the menstrual cycle, discharge (blood and pus) increases.
Bacterial non-gonococcal urethritis and acute gonorrhea have almost the same symptoms, so without a smear on the flora it is almost impossible to accurately determine the pathogen.
Therapy of nonspecific urethritis
Below are selected treatment regimens for nonspecific urethritis. This information is for informational purposes only and in no way can replace the advice of your attending physician.
Treatment regimen depending on the type of nonspecific infectious urethritis:
Antibiotics are prescribed after an antibiogram. This study takes from 5 to 7 days, but until the pathogen is identified, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics.
For urethritis, these are: erythromycin, chloramphenicol, cefazolin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, doxycycline and its analogues. Additionally, sulfonamides and uroantiseptics - palin, nitroxoline, urolesan - can be prescribed. If the antibiotic does not help within 72 hours, it is replaced.
Bacterial.
- Antibiotics: for staphylococcus: toxoid, antifagin (vaccine), human immunoglobulin;
- for streptococcus: penicillin antibiotics;
- for mycoplasmosis: azithromycin, clarithromycin, ofloxacin.
For chronic bacterial urethritis: metacin, pentoxyl, prodigiosan.
Tuberculous.
- Pathogenetic drugs: isoniazid, rifampicin, mycobutin;
- Local therapy: destruction of granulations, bougienage (stretching) of the urethra in the presence of stricture.
Mycotic (candidal).
- Antifungal drugs: nystatin, levorin, fluconazole, clotrimazole;
- B vitamins.
Trichomonas.
- Antibiotics: metronidazole, trichopolum, nitazole, chlorhexidine, trichomonacid, nitazole;
- Installations of 1% trichomonacid solution.
Chlamydial.
- Antibiotics: tetracycline: doxycycline, vibramycin, doxibene;
- group of fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, uniflox.
Viral.
- Antibiotics (not always): tetracyclines, erythromycin, trimethoprim;
- Antiviral drugs: acyclovir, ribavirin, ganciclovir;
- Corticosteroids: prednisolone, dexamethasone.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine suggests the use of plants with natural antiseptic, antipruritic, regenerating properties for the preparation of decoctions. Prepared herbal infusions can be taken orally or applied to the genitals in the form of douching.
- A decoction prepared from 1 tbsp. spoons of oak bark and 0.5 liters of water, you can treat the genital area daily during hygiene procedures. A decoction of chamomile is prepared in a similar way.
- Walnut leaves have natural antiseptic properties (due to their high iodine content). A decoction of the leaves is used for douching for 10-14 days. To prepare it you will need 2 tbsp. l. dry leaves per 1 liter of water. As an alternative, you can use calendula flowers, which have disinfectant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Systemic antifungal drugs have many side effects, which limits their use for some diseases. An experienced specialist will make a choice in favor of an effective drug with the least possible health consequences.
Particular attention in the treatment of candidal urethritis should be given to pregnant and lactating women and puberty girls. The risk-benefit ratio must be agreed upon with the attending physician.