Diet features
There are some nuances in the diet indicated after a kidney transplant:
Food should be prepared without the use of oil:
- steamed;
- baking;
- stewing;
- boiling;
- allowance.
Meals should be fractional. It is better to organize 5-7 approaches in small portions. This will allow you to gradually digest foods, not burden the digestive tract, and will ensure a constant flow of microelements into the bloodstream. You need to give up fast food and snacks. It is better to organize meals every 2 hours. It is necessary to reduce or completely eliminate flavor enhancers:
spices; salt; Sahara; seasoning
Eating foods high in potassium and magnesium has a positive effect on the body's condition.
These elements support cardiac activity and vascular tone, which is very important in the process of kidney engraftment. The most famous “storehouses” of potassium are dried apricots, prunes, raisins
Magnesium - bran, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, lentils and peas.
Foods rich in potassium and magnesium Consumption of excessive amounts of calcium and phosphorus, as well as their poor absorption, lead to the deposition of salts in the kidney and lead to the formation of stones. This is a very dangerous condition for a person who has undergone a transplant, especially if the damage to their own kidneys was caused by chronic kidney stones. Calcium, its salts and phosphates are of course necessary for the body, especially at the age of over 45-50 years, when the risk of developing osteoporosis is high, but it is recommended to use them in moderation and only after consultation and approval of the attending physician.
What can you eat
Recommended products include:
- Green vegetables (all types of cabbage, green beans, young peas, spinach, asparagus, celery, herbs: onions, dill, parsley, cilantro, etc.)
- Root vegetables: turnips, radishes, beets, Jerusalem artichokes, carrots.
- Pumpkin: pumpkins themselves, squash, zucchini and zucchini.
- Legumes: peas, beans, lentils, mung beans, chickpeas.
- Nightshades: tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants.
- Durum pasta, whole grain bread with the addition of bran and sesame.
- Cereals: corn, barley, pearl barley, buckwheat, millet, oatmeal.
- Lean meat (turkey, rabbit, chicken breasts, river fish, seafood).
- Fruits and dried fruits. They contain many useful elements and minerals, vitamins and microcompounds.
- Dairy products.
Acceptable foods, the consumption of which is recommended in small quantities no more than once a week, include:
- Diuretic foods: watermelon, melon, cucumbers, fennel.
- White bread is a rich product.
- Nuts (any kind, as they contain a lot of proteins and fats).
- Sweets (these are simple carbohydrates - the shortest path to rapid weight gain).
- Coffee. It is recommended to abandon instant coffee, giving preference to ground coffee beans. Large amounts of coffee have a bad effect on all body systems. It is also not recommended to drink strong tea and it is better to avoid adding sugar.
For lunch - full-fledged main courses: home-made steamed cutlets, meatballs, baked or boiled meat. Garnish: lentil or pea puree, green beans, pasta. For dinner - salads or side dishes (stew) with carrots, turnips, cabbage (any type), beets. You can add a little meat or fish, but it is better to refrain from carbohydrates. Main meals can be divided into 4 or 5 times. Between them, snacks should be organized, for which the following are suitable: dried fruits, fermented milk products or fruits.
What is prohibited
A categorical ban is imposed on salted and pickled foods, for example:
- salted tomatoes;
- pickles;
- canned, salted, dried fish;
- sausages (sausages, smoked and boiled sausages, bacon, sausages, etc.);
- margarine and butter;
- cheeses (especially highly salted and smoked products);
- carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, including kvass.
All of the above products have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the kidneys and put an increased burden on the transplanted organ.
After a kidney transplant, it is extremely important that the transplanted organ takes root and functions normally for as long as possible. For this purpose, a number of measures are being carried out that are aimed at reducing the load on the urinary system, preventing various infectious infections, adjusting the functioning of the body’s immune system, etc.
An important aspect of the rehabilitation period is the patient’s diet. After all, exactly what he consumes as drinks and food will, after some time, be eliminated from the body in a processed form with the participation of the urinary system. Therefore, in our article we will understand in detail all the intricacies of the question of what a diet after a kidney transplant is.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet after a kidney transplant involves the exclusion of any concentrated broths containing meat/fish/mushrooms, or soups containing legumes and vegetables. All fatty types of red meat and waterfowl (pork, fatty lamb, duck, goose), sausages, smoked meats, fried foods, canned food, baked/stewed meat without prior boiling are excluded.
It is not allowed to consume animal refractory fats, fatty dairy products (cream, sour cream), milk soups and porridges with milk, salted fish, canned fish, fish caviar, spinach, garlic, radishes, onions, sorrel, radishes, mushrooms, pickled/pickled vegetables , regular bread, flour and confectionery products (cakes, pancakes, cookies, pies, pancakes), cheeses.
It is forbidden to use hot sauces/seasonings - horseradish, mayonnaise, pepper, mustard. Limit the consumption of salt and any salty foods. As for drinks, it is prohibited to consume cocoa, strong coffee, Pepsi, cola, Sprite, energy drinks, sodium mineral waters, and alcohol.
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| pancakes | 6,3 | 7,3 | 51,4 | 294 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| brewer's yeast | 12,7 | 2,7 | 0,0 | 75 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| salt | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| sour cream 18% | 2,5 | 18,0 | 3,6 | 184 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| semi-finished fish products | 12,5 | 6,7 | 14,7 | 209 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| tuna | 23,0 | 1,0 | — | 101 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product |
Diet menu after kidney transplant (Diet)
The diet of patients in the long-term postoperative period (after a month) is not too different from the usual diet, with the exception of fatty fried, processed and salty foods. Since the diet contains meat, cereals, cottage cheese and various vegetables, the diet can be varied, and the limitation of salt and hot seasonings can be compensated for with homemade herbs, dried herbs, and homemade sauces. An approximate menu for three days is given below.
First day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch | |
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack | |
| Dinner |
|
Second day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch | |
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack | |
| Dinner |
|
The third day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Authorized Products
The diet after a kidney transplant involves the inclusion of soups cooked in vegetable broth in the diet. The choice of vegetables and cereals for making soups is unlimited, however, they should not be very sour or spicy. You can add garden herbs to ready-made dishes, and you can season soups with unsalted butter or sour cream.
For second courses, lean types of red meat and poultry and rabbit are recommended, which should be pre-boiled before cooking and the liquid should be drained. For fish, low-fat varieties of white fish are recommended, which can be boiled and baked with vegetables as a side dish. Almost all cereals can be included in the diet; yogurt, milk, omelet and soft-boiled eggs, low-fat cream, yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese and dishes made from it are allowed.
Sour cream is added only to ready-made dishes; all vegetables (except celery, radish, garlic, radishes, fresh onions). It is important to have a sufficient amount of vegetables in the diet, which can be boiled, stewed, baked, made into casseroles, salads, cutlets with the addition of cereals. It is useful to eat ripe, non-acidic fruits and berries, both fresh and processed (jelly, compotes, purees, preserves, jelly) or baked, as well as marshmallows, honey, marshmallows, caramel. Drinks allowed: rosehip infusion, freshly prepared juices, tea with lemon and sugar.
Sometimes life doesn't end - it gives a new one
Operation technique
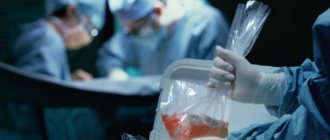
From the moment the kidney is removed, the donor has 24 or 48 hours (the time depends on the type of preservation solution) to transplant the organ to the recipient. However, the sooner the operation is performed, the greater the chances of successful implantation of the organ. There are two types of anesthesia for kidney transplantation: anesthesia and epidural anesthesia. In the first case, the drug is supplied first into a vein, then in gaseous form through an endotracheal tube installed in the respiratory tract. In the second, a catheter is inserted into the spinal canal, anesthesia turns off the sensitivity of the body below the injection site, while consciousness is preserved.
Kidney transplantation can be performed under epidural anesthesia
The same methodology is used for adults and children:
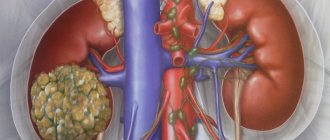
- An incision is made in the lumbar region with a transition to the abdomen (lumbotomy).
- The kidney is now placed in a heterotopic position in all cases. If your own organ is located in the lumbar region, then the donor organ is implanted slightly lower - in the iliac region. If the donor’s body had a kidney on the right side, then it is advisable to transplant it to the left iliac region.
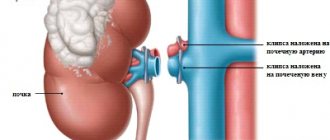
- It is necessary to apply a suture between the vessels of the donor organ and the iliac vessels of the recipient. With the help of an anastomosis (anastomosis), the kidney will receive blood supply in the new body.
- To separate urine, the donor organ's ureter must be sutured to the patient's bladder or ureter.
- The transplanted kidney is placed so that there is no twisting of the vessels and ureter.
- Sutures are placed on the surgical wound, and a small rubber tube (drainage) is left in the corner to drain fluid.
Is it possible to perform surgery on children?
Kidney transplantation for children is prescribed if the child is on dialysis. Young patients have a hard time with blood purification using this method, both physically and morally, and their overall development is significantly slowed down.
Most often, children need a transplant as quickly as possible, but for patients of this age there is a problem with the availability of donor organs. It is partially solved with the help of transplants from adult donors, but they are not suitable for all patients due to size discrepancy (kidneys in children are smaller than in adults).
For children, the kidney is transplanted into the abdominal cavity.
Kidney transplantation is contraindicated if the child has the following health problems:
- heart pathologies;
- circulatory disorders;
- mental disorders.
The transplant can be performed at a wide variety of clinical sites throughout Russia. Kidney transplantation in the Russian Federation is carried out at the Research Institute of Transplantology named after.
Sklifasovsky. The center for kidney transplantation in the Russian Federation is the Russian Scientific Center of Surgery of the Russian Scientific Center for Surgery named after.
Academician B.V
Petrovsky. The kidney transplant department is headed by Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Professor Kaabak Mikhail Mikhailovich. This center performs kidney transplants not only for adults, but also for children, because... specialized medical care for a child may not be provided in all regions of the Russian Federation.
Despite the widespread use of such surgical interventions in our country, transplantation is performed in Kazakhstan, Israel and other countries where transplantation is at a high level. It is worth noting that the Volga Federal District has a developed transplant center, on the basis of which kidney transplant operations have been carried out for more than 10 years.
Once again, it is worth noting that only people in need of transplantation and included in the waiting list can be referred to specialized departments and transplant centers in the Russian Federation.
General rules
In a diet with one kidney removed, the frequency of meals is important. The total daily amount of food is divided into 5-6 equal portions and consumed at regular intervals, excluding the period of sleep.
Other recommendations from nutritionists for patients after nephrectomy:
- limit water intake to 1–1.5 liters per day (including soups and other liquid dishes);
- reduce the amount of salt to 3 g per day;
- reduce the proportion of proteins in the diet;
- maintain the daily energy value of the diet at the level of 2750–3000 kcal.
When compiling a treatment table, it is necessary to take into account the daily activity of a healthy kidney. It is known that the maximum performance of the urinary organs is observed in the period up to 13 hours of the day. It is at this time that the patient should consume the bulk of food.
In the second half of the day, kidney functionality drops noticeably, which should affect the range of acceptable dishes - food should be light and simple. It is best to prepare a simple vegetable or fruit dessert and wash it down with compote, jelly or vitamin broth.
In the first days after nephrectomy
After a patient has had a kidney removed, strict dietary restrictions are necessary.
Particular attention is paid to the first one and a half months of life with one organ
Let's consider a therapeutic diet according to the stages of recovery:
- 2 hours after nephrectomy, if the patient is conscious, it is allowed to moisten the lips and rinse the mouth with plain boiled water. If you are very thirsty, you can take a sip of liquid.
- After 4–6 hours, the patient is allowed to drink.
- One day after removal of the kidney, you can drink unsweetened rosehip decoction or table mineral water (mineralization less than 1 g / l.) in an amount not exceeding 1 liter per 24 hours.
- On the third day, it is allowed to take boiled and ground dried fruits without sugar, low-fat kefir, and weak tea with milk according to the scheme - 200 ml of liquid every 4 hours. If you are feeling well, your diet includes porridge with water, crackers, fruit and vegetable juices, mashed potatoes and jelly.
- Until the end of the first week after the operation, low-fat cottage cheese, boiled fish, protein omelet, vegetable puree and all fermented milk products are introduced into the patient's diet.
It is recommended to follow this diet for at least 1.5 months. Feeling good should not be a reason to deviate from your diet and eat prohibited foods.
During the rehabilitation period
Recovery after kidney removal can take 1–1.5 years, sometimes longer. During this time, the patient must strictly adhere to the following recommendations:
- do not exceed the recommended caloric intake of the diet;
- eat in small portions;
- only add salt to the prepared food on the plate;
- adhere to strict standards for proteins and fats;
- eat warm, gently processed food;
- observe the drinking regime.
During the rehabilitation period, you should not eat canned food, fast food, fast food and semi-finished products, as they contain a huge amount of salt and preservatives.
Complications during kidney transplant
There are two fundamentally different groups of complications that arise during the transplantation process and in the postoperative period. The first row is surgical problems associated with creating access to the iliac region and connecting the graft with the recipient’s vascular system and urinary tract:
- bleeding from crossed vessels of the donor organ and recipient;
- formation of blood clots (thrombi) in the vessels of the patient and the transplanted organ;
- significant narrowing (stenosis) of vascular and urinary anastomoses;
- failure of anastomotic sutures and surgical wound;
- penetration of infection into the wound.
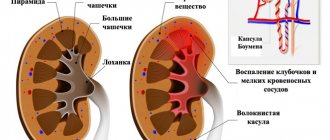
These complications make themselves felt during the transplantation procedure or the immediate postoperative period. To prevent the formation of blood clots, blood thinning drugs (Heparin, Fraxiparine) are used, and broad-spectrum antibiotics are used for wound infections. A more specific problem is graft rejection. According to the time of occurrence, they distinguish: hyperacute rejection, accelerated, acute and chronic. Depending on the type of process, symptoms are observed.
Transplant rejection depends on immune cells and antibodies
Transplant rejection reaction - table
| Type of rejection | Super sharp | Accelerated | Acute | Chronic |
| Time of occurrence | Within 15–20 minutes after the start of blood circulation in the donor kidney | Between 12 and 72 hours after surgery | During the first 3 months after surgery | Throughout life with a transplanted kidney |
| Symptoms |
| No urine output |
|
|
To prevent rejection, special treatment is prescribed, the task of which is to suppress the immune reactions of the recipient's body. The following drugs are used:
- Cyclosporine A;
- Prednisolone;
- Azathioprine;
- Diltiazem;
- Verapamil;
- Myfortic;
- antibodies against the recipient's immune cells.
Drugs that suppress the immune system - photo gallery
To assess the performance of the donor organ and the quality of immunosuppressive treatment, the following indicators are used: the amount of urine excreted, the level of blood pressure, urea, creatinine and potassium. In some people, the kidney takes root immediately and begins to produce urine, but in most cases the period extends to seven days. At this time, blood purification is carried out using hemodialysis.
Possible complications
Since the transplanted kidney does not always take root normally, after the operation in a hospital setting the patient takes samples daily for laboratory urine tests and undergoes instrumental examinations. In this case, it is possible to identify the following complications:
- bleeding and hematomas in the peritoneal area due to artificial connection;
- inflammatory processes and formation of pus in the suture area;
- thrombosis of the iliac vessels or veins of the lower extremities;
- hyperacute rejection of the transplanted kidney by the body, due to which it dies.
There are two main types of surgery.
Features of cooking and eating
It is necessary to organize split meals every 2 hours with small portions
After kidney transplantation, cooking also has its own significant features:
- It is necessary to completely avoid snacks and fast food products;
- Organize split meals every 2 hours with small portions. With this rhythm, food is digested gradually, and accordingly nutrients are absorbed better;
- You need to cook food without using oil, you can:
- bake;
- stew;
- boil;
- steam;
- let go;
- Avoid or minimize the addition of flavor enhancers:
- salt;
- sugar;
- seasonings;
- spices.
- The foods consumed should contain large amounts of magnesium and potassium, which support the proper functioning of blood vessels. Potassium is found in dried apricots, raisins, prunes, and magnesium is present in large quantities in peas, lentils, bran, sunflower and pumpkin seeds. Magnesium and potassium are also found in other plant foods, here are some of them:
- Beans;
- Lentils;
- Peas;
- Sea kale;
- Potato;
- Dried apricots;
- Raisin;
- Prunes;
- Mustard;
- Hazelnut;
- Peanut;
- Walnut;
- Almond;
- Pine nuts;
- Cashew nuts.
Large amounts of calcium and phosphorus can cause salt deposits in the kidneys and stone formation. This is extremely dangerous for patients who have undergone a kidney transplant, especially for those who are predisposed to urolithiasis. These elements are undoubtedly necessary for the human body, but their use should be strictly limited and approved by the attending physician.
Life after kidney transplant
The prognosis for transplantation is individual and depends on many factors. Overall evidence suggests that survival will differ between living donor and cadaveric organ transplants.
Survival after kidney transplant - table
| Donor type | 1 year | 3 years | 5 years | 10 years | |
| Living donor | Graft survival | 95% | 88% | 80% | 57% |
| Patient survival | 98% | 95% | 90% | 64% | |
| Deceased donor | Graft survival | 90% | 79% | 67% | 41% |
| Patient survival | 95% | 88% | 81% | 61% |
Discharge from the hospital usually occurs three weeks after surgery. Until the sutures heal, it is recommended to limit physical activity, including heavy lifting (no more than 5 kg). A diet can help a transplanted kidney adapt to its new location. Several meals a day, the use of boiled and baked foods, avoiding alcohol, spices, salt and canned food, as well as eating vegetables, dietary meat (turkey, rabbit) and fruits are the basic principles of nutrition.
Foods containing excess potassium should be avoided after a kidney transplant
Women with a kidney transplant can carry and give birth to a child. However, all risks should be discussed with your doctor in advance. To prevent infection with sexually transmitted diseases, barrier contraception methods should be used. Taking drugs to suppress the immune system is the key to successful intervention. After discharge, the patient must undergo a medical examination once a month with the attending physician. Assigning a disability group is an individual process in each case. The commission may give the first, second or even third group (usually the second).
Consequences of the operation
The kidney begins to function normally only a few days after the operation. Kidney failure completely disappears after a while. To prevent the human body from rejecting the organ, the patient needs to take cytostatics, that is, drugs that suppress the immune system.
This is very important because immune cells may consider the donor kidney to be foreign. But the lack of normal functioning of the immune system can cause negative consequences - the body is damaged by infectious pathologies. Because of this, no visitors are allowed to patients for the first week after transplantation.
Nutrition after a kidney transplant involves avoiding eating sweets, flour, salty, spicy, and fatty foods. But this is only during the first stage of rehabilitation.
Doctors cannot accurately determine the patient’s life expectancy after surgery, since it correlates with a large number of factors, for example, additional pathologies of the body, etc. Sometimes people with a kidney transplant live twenty years or more.
How to eat after surgery?
Transplant operations involving foreign organs have one serious feature. In order for a foreign organ to take root in a new host, it is necessary to suppress the body’s immune system. After all, otherwise, rejection will occur. Suppressing your own immunity, as well as the healing process after surgery, is a serious test for the body. Proper food is designed to support his strength at this stage, as well as help prevent organ rejection and the development of an infectious disease.
About five hours after the operation, the patient is allowed to drink a little. Drinking heavily is prohibited to avoid swelling. During the first half of the day, this is perhaps the only thing that the patient can consume.
In order not to provoke a possible deterioration in intestinal function, stagnation of feces, flatulence due to decreased physical activity, the patient is recommended to eat the following after a kidney transplant:
- The day after surgery, you are allowed to take liquid mucous food in small portions, but up to eight times a day. These can be very liquid jelly and oatmeal, lean pureed soups. All food should be very lightly salted.
- After three days, you can introduce steamed omelettes, low-fat kefir, weak tea, low-fat chicken broth, grated vegetables, well-cooked soups into your diet.
- About a week after the operation, you can eat lean chicken and turkey, pea porridge, lean fish, and boiled eggs. You cannot drink citrus juices, eat bananas, tomatoes, nuts and chocolate.
- If the doctor does not observe any deterioration, then after a month you can smoothly switch to a permanent diet after a kidney transplant.
Basic principles
The transplantation operation does not end the entire transplantation process; it also includes the rehabilitation process, during which complete engraftment of the organ occurs. During this period, complete rejection of the kidney can occur, which can lead to the death of the patient. Therefore, it is extremely important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, follow a strict diet and monitor your general condition.
Diet features
The diet indicated after a kidney transplant has some nuances:
- Food should be prepared without using oil: steamed;
- baking;
- stewing;
- boiling;
- allowance.
- spices;
Eating foods high in potassium and magnesium has a positive effect on the body's condition.
These elements support cardiac activity and vascular tone, which is very important in the process of kidney engraftment. The most famous “storehouses” of potassium are dried apricots, prunes, raisins
Magnesium - bran, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, lentils and peas.
Foods rich in potassium and magnesium
What can you eat
Recommended products include:
- Green vegetables (all types of cabbage, green beans, young peas, spinach, asparagus, celery, herbs: onions, dill, parsley, cilantro, etc.)
- Root vegetables: turnips, radishes, beets, Jerusalem artichokes, carrots.
- Pumpkin: pumpkins themselves, squash, zucchini and zucchini.
- Legumes: peas, beans, lentils, mung beans, chickpeas.
- Nightshades: tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants.
- Durum pasta, whole grain bread with the addition of bran and sesame.
- Cereals: corn, barley, pearl barley, buckwheat, millet, oatmeal.
- Lean meat (turkey, rabbit, chicken breasts, river fish, seafood).
- Fruits and dried fruits. They contain many useful elements and minerals, vitamins and microcompounds.
- Dairy products.
Acceptable foods, the consumption of which is recommended in small quantities no more than once a week, include:
- Diuretic foods: watermelon, melon, cucumbers, fennel.
- White bread is a rich product.
- Nuts (any kind, as they contain a lot of proteins and fats).
- Sweets (these are simple carbohydrates - the shortest path to rapid weight gain).
- Coffee. It is recommended to abandon instant coffee, giving preference to ground coffee beans. Large amounts of coffee have a bad effect on all body systems. It is also not recommended to drink strong tea and it is better to avoid adding sugar.
Patients should reduce the amount of soups and rich broths. It is better to eat semi-liquid foods, for example, cream soup or main courses. For breakfast, it is good to eat slow carbohydrates: whole grain bread, cereals with water, dairy products.
For lunch - full-fledged main courses: home-made steamed cutlets, meatballs, baked or boiled meat. Garnish: lentil or pea puree, green beans, pasta. For dinner - salads or side dishes (stew) with carrots, turnips, cabbage (any type), beets. You can add a little meat or fish, but it is better to refrain from carbohydrates. Main meals can be divided into 4 or 5 times. Between them, snacks should be organized, for which the following are suitable: dried fruits, fermented milk products or fruits.
What is prohibited
A categorical ban is imposed on salted and pickled foods, for example:
- salted tomatoes;
- pickles;
- canned, salted, dried fish;
- sausages (sausages, smoked and boiled sausages, bacon, sausages, etc.);
- margarine and butter;
- cheeses (especially highly salted and smoked products);
- carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, including kvass.
All of the above products have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the kidneys and put an increased burden on the transplanted organ.
Source: gidmed.com
Main objectives of diet therapy
In the postoperative period, dietary nutrition helps to improve the healing of wound surfaces, reduce the factors of bacterial infection, as well as correct water and electrolyte dysfunctions (in case of disturbances in the functioning of the graft).
Diet therapy at the subsequent stage helps reduce the frequency and severity of side effects from taking immunosuppressive drugs (suppressing the organ rejection reaction) and restore disturbances in the nutritional status of the patient’s body. This reduces the risks of diabetes (steroid), cardiovascular complications and metabolic disorders.
Chronic use of immunosuppressants can stimulate the accumulation of fat in the body, which can cause the patient to become overweight. In this regard, you should strictly control the amount of fat consumed.
Diet features
The diet indicated after a kidney transplant has some nuances:
- Food should be prepared without using oil: steamed;
- baking;
- stewing;
- boiling;
- allowance.
- spices;
Eating foods high in potassium and magnesium has a positive effect on the body's condition.
These elements support cardiac activity and vascular tone, which is very important in the process of kidney engraftment. The most famous “storehouses” of potassium are dried apricots, prunes, raisins
Magnesium - bran, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, lentils and peas.
Foods rich in potassium and magnesium
What can you eat
Recommended products include:
- Green vegetables (all types of cabbage, green beans, young peas, spinach, asparagus, celery, herbs: onions, dill, parsley, cilantro, etc.)
- Root vegetables: turnips, radishes, beets, Jerusalem artichokes, carrots.
- Pumpkin: pumpkins themselves, squash, zucchini and zucchini.
- Legumes: peas, beans, lentils, mung beans, chickpeas.
- Nightshades: tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants.
- Durum pasta, whole grain bread with the addition of bran and sesame.
- Cereals: corn, barley, pearl barley, buckwheat, millet, oatmeal.
- Lean meat (turkey, rabbit, chicken breasts, river fish, seafood).
- Fruits and dried fruits. They contain many useful elements and minerals, vitamins and microcompounds.
- Dairy products.
Acceptable foods, the consumption of which is recommended in small quantities no more than once a week, include:
- Diuretic foods: watermelon, melon, cucumbers, fennel.
- White bread is a rich product.
- Nuts (any kind, as they contain a lot of proteins and fats).
- Sweets (these are simple carbohydrates - the shortest path to rapid weight gain).
- Coffee. It is recommended to abandon instant coffee, giving preference to ground coffee beans. Large amounts of coffee have a bad effect on all body systems. It is also not recommended to drink strong tea and it is better to avoid adding sugar.
For lunch - full-fledged main courses: home-made steamed cutlets, meatballs, baked or boiled meat. Garnish: lentil or pea puree, green beans, pasta. For dinner - salads or side dishes (stew) with carrots, turnips, cabbage (any type), beets. You can add a little meat or fish, but it is better to refrain from carbohydrates. Main meals can be divided into 4 or 5 times. Between them, snacks should be organized, for which the following are suitable: dried fruits, fermented milk products or fruits.
What is prohibited
A categorical ban is imposed on salted and pickled foods, for example:
- salted tomatoes;
- pickles;
- canned, salted, dried fish;
- sausages (sausages, smoked and boiled sausages, bacon, sausages, etc.);
- margarine and butter;
- cheeses (especially highly salted and smoked products);
- carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, including kvass.
All of the above products have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the kidneys and put an increased burden on the transplanted organ.
Absolutely prohibited products
Pickles and marinades are strictly prohibited for consumption after a kidney transplant.
The following products are strictly prohibited for consumption after a kidney transplant:
- Salted and pickled tomatoes;
- Salted and pickled cucumbers;
- Sauerkraut;
- Salted, dried fish and canned fish;
- All types of sausages;
- Smoked and highly salted cheeses;
- Butter and margarine;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Any types of alcohol, including low-alcohol drinks;
- Kvass.
These products have an extremely negative effect on the functioning of the kidneys, which is especially dangerous after a transplant of these organs.
Food restrictions
First of all, you need to pay attention to plant foods
Let's figure out what you can eat after a kidney transplant
First of all, you need to pay attention to plant foods
It is rich in fiber, which has a very positive effect on intestinal function (which is important in the period after surgery). Products with minimal heat treatment (preferably steamed) and raw vegetables and fruits contain essential microelements, vitamins and other beneficial compounds, which have a good effect on both the kidneys and the entire body as a whole.
As part of the diet, in the postoperative period, it is necessary to limit the consumption of animal fats, replacing them with vegetable oils in a minimum amount, and avoid frying foods
Products with minimal heat treatment (preferably steamed) and raw vegetables and fruits contain essential microelements, vitamins and other beneficial compounds, and have a good effect on both the kidneys and the entire body as a whole. As part of the diet, in the postoperative period, it is necessary to limit the consumption of animal fats, replacing them with vegetable oils in a minimum amount, and avoid frying foods.
| Not recommended for use | Can be consumed |
| · Pork; · Mutton; · Duck; · Oily fish. | · Chicken breast; · Rabbit meat; · Lean veal and beef; · Turkey; · Seafood; · River fish. |
The following fermented milk products are allowed: cottage cheese and unsalted curd cheeses, ricotta, matsoni.
What foods should you not eat?
Meals after kidney transplantation should not contain:
- fatty meat, fish, tartare;
It is not recommended to buy ready-made food.
- oysters, raw fish, sushi;
- low quality dairy products;
- fast food;
- strong tea, coffee;
- sparkling water with sugar;
- undercooked eggs.
Buffets and salad bars are prohibited for people who have had a transplant.
It is better to eat food that you prepare yourself. This is the only way to be sure that the body has received good quality products. All alcohol is prohibited for the rest of your life. Despite the high survival rate, you should not expose your body to unnecessary risks. Alcoholic drinks lead to cell death and reduce the likelihood of recovery.
Important dietary points
In the first month after organ removal, you must strictly follow medical recommendations. If you ignore nutritional rules, the urinary system experiences excessive stress, which leads to complications. Diet after kidney surgery stimulates adaptation of the functioning organ.
Diet
Fractional nutrition is a key principle of the diet that must be followed during rehabilitation. If a person has only one kidney, they should:
- have breakfast 30-40 minutes after waking up;
- eat every 1.5-2 hours;
- have dinner at least 2 hours before bedtime.
Fasting during organ removal is contraindicated. Violation of diet conditions leads to an increase in the amount of purines and other metabolites in the blood. Because of this, the toxic load on the kidney increases. Therefore, during rehabilitation, it is advisable to eat food 5 times a day.
Serving Size
Dietary nutrition after kidney removal is recommended for 6 months to 1.5 years. The serving size is determined by the fist rule - the volume of a person’s stomach corresponds to a fist. Therefore, at one time they eat an amount of food that is approximately equal to its size.
More precisely, the serving volume is determined as follows:
- a woman's palm corresponds to 100 g of poultry or fish;
- 1 handful contains a serving of pasta, vegetable salad or porridge;
- 200 g of meat corresponds to the volume of a woman’s fist.
According to statistics, more than 25-30% of people cannot determine the serving size in grams by eye. To prevent overeating, it is better to purchase a kitchen scale.
Cooking methods
As part of the diet, it is advisable to avoid fried meat, vegetables and fish. Such dishes contain carcinogens and purines, which increase the load on the kidney by 1.5-2 times. Postoperative nutrition should be gentle, so nephrologists advise stewing, boiling and baking foods.
If you are prone to constipation, you should eat baked apples three times a week.
How much are you allowed to drink?
After nephrectomy, the load on the remaining kidney increases significantly. Therefore, when an organ is removed, patients are warned about the need to adhere to the drinking regime:
- in the first month after discharge, drink no more than 0.5-0.7 liters of liquid per day;
- gradually the daily volume of water is increased to 1 liter;
- 1.5 hours before bedtime, try not to drink fermented milk drinks.
If the performance of the second kidney is reduced, the diet is adjusted. If there are stones in the organ, preference is given to acidic or alkaline mineral waters, depending on the type of stones.
Daily calorie content
If a person has had one kidney removed, he must monitor the calorie content of his diet. The permissible energy value of the daily menu is 2800-3000 kcal/day.
Optimal amount of nutrients:
- carbohydrates – 450-500 g;
- fats – up to 90 g;
- proteins – no more than 80 g.
With concomitant pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system, the calorie content of the diet is adjusted.
If a kidney is removed, they eat only natural, easily digestible food without dyes.
After operation
A new kidney is not always easily accepted by the body. As a rule, within a day the entire kidney urinary system is activated. Doctors also monitor the body’s reaction to the new organ. All this time the person takes powerful drugs. The kidney is gradually accepted by the body. But problems of rejection of a foreign body are present.
After transplantation, the kidneys do not feel the best, but their performance is gradually improving. Sometimes very serious consequences require more stringent treatment. Tests will be taken for a long time even after discharge.
A diet will also be prescribed for the patient after the kidney transplant. They may limit themselves to advice such as the amount of fat consumed (about 25%), carbohydrates (50%) and other substances. They will also give you a sample menu for the day. Usually several options. This menu already takes into account the requirements.
Reviews and results
According to reviews, dietary nutrition after a kidney transplant for patients shortens the rehabilitation period and normalizes both kidney function and the general condition of the body. Some patients find it difficult to get used to limiting salt and salty foods, considering food tasteless, but they believe that they can gradually get used to it. Strict adherence to the diet after a few days reduces swelling, normalizes blood pressure, and improves general condition.
- Diet for cystitis and pyelonephritis
- “... When I underwent a kidney transplant, I was prescribed strong immunosuppressants and a therapeutic diet. In general, the diet is doable, the most unpleasant thing is the unsalted food, which at first simply “didn’t fit” into your mouth. But the understanding that you need to get used to this (if you want to live) gradually developed new taste preferences. Now I almost effortlessly eat all cereals, any soups, meat with virtually no salt. Garden herbs, dried overseas herbs, lemon juice, and homemade sauces are very helpful. I bake myself unsalted grain bread and crispbread, make homemade pastries with cottage cheese, various vegetable fillings and jam. A year later, I was allowed to slightly increase the amount of salt in my diet, and in general everything with my diet returned to normal. I periodically undergo tests and am observed at the clinic.”