The daily rate of urine excretion from the human body is 1000-1500 ml. With the development of polyuria, the volume of urine excreted per day increases to 2000 and 3000 ml. This disorder is caused by a decrease in the absorption of water in the renal tubules due to one reason or another. Clinically, it manifests itself as an increased urge to urinate.
Polyuria in men is not necessarily an indicator of any disease, since there is a physiological type of polyuria associated with excessive drinking in excess of normal fluid requirements. The danger of this condition is that isolated polyuria does not have any other clinical manifestations. In this regard, people suffering from this disorder rarely seek specialized medical help, while the underlying disease progresses, worsening the further prognosis.
Etiology
In some cases, excessive urine output may be a completely normal condition caused by drinking large amounts of fluid or taking medications specifically aimed at increasing urine production.
However, the progression of a completely different pathology is often a predisposing factor in the appearance of such a disease. Thus, among the provocateurs of the disease it is worth highlighting:
- chronic renal failure;
- the occurrence of pyelonephritis;
- a history of sarcoidosis;
- formation of oncological tumors in the pelvic area;
- heart failure;
- a wide range of nervous system disorders;
- diabetes;
- inflammation or other damage to the prostate;
- formation of kidney stones;
- inflammatory process localized in the bladder;
- diverticulitis and myeloma;
- cystic neoplasm of the kidney, which can be single or multiple;
- Barter syndrome;
- hydronephrosis;
- secondary form of amyloid nephrosis.
In women, the reasons may be pregnancy - on the one hand, such a sign is one of the manifestations of the fact that a female representative is preparing to become a mother, and on the other hand, polyuria may indicate an asymptomatic course of pyelonephritis. In any case, consultation with a clinician is necessary.
However, not only the course of internal processes in the body can cause an increased urge to urinate. An increase in the daily volume of such human biological fluid can also be caused by:
- taking diuretics prescribed by the attending physician to eliminate completely different kidney pathologies.
- ingestion of large quantities of drinks, in particular carbonated ones.
The above factors most often lead to the development of polyuria at night, which in the medical field is a separate disease called nocturia. It is extremely rare, in approximately 5% of cases, that the causes of excessive urine production are genetic predisposition.
Etiological factors
If after urination you want to pee more, then this is an alarming sign, which usually signals disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the urinary system. The following pathological conditions can provoke the occurrence of this sensation in a person:
- . The presence of formed conglomerates of various sizes in the bladder significantly reduces the volume of this organ. All this leads to the fact that a person, after visiting the restroom, wants to pee again. Simultaneously with this symptom, a picture of this particular illness appears - pain in the lumbar region, the presence of pathological impurities in the urine, and hyperthermia may also be noted;
- Diabetes. Diabetics often experience this symptom;
- Cystitis. If after urination you want more, then in most cases it is cystitis that causes such an unpleasant sensation. With this infectious process, not only the urethral mucosa is affected, but also the bladder mucosa, which leads to disruption of its functioning. Therefore, a person has a regular urge to evacuate, after which there is an uncomfortable feeling that he has not emptied completely;
- Often the cause of the feeling that you want to urinate again is progressive renal failure. This is due to the fact that the patient experiences a constant feeling of thirst and consumes a lot of fluid. Accordingly, a fairly large volume of urine is excreted naturally. Due to the irritation of the bladder, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying (I want to write more);
- In men, such a discomfort may occur due to damage to the prostate;
- Various sexually transmitted infections can also provoke the feeling that after passing urine you want to visit the toilet again. This group includes gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.
Physiological factors:
- period of bearing a child. At this time, the bladder is under pressure from the ever-expanding uterus. Therefore, pregnant women often have the feeling that after emptying their bladder they want to visit the toilet again;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- consuming too much liquid per day (the norm is no more than 2.2 liters).
Video
: Signs of prostatitis
Classification
Currently, several forms of this pathology are known. Depending on the nature of the course, polyuria is divided into:
- temporary - considered as such if it was provoked by the presence of one or another infectious process in the human body or by the period of gestation;
- permanent - this means that the disease was formed by a pathological disorder of the functioning of the kidneys.
According to etiological factors, polyuria syndrome is:
- Polyuria in diabetes mellitus: causes of development and treatment
- pathological - in such cases, the illness is a complication of one or another illness. This type includes nocturnal polyuria and frequent urge to urinate in diabetes mellitus.
- physiological – associated with the use of diuretics prescribed by the attending physician or at one’s own request, which is strictly prohibited.
Colorless urine (clear like water)
The human body is a complex mechanism. One of its important functions is urination. Thanks to this process, the body gets rid of excess fluid. The color and smell of urine can indicate certain human diseases. Is it normal for a person to produce clear urine? Noticing such changes, many patients sound the alarm and rush to the doctor. Whether discoloration of urine is really a reason to sound the alarm or whether this condition is normal should be considered in more detail.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
In a healthy person, urine has a straw-yellow color without turbidity or impurities. This color depends on bile pigments, which are found in the urine in predominant quantities. Sometimes the shade becomes almost colorless. This is influenced by various reasons. Discoloration of urine occurs with frequent urination. At the same time, it does not linger in the bladder and does not have time to become saturated with yellow pigments. Sometimes this phenomenon occurs in people who drink large amounts of liquid, coffee, and tea.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
What to pay attention to:
- It’s bad when the excretion product has a sweetish odor and a light color. This most likely indicates the presence of diabetes mellitus. The patient is advised to limit fluid intake for 10-14 days, then check the color of the urine. If the urine is still light, it is important to get tested;
- Light colored urine and a sweet odor may also indicate pregnancy;
- The brown color of the discharge product often indicates a lack of fluid or dehydration. This means that you should reconsider your drinking regime, increase the amount of fluid you drink;
- an intense yellow tint is a sign of excess vitamin B;
- red or burgundy urine appears after eating certain foods (beets, mulberries, red juices). If a person has not eaten such food, and the discharge has a similar color, he should definitely get tested.
If there is a temporary change in the color of urine, do not sound the alarm and run to the doctor. If the discoloration of the product is permanent and is accompanied by other manifestations (pain, burning, change in odor), it is important to make an appointment with a specialist and undergo laboratory testing.
Causes of urine color change
If the urine has changed color for no apparent reason, you should undergo an examination in order to prevent serious violations. Such harmless signs as discoloration, change in shade, bad odor, often indicate serious pathologies in the body. The triggering factors for colorless urine in women, men and children can be both common and different.
Common pathologies that cause changes in the color of the discharge product include:
- renal failure - occurs due to impaired renal function;
- diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus - these diseases require immediate medical treatment, as they pose a serious risk to the health and life of the patient;
- urolithiasis – characterized by the formation of kidney stones of various shapes and sizes;
- pathologies of the urinary tract;
- hepatitis is an inflammatory liver disease, predominantly of viral origin;
- liver dysfunction.
The diseases described above are diagnosed using laboratory tests and other diagnostic methods.
Urine color in children
Colorless urine in an infant is considered normal, since children receive only breast milk or formula. With age, the color of urine becomes yellow, which indicates the normal functioning of the urinary system. You should consult a doctor if the baby's discharge product has turned from yellow to colorless, while the baby's drinking regimen and nutrition have not changed. Sometimes clear urine appears in a child while taking diuretics prescribed by a doctor. This phenomenon is temporary and goes away on its own without medication. Laboratory tests prescribed by the doctor will help find out why the urine is colorless and whether the child has any diseases.
Possible causes in women
In addition to kidney failure and other diseases of the body, in women, urine as clear as water can indicate pregnancy. This is explained by changes in the level of hormones in the body. During toxicosis, many mothers drink large amounts of liquid, this also causes a change in the color of the discharge product.
Another provoking factor for a change in shade and the appearance of transparent urine during pregnancy is the exacerbation of chronic diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Women are more susceptible to pathologies such as diabetes. One of the common reasons for changes in the color of urine is this disease.
Provoking factors in men
Many factors influence the clarity of urine and its color in men. White urine often indicates such a feature as sperm entering the urinary canal. If after a few hours after this the shade becomes the same, do not worry. The situation is different with constant discoloration of urine. In addition, male diseases that provoke a change in the color of the excretory product include diabetes mellitus, kidney failure, and inflammation in the urinary organs.
Associated symptoms
In addition to the shade of urine, during laboratory testing, much attention is paid to such a sign as complete or incomplete transparency of urine. This helps in making a diagnosis for a particular disease. The cloudy nature of urine indicates the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the organs of the genitourinary system. Often, opaque urine indicates insufficient intimate hygiene, increased levels of leukocytes, epithelial cells and other conditions.
A change in odor combined with colorless urine is another reason to see a doctor. A strange, pungent, unpleasant odor of the product in women and men often indicates diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and infectious diseases of the urinary system. Cramps and pains when going to the toilet indicate cystitis, urethritis and other diseases.
Blood in the urine is a very bad sign, indicating internal bleeding of the kidneys or bladder. If this sign appears, you should immediately go to the hospital.
What to do
To determine the cause of discoloration, which is not caused by food and drinking regime, you should take tests and undergo a full medical examination. Therapy always depends on the diagnosis. For kidney disease, patients are prescribed drug therapy, including the following medications:
- antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Mebeverine, No-shpa);
- analgesics (Ibuprofen, Indomethacin);
- antiseptic drugs (Morphocycline, metacycline);
- diuretics – diuretic drugs (Furosemide, Aldactone);
- drugs, stone dissolvers - prescribed for the formation of stones in the kidneys (Cyston, Canephron, Cystenal).
For diabetes mellitus, medications containing insulin or agents that promote its natural production are used. Patients with diabetes are advised to follow a strict diet. Diet excludes fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods. Smoked sausages, lard, hot spices, seasonings, chocolate, cocoa, and alcohol are prohibited. A diet is recommended that includes cereals, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, herbal teas, and juices.
If the water-salt balance is disturbed in the human body, excess water can be produced. As a result of this phenomenon, urine becomes transparent and colorless.
Treatment for this condition is as follows:
- Correction of drinking regime.
- Exclusion of diuretic products from food.
- Limiting the amount of salt.
- Saturation of the body with essential vitamins and minerals.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases.
Physical exercises have proven themselves to be effective in the treatment of water-salt imbalance. Therapeutic gymnastics improves metabolism and restores body functions.
Conclusion and prevention
Discoloration of the color of urine does not always signal serious problems. Sometimes urine levels change due to the consumption of certain foods, a person’s drinking regimen and some other factors. To prevent diseases that provoke changes in urine characteristics, you should follow the rules of intimate hygiene, promptly treat infectious diseases, undergo regular preventive examinations, maintain proper nutrition and daily routine.
How does the disease manifest itself?
As mentioned above, the first and most important symptom of polyuria is an increased amount of fluid coming out during urination. Its volume may vary depending on the disease accompanied by this pathology. So, with some types of diabetes, daily diuresis can be up to five liters. The urge to go to the toilet in this situation may become more frequent, or may remain as before - up to five times a day. There are times when the daily volume of urine reaches up to ten liters. Patients suffering from aggravated renal canal dysfunction may be susceptible to this. This form of polyuria is accompanied by increased loss of sodium, calcium, potassium, water and chlorides.
With the disease, the density of urine decreases
The disease is characterized by a strong decrease in urine density. This is facilitated by the retention of toxins in the body due to the fact that the kidneys lose their concentration function. The only exceptions are patients with diabetes. Due to the increased level of sugar in their blood, glucose also enters the urine - glucosuria. Therefore, its density is relatively high.
It is worth noting that in the first place, patients pay attention not to the amount of fluid released during urination, but to the signs of the underlying disease, which subsequently provokes this pathology.
What are the characteristic signs to use to diagnose the disease?
Since a large number of diseases can provoke a feeling as if the organ is full, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis before prescribing treatment. When making a diagnosis, not only the patient’s symptoms are taken into account, but also diseases of any nature that he had previously suffered from, gender and age. According to statistics, women are more often susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system.
Inflammation of the urinary system
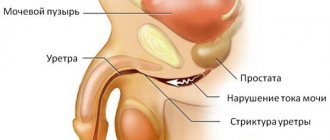
With the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system, the most common diseases are cystitis and urethritis. If you do not pay attention to the felt filling of the bladder and other manifestations, the disease will develop into pyelonephritis. Most often it is women who get sick due to physiological characteristics. Characteristic manifestations of the inflammatory process: In men, sensations of incomplete emptying may occur due to problems with the prostate
outward and there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The main signs indicating prostatitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- a weak, intermittent stream when a man relieves himself;
- involuntary leakage of a certain amount of urine.
Also, swelling and similar symptoms are characteristic of the development of impotence. If the patient has prostate adenoma, in addition to the previously listed signs, weight loss and prolonged elevated temperature will be added. In addition to prostate tumors, neoplasms can also occur in other organs of the genitourinary system. The appearance of blood in urine is a signal of the onset of bladder cancer.
The process of urine excretion for each person is purely individual. Some people visit the restroom five times a day, while others go to the toilet after every cup of liquid they drink. Normally, it is believed that if a person visits the toilet no more than 10-12 times a day, then his urinary system functions normally. A change in this frequency may indicate progression of the pathology. Also, patients often complain that after urination there is a feeling that they want more. The causes of this condition can be both pathological and physiological.
This suggests that you should not immediately panic and run to the doctor. But if such a feeling occurs systematically, then this is a serious reason to consult a urologist.
This specific sensation can occur in people of different age categories. It is worth noting that the pathology is more often diagnosed in the fair sex. This is due, for the most part, to the structural features of their urinary system. The urethra in women is much shorter than in men, so various pathogenic microorganisms can easily penetrate it and provoke the progression of the inflammatory process (this reason is one of the main reasons that provoke the feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder).
Symptoms
The only clinical manifestation of polyuria in women and men is an increase in the amount of urine secreted by the body throughout the day.
Normally, daily urine volumes can vary from one to one and a half liters. However, in the presence of such a disease, they can increase threefold. When the disease is severe, the human body produces up to ten liters of urine in one day.
Other characteristic features will be:
- frequent urge to visit the toilet - a distinctive feature is that they will never be false or scanty, as happens, for example, with cystitis;
- decrease in urine density - only a clinician can determine this during diagnostic measures. This condition is caused by the fact that the kidneys lose their ability to concentrate to a small extent, and this occurs against the background of retention of toxins. The only exception is patients diagnosed with diabetes - only their urine density will be excessively high. This is explained by the content of a large amount of glucose, which prevents urine from losing its density;
Polyuria does not have other characteristic signs. However, it is worth noting that there are secondary symptoms of polyuria that the patient may experience, such as pain and burning when urinating. In fact, they are symptoms of those diseases or infections that caused excessive urine production.
Depending on what pathological process became the source of the increase in daily urine volumes, additional symptoms will be present.
Symptoms
The only symptom of polyuria is an increase in the amount of urine produced by the body per day. The volume of urine excreted in the presence of polyuria can exceed two liters, in case of complications or pregnancy - three. In the case when the disease appears due to diabetes mellitus, the number of liters of urine emitted per day can reach ten.
The secondary symptoms of polyuria that a person feels are actually signs of painful or infectious processes occurring in his body (against the background of which polyuria arose). Depending on what disease caused the increase in daily urine volume, additional symptoms characteristic of this particular pathological process will appear.
Diagnostics
- Nocturnal polyuria in men and women: causes and treatment
To find out the exact cause of polyuria, the doctor must first take a medical history. It includes information about the volumes of fluid consumed and excreted over a certain period of time. This is necessary to differentiate polyuria from pollakiuria.
The patient is questioned about the time of development of polyuria, the speed of manifestation (suddenly or gradually), as well as possible factors that could provoke the syndrome (medication, injury, surgery).
An external examination allows you to find out symptoms that may indicate the presence of certain disorders in the body. The presence or absence of this phenomenon in the family history is determined. A physical examination makes it possible to identify signs of obesity, or, conversely, exhaustion. When examining the skin, the presence of hyperemic areas, ulcers, subcutaneous nodules, and dryness are taken into account.
Laboratory research
To differentiate polyuria from simple frequent urination, you need to conduct a urine sample according to Zimnitsky. Urine is collected throughout the day, its volume and specific gravity are determined. If polyuria is detected, it is necessary to determine the glucose content in the urine or blood to exclude decompensated diabetes mellitus.
In the absence of hyperglycemia, tests are performed:
- biochemistry of blood and urine;
- osmolality of urine or blood serum (assessment of the body's water balance).
These studies make it possible to identify hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, sodium excess or deficiency. Comparison of urine and blood osmolality at different times makes it possible to distinguish polyuria associated with nervous polydipsia caused by diabetes insipidus and other diseases. Since this test can lead to severe dehydration, it is carried out under the close supervision of specialists in a hospital setting.
In the morning, the patient is weighed and blood is taken from a vein to determine the concentration of electrolytes and osmolality. Urine osmolality should be measured every hour. In this case, the patient should not drink anything until orthostatic hypotension appears and the initial weight loss is 5% or the osmolality increases by more than 30 mOsm/kg. Then an injection of Vasoperssin is administered. And an hour after the injection, urine osmolality is determined for the last time.
Diagnosis of patients with this problem
Diagnosis begins with clarifying complaints by which a doctor can suspect a person has a disease and make a preliminary diagnosis. A patient with an infectious-inflammatory process, in addition to the feeling of wanting more after urinating, may complain:
- The pain that accompanies the urge occurs during the act of urination or after the release of urine;
- Itching, burning in the urethra;
- Change in the amount of urine released (with each urge, little urine is released, it comes out drop by drop, or, conversely, with frequent urges, a large amount of liquid is released);
- Change in color (white, red, brown or green) and clarity of urine, appearance of foam;
- Violation of general condition, weakness, fatigue, increased body temperature, headache, decreased ability to work;
- Decreased sexual function, lack of libido, erectile dysfunction in men.
For patients with suspected malignancy or urolithiasis, the appearance of blood in the urine is typical. The patient may notice both streaks of blood and a change in the color of the urine to red, brown or pink, depending on the degree of hematuria.
A mandatory diagnostic measure is passing a clinical test of blood and urine. In the blood you can detect leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, increased ESR (characteristic of an infectious process), anemia (with hematuria). The level of protein, leukocytes, and red blood cells increases in the urine. The organoleptic properties of urine change. With urolithiasis, salts appear, which can indicate the structure of the stone.
It is also necessary to culture the urine and determine the sensitivity of the microflora to antibiotics. If a sexually transmitted disease is suspected, PCR is performed to identify the pathogen.
Ultrasound is used to detect changes in the genitourinary organs. Helps determine the location of a tumor or stone (if present), determine the size of the prostate gland or uterus during the inflammatory process.
If a malignant neoplasm is suspected, the following is carried out:
- MRI or CT, which will help determine the location and size of the tumor;
- Cystoscopy to visualize the tumor;
- Biopsy to determine the nature of the process.
If you feel like you want to go to the toilet again after urinating, you should not engage in self-diagnosis. Diseases that cause such sensations can lead to serious complications if you do not seek help from a specialist in time.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that this pathology does not have many symptoms, establishing the correct diagnosis is a problem. Before carrying out specific diagnostic measures, the clinician needs to conduct a primary diagnosis, which will include:
- studying the medical history and collecting a life history of both the patient and his immediate relatives - this will help to identify the most characteristic etiological factor. However, to find out what actually caused the pathology, special tests are needed.
- a thorough physical examination, which will help identify symptoms associated with diseases that cause polyuria.
- a detailed survey of the patient is necessary to determine the first time of appearance and intensity of expression of both the main and possible additional symptoms.
The following laboratory tests have the greatest diagnostic value:
- What is polyuria in men: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
- Zimnitsky test - the need for such a procedure is to differentiate polyuria from frequent urination, accompanied by small portions of excreted fluid. To do this, all urine excreted per day is collected from the patient. After this, experts calculate not only its volume, but also its quantity and specific gravity. Such parameters are taken into account for each portion of urine;
- fluid deprivation test - to carry it out, the patient is forcibly deprived of fluid, causing the body to become dehydrated. It can last from four to eighteen hours. After the required period has passed, the patient is injected with a solution that contains an antidiuretic hormone. After this, several urine tests are taken again. Then clinicians compare the indicators both before and after administration of the drug, taking into account the water balance of the blood plasma.
A comparison of all tests will make it possible to determine the true cause of polyuria, depending on which the patient may be referred for consultation to other specialists and additional instrumental and laboratory diagnostic examinations may be prescribed.
Only after this an individual scheme is selected on how a particular patient can get rid of polyuria.
Excessive urine output - symptoms and treatment
Polyuria is a disorder in which there is an increase in the daily volume of urine excreted. Such a deviation in the functioning of the genitourinary system is typical for both adults and children. Treatment tactics are often conservative.
Polyuria is a rather specific disease in which the volume of urine excreted per day increases approximately two or three times. In this case, one should distinguish this ailment from ordinary frequent urination caused by a large amount of liquid drunk.
In the vast majority of cases, the underlying factors are kidney pathologies, but clinicians identify a large number of other sources, which also contribute to the course of a particular disease. In adults and children, the causes of the disease will be the same.
The symptoms of such a syndrome are difficult to ignore, since it is expressed in a private urge to urinate. Some patients report pain and other discomfort in the groin area.
Diagnosis is based on laboratory tests, but instrumental examinations may be needed to identify some etiological factors.
Since such a disease can be one of the manifestations of another pathology, treatment is often aimed at eliminating the source, against the background of which daily urine volumes return to normal.
The content of the article:
Etiology
In some cases, excessive urine output may be a completely normal condition caused by drinking large amounts of fluid or taking medications specifically aimed at increasing urine production.
However, the progression of a completely different pathology is often a predisposing factor in the appearance of such a disease. Thus, among the provocateurs of the disease it is worth highlighting:
- chronic renal failure;
- the occurrence of pyelonephritis;
- a history of sarcoidosis;
- formation of oncological tumors in the pelvic area;
- heart failure;
- a wide range of nervous system disorders;
- diabetes;
- inflammation or other damage to the prostate;
- formation of kidney stones;
- inflammatory process localized in the bladder;
- diverticulitis and myeloma;
- cystic neoplasm of the kidney, which can be single or multiple;
- Barter syndrome;
- hydronephrosis;
- secondary form of amyloid nephrosis.
In women, the reasons may be pregnancy - on the one hand, such a sign is one of the manifestations of the fact that a female representative is preparing to become a mother, and on the other hand, polyuria may indicate an asymptomatic course of pyelonephritis. In any case, consultation with a clinician is necessary.
However, not only the course of internal processes in the body can cause an increased urge to urinate. An increase in the daily volume of such human biological fluid can also be caused by:
- taking diuretics prescribed by the attending physician to eliminate completely different kidney pathologies.
- ingestion of large quantities of drinks, in particular carbonated ones.
The above factors most often lead to the development of polyuria at night, which in the medical field is a separate disease called nocturia. It is extremely rare, in approximately 5% of cases, that the causes of excessive urine production are genetic predisposition.
Classification
Currently, several forms of this pathology are known. Depending on the nature of the course, polyuria is divided into:
- temporary - considered as such if it was provoked by the presence of one or another infectious process in the human body or by the period of gestation;
- permanent - this means that the disease was formed by a pathological disorder of the functioning of the kidneys.
According to etiological factors, polyuria syndrome is:
- pathological - in such cases, the illness is a complication of one or another illness. This type includes nocturnal polyuria and frequent urge to urinate in diabetes mellitus.
- physiological – associated with the use of diuretics prescribed by the attending physician or at one’s own request, which is strictly prohibited.
Symptoms
The only clinical manifestation of polyuria in women and men is an increase in the amount of urine secreted by the body throughout the day.
Normally, daily urine volumes can vary from one to one and a half liters. However, in the presence of such a disease, they can increase threefold. When the disease is severe, the human body produces up to ten liters of urine in one day.
Other characteristic features will be:
- frequent urge to visit the toilet - a distinctive feature is that they will never be false or scanty, as happens, for example, with cystitis;
- decrease in urine density - only a clinician can determine this during diagnostic measures. This condition is caused by the fact that the kidneys lose their ability to concentrate to a small extent, and this occurs against the background of retention of toxins. The only exception is patients diagnosed with diabetes - only their urine density will be excessively high. This is explained by the content of a large amount of glucose, which prevents urine from losing its density;
Polyuria does not have other characteristic signs. However, it is worth noting that there are secondary symptoms of polyuria that the patient may experience, such as pain and burning when urinating. In fact, they are symptoms of those diseases or infections that caused excessive urine production.
Depending on what pathological process became the source of the increase in daily urine volumes, additional symptoms will be present.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that this pathology does not have many symptoms, establishing the correct diagnosis is a problem. Before carrying out specific diagnostic measures, the clinician needs to conduct a primary diagnosis, which will include:
- studying the medical history and collecting a life history of both the patient and his immediate relatives - this will help to identify the most characteristic etiological factor. However, to find out what actually caused the pathology, special tests are needed.
- a thorough physical examination, which will help identify symptoms associated with diseases that cause polyuria.
- a detailed survey of the patient is necessary to determine the first time of appearance and intensity of expression of both the main and possible additional symptoms.
The following laboratory tests have the greatest diagnostic value:
- Zimnitsky test - the need for such a procedure is to differentiate polyuria from frequent urination, accompanied by small portions of excreted fluid. To do this, all urine excreted per day is collected from the patient. After this, experts calculate not only its volume, but also its quantity and specific gravity. Such parameters are taken into account for each portion of urine;
- fluid deprivation test - to carry it out, the patient is forcibly deprived of fluid, causing the body to become dehydrated. It can last from four to eighteen hours. After the required period has passed, the patient is injected with a solution that contains an antidiuretic hormone. After this, several urine tests are taken again. Then clinicians compare the indicators both before and after administration of the drug, taking into account the water balance of the blood plasma.
A comparison of all tests will make it possible to determine the true cause of polyuria, depending on which the patient may be referred for consultation to other specialists and additional instrumental and laboratory diagnostic examinations may be prescribed.
Only after this an individual scheme is selected on how a particular patient can get rid of polyuria.
Treatment
Therapy for such a disease is primarily aimed at eliminating the disease that provoked its appearance. After diagnosis, the doctor may identify a deficiency of certain substances in the body, including:
- potassium and calcium.
- sodium and chlorides.
To restore their normal level, it is necessary to draw up an individual diet and volumes of fluid consumed.
In severe cases of the disease and severe dehydration, they resort to the introduction of special substances into a vein.
Additional methods for treating polyuria are:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- performing exercise therapy designed to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis and bladder, in particular, they often resort to Kegel exercises;
- use of alternative medicine recipes;
Treatment with folk remedies is carried out using:
- anise
- plantain.
- oats or millet.
- immortelle.
- nettles
- motherwort.
- St. John's wort.
- dill.
- burdock.
It is worth noting that this type of therapy must be previously agreed upon with the attending physician.
Prevention and prognosis
Preventive measures to prevent the development of such a disease are aimed at observing the following general recommendations:
- eat properly and balanced;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- take diuretics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- maintain a plentiful drinking regime - normally you need to drink at least two liters per day;
- promptly identify and eliminate pathologies that provoke the occurrence of polyuria;
- regularly, several times a year, undergo a full preventive examination at a medical institution;
The outcome of polyuria will directly depend on the etiological factor. However, in the vast majority of cases, complete recovery is observed - this can be achieved by timely seeking qualified help.
Diagnosis of polyuria
If an increase in urine output is suspected, the examination should begin with a general urine test (collected in the morning after hygiene procedures) and a Zimnitsky urine sample, when each portion of biomaterial per day is examined.
If it is polyuria, then the volume will be increased, and if a person has frequent urination, then the total amount of urine will not exceed the norm. According to OAM, polyuria is diagnosed when the specific gravity of the test material decreases - this is a sign of excess water content in it. Due to the decrease in density, the color of urine changes - it becomes transparent. It is important to note that polyuria in diabetes mellitus has one feature: the specific gravity of urine will not decrease due to the high level of glucose, which increases it.
At the same time, an ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal cavity is prescribed; in some cases, urography or cystoscopy may be required. Biochemical parameters evaluate the level of alkaline phosphatase, electrolytes and residual nitrogen.
If the doctor suspects endocrine disorders, then a hormonal panel, glucose volume is additionally examined, a glucose tolerance test and an x-ray of the sella turcica are performed to determine the size of the pituitary gland. If polyuria is confirmed, a fluid deprivation study is performed. After artificial dehydration, an injection with a hormonal antidiuretic drug is given, then a repeat OAM is performed. By comparing both tests - before and after the hormone is administered, the cause of increased urination is determined.
Prevention and treatment of polyuria
When talking about treatment, we mean eliminating the cause of increased diuresis. If it is impaired due to kidney disease, you will need a diet with limited salt, excluding spicy, fatty foods, sweets and coffee. If the cause lies in diabetes, then a necessary condition for complex therapy is the rejection of all types of fats and sugars in the diet, limiting the intake of foods rich in carbohydrates: potatoes, pasta. Do not forget about traditional medicine - at home you can treat polyuria with herbal infusions.
Most of them have an anti-inflammatory effect.
For example, plantain will help normalize the functioning of the kidneys and urea (2 tablespoons of seeds are poured with boiling water, after half an hour the prepared broth can be taken 1 spoon 3 times a day before meals). This should be done only after consultation with a urologist or nephrologist. Drug treatment is determined only by a doctor, since any pills and injections can have serious side effects. For example, autoimmune polyuria is treated with hormonal drugs (Prednisolone, glucocorticoids).
The selection of the dose of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is individual, especially when it comes to children. The first days of taking medications are usually diagnostic - the doctor assesses the dynamics of the patient’s condition and adjusts the dose of the medications. Prevention of polyuria involves paying close attention to your health and the health of your children. It is important to identify the disorder in the early stages and promptly get rid of provoking factors in order to prevent fluid deficiency in the body.
Treatment
Therapy for such a disease is primarily aimed at eliminating the disease that provoked its appearance. After diagnosis, the doctor may identify a deficiency of certain substances in the body, including:
- potassium and calcium.
- sodium and chlorides.
To restore their normal level, it is necessary to draw up an individual diet and volumes of fluid consumed.
In severe cases of the disease and severe dehydration, they resort to the introduction of special substances into a vein.
Additional methods for treating polyuria are:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- performing exercise therapy designed to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis and bladder, in particular, they often resort to Kegel exercises;
- use of alternative medicine recipes;
Treatment with folk remedies is carried out using:
- anise
- plantain.
- oats or millet.
- immortelle.
- nettles
- motherwort.
- St. John's wort.
- dill.
- burdock.
It is worth noting that this type of therapy must be previously agreed upon with the attending physician.
How is polyuria treated?
If the examination reveals polyuria, then, first of all, the underlying disease is treated. In case of moderate losses of such basic electrolytes as potassium, calcium, sodium, chlorides, they are replenished using an appropriate diet.
Seriously ill people are prescribed special therapy taking into account the loss of electrolytes in red blood cells and blood serum. The amount of fluid lost is administered urgently, taking into account the volume of circulating blood, as well as the state of the cardiovascular system, since there is a risk of developing hypovolemia, when the volume of circulating blood decreases below normal due to dehydration.
Other treatment options include Kegel exercises. By doing such exercises every day, in addition to strengthening the pelvic muscles, you can also strengthen the bladder muscles. It is very important to learn how to do them correctly and practice them every day, approximately twenty to eighty times for ten weeks.
Diet
Particular attention should be paid to changing the diet.
The patient needs to reduce the consumption of foods that irritate the urinary system or are a diuretic. This could be alcohol, caffeine, chocolate, various spices, artificial sweeteners. Eating foods that contain high levels of fiber helps with constipation, but it makes the situation worse if you have an overactive bladder. It is also necessary to control the amount of liquid you drink. The reason for frequent urination, for example, may be a large amount of liquid that was drunk before bed.
Our urologists will offer you treatment for hemiria using the most modern technologies and methods. The urologists of our clinics are exclusively highly qualified doctors with whom you don’t have to worry about your health. Make an appointment now!
Clinical picture
The main symptom of polyuria is increased diuresis, amounting to more than 1.8 liters of urine per day. Various disorders in the body can cause diuresis of different nature. In severe cases, some patients experience daily urine output of up to 10 liters. At the same time, the body catastrophically quickly loses water and minerals.
The density of urine with increased diuresis is reduced. This is due to the retention of toxins due to impaired filtration capacity of the kidneys. The compensatory volume of urine increases. The exception is patients with diabetes. Their urine has a high density due to the high concentration of glucose.
There are no other manifestations of polyuria. The accompanying symptoms depend on the underlying disease that led to increased diuresis. Polyuria should not be confused with cystitis. Cystitis is often accompanied by frequent urination and a false urge to empty the bladder. At the same time, the volume of urine released is insignificant. Polyuria is also accompanied by frequent urges, but the amount of urine produced greatly exceeds the daily norm.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, polyuria can lead to the following complications:
- dehydration;
- intoxication;
- clouding of consciousness;
- proteinuria;
- coma;
- psychological disorders.
Polyuria in children
In childhood, this is most often a temporary phenomenon. The main reason for the increase in urine volume is the imperfection of neuroendocrine processes regulating urine production. The child's body is very sensitive to both excess and lack of water. Before talking about the presence of polyuria in a child, it is worth analyzing whether he is drinking too much fluid or whether he is hypothermic, since in a cold environment sweating slows down and more fluid comes out in the urine. Perhaps the baby has developed a habit of frequently going to the toilet to attract attention.
If a child has increased thirst, he can drink up to 15 liters of water per day, urinating in large portions, on average 700 ml. Since there is a possibility of confusing polyuria with a neurogenic bladder condition or mental disorders, if symptoms appear, it is better to immediately consult a pediatrician for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostics
To find out how much urine a person excretes per day, a Zimnitsky analysis is performed. To do this, the patient collects all his urine in one container throughout the day. Each collected portion is carefully analyzed: its volume and specific gravity are calculated. This method will also help to distinguish the pathology in question from the usual increased urge to go to the toilet with a small volume of urine excreted.
Dysfunction of all functions is one of the causes of the disease
To find out what exactly caused the polyuria that has arisen, an analysis is carried out with the patient deprived of fluid. This will lead to dehydration, which usually promotes maximum production of antidiuretic hormone, ensuring optimal urine concentration. The patient does not drink liquid until he becomes dehydrated enough to actively secrete the above-mentioned hormone. As a rule, this process can last no more than 18 hours. In this case, urine is sampled hourly and its osmolality is calculated, that is, the water balance is assessed. If the osmolality of each subsequent dose of urine differs from the previous one by less than 30 mOsm/kg, the patient is given a drug that contains vasopressin. And then every half hour the osmolality is measured again. At the beginning and at the end of this study, the osmolality of the blood plasma is also calculated. By comparing the water balance of blood and urine at different times, doctors are able to distinguish polyuria caused by diabetes insipidus from a similar pathology that has developed due to other diseases.
Frequent and painful urination with cystitis. Causes and treatments
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The only remedy for CYSTITIS and its prevention, recommended by our subscribers! Read more…
Recently, women have increasingly begun to seek help from specialists regarding a common disease – cystitis. Painful urge to urinate, when you constantly want to go to the toilet, makes a woman feel uncomfortable. Women's health is one of the most important principles of successful childbearing. It is necessary to start paying attention to your health from a very early age, since the slightest hypothermia in early or teenage years can lead to serious consequences in youth and old age. Painful and very frequent urination, when the urge to go to the toilet is accompanied by acute pain, can cause serious pathologies.
What is cystitis?
Cystitis is the most common disease of the female genital organs, characterized by inflammation of the bladder. Cystitis most often affects women, not men. This feature is associated with the anatomical structure of the female genital organs. It is worth emphasizing that it is into the female body that the infection penetrates more easily and quickly, since the urethra in the female body has a short and wide shape.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
This disease is dangerous for all women. Statistics show that each of them was susceptible to bladder inflammation, that is, cystitis, at least once in her life. But only a small percentage of women (10–20%) develop chronic cystitis.
It will not be possible to find out exact statistics on the spread of a disease such as cystitis in our country, since many women prefer self-medication at home. Of course, everyone should understand that self-medication does not always give a positive result. Therefore, with this and other diseases, you should immediately seek help from qualified specialists.
Cystitis is a complex disease that occurs due to many factors. Alarming symptoms, when you always want to go to the toilet, may indicate that microorganisms have entered the genitourinary system. The most common pathogens of the disease are Escherichia coli, streptococci, staphylococci and many others. etc. The appearance of bladder disease is promoted not only by bacterial microorganisms, but also by viruses, fungi of the genus Candida, mycoplasma, chlamydia and even trichomonas. A very common cause of infection is a procedure such as catheterization of the bladder. Instrumental urological examinations (for example, catheterization) very often cause the appearance of pathogenic bacteria in the genitourinary system.
Pathogenesis of bladder infection
Pathways for pathogens to enter the human body can be ascending, descending, lymphogenous, hematogenous and direct.
- The ascending tract is characterized by the entry of the pathogen from the urethra.
- Descending pathways allow infection directly from the kidney. This route of infection occurs during inflammatory processes in the kidney (for example, pyelonephritis).
- The hematogenous route is characterized by the entry of infectious microorganisms from distant foci.
- Direct routes of spread of pathogens are observed when opening ulcers in organs that are nearby (parametritis, abscesses, appendicitis).
Cystitis is the result of a wide variety of clinical signs that may indicate the development of pathological diseases such as pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and urolithiasis. Chronic cystitis can provoke the development of various inflammatory processes in the kidneys. At the same time, when you want to go to the toilet, severe, sharp pain may occur.
The bladder is surrounded by a mucous membrane that is very resistant to infection. The presence of pathogenic microflora may not be sufficient for the development of cystitis. Predisposing factors in the genitourinary system include: impaired blood circulation in the bladder wall and pelvis, problems with emptying the bladder, reduced immune resistance to infections, the effect of radiation therapy and chemicals on the bladder mucosa.
Classification of cystitis
Cystitis is classified according to the following criteria:
- Stages: acute and chronic. In both cases, there is a urge to urinate with painful sensations. I want to go to the toilet, but sometimes I can’t even do it.
- Course: the disease is divided into primary and secondary.
- Etiological factors and pathogenesis: infectious, chemical, allergic and radiation disease.
- Localization and depth of penetration of the inflammatory process: cystitis can be focal or diffuse.
- The nature of the changes from a morphological point of view: the disease is divided into catarrhal, hemorrhagic, ulcerative, gangrenous, interstitial.
Causes of acute infectious and non-infectious cystitis
Acute cystitis is divided into infectious and non-infectious. As described above, cystitis of infectious origin can be caused by E. coli. But cystitis of non-infectious origin is caused by the action of irritating factors on the mucous membrane of the bladder (chemicals, foreign bodies, burns and others). In addition, there are many more irritants that affect the condition of the mucous membrane (flavored shower additives, spermicides, drugs, radiation therapy, alcohol, and in rare cases, coffee, chocolate and tomatoes).
The main reasons that provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- The first and most important thing is non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and sexual hygiene. During menstruation, you should often change pads and tampons. When you want to go to the toilet, you must wash yourself after this activity, and you should wipe from front to back.
- It is worth remembering that even the slightest hypothermia can contribute to the development of clinical signs of infection (with cystitis - painful urge to urinate).
- Retention of urine in the bladder. When you have the urge, you need to urgently visit the restroom, even if urination is too frequent and very painful.
- Underwear and clothes of a non-physiological type (synthetic, short skirts, tight jeans) can lead to the spread of infections.
- Constipation also contributes to a painful and unpleasant urge to pee.
- Consumption of spicy foods, spices, fatty foods (you cannot be guided by the word “want”).
- The presence of chronic foci in the body (caries, chronic diseases).
- Constant stress.
- Drowsiness.
- Fatigue at work.
- Poor nutrition.
- Decreased immunity.
The most common clinical manifestation that will immediately indicate the disease is painful urination and frequent urge. A woman constantly needs to go to the toilet. Urine comes out in small portions; at the end of this process, pain of a cutting, burning nature appears. It is these symptoms that make a woman suffer, depriving her of her ability to work. In this case, the woman has a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied. You may even experience urinary incontinence with a strong urge to urinate. At night, the symptoms intensify, the urge becomes more frequent. Usually the acute phase of the disease lasts for 4 – 6 days. At the same time, the woman’s activity and ability to work is noticeably reduced.
Treatment of painful urination
Many people wonder whether it is worth contacting a doctor for help when painful and very frequent urination begins to bother them, if the infection can be treated at home. It should be remembered: another pathology (pyelonephritis, kidney stones, etc.) may be “hiding” behind the signs of the disease. Only a doctor will help you identify this or that disease, and also prescribe an antibiotic that suits your body. An important rule in antibiotic treatment is to follow the course prescribed by a specialist.
Self-medication is dangerous for you because an acute, untreated form of the disease can turn into a chronic one. When treating cystitis, you can use warm heating pads, tincture of horsetail, and corn silk. Treatment with drugs should be started after examination by a doctor.
Preventive measures are aimed at sanitizing chronic foci of infection, maintaining one’s immunity, and observing the rules of personal hygiene. With proper and timely treatment, you will forever forget about the frequent urge to go to the toilet, and the pain will disappear forever.
Remember, self-medication is harmful to your health. Be attentive to yourself and your body!
By secret
- Incredible... Chronic cystitis can be cured forever!
- This time.
- Without taking antibiotics!
- That's two.
- During the week!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
×
Reasons for development
Factors in the development of the disease can be physiological (refer to a temporary type of disease) and pathological (permanent polyuria).
Physiological root causes are a lot of fluids drunk or diuretic foods eaten, as well as the use of medications that cause an increased desire to urinate.
Pathological causes are precursor diseases that result in constant polyuria. Provocateurs for the development of this type of disease include:
Diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus can also cause an increase in the daily volume of fluid during urination.
Causes
Depending on the mechanism of development and the level of dysregulation, experts identify six causes of polyuria.
Common reasons
These include psychogenic polydipsia, salt abuse and hemachromatosis.
Psychogenic polydipsia is an increase in fluid intake in the absence of physiological need, associated with psychological causes or mental disorders such as schizophrenia. Increased salt intake leads to an increase in sodium levels in the blood, which increases plasma osmolarity, causing thirst. In response to thirst, a person increases fluid intake, causing polyuria. This type of condition is short-term and disappears after normalization of nutrition.
Hemachromatosis is a hereditary disease in which iron accumulates in the body and the liver begins to suffer. The organ is involved in the synthesis of many hormones, so disruption of its functioning, in this case, leads to diabetes mellitus and the appearance of polyuria.
Diseases of the genitourinary system
Polyuria develops with interstitial cystitis, pyelonephritis, urinary tract infection, renal tubular acidosis, Fanconi syndrome, nephronophthisis and acute renal failure.
Inflammatory processes during cystitis and other infections lead to irritation of nerve receptors, stimulating excessive urination. Once the infectious process is eliminated, all symptoms will disappear.
Renal tubular acidosis is a syndrome in which the body is in a state of acidosis. Normally, the blood is slightly alkaline, but with acidosis it becomes acidic. This is caused by a hereditary defect in the structure of the kidney. To cope with the acidic environment, the body begins to actively remove fluid, which is manifested by polyuria. The disease occurs in infancy and has a number of other symptoms. Fanconi syndrome has a wide range of causes. It can be hereditary and acquired. It is manifested by a violation of the reuptake of amino acids, glucose, phosphates and bicarbonates in the renal tubules. The clinical picture includes pollakiuria, polydipsia (increased fluid intake), and impaired psychomotor functions. Also, in acute renal failure, the stage of polyuria is distinguished.
Endocrine system diseases
All body processes, including urine formation, depend on the proper functioning of the endocrine glands.
Polyuria is one of the main symptoms of diabetes. The disease can be sugar or non-sugar. Diabetes mellitus is manifested by an increase in blood glucose levels. The body, trying to reduce the amount of sugar, begins to actively excrete it in the urine, and since this substance has osmotic properties, it “pulls water along with it” and polyuria develops.
The pathogenesis of the development of polyuria in diabetes insipidus is different. With this pathology, an absolute deficiency of antidiuretic hormone is determined. Normally, the hormone has an inhibitory effect on urine formation, so in its absence, the volume of fluid released increases.
Circulatory disorders
Urine is formed by filtering blood, so cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome can also lead to polyuria.
Heart failure is characterized by a decrease in the pumping function of the heart, which leads to fluid retention and the development of edema. If the kidneys maintain their function, they are able to remove excess fluid, increasing diuresis.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is manifested by a sharp decrease in pressure and an increase in heart rate when changing position. One symptom may be an increase in the volume of urination.
Nervous system diseases
Neurological conditions that cause polyuria include cerebral salt wasting syndrome, brain injury, and migraine.
Cerebral salt wasting syndrome is a rare condition that can develop due to brain injury or tumor. Characterized by excessive excretion of sodium by a normally functioning kidney. Fluid is excreted along with sodium, which leads to polyuria.
Taking medications
An increase in diuresis occurs when taking diuretics, high doses of riboflavin, vitamin D and lithium preparations.
Diuretics are used for edema of various etiologies and as a treatment for arterial hypertension. The use of thiazide diuretics increases fluid excretion, reducing circulating blood volume. Less blood reduces the pressure on the walls of blood vessels and at the same time lowers blood pressure.
Riboflavin and vitamin D are used in the treatment of corresponding hypovitaminosis.
Lithium salts are most often used to treat neuroses, mental disorders, depression, oncological blood diseases, as well as in the treatment of dermatological diseases.
Causes of frequent urination Polyuria may be a variant of the norm if a person has eaten water-containing foods in large quantities: watermelon, jelly or compote. In this case, the increase in diuresis will be one-time.
Polyuria in children most often develops due to hereditary diseases: type I diabetes mellitus, Conn's syndrome, de Toni-Debreu-Fanconi disease, hereditary form of diabetes insipidus, Fanconi nephronophthisis. Dehydration occurs more quickly in children than in adults and is more difficult to correct.
Probable causes of pathology development
Physiological and pathological factors can cause polyuria. Physiological causes of pathology include the use of diuretics and excessive fluid intake. That is, these factors are not associated with internal disorders of the body.
There can be many pathological causes of polyuria:
- kidney cysts;
- pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- diabetes;
- Barter's disease;
- urolithiasis disease;
- sarcoidosis;
- tumor formations;
- mental disorders.
Pregnant women often experience excessive urination, especially in the 3rd trimester. This may be due to hormonal changes in the woman’s body and strong pressure from the fetus on the bladder. But the cause of polyuria can also be asymptomatic pyelonephritis.
Important! The appearance of a symptom of polyuria during pregnancy requires mandatory and immediate consultation with a specialist.
Most common reasons
Based on the above facts, we can draw an absolutely logical conclusion: urine does not completely leave the bladder when the body “eats” a disease - chronic or acute. There are many factors leading to the problem:
- Mechanical causes are diseases of the genitourinary system and kidney infections. For example, trauma to these organs, the presence of tumor formations on them, as well as prostate cancer, adenoma, phimosis, and the presence of stones.
- Diseases of the nervous system: spinal cord or brain injuries, tumors, myelitis, and so on.
- Drug intoxication. It is diagnosed when the patient takes narcotic drugs or sleeping pills for a long time.
The most common cause of urinary retention in men is adenoma. The problem occurs when blood rushes too much to this organ. The acute form is caused by severe hypothermia, alcohol abuse, a sedentary lifestyle and digestive tract disorders.
Variants of manifestation and clinical picture
The most common and reliable method of differential diagnosis of polyuric syndromes is a fluid deprivation test
The clinical picture is typical. The main symptom is frequent and copious urination, ranging from 2.1 to 20 or more liters per day. However, depending on the underlying cause of diabetes, it manifests itself differently.
- As a rule, pathology makes itself known through intense urination during daylight hours. At night, during sleep, the hypothalamus produces more vasopressin, and urination is inhibited. Nocturia (frequent nighttime visits to the toilet) most likely indicates central or nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
- Psychogenic polyuria. It is rare (especially in men). It is considered a variant of the norm. Develops as a result of stress.
Causes and treatment of frequent night urination in men
- Symptoms of nocturia
- Causes
- Diseases of the urinary system
- Diseases of the genital organs
- Other factors
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
Frequent urination in men at night, in which nighttime diuresis exceeds daytime urine output, is called nocturia. This concept should not be confused with pollakiuria, in which the frequency of micturition increases during the daytime. In a healthy person, nocturnal diuresis is normally less than 1/3 of the daily diuresis.
Symptoms of nocturia
Frequent and heavy urination at night is rarely the only symptom. Men normally urinate 1-2 times after midnight. The number of daily migrations they have is on average 5-8. There is no exact norm for the number of urinations. Along with nocturia, the following symptoms are possible:
- inability to hold urine;
- painful urges;
- excretion of urine in small portions;
- pain or burning during movements;
- thirst;
- dry mouth;
- temperature increase;
- instability of blood pressure;
- swelling;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- lower abdominal pain;
- unpleasant odor of urine;
- change in the appearance of urine (presence of sediment, pus or flakes);
- pale skin;
- hematuria (presence of red blood cells in the urine);
- weight loss;
- dry skin and mucous membranes.
Night urges may be constant. They occur even with an incomplete bladder.
Causes
The reasons for frequent urination in men at night are:
- Diabetes insipidus. This pathology is caused by dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, as a result of which the synthesis of antidiuretic hormone decreases (prevents the excretion of urine) or the sensitivity of cells to it decreases. In this case, nocturia is combined with polyuria (increased diuresis), sleep disturbance, thirst, weakness, neurosis, loss of appetite, dry skin and decreased potency. Urine excreted at night is colorless and of low density.
- Pathology of the prostate gland.
- Diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs.
- Brain injuries.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Cysts.
- Reactive arthritis (inflammation of the joints).
- Overactive bladder.
- Heart failure.
- Kidney failure. Often develops against the background of glomerulonephritis.
The occurrence of nocturia is based on dysfunction of the bladder, when the tone of the detrusor (muscle layer) prevails over the tone of the sphincter, which prevents the excretion of urine.
Diseases of the urinary system
Common causes of nocturia are:
- Stones in the bladder and ureters. They occur in men who drink water with a high salt content, lead a sedentary lifestyle and experience occupational harm. Risk factors for the formation of stones are impaired phosphorus-calcium metabolism, a monotonous diet, addiction to meat and the presence of chronic diseases of the digestive system. Stones enter the bladder, irritating the mucous membrane, which leads to frequent urges at night.
- Cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Most often caused by a bacterial infection. Predisposing factors are hypothermia, delayed sexual intercourse, insufficient fluid intake, decreased immunity, schistosomiasis, having sex without using a condom and stress.
- Inflammation of the urethra (urethritis). It can be specific (caused by STI pathogens) and nonspecific (caused by opportunistic microbes). Often develops against the background of chlamydia, gonorrhea, candidiasis and trichomoniasis.
- Nephritis (kidney inflammation). Most often, nocturia occurs against the background of pyelonephritis (damage to the tubules and pyelocaliceal apparatus). Night urges are accompanied by lower back pain, fever, sweating, headache and nausea. Intense abdominal pain is possible.
Diseases of the genital organs
The following diseases of the male genital organs can manifest as nocturia:
- Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland). Dysuria is most pronounced in acute parenchymal inflammation. Nocturia can be combined with impaired potency, pain and burning in the perineum or anus, prostatorrhea (discharge of prostate secretions in the urine), pain during bowel movements and discomfort in the lower back.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma). With this tumor, a man can urinate up to 3 times or more often at night. The tumor puts pressure on the bladder, leading to bladder dysfunction. With adenoma, nocturia is combined with sluggish stream pressure, urinary retention when the sphincter relaxes, intermittent micturition and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles).
Other factors
Often nocturia in men occurs during alcohol intoxication.
This is due to the diuretic effect of the breakdown products of ethyl alcohol. Other possible causes of frequent nighttime urination include:
- schistosomiasis (a disease caused by blood flukes);
- drinking large amounts of water before bed;
- taking diuretics (diuretics);
- consumption of foods that have a diuretic effect (watermelon, tomatoes, celery, cucumbers, lingonberries, cranberries, pumpkin, as well as some fruits).
Diagnostics
If you urinate frequently at night, you should visit a urologist. To make a diagnosis you will need:
- blood sugar test;
- test according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- Ultrasound;
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- CT or MRI of the brain and kidneys;
- uroflowmetry (measurement of urine outflow rate);
- neurological examination;
- urine culture for sterility;
- cytological analysis (if a tumor is detected);
- radiography;
- dry food test (if diabetes insipidus is suspected);
- test with 3 glasses.
With frequent and copious urination at night without pain, thirst, signs of dehydration, a decrease in the relative density of urine, high calcium levels and low potassium levels, diabetes insipidus can be suspected. Nocturia in combination with pain and blood indicates hemorrhagic cystitis, renal failure or urolithiasis (stones).
Treatment
For frequent urination at night, treatment is most often conservative. Surgery may be necessary for urolithiasis, adenoma, chronic prostatitis, cysts and tumors. The treatment regimen depends on the cause of nocturia.
If you have inflammation of the kidneys or bladder, you need to rest, drink more and take medications.
In severe cases, infusion therapy is performed. Diabetes insipidus may require replacement therapy. With this pathology, it is important to reduce protein intake.
Medicines
The following medications may be prescribed for nocturia:
- Antibiotics (Monural, Fosfomycin, Tsiprolet, Augmentin, Nolitsin). They are used for frequent urination due to inflammatory diseases caused by bacteria sensitive to this drug.
- Uroantiseptics (Furadonin-LekT, Furagin-LekT).
- Antispasmodics (Drotaverine). Eliminate pain and muscle spasms of the bladder.
- Vasopressin analogues (Desmopressin, Minirin, Nativa, Nourem). Indicated for diabetes insipidus.
- Diuretics.
- Products of plant and animal origin (Canephron N, Fitolysin, Vitaprost, Prostatilen).
- Immunostimulants.
- Alpha-1 adrenergic blockers (Alfuzosin, Dalfaz Retard). Used for prostate adenoma.
Childhood polyuria
This disease is quite rare in children. Increased urine output in this case may be associated with various mental disorders and stress; with heart and kidney diseases; with the development of diabetes mellitus, Conn's disease; with manifestations of adynamia, hypertension and periodic paralysis. Also, a similar disorder in children can be caused by the common habit of urinating at night and drinking a lot of water.
Sources used:
- https://brulant.ru/health/poliuriya/
- https://adella.ru/health/prichiny-chastyh-pozyvov-k-mocheispuskaniyu-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://tvoyaurologia.ru/andrology/poliuriya-ochen-mnogo-mochi-pri-mocheispuskanii.html
- https://vseopochkah.com/mochevoj/mocheispuskanie/poliuriya.html
- https://analiztut.ru/perechen-analizov/mocha/poliuriya.html
- https://menquestions.ru/urologiya/mocheispuskanie/poliuriya-u-muzhchin.html
What is polyuria?
This is a syndrome characterized by a decrease in the concentration function of the kidneys as a result of a violation of their secretory abilities or as a result of the influence of the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin, which is produced by the neuroendocrine cells of the hypothalamus.
ICD-10 code: R35
Once in the bloodstream, it enhances the reabsorption of water (reverse absorption) from the collecting ducts of the kidneys.
If its deficiency is noted, this leads to ineffective renal function. They stop reabsorbing water, which leads to polyuria - excessive urine production.
Polyuria is an increased amount of urine excreted in a person. The causes of the disease are different. This can be a symptom of dangerous diseases: diabetes mellitus, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, urolithiasis. If treatment is not followed soon, the consequences can be dire. After all, such an organism is at risk of dehydration.
How much urine is produced can be easily checked at home. To do this, you need to prepare a special container and urinate not into the toilet, but only into it. Usually this disease is associated with a predominance of diuresis at night and frequent urination. Patients suffering from polyuria are forced to wake up and get up at night in order to empty the bladder.
But sometimes polyuria is not a manifestation of the disease at all. This also happens in healthy people if they drink a lot of fluids per day or take diuretics. But, in any case, it is necessary to be examined.
Polyuria is the medical term that describes excessive urination. Excessive urination may indicate not only an unusually high water intake, but also an underlying medical condition. The most common causes of polyuria are diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus. Additionally, polyuria can be caused by medications, caffeine, alcohol, kidney disease, and electrolyte imbalances.
Urine produced in the kidneys consists of water and particulate matter filtered by the bloodstream. Each adult should urinate no more than 2.5 liters per day. Polyuria occurs when an adult produces more than 3 liters of urine (urine), regardless of how often he urinates.
The prevalence of polyuria is not well documented. Nocturia has been studied more than polyuria. There is evidence that nocturia and polyuria are more common in older patients.
The volume of urine in severe polyuria can reach three liters. Unfortunately, many people continue to believe that this violation must be reconciled and accepted, but they do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, considering it a trifle that is not worth worrying about. There are also those who fear that the disease is very serious and do not go to the doctor.
Polyuria is accompanied by frequent urination, but it should not be confused with pollakiuria, the so-called frequent urination. With pollakiuria, there is a strong urge to go to the toilet, and, as a rule, urine is passed quite often, but in small portions. It should be noted that its daily volume does not exceed the norm.
The disease occurs as a result of consuming too much liquid that contains alcohol or caffeine. This condition is often noticeable in pregnant women due to increased pressure from the uterus on the bladder. Frequent urination should not be confused with urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence causes involuntary bladder function, which resembles an unconditioned childhood reflex.
Therapy methods
Treatment of polyuria involves therapy aimed at suppressing the provoking factor. More often, a tactic is chosen that involves restoring renal function.
The basis of treatment for the pathological condition is medications containing thiazides. These substances reduce sodium concentration, thereby promoting the removal of excess fluid.
Preparations with thiazides improve the body's absorption of water, thereby reducing its volume in the urine.
If the diagnosis shows the absence of diabetes mellitus, treatment of polyuria is supplemented with diuretics. Drugs in this group prevent urine dilution. In severe cases, when the body has lost a lot of electrolytes due to excessive urine production, they are injected into the blood.
It is possible to stop the course of the pathological syndrome using traditional medicine methods. If the daily volume of urine excreted exceeds the permissible norms, then to normalize the functioning of internal organs it is recommended to use:
- Infusion or decoction of plantain . The drugs normalize the functions of the kidneys and bladder. To prepare them you will need 20 g of plantain seeds, which should be poured with a glass of boiling water and left for half an hour. After straining, the product should be consumed 3 times a day before meals, a teaspoon.
- Anise infusion . The medicine is prepared from a teaspoon of the plant’s fruits, which are poured into a glass of boiling water. The product is infused for 20 minutes, filtered, after which it can be consumed in an amount of 50 ml 4 times a day. The course of treatment with infusion takes about one month.
Due to the fact that due to excessive urine production, the body loses many useful microelements, it is important to adhere to a certain diet and drinking regimen during the treatment process. The patient must avoid consuming foods that irritate the urinary system or have a diuretic effect:
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- spices;
- sweeteners.
You should also exclude foods high in fiber from your diet. The drinking regime and diet are developed individually for each patient based on his clinical picture and body characteristics.
How is polyuria treated?
Pathology therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause. To restore normal concentrations of calcium, sodium, chloride and potassium, the patient is prescribed an individual nutrition plan. Additionally, the doctor calculates the amount of fluid consumed. If the body experiences severe dehydration, rehydration is necessary. It is carried out in two ways:
- Infusion of sterile solutions into a vein. Ready-made products are used that contain a certain proportion of electrolytes and carbohydrates, for example, Oralit, Regidron.
- Parenteral rehydration is indicated for more severe degrees of dehydration. Such patients are given intravenous saline, the amount being calculated taking into account their weight.
As soon as the water balance is restored, droppers and injections are canceled. Increased nighttime diuresis is eliminated by limiting drinking and avoiding diuretics in the afternoon. If the cause of the pathology is weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, then special exercises are prescribed to strengthen them. Gymnastics, which was developed by the famous doctor Kegel, brings good results.
Diet food
With an increase in daily diuresis, electrolytes - solutions of necessary chemical elements - are excreted from the human body in large quantities. Following a special diet helps restore their levels. It is necessary to exclude coffee, confectionery, preserves containing vinegar, fatty foods, and spices from the diet. Table salt is limited to 5-6 g per day.
You also need to reduce your intake of carbohydrate foods, including pasta, potatoes, and baked goods. To restore the level of a specific microelement, the menu includes:
- Potassium. It contains nuts, spinach, legumes, and dried fruits.
- Calcium. Found in cheese, dairy products, buckwheat, greens, and nuts.
- Sodium. Contained in lamb, beef, dill, beets, carrots, garlic, white beans.
Features of manifestation in adults and children
In men and women, polyuria develops under the influence of the same factors. In the former, the pathological condition also occurs against the background of prostatitis and other diseases of the prostate gland.
In children, the volume of urine produced is not constant as the child grows. In the first year of life, their body produces no more than 820 ml of urine per day. By the age of 18, this figure gradually increases, reaching 1500 ml.
Exceeding the norm indicates that children have:
- heart defects;
- kidney diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- mental state disorder;
- Conn's syndrome, indicating a tumor in the adrenal glands;
- Fanconi disease (hereditary mutation of a number of genes).
Polyuria during pregnancy may indicate latent (asymptomatic) pyelonephritis.
Types of polyuria and diuresis
Polyuria is most often divided into:
- temporary – for example, after a hypertensive crisis;
- permanent - formed in diseases of the kidneys and endocrine glands.
There are several types of increased diuresis. Aqueous - urine of low concentration is released (hypoosmolar), this is due to a lack of antidiuretic hormone, decreased permeability of the tubules and collecting ducts, the ratio of dissolved substances in the urine to their content in the blood plasma is less than one.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for the development of polyuria. Compliance with general preventive measures significantly reduces the risk of diseases of the urinary and other body systems. These include:
- moderate fluid intake (up to 3-4 liters, depending on climatic conditions);
- control over the consumption of table salt;
- drawing up a balanced nutrition plan that excludes fast food, processed foods and other foods harmful to the body;
- refusal of strong tea and coffee;
- annual medical examination at least once a year.
Polyuria is only a manifestation of an underlying disease. In order to get rid of the root cause, you should not delay visiting doctors, because modern medicine is able to diagnose most diseases and prescribe effective treatment.
- diuretics. Medicines in this category prevent disruption of the urine excretion process. Hypothiazide, Hydrochlorothiazide can be used;
- antibiotics. Drugs in this category are used if the disorder is caused by a bacterial infection. Most often, broad-spectrum medications are prescribed, such as Amoxicillin, Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin.
- neurological disorders;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- decreased reproductive capacity in women and men;
- rapid weight loss.
We suggest you read: Treatment of Peyronie's disease without surgery - Androspok